Humulin on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
As a
 Insulin is used to treat a number of diseases including
Insulin is used to treat a number of diseases including
 Insulin is an endogenous
Insulin is an endogenous
FDA importation process
is required to obtain bovine or porcine derived insulin for use in the U.S., although there may be some remaining stocks of porcine insulin made by Lilly in 2005 or earlier, and porcine lente insulin is also sold and marketed under the brand name Vetsulin(SM) in the U.S. for veterinary usage in the treatment of companion animals with diabetes.
 Unlike many medicines, insulin cannot be taken orally at the present time. Like nearly all other proteins introduced into the gastrointestinal tract, it is reduced to fragments (single amino acid components), whereupon all activity is lost. There has been some research into ways to protect insulin from the digestive tract, so that it can be administered in a pill. So far this is entirely experimental.
Unlike many medicines, insulin cannot be taken orally at the present time. Like nearly all other proteins introduced into the gastrointestinal tract, it is reduced to fragments (single amino acid components), whereupon all activity is lost. There has been some research into ways to protect insulin from the digestive tract, so that it can be administered in a pill. So far this is entirely experimental.
 The central problem for those requiring external insulin is picking the right dose of insulin and the right timing.
Physiological regulation of blood glucose, as in the non-diabetic, would be best. Increased blood glucose levels after a meal is a stimulus for prompt release of insulin from the pancreas. The increased insulin level causes glucose absorption and storage in cells, reduces glycogen to glucose conversion, reducing blood glucose levels, and so reducing insulin release. The result is that the blood glucose level rises somewhat after eating, and within an hour or so, returns to the normal 'fasting' level. Even the best diabetic treatment with synthetic human insulin or even insulin analogs, however administered, falls far short of normal glucose control in the non-diabetic.
Complicating matters is that the composition of the food eaten (see ''
The central problem for those requiring external insulin is picking the right dose of insulin and the right timing.
Physiological regulation of blood glucose, as in the non-diabetic, would be best. Increased blood glucose levels after a meal is a stimulus for prompt release of insulin from the pancreas. The increased insulin level causes glucose absorption and storage in cells, reduces glycogen to glucose conversion, reducing blood glucose levels, and so reducing insulin release. The result is that the blood glucose level rises somewhat after eating, and within an hour or so, returns to the normal 'fasting' level. Even the best diabetic treatment with synthetic human insulin or even insulin analogs, however administered, falls far short of normal glucose control in the non-diabetic.
Complicating matters is that the composition of the food eaten (see ''
DAFNE
In Europe, people who are not familiar with the DAFNE regime can take a
educational course
where the basic starting insulin dose guideline is "for every 10 g of carbohydrates you eat, take 1 unit of insulin". DAFNE courses also cover topics that naturally work alongside this regime, such as blood glucose monitoring, exercise and carbohydrate estimation to help the person work out their personal control requirements. People can also use their total daily dose (TDD) of insulin to estimate how many grams of carbohydrates will be "covered" by 1 unit of insulin, and using this result, estimate how many units of insulin should be administered depending on the carbohydrate content of their meal. For example, if the person determines that 1 unit of insulin will cover 15 grams of carbohydrates, then they must administer 5 units of insulin before consuming a meal that contains 75 grams of carbohydrates. Some alternative methods also consider the protein content of the meal (since excess dietary protein can be converted to glucose via gluconeogenesis). With DAFNE, most dosages involve a fair degree of guesswork, especially with non-labeled foods, and will only work fairly consistently from one dosage to the next if the person is aware of their body's requirements. For example, a person finds they can take 1 unit of insulin to 10 g of carbohydrates in the morning and the evening, but find that their body requires more insulin for a meal in the middle of the day so they have to adjust to 1 unit per 8.5g of carbohydrates. Other less obvious factors that affect the body's use of insulin must also be taken into account. For example, some people may find that their bodies process insulin better on hot days so require less insulin. With this, the person again has to adjust their dose to the best of their understanding from their past experiences. The DAFNE regime requires the person to learn about their body's needs through experience, which takes time and patience, but it can then become effective.
medication
A medication (also called medicament, medicine, pharmaceutical drug, medicinal drug or simply drug) is a drug used to diagnose, cure, treat, or prevent disease. Drug therapy ( pharmacotherapy) is an important part of the medical field and ...
, insulin is any pharmaceutical
A medication (also called medicament, medicine, pharmaceutical drug, medicinal drug or simply drug) is a drug used to diagnose, cure, treat, or prevent disease. Drug therapy (pharmacotherapy) is an important part of the medical field an ...
preparation of the protein hormone insulin that is used to treat high blood glucose. Such conditions include type 1 diabetes
Type 1 diabetes (T1D), formerly known as juvenile diabetes, is an autoimmune disease that originates when cells that make insulin (beta cells) are destroyed by the immune system. Insulin is a hormone required for the cells to use blood sugar ...
, type 2 diabetes
Type 2 diabetes, formerly known as adult-onset diabetes, is a form of diabetes mellitus that is characterized by high blood sugar, insulin resistance, and relative lack of insulin. Common symptoms include increased thirst, frequent urinatio ...
, gestational diabetes
Gestational diabetes is a condition in which a woman without diabetes develops high blood sugar levels during pregnancy. Gestational diabetes generally results in few symptoms; however, it increases the risk of pre-eclampsia, depression, and of ...
, and complications of diabetes
Diabetes, also known as diabetes mellitus, is a group of metabolic disorders characterized by a high blood sugar level ( hyperglycemia) over a prolonged period of time. Symptoms often include frequent urination, increased thirst and increased ...
such as diabetic ketoacidosis
Diabetic ketoacidosis (DKA) is a potentially life-threatening complication of diabetes mellitus. Signs and symptoms may include vomiting, abdominal pain, deep gasping breathing, increased urination, weakness, confusion and occasionally loss of ...
and hyperosmolar hyperglycemic states. Insulin is also used along with glucose
Glucose is a simple sugar with the molecular formula . Glucose is overall the most abundant monosaccharide, a subcategory of carbohydrates. Glucose is mainly made by plants and most algae during photosynthesis from water and carbon dioxide, u ...
to treat hyperkalemia
Hyperkalemia is an elevated level of potassium (K+) in the blood. Normal potassium levels are between 3.5 and 5.0mmol/L (3.5 and 5.0mEq/L) with levels above 5.5mmol/L defined as hyperkalemia. Typically hyperkalemia does not cause symptoms. Occasi ...
(high blood potassium levels). Typically it is given by injection under the skin
Subcutaneous administration is the insertion of medications beneath the skin either by injection or infusion.
A subcutaneous injection is administered as a bolus into the subcutis, the layer of skin directly below the dermis and epidermis, col ...
, but some forms may also be used by injection into a vein
Intravenous therapy (abbreviated as IV therapy) is a medical technique that administers fluids, medications and nutrients directly into a person's vein. The intravenous route of administration is commonly used for rehydration or to provide nutri ...
or muscle. There are various types of insulin, suitable for various time spans. The types are often all called ''insulin'' in the broad sense
A sense is a biological system used by an organism for sensation, the process of gathering information about the world through the detection of stimuli. (For example, in the human body, the brain which is part of the central nervous system re ...
, although in a more precise sense, insulin is identical to the naturally occurring molecule whereas insulin analog
An insulin analog ( also called an insulin analogue) is any of several types of medical insulin that are altered forms of the hormone insulin, different from any occurring in nature, but still available to the human body for performing the same a ...
ues have slightly different molecules that allow for modified time of action. It is on the World Health Organization's List of Essential Medicines
The WHO Model List of Essential Medicines (aka Essential Medicines List or EML), published by the World Health Organization (WHO), contains the medications considered to be most effective and safe to meet the most important needs in a health s ...
. In 2020, regular human insulin was the 307th most commonly prescribed medication in the United States, with more than 1million prescriptions.
Insulin can be made from the pancreas
The pancreas is an organ of the digestive system and endocrine system of vertebrates. In humans, it is located in the abdomen behind the stomach and functions as a gland. The pancreas is a mixed or heterocrine gland, i.e. it has both an en ...
of pigs or cows. Human versions can be made either by modifying pig versions or recombinant technology
Recombinant DNA (rDNA) molecules are DNA molecules formed by laboratory methods of genetic recombination (such as molecular cloning) that bring together genetic material from multiple sources, creating sequences that would not otherwise be fou ...
. It comes in three main types: short–acting (such as regular insulin
Regular insulin, also known as neutral insulin and soluble insulin, is a type of short-acting medical insulin. It is used to treat type 1 diabetes, type 2 diabetes, gestational diabetes, and complications of diabetes such as diabetic ketoacid ...
), intermediate-acting (such as neutral protamine Hagedorn (NPH) insulin), and longer-acting (such as insulin glargine
Insulin glargine, sold under the brand name Lantus among others, is a long-acting modified form of medical insulin, used in the management of type I and type II diabetes. It is typically the recommended long acting insulin in the United King ...
