History of general anesthesia on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Attempts at producing a state of
 The Sumerians are said to have cultivated and harvested the
The Sumerians are said to have cultivated and harvested the
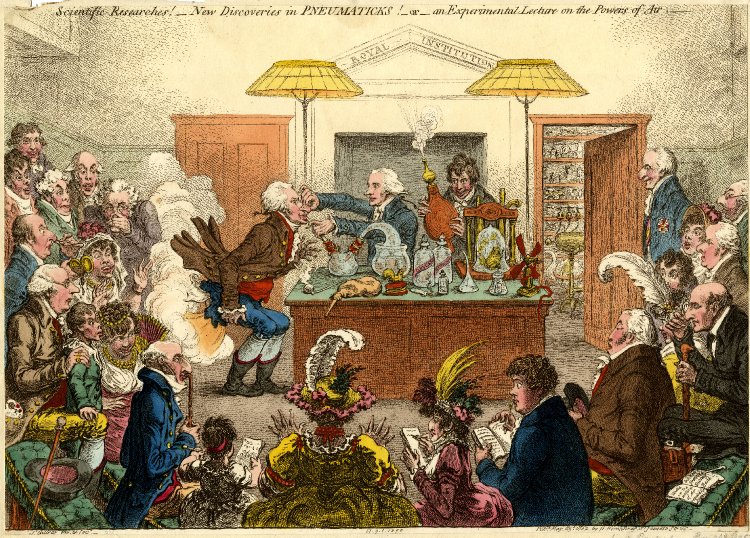
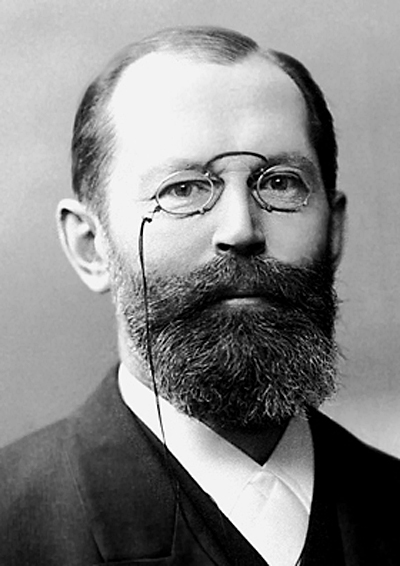





 The 20th century saw the transformation of the practices of tracheotomy,
The 20th century saw the transformation of the practices of tracheotomy,
general anesthesia
General anaesthesia (UK) or general anesthesia (US) is a medically induced loss of consciousness that renders the patient unarousable even with painful stimuli. This effect is achieved by administering either intravenous or inhalational general ...
can be traced throughout recorded history
Recorded history or written history describes the historical events that have been recorded in a written form or other documented communication which are subsequently evaluated by historians using the historical method. For broader world hist ...
in the writings of the ancient Sumer
Sumer () is the earliest known civilization in the historical region of southern Mesopotamia (south-central Iraq), emerging during the Chalcolithic and early Bronze Ages between the sixth and fifth millennium BC. It is one of the cradles of c ...
ians, Babylonia
Babylonia (; Akkadian: , ''māt Akkadī'') was an ancient Akkadian-speaking state and cultural area based in the city of Babylon in central-southern Mesopotamia (present-day Iraq and parts of Syria). It emerged as an Amorite-ruled state c. ...
ns, Assyria
Assyria (Neo-Assyrian cuneiform: , romanized: ''māt Aššur''; syc, ܐܬܘܪ, ʾāthor) was a major ancient Mesopotamian civilization which existed as a city-state at times controlling regional territories in the indigenous lands of the A ...
ns, Egyptians
Egyptians ( arz, المَصرِيُون, translit=al-Maṣriyyūn, ; arz, المَصرِيِين, translit=al-Maṣriyyīn, ; cop, ⲣⲉⲙⲛ̀ⲭⲏⲙⲓ, remenkhēmi) are an ethnic group native to the Nile, Nile Valley in Egypt. Egyptian ...
, Indians, and Chinese
Chinese can refer to:
* Something related to China
* Chinese people, people of Chinese nationality, citizenship, and/or ethnicity
**''Zhonghua minzu'', the supra-ethnic concept of the Chinese nation
** List of ethnic groups in China, people of ...
.
The Renaissance
The Renaissance ( , ) , from , with the same meanings. is a period in European history marking the transition from the Middle Ages to modernity and covering the 15th and 16th centuries, characterized by an effort to revive and surpass ideas ...
saw significant advances in anatomy
Anatomy () is the branch of biology concerned with the study of the structure of organisms and their parts. Anatomy is a branch of natural science that deals with the structural organization of living things. It is an old science, having its ...
and surgical technique
Surgery ''cheirourgikē'' (composed of χείρ, "hand", and ἔργον, "work"), via la, chirurgiae, meaning "hand work". is a medical specialty that uses operative manual and instrumental techniques on a person to investigate or treat a pat ...
. However, despite all this progress, surgery remained a treatment of last resort. Largely because of the associated pain
Pain is a distressing feeling often caused by intense or damaging stimuli. The International Association for the Study of Pain defines pain as "an unpleasant sensory and emotional experience associated with, or resembling that associated with, ...
, many patients with surgical disorders chose certain death rather than undergo surgery. Although there has been a great deal of debate as to who deserves the most credit for the discovery of general anesthesia, it is generally agreed that certain scientific discoveries in the late 18th and early 19th centuries were critical to the eventual introduction and development of modern anesthetic techniques.
Two major advances occurred in the late 19th century, which together allowed the transition to modern surgery. An appreciation of the germ theory of disease
The germ theory of disease is the currently accepted scientific theory for many diseases. It states that microorganisms known as pathogens or "germs" can lead to disease. These small organisms, too small to be seen without magnification, invade h ...
led rapidly to the development and application of antiseptic
An antiseptic (from Greek ἀντί ''anti'', "against" and σηπτικός ''sēptikos'', "putrefactive") is an antimicrobial substance or compound that is applied to living tissue/skin to reduce the possibility of infection, sepsis, or putre ...
techniques in surgery. Antisepsis, which soon gave way to asepsis
Asepsis is the state of being free from disease-causing micro-organisms (such as pathogenic bacteria, viruses, pathogenic fungi, and parasites). There are two categories of asepsis: medical and surgical. The modern day notion of asepsis is deriv ...
, reduced the overall morbidity
A disease is a particular abnormal condition that negatively affects the structure or function of all or part of an organism, and that is not immediately due to any external injury. Diseases are often known to be medical conditions that a ...
and mortality
Mortality is the state of being mortal, or susceptible to death; the opposite of immortality.
Mortality may also refer to:
* Fish mortality, a parameter used in fisheries population dynamics to account for the loss of fish in a fish stock throug ...
of surgery to a far more acceptable rate than in previous eras. Concurrent with these developments were the significant advances in pharmacology
Pharmacology is a branch of medicine, biology and pharmaceutical sciences concerned with drug or medication action, where a drug may be defined as any artificial, natural, or endogenous (from within the body) molecule which exerts a biochemica ...
and physiology
Physiology (; ) is the scientific study of functions and mechanisms in a living system. As a sub-discipline of biology, physiology focuses on how organisms, organ systems, individual organs, cells, and biomolecules carry out the chemical ...
which led to the development of general anesthesia and the control of pain.
