House Energy Rating on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
The Nationwide House Energy Rating Scheme (NatHERS) is a national scheme to measure the energy efficiency of a residential dwelling in Australia. An accredited software tool assesses the home based on a variety of criteria and produces an energy star rating.
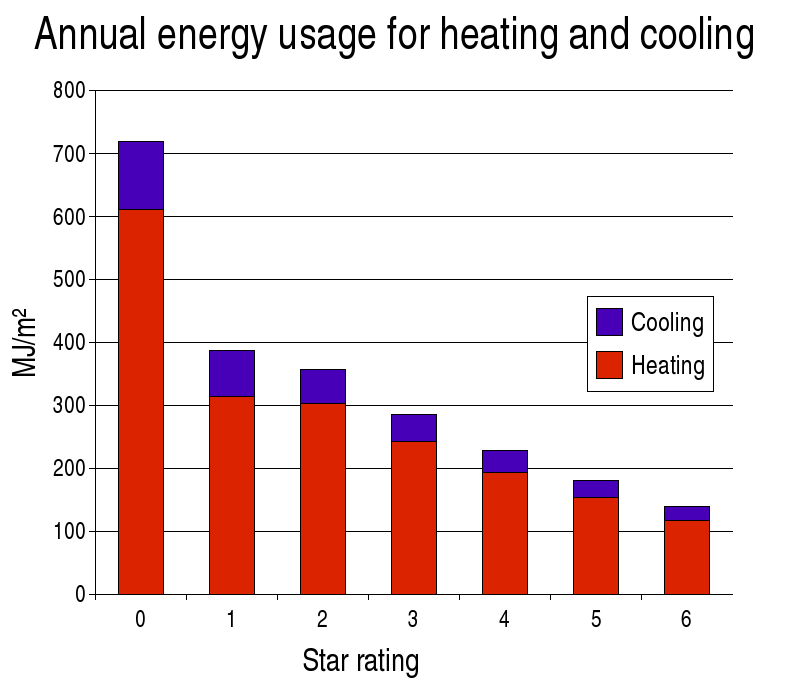
Queensland’s implementation of energy efficiency requirements from 1 May 2010
{{Energy conservation in Australia Building energy rating Energy conservation in Australia
Background and history
The Five Star Design Rating (FSDR) was an award developed in the 1980s for "high efficiency through excellence in design and construction" which assisted builders in marketing energy efficient home designs. The certification was developed by the Glass, Mass and Insulation Council of Australia (GMI Council) together withCSIRO
The Commonwealth Scientific and Industrial Research Organisation (CSIRO) is an Australian Government agency responsible for scientific research.
CSIRO works with leading organisations around the world. From its headquarters in Canberra, CSIRO ...
Division of Building Research. The GMI Council was funded by Federal and state governments (New South Wales
)
, nickname =
, image_map = New South Wales in Australia.svg
, map_caption = Location of New South Wales in AustraliaCoordinates:
, subdivision_type = Country
, subdivision_name = Australia
, established_title = Before federation
, es ...
, South Australia
South Australia (commonly abbreviated as SA) is a States and territories of Australia, state in the southern central part of Australia. It covers some of the most arid parts of the country. With a total land area of , it is the fourth-largest o ...
, Tasmania
)
, nickname =
, image_map = Tasmania in Australia.svg
, map_caption = Location of Tasmania in AustraliaCoordinates:
, subdivision_type = Country
, subdi ...
, and Victoria) and by private investors.
Under FSDR, the basic elements of glass, mass and insulation were the basis of the design principles of a five-star home. The building industry did not widely accept the system due to its simple pass/fail rating and its restrictive guidelines.Development of a new framework for a House Rating Scheme (HRS) Maria Kordjamshidi. August 1997. University of New South Wales.