).
History
Insulin was first used as a medication in Canada by Charles Best andFrederick Banting
Sir Frederick Grant Banting (November 14, 1891 – February 21, 1941) was a Canadian medical scientist, physician, painter, and Nobel laureate noted as the co-discoverer of insulin and its therapeutic potential.
In 1923, Banting and Joh ...
in 1922.
''This is a chronology of key milestones in the history of the medical use of insulin. For more details on the discovery, extraction, purification, clinical use, and synthesis of insulin, see Insulin''
* 1921 Research on the role of pancreas in the nutritive assimilation
* 1922 Frederick Banting
Sir Frederick Grant Banting (November 14, 1891 – February 21, 1941) was a Canadian medical scientist, physician, painter, and Nobel laureate noted as the co-discoverer of insulin and its therapeutic potential.
In 1923, Banting and Joh ...
, Charles Best and James Collip
James Bertram Collip (November 20, 1892 – June 19, 1965) was a Canadian biochemist who was part of the Toronto group which isolated insulin. He served as the Chair of the Department of Biochemistry at McGill University from 1928–1941 a ...
use bovine insulin extract in humans at Connaught Laboratories
The Connaught Medical Research Laboratories was a non-commercial public health entity established by Dr. John G. FitzGerald in 1914 in Toronto to produce the diphtheria antitoxin. Contemporaneously, the institution was likened to the Pasteur Inst ...
in Toronto, Canada.
* 1922 Leonard Thompson becomes the first human to be treated with insulin.
* 1922 James D. Havens
James Dexter Havens (1900–1960) was a printmaker and painter in Rochester, New York, who is considered part of the color woodblock printing, woodblock revival in America.Watrous, James: "The American Color Woodcuts: Bounty from the Block, 1890s-1 ...
, son of former congressman James S. Havens, becomes the first American to be treated with insulin.
* 1922 Elizabeth Hughes Gossett
Elizabeth Evans Hughes Gossett (August 19, 1907 April 21, 1981), the daughter of U.S. statesman Charles Evans Hughes, was the first American, and one of the first people in the world, treated with insulin for type 1 diabetes. She received over 42 ...
, daughter of the U.S. Secretary of State, becomes the first American to be (officially) treated in Toronto.
* 1923 Eli Lilly
Eli Lilly (July 8, 1838 – June 6, 1898) was an American soldier, pharmacist, chemist, and businessman who founded the Eli Lilly and Company pharmaceutical corporation. Lilly enlisted in the Union Army during the American Civil War and ...
produces commercial quantities of much purer bovine insulin than Banting et al. had used
* 1923 Farbwerke Hoechst, one of the forerunners of today's Sanofi Aventis
Sanofi S.A. is a French multinational pharmaceutical and healthcare company headquartered in Paris, France. Originally, the corporation was established in 1973 and merged with Synthélabo in 1999 to form Sanofi-Synthélabo. In 2004, Sanofi-Syn ...
, produces commercial quantities of bovine insulin in Germany
* 1923 Hans Christian Hagedorn founds the Nordisk Insulinlaboratorium in Denmark – forerunner of today's Novo Nordisk
Novo Nordisk A/S is a Danish multinational pharmaceutical company headquartered in Bagsværd, Denmark, with production facilities in nine countries, and affiliates or offices in five countries. Novo Nordisk is controlled by majority shareholder ...
* 1923 Constance Collier
Constance Collier (born Laura Constance Hardie; 22 January 1878 – 25 April 1955) was an English stage and film actress and acting coach. She wrote hit plays and films with Ivor Novello and she was the first person to be treated with insul ...
returns to health after being successfully treated with insulin in Strasbourg
* 1926 Nordisk receives a Danish charter to produce insulin as a non-profit
* 1936 Canadians David M. Scott and Albert M. Fisher formulate a zinc insulin mixture at Connaught Laboratories
The Connaught Medical Research Laboratories was a non-commercial public health entity established by Dr. John G. FitzGerald in 1914 in Toronto to produce the diphtheria antitoxin. Contemporaneously, the institution was likened to the Pasteur Inst ...
in Toronto and license it to Novo
* 1936 Hagedorn discovers that adding protamine to insulin prolongs the duration of action of insulin
* 1946 Nordisk formulates Isophane porcine insulin aka Neutral Protamine Hagedorn or NPH insulin
Neutral Protamine Hagedorn (NPH) insulin, also known as isophane insulin, is an intermediate-acting insulin given to help control blood sugar levels in people with diabetes. It is used by injection under the skin once to twice a day. Onset of ...
* 1946 Nordisk crystallizes a protamine and insulin mixture
* 1950 Nordisk markets NPH insulin
Neutral Protamine Hagedorn (NPH) insulin, also known as isophane insulin, is an intermediate-acting insulin given to help control blood sugar levels in people with diabetes. It is used by injection under the skin once to twice a day. Onset of ...
* 1953 Novo formulates Lente porcine and bovine insulins by adding zinc for longer lasting insulin
* 1955 Frederick Sanger determines the amino acid sequence
Protein primary structure is the linear sequence of amino acids in a peptide or protein. By convention, the primary structure of a protein is reported starting from the amino-terminal (N) end to the carboxyl-terminal (C) end. Protein biosynthe ...
of insulin
* 1965 Synthesized by total synthesis by Wang Yinglai, Chen-Lu Tsou, et al.
* 1969 Dorothy Crowfoot Hodgkin solves the crystal structure of insulin by X-ray crystallography
X-ray crystallography is the experimental science determining the atomic and molecular structure of a crystal, in which the crystalline structure causes a beam of incident X-rays to diffract into many specific directions. By measuring the angles ...
* 1973 Purified monocomponent (MC) insulin is introduced
* 1973 The U.S. officially "standardized" insulin sold for human use in the U.S. to U-100 (100 units per milliliter). Prior to that, insulin was sold in different strengths, including U-80 (80 units per milliliter) and U-40 formulations (40 units per milliliter), so the effort to "standardize" the potency aimed to reduce dosage errors and ease doctors' job of prescribing insulin for people. Other countries also followed suit.
* 1978 Genentech produces biosynthetic human insulin in ''Escherichia coli'' bacteria using recombinant DNA techniques, licenses to Eli Lilly
* 1981 Novo Nordisk
Novo Nordisk A/S is a Danish multinational pharmaceutical company headquartered in Bagsværd, Denmark, with production facilities in nine countries, and affiliates or offices in five countries. Novo Nordisk is controlled by majority shareholder ...
chemically and enzymatically converts porcine to human insulin
* 1982 Genentech synthetic human insulin (above) approved
* 1983 Eli Lilly and Company produces biosynthetic human insulin with recombinant DNA
Recombinant DNA (rDNA) molecules are DNA molecules formed by laboratory methods of genetic recombination (such as molecular cloning) that bring together genetic material from multiple sources, creating sequences that would not otherwise be fo ...
technology, Humulin
* 1985 Axel Ullrich
Axel Ullrich (born 19 October 1943) is a German cancer researcher and has been the director of the molecular biology department at the Max Planck Institute of Biochemistry in Martinsried, Germany since 1988. This department's research has primar ...
sequences a human cell membrane insulin receptor.
* 1988 Novo Nordisk
Novo Nordisk A/S is a Danish multinational pharmaceutical company headquartered in Bagsværd, Denmark, with production facilities in nine countries, and affiliates or offices in five countries. Novo Nordisk is controlled by majority shareholder ...
produces recombinant biosynthetic human insulin
* 1996 Lilly Humalog "lispro" insulin analogue approved.
* 2000 Sanofi Aventis
Sanofi S.A. is a French multinational pharmaceutical and healthcare company headquartered in Paris, France. Originally, the corporation was established in 1973 and merged with Synthélabo in 1999 to form Sanofi-Synthélabo. In 2004, Sanofi-Syn ...
Lantus insulin "glargine" analogue approved for clinical use in the US and Europe.
* 2004 Sanofi Aventis
Sanofi S.A. is a French multinational pharmaceutical and healthcare company headquartered in Paris, France. Originally, the corporation was established in 1973 and merged with Synthélabo in 1999 to form Sanofi-Synthélabo. In 2004, Sanofi-Syn ...
Apidra insulin "glulisine" insulin analogue approved for clinical use in the US.
* 2006 Novo Nordisk
Novo Nordisk A/S is a Danish multinational pharmaceutical company headquartered in Bagsværd, Denmark, with production facilities in nine countries, and affiliates or offices in five countries. Novo Nordisk is controlled by majority shareholder ...
Levemir "detemir" insulin analogue approved for clinical use in the US.
