Hookworm infection on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Hookworm infection is an infection by a type of
 Hookworm infections in humans include
Hookworm infections in humans include
 The hookworm thrives in warm soil where temperatures are over . They exist primarily in
The hookworm thrives in warm soil where temperatures are over . They exist primarily in  They mate inside the host, females laying up to 30,000 eggs per day and some 18 to 54 million eggs during their lifetimes, which pass out in feces. Because 5 to 7 weeks are needed for adult worms to mature, mate, and produce eggs, in the early stages of very heavy infection, acute symptoms might occur without any eggs being detected in the patient's feces. This can make diagnosis very difficult.
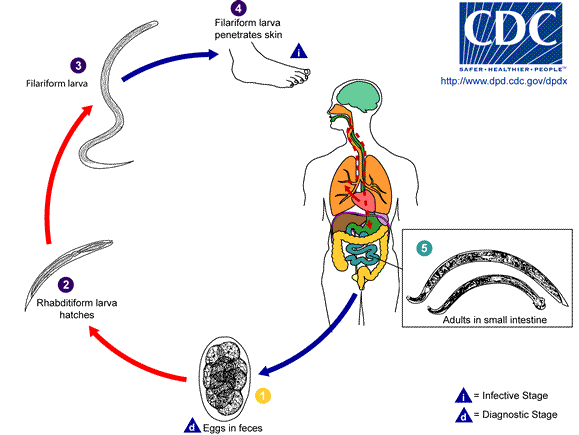
''N. americanus'' and ''A. duodenale'' eggs can be found in warm, moist soil where they eventually hatch into first-stage larvae, or L1. L1, the feeding noninfective rhabditoform stage, will feed on soil microbes and eventually molt into second-stage larvae, L2, which is also in the rhabditoform stage. It will feed for about 7 days and then molt into the third-stage larvae, or L3. This is the filariform stage of the parasite, that is, the nonfeeding infective form of the larvae. The L3 larvae are extremely motile and seek higher ground to increase their chances of penetrating the skin of a human host. The L3 larvae can survive up to 2 weeks without finding a host. While ''N. americanus'' larvae only infect through penetration of skin, ''A. duodenale'' can infect both through penetration and orally. After the L3 larvae have successfully entered the host, they then travel through the subcutaneous venules and lymphatic vessels of the human host. Eventually, the L3 larvae enter the lungs through the pulmonary capillaries and break out into the alveoli. They then travel up the trachea to be coughed and swallowed by the host. After being swallowed, the L3 larvae are then found in the small intestine, where they molt into the L4, or adult worm stage. The entire process from skin penetration to adult development takes about 5–9 weeks. The female adult worms release eggs (''N. americanus'' about 9,000–10,000 eggs/day and ''A. duodenale'' 25,000–30,000 eggs/day), which are passed in the feces of the human host. These eggs hatch in the environment within several days and the cycle starts anew.
They mate inside the host, females laying up to 30,000 eggs per day and some 18 to 54 million eggs during their lifetimes, which pass out in feces. Because 5 to 7 weeks are needed for adult worms to mature, mate, and produce eggs, in the early stages of very heavy infection, acute symptoms might occur without any eggs being detected in the patient's feces. This can make diagnosis very difficult.
''N. americanus'' and ''A. duodenale'' eggs can be found in warm, moist soil where they eventually hatch into first-stage larvae, or L1. L1, the feeding noninfective rhabditoform stage, will feed on soil microbes and eventually molt into second-stage larvae, L2, which is also in the rhabditoform stage. It will feed for about 7 days and then molt into the third-stage larvae, or L3. This is the filariform stage of the parasite, that is, the nonfeeding infective form of the larvae. The L3 larvae are extremely motile and seek higher ground to increase their chances of penetrating the skin of a human host. The L3 larvae can survive up to 2 weeks without finding a host. While ''N. americanus'' larvae only infect through penetration of skin, ''A. duodenale'' can infect both through penetration and orally. After the L3 larvae have successfully entered the host, they then travel through the subcutaneous venules and lymphatic vessels of the human host. Eventually, the L3 larvae enter the lungs through the pulmonary capillaries and break out into the alveoli. They then travel up the trachea to be coughed and swallowed by the host. After being swallowed, the L3 larvae are then found in the small intestine, where they molt into the L4, or adult worm stage. The entire process from skin penetration to adult development takes about 5–9 weeks. The female adult worms release eggs (''N. americanus'' about 9,000–10,000 eggs/day and ''A. duodenale'' 25,000–30,000 eggs/day), which are passed in the feces of the human host. These eggs hatch in the environment within several days and the cycle starts anew.
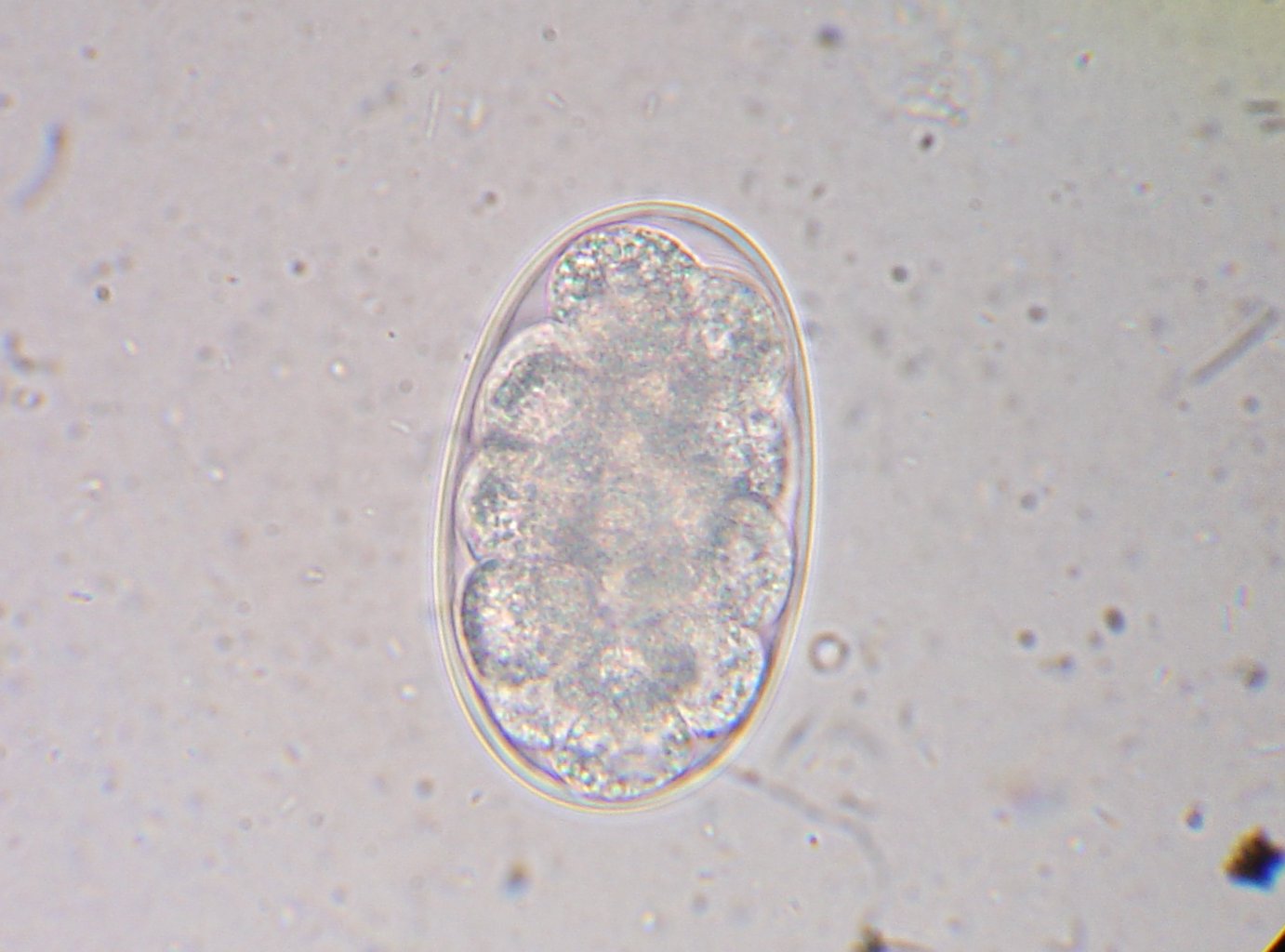 Diagnosis depends on finding characteristic worm eggs on microscopic examination of the stools, although this is not possible in early infection. Early signs of infection in most dogs include limbular limping and anal itching. The eggs are oval or elliptical, measuring 60 by 40 µm, colorless, not
Diagnosis depends on finding characteristic worm eggs on microscopic examination of the stools, although this is not possible in early infection. Early signs of infection in most dogs include limbular limping and anal itching. The eggs are oval or elliptical, measuring 60 by 40 µm, colorless, not
 It is estimated that between 576 and 740 million individuals are infected with hookworm. Of these infected individuals, about 80 million are severely affected. The major cause of hookworm infection is ''N. americanus'' which is found in the Americas, sub-Saharan Africa, and Asia. ''A. duodenale'' is found in more scattered focal environments, namely Europe and the Mediterranean. Most infected individuals are concentrated in sub-Saharan Africa and East Asia/the Pacific Islands with each region having estimates of 198 million and 149 million infected individuals, respectively. Other affected regions include: South Asia (50 million), Latin America and the Caribbean (50 million), South Asia (59 million), Middle East/North Africa (10 million). A majority of these infected individuals live in poverty-stricken areas with poor sanitation. Hookworm infection is most concentrated among the world's poorest who live on less than $2 a day.
While hookworm infection may not directly lead to mortality, its effects on morbidity demand immediate attention. When considering
It is estimated that between 576 and 740 million individuals are infected with hookworm. Of these infected individuals, about 80 million are severely affected. The major cause of hookworm infection is ''N. americanus'' which is found in the Americas, sub-Saharan Africa, and Asia. ''A. duodenale'' is found in more scattered focal environments, namely Europe and the Mediterranean. Most infected individuals are concentrated in sub-Saharan Africa and East Asia/the Pacific Islands with each region having estimates of 198 million and 149 million infected individuals, respectively. Other affected regions include: South Asia (50 million), Latin America and the Caribbean (50 million), South Asia (59 million), Middle East/North Africa (10 million). A majority of these infected individuals live in poverty-stricken areas with poor sanitation. Hookworm infection is most concentrated among the world's poorest who live on less than $2 a day.