In the 20th century, the safety and efficacy of general anesthesia was improved by the routine use of tracheal intubation
Tracheal intubation, usually simply referred to as intubation, is the placement of a flexible plastic catheter, tube into the vertebrate trachea, trachea (windpipe) to maintain an open airway or to serve as a conduit through which to administer ce ...
and other advanced airway management
Airway management includes a set of maneuvers and medical procedures performed to prevent and relieve airway obstruction. This ensures an open pathway for gas exchange between a patient's lungs and the atmosphere. This is accomplished by either cl ...
techniques. Significant advances in monitoring
Monitoring may refer to:
Science and technology Biology and healthcare
* Monitoring (medicine), the observation of a disease, condition or one or several medical parameters over time
* Baby monitoring
* Biomonitoring, of toxic chemical compounds, ...
and new anesthetic agents
Anesthesia is a state of controlled, temporary loss of sensation or awareness that is induced for medical or veterinary purposes. It may include some or all of analgesia (relief from or prevention of pain), paralysis (muscle relaxation), am ...
with improved pharmacokinetic
Pharmacokinetics (from Ancient Greek ''pharmakon'' "drug" and ''kinetikos'' "moving, putting in motion"; see chemical kinetics), sometimes abbreviated as PK, is a branch of pharmacology dedicated to determining the fate of substances administered ...
and pharmacodynamic
Pharmacodynamics (PD) is the study of the biochemical and physiologic effects of drugs (especially pharmaceutical drugs). The effects can include those manifested within animals (including humans), microorganisms, or combinations of organisms (for ...
characteristics also contributed to this trend. Standardized training programs for anesthesiologist
Anesthesiology, anaesthesiology, or anaesthesia is the medical specialty concerned with the total perioperative care of patients before, during and after surgery. It encompasses anesthesia, intensive care medicine, critical emergency medicine, ...
s and nurse anesthetist
A nurse anesthetist is an advanced practice nurse who administers anesthesia for surgery or other medical procedures. They are involved in the administration of anesthesia in a majority of countries, with varying levels of autonomy.
A survey pu ...
s emerged during this period. The increased application of economic and business administration principles to health care in the late 20th and early 21st centuries led to the introduction of management practices such as transfer pricing
In taxation and accounting, transfer pricing refers to the rules and methods for pricing transactions within and between enterprises under common ownership or control. Because of the potential for cross-border controlled transactions to distort ...
to improve the efficiency of anesthetists.
Etymology of "anesthesia"
The word "anesthesia", coined by Oliver Wendell Holmes (1809–1894) in 1846 from theGreek
Greek may refer to:
Greece
Anything of, from, or related to Greece, a country in Southern Europe:
*Greeks, an ethnic group.
*Greek language, a branch of the Indo-European language family.
**Proto-Greek language, the assumed last common ancestor ...
, ''an-'', "without"; and , ''aisthēsis'', "sensation", refers to the inhibition of sensation
Sensation (psychology) refers to the processing of the senses by the sensory system.
Sensation or sensations may also refer to:
In arts and entertainment In literature
*Sensation (fiction), a fiction writing mode
*Sensation novel, a British ...
.
Antiquity
The first attempts at general anesthesia were probablyherbal remedies
Herbal medicine (also herbalism) is the study of pharmacognosy and the use of medicinal plants, which are a basis of traditional medicine. With worldwide research into pharmacology, some herbal medicines have been translated into modern remedie ...
administered in prehistory
Prehistory, also known as pre-literary history, is the period of human history between the use of the first stone tools by hominins 3.3 million years ago and the beginning of recorded history with the invention of writing systems. The use of ...
. Alcohol
Alcohol most commonly refers to:
* Alcohol (chemistry), an organic compound in which a hydroxyl group is bound to a carbon atom
* Alcohol (drug), an intoxicant found in alcoholic drinks
Alcohol may also refer to:
Chemicals
* Ethanol, one of sev ...
is the oldest known sedative
A sedative or tranquilliser is a substance that induces sedation by reducing irritability or excitement. They are CNS depressants and interact with brain activity causing its deceleration. Various kinds of sedatives can be distinguished, but t ...
; it was used in ancient Mesopotamia
Mesopotamia ''Mesopotamíā''; ar, بِلَاد ٱلرَّافِدَيْن or ; syc, ܐܪܡ ܢܗܪ̈ܝܢ, or , ) is a historical region of Western Asia situated within the Tigris–Euphrates river system, in the northern part of the F ...
thousands of years ago.
Opium
 The Sumerians are said to have cultivated and harvested the
The Sumerians are said to have cultivated and harvested the opium
Opium (or poppy tears, scientific name: ''Lachryma papaveris'') is dried latex obtained from the seed capsules of the opium poppy ''Papaver somniferum''. Approximately 12 percent of opium is made up of the analgesic alkaloid morphine, which i ...
poppy (''Papaver somniferum
''Papaver somniferum'', commonly known as the opium poppy or breadseed poppy, is a species of flowering plant in the family Papaveraceae. It is the species of plant from which both opium and poppy seeds are derived and is also a valuable orname ...
'') in lower Mesopotamia as early as 3400 BC, though this has been disputed. The most ancient testimony concerning the opium poppy found to date was inscribed in cuneiform script
Cuneiform is a logo-syllabic script that was used to write several languages of the Ancient Middle East. The script was in active use from the early Bronze Age until the beginning of the Common Era. It is named for the characteristic wedge-sha ...
on a small white clay tablet at the end of the third millennium BC. This tablet was discovered in 1954 during excavations at Nippur
Nippur (Sumerian language, Sumerian: ''Nibru'', often logogram, logographically recorded as , EN.LÍLKI, "Enlil City;"The Cambridge Ancient History: Prolegomena & Prehistory': Vol. 1, Part 1. Accessed 15 Dec 2010. Akkadian language, Akkadian: '' ...
, and is currently kept at the University of Pennsylvania Museum of Archaeology and Anthropology
The University of Pennsylvania Museum of Archaeology and Anthropology—commonly known as the Penn Museum—is an archaeology and anthropology museum at the University of Pennsylvania. It is located on Penn's campus in the University City neighb ...
. Deciphered by Samuel Noah Kramer
Samuel Noah Kramer (September 28, 1897 – November 26, 1990) was one of the world's leading Assyriologists, an expert in Sumerian history and Sumerian language. After high school, he attended Temple University, before Dropsie and Penn, both in ...
and Martin Leve, it is considered to be the most ancient pharmacopoeia
A pharmacopoeia, pharmacopeia, or pharmacopoea (from the obsolete typography ''pharmacopœia'', meaning "drug-making"), in its modern technical sense, is a book containing directions for the identification of compound medicines, and published by ...
in existence. Some Sumerian tablets of this era have an ideogram
An ideogram or ideograph (from Greek "idea" and "to write") is a graphic symbol that represents an idea or concept, independent of any particular language, and specific words or phrases. Some ideograms are comprehensible only by familiarit ...
inscribed upon them, "hul gil", which translates to "plant of joy", believed by some authors to refer to opium. The term ''gil'' is still used for opium in certain parts of the world. The Sumerian goddess Nidaba
Nisaba was the Mesopotamian goddess of writing and grain. She is one of the oldest Sumerian deities attested in writing, and remained prominent through many periods of Mesopotamian history. She was commonly worshiped by scribes, and numerous Su ...
is often depicted with poppies growing out of her shoulders. About 2225 BC, the Sumerian territory became a part of the Babylonian empire. Knowledge and use of the opium poppy and its euphoric
Euphoria ( ) is the experience (or affect) of pleasure or excitement and intense feelings of well-being and happiness. Certain natural rewards and social activities, such as aerobic exercise, laughter, listening to or making music and da ...
effects thus passed to the Babylonians, who expanded their empire eastwards to Persia
Iran, officially the Islamic Republic of Iran, and also called Persia, is a country located in Western Asia. It is bordered by Iraq and Turkey to the west, by Azerbaijan and Armenia to the northwest, by the Caspian Sea and Turkmeni ...
and westwards to Egypt, thereby extending its range to these civilizations. British archaeologist and cuneiformist Reginald Campbell Thompson
Reginald Campbell Thompson (21 August 1876 – 23 May 1941) was a British archaeologist, assyriologist, and cuneiformist. He excavated at Nineveh, Ur, Nebo and Carchemish among many other sites.