Medical uses
 Insulin is used to treat a number of diseases including
Insulin is used to treat a number of diseases including diabetes
Diabetes, also known as diabetes mellitus, is a group of metabolic disorders characterized by a high blood sugar level ( hyperglycemia) over a prolonged period of time. Symptoms often include frequent urination, increased thirst and increased ...
and its acute complications such as diabetic ketoacidosis
Diabetic ketoacidosis (DKA) is a potentially life-threatening complication of diabetes mellitus. Signs and symptoms may include vomiting, abdominal pain, deep gasping breathing, increased urination, weakness, confusion and occasionally loss of ...
and hyperosmolar hyperglycemic states. It is also used along with glucose
Glucose is a simple sugar with the molecular formula . Glucose is overall the most abundant monosaccharide, a subcategory of carbohydrates. Glucose is mainly made by plants and most algae during photosynthesis from water and carbon dioxide, u ...
to treat high blood potassium levels. Use during pregnancy
Pregnancy is the time during which one or more offspring develops (gestation, gestates) inside a woman, woman's uterus (womb). A multiple birth, multiple pregnancy involves more than one offspring, such as with twins.
Pregnancy usually occur ...
is relatively safe for the baby. Insulin was formerly used in a psychiatric treatment called insulin shock therapy
Insulin shock therapy or insulin coma therapy was a form of psychiatric treatment in which patients were repeatedly injected with large doses of insulin in order to produce daily comas over several weeks.Neustatter WL (1948) ''Modern psychiatry ...
.
Side effects
Some side effects arehypoglycemia
Hypoglycemia, also called low blood sugar, is a fall in blood sugar to levels below normal, typically below 70 mg/dL (3.9 mmol/L). Whipple's triad is used to properly identify hypoglycemic episodes. It is defined as blood glucose bel ...
(low blood sugar), hypokalemia
Hypokalemia is a low level of potassium (K+) in the blood serum. Mild low potassium does not typically cause symptoms. Symptoms may include feeling tired, leg cramps, weakness, and constipation. Low potassium also increases the risk of an abno ...
(low blood potassium), and allergic reactions
Allergies, also known as allergic diseases, refer a number of conditions caused by the hypersensitivity of the immune system to typically harmless substances in the environment. These diseases include hay fever, food allergies, atopic derm ...
. Allergy to insulin affected about 2% of people, of which most reactions are not due to the insulin itself but to preservatives added to insulin such as zinc, protamine
Protamines are small, arginine-rich, nuclear proteins that replace histones late in the haploid phase of spermatogenesis and are believed essential for sperm head condensation and DNA stabilization. They may allow for denser packaging of DNA in t ...
, and meta-cresol
''meta''-Cresol, also 3-methylphenol, is an organic compound with the formula CH3C6H4(OH). It is a colourless, viscous liquid that is used as an intermediate in the production of other chemicals. It is a derivative of phenol and is an isomer of ...
. Most reactions are Type I hypersensitivity
Type I hypersensitivity (or immediate hypersensitivity), in the Gell and Coombs classification of allergic reactions, is an allergic reaction provoked by re-exposure to a specific type of antigen referred to as an allergen. Type I is distinct fro ...
reactions and rarely cause anaphylaxis
Anaphylaxis is a serious, potentially fatal allergic reaction and medical emergency that is rapid in onset and requires immediate medical attention regardless of use of emergency medication on site. It typically causes more than one of the foll ...
. A suspected allergy to insulin can be confirmed by skin prick testing, patch testing and occasionally skin biopsy
Skin biopsy is a biopsy technique in which a skin lesion is removed to be sent to a pathologist to render a microscopic diagnosis. It is usually done under local anesthetic in a physician's office, and results are often available in 4 to 10 days. ...
. First line therapy against insulin hypersensitivity reactions include symptomatic therapy with antihistamines. The affected persons are then switched to a preparation that does not contain the specific agent they are reacting to or undergo desensitization.
Cutaneous adverse effects
Other side effects may include pain or skin changes at the sites of injection. Repeated subcutaneous injection without site rotation can lead to lipohypertrophy and amyloidomas, which manifest as firm palpable nodules under the skin.
Principles
 Insulin is an endogenous
Insulin is an endogenous hormone
A hormone (from the Greek participle , "setting in motion") is a class of signaling molecules in multicellular organisms that are sent to distant organs by complex biological processes to regulate physiology and behavior. Hormones are require ...
, which is produced by the pancreas
The pancreas is an organ of the digestive system and endocrine system of vertebrates. In humans, it is located in the abdomen behind the stomach and functions as a gland. The pancreas is a mixed or heterocrine gland, i.e. it has both an en ...
.
The insulin protein
Proteins are large biomolecules and macromolecules that comprise one or more long chains of amino acid residues. Proteins perform a vast array of functions within organisms, including catalysing metabolic reactions, DNA replication, res ...
has been highly conserved across evolutionary time, and is present in both mammals
Mammals () are a group of vertebrate animals constituting the class Mammalia (), characterized by the presence of mammary glands which in females produce milk for feeding (nursing) their young, a neocortex (a region of the brain), fur o ...
and invertebrates
Invertebrates are a paraphyletic group of animals that neither possess nor develop a vertebral column (commonly known as a ''backbone'' or ''spine''), derived from the notochord. This is a grouping including all animals apart from the chordat ...
. The insulin/insulin-like growth factor
The insulin-like growth factors (IGFs) are proteins with high sequence similarity to insulin. IGFs are part of a complex system that cells use to communicate with their physiologic environment. This complex system (often referred to as the IGF " ...
signalling pathway (IIS) has been extensively studied in species including nematode worms (e.g.'' C. elegans''), flies (''Drosophila melanogaster
''Drosophila melanogaster'' is a species of fly (the taxonomic order Diptera) in the family Drosophilidae. The species is often referred to as the fruit fly or lesser fruit fly, or less commonly the " vinegar fly" or "pomace fly". Starting with ...
'') and mice (''Mus musculus
Mus or MUS may refer to:
Abbreviations
* MUS, the NATO country code for Mauritius
* MUS, the IATA airport code for Minami Torishima Airport
* MUS, abbreviation for the Centre for Modern Urban Studies on Campus The Hague, Leiden University, Net ...
''). Its mechanisms of action are highly similar across species.
Both type 1 diabetes
Type 1 diabetes (T1D), formerly known as juvenile diabetes, is an autoimmune disease that originates when cells that make insulin (beta cells) are destroyed by the immune system. Insulin is a hormone required for the cells to use blood sugar ...
and type 2 diabetes
Type 2 diabetes, formerly known as adult-onset diabetes, is a form of diabetes mellitus that is characterized by high blood sugar, insulin resistance, and relative lack of insulin. Common symptoms include increased thirst, frequent urinatio ...
are marked by a loss of pancreatic function, though to differing degrees. People who are affected with diabetes are referred to as diabetics. Many diabetics require an exogenous source of insulin to keep their blood sugar levels within a safe target range.
In 1916, Nicolae C. Paulescu (1869–1931) succeeded in developing an aqueous pancreatic extract that normalized a diabetic dog. In 1921, he published 4 papers in the Society of Biology in Paris centering on the successful effects of the pancreatic extract in diabetic dogs. Research on the Role of the Pancreas in Food Assimilation by Paulescu was published in August 1921 in the Archives Internationales de Physiologie, Liège, Belgium.
Initially, the only way to obtain insulin for clinical use was to extract it from the pancreas of another creature. Animal glands were obtainable as a waste product of the meatpacking industry. Insulin was derived primarily from cows
Cattle (''Bos taurus'') are large, domesticated, cloven-hooved, herbivores. They are a prominent modern member of the subfamily Bovinae and the most widespread species of the genus ''Bos''. Adult females are referred to as cows and adult mal ...
( Eli Lilly and Company) and pigs
The pig (''Sus domesticus''), often called swine, hog, or domestic pig when distinguishing from other members of the genus '' Sus'', is an omnivorous, domesticated, even-toed, hoofed mammal. It is variously considered a subspecies of ''Sus ...
(Nordisk Insulinlaboratorium
Novo Nordisk A/S is a Danish multinational pharmaceutical company headquartered in Bagsværd, Denmark, with production facilities in nine countries, and affiliates or offices in five countries. Novo Nordisk is controlled by majority shareholder ...
). The making of eight ounces of purified insulin could require as much as two tons of pig parts.
Insulin from these sources is effective in humans as it is highly similar to human insulin (three amino acid difference in bovine insulin, one amino acid difference in porcine). Initially, lower preparation purity resulted in allergic reactions to the presence of non-insulin substances. Purity has improved steadily since the 1920s ultimately reaching purity of 99% by the mid-1970s thanks to high-pressure liquid chromatography (HPLC) methods. Minor allergic reactions still occur occasionally, even to synthetic "human" insulin varieties.