While hookworm infection may not directly lead to mortality, its effects on morbidity demand immediate attention. When considering
 On October 26, 1909, the Rockefeller Sanitary Commission for the Eradication of Hookworm Disease was organized as a result of a gift of US$1 million from John D. Rockefeller, Sr. The five-year program was a remarkable success and a great contribution to the United States' public health, instilling public education, medication, field work and modern government health departments in eleven southern states.
The hookworm exhibit was a prominent part of the 1910 Mississippi state fair.
The commission found that an average of 40% of school-aged children were infected with hookworm. Areas with higher levels of hookworm infection prior to the eradication program experienced greater increases in school enrollment, attendance, and literacy after the intervention. Econometric studies have shown that this effect cannot be explained by a variety of alternative factors, including differential trends across areas, changing crop prices, shifts in certain educational and health policies and the effect of malaria eradication. No significant contemporaneous results were found for adults who should have benefited less from the intervention owing to their substantially lower (prior) infection rates. The program nearly eradicated hookworm and would flourish afterward with new funding as the
On October 26, 1909, the Rockefeller Sanitary Commission for the Eradication of Hookworm Disease was organized as a result of a gift of US$1 million from John D. Rockefeller, Sr. The five-year program was a remarkable success and a great contribution to the United States' public health, instilling public education, medication, field work and modern government health departments in eleven southern states.
The hookworm exhibit was a prominent part of the 1910 Mississippi state fair.
The commission found that an average of 40% of school-aged children were infected with hookworm. Areas with higher levels of hookworm infection prior to the eradication program experienced greater increases in school enrollment, attendance, and literacy after the intervention. Econometric studies have shown that this effect cannot be explained by a variety of alternative factors, including differential trends across areas, changing crop prices, shifts in certain educational and health policies and the effect of malaria eradication. No significant contemporaneous results were found for adults who should have benefited less from the intervention owing to their substantially lower (prior) infection rates. The program nearly eradicated hookworm and would flourish afterward with new funding as the
CDC Department of Parasitic Diseases images of the hookworm life cycle
!-- includes copyright-free images that could be used for the article -->
Centers for Disease Control and Prevention
Dog hookworm (''Ancylostoma caninum'') at MetaPathogen: facts, life cycle, references
Human hookworms (''Ancylostoma duodenale'' and ''Necator americanus'') at MetaPathogen: facts, life cycle, references
{{Portal bar, Biology, Medicine Strongylida Parasitic nematodes of humans Tropical diseases Conditions diagnosed by stool test Zoonoses Parasites of cats Cat diseases Parasites of dogs Dog diseases Infectious diseases with eradication efforts Wikipedia medicine articles ready to translate Wikipedia infectious disease articles ready to translate
intestinal parasite
An intestinal parasite infection is a condition in which a parasite infects the gastro-intestinal tract of humans and other animals. Such parasites can live anywhere in the body, but most prefer the intestinal wall.
Routes of exposure and inf ...
known as a hookworm
Hookworms are intestinal, blood-feeding, parasitic roundworms that cause types of infection known as helminthiases. Hookworm infection is found in many parts of the world, and is common in areas with poor access to adequate water, sanitation, ...
. Initially, itching and a rash may occur at the site of infection. Those only affected by a few worms may show no symptoms. Those infected by many worms may experience abdominal pain
Abdominal pain, also known as a stomach ache, is a symptom associated with both non-serious and serious medical issues.
Common causes of pain in the abdomen include gastroenteritis and irritable bowel syndrome. About 15% of people have a m ...
, diarrhea, weight loss, and tiredness
Fatigue describes a state of tiredness that does not resolve with rest or sleep. In general usage, fatigue is synonymous with extreme tiredness or exhaustion that normally follows prolonged physical or mental activity. When it does not resolve ...
. The mental and physical development of children may be affected. Anemia
Anemia or anaemia (British English) is a blood disorder in which the blood has a reduced ability to carry oxygen due to a lower than normal number of red blood cells, or a reduction in the amount of hemoglobin. When anemia comes on slowly, t ...
may result.
Two common hookworm infections in humans are ancylostomiasis
Ancylostomiasis is a hookworm disease caused by infection with Ancylostoma hookworms. The name is derived from Greek ancylos αγκύλος "crooked, bent" and stoma στόμα "mouth".
Ancylostomiasis is also known as miner's anaemia, tunnel d ...
and necatoriasis, caused by the species ''Ancylostoma duodenale
''Ancylostoma'' is a genus of nematodes that includes some species of hookworms.
Species include:
: ''Ancylostoma braziliense'', commonly infects cats, popularly known in Brazil as ''bicho-geográfico''
: ''Ancylostoma caninum'', commonly infect ...
'' and ''Necator americanus
''Necator americanus'' is a species of hookworm (a type of helminth) commonly known as the New World hookworm. Like other hookworms, it is a member of the phylum Nematoda. It is an obligatory parasitic nematode that lives in the small intestine ...
'' respectively. Hookworm eggs are deposited in the stools of infected people. If these end up in the environment, they can hatch into larva
A larva (; plural larvae ) is a distinct juvenile form many animals undergo before metamorphosis into adults. Animals with indirect development such as insects, amphibians, or cnidarians typically have a larval phase of their life cycle.
...
e (immature worms), which can then penetrate the skin. One type can also be spread through contaminated food. Risk factors include walking barefoot
Barefoot is the state of not wearing any footwear.
There are health benefits and some risks associated with going barefoot. Shoes, while they offer protection, can limit the flexibility, strength, and mobility of the foot and can lead to h ...
in warm climates, where sanitation
Sanitation refers to public health conditions related to clean drinking water and treatment and disposal of human excreta and sewage. Preventing human contact with feces is part of sanitation, as is hand washing with soap. Sanitation syste ...
is poor. Diagnosis is by examination of a stool sample with a microscope
A microscope () is a laboratory instrument used to examine objects that are too small to be seen by the naked eye. Microscopy is the science of investigating small objects and structures using a microscope. Microscopic means being invisi ...
.
The disease can be prevented on an individual level by not walking barefoot in areas where the disease is common. At a population level, decreasing outdoor defecation, not using raw feces as fertilizer
A fertilizer (American English) or fertiliser (British English; see spelling differences) is any material of natural or synthetic origin that is applied to soil or to plant tissues to supply plant nutrients. Fertilizers may be distinct from ...
, and mass deworming is effective. Treatment is typically with the medications albendazole
Albendazole (also known as albendazolum) is a broad-spectrum anthelmintic and antiprotozoal agent of the benzimidazole type. It is used for the treatment of a variety of intestinal parasite infections, including ascariasis, pinworm infection, ho ...
or mebendazole
Mebendazole (MBZ), sold under the brand name Vermox among others, is a medication used to treat a number of parasitic worm infestations. This includes ascariasis, pinworm infection, hookworm infections, guinea worm infections, hydatid disea ...
for one to three days. Iron supplements
Iron supplements, also known as iron salts and iron pills, are a number of iron formulations used to treat and prevent iron deficiency including iron deficiency anemia. For prevention they are only recommended in those with poor absorption, h ...
may be needed in those with anemia.
Hookworms infected about 428 million people in 2015. Heavy infections can occur in both children and adults, but are less common in adults. They are rarely fatal. Hookworm infection is a soil-transmitted helminthiasis
Soil-transmitted helminthiasis is a type of helminth infection (helminthiasis) caused by different species of roundworms. It is caused specifically by those worms which are transmitted through soil contaminated with faecal matter and are therefo ...
and classified as a neglected tropical disease
Neglected tropical diseases (NTDs) are a diverse group of tropical infections that are common in low-income populations in developing regions of Africa, Asia, and the Americas. They are caused by a variety of pathogens, such as viruses, bac ...
.
Signs and symptoms
No symptoms or signs are specific for hookworm infection, but they give rise to a combination of intestinalinflammation
Inflammation (from la, inflammatio) is part of the complex biological response of body tissues to harmful stimuli, such as pathogens, damaged cells, or irritants, and is a protective response involving immune cells, blood vessels, and molec ...
and progressive iron-deficiency anemia
Iron-deficiency anemia is anemia caused by a lack of iron. Anemia is defined as a decrease in the number of red blood cells or the amount of hemoglobin in the blood. When onset is slow, symptoms are often vague such as feeling tired, weak, shor ...
and protein deficiency. Coughing, chest pain, wheezing, and fever sometimes result from severe infection. Epigastric pains, indigestion, nausea, vomiting
Vomiting (also known as emesis and throwing up) is the involuntary, forceful expulsion of the contents of one's stomach through the mouth and sometimes the nose.
Vomiting can be the result of ailments like food poisoning, gastroenter ...
, constipation
Constipation is a bowel dysfunction that makes bowel movements infrequent or hard to pass. The stool is often hard and dry. Other symptoms may include abdominal pain, bloating, and feeling as if one has not completely passed the bowel moveme ...
, and diarrhea
Diarrhea, also spelled diarrhoea, is the condition of having at least three loose, liquid, or watery bowel movements each day. It often lasts for a few days and can result in dehydration due to fluid loss. Signs of dehydration often begin w ...
can occur early or in later stages, as well, although gastrointestinal symptoms tend to improve with time. Signs of advanced severe infection are those of anemia and protein deficiency, including emaciation
Emaciation is defined as the state of extreme thinness from absence of body fat and muscle wasting usually resulting from malnutrition.
Characteristics
In humans, the physical appearance of emaciation includes thinned limbs, pronounced and protrud ...
, cardiac failure
Heart failure (HF), also known as congestive heart failure (CHF), is a syndrome, a group of signs and symptoms caused by an impairment of the heart's blood pumping function. Symptoms typically include shortness of breath, excessive fatigue, ...
, and abdominal distension with ascites
Ascites is the abnormal build-up of fluid in the abdomen. Technically, it is more than 25 ml of fluid in the peritoneal cavity, although volumes greater than one liter may occur. Symptoms may include increased abdominal size, increased weight, a ...
.
Larva
A larva (; plural larvae ) is a distinct juvenile form many animals undergo before metamorphosis into adults. Animals with indirect development such as insects, amphibians, or cnidarians typically have a larval phase of their life cycle.
...
l invasion of the skin
Skin is the layer of usually soft, flexible outer tissue covering the body of a vertebrate animal, with three main functions: protection, regulation, and sensation.
Other animal coverings, such as the arthropod exoskeleton, have different ...