Biography
Thompson was born in Kensington, and ...
writes that opium was known to the Assyrians in the 7th century BC. The term "Arat Pa Pa" occurs in the ''Assyrian Herbal
A herbal is a book containing the names and descriptions of plants, usually with information on their medicinal, tonic, culinary, toxic, hallucinatory, aromatic, or magical powers, and the legends associated with them.Arber, p. 14. A herbal m ...
'', a collection of inscribed Assyrian tablets dated to c. 650 BC. According to Thompson, this term is the Assyrian name for the juice of the poppy and it may be the etymological
Etymology ()The New Oxford Dictionary of English (1998) – p. 633 "Etymology /ˌɛtɪˈmɒlədʒi/ the study of the class in words and the way their meanings have changed throughout time". is the study of the history of the form of words and ...
origin of the Latin "''papaver
''Papaver'' is a genus of 70–100 species of frost-tolerant annuals, biennials, and perennials native to temperate and cold regions of Eurasia, Africa and North America. It is the type genus of the poppy family, Papaveraceae.
Description
The ...
''".
The ancient Egyptians had some surgical instruments, as well as crude analgesics and sedatives, including possibly an extract prepared from the mandrake
A mandrake is the root of a plant, historically derived either from plants of the genus '' Mandragora'' found in the Mediterranean region, or from other species, such as ''Bryonia alba'', the English mandrake, which have similar properties. The ...
fruit. The use of preparations similar to opium in surgery is recorded in the Ebers Papyrus, an Egyptian medical papyrus written in the Eighteenth dynasty. However, it is questionable whether opium itself was known in ancient Egypt. The Greek gods Hypnos
In Greek mythology, Hypnos (; Ancient Greek: means 'sleep') also spelled Hypnus is the personification of sleep; the Roman equivalent is known as Somnus. His name is the origin of the word hypnosis. Pausanias wrote that Hypnos was a dearest fr ...
(Sleep), Nyx (Night), and Thanatos
In Greek mythology, Thanatos (; grc, Θάνατος, pronounced in "Death", from θνῄσκω ''thnēskō'' "(I) die, am dying") was the personification of death. He was a minor figure in Greek mythology, often referred to but rarely appe ...
(Death) were often depicted holding poppies.
Prior to the introduction of opium to ancient India
According to consensus in modern genetics, anatomically modern humans first arrived on the Indian subcontinent from Africa between 73,000 and 55,000 years ago. Quote: "Y-Chromosome and Mt-DNA data support the colonization of South Asia by m ...
and China
China, officially the People's Republic of China (PRC), is a country in East Asia. It is the world's most populous country, with a population exceeding 1.4 billion, slightly ahead of India. China spans the equivalent of five time zones and ...
, these civilizations pioneered the use of cannabis
''Cannabis'' () is a genus of flowering plants in the family Cannabaceae. The number of species within the genus is disputed. Three species may be recognized: ''Cannabis sativa'', '' C. indica'', and '' C. ruderalis''. Alternatively ...
incense
Incense is aromatic biotic material that releases fragrant smoke when burnt. The term is used for either the material or the aroma. Incense is used for aesthetic reasons, religious worship, aromatherapy, meditation, and ceremony. It may also be ...
and aconitum
''Aconitum'' (), also known as aconite, monkshood, wolf's-bane, leopard's bane, mousebane, women's bane, devil's helmet, queen of poisons, or blue rocket, is a genus of over 250 species of flowering plants belonging to the family Ranunculaceae. ...
. c. 400 BC, the Sushruta Samhita
The ''Sushruta Samhita'' (सुश्रुतसंहिता, IAST: ''Suśrutasaṃhitā'', literally "Suśruta's Compendium") is an ancient Sanskrit text on medicine and surgery, and one of the most important such treatises on this subj ...
(a text from the Indian subcontinent
The Indian subcontinent is a list of the physiographic regions of the world, physiographical region in United Nations geoscheme for Asia#Southern Asia, Southern Asia. It is situated on the Indian Plate, projecting southwards into the Indian O ...
on ayurvedic medicine
Ayurveda () is an alternative medicine system with historical roots in the Indian subcontinent. The theory and practice of Ayurveda is pseudoscientific. Ayurveda is heavily practiced in India and Nepal, where around 80% of the population rep ...
and surgery) advocates the use of wine
Wine is an alcoholic drink typically made from fermented grapes. Yeast consumes the sugar in the grapes and converts it to ethanol and carbon dioxide, releasing heat in the process. Different varieties of grapes and strains of yeasts are m ...
with incense of cannabis for anesthesia. By the 8th century AD, Arab traders had brought opium to India and China.
Classical antiquity
InClassical antiquity
Classical antiquity (also the classical era, classical period or classical age) is the period of cultural history between the 8th century BC and the 5th century AD centred on the Mediterranean Sea, comprising the interlocking civilizations of ...
, anaesthetics were described by:
* Dioscorides
Pedanius Dioscorides ( grc-gre, Πεδάνιος Διοσκουρίδης, ; 40–90 AD), “the father of pharmacognosy”, was a Greek physician, pharmacologist, botanist, and author of ''De materia medica'' (, On Medical Material) —a 5-vol ...
(''De Materia Medica
(Latin name for the Greek work , , both meaning "On Medical Material") is a pharmacopoeia of medicinal plants and the medicines that can be obtained from them. The five-volume work was written between 50 and 70 CE by Pedanius Dioscorides, a ...
'')
* Galen
Aelius Galenus or Claudius Galenus ( el, Κλαύδιος Γαληνός; September 129 – c. AD 216), often Anglicized as Galen () or Galen of Pergamon, was a Greek physician, surgeon and philosopher in the Roman Empire. Considered to be one of ...
* Hippocrates
Hippocrates of Kos (; grc-gre, Ἱπποκράτης ὁ Κῷος, Hippokrátēs ho Kôios; ), also known as Hippocrates II, was a Greek physician of the classical period who is considered one of the most outstanding figures in the history of ...
* Theophrastus
Theophrastus (; grc-gre, Θεόφραστος ; c. 371c. 287 BC), a Greek philosopher and the successor to Aristotle in the Peripatetic school. He was a native of Eresos in Lesbos.Gavin Hardy and Laurence Totelin, ''Ancient Botany'', Routledge ...
