IBM System/360 Model 40 on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
The IBM System/360 Model 40 was a mid-range member of the IBM System/360 family. It was announced on April 7, 1964, shipped in 1965, and withdrawn on October 7, 1977.
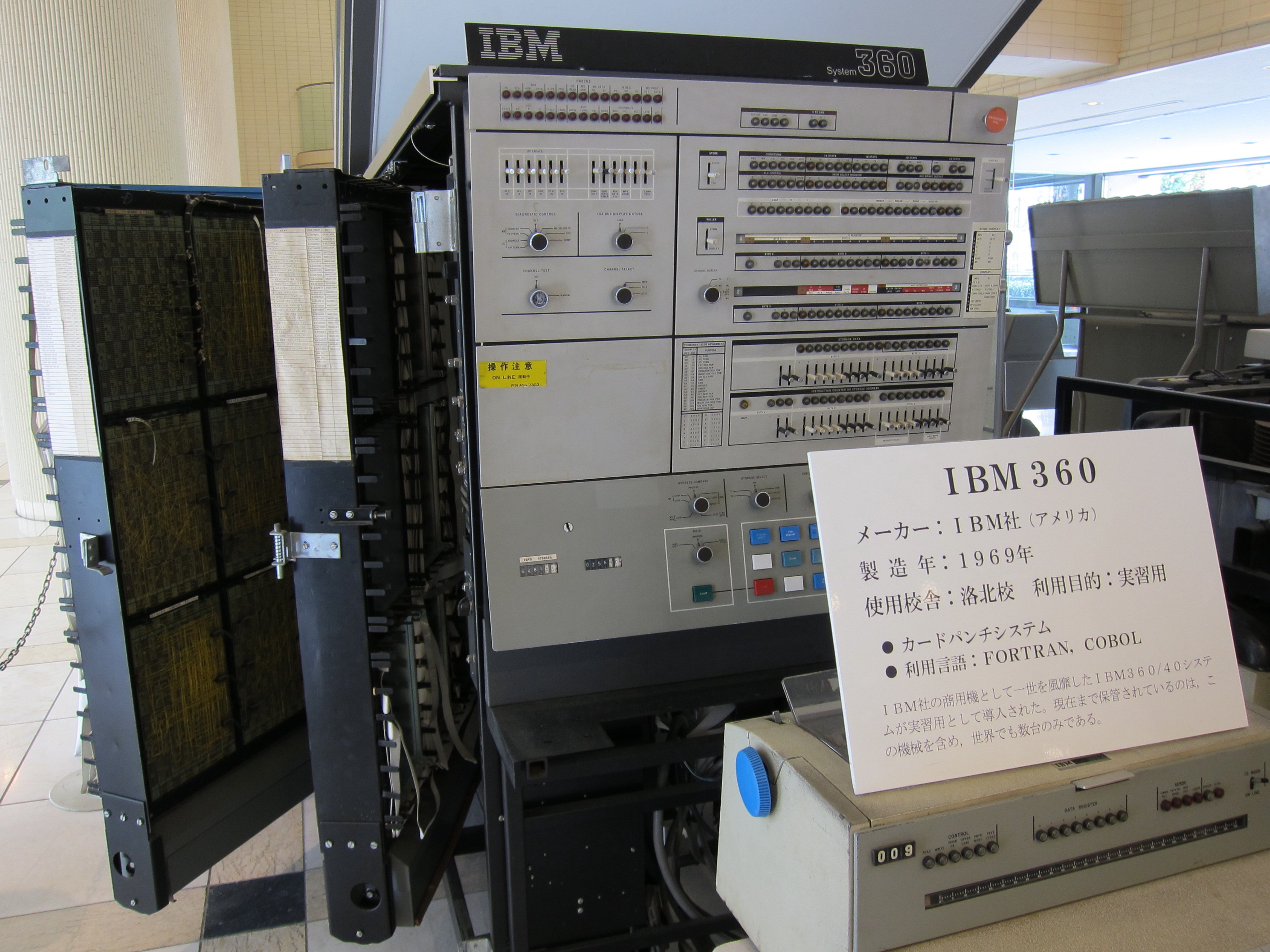



History
On April 7, 1964, IBM announced the IBM System/360, to be available in six models. The 360/40 was first delivered in April 1965. The 360/30 and the 360/40 were the two largest revenue producing System/360 models, accounting for over half of the units sold.Models
Five models of the 360/40 were offered. The D40, E40, F40, G40 and H40 were configured with 16K, 32K, 64K, 128K and 256K ofcore memory
Core or cores may refer to:
Science and technology
* Core (anatomy), everything except the appendages
* Core (manufacturing), used in casting and molding
* Core (optical fiber), the signal-carrying portion of an optical fiber
* Core, the centra ...
and correspondingly 16, 32, 64, 128 and 128 not a typo: the physical limit seemed to be 224; see p. 17 of the Model 30 Functional Characteristics multiplexer subchannels.
The H40 occupied "more floor space than the other models."
Configuration
Microprogramming
Like most System/360 models the Model 40 was microprogrammed. The microcode was stored intransformer read-only storage
Transformer read-only storage (TROS) was a type of read-only memory (ROM) used in the 1960s and early 1970s before solid-state memory devices were developed.
Overview
TROS was created by IBM as a read-only storage method for storing microcode f ...
(TROS), organized as up to 8192 words of 56 bits each. Standard microcode consisted of up to 4096 words. The additional 4096 words were used for the 1401 or 1410 compatibility feature.
IBM 1400 series emulation
With the additional Compatibility Feature hardware and Compatibility Support software under DOS/360, theIBM 1401
The IBM 1401 is a variable-wordlength decimal computer that was announced by IBM on October 5, 1959. The first member of the highly successful IBM 1400 series, it was aimed at replacing unit record equipment for processing data stored on pu ...
/ 1440/1460 object programs could be run in the emulation mode, with little or no reprogramming.
Other
Although the cover of IBM's MVT Guide indicates that even a 360/40 could run MVT, the IBMoperating system
An operating system (OS) is system software that manages computer hardware, software resources, and provides common services for computer programs.
Time-sharing operating systems schedule tasks for efficient use of the system and may also i ...
used was usually the realistically sized DOS/360, because all but one model of the 360/40 had less than MVT's minimum memory requirements of 256KB.
The IBM System/360 Model 40 was developed at IBM Hursley and manufactured at IBM's facilities in: Poughkeepsie, U.S., Mainz
Mainz () is the capital and largest city of Rhineland-Palatinate, Germany.
Mainz is on the left bank of the Rhine, opposite to the place that the Main joins the Rhine. Downstream of the confluence, the Rhine flows to the north-west, with Ma ...
, Germany; and Fujisawa, Japan.
A modified Model 40 ran CP-40
CP-40 was a research precursor to CP-67, which in turn was part of IBM's then-revolutionary CP/CMS, CP 67CMS – a virtual machine/virtual memory time-sharing operating system for the IBM System/360 Model 67, and the parent of IBM's VM (operati ...
, the ancestor of CP/CMS
CP/CMS (Control Program/Cambridge Monitor System) is a discontinued time-sharing operating system of the late 1960s and early 1970s, known for its excellent performance and advanced features. It had three distinct versions:
* CP-40/CMS, an im ...
, which in turn was the progenitor of the VM line.
Notes
References
{{DEFAULTSORT:IBM System 360 Model 40 System 360 Model 40