(mostly in the Americas) can produce a skin disease called cutaneous larva migrans
Cutaneous larva migrans (abbreviated CLM) is a skin disease in humans, caused by the larvae of various nematode parasites of the hookworm family (Ancylostomatidae). These parasites live in the intestines of dogs, cats, and wild animals and should ...
also known as creeping eruption. The hosts of these worms are not human and the larvae can only penetrate the upper five layers of the skin, where they give rise to intense, local itching
Itch (also known as pruritus) is a sensation that causes the desire or reflex to scratch. Itch has resisted many attempts to be classified as any one type of sensory experience. Itch has many similarities to pain, and while both are unpleasan ...
, usually on the foot or lower leg, known as ground itch. This infection is due to larvae from the ''A. braziliense'' hookworm. The larvae migrate in tortuous tunnels between the stratum basale
The ''stratum basale'' (basal layer, sometimes referred to as ''stratum germinativum'') is the deepest layer of the five layers of the epidermis, the external covering of skin in mammals.
The ''stratum basale'' is a single layer of columnar or ...
and stratum corneum
The stratum corneum (Latin for 'horny layer') is the outermost layer of the epidermis. The human stratum corneum comprises several levels of flattened corneocytes that are divided into two layers: the ''stratum disjunctum'' and ''stratum compa ...
of the skin, causing serpiginous
Serpiginous, first known to be used in the 15th century, is a term from Latin serpere to creep, usually referring to a creeping, snakelike or slowly progressive skin disease.
It is used to describe the rash in cutaneous larvae migrans, erythema an ...
vesicular lesion
A lesion is any damage or abnormal change in the tissue of an organism, usually caused by disease or trauma. ''Lesion'' is derived from the Latin "injury". Lesions may occur in plants as well as animals.
Types
There is no designated classif ...
s. With advancing movement of the larvae, the rear portions of the lesions become dry and crusty. The lesions are typically intensely itchy.
Incubation period
The incubation period can vary between a few weeks to many months, and is largely dependent on the number of hookworm parasites an individual is infected with.Cause
 Hookworm infections in humans include
Hookworm infections in humans include ancylostomiasis
Ancylostomiasis is a hookworm disease caused by infection with Ancylostoma hookworms. The name is derived from Greek ancylos αγκύλος "crooked, bent" and stoma στόμα "mouth".
Ancylostomiasis is also known as miner's anaemia, tunnel d ...
and necatoriasis. Ancylostomiasis is caused by ''Ancylostoma duodenale
''Ancylostoma'' is a genus of nematodes that includes some species of hookworms.
Species include:
: ''Ancylostoma braziliense'', commonly infects cats, popularly known in Brazil as ''bicho-geográfico''
: ''Ancylostoma caninum'', commonly infect ...
,'' which is the more common type found in the Middle East
The Middle East ( ar, الشرق الأوسط, ISO 233: ) is a geopolitical region commonly encompassing Arabian Peninsula, Arabia (including the Arabian Peninsula and Bahrain), Anatolia, Asia Minor (Asian part of Turkey except Hatay Pro ...
, North Africa
North Africa, or Northern Africa is a region encompassing the northern portion of the African continent. There is no singularly accepted scope for the region, and it is sometimes defined as stretching from the Atlantic shores of Mauritania in ...
, India
India, officially the Republic of India (Hindi: ), is a country in South Asia. It is the List of countries and dependencies by area, seventh-largest country by area, the List of countries and dependencies by population, second-most populous ...
, and (formerly) in southern Europe
Southern Europe is the southern region of Europe. It is also known as Mediterranean Europe, as its geography is essentially marked by the Mediterranean Sea. Definitions of Southern Europe include some or all of these countries and regions: Alb ...
. Necatoriasis is caused by ''Necator americanus
''Necator americanus'' is a species of hookworm (a type of helminth) commonly known as the New World hookworm. Like other hookworms, it is a member of the phylum Nematoda. It is an obligatory parasitic nematode that lives in the small intestine ...
,'' the more common type in the Americas
The Americas, which are sometimes collectively called America, are a landmass comprising the totality of North and South America. The Americas make up most of the land in Earth's Western Hemisphere and comprise the New World.
Along with th ...
, sub-Saharan Africa
Sub-Saharan Africa is, geographically, the area and regions of the continent of Africa that lies south of the Sahara. These include West Africa, East Africa, Central Africa, and Southern Africa. Geopolitically, in addition to the List of sov ...
, Southeast Asia
Southeast Asia, also spelled South East Asia and South-East Asia, and also known as Southeastern Asia, South-eastern Asia or SEA, is the geographical south-eastern region of Asia, consisting of the regions that are situated south of mainland ...
, China
China, officially the People's Republic of China (PRC), is a country in East Asia. It is the world's List of countries and dependencies by population, most populous country, with a Population of China, population exceeding 1.4 billion, slig ...
, and Indonesia
Indonesia, officially the Republic of Indonesia, is a country in Southeast Asia and Oceania between the Indian and Pacific oceans. It consists of over 17,000 islands, including Sumatra, Java, Sulawesi, and parts of Borneo and New Gui ...
.
Other animals such as bird
Birds are a group of warm-blooded vertebrates constituting the class Aves (), characterised by feathers, toothless beaked jaws, the laying of hard-shelled eggs, a high metabolic rate, a four-chambered heart, and a strong yet lightweig ...
s, dogs, and cat
The cat (''Felis catus'') is a domestic species of small carnivorous mammal. It is the only domesticated species in the family Felidae and is commonly referred to as the domestic cat or house cat to distinguish it from the wild members of ...
s may also be affected. ''A. tubaeforme'' infects cats, '' A. caninum'' infects dogs, and '' A. braziliense'' and '' Uncinaria stenocephala'' infect both cats and dogs. Some of these infections can be transmitted to humans.
Morphology
''A. duodenale'' worms are grayish white or pinkish with the head slightly bent in relation to the rest of the body. This bend forms a definitive hook shape at the anterior end for which hookworms are named. They possess well-developed mouths with two pairs of teeth. While males measure approximately one centimeter by 0.5 millimeter, the females are often longer and stouter. Additionally, males can be distinguished from females based on the presence of a prominent posterior copulatory bursa. ''N. americanus'' is very similar in morphology to ''A. duodenale''. ''N. americanus'' is generally smaller than ''A. duodenale'' with males usually 5 to 9 mm long and females about 1 cm long. Whereas ''A. duodenale'' possesses two pairs of teeth, ''N. americanus'' possesses a pair of cutting plates in the buccal capsule. Additionally, the hook shape is much more defined in ''Necator'' than in ''Ancylostoma''.Life cycle
 The hookworm thrives in warm soil where temperatures are over . They exist primarily in
The hookworm thrives in warm soil where temperatures are over . They exist primarily in sand
Sand is a granular material composed of finely divided mineral particles. Sand has various compositions but is defined by its grain size. Sand grains are smaller than gravel and coarser than silt. Sand can also refer to a textural class ...
y or loam
Loam (in geology and soil science) is soil composed mostly of sand ( particle size > ), silt (particle size > ), and a smaller amount of clay (particle size < ). By weight, its mineral composition is about 40–40–20% concentration of sand–si ...
y soil and cannot live in clay
Clay is a type of fine-grained natural soil material containing clay minerals (hydrous aluminium phyllosilicates, e.g. kaolin, Al2 Si2 O5( OH)4).
Clays develop plasticity when wet, due to a molecular film of water surrounding the clay pa ...
or muck. Rainfall
Rain is water droplets that have condensed from atmospheric water vapor and then fall under gravity. Rain is a major component of the water cycle and is responsible for depositing most of the fresh water on the Earth. It provides water f ...
averages must be more than a year for them to survive. Only if these conditions exist can the eggs hatch. Infective larvae of ''N. americanus'' can survive at higher temperatures, whereas those of ''A. duodenale'' are better adapted to cooler climates. Generally, they live for only a few weeks at most under natural conditions, and die almost immediately on exposure to direct sunlight or desiccation
Desiccation () is the state of extreme dryness, or the process of extreme drying. A desiccant is a hygroscopic (attracts and holds water) substance that induces or sustains such a state in its local vicinity in a moderately sealed container.
...
.
Infection of the host is by the larvae, not the eggs. While ''A. duodenale'' can be ingested, the usual method of infection is through the skin; this is commonly caused by walking barefoot
Barefoot is the state of not wearing any footwear.
There are health benefits and some risks associated with going barefoot. Shoes, while they offer protection, can limit the flexibility, strength, and mobility of the foot and can lead to h ...
through areas contaminated with fecal matter. The larvae are able to penetrate the skin of the foot, and once inside the body, they migrate through the vascular system
The blood circulatory system is a system of organs that includes the heart, blood vessels, and blood which is circulated throughout the entire body of a human or other vertebrate. It includes the cardiovascular system, or vascular system, t ...
to the lung
The lungs are the primary organs of the respiratory system in humans and most other animals, including some snails and a small number of fish. In mammals and most other vertebrates, two lungs are located near the backbone on either side of ...
s, and from there up the trachea
The trachea, also known as the windpipe, is a cartilaginous tube that connects the larynx to the bronchi of the lungs, allowing the passage of air, and so is present in almost all air- breathing animals with lungs. The trachea extends from t ...
, and are swallowed. They then pass down the esophagus
The esophagus (American English) or oesophagus (British English; both ), non-technically known also as the food pipe or gullet, is an organ in vertebrates through which food passes, aided by peristaltic contractions, from the pharynx to t ...
and enter the digestive system, finishing their journey in the intestine
The gastrointestinal tract (GI tract, digestive tract, alimentary canal) is the tract or passageway of the digestive system that leads from the mouth to the anus. The GI tract contains all the major organs of the digestive system, in humans an ...
, where the larvae mature into adult worms.
Once in the host gut, ''Necator'' tends to cause a prolonged infection, generally 1 to 5 years (many worms die within a year or two of infecting), though some adult worms have been recorded to live for 15 years or more. ''Ancylostoma'' adults are short-lived, surviving on average for only about 6 months. However, the infection can be prolonged because dormant larvae can be "recruited" sequentially from tissue "stores" (see Pathology, above) over many years, to replace expired adult worms. This can give rise to seasonal fluctuations in infection prevalence and intensity (apart from normal seasonal variations in transmission).
 They mate inside the host, females laying up to 30,000 eggs per day and some 18 to 54 million eggs during their lifetimes, which pass out in feces. Because 5 to 7 weeks are needed for adult worms to mature, mate, and produce eggs, in the early stages of very heavy infection, acute symptoms might occur without any eggs being detected in the patient's feces. This can make diagnosis very difficult.