(''Historia Plantarum
Historia may refer to:
* Historia, the local version of the History channel in Spain and Portugal
* Historia (TV channel), a Canadian French language specialty channel
* Historia (newspaper), a French monthly newspaper devoted to History topics
* ...
'')
China and Hua Tuo's Ancient Chemical Mixture

Bian Que
Bian Que (; 407 – 310 BC) was an ancient Chinese figure traditionally said to be the earliest known Chinese physician during the Warring States period. His real name is said to be Qin Yueren (), but his medical skills were so amazing that peop ...
(Chinese
Chinese can refer to:
* Something related to China
* Chinese people, people of Chinese nationality, citizenship, and/or ethnicity
**''Zhonghua minzu'', the supra-ethnic concept of the Chinese nation
** List of ethnic groups in China, people of ...
: 扁鵲, Wade–Giles
Wade–Giles () is a romanization system for Mandarin Chinese. It developed from a system produced by Thomas Francis Wade, during the mid-19th century, and was given completed form with Herbert A. Giles's '' Chinese–English Dictionary'' of ...
: ''Pien Ch'iao'', ) was a legendary Chinese internist and surgeon who reportedly used general anesthesia for surgical procedures. It is recorded in the '' Book of Master Han Fei'' (), the ''Records of the Grand Historian
''Records of the Grand Historian'', also known by its Chinese name ''Shiji'', is a monumental history of China that is the first of China's 24 dynastic histories. The ''Records'' was written in the early 1st century by the ancient Chinese hist ...
'' (), and the '' Book of Master Lie'' () that Bian Que gave two men, named "Lu" and "Chao", a toxic drink which rendered them unconscious for three days, during which time he performed a gastrostomy
Gastrostomy is the creation of an artificial external opening into the stomach for nutritional support or gastric decompression.
Typically this would include an incision in the patient's epigastrium as part of a formal operation. It can be perfor ...
upon them.
Hua Tuo
Hua Tuo ( 140–208), courtesy name Yuanhua, was a Chinese physician who lived during the late Eastern Han dynasty. The historical texts '' Records of the Three Kingdoms'' and '' Book of the Later Han'' record Hua Tuo as the first person in Ch ...
(Chinese
Chinese can refer to:
* Something related to China
* Chinese people, people of Chinese nationality, citizenship, and/or ethnicity
**''Zhonghua minzu'', the supra-ethnic concept of the Chinese nation
** List of ethnic groups in China, people of ...
:華佗, ) was a Chinese surgeon
In modern medicine, a surgeon is a medical professional who performs surgery. Although there are different traditions in different times and places, a modern surgeon usually is also a licensed physician or received the same medical training as ...
of the 2nd century AD. According to the ''Records of Three Kingdoms
The ''Records or History of the Three Kingdoms'', also known by its Chinese name as the Sanguo Zhi, is a Chinese historical text which covers the history of the late Eastern Han dynasty (c. 184–220 AD) and the Three Kingdoms period (220– ...
'' () and the ''Book of the Later Han
The ''Book of the Later Han'', also known as the ''History of the Later Han'' and by its Chinese name ''Hou Hanshu'' (), is one of the Twenty-Four Histories and covers the history of the Han dynasty from 6 to 189 CE, a period known as the Later ...
'' (), Hua Tuo performed surgery under general anesthesia using a formula he had developed by mixing wine with a mixture of herbal extract
An extract is a substance made by extracting a part of a raw material, often by using a solvent such as ethanol, oil or water. Extracts may be sold as tinctures, absolutes or in powder form.
The aromatic principles of many spices, nuts, h ...
s he called '' mafeisan'' (麻沸散). Hua Tuo reportedly used mafeisan to perform even major operations such as resection of gangrenous
Gangrene is a type of tissue death caused by a lack of blood supply. Symptoms may include a change in skin color to red or black, numbness, swelling, pain, skin breakdown, and coolness. The feet and hands are most commonly affected. If the ga ...
intestines
The gastrointestinal tract (GI tract, digestive tract, alimentary canal) is the tract or passageway of the digestive system that leads from the mouth to the anus. The GI tract contains all the major organs of the digestive system, in humans ...
. Before the surgery, he administered an oral anesthetic potion
A potion () is a liquid "that contains medicine, poison, or something that is supposed to have magic powers.” It derives from the Latin word ''potus'' which referred to a drink or drinking. The term philtre is also used, often specifically ...
, probably dissolved in wine, in order to induce a state of unconsciousness
Unconsciousness is a state in which a living individual exhibits a complete, or near-complete, inability to maintain an consciousness, awareness of self and environment or to respond to any human or environmental Stimulus (physiology), stimulus. ...
and partial neuromuscular blockade
Neuromuscular-blocking drugs block neuromuscular transmission at the neuromuscular junction, causing paralysis of the affected skeletal muscles. This is accomplished via their action on the post-synaptic acetylcholine (Nm) receptors.
In clin ...
.
The exact composition of mafeisan, similar to all of Hua Tuo's clinical knowledge, was lost when he burned his manuscripts, just before his death. The composition of the anesthetic powder was not mentioned in either the ''Records of Three Kingdoms'' or the ''Book of the Later Han''. Because Confucian
Confucianism, also known as Ruism or Ru classicism, is a system of thought and behavior originating in ancient China. Variously described as tradition, a philosophy, a Religious Confucianism, religion, a humanistic or rationalistic religion, ...
teachings regarded the body as sacred
Sacred describes something that is dedicated or set apart for the service or worship of a deity; is considered worthy of spiritual respect or devotion; or inspires awe or reverence among believers. The property is often ascribed to objects (a ...
and surgery was considered a form of body mutilation, surgery was strongly discouraged in ancient China
The earliest known written records of the history of China date from as early as 1250 BC, from the Shang dynasty (c. 1600–1046 BC), during the reign of king Wu Ding. Ancient historical texts such as the '' Book of Documents'' (early chapte ...
. Because of this, despite Hua Tuo's reported success with general anesthesia, the practice of surgery in ancient China ended with his death.
The name ''mafeisan'' combines ''ma'' ( 麻, meaning "cannabis, hemp
Hemp, or industrial hemp, is a botanical class of ''Cannabis sativa'' cultivars grown specifically for industrial or medicinal use. It can be used to make a wide range of products. Along with bamboo, hemp is among the fastest growing plants o ...
, numbed or tingling
Paresthesia is an abnormal sensation of the skin (tingling, pricking, chilling, burning, numbness) with no apparent physical cause. Paresthesia may be transient or chronic, and may have any of dozens of possible underlying causes. Paresthesias ar ...