Beginning in 1982, biosynthetic "human" insulin has been manufactured for clinical use through genetic engineering techniques using recombinant DNA
Recombinant DNA (rDNA) molecules are DNA molecules formed by laboratory methods of genetic recombination (such as molecular cloning) that bring together genetic material from multiple sources, creating sequences that would not otherwise be fo ...
technology. Genentech developed the technique used to produce the first such insulin, Humulin, but did not commercially market the product themselves. Eli Lilly
Eli Lilly (July 8, 1838 – June 6, 1898) was an American soldier, pharmacist, chemist, and businessman who founded the Eli Lilly and Company pharmaceutical corporation. Lilly enlisted in the Union Army during the American Civil War and ...
marketed Humulin in 1982. Humulin was the first medication produced using modern genetic engineering techniques in which actual human DNA is inserted into a host cell ('' E. coli'' in this case). The host cells are then allowed to grow and reproduce normally, and due to the inserted human DNA, they produce a synthetic version of human insulin. Manufacturers claim this reduces the presence of many impurities. However, the clinical preparations prepared from such insulins differ from endogenous human insulin in several important respects; an example is the absence of C-peptide
The connecting peptide, or C-peptide, is a short 31-amino-acid polypeptide that connects insulin's A-chain to its B-chain in the proinsulin molecule. In the context of diabetes or hypoglycemia, a measurement of C-peptide blood serum levels can ...
which has in recent years been shown to have systemic effects itself.
Novo Nordisk
Novo Nordisk A/S is a Danish multinational pharmaceutical company headquartered in Bagsværd, Denmark, with production facilities in nine countries, and affiliates or offices in five countries. Novo Nordisk is controlled by majority shareholder ...
has also developed a genetically engineered insulin independently using a yeast process.
According to a survey that the International Diabetes Federation conducted in 2002 on the access to and availability of insulin in its member countries, approximately 70% of the insulin that is currently sold in the world is recombinant, biosynthetic 'human' insulin. A majority of insulin used clinically today is produced this way, although clinical experience has provided conflicting evidence on whether these insulins are any less likely to produce an allergic reaction. Adverse reactions have been reported; these include loss of warning signs that patients may slip into a coma through hypoglycemia
Hypoglycemia, also called low blood sugar, is a fall in blood sugar to levels below normal, typically below 70 mg/dL (3.9 mmol/L). Whipple's triad is used to properly identify hypoglycemic episodes. It is defined as blood glucose bel ...
, convulsions, memory lapse and loss of concentration. However, the International Diabetes Federation's position statement from 2005 is very clear in stating that "there is NO overwhelming evidence to prefer one species of insulin over another" and " odern, highly purifiedanimal insulins remain a perfectly acceptable alternative."
Since January 2006, all insulins distributed in the U.S. and some other countries are synthetic "human" insulins or their analogues. A speciaFDA importation process
is required to obtain bovine or porcine derived insulin for use in the U.S., although there may be some remaining stocks of porcine insulin made by Lilly in 2005 or earlier, and porcine lente insulin is also sold and marketed under the brand name Vetsulin(SM) in the U.S. for veterinary usage in the treatment of companion animals with diabetes.
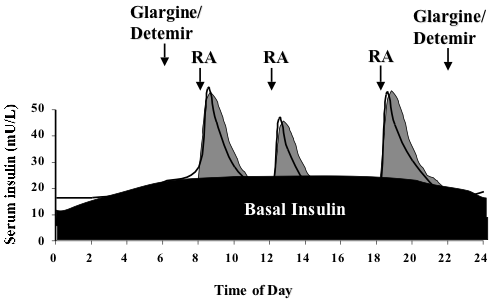
Basal insulin
In type 1 diabetes, insulin production is extremely low, and as such the body requiresexogenous
In a variety of contexts, exogeny or exogeneity () is the fact of an action or object originating externally. It contrasts with endogeneity or endogeny, the fact of being influenced within a system.
Economics
In an economic model, an exogeno ...
insulin. Some people with type 2 diabetes, particularly those with very high hemoglobin A1c values, may also require a baseline rate of insulin, as their body is desensitized to the level of insulin being produced. Basal insulin regulates the body's blood glucose between mealtimes, as well as overnight. This basal rate of insulin action is generally achieved via the use of an intermediate-acting insulin (such as NPH) or a long-acting insulin analog. In type 1 diabetics, it may also be achieved via continuous infusion of rapid-acting insulin using an insulin pump
An insulin pump is a medical device used for the administration of insulin in the treatment of diabetes mellitus, also known as continuous subcutaneous insulin therapy.
The device configuration may vary depending on design. A traditional pump ...
. Approximately half of a person's daily insulin requirement is administered as a basal insulin, usually administered once per day at night.
Prandial insulin
When a person eats food containing carbohydrates and glucose, insulin helps regulate the body's metabolism of the food. Prandial insulin, also called mealtime or bolus insulin, is designed as a bolus dose of insulin prior to a meal to regulate the spike in blood glucose that occurs following a meal. The dose of prandial insulin may be static, or may be calculated by the patient using either their current blood sugar, planned carbohydrate intake, or both. This calculation may also be performed by an insulin pump in patients using a pump. Insulin regiments that consist of doses calculated in this manner are considered intensive insulin regimens. Prandial insulin is usually administered no more than 15–30 minutes prior to a meal using a rapid-acting insulin or a regular insulin. In some patients, a combination insulin may be used that contains both NPH (long acting) insulin and a rapid/regular insulin to provide both a basal insulin and prandial insulin.Challenges in treatment
There are several challenges involved in the use of insulin as a clinical treatment for diabetes: * Mode of administration. * Selecting the 'right' dose and timing. The amount of carbohydrates one unit of insulin handles varies widely between persons and over the day but values between 7 and 20 grams per 1 IE is typical. * Selecting an appropriate insulin preparation (typically on 'speed of onset and duration of action' grounds). * Adjusting dosage and timing to fit food intake timing, amounts, and types. * Adjusting dosage and timing to fit exercise undertaken. * Adjusting dosage, type, and timing to fit other conditions, for instance the increased stress of illness. * Variability in absorption into the bloodstream via subcutaneous delivery * The dosage is non-physiological in that a subcutaneous bolus dose of insulin alone is administered instead of combination of insulin andC-peptide
The connecting peptide, or C-peptide, is a short 31-amino-acid polypeptide that connects insulin's A-chain to its B-chain in the proinsulin molecule. In the context of diabetes or hypoglycemia, a measurement of C-peptide blood serum levels can ...
being released gradually and directly into the portal vein.
* It is simply a nuisance for people to inject whenever they eat carbohydrate or have a high blood glucose reading.
* It is dangerous in case of mistake (most especially 'too much' insulin).
Types
Medical preparations of insulin are never just insulin in water (with nothing else). Clinical insulins are mixtures of insulin plus other substances including preservatives. These prevent the protein from spoiling or denaturing too rapidly, delay absorption of the insulin, adjust the pH of the solution to reduce reactions at the injection site, and so on. Slight variations of the human insulin molecule are calledinsulin analog
An insulin analog ( also called an insulin analogue) is any of several types of medical insulin that are altered forms of the hormone insulin, different from any occurring in nature, but still available to the human body for performing the same a ...
ues, (technically "insulin receptor ligand
In coordination chemistry, a ligand is an ion or molecule ( functional group) that binds to a central metal atom to form a coordination complex. The bonding with the metal generally involves formal donation of one or more of the ligand's elec ...
s") so named because they are not technically insulin, rather they are analogues which retain the hormone's glucose management functionality. They have absorption and activity characteristics not currently possible with subcutaneously injected insulin proper. They are either absorbed rapidly in an attempt to mimic real beta cell insulin (as with insulin lispro
Insulin lispro, sold under the brand name Humalog among others, is a modified type of medical insulin used to treat type 1 and type 2 diabetes. It is used by injection under the skin or within an insulin pump. Onset of effects typically occu ...
, insulin aspart
Insulin aspart, sold under the brand name NovoLog and Fiasp, among others, is a insulin analog, modified type of Insulin (medication), medical insulin used to treat type I diabetes, type 1 and type 2 diabetes. It is generally used by injection ...
, and insulin glulisine
Insulin glulisine is a rapid-acting modified form of medical insulin that differs from human insulin in that the amino acid asparagine at position B3 is replaced by lysine and the lysine in position B29 is replaced by glutamic acid. It was devel ...
), or steadily absorbed after injection instead of having a 'peak' followed by a more or less rapid decline in insulin action (as with insulin detemir
Insulin detemir, sold under the brand name Levemir among others, is a long-acting modified form of medical insulin used to treat both type 1 and type 2 diabetes. It is used by injection under the skin. It is effective for up to 24 hours.
C ...
and insulin glargine
Insulin glargine, sold under the brand name Lantus among others, is a long-acting modified form of medical insulin, used in the management of type I and type II diabetes. It is typically the recommended long acting insulin in the United King ...
), all while retaining insulin's glucose-lowering action in the human body. However, a number of meta-analyses
A meta-analysis is a statistical analysis that combines the results of multiple scientific studies. Meta-analyses can be performed when there are multiple scientific studies addressing the same question, with each individual study reporting m ...