''N. americanus'' and ''A. duodenale'' eggs can be found in warm, moist soil where they eventually hatch into first-stage larvae, or L1. L1, the feeding noninfective rhabditoform stage, will feed on soil microbes and eventually molt into second-stage larvae, L2, which is also in the rhabditoform stage. It will feed for about 7 days and then molt into the third-stage larvae, or L3. This is the filariform stage of the parasite, that is, the nonfeeding infective form of the larvae. The L3 larvae are extremely motile and seek higher ground to increase their chances of penetrating the skin of a human host. The L3 larvae can survive up to 2 weeks without finding a host. While ''N. americanus'' larvae only infect through penetration of skin, ''A. duodenale'' can infect both through penetration and orally. After the L3 larvae have successfully entered the host, they then travel through the subcutaneous venules and lymphatic vessels of the human host. Eventually, the L3 larvae enter the lungs through the pulmonary capillaries and break out into the alveoli. They then travel up the trachea to be coughed and swallowed by the host. After being swallowed, the L3 larvae are then found in the small intestine, where they molt into the L4, or adult worm stage. The entire process from skin penetration to adult development takes about 5–9 weeks. The female adult worms release eggs (''N. americanus'' about 9,000–10,000 eggs/day and ''A. duodenale'' 25,000–30,000 eggs/day), which are passed in the feces of the human host. These eggs hatch in the environment within several days and the cycle starts anew.
They mate inside the host, females laying up to 30,000 eggs per day and some 18 to 54 million eggs during their lifetimes, which pass out in feces. Because 5 to 7 weeks are needed for adult worms to mature, mate, and produce eggs, in the early stages of very heavy infection, acute symptoms might occur without any eggs being detected in the patient's feces. This can make diagnosis very difficult.
''N. americanus'' and ''A. duodenale'' eggs can be found in warm, moist soil where they eventually hatch into first-stage larvae, or L1. L1, the feeding noninfective rhabditoform stage, will feed on soil microbes and eventually molt into second-stage larvae, L2, which is also in the rhabditoform stage. It will feed for about 7 days and then molt into the third-stage larvae, or L3. This is the filariform stage of the parasite, that is, the nonfeeding infective form of the larvae. The L3 larvae are extremely motile and seek higher ground to increase their chances of penetrating the skin of a human host. The L3 larvae can survive up to 2 weeks without finding a host. While ''N. americanus'' larvae only infect through penetration of skin, ''A. duodenale'' can infect both through penetration and orally. After the L3 larvae have successfully entered the host, they then travel through the subcutaneous venules and lymphatic vessels of the human host. Eventually, the L3 larvae enter the lungs through the pulmonary capillaries and break out into the alveoli. They then travel up the trachea to be coughed and swallowed by the host. After being swallowed, the L3 larvae are then found in the small intestine, where they molt into the L4, or adult worm stage. The entire process from skin penetration to adult development takes about 5–9 weeks. The female adult worms release eggs (''N. americanus'' about 9,000–10,000 eggs/day and ''A. duodenale'' 25,000–30,000 eggs/day), which are passed in the feces of the human host. These eggs hatch in the environment within several days and the cycle starts anew.
Pathophysiology
Hookworm infection is generally considered to be asymptomatic, but as Norman Stoll described in 1962, it is an extremely dangerous infection because its damage is "silent and insidious." An individual may experience general symptoms soon after infection. Ground-itch, which is an allergic reaction at the site of parasitic penetration and entry, is common in patients infected with ''N. americanus''. Additionally, cough andpneumonitis
Pneumonitis describes general inflammation of lung tissue. Possible causative agents include radiation therapy of the chest, exposure to medications used during chemo-therapy, the inhalation of debris (e.g., animal dander), aspiration, herbicide ...
may result as the larvae begin to break into the alveoli Alveolus (; pl. alveoli, adj. alveolar) is a general anatomical term for a concave cavity or pit.
Uses in anatomy and zoology
* Pulmonary alveolus, an air sac in the lungs
** Alveolar cell or pneumocyte
** Alveolar duct
** Alveolar macrophage
* M ...
and travel up the trachea. Then once the larvae reach the small intestine of the host and begin to mature, the infected individual will experience diarrhea and other gastrointestinal discomfort. However, the "silent and insidious" symptoms referred to by Stoll are related to chronic, heavy-intensity hookworm infections. Major morbidity associated with hookworm infection is caused by intestinal blood loss, iron deficiency anemia, and protein malnutrition. They result mainly from adult hookworms in the small intestine ingesting blood, rupturing erythrocyte
Red blood cells (RBCs), also referred to as red cells, red blood corpuscles (in humans or other animals not having nucleus in red blood cells), haematids, erythroid cells or erythrocytes (from Greek ''erythros'' for "red" and ''kytos'' for "hol ...
s, and degrading hemoglobin
Hemoglobin (haemoglobin BrE) (from the Greek word αἷμα, ''haîma'' 'blood' + Latin ''globus'' 'ball, sphere' + ''-in'') (), abbreviated Hb or Hgb, is the iron-containing oxygen-transport metalloprotein present in red blood cells (erythroc ...
in the host. This long-term blood loss can manifest itself physically through facial and peripheral edema
Edema, also spelled oedema, and also known as fluid retention, dropsy, hydropsy and swelling, is the build-up of fluid in the body's tissue. Most commonly, the legs or arms are affected. Symptoms may include skin which feels tight, the area ma ...
; eosinophilia
Eosinophilia is a condition in which the eosinophil count in the peripheral blood exceeds . Hypereosinophilia is an elevation in an individual's circulating blood eosinophil count above 1.5 x 109/ L (i.e. 1,500/ μL). The hypereosinophilic sy ...
and pica/geophagy
Geophagia (), also known as geophagy (), is the intentional practice of eating earth or soil-like substances such as clay, chalk, or termite mounds. It is a behavioural adaptation that occurs in many non-human animals and has been documented in ...
caused by iron deficiency anemia are also experienced by some hookworm-infected patients. Recently, more attention has been given to other important outcomes of hookworm infection that play a large role in public health. It is now widely accepted that children who have chronic hookworm infection can experience growth retardation as well as intellectual and cognitive impairments. Additionally, recent research has focused on the potential of adverse maternal-fetal outcomes when the mother is infected with hookworm during pregnancy.
The disease was linked to nematode worms (''Ankylostoma duodenalis'') from one-third to half an inch long in the intestine chiefly through the labours of Theodor Bilharz and Griesinger Griesinger is a German surname. Notable people with the surname include:
*Georg August Griesinger (1769–1845), German diplomat and writer
* Jakob Griesinger (c. 1407 – 1491), German Dominican
*Wilhelm Griesinger
Wilhelm Griesinger (29 July ...
in Egypt (1854).
The symptoms can be linked to inflammation in the gut stimulated by feeding hookworms, such as nausea, abdominal pain and intermittent diarrhea, and to progressive anemia in prolonged disease: capricious
Capricious may refer to:
* Capricieuse, also spelled Capricious, a solitaire card game
* Capricious (cheese), an aged goat's milk cheese
See also
* Arbitrary and capricious
In law, the standard of review is the amount of deference given by one ...
appetite, pica/geophagy
Geophagia (), also known as geophagy (), is the intentional practice of eating earth or soil-like substances such as clay, chalk, or termite mounds. It is a behavioural adaptation that occurs in many non-human animals and has been documented in ...
(or dirt-eating), obstinate constipation followed by diarrhea
Diarrhea, also spelled diarrhoea, is the condition of having at least three loose, liquid, or watery bowel movements each day. It often lasts for a few days and can result in dehydration due to fluid loss. Signs of dehydration often begin w ...
, palpitations
Palpitations are perceived abnormalities of the heartbeat characterized by awareness of cardiac muscle contractions in the chest, which is further characterized by the hard, fast and/or irregular beatings of the heart.
Symptoms include a rap ...
, thready pulse, coldness of the skin, pallor of the mucous membranes, fatigue and weakness, shortness of breath and in cases running a fatal course, dysentery
Dysentery (UK pronunciation: , US: ), historically known as the bloody flux, is a type of gastroenteritis that results in bloody diarrhea. Other symptoms may include fever, abdominal pain, and a feeling of incomplete defecation. Complications ...
, hemorrhages
Bleeding, hemorrhage, haemorrhage or blood loss, is blood escaping from the circulatory system from damaged blood vessels. Bleeding can occur internally, or externally either through a natural opening such as the mouth, nose, ear, urethra, ...
and edema
Edema, also spelled oedema, and also known as fluid retention, dropsy, hydropsy and swelling, is the build-up of fluid in the body's tissue. Most commonly, the legs or arms are affected. Symptoms may include skin which feels tight, the area ma ...
. The worms suck blood
Blood is a body fluid in the circulatory system of humans and other vertebrates that delivers necessary substances such as nutrients and oxygen to the cells, and transports metabolic waste products away from those same cells. Blood in the cir ...
and damage the mucosa
A mucous membrane or mucosa is a membrane that lines various cavities in the body of an organism and covers the surface of internal organs. It consists of one or more layers of epithelial cells overlying a layer of loose connective tissue. It i ...
. However, the blood loss in the stools is not visibly apparent.
Blood tests in early infection often show a rise in numbers of eosinophils, a type of white blood cell that is preferentially stimulated by worm infections in tissues (large numbers of eosinophils are also present in the local inflammatory response). Falling blood hemoglobin levels will be seen in cases of prolonged infection with anemia.
In contrast to most intestinal helminthiases
Helminthiasis, also known as worm infection, is any macroparasitic disease of humans and other animals in which a part of the body is infected with parasitic worms, known as helminths. There are numerous species of these parasites, which are b ...
, where the heaviest parasitic loads tend to occur in children, hookworm prevalence and intensity can be higher among adult males. The explanation for this is that hookworm infection tends to be occupational, so that coworkers and other close groups maintain a high prevalence of infection among themselves by contaminating their work environment. However, in most endemic areas, adult women are the most severely affected by anemia, mainly because they have much higher physiological needs for iron (menstruation, repeated pregnancy).An interesting consequence of this in the case of ''Ancylostoma duodenale'' infection is translactational transmission of infection: the skin-invasive larvae of this species do not all immediately pass through the lungs and on into the gut, but spread around the body via the circulation, to become dormant inside muscle fibers. In a pregnant woman, after childbirth some or all of these larvae are stimulated to re-enter the circulation (presumably by sudden hormonal changes), then to pass into the mammary glands, so that the newborn baby can receive a large dose of infective larvae through its mother's milk. This accounts for otherwise inexplicable cases of very heavy, even fatal, hookworm infections in children a month or so of age, in places such as China, India and northern Australia.
An identical phenomenon is much more commonly seen with ''Ancylostoma caninum
''Ancylostoma caninum'' is a species of nematode known as a hookworm, which principally infects the small intestine of dogs. The result of ''A. caninum'' infection ranges from asymptomatic cases to death of the dog; better nourishment, increasi ...