"), ''fei'' ( 沸, meaning "boiling
Boiling is the rapid vaporization of a liquid, which occurs when a liquid is heated to its boiling point, the temperature at which the vapour pressure of the liquid is equal to the pressure exerted on the liquid by the surrounding atmosphere. Th ...
or bubbling"), and ''san'' ( 散, meaning "to break up or scatter", or "medicine in powder form"). Therefore, the word ''mafeisan'' probably means something like "cannabis boil powder". Many sinologists
Sinology, or Chinese studies, is an academic discipline that focuses on the study of China primarily through Chinese philosophy, language, literature, culture and history and often refers to Western scholarship. Its origin "may be traced to the ex ...
and scholars of traditional Chinese medicine
Traditional Chinese medicine (TCM) is an alternative medical practice drawn from traditional medicine in China. It has been described as "fraught with pseudoscience", with the majority of its treatments having no logical mechanism of action ...
have guessed at the composition of Hua Tuo's mafeisan powder, but the exact components still remain unclear. His formula is believed to have contained some combination of:
* ''bai zhi'' (''Chinese
Chinese can refer to:
* Something related to China
* Chinese people, people of Chinese nationality, citizenship, and/or ethnicity
**''Zhonghua minzu'', the supra-ethnic concept of the Chinese nation
** List of ethnic groups in China, people of ...
:白芷'','' Angelica dahurica''),
* ''cao wu'' (''Chinese
Chinese can refer to:
* Something related to China
* Chinese people, people of Chinese nationality, citizenship, and/or ethnicity
**''Zhonghua minzu'', the supra-ethnic concept of the Chinese nation
** List of ethnic groups in China, people of ...
:草烏'', '' Aconitum kusnezoffii'', '' Aconitum kusnezoffii'', Kusnezoff's monkshood, or wolfsbane root),
* ''chuān xiōng'' (''Chinese
Chinese can refer to:
* Something related to China
* Chinese people, people of Chinese nationality, citizenship, and/or ethnicity
**''Zhonghua minzu'', the supra-ethnic concept of the Chinese nation
** List of ethnic groups in China, people of ...
:川芎, Ligusticum wallichii'', or Szechuan lovage),
* ''dong quai'' (''Chinese
Chinese can refer to:
* Something related to China
* Chinese people, people of Chinese nationality, citizenship, and/or ethnicity
**''Zhonghua minzu'', the supra-ethnic concept of the Chinese nation
** List of ethnic groups in China, people of ...
:当归'', ''Angelica sinensis
''Angelica sinensis'', commonly known as ''dong quai'' () or female ginseng, is a herb belonging to the family Apiaceae, indigenous to China. ''Angelica sinensis'' grows in cool high altitude mountains in East Asia. The yellowish brown root of t ...
'', or "female ginseng
Ginseng () is the root of plants in the genus ''Panax'', such as Korean ginseng ('' P. ginseng''), South China ginseng ('' P. notoginseng''), and American ginseng ('' P. quinquefolius''), typically characterized by the presence of ginsenosides an ...
"),
* ''wu tou'' (烏頭, ''Aconitum carmichaelii
''Aconitum carmichaelii'' is a species of flowering plant of the genus ''Aconitum'', family Ranunculaceae. It is native to East Asia and eastern Russia. It is commonly known as Chinese aconite, Carmichael's monkshood or Chinese wolfsbane. In Ma ...
'', rhizome of ''Aconitum'', or "Chinese monkshood"),
* ''yang jin hua'' (洋金花, '' Flos Daturae metelis'', or ''Datura stramonium
''Datura stramonium'', known by the common names thorn apple, jimsonweed (jimson weed), devil's snare, or devil's trumpet, is a poisonous flowering plant of the nightshade family Solanaceae. It is a species belonging to the ''Datura'' genus a ...
'', jimson weed, devil's trumpet, thorn apple, locoweed, moonflower),
* ''ya pu lu'' (押不芦,''Mandragora officinarum
''Mandragora officinarum'' is the type species of the plant genus '' Mandragora'' in the nightshade family Solanaceae. It is often known as mandrake, although this name is also used for other plants. , sources differed significantly in the specie ...
'')
* rhododendron
''Rhododendron'' (; from Ancient Greek ''rhódon'' "rose" and ''déndron'' "tree") is a very large genus of about 1,024 species of woody plants in the heath family (Ericaceae). They can be either evergreen or deciduous. Most species are nati ...
flower, and
* jasmine
Jasmine ( taxonomic name: ''Jasminum''; , ) is a genus of shrubs and vines in the olive family (Oleaceae). It contains around 200 species native to tropical and warm temperate regions of Eurasia, Africa, and Oceania. Jasmines are widely cultiva ...
root.
Others have suggested the potion may have also contained hashish
Hashish ( ar, حشيش, ()), also known as hash, "dry herb, hay" is a drug made by compressing and processing parts of the cannabis plant, typically focusing on flowering buds (female flowers) containing the most trichomes. European Monitorin ...
, bhang
Bhang (IAST: ''Bhāṅg'') is an edible preparation made from the leaves of the cannabis plant originating from the Indian subcontinent. It has been used in food and drink as early as 1000 BC in ancient India. Bhang is traditionally distribu ...
, ''shang-luh'', or opium. Victor H. Mair
Victor Henry Mair (; born March 25, 1943) is an American sinologist. He is a professor of Chinese at the University of Pennsylvania. Among other accomplishments, Mair has edited the standard '' Columbia History of Chinese Literature'' and the ''C ...
wrote that ''mafei'' "appears to be a transcription of some Indo-European
The Indo-European languages are a language family native to the overwhelming majority of Europe, the Iranian plateau, and the northern Indian subcontinent. Some European languages of this family, English, French, Portuguese, Russian, Dutch ...
word related to "morphine"." Some authors believe that Hua Tuo may have discovered surgical analgesia by acupuncture
Acupuncture is a form of alternative medicine and a component of traditional Chinese medicine (TCM) in which thin needles are inserted into the body. Acupuncture is a pseudoscience; the theories and practices of TCM are not based on scientifi ...
, and that mafeisan either had nothing to do with or was simply an adjunct to his strategy for anesthesia. Many physicians have attempted to re-create the same formulation based on historical records but none have achieved the same clinical efficacy as Hua Tuo's. In any event, Hua Tuo's formula did not appear to be effective for major operations.
Other substances used from antiquity for anesthetic purposes include extracts of juniper
Junipers are coniferous trees and shrubs in the genus ''Juniperus'' () of the cypress family Cupressaceae. Depending on the taxonomy, between 50 and 67 species of junipers are widely distributed throughout the Northern Hemisphere, from the Arcti ...
and coca
Coca is any of the four cultivated plants in the family Erythroxylaceae, native to western South America. Coca is known worldwide for its psychoactive alkaloid, cocaine.
The plant is grown as a cash crop in the Argentine Northwest, Bolivia, Al ...
.
Middle Ages and Renaissance
Ferdowsi
Abul-Qâsem Ferdowsi Tusi ( fa, ; 940 – 1019/1025 CE), also Firdawsi or Ferdowsi (), was a Persians, Persian poet and the author of ''Shahnameh'' ("Book of Kings"), which is one of the world's longest epic poetry, epic poems created by a sin ...
(940–1020) was a Persian
Persian may refer to:
* People and things from Iran, historically called ''Persia'' in the English language
** Persians, the majority ethnic group in Iran, not to be conflated with the Iranic peoples
** Persian language, an Iranian language of the ...
poet
A poet is a person who studies and creates poetry. Poets may describe themselves as such or be described as such by others. A poet may simply be the creator ( thinker, songwriter, writer, or author) who creates (composes) poems (oral or writte ...
who lived in the Abbasid Caliphate
The Abbasid Caliphate ( or ; ar, الْخِلَافَةُ الْعَبَّاسِيَّة, ') was the third caliphate to succeed the Islamic prophet Muhammad. It was founded by a dynasty descended from Muhammad's uncle, Abbas ibn Abdul-Muttalib ...