, including those done by the Cochrane Collaboration
Cochrane (previously known as the Cochrane Collaboration) is a British international charitable organisation formed to organise medical research findings to facilitate evidence-based choices about health interventions involving health profess ...
in 2005, Germany's Institute for Quality and Cost Effectiveness in the Health Care Sector QWiGreleased in 2007, and the Canadian Agency for Drugs and Technology in Health (CADTH) also released in 2007 have shown no unequivocal advantages in clinical use of insulin analogues over more conventional insulin types.
Choosing insulin type and dosage/timing should be done by an experienced medical professional working closely with people who are diabetic .
The commonly used types of insulin are as follows.
Fast-acting (Rapid-acting)
Includes the insulin analogues ''aspart'', ''lispro'', and ''glulisine''. These begin to work within 5 to 15 minutes and are active for 3 to 4 hours. Most insulins formhexamer
In chemistry and biochemistry, an oligomer () is a molecule that consists of a few repeating units which could be derived, actually or conceptually, from smaller molecules, monomers.Quote: ''Oligomer molecule: A molecule of intermediate relative ...
s, which delay entry into the blood in active form; these analog insulins do not but have normal insulin activity. Newer varieties are now pending regulatory approval in the U.S. which are designed to work rapidly, but retain the same genetic structure as regular human insulin.
Short-acting
Includes ''regular insulin
Regular insulin, also known as neutral insulin and soluble insulin, is a type of short-acting medical insulin. It is used to treat type 1 diabetes, type 2 diabetes, gestational diabetes, and complications of diabetes such as diabetic ketoacid ...
'', which begins working within 30 minutes and is active about 5 to 8 hours.
Intermediate-acting
Includes ''NPH insulin
Neutral Protamine Hagedorn (NPH) insulin, also known as isophane insulin, is an intermediate-acting insulin given to help control blood sugar levels in people with diabetes. It is used by injection under the skin once to twice a day. Onset of ...
'', which begins working in 1 to 3 hours and is active for 16 to 24 hours.
Long-acting
Includes the analogues ''glargine
Insulin glargine, sold under the brand name Lantus among others, is a long-acting modified form of medical insulin, used in the management of type I and type II diabetes. It is typically the recommended long acting insulin in the United Kingd ...
'' U100 and '' detemir'', each of which begins working within 1 to 2 hours and continues to be active, without major peaks or dips, for about 24 hours, although this varies in many individuals.
Ultra-long acting
Includes the analogues ''insulin glargine
Insulin glargine, sold under the brand name Lantus among others, is a long-acting modified form of medical insulin, used in the management of type I and type II diabetes. It is typically the recommended long acting insulin in the United King ...
'' U300 and '' degludec'', which begin working within 30 to 90 minutes and continues to be active for greater than 24 hours.
Combination insulin products
Includes a combination of either fast-acting or short-acting insulin with a longer acting insulin, typically an ''NPH insulin
Neutral Protamine Hagedorn (NPH) insulin, also known as isophane insulin, is an intermediate-acting insulin given to help control blood sugar levels in people with diabetes. It is used by injection under the skin once to twice a day. Onset of ...
''. The combination products begin to work with the shorter acting insulin (5–15 minutes for fast-acting, and 30 minutes for short acting), and remain active for 16 to 24 hours. There are several variations with different proportions of the mixed insulins (e.g. Novolog Mix 70/30 contains 70% aspart protamine kin to NPH and 30% aspart.)
Methods of administration
 Unlike many medicines, insulin cannot be taken orally at the present time. Like nearly all other proteins introduced into the gastrointestinal tract, it is reduced to fragments (single amino acid components), whereupon all activity is lost. There has been some research into ways to protect insulin from the digestive tract, so that it can be administered in a pill. So far this is entirely experimental.
Unlike many medicines, insulin cannot be taken orally at the present time. Like nearly all other proteins introduced into the gastrointestinal tract, it is reduced to fragments (single amino acid components), whereupon all activity is lost. There has been some research into ways to protect insulin from the digestive tract, so that it can be administered in a pill. So far this is entirely experimental.
Subcutaneous
Insulin is usually taken as subcutaneous injections by single-use syringes with needles, aninsulin pump
An insulin pump is a medical device used for the administration of insulin in the treatment of diabetes mellitus, also known as continuous subcutaneous insulin therapy.
The device configuration may vary depending on design. A traditional pump ...
, or by repeated-use insulin pens with needles. People who wish to reduce repeated skin puncture of insulin injections often use an injection port
An injection port is a medical device used for the administration of insulin or other physician approved medicine into the subcutaneous tissue (the tissue layer just below the skin). The device is similar to infusion sets used by insulin pumps, ...
in conjunction with syringes.
The use of subcutaneous injections of insulin is designed to mimic the natural physiological cycle of insulin secretion, while taking into account the various properties of the formulations used such as half-life, onset of action, and duration of action. In many people, both a rapid- or short-acting insulin product as well as an intermediate- or long-acting product are used to decrease the amount of injections per day. In some, insulin injections may be combined with other injection therapy such as GLP-1 agonist
Glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor agonists, also known as GLP-1 receptor agonists (GLP-1-RA) or incretin mimetics, are agonists of the GLP-1 receptor. This class of medications is used for the treatment of type 2 diabetes Some drugs are also approv ...
s. Cleansing of the injection site and injection technique are required to ensure effective insulin therapy.
Insulin pump
Insulin pump
An insulin pump is a medical device used for the administration of insulin in the treatment of diabetes mellitus, also known as continuous subcutaneous insulin therapy.
The device configuration may vary depending on design. A traditional pump ...
s are a reasonable solution for some. Advantages to the person are better control over background or basal insulin dosage, bolus doses calculated to fractions of a unit, and calculators in the pump that may help with determining bolus infusion dosages. The limitations are cost, the potential for hypoglycemic and hyperglycemic episodes, catheter problems, and no "closed loop" means of controlling insulin delivery based on current blood glucose levels.
Insulin pumps may be like 'electrical injectors' attached to a temporarily implanted catheter
In medicine, a catheter (/ˈkæθətər/) is a thin tubing (material), tube made from medical grade materials serving a broad range of functions. Catheters are medical devices that can be inserted in the body to treat diseases or perform a surgi ...
or cannula
A cannula (; Latin meaning 'little reed'; plural or ) is a tube that can be inserted into the body, often for the delivery or removal of fluid or for the gathering of samples. In simple terms, a cannula can surround the inner or outer surfaces ...
. Some who cannot achieve adequate glucose control by conventional (or jet) injection are able to do so with the appropriate pump.
Indwelling catheters pose the risk of infection and ulceration, and some peoples may also develop lipodystrophy
Lipodystrophy syndromes are a group of genetic or acquired disorders in which the body is unable to produce and maintain healthy fat tissue. The medical condition is characterized by abnormal or degenerative conditions of the body's adipose tissue. ...
due to the infusion sets. These risks can often be minimized by keeping infusion sites clean. Insulin pumps require care and effort to use correctly.
Dosage and timing
Dosage units
Oneinternational unit
In pharmacology, the international unit (IU) is a unit of measurement for the effect, not mass of a substance; the variance is based on the biological activity or effect, for the purpose of easier comparison across similar ''forms'' of substan ...
of insulin (1 IU) is defined as the "biological equivalent" of 34.7 μg pure crystalline insulin.
The first definition of a unit of insulin was the amount required to induce hypoglycemia
Hypoglycemia, also called low blood sugar, is a fall in blood sugar to levels below normal, typically below 70 mg/dL (3.9 mmol/L). Whipple's triad is used to properly identify hypoglycemic episodes. It is defined as blood glucose bel ...
in a rabbit. This was set by James Collip
James Bertram Collip (November 20, 1892 – June 19, 1965) was a Canadian biochemist who was part of the Toronto group which isolated insulin. He served as the Chair of the Department of Biochemistry at McGill University from 1928–1941 a ...
at the University of Toronto in 1922. Of course, this was dependent on the size and diet of the rabbits. The unit of insulin was set by the insulin committee at the University of Toronto. The unit evolved eventually to the old USP insulin unit, where one unit (U) of insulin was set equal to the amount of insulin required to reduce the concentration of blood glucose
Glycaemia, also known as blood sugar level, blood sugar concentration, or blood glucose level is the measure of glucose concentrated in the blood of humans or other animals. Approximately 4 grams of glucose, a simple sugar, is present in the blo ...
in a fasting
Fasting is the abstention from eating and sometimes drinking. From a purely physiological context, "fasting" may refer to the metabolic status of a person who has not eaten overnight (see " Breakfast"), or to the metabolic state achieved after ...
rabbit to 45 m g/ d l (2.5 m mol/ L). Once the chemical structure and mass of insulin was known, the unit of insulin was defined by the mass of pure crystalline insulin required to obtain the USP unit.