'' infections in dogs, where the newborn pups can even die of hemorrhaging from their intestines caused by massive numbers of feeding hookworms. This also reflects the close evolutionary link between the human and canine parasites, which probably have a common ancestor dating back to when humans and dogs first started living closely together.
Filariform larvae is the infective stage of the parasite: infection occurs when larvae in soil penetrate the skin, or when they are ingested through contaminated food and water following skin penetration.
Diagnosis
bile
Bile (from Latin ''bilis''), or gall, is a dark-green-to-yellowish-brown fluid produced by the liver of most vertebrates that aids the digestion of lipids in the small intestine. In humans, bile is produced continuously by the liver (liver bi ...
stained and with a thin transparent hyaline
A hyaline substance is one with a glassy appearance. The word is derived from el, ὑάλινος, translit=hyálinos, lit=transparent, and el, ὕαλος, translit=hýalos, lit=crystal, glass, label=none.
Histopathology
Hyaline cartilage is ...
shell membrane. When released by the worm in the intestine, the egg contains an unsegmented ovum
The egg cell, or ovum (plural ova), is the female reproductive cell, or gamete, in most anisogamous organisms (organisms that reproduce sexually with a larger, female gamete and a smaller, male one). The term is used when the female gamete i ...
. During its passage down the intestine, the ovum develops and thus the eggs passed in feces have a segmented ovum, usually with 4 to 8 blastomeres
In biology, a blastomere is a type of Cell (biology), cell produced by cleavage (embryo), cell division (cleavage) of the zygote after fertilization; blastomeres are an essential part of blastula formation, and blastocyst formation in mammals.
Hum ...
.
As the eggs of both ''Ancylostoma'' and ''Necator'' (and most other hookworm species) are indistinguishable, to identify the genus, they must be cultured in the lab to allow larvae to hatch out. If the fecal sample is left for a day or more under tropical conditions, the larvae will have hatched out, so eggs might no longer be evident. In such a case, it is essential to distinguish hookworms from ''Strongyloides
''Strongyloides'' (from Greek ''strongylos'', round, + ''eidos'', resemblance), anguillula, or threadworm is a genus of small nematode parasites, belonging to the family Strongylidae, commonly found in the small intestine of mammals (particularl ...
'' larvae, as infection with the latter has more serious implications and requires different management. The larvae of the two hookworm species can also be distinguished microscopically, although this would not be done routinely, but usually for research purposes. Adult worms are rarely seen (except via endoscopy, surgery or autopsy), but if found, would allow definitive identification of the species. Classification can be performed based on the length of the buccal cavity, the space between the oral opening and the esophagus: hookworm rhabditoform larvae have long buccal cavities whereas ''Strongyloides'' rhabditoform larvae have short buccal cavities.
Recent research has focused on the development of DNA-based tools for diagnosis of infection, specific identification of hookworm, and analysis of genetic variability within hookworm populations. Because hookworm eggs are often indistinguishable from other parasitic eggs, PCR assays could serve as a molecular approach for accurate diagnosis of hookworm in the feces.
Prevention
The infective larvae develop and survive in an environment of damp dirt, particularly sandy and loamy soil. They cannot survive in clay or muck. The main lines of precaution are those dictated by goodhygiene
Hygiene is a series of practices performed to preserve health.
According to the World Health Organization (WHO), "Hygiene refers to conditions and practices that help to maintain health and prevent the spread of diseases." Personal hygiene refer ...
behaviors:
* Do not defecate in the open, but rather in toilet
A toilet is a piece of sanitary hardware that collects human urine and feces, and sometimes toilet paper, usually for disposal. Flush toilets use water, while dry or non-flush toilets do not. They can be designed for a sitting position popu ...
s.
* Do not use untreated human excreta or raw sewage
Sewage (or domestic sewage, domestic wastewater, municipal wastewater) is a type of wastewater that is produced by a community of people. It is typically transported through a sewer system. Sewage consists of wastewater discharged from reside ...
as fertilizer
A fertilizer (American English) or fertiliser (British English; see spelling differences) is any material of natural or synthetic origin that is applied to soil or to plant tissues to supply plant nutrients. Fertilizers may be distinct from ...
in agriculture.
* Do not walk barefoot in known infected areas.
* Deworm pet dogs and cats. Canine and feline hookworms rarely develop to adulthood in humans. ''Ancylostoma caninum'', the common dog hookworm, occasionally develops into an adult to cause eosinophilic enteritis in people, but their invasive larvae can cause an itchy rash called cutaneous larva migrans
Cutaneous larva migrans (abbreviated CLM) is a skin disease in humans, caused by the larvae of various nematode parasites of the hookworm family (Ancylostomatidae). These parasites live in the intestines of dogs, cats, and wild animals and should ...
.
Moxidectin is available in the United States as (imidacloprid
Imidacloprid is a systemic insecticide belonging to a class of chemicals called the neonicotinoids which act on the central nervous system of insects. The chemical works by interfering with the transmission of stimuli in the insect nervous system ...
+ moxidectin) topical solution for dogs and cats. It utilizes moxidectin for control and prevention of roundworms, hookworms, heartworm
''Dirofilaria immitis'', also known as heartworm or dog heartworm, is a parasitic roundworm that is a type of filarial worm, a small thread-like worm, that causes dirofilariasis. It is spread from host to host through the bites of mosquitoe ...
s, and whipworms.
Children
Most of these public health concerns have focused on children who are infected with hookworm. This focus on children is largely due to the large body of evidence that has demonstrated strong associations between hookworm infection and impaired learning, increased absences from school, and decreased future economic productivity. In 2001, the 54th World Health Assembly passed a resolution demanding member states to attain a minimum target of regular deworming of at least 75% of all at-risk school children by the year 2010. A 2008 World Health Organization publication reported on these efforts to treat at-risk school children. Some of the interesting statistics were as follows: 1) only 9 out of 130 endemic countries were able to reach the 75% target goal; and 2) less than 77 million school-aged children (of the total 878 million at risk) were reached, which means that only 8.78% of at-risk children are being treated for hookworm infection.School-based mass deworming
School-based mass deworming programs have been the most popular strategy to address the issue of hookworm infection in children. School-based programs are extremely cost-effective as schools already have an available, extensive, and sustained infrastructure with a skilled workforce that has a close relationship with the community. With little training from a local health system, teachers can easily administer the drugs which often cost less than US$0.50 per child per year. Recently, many people have begun to question if the school-based programs are necessarily the most effective approach. An important concern with school-based programs is that they often do not reach children who do not attend school, thus ignoring a large number of at-risk children. A 2008 study by Massa ''et al.'' continued the debate regarding school-based programs. They examined the effects of community-directed treatments versus school-based treatments in the Tanga Region of Tanzania. A major conclusion was that the mean infection intensity of hookworm was significantly lower in the villages employing the community-directed treatment approach than the school-based approach. The community-directed treatment model used in this specific study allowed villagers to take control of the child's treatment by having villagers select their own community drug distributors to administer the antihelminthic drugs. Additionally, villagers organized and implemented their own methods for distributing the drugs to all children. The positive results associated with this new model highlight the need for large-scale community involvement in deworming campaigns.Public health education
Many mass deworming programs also combine their efforts with a public health education. These health education programs often stress important preventative techniques such as: washing your hands before eating, and staying away from water/areas contaminated by human feces. These programs may also stress that shoes must be worn, however, these come with their own health risks and may not be effective. Shoe wearing patterns in towns and villages across the globe are determined by cultural beliefs, and the levels of education within that society. The wearing of shoes will prevent the entry of hookworm infections from the surrounding soils into tender skin regions; such as areas between the toes.Sanitation
Historical examples, such as the hookworm campaigns in Mississippi and Florida from 1943 to 1947 have shown that the primary cause of hookworm infection is poor sanitation, which can be solved by building and maintainingtoilet
A toilet is a piece of sanitary hardware that collects human urine and feces, and sometimes toilet paper, usually for disposal. Flush toilets use water, while dry or non-flush toilets do not. They can be designed for a sitting position popu ...
s. But while these may seem like simple tasks, they raise important public health challenges. Most infected populations are from poverty-stricken areas with very poor sanitation. Thus, it is most likely that at-risk children do not have access to clean water
Drinking water is water that is used in drink or food preparation; potable water is water that is safe to be used as drinking water. The amount of drinking water required to maintain good health varies, and depends on physical activity level, ...
to wash their hands and live in environments with no proper sanitation infrastructure. Health education, therefore, must address preventive measures in ways that are both feasible and sustainable in the context of resource-limited settings.
Integrated approaches
Evaluation of numerous public health interventions has generally shown that improvement in each individual component ordinarily attributed to poverty (for example, sanitation, health education and underlying nutrition status) often have minimal impact on transmission. For example, one study found that the introduction of latrines into a resource-limited community only reduced the prevalence of hookworm infection by four percent. However, another study in Salvador, Brazil found that improveddrainage
Drainage is the natural or artificial removal of a surface's water and sub-surface water from an area with excess of water. The internal drainage of most agricultural soils is good enough to prevent severe waterlogging (anaerobic condition ...
and sewerage
Sewerage (or sewage system) is the infrastructure that conveys sewage or surface runoff (stormwater, meltwater, rainwater) using sewers. It encompasses components such as receiving drainage, drains, manholes, pumping stations, storm overflows, a ...
had a significant impact on the prevalence of hookworm infection but no impact at all on the intensity of hookworm infection. This seems to suggest that environmental control alone has a limited but incomplete effect on the transmission of hookworms. It is imperative, therefore, that more research is performed to understand the efficacy and sustainability of integrated programs that combine numerous preventive methods including education, sanitation, and treatment.
Treatment
Anthelmintic drugs
The most common treatment for hookworm arebenzimidazole
Benzimidazole is a heterocyclic aromatic organic compound. This bicyclic compound may be viewed as fused rings of the aromatic compounds benzene and imidazole. It is a colorless solid.
Preparation
Benzimidazole is produced by condensation of o ...
s, specifically albendazole
Albendazole (also known as albendazolum) is a broad-spectrum anthelmintic and antiprotozoal agent of the benzimidazole type. It is used for the treatment of a variety of intestinal parasite infections, including ascariasis, pinworm infection, ho ...
and mebendazole
Mebendazole (MBZ), sold under the brand name Vermox among others, is a medication used to treat a number of parasitic worm infestations. This includes ascariasis, pinworm infection, hookworm infections, guinea worm infections, hydatid disea ...