. In ''Shahnameh
The ''Shahnameh'' or ''Shahnama'' ( fa, شاهنامه, Šāhnāme, lit=The Book of Kings, ) is a long epic poem written by the Persian poet Ferdowsi between c. 977 and 1010 CE and is the national epic of Greater Iran. Consisting of some 50,00 ...
'', his national epic
A national epic is an epic poem or a literary work of epic scope which seeks or is believed to capture and express the essence or spirit of a particular nation—not necessarily a nation state, but at least an ethnic or linguistic group with as ...
poem, Ferdowsi described a caesarean section
Caesarean section, also known as C-section or caesarean delivery, is the surgical procedure by which one or more babies are delivered through an incision in the mother's abdomen, often performed because vaginal delivery would put the baby or mo ...
performed on Rudaba
Rudāba or Rudābeh ( fa, رودابه ) is a Persian mythological female figure in Ferdowsi's epic Shahnameh. She is the princess of Kabul, daughter of Mehrab Kaboli and Sindukht, and later she becomes married to Zal, as they become lovers. The ...
. A special wine prepared by a Zoroastrian
Zoroastrianism is an Iranian religion and one of the world's oldest organized faiths, based on the teachings of the Iranian-speaking prophet Zoroaster. It has a dualistic cosmology of good and evil within the framework of a monotheistic on ...
priest was used as an anesthetic for this operation.
c. 1020, Ibn Sīnā
Ibn Sina ( fa, ابن سینا; 980 – June 1037 CE), commonly known in the West as Avicenna (), was a Persian polymath who is regarded as one of the most significant physicians, astronomers, philosophers, and writers of the Islamic ...
(980–1037) in ''The Canon of Medicine
''The Canon of Medicine'' ( ar, القانون في الطب, italic=yes ''al-Qānūn fī al-Ṭibb''; fa, قانون در طب, italic=yes, ''Qanun-e dâr Tâb'') is an encyclopedia of medicine in five books compiled by Persian physician-phi ...
'' described the "soporific sponge", a sponge
Sponges, the members of the phylum Porifera (; meaning 'pore bearer'), are a basal animal clade as a sister of the diploblasts. They are multicellular organisms that have bodies full of pores and channels allowing water to circulate through t ...
imbued with aromatics
Aromatic compounds, also known as "mono- and polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons", are organic compounds containing one or more aromatic rings. The parent member of aromatic compounds is benzene. The word "aromatic" originates from the past groupin ...
and narcotic
The term narcotic (, from ancient Greek ναρκῶ ''narkō'', "to make numb") originally referred medically to any psychoactive compound with numbing or paralyzing properties. In the United States, it has since become associated with opiates ...
s, which was to be placed under a patient's nose during surgical operations. Opium made its way from Asia Minor to all parts of Europe between the 10th and 13th centuries.
Throughout 1200–1500 AD in England, a potion called dwale was used as an anesthetic. This alcohol
Alcohol most commonly refers to:
* Alcohol (chemistry), an organic compound in which a hydroxyl group is bound to a carbon atom
* Alcohol (drug), an intoxicant found in alcoholic drinks
Alcohol may also refer to:
Chemicals
* Ethanol, one of sev ...
-based mixture contained bile
Bile (from Latin ''bilis''), or gall, is a dark-green-to-yellowish-brown fluid produced by the liver of most vertebrates that aids the digestion of lipids in the small intestine. In humans, bile is produced continuously by the liver (liver bile ...
, opium
Opium (or poppy tears, scientific name: ''Lachryma papaveris'') is dried latex obtained from the seed capsules of the opium poppy ''Papaver somniferum''. Approximately 12 percent of opium is made up of the analgesic alkaloid morphine, which i ...
, lettuce
Lettuce (''Lactuca sativa'') is an annual plant of the family Asteraceae. It is most often grown as a leaf vegetable, but sometimes for its stem and seeds. Lettuce is most often used for salads, although it is also seen in other kinds of food, ...
, bryony, henbane
''Hyoscyamus niger'', commonly known as henbane, black henbane, or stinking nightshade, is a poisonous plant in the nightshade family Solanaceae. It is native to temperate Europe and Siberia, and naturalised in Great Britain and Ireland.
...
, hemlock and vinegar
Vinegar is an aqueous solution of acetic acid and trace compounds that may include flavorings. Vinegar typically contains 5–8% acetic acid by volume. Usually, the acetic acid is produced by a double fermentation, converting simple sugars to et ...
. Surgeons roused them by rubbing vinegar and salt on their cheekbones. One can find records of dwale in numerous literary sources, including Shakespeare's
William Shakespeare ( 26 April 1564 – 23 April 1616) was an English playwright, poet and actor. He is widely regarded as the greatest writer in the English language and the world's pre-eminent dramatist. He is often called England's nation ...
''Hamlet
''The Tragedy of Hamlet, Prince of Denmark'', often shortened to ''Hamlet'' (), is a tragedy written by William Shakespeare sometime between 1599 and 1601. It is Shakespeare's longest play, with 29,551 words. Set in Denmark, the play depicts ...
'', and the John Keats
John Keats (31 October 1795 – 23 February 1821) was an English poet of the second generation of Romantic poets, with Lord Byron and Percy Bysshe Shelley. His poems had been in publication for less than four years when he died of tuberculo ...
poem "Ode to a Nightingale
"Ode to a Nightingale" is a poem by John Keats written either in the garden of the Spaniards Inn, Hampstead, London or, according to Keats' friend Charles Armitage Brown, under a plum tree in the garden of Keats' house at Wentworth Place, also ...
". In the 13th century, we have the first prescription of the "spongia soporifica"—a sponge soaked in the juices of unripe mulberry, flax, mandragora leaves, ivy, lettuce seeds, lapathum, and hemlock with hyoscyamus. After treatment and/or storage, the sponge could be heated and the vapors inhaled with anesthetic effect.
Alchemist
Alchemy (from Arabic: ''al-kīmiyā''; from Ancient Greek: χυμεία, ''khumeía'') is an ancient branch of natural philosophy, a philosophical and protoscience, protoscientific tradition that was historically practiced in Chinese alchemy, C ...
Ramon Llull
Ramon Llull (; c. 1232 – c. 1315/16) was a philosopher, theologian, poet, missionary, and Christian apologist from the Kingdom of Majorca.
He invented a philosophical system known as the ''Art'', conceived as a type of universal logic to pro ...
has been credited with discovering diethyl ether
Diethyl ether, or simply ether, is an organic compound in the ether class with the formula , sometimes abbreviated as (see Pseudoelement symbols). It is a colourless, highly volatile, sweet-smelling ("ethereal odour"), extremely flammable liq ...
in 1275. Aureolus Theophrastus Bombastus von Hohenheim (1493–1541), better known as Paracelsus
Paracelsus (; ; 1493 – 24 September 1541), born Theophrastus von Hohenheim (full name Philippus Aureolus Theophrastus Bombastus von Hohenheim), was a Swiss physician, alchemist, lay theologian, and philosopher of the German Renaissance.
He w ...
, discovered the analgesic
An analgesic drug, also called simply an analgesic (American English), analgaesic (British English), pain reliever, or painkiller, is any member of the group of drugs used to achieve relief from pain (that is, analgesia or pain management). It ...
properties of diethyl ether around 1525. It was first synthesized in 1540 by Valerius Cordus
Valerius Cordus (18 February 1515 – 25 September 1544) was a German physician, botanist and pharmacologist who authored the first pharmacopoeia North of the Alps and one of the most celebrated herbals in history. He is also widely credited wit ...