The unit of measurement
A unit of measurement is a definite magnitude of a quantity, defined and adopted by convention or by law, that is used as a standard for measurement of the same kind of quantity. Any other quantity of that kind can be expressed as a multi ...
used in insulin therapy is not part of the International System of Units (abbreviated SI) which is the modern form of the metric system
The metric system is a system of measurement that succeeded the decimalised system based on the metre that had been introduced in France in the 1790s. The historical development of these systems culminated in the definition of the Interna ...
. Instead the pharmacological
Pharmacology is a branch of medicine, biology and pharmaceutical sciences concerned with drug or medication action, where a drug may be defined as any artificial, natural, or endogenous (from within the body) molecule which exerts a biochemica ...
international unit
In pharmacology, the international unit (IU) is a unit of measurement for the effect, not mass of a substance; the variance is based on the biological activity or effect, for the purpose of easier comparison across similar ''forms'' of substan ...
(IU) is defined by the WHO Expert Committee on Biological Standardization.
Potential complications
 The central problem for those requiring external insulin is picking the right dose of insulin and the right timing.
Physiological regulation of blood glucose, as in the non-diabetic, would be best. Increased blood glucose levels after a meal is a stimulus for prompt release of insulin from the pancreas. The increased insulin level causes glucose absorption and storage in cells, reduces glycogen to glucose conversion, reducing blood glucose levels, and so reducing insulin release. The result is that the blood glucose level rises somewhat after eating, and within an hour or so, returns to the normal 'fasting' level. Even the best diabetic treatment with synthetic human insulin or even insulin analogs, however administered, falls far short of normal glucose control in the non-diabetic.
Complicating matters is that the composition of the food eaten (see ''
The central problem for those requiring external insulin is picking the right dose of insulin and the right timing.
Physiological regulation of blood glucose, as in the non-diabetic, would be best. Increased blood glucose levels after a meal is a stimulus for prompt release of insulin from the pancreas. The increased insulin level causes glucose absorption and storage in cells, reduces glycogen to glucose conversion, reducing blood glucose levels, and so reducing insulin release. The result is that the blood glucose level rises somewhat after eating, and within an hour or so, returns to the normal 'fasting' level. Even the best diabetic treatment with synthetic human insulin or even insulin analogs, however administered, falls far short of normal glucose control in the non-diabetic.
Complicating matters is that the composition of the food eaten (see ''glycemic index
The glycemic (glycaemic) index (GI; ) is a number from 0 to 100 assigned to a food, with pure glucose arbitrarily given the value of 100, which represents the relative rise in the blood glucose level two hours after consuming that food. The GI of ...
'') affects intestinal absorption rates. Glucose from some foods is absorbed more (or less) rapidly than the same amount of glucose in other foods. In addition, fats and proteins cause delays in absorption of glucose from carbohydrates eaten at the same time. As well, exercise reduces the need for insulin even when all other factors remain the same, since working muscle has some ability to take up glucose without the help of insulin.
Because of the complex and interacting factors, it is, in principle, impossible to know for certain how much insulin (and which type) is needed to 'cover' a particular meal to achieve a reasonable blood glucose level within an hour or two after eating. Non-diabetics' beta cells routinely and automatically manage this by continual glucose level monitoring and insulin release. All such decisions by a diabetic must be based on experience and training (i.e., at the direction of a physician, PA, or in some places a specialist diabetic educator) and, further, specifically based on the individual experience of the person. But it is not straightforward and should never be done by habit or routine. With some care however, it can be done reasonably well in clinical practice. For example, some people with diabetes require more insulin after drinking skim milk
Skimmed milk (British English), or skim milk (American English), is made when all the milkfat is removed from whole milk. It tends to contain around 0.1% fat.
Background
Historically, skimmed milk was used for fattening pigs, and was recommended ...
than they do after taking an equivalent amount of fat, protein, carbohydrate, and fluid in some other form. Their particular reaction to skimmed milk is different from other people with diabetes, but the same amount of whole milk is likely to cause a still different reaction even in that person. Whole milk contains considerable fat while skimmed milk has much less. It is a continual balancing act for all people with diabetes, especially for those taking insulin.
People with insulin-dependent diabetes typically require some base level of insulin (basal insulin), as well as short-acting insulin to cover meals (bolus also known as mealtime or prandial insulin). Maintaining the basal rate and the bolus rate is a continuous balancing act that people with insulin-dependent diabetes must manage each day. This is normally achieved through regular blood tests, although continuous blood sugar testing equipment (Continuous Glucose Monitor
A continuous glucose monitor (CGM) is a device used for monitoring blood glucose on a continual basis by insulin-requiring people with diabetes, e.g. people with type I, type II diabetes or other types of diabetes (e.g. gestational diabetes). A ...
s or CGMs) are now becoming available which could help to refine this balancing act once widespread usage becomes common.
Strategies
A long-acting insulin is used to approximate the basal secretion of insulin by the pancreas, which varies in the course of the day. NPH/isophane, lente, ultralente, glargine, and detemir may be used for this purpose. The advantage of NPH is its low cost, the fact that you can mix it with short-acting forms of insulin, thereby minimizing the number of injections that must be administered, and that the activity of NPH will peak 4–6 hours after administration, allowing a bedtime dose to balance the tendency of glucose to rise with the dawn, along with a smaller morning dose to balance the lower afternoon basal need and possibly an afternoon dose to cover evening need. A disadvantage of bedtime NPH is that if not taken late enough (near midnight) to place its peak shortly before dawn, it has the potential of causing hypoglycemia. One theoretical advantage of glargine and detemir is that they only need to be administered once a day, although in practice many people find that neither lasts a full 24 hours. They can be administered at any time during the day as well, provided that they are given at the same time every day. Another advantage of long-acting insulins is that the basal component of an insulin regimen (providing a minimum level of insulin throughout the day) can be decoupled from the prandial or bolus component (providing mealtime coverage via ultra-short-acting insulins), while regimens using NPH and regular insulin have the disadvantage that any dose adjustment affects both basal and prandial coverage. Glargine and detemir are significantly more expensive than NPH, lente and ultralente, and they cannot be mixed with other forms of insulin. A short-acting insulin is used to simulate the endogenous insulin surge produced in anticipation of eating. Regular insulin, lispro, aspart and glulisine can be used for this purpose. Regular insulin should be given with about a 30-minute lead-time prior to the meal to be maximally effective and to minimize the possibility of hypoglycemia. Lispro, aspart and glulisine are approved for dosage with the first bite of the meal, and may even be effective if given after completing the meal. The short-acting insulin is also used to correct hyperglycemia. The usual schedule for checking fingerstick blood glucose and administering insulin is before all meals and sometimes also at bedtime. More recent guidelines also call for a check 2 hours after a meal to ensure the meal has been 'covered' effectively.Sliding scales
First described in 1934, what physicians typically refer to as sliding-scale insulin (SSI) is fast- or rapid-acting insulin only, given subcutaneously, typically at meal times and sometimes bedtime, but only when blood glucose is above a threshold (e.g. 10 mmol/L, 180 mg/dL). The so-called "sliding-scale" method is widely taught, although it has been heavily criticized. Sliding scale insulin (SSI) is not an effective way of managing long-term diabetes in individuals residing in nursing homes., which cites: * * * Sliding scale insulin leads to greater discomfort and increased nursing time. Sample regimen using insulin glargine and insulin lispro: * Insulin glargine: 20 units at bedtimeCarb counting and DAFNE
A more complicated method that allows greater freedom with meal times and snacks is " carb counting." This approach is taught to people who are diabetic in the UK and elsewhere as "Dose Adjustment For Normal Eating" oDAFNE
In Europe, people who are not familiar with the DAFNE regime can take a
educational course
where the basic starting insulin dose guideline is "for every 10 g of carbohydrates you eat, take 1 unit of insulin". DAFNE courses also cover topics that naturally work alongside this regime, such as blood glucose monitoring, exercise and carbohydrate estimation to help the person work out their personal control requirements. People can also use their total daily dose (TDD) of insulin to estimate how many grams of carbohydrates will be "covered" by 1 unit of insulin, and using this result, estimate how many units of insulin should be administered depending on the carbohydrate content of their meal. For example, if the person determines that 1 unit of insulin will cover 15 grams of carbohydrates, then they must administer 5 units of insulin before consuming a meal that contains 75 grams of carbohydrates. Some alternative methods also consider the protein content of the meal (since excess dietary protein can be converted to glucose via gluconeogenesis). With DAFNE, most dosages involve a fair degree of guesswork, especially with non-labeled foods, and will only work fairly consistently from one dosage to the next if the person is aware of their body's requirements. For example, a person finds they can take 1 unit of insulin to 10 g of carbohydrates in the morning and the evening, but find that their body requires more insulin for a meal in the middle of the day so they have to adjust to 1 unit per 8.5g of carbohydrates. Other less obvious factors that affect the body's use of insulin must also be taken into account. For example, some people may find that their bodies process insulin better on hot days so require less insulin. With this, the person again has to adjust their dose to the best of their understanding from their past experiences. The DAFNE regime requires the person to learn about their body's needs through experience, which takes time and patience, but it can then become effective.
Closed-loop predictive modeling
People with fluctuating insulin requirements may benefit from a closed-looppredictive modeling
Predictive modelling uses statistics to predict outcomes. Most often the event one wants to predict is in the future, but predictive modelling can be applied to any type of unknown event, regardless of when it occurred. For example, predictive mod ...
approach. As an extension on "carb counting", in this closed-loop predictive modeling approach, the four daily insulin dosages needed to reach the target blood sugar levels for the "normal" daily carbohydrate consumption and amount of physical activity, are continuously adjusted based on the pre-meal and pre-night blood sugar level readings. Each new blood sugar reading provides the feedback to fine-tune and track the body's insulin requirements. Within this strategy, the key specific factors, which have to be determined experimentally, are the blood sugar correction factor and the carbohydrate ratio. The blood sugar correction factor sets both the "proportional gain" and "integral gain" factors for the four feedback loops. When taken too low, deviations from the target blood sugar level are not corrected for effectively, when taken too high, the blood sugar regulation will become unstable. Since in this approach, the carbohydrate ratio is only used to account for non-standard carbohydrate intakes, it is usually not required to work with meal specific ratios.
Dose calculation
Insulin dosage is given by the formula : based on the person's blood glucose and carbohydrate intake and these constants: * ''TR'' = target rate * ''CF'' = corrective factor * ''KF'' = carbohydrate factor Blood glucose and target rate are expressed in mg/dL or mmol/L. Constants should be set by a physician or clinical pharmacist.Abuse
The abuse of exogenous insulin carries with it an attendant risk of hypoglycemic coma and death when the amount used is in excess of that required to handle ingested carbohydrate. Acute risks include brain damage, paralysis, anddeath
Death is the irreversible cessation of all biological functions that sustain an organism. For organisms with a brain, death can also be defined as the irreversible cessation of functioning of the whole brain, including brainstem, and brain ...
. Symptoms may include dizziness, weakness, trembling, palpitations, seizures, confusion, headache, drowsiness, coma, diaphoresis
Perspiration, also known as sweating, is the production of fluids secreted by the sweat glands in the skin of mammals.
Two types of sweat glands can be found in humans: eccrine glands and apocrine glands. The eccrine sweat glands are distribu ...
and nausea
Nausea is a diffuse sensation of unease and discomfort, sometimes perceived as an urge to vomit. While not painful, it can be a debilitating symptom if prolonged and has been described as placing discomfort on the chest, abdomen, or back of the ...
. All persons with overdoses should be referred for medical assessment and treatment, which may last for hours or days.
Data from the US National Poison Data System (2013) indicates that 89.3% of insulin cases reported to poison centers are unintentional, as a result of therapeutic error. Another 10% of cases are intentional, and may reflect attempted suicide, abuse, criminal intent, secondary gain or other unknown reasons. Hypoglycemia that has been induced by exogenous insulin can be chemically detected by examining the ratio of insulin to C-peptide
The connecting peptide, or C-peptide, is a short 31-amino-acid polypeptide that connects insulin's A-chain to its B-chain in the proinsulin molecule. In the context of diabetes or hypoglycemia, a measurement of C-peptide blood serum levels can ...
in peripheral circulation. It has been suggested that this type of approach could be used to detect exogenous insulin abuse by athletes.
The possibility of using insulin in an attempt to improve athletic performance was suggested as early as the 1998 Winter Olympics
The 1998 Winter Olympics, officially known as the and commonly known as Nagano 1998 ( ja, 長野1998), was a winter multi-sport event held from 7 to 22 February 1998, mainly in Nagano, Japan, with some events taking place in the ...
in Nagano, Japan, as reported by Peter Sönksen in the July 2001 issue of ''Journal of Endocrinology
The ''Journal of Endocrinology'' is a monthly peer-reviewed scientific journal that publishes original research articles, reviews and commentaries. Its focus is on endocrine physiology and metabolism, including hormone secretion, hormone action, an ...
''. The question of whether non-diabetic athletes could legally use insulin was raised by a Russian medical officer. Whether insulin would actually improve athletic performance is unclear, but concerns about its use led the International Olympic Committee to ban use of the hormone by non-diabetic athletes in 1998.
The book ''Game of Shadows
''Game of Shadows: Barry Bonds, BALCO, and the Steroids Scandal that Rocked Professional Sports'' is a bestselling non-fiction book published on March 23, 2006, and written by Mark Fainaru-Wada and Lance Williams, reporters for the ''San Franc ...
'' (2001), by reporters Mark Fainaru-Wada and Lance Williams, included allegations that baseball player Barry Bonds used insulin (as well as other drugs) in the apparent belief that it would increase the effectiveness of the growth hormone he was alleged to be taking.
Bonds eventually testified in front of a federal grand jury as part of a government investigation of BALCO
The Bay Area Laboratory Co-operative (BALCO) (1984–2003) was an American company led by founder and owner Victor Conte. In 2003, journalists Lance Williams and Mark Fainaru-Wada investigated the company's role in a drug sports scandal later re ...
.
Bodybuilders in particular are claimed to be using exogenous insulin and other drugs in the belief that they will increase muscle mass. Bodybuilders have been described as injecting up to 10 IU of regular synthetic insulin before eating sugary meals.
A 2008 report suggested that insulin is sometimes used in combination with anabolic steroids and growth hormone
Growth hormone (GH) or somatotropin, also known as human growth hormone (hGH or HGH) in its human form, is a peptide hormone that stimulates growth, cell reproduction, and cell regeneration in humans and other animals. It is thus important in h ...
(GH), and that "Athletes are exposing themselves to potential harm by self‐administering large doses of GH, IGF‐I and insulin".
Insulin abuse has been mentioned as a possible factor in the deaths of bodybuilders Ghent Wakefield and Rich Piana.
Insulin, human growth hormone (HGH) and insulin-like growth factor 1 (IGF-1) are self-administered by those looking to increase muscle mass beyond the scope offered by anabolic steroids alone. Their rationale is that since insulin and HGH act synergistically to promote growth, and since IGF-1 is a primary mediator of musculoskeletal growth, the 'stacking' of insulin, HGH and IGF-1 should offer a synergistic growth effect on skeletal muscle. This theory has been supported in recent years by top-level bodybuilders whose competition weight is in excess of of muscle, larger than that of competitors in the past, and with even lower levels of body fat.
Detection in biological fluids
Insulin is often measured in serum, plasma or blood in order to monitor therapy in people who are diabetic, confirm a diagnosis of poisoning in hospitalized persons or assist in a medicolegal investigation of suspicious death. Interpretation of the resulting insulin concentrations is complex, given the numerous types of insulin available, various routes of administration, the presence of anti-insulin antibodies in insulin-dependent diabetics and the ''ex vivo'' instability of the drug. Other potential confounding factors include the wide-ranging cross-reactivity of commercial insulin immunoassays for the biosynthetic insulin analogs, the use of high-dose intravenous insulin as an antidote to antihypertensive drug overdosage and postmortem redistribution of insulin within the body. The use of a chromatographic technique for insulin assay may be preferable to immunoassay in some circumstances, to avoid the issue of cross-reactivity affecting the quantitative result and also to assist identifying the specific type of insulin in the specimen.Combination with other antidiabetic drugs
A combination therapy of insulin and otherantidiabetic drug
Drugs used in diabetes treat diabetes mellitus by altering the glucose level in the blood. With the exceptions of insulin, most GLP receptor agonists ( liraglutide, exenatide, and others), and pramlintide, all are administered orally and are t ...
s appears to be most beneficial in people who are diabetic, who still have residual insulin secretory capacity. A combination of insulin therapy and sulfonylurea
Sulfonylureas (UK: sulphonylurea) are a class of organic compounds used in medicine and agriculture, for example as antidiabetic drugs widely used in the management of diabetes mellitus type 2. They act by increasing insulin release from the bet ...
is more effective than insulin alone in treating people with type 2 diabetes after secondary failure to oral drugs, leading to better glucose profiles and/or decreased insulin needs.
Society and culture
Economics
In the United States the unit price of insulin has increased steadily from 1991 to 2019. It rose threefold from 2002 to 2013. Costs can be as high as US$900 per month. Concerns were raised in 2016 of pharmaceutical companies working together to increase prices. In January 2019, lawmakers from theUnited States House of Representatives
The United States House of Representatives, often referred to as the House of Representatives, the U.S. House, or simply the House, is the lower chamber of the United States Congress, with the Senate being the upper chamber. Together they ...
sent letters to insulin manufacturers Eli Lilly and Co.
Eli Lilly and Company is an American pharmaceutical company headquartered in Indianapolis, Indiana, with offices in 18 countries. Its products are sold in approximately 125 countries. The company was founded in 1876 by, and named after, Colonel ...
, Sanofi
Sanofi S.A. is a French multinational pharmaceutical and healthcare company headquartered in Paris, France. Originally, the corporation was established in 1973 and merged with Synthélabo in 1999 to form Sanofi-Synthélabo. In 2004, Sanofi-Syn ...
and Novo Nordisk
Novo Nordisk A/S is a Danish multinational pharmaceutical company headquartered in Bagsværd, Denmark, with production facilities in nine countries, and affiliates or offices in five countries. Novo Nordisk is controlled by majority shareholder ...
asking for explanations for their rapidly raising insulin prices. The annual cost of insulin for people with type 1 diabetes in the U.S. almost doubled from $2,900 to $5,700 over the period from 2012 to 2016.
People in the U.S. pay two to six times more than the rest of the world, including Canada, for brand name prescription medicine, according to the International Federation of Health Plans. Canada, like many other industrialized countries, has price controls on the cost of pharmaceuticals.
California, in July 2022, approved a budget that allocates $100 million for the state to create its own insulin at a close-to-cost price.
Insulin, and all other medications, are supplied free of charge to people with diabetes by the National Health Service
The National Health Service (NHS) is the umbrella term for the publicly funded healthcare systems of the United Kingdom (UK). Since 1948, they have been funded out of general taxation. There are three systems which are referred to using the " ...
in the countries of the United Kingdom.
Regulatory status
In March 2020, the FDA changed the regulatory pathway for approval of new insulin products. Insulin is regulated as a biologic rather than as a drug. The changed status gives the FDA more flexibility for approval and labeling. In July 2021, the FDA approved insulin glargine-yfgn (Semglee), a biosimilar product that contains the long acting analog insulin glargine. Insulin glargine-yfgn is interchangeable and less expensive than the reference product,insulin glargine
Insulin glargine, sold under the brand name Lantus among others, is a long-acting modified form of medical insulin, used in the management of type I and type II diabetes. It is typically the recommended long acting insulin in the United King ...
(Lantus), which had been approved in 2000. The FDA requires that new insulin products are not inferior to existing insulin products with respect to reduction in hemoglobin A1c. See Misbin, RI (February 2022). Insulin – History from an FDA Insider. Politics and Prose Publishing, Washington DC. Text ISBN 978-I-62429-391-77
Research
Inhalation
In 2006 the U.S.Food and Drug Administration
The United States Food and Drug Administration (FDA or US FDA) is a List of United States federal agencies, federal agency of the United States Department of Health and Human Services, Department of Health and Human Services. The FDA is respon ...
(FDA) approved the use of Exubera, the first inhalable insulin. It was withdrawn from the market by its maker as of third quarter 2007, due to lack of acceptance.
Inhaled insulin claimed to have similar efficacy to injected insulin, both in terms of controlling glucose levels and blood half-life. Currently, inhaled insulin is short acting and is typically taken before meals; an injection of long-acting insulin at night is often still required. When people were switched from injected to inhaled insulin, no significant difference was observed in HbA1c levels over three months. Accurate dosing was a particular problem, although people showed no significant weight gain or pulmonary function decline over the length of the trial, when compared to the baseline.
Following its commercial launch in 2005 in the United Kingdom, it was not (as of July 2006) recommended by National Institute for Health and Clinical Excellence
The National Institute for Health and Care Excellence (NICE) is an executive non-departmental public body of the Department of Health and Social Care in England that publishes guidelines in four areas:
* the use of health technologies withi ...
for routine use, except in cases where there is "proven injection phobia diagnosed by a psychiatrist or psychologist".
In January 2008, the world's largest insulin manufacturer, Novo Nordisk
Novo Nordisk A/S is a Danish multinational pharmaceutical company headquartered in Bagsværd, Denmark, with production facilities in nine countries, and affiliates or offices in five countries. Novo Nordisk is controlled by majority shareholder ...
, also announced that the company was discontinuing all further development of the company's own version of inhalable insulin, known as the AERx iDMS inhaled insulin system. Similarly, Eli Lilly and Company ended its efforts to develop its inhaled Air Insulin in March 2008. However, MannKind Corp. (majority owner, Alfred E. Mann) remains optimistic about the concept.
Transdermal
There are several methods for transdermal delivery of insulin. Pulsatile insulin uses microjets to pulse insulin into the person, mimicking the physiological secretions of insulin by the pancreas. Jet injection had different insulin delivery peaks and durations as compared to needle injection. Some diabetics may prefer jet injectors to hypodermic injection. Both electricity using iontophoresis and ultrasound have been found to make the skin temporarily porous. The insulin administration aspect remains experimental, but the blood glucose test aspect of "wrist appliances" is commercially available. Researchers have produced a watch-like device that tests for blood glucose levels through the skin and administers corrective doses of insulin through pores in the skin. A similar device, but relying on skin-penetrating "microneedles", was in the animal testing stage in 2015.Intranasal
Intranasal insulin is being investigated. A randomized controlled trial that will determine whether intranasal insulin can delay or prevent the onset of type 1 diabetes in at-risk children and young adults is expected to yield results in 2016.By mouth
The basic appeal of hypoglycemic agents by mouth is that most people would prefer a pill or an oral liquid to an injection. However, insulin is apeptide hormone
Peptide hormones or protein hormones are hormones whose molecules are peptide, or proteins, respectively. The latter have longer amino acid chain lengths than the former. These hormones have an effect on the endocrine system of animals, including h ...
, which is digested in the stomach
The stomach is a muscular, hollow organ in the gastrointestinal tract of humans and many other animals, including several invertebrates. The stomach has a dilated structure and functions as a vital organ in the digestive system. The stomach i ...
and gut and in order to be effective at controlling blood sugar, cannot be taken orally in its current form.
The potential market for an oral form of insulin is assumed to be enormous, thus many laboratories have attempted to devise ways of moving enough intact insulin from the gut to the portal vein to have a measurable effect on blood sugar.
A number of derivatization and formulation strategies are currently being pursued to in an attempt to develop an orally available insulin. Many of these approaches employ nanoparticle
A nanoparticle or ultrafine particle is usually defined as a particle of matter that is between 1 and 100 nanometres (nm) in diameter. The term is sometimes used for larger particles, up to 500 nm, or fibers and tubes that are less than 10 ...
delivery systems and several are being tested in clinical trial
Clinical trials are prospective biomedical or behavioral research studies on human participants designed to answer specific questions about biomedical or behavioral interventions, including new treatments (such as novel vaccines, drugs, diet ...
s.
Pancreatic transplantation
Another improvement would be a transplantation of the pancreas or beta cell to avoid periodic insulin administration. This would result in a self-regulating insulin source. Transplantation of an entire pancreas (as an individual organ) is difficult and relatively uncommon. It is often performed in conjunction withliver
The liver is a major organ only found in vertebrates which performs many essential biological functions such as detoxification of the organism, and the synthesis of proteins and biochemicals necessary for digestion and growth. In humans, it ...
or kidney
The kidneys are two reddish-brown bean-shaped organs found in vertebrates. They are located on the left and right in the retroperitoneal space, and in adult humans are about in length. They receive blood from the paired renal arteries; blo ...
transplant, although it can be done by itself. It is also possible to do a transplantation of only the pancreatic beta cells. However, islet transplants had been highly experimental for many years, but some researchers in Alberta, Canada
Alberta ( ) is one of the thirteen provinces and territories of Canada. It is part of Western Canada and is one of the three prairie provinces. Alberta is bordered by British Columbia to the west, Saskatchewan to the east, the Northwest Territ ...
, have developed techniques with a high ''initial'' success rate (about 90% in one group). Nearly half of those who got an islet cell transplant were insulin-free one year after the operation; by the end of the second year that number drops to about one in seven. However, researchers at the University of Illinois at Chicago (UIC) have slightly modified the Edmonton Protocol procedure for islet cell transplantation and achieved insulin independence in diabetic people, with fewer but better-functioning pancreatic islet cells. Longer-term studies are needed to validate whether it improves the rate of insulin-independence.
Beta cell transplant may become practical in the near future. Additionally, some researchers have explored the possibility of transplanting genetically engineered
Genetic engineering, also called genetic modification or genetic manipulation, is the modification and manipulation of an organism's genes using technology. It is a set of technologies used to change the genetic makeup of cells, including t ...
non-beta cells to secrete insulin. Clinically testable results are far from realization at this time. Several other non-transplant methods of automatic insulin delivery are being developed in research labs, but none is close to clinical approval.
References
External links
* * * {{DEFAULTSORT:Insulin Medication Insulin therapies Eli Lilly and Company brands Wikipedia medicine articles ready to translate World Health Organization essential medicines