. BZAs kill adult worms by binding to the nematode's β-tubulin
Tubulin in molecular biology can refer either to the tubulin protein superfamily of globular proteins, or one of the member proteins of that superfamily. α- and β-tubulins polymerize into microtubules, a major component of the eukaryotic cytoske ...
and subsequently inhibiting microtubule
Microtubules are polymers of tubulin that form part of the cytoskeleton and provide structure and shape to eukaryotic cells. Microtubules can be as long as 50 micrometres, as wide as 23 to 27 nm and have an inner diameter between 1 ...
polymerization within the parasite. In certain circumstances, levamisole
Levamisole, sold under the brand name Ergamisol among others, is a medication used to treat parasitic worm infections, specifically ascariasis and hookworm infections. It is taken by mouth.
Side effects may include abdominal pain, vomiting, ...
and pyrantel pamoate
Pyrantel is a medication used to treat a number of parasitic worm infections. This includes ascariasis, hookworm infections, enterobiasis (pinworm infection), trichostrongyliasis, and trichinellosis. It is taken by mouth.
Side effects inclu ...
may be used. A 2008 review found that the efficacy of single-dose treatments for hookworm infections were as follows: 72% for albendazole, 15% for mebendazole, and 31% for pyrantel pamoate. This substantiates prior claims that albendazole is much more effective than mebendazole for hookworm infections. Also of note is that the World Health Organization does recommend anthelmintic treatment in pregnant women after the first trimester. It is also recommended that if the patient also has anemia that ferrous sulfate
Iron(II) sulfate (British English: iron(II) sulphate) or ferrous sulfate denotes a range of salts with the formula Fe SO4·''x''H2O. These compounds exist most commonly as the hepta hydrate (''x'' = 7) but several values for x are kn ...
(200 mg) be administered three times daily at the same time as anthelmintic treatment; this should be continued until hemoglobin values return to normal which could take up to 3 months.
Hookworm infection can be treated with local cryotherapy
Cryotherapy, sometimes known as cold therapy, is the local or general use of low temperatures in medical therapy. Cryotherapy may be used to treat a variety of tissue lesions. The most prominent use of the term refers to the surgical treatment, s ...
when the hookworm is still in the skin.
Albendazole is effective both in the intestinal stage and during the stage the parasite is still migrating under the skin.
In case of anemia, iron
Iron () is a chemical element with symbol Fe (from la, ferrum) and atomic number 26. It is a metal that belongs to the first transition series and group 8 of the periodic table. It is, by mass, the most common element on Earth, right in ...
supplementation can cause relief symptoms of iron-deficiency anemia
Iron-deficiency anemia is anemia caused by a lack of iron. Anemia is defined as a decrease in the number of red blood cells or the amount of hemoglobin in the blood. When onset is slow, symptoms are often vague such as feeling tired, weak, shor ...
. However, as red blood cell levels are restored, shortage of other essentials such as folic acid
Folate, also known as vitamin B9 and folacin, is one of the B vitamins. Manufactured folic acid, which is converted into folate by the body, is used as a dietary supplement and in food fortification as it is more stable during processing a ...
or vitamin B12 may develop, so these might also be supplemented.
During the 1910s, common treatments for hookworm included thymol
Thymol (also known as 2-isopropyl-5-methylphenol, IPMP), , is a natural monoterpenoid phenol derivative of ''p''-Cymene, isomeric with carvacrol, found in oil of thyme, and extracted from '' Thymus vulgaris'' (common thyme), ajwain, and va ...
, 2-naphthol, chloroform
Chloroform, or trichloromethane, is an organic compound with formula C H Cl3 and a common organic solvent. It is a colorless, strong-smelling, dense liquid produced on a large scale as a precursor to PTFE. It is also a precursor to various ...
, gasoline
Gasoline (; ) or petrol (; ) (see ) is a transparent, petroleum-derived flammable liquid that is used primarily as a fuel in most spark-ignited internal combustion engines (also known as petrol engines). It consists mostly of organic c ...
, and eucalyptus oil
Eucalyptus oil is the generic name for distilled oil from the leaf of ''Eucalyptus'', a genus of the plant family Myrtaceae native to Australia and cultivated worldwide. Eucalyptus oil has a history of wide application, as a pharmaceutical, anti ...
. By the 1940s, the treatment of choice used tetrachloroethylene
Tetrachloroethylene, also known under the systematic name tetrachloroethene, or perchloroethylene, and many other names (and abbreviations such as "perc" or "PERC", and "PCE"), is a chlorocarbon with the formula Cl2C=CCl2 . It is a colorless li ...
, given as 3 to 4 cc in the fasting state, followed by 30 to 45 g of sodium sulfate
Sodium sulfate (also known as sodium sulphate or sulfate of soda) is the inorganic compound with formula Na2SO4 as well as several related hydrates. All forms are white solids that are highly soluble in water. With an annual production of 6 mil ...
. Tetrachloroethylene was reported to have a cure rate of 80 percent for Necator infections, but 25 percent in Ancylostoma infections, and often produced mild intoxication in the patient.
Reinfection and drug resistance
Other important issues related to the treatment of hookworm are reinfection and drug resistance. It has been shown that reinfection after treatment can be extremely high. Some studies even show that 80% of pretreatment hookworm infection rates can be seen in treated communities within 30–36 months. While reinfection may occur, it is still recommended that regular treatments be conducted as it will minimize the occurrence of chronic outcomes. There are also increasing concerns about the issue of drug resistance. Drug resistance has appeared in front-line anthelmintics used for livestock nematodes. Generally human nematodes are less likely to develop resistance due to longer reproducing times, less frequent treatment, and more targeted treatment. Nonetheless, the global community must be careful to maintain the effectiveness of current anthelmintic as no new anthelmintic drugs are in the late-stage development.Epidemiology
disability-adjusted life year
The disability-adjusted life year (DALY) is a measure of overall disease burden, expressed as the number of years lost due to ill-health, disability or early death. It was developed in the 1990s as a way of comparing the overall health and life ex ...
s (DALYs), neglected tropical diseases, including hookworm infection, rank among diarrheal diseases, ischemic heart disease
Coronary artery disease (CAD), also called coronary heart disease (CHD), ischemic heart disease (IHD), myocardial ischemia, or simply heart disease, involves the reduction of blood flow to the heart muscle due to build-up of atherosclerotic pl ...
, malaria
Malaria is a mosquito-borne infectious disease that affects humans and other animals. Malaria causes symptoms that typically include fever, tiredness, vomiting, and headaches. In severe cases, it can cause jaundice, seizures, coma, or death. ...
, and tuberculosis
Tuberculosis (TB) is an infectious disease usually caused by '' Mycobacterium tuberculosis'' (MTB) bacteria. Tuberculosis generally affects the lungs, but it can also affect other parts of the body. Most infections show no symptoms, ...
as one of the most important health problems of the developing world.
It has been estimated that as many as 22.1 million DALYs
The disability-adjusted life year (DALY) is a measure of overall disease burden, expressed as the number of years lost due to ill-health, disability or early death. It was developed in the 1990s as a way of comparing the overall health and life ex ...
have been lost due to hookworm infection. Recently, there has been increasing interest to address the public health concerns associated with hookworm infection. For example, the Bill & Melinda Gates Foundation
The Bill & Melinda Gates Foundation (BMGF), a merging of the William H. Gates Foundation and the Gates Learning Foundation, is an American private foundation founded by Bill Gates and Melinda French Gates. Based in Seattle, Washington, it was ...
recently donated US$34 million to fight Neglected Tropical Diseases including hookworm infection. Former US President Clinton also announced a mega-commitment at the Clinton Global Initiative (CGI) 2008 Annual Meeting to de-worm 10 million children.
Many of the numbers regarding the prevalence of hookworm infection are estimates as there is no international surveillance mechanism currently in place to determine prevalence and global distribution. Some prevalence rates have been measured through survey data in endemic regions around the world. The following are some of the most recent findings on prevalence rates in regions endemic with hookworm.
Darjeeling
Darjeeling (, , ) is a town and municipality in the northernmost region of the Indian state of West Bengal. Located in the Eastern Himalayas, it has an average elevation of . To the west of Darjeeling lies the easternmost province of Nep ...
, Hooghly District
Hooghly district () is one of the districts of the Indian state of West Bengal. It can alternatively be spelt ''Hoogli'' or ''Hugli''. The district is named after the Hooghly River.
The headquarters of the district are at Hooghly-Chinsura (''C ...
, West Bengal
West Bengal (, Bengali: ''Poshchim Bongo'', , abbr. WB) is a state in the eastern portion of India. It is situated along the Bay of Bengal, along with a population of over 91 million inhabitants within an area of . West Bengal is the fou ...
, India (Pal ''et al.'' 2007)
* 43% infection rate of predominantly ''N. americanus'' although with some ''A. duodenale'' infection
* Both hookworm infection load and degree of anemia in the mild range
Xiulongkan Village, Hainan Province
Hainan (, ; ) is the smallest and southernmost province of the People's Republic of China (PRC), consisting of various islands in the South China Sea. , the largest and most populous island in China,The island of Taiwan, which is slightly l ...
, China (Gandhi ''et al.'' 2001)
* 60% infection rate of predominantly ''N. americanus''
* Important trends noted were that prevalence increased with age (plateau of about 41 years) and women had higher prevalence rates than men
Hòa Bình, Northwest Vietnam (Verle ''et al.'' 2003)
* 52% of a total of 526 tested households infected
* Could not identify species, but previous studies in North Vietnam reported ''N. americanus'' in more than 95% of hookworm larvae
Minas Gerais
Minas Gerais () is a state in Southeastern Brazil. It ranks as the second most populous, the third by gross domestic product (GDP), and the fourth largest by area in the country. The state's capital and largest city, Belo Horizonte (literall ...
, Brazil (Fleming ''et al.'' 2006)
* 63% infection rate of predominantly ''N. americanus''
KwaZulu-Natal
KwaZulu-Natal (, also referred to as KZN and known as "the garden province") is a province of South Africa that was created in 1994 when the Zulu bantustan of KwaZulu ("Place of the Zulu" in Zulu) and Natal Province were merged. It is loca ...
, South Africa (Mabaso ''et al.'' 2004)
* Inland areas had a prevalence rate of 9% of ''N. americanus''
* Coastal plain areas had a prevalence rate of 63% of ''N. americanus''
Lowndes County, Alabama
Lowndes County is in the central part of the U.S. state of Alabama. As of the 2020 census, the county's population was 10,311. Its county seat is Hayneville. The county is named in honor of William Lowndes, a member of the United States Con ...