, who noted some of its medicinal properties. He called it ''oleum dulce vitrioli'', a name that reflects the fact that it is synthesized by distilling a mixture of ethanol and sulfuric acid
Sulfuric acid (American spelling and the preferred IUPAC name) or sulphuric acid ( Commonwealth spelling), known in antiquity as oil of vitriol, is a mineral acid composed of the elements sulfur, oxygen and hydrogen, with the molecular formu ...
(known at that time as oil of vitriol). August Sigmund Frobenius gave the name ''Spiritus Vini Æthereus'' to the substance in 1730.
18th century

Joseph Priestley
Joseph Priestley (; 24 March 1733 – 6 February 1804) was an English chemist, natural philosopher, separatist theologian, grammarian, multi-subject educator, and liberal political theorist. He published over 150 works, and conducted exp ...
(1733–1804) was an English polymath
A polymath ( el, πολυμαθής, , "having learned much"; la, homo universalis, "universal human") is an individual whose knowledge spans a substantial number of subjects, known to draw on complex bodies of knowledge to solve specific pro ...
who discovered nitrous oxide
Nitrous oxide (dinitrogen oxide or dinitrogen monoxide), commonly known as laughing gas, nitrous, or nos, is a chemical compound, an oxide of nitrogen with the formula . At room temperature, it is a colourless non-flammable gas, and has a ...
, nitric oxide
Nitric oxide (nitrogen oxide or nitrogen monoxide) is a colorless gas with the formula . It is one of the principal oxides of nitrogen. Nitric oxide is a free radical: it has an unpaired electron, which is sometimes denoted by a dot in its che ...
, ammonia
Ammonia is an inorganic compound of nitrogen and hydrogen with the formula . A stable binary hydride, and the simplest pnictogen hydride, ammonia is a colourless gas with a distinct pungent smell. Biologically, it is a common nitrogenous was ...
, hydrogen chloride
The compound hydrogen chloride has the chemical formula and as such is a hydrogen halide. At room temperature, it is a colourless gas, which forms white fumes of hydrochloric acid upon contact with atmospheric water vapor. Hydrogen chloride ga ...
and (along with Carl Wilhelm Scheele
Carl Wilhelm Scheele (, ; 9 December 1742 – 21 May 1786) was a Swedish German pharmaceutical chemist.
Scheele discovered oxygen (although Joseph Priestley published his findings first), and identified molybdenum, tungsten, barium, hydrog ...
and Antoine Lavoisier
Antoine-Laurent de Lavoisier ( , ; ; 26 August 17438 May 1794), When reduced without charcoal, it gave off an air which supported respiration and combustion in an enhanced way. He concluded that this was just a pure form of common air and th ...
) oxygen
Oxygen is the chemical element with the symbol O and atomic number 8. It is a member of the chalcogen group in the periodic table, a highly reactive nonmetal, and an oxidizing agent that readily forms oxides with most elements as wel ...
. Beginning in 1775, Priestley published his research in ''Experiments and Observations on Different Kinds of Air
''Experiments and Observations on Different Kinds of Air'' (1774–86) is a six-volume work published by 18th-century British polymath Joseph Priestley which reports a series of his experiments on "airs" or gases, most notably his discovery of ...
'', a six-volume work. The recent discoveries about these and other gas
Gas is one of the four fundamental states of matter (the others being solid, liquid, and plasma).
A pure gas may be made up of individual atoms (e.g. a noble gas like neon), elemental molecules made from one type of atom (e.g. oxygen), or ...
es stimulated a great deal of interest in the European scientific community. Thomas Beddoes
Thomas Beddoes (13 April 176024 December 1808) was an English physician and scientific writer. He was born in Shifnal, Shropshire and died in Bristol fifteen years after opening his medical practice there. He was a reforming practitioner and t ...
(1760–1808) was an English philosopher
A philosopher is a person who practices or investigates philosophy. The term ''philosopher'' comes from the grc, φιλόσοφος, , translit=philosophos, meaning 'lover of wisdom'. The coining of the term has been attributed to the Greek th ...
, physician and teacher of medicine, and like his older colleague Priestley, was also a member of the Lunar Society of Birmingham
The Lunar Society of Birmingham was a British dinner club and informal learned society of prominent figures in the Midlands Enlightenment, including industrialists, natural philosophers and intellectuals, who met regularly between 1765 and 1813 ...
. With an eye toward making further advances in this new science as well as offering treatment for diseases previously thought to be untreatable (such as asthma
Asthma is a long-term inflammatory disease of the airways of the lungs. It is characterized by variable and recurring symptoms, reversible airflow obstruction, and easily triggered bronchospasms. Symptoms include episodes of wheezing, cou ...
and tuberculosis
Tuberculosis (TB) is an infectious disease usually caused by '' Mycobacterium tuberculosis'' (MTB) bacteria. Tuberculosis generally affects the lungs, but it can also affect other parts of the body. Most infections show no symptoms, in ...
), Beddoes founded the ''Pneumatic Institution
The Pneumatic Institution (also referred to as Pneumatic Institute) was a medical research facility in Bristol, England, in 1799–1802. It was established by physician and science writer Thomas Beddoes to study the medical effects of gases, know ...
'' for inhalation gas therapy in 1798 at Dowry Square
Dowry Square is in the Hotwells area of Bristol.
It was laid out in 1727 by George Tully and building continued until 1750. The houses are three-storeyed with attics, simply detailed and with channelled pilasters to the party walls.
In 1799 Dr ...
in Clifton, Bristol
Clifton is both a suburb of Bristol, England, and the name of one of the city's thirty-five council wards. The Clifton ward also includes the areas of Cliftonwood and Hotwells. The eastern part of the suburb lies within the ward of Clifton Do ...
. Beddoes employed chemist
A chemist (from Greek ''chēm(ía)'' alchemy; replacing ''chymist'' from Medieval Latin ''alchemist'') is a scientist trained in the study of chemistry. Chemists study the composition of matter and its properties. Chemists carefully describe th ...
and physicist Humphry Davy
Sir Humphry Davy, 1st Baronet, (17 December 177829 May 1829) was a British chemist and inventor who invented the Davy lamp and a very early form of arc lamp. He is also remembered for isolating, by using electricity, several elements for t ...
(1778–1829) as superintendent of the institute, and engineer
Engineers, as practitioners of engineering, are professionals who invent, design, analyze, build and test machines, complex systems, structures, gadgets and materials to fulfill functional objectives and requirements while considering the l ...
James Watt
James Watt (; 30 January 1736 (19 January 1736 OS) – 25 August 1819) was a Scottish inventor, mechanical engineer, and chemist who improved on Thomas Newcomen's 1712 Newcomen steam engine with his Watt steam engine in 1776, which was fun ...
(1736–1819) to help manufacture the gases. Other members of the Lunar Society such as Erasmus Darwin
Erasmus Robert Darwin (12 December 173118 April 1802) was an English physician. One of the key thinkers of the Midlands Enlightenment, he was also a natural philosopher, physiologist, slave-trade abolitionist, inventor, and poet.
His poems ...
and Josiah Wedgwood
Josiah Wedgwood (12 July 1730 – 3 January 1795) was an English potter, entrepreneur and abolitionist. Founding the Wedgwood company in 1759, he developed improved pottery bodies by systematic experimentation, and was the leader in the indust ...
were also actively involved with the institute.