In the 1990s, individual states developed their own schemes. The Victorian scheme, based on a computer program, was eventually accepted as the most effective. However, it worked poorly in warm humid climates such as found in Queensland. The development of a nationwide House Energy Rating Scheme (NatHERS) began in 1993, based on the Victorian scheme, using the CHEETAH / CHEENATH engine developed at CSIRO. Software products NatHERS, FirstRate and Quick Rate, BERS, Q Rate and ACTHERS are based on this engine. NatHERS and BERS run the engine directly, while others use correlations based on the engine.
The NatHERS scheme was introduced in 1993. The Australian Building Codes Board introduced energy efficiency measures for houses into the Building Code of Australia (BCA) on 1 January 2003.
It has been adopted by all Australian states and territories which did not already have an equivalent system in place. During 2006, requirements for 5-star energy ratings were introduced for new homes through the BCA in Western Australia
Western Australia (commonly abbreviated as WA) is a state of Australia occupying the western percent of the land area of Australia excluding external territories. It is bounded by the Indian Ocean to the north and west, the Southern Ocean to t ...
and the Australian Capital Territory
The Australian Capital Territory (commonly abbreviated as ACT), known as the Federal Capital Territory (FCT) until 1938, is a landlocked federal territory of Australia containing the national capital Canberra and some surrounding township#Aust ...
. As of 2010, Queensland had adopted 6-star requirements for new homes. Victoria
Victoria most commonly refers to:
* Victoria (Australia), a state of the Commonwealth of Australia
* Victoria, British Columbia, provincial capital of British Columbia, Canada
* Victoria (mythology), Roman goddess of Victory
* Victoria, Seychelle ...
and South Australia
South Australia (commonly abbreviated as SA) is a States and territories of Australia, state in the southern central part of Australia. It covers some of the most arid parts of the country. With a total land area of , it is the fourth-largest o ...
have gone beyond the standard, and mandated, instead of 4 stars, a 5-star rating (enacted July 2004) – all new homes and apartments built in Victoria must since 2010 comply with the 6-star standard.
Description
The house energy rating is the index of a building's thermal performance (''i.e.'' heating and cooling requirements to keep the home comfortable) for residential homes. , house plans and building specifications, which outline the structure, design and materials, are used as input data. A NatHERS-accredited software tool estimates how much heat is required to be added or removed to keep the building thermally comfortable, and generates a star rating out of 10, along with a certificate. By 2020-2021, approximately 90 per cent of building approvals were assessed using the scheme, in order to show compliance with theNational Construction Code
The National Construction Code (NCC) is a set of minimum requirements for buildings in Australia. The requirements concern the aspects of health, safety, accessibility, amenity and sustainability of the types of buildings that the code applies to ...
. Detached home
A stand-alone house (also called a single-detached dwelling, detached residence or detached house) is a free-standing residential building. It is sometimes referred to as a single-family home, as opposed to a multi-family residential dwelling ...
s in most parts of Australia require a 6-star rating or above.
Future plans include offering energy assessments for Whole of Home (including energy performance of common household appliances), and In Home energy assessments for existing homes.Governance
NatHERS is administered by theDepartment of Climate Change, Energy, the Environment and Water
The Department of Climate Change, Energy, the Environment and Water (DCCEEW) is a department of the Australian Government. The department was established on 1 July 2022, superseding the water and environment functions from the Department of Agri ...
on behalf of the states and territories.Ratings

6-Star rating
A 6-Star rating indicates that a building achieves a higher level of thermal energy performance than, say a 5 star rating. As of November 2011, 6-star equivalence is the current minimum requirement in most of Australia.5-Star rating
A 5-Star rating indicates that a building achieves a high level of thermal energyperformance
A performance is an act of staging or presenting a play, concert, or other form of entertainment. It is also defined as the action or process of carrying out or accomplishing an action, task, or function.
Management science
In the work place ...
, and will require minimum levels of heating and cooling to be comfortable in winter and summer. Houses which achieve a 5 star rating, compared to the average 2 star home, should be more comfortable to live in, have lower energy bills, and costs to install heating and cooling equipment should also be lower.