, United States
The United States of America (U.S.A. or USA), commonly known as the United States (U.S. or US) or America, is a country Continental United States, primarily located in North America. It consists of 50 U.S. state, states, a Washington, D.C., ...
* 35% infection rate of predominantly ''N. americanus''
There have also been technological developments that may facilitate more accurate mapping of hookworm prevalence. Some researchers have begun to use geographical information systems (GIS) and remote sensing (RS) to examine helminth ecology and epidemiology. Brooker ''et al.'' utilized this technology to create helminth distribution maps of sub-Saharan Africa. By relating satellite derived environmental data with prevalence data from school-based surveys, they were able to create detailed prevalence maps. The study focused on a wide range of helminths, but interesting conclusions about hookworm specifically were found. As compared to other helminths, hookworm is able to survive in much hotter conditions and was highly prevalent throughout the upper end of the thermal range.
Improved molecular diagnostic tools are another technological advancement that could help improve existing prevalence statistics. Recent research has focused on the development of a DNA-based tool that can be used for diagnosis of infection, specific identification of hookworm, and analysis of genetic variability in hookworm populations. Again this can serve as a major tool for different public health measures against hookworm infection. Most research regarding diagnostic tools is now focused on the creation of a rapid and cost-effective assay for the specific diagnosis of hookworm infection. Many are hopeful that its development can be achieved within the next five years.
History
Discovery
The symptoms now attributed to hookworm appear inpapyrus
Papyrus ( ) is a material similar to thick paper that was used in ancient times as a writing surface. It was made from the pith of the papyrus plant, '' Cyperus papyrus'', a wetland sedge. ''Papyrus'' (plural: ''papyri'') can also refer to ...
papers of ancient Egypt
Egypt ( ar, مصر , ), officially the Arab Republic of Egypt, is a List of transcontinental countries, transcontinental country spanning the North Africa, northeast corner of Africa and Western Asia, southwest corner of Asia via a land bridg ...
(), described as a derangement characterized by anemia. Avicenna
Ibn Sina ( fa, ابن سینا; 980 – June 1037 CE), commonly known in the West as Avicenna (), was a Persian polymath who is regarded as one of the most significant physicians, astronomers, philosophers, and writers of the Islamic ...
, a Persian physician of the eleventh century, discovered the worm in several of his patients and related it to their disease. In later times, the condition was noticeably prevalent in the mining industry in England
England is a country that is part of the United Kingdom. It shares land borders with Wales to its west and Scotland to its north. The Irish Sea lies northwest and the Celtic Sea to the southwest. It is separated from continental Europe ...
, France
France (), officially the French Republic ( ), is a country primarily located in Western Europe. It also comprises of Overseas France, overseas regions and territories in the Americas and the Atlantic Ocean, Atlantic, Pacific Ocean, Pac ...
, Germany
Germany,, officially the Federal Republic of Germany, is a country in Central Europe. It is the second most populous country in Europe after Russia, and the most populous member state of the European Union. Germany is situated betwee ...
, Belgium
Belgium, ; french: Belgique ; german: Belgien officially the Kingdom of Belgium, is a country in Northwestern Europe. The country is bordered by the Netherlands to the north, Germany to the east, Luxembourg to the southeast, France to ...
, North Queensland
North Queensland or the Northern Region is the northern part of the Australian state of Queensland that lies just south of Far North Queensland. Queensland is a massive state, larger than many countries, and its tropical northern part has been ...
, and elsewhere.
Italian physician Angelo Dubini
Angelo Dubini (8 December 1813 – 28 March 1902) was an Italian physician born in Milan.
He earned his doctorate from the University of Pavia in 1837 and spent most of his professional career at the ''Ospedale Maggiore'' in Milan. In 1865 he ...
was the modern-day discoverer of the worm in 1838 after an autopsy
An autopsy (post-mortem examination, obduction, necropsy, or autopsia cadaverum) is a surgical procedure that consists of a thorough examination of a corpse by dissection to determine the cause, mode, and manner of death or to evaluate any d ...
of a peasant woman. Dubini published details in 1843 and identified the species as ''A. duodenale''. Working in the Egyptian medical system in 1852 German physician Theodor Bilharz, drawing upon the work of colleague Wilhelm Griesinger
Wilhelm Griesinger (29 July 1817 – 26 October 1868) was a German neurologist and psychiatrist born in Stuttgart.
Life and career
He studied under Johann Lukas Schönlein at the University of Zurich and physiologist François Magendie in Paris ...
, found these worms during autopsies and went a step further in linking them to local endemic occurrences of chlorosis
In botany, chlorosis is a condition in which leaves produce insufficient chlorophyll. As chlorophyll is responsible for the green color of leaves, chlorotic leaves are pale, yellow, or yellow-white. The affected plant has little or no ability to ...
, which would probably be called iron-deficiency anemia
Iron-deficiency anemia is anemia caused by a lack of iron. Anemia is defined as a decrease in the number of red blood cells or the amount of hemoglobin in the blood. When onset is slow, symptoms are often vague such as feeling tired, weak, shor ...
today.
A breakthrough came 25 years later following a diarrhea
Diarrhea, also spelled diarrhoea, is the condition of having at least three loose, liquid, or watery bowel movements each day. It often lasts for a few days and can result in dehydration due to fluid loss. Signs of dehydration often begin w ...
and anemia
Anemia or anaemia (British English) is a blood disorder in which the blood has a reduced ability to carry oxygen due to a lower than normal number of red blood cells, or a reduction in the amount of hemoglobin. When anemia comes on slowly, t ...
epidemic that took place among Italian
Italian(s) may refer to:
* Anything of, from, or related to the people of Italy over the centuries
** Italians, an ethnic group or simply a citizen of the Italian Republic or Italian Kingdom
** Italian language, a Romance language
*** Regional Ita ...
workmen employed on the Gotthard Rail Tunnel
, it, Galleria del San Gottardo
, other_name =
, line = Gotthard Line
, location = Traversing the Saint-Gotthard Massif in the middle of the Swiss Alps
, coordinates =
, os_grid_ref =
, status =
, system ...
. In an 1880 paper, physicians Camillo Bozzolo, Edoardo Perroncito, and Luigi Pagliani correctly hypothesized that hookworm was linked to the fact that workers had to defecate inside the 15 km tunnel, and that many wore worn-out shoes. The work environment often contained standing water, sometimes knee-deep, and the larvae were capable of surviving several weeks in the water, allowing them to infect many of the workers. In 1897, it was established that the skin was the principal avenue of infection and the biological life cycle
In biology, a biological life cycle (or just life cycle or lifecycle when the biological context is clear) is a series of changes in form that an organism undergoes, returning to the starting state. "The concept is closely related to those of the ...
of the hookworm was clarified.
Eradication programmes
In 1899, American zoologistCharles Wardell Stiles
Charles Wardell Stiles (May 15, 1867 – January 24, 1941) was an American parasitologist born in Spring Valley, New York. He was notable for working on a campaign against hookworm infestation in the American South, where it had been found to cau ...
identified progressive pernicious anemia
Pernicious anemia is a type of vitamin B12 deficiency anemia, a disease in which not enough red blood cells are produced due to the malabsorption of vitamin B12. Malabsorption in pernicious anemia results from the lack or loss of intrinsic ...
seen in the southern United States as being caused by the hookworm ''A. duodenale''. Testing in the 1900s revealed very heavy infestations in school-age children. In Puerto Rico
Puerto Rico (; abbreviated PR; tnq, Boriken, ''Borinquen''), officially the Commonwealth of Puerto Rico ( es, link=yes, Estado Libre Asociado de Puerto Rico, lit=Free Associated State of Puerto Rico), is a Caribbean island and unincorporated ...
, Dr. Bailey K. Ashford, a US Army physician, organized and conducted a parasite treatment campaign, which cured approximately 300,000 people (one-third of the Puerto Rican population) and reduced the death rate from this anemia by 90 percent during the years 1903–04.
 On October 26, 1909, the Rockefeller Sanitary Commission for the Eradication of Hookworm Disease was organized as a result of a gift of US$1 million from John D. Rockefeller, Sr. The five-year program was a remarkable success and a great contribution to the United States' public health, instilling public education, medication, field work and modern government health departments in eleven southern states.
The hookworm exhibit was a prominent part of the 1910 Mississippi state fair.
The commission found that an average of 40% of school-aged children were infected with hookworm. Areas with higher levels of hookworm infection prior to the eradication program experienced greater increases in school enrollment, attendance, and literacy after the intervention. Econometric studies have shown that this effect cannot be explained by a variety of alternative factors, including differential trends across areas, changing crop prices, shifts in certain educational and health policies and the effect of malaria eradication. No significant contemporaneous results were found for adults who should have benefited less from the intervention owing to their substantially lower (prior) infection rates. The program nearly eradicated hookworm and would flourish afterward with new funding as the
On October 26, 1909, the Rockefeller Sanitary Commission for the Eradication of Hookworm Disease was organized as a result of a gift of US$1 million from John D. Rockefeller, Sr. The five-year program was a remarkable success and a great contribution to the United States' public health, instilling public education, medication, field work and modern government health departments in eleven southern states.
The hookworm exhibit was a prominent part of the 1910 Mississippi state fair.
The commission found that an average of 40% of school-aged children were infected with hookworm. Areas with higher levels of hookworm infection prior to the eradication program experienced greater increases in school enrollment, attendance, and literacy after the intervention. Econometric studies have shown that this effect cannot be explained by a variety of alternative factors, including differential trends across areas, changing crop prices, shifts in certain educational and health policies and the effect of malaria eradication. No significant contemporaneous results were found for adults who should have benefited less from the intervention owing to their substantially lower (prior) infection rates. The program nearly eradicated hookworm and would flourish afterward with new funding as the Rockefeller Foundation
The Rockefeller Foundation is an American private foundation and philanthropy, philanthropic medical research and arts funding organization based at 420 Fifth Avenue, New York City. The second-oldest major philanthropic institution in America, aft ...
International Health Division.
The RF's hookworm campaign in Mexico showed how science and politics play a role in developing health policies. It brought together government officials, health officials, public health workers, Rockefeller officials and the community. This campaign was launched to eradicate hookworms in Mexico. Although the campaign did not focus on long-term treatments, it did set the terms of the relationship between Mexico and the Rockefeller Foundation. The scientific knowledge behind this campaign helped shape public health policies, improved public health and built a strong relationship between US and Mexico.
In the 1920s, hookworm eradication reached the Caribbean and Latin America, where great mortality was reported among people in the West Indies
The West Indies is a subregion of North America, surrounded by the North Atlantic Ocean and the Caribbean Sea that includes 13 independent island countries and 18 dependencies and other territories in three major archipelagos: the Greate ...
towards the end of the 18th century, as well as through descriptions sent from Brazil
Brazil ( pt, Brasil; ), officially the Federative Republic of Brazil (Portuguese: ), is the largest country in both South America and Latin America. At and with over 217 million people, Brazil is the world's fifth-largest country by area ...
and various other tropical and sub-tropical regions.
Treatments
Treatment in the early 20th century relied on the use ofEpsom salt
Epsomite, Epsom salt, or magnesium sulfate heptahydrate, is a hydrous magnesium sulfate mineral with formula MgSO4·7H2O.
Epsomite crystallizes in the orthorhombic system as rarely found acicular or fibrous crystals, the normal form is as massiv ...
to reduce protective mucus, followed by thymol
Thymol (also known as 2-isopropyl-5-methylphenol, IPMP), , is a natural monoterpenoid phenol derivative of ''p''-Cymene, isomeric with carvacrol, found in oil of thyme, and extracted from '' Thymus vulgaris'' (common thyme), ajwain, and va ...
to kill the worms. By the 1940s, tetrachloroethylene
Tetrachloroethylene, also known under the systematic name tetrachloroethene, or perchloroethylene, and many other names (and abbreviations such as "perc" or "PERC", and "PCE"), is a chlorocarbon with the formula Cl2C=CCl2 . It is a colorless li ...
was the leading method. It was not until later in the mid-20th century when new organic drug compounds were developed.
Research
Anemia in pregnancy
It is estimated that a third of all pregnant women in developing countries are infected with hookworm, 56% of all pregnant women in developing countries experience anemia, 20% of all maternal deaths are either directly or indirectly related to anemia. Numbers like this have led to an increased interest in the topic of hookworm-related anemia during pregnancy. With the understanding that chronic hookworm infection can often lead to anemia, many people are now questioning if the treatment of hookworm could effect change in severe anemia rates and thus also on maternal and child health as well. Most evidence suggests that the contribution of hookworm to maternal anemia merits that all women of child-bearing age living in endemic areas be subject to periodic anthelmintic treatment. The World Health Organization even recommends that infected pregnant women be treated after their first trimester. Regardless of these suggestions, only Madagascar, Nepal and Sri Lanka have added deworming to their antenatal care programs. This lack of deworming of pregnant women is explained by the fact that most individuals still fear that anthelmintic treatment will result in adverse birth outcomes. But a 2006 study by Gyorkos et al. found that when comparing a group of pregnant women treated with mebendazole with a control placebo group, both illustrated rather similar rates in adverse birth outcomes. The treated group demonstrated 5.6% adverse birth outcomes, while the control group had 6.25% adverse birth outcomes. Furthermore, Larocque et al. illustrated that treatment for hookworm infection actually led to positive health results in the infant. This study concluded that treatment with mebendazole plus iron supplements during antenatal care significantly reduced the proportion of very low birth weight infants when compared to a placebo control group. Studies so far have validated recommendations to treat infected pregnant women for hookworm infection during pregnancy. A review found that a single dose of antihelminthics (anti-worm drugs) given in the second trimester of pregnancy "may reduce maternal anaemia and worm prevalence when used in settings with high prevalence of maternal helminthiasis".Malaria co-infection
Co-infection with hookworm and ''Plasmodium falciparum
''Plasmodium falciparum'' is a unicellular protozoan parasite of humans, and the deadliest species of ''Plasmodium'' that causes malaria in humans. The parasite is transmitted through the bite of a female '' Anopheles'' mosquito and causes the ...
'' is common in Africa. Although exact numbers are unknown, preliminary analyses estimate that as many as a quarter of African schoolchildren (17.8–32.1 million children aged 5–14 years) may be coincidentally at-risk of both ''P. falciparum'' and hookworm. While original hypotheses stated that co-infection with multiple parasites would impair the host's immune response to a single parasite and increase susceptibility to clinical disease, studies have yielded contrasting results. For example, one study in Senegal showed that the risk of clinical malaria infection was increased in helminth-infected children in comparison to helminth-free children while other studies have failed to reproduce such results, and even among laboratory mouse experiments the effect of helminths on malaria is variable.
Some hypotheses and studies suggest that helminth infections may protect against cerebral malaria due to the possible modulation of pro-inflammatory and anti-inflammatory cytokines responses. Furthermore, the mechanisms underlying this supposed increased susceptibility to disease are unknown. For example, helminth infections cause potent and highly polarized immune response characterized by increased T-helper cell
The T helper cells (Th cells), also known as CD4+ cells or CD4-positive cells, are a type of T cell that play an important role in the adaptive immune system. They aid the activity of other immune cells by releasing cytokines. They are considere ...
type 2 (Th2) cytokine
Cytokines are a broad and loose category of small proteins (~5–25 kDa) important in cell signaling. Cytokines are peptides and cannot cross the lipid bilayer of cells to enter the cytoplasm. Cytokines have been shown to be involved in au ...
and Immunoglobulin E
Immunoglobulin E (IgE) is a type of antibody (or immunoglobulin (Ig) " isotype") that has been found only in mammals. IgE is synthesised by plasma cells. Monomers of IgE consist of two heavy chains (ε chain) and two light chains, with the � ...
(IgE) production. However, the effect of such responses on the human immune response is unknown. Additionally, both malaria and helminth infection can cause anemia, but the effect of co-infection and possible enhancement of anemia is poorly understood.
Hygiene hypothesis and hookworm as therapy
Thehygiene hypothesis
In medicine, the hygiene hypothesis states that early childhood exposure to particular microorganisms (such as the gut flora and helminth parasites) protects against allergic diseases by contributing to the development of the immune system. In pa ...
states that infants and children who lack exposure to infectious agents are more susceptible to allergic diseases via modulation of immune system development. The theory was first proposed by David P. Strachan who noted that hay fever
Allergic rhinitis, of which the seasonal type is called hay fever, is a type of inflammation in the nose that occurs when the immune system overreacts to allergens in the air. Signs and symptoms include a runny or stuffy nose, sneezing, red, i ...
and eczema
Dermatitis is inflammation of the skin, typically characterized by itchiness, redness and a rash. In cases of short duration, there may be small blisters, while in long-term cases the skin may become thickened. The area of skin involved c ...
were less common in children who belonged to large families. Since then, studies have noted the effect of gastrointestinal worms on the development of allergies in the developing world. For example, a study in Gambia found that eradication of worms in some villages led to increased skin reactions to allergies among children.
Vaccines
While annual or semi-annual mass antihelminthic administration is a critical aspect of any public health intervention, many have begun to realize how unsustainable it is due to aspects such as poverty, high rates of re-infection, and diminished efficacy of drugs with repeated use. Current research, therefore, has focused on the development of a vaccine that could be integrated into existing control programs. The goal of vaccine development is not necessarily to create a vaccine with sterilizing immunity or complete protection against immunity. A vaccine that reduces the likelihood of vaccinated individuals developing severe infections and thus reduced blood and nutrient levels could still have a significant impact on the high burden of disease throughout the world. Current research focuses on targeting two stages in the development of the worm: the larval stage and the adult stage. Research on larval antigens has focused on proteins that are members of thepathogenesis-related protein Pathogenesis-related (PR) proteins are proteins produced in plants in the event of a pathogen attack. They are induced as part of systemic acquired resistance. Infections activate genes that produce PR proteins. Some of these proteins are antimicr ...
superfamily, ''Ancylostoma'' Secreted Proteins. Although they were first described in ''Anyclostoma'', these proteins have also been successfully isolated from the secreted product of ''N. americanus''. ''N. americanus'' ASP-2 (Na-ASP-2) is currently the leading larval-stage hookworm vaccine candidate. A randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled study has already been performed; 36 healthy adults without a history of hookworm infection were given three intramuscular injections of three different concentrations of Na-ASP-2 and observed for six months after the final vaccination. The vaccine induced significant anti-Na-ASP-2 IgG and cellular immune responses. In addition, it was safe and produced no debilitating side effects. The vaccine is now in a phase one trial; healthy adult volunteers with documented evidence of previous infection in Brazil are being given the same dose concentration
In chemistry, concentration is the abundance of a constituent divided by the total volume of a mixture. Several types of mathematical description can be distinguished: '' mass concentration'', '' molar concentration'', ''number concentration'', ...
on the same schedule used in the initial study. If this study is successful, the next step would be to conduct a phase two trial to assess the rate and intensity of hookworm infection among vaccinated persons. Because the Na-ASP-2 vaccine only targets the larval stage, it is critical that all subjects enrolled in the study be treated with antihelminthic drugs to eliminate adult worms prior to vaccination.
Adult hookworm antigens have also been identified as potential candidates for vaccines. When adult worms attach to the intestinal mucosa of the human host, erythrocytes are ruptured in the worm's digestive tract which causes the release of free hemoglobin which is subsequently degraded by a proteolytic cascade. Several of these proteins that are responsible for this proteolytic cascade are also essential for the worm's nutrition and survival. Therefore, a vaccine that could induce antibodies for these antigens could interfere with the hookworm's digestive pathway and impair the worm's survival. Three proteins have been identified: the aspartic protease-hemoglobinase APR-1, the cysteine protease-hemoglobinase CP-2, and a glutathione S-transferase. Vaccination with APR-1 and CP-2 led to reduced host blood loss and fecal egg counts in dogs. With APR-1, vaccination even led to reduced worm burden. Research is currently stymied at the development of at least one of these antigens as a recombinant protein for testing in clinical trials.
Terminology
The term "hookworm" is sometimes used to refer to hookworm infection. A hookworm is a type of parasitic worm (helminth
Parasitic worms, also known as helminths, are large macroparasites; adults can generally be seen with the naked eye. Many are intestinal worms that are soil-transmitted and infect the gastrointestinal tract. Other parasitic worms such as ...
).
See also
* List of parasites (human)References
External links
CDC Department of Parasitic Diseases images of the hookworm life cycle
!-- includes copyright-free images that could be used for the article -->
Centers for Disease Control and Prevention
Dog hookworm (''Ancylostoma caninum'') at MetaPathogen: facts, life cycle, references
Human hookworms (''Ancylostoma duodenale'' and ''Necator americanus'') at MetaPathogen: facts, life cycle, references
{{Portal bar, Biology, Medicine Strongylida Parasitic nematodes of humans Tropical diseases Conditions diagnosed by stool test Zoonoses Parasites of cats Cat diseases Parasites of dogs Dog diseases Infectious diseases with eradication efforts Wikipedia medicine articles ready to translate Wikipedia infectious disease articles ready to translate