During the course of his research at the Pneumatic Institution, Davy discovered the anesthetic properties of nitrous oxide. Davy, who coined the term "laughing gas" for nitrous oxide, published his findings the following year in the now-classic treatise
A treatise is a formal and systematic written discourse on some subject, generally longer and treating it in greater depth than an essay, and more concerned with investigating or exposing the principles of the subject and its conclusions."Treat ...
, ''Researches, chemical and philosophical–chiefly concerning nitrous oxide or dephlogisticated nitrous air, and its respiration''. Davy was not a physician, and he never administered nitrous oxide during a surgical procedure. He was, however, the first to document the analgesic effects of nitrous oxide, as well as its potential benefits in relieving pain during surgery:
19th century
Eastern hemisphere
Takamine Tokumei
was an Okinawan interpreter (Chinese-Okinawan). He was ordered to learn harelip surgery and successfully performed the surgery for the grandson of King Shō Tei, Shō Eki, under general anesthesia.
It was standard at the time for members of Ry ...
from Shuri, Ryūkyū Kingdom
The Ryukyu Kingdom, Middle Chinese: , , Classical Chinese: (), Historical English language, English names: ''Lew Chew'', ''Lewchew'', ''Luchu'', and ''Loochoo'', Historical French name: ''Liou-tchou'', Historical Dutch name: ''Lioe-kioe'' wa ...
, is reported to have made a general anesthesia in 1689 in the Ryukyus, now known as Okinawa. He passed on his knowledge to the Satsuma Satsuma may refer to:
* Satsuma (fruit), a citrus fruit
* ''Satsuma'' (gastropod), a genus of land snails
Places Japan
* Satsuma, Kagoshima, a Japanese town
* Satsuma District, Kagoshima, a district in Kagoshima Prefecture
* Satsuma Domain, a sou ...
doctors in 1690 and to Ryūkyūan doctors in 1714.

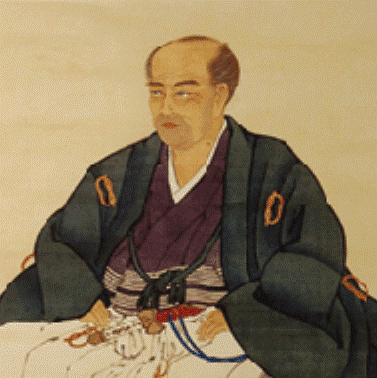
Hanaoka Seishū
was a Japanese surgeon of the Edo period with a knowledge of Chinese herbal medicine, as well as Western surgical techniques he had learned through ''Rangaku'' (literally "Dutch learning", and by extension "Western learning"). Hanaoka is said t ...
(華岡 青洲, 1760–1835) of Osaka
is a designated city in the Kansai region of Honshu in Japan. It is the capital of and most populous city in Osaka Prefecture, and the third most populous city in Japan, following Special wards of Tokyo and Yokohama. With a population of 2. ...
was a Japanese surgeon of the Edo period
The or is the period between 1603 and 1867 in the history of Japan, when Japan was under the rule of the Tokugawa shogunate and the country's 300 regional '' daimyo''. Emerging from the chaos of the Sengoku period, the Edo period was characteriz ...
with a knowledge of Chinese herbal medicine, as well as Western surgical techniques he had learned through ''Rangaku
''Rangaku'' (Kyūjitai: /Shinjitai: , literally "Dutch learning", and by extension "Western learning") is a body of knowledge developed by Japan through its contacts with the Dutch enclave of Dejima, which allowed Japan to keep abreast of Wester ...
'' (literally "Dutch learning", and by extension "Western learning"). Beginning in about 1785, Hanaoka embarked on a quest to re-create a compound that would have pharmacologic properties similar to Hua Tuo's mafeisan. After years of research and experimentation, he finally developed a formula which he named ''tsūsensan'' (also known as ''mafutsu-san''). Like that of Hua Tuo, this compound was composed of extracts of several different plants, including:
* 2 parts ''bai zhi'' (''Chinese
Chinese can refer to:
* Something related to China
* Chinese people, people of Chinese nationality, citizenship, and/or ethnicity
**''Zhonghua minzu'', the supra-ethnic concept of the Chinese nation
** List of ethnic groups in China, people of ...
:白芷'',''Angelica dahurica'');
* 2 parts ''cao wu'' (''Chinese
Chinese can refer to:
* Something related to China
* Chinese people, people of Chinese nationality, citizenship, and/or ethnicity
**''Zhonghua minzu'', the supra-ethnic concept of the Chinese nation
** List of ethnic groups in China, people of ...
:草烏'',''Aconitum sp.'', ''monkshood'' or ''wolfsbane'');
* 2 parts ''chuān ban xia'' (''Pinellia ternata
''Pinellia ternata'' (, ja, カラスビシャク), crow-dipper, is a plant that is native to China, Japan, and Korea. However, it also grows as an invasive weed in parts of Europe (Austria, Germany) and in North America (California, Ontario, t ...
'');
* 2 parts ''chuān xiōng'' (''Ligusticum wallichii'', ''Cnidium rhizome'', ''Cnidium officinale'' or ''Szechuan lovage'');
* 2 parts ''dong quai'' (''Angelica sinensis'' or ''female ginseng
Ginseng () is the root of plants in the genus ''Panax'', such as Korean ginseng ('' P. ginseng''), South China ginseng ('' P. notoginseng''), and American ginseng ('' P. quinquefolius''), typically characterized by the presence of ginsenosides an ...
'');
* 1 part ''tian nan xing'' ('' Arisaema rhizomatum'' or ''cobra lily'')
* 8 parts ''yang jin hua'' (''Datura stramonium'', ''Korean morning glory'', ''thorn apple'', ''jimson weed'', ''devil's trumpet'', ''stinkweed'', or ''locoweed'').
The active ingredients in tsūsensan are scopolamine, hyoscyamine, atropine
Atropine is a tropane alkaloid and anticholinergic medication used to treat certain types of nerve agent and pesticide poisonings as well as some types of slow heart rate, and to decrease saliva production during surgery. It is typically given i ...
, aconitine
Aconitine is an alkaloid toxin produced by various plant species belonging to the genus ''Aconitum'' (family Ranunculaceae), known also commonly by the names wolfsbane and monkshood. Monkshood is notorious for its toxic properties. Aconitine is ...
and angelicotoxin. When consumed in sufficient quantity, tsūsensan produces a state of general anesthesia and skeletal muscle
Skeletal muscles (commonly referred to as muscles) are organs of the vertebrate muscular system and typically are attached by tendons to bones of a skeleton. The muscle cells of skeletal muscles are much longer than in the other types of muscl ...
paralysis
Paralysis (also known as plegia) is a loss of motor function in one or more muscles. Paralysis can also be accompanied by a loss of feeling (sensory loss) in the affected area if there is sensory damage. In the United States, roughly 1 in 50 ...
. Shutei Nakagawa (1773–1850), a close friend of Hanaoka, wrote a small pamphlet titled "Mayaku-ko" ("narcotic powder") in 1796. Although the original manuscript was lost in a fire in 1867, this brochure described the current state of Hanaoka's research on general anesthesia.
On 13 October 1804, Hanaoka performed a partial mastectomy
Mastectomy is the