Energy assessments take into account different climatic conditions in different parts of the country and are benchmarked according to average household energy consumption particular to a given climatic region.
The house energy rating does not currently include the efficiency of any appliances fitted or used within the house. There are also no physical testing requirements, so air tightness testing is not required as it is with the regulations in the UK.
State government initiatives
* ACT House Energy Rating Scheme (ACTHERS), requires new or previously lived in residential homes to have an Energy Efficiency Rating (EER) Statement, prepared by an accredited ACTHERS assessor, if they are to be sold. As of the February 2006, the required software used in assessment is FirstRate, Version 3.1 or Version 4. * InVictoria
Victoria most commonly refers to:
* Victoria (Australia), a state of the Commonwealth of Australia
* Victoria, British Columbia, provincial capital of British Columbia, Canada
* Victoria (mythology), Roman goddess of Victory
* Victoria, Seychelle ...
all new homes built since 2005 are required to achieve a 5 Star rating. Rating can be performed using any software approved by NatHERS.
* In South Australia
South Australia (commonly abbreviated as SA) is a States and territories of Australia, state in the southern central part of Australia. It covers some of the most arid parts of the country. With a total land area of , it is the fourth-largest o ...
, all new homes (and alterations to existing homes) are required to achieve a 6 star rating. This requirement was introduced on 1 September 2010.
* Western Australia: in 2007 the WA Government introduced further energy and water usage regulatory requirements. 5 Star Plus consists of two codes: the Energy Use in Houses Code, which requires a minimum standard of energy performance for a hot water system; and the Water Use in Houses Code, which includes provisions for alternative water supplies, efficient fixtures and fittings, and grey water diversion.
* In Queensland
)
, nickname = Sunshine State
, image_map = Queensland in Australia.svg
, map_caption = Location of Queensland in Australia
, subdivision_type = Country
, subdivision_name = Australia
, established_title = Before federation
, establishe ...
it is proposed that from either 1 January 2009, or when the Building Code of Australia 2009 update is released in May 2009, that all new homes built in Queensland will be required to achieve a 5 star energy equivalent rating. Currently the minimum requirement is 3.5 stars.
See also
*Green Star (Australia)
Green Star is a voluntary sustainability rating system for buildings in Australia. It was launched in 2003 by the Green Building Council of Australia (GBCA).
The Green Star rating system assesses the sustainability of projects at all stages of ...
* BASIX (NSW)
* (Canada)
* (UK)
* (United States)
* Energy conservation
Energy conservation is the effort to reduce wasteful energy consumption by using fewer energy services. This can be done by using energy more effectively (using less energy for continuous service) or changing one's behavior to use less service (f ...
* Environmental economics
Environmental economics is a sub-field of economics concerned with environmental issues. It has become a widely studied subject due to growing environmental concerns in the twenty-first century. Environmental economics "undertakes theoretical or ...
* Green building
Green building (also known as green construction or sustainable building) refers to both a structure and the application of processes that are environmentally responsible and resource-efficient throughout a building's life-cycle: from planni ...
* Zero-energy building
A Zero Energy Building (ZEB), also known as a Net Zero Energy (NZE) building, is a building with net zero energy consumption, meaning the total amount of energy used by the building on an annual basis is equal to the amount of renewable energy ...
* Low-energy house
A low-energy house is characterized by an energy-efficient design and technical features which enable it to provide high living standards and comfort with low energy consumption and carbon emissions. Traditional heating and active cooling systems ...
* Passive house
"Passive house" (german: Passivhaus) is a voluntary standard for energy efficiency in a building, which reduces the building's ecological footprint. It results in ultra-low energy buildings that require little energy for space heating or coo ...
References
External links
Queensland’s implementation of energy efficiency requirements from 1 May 2010
{{Energy conservation in Australia Building energy rating Energy conservation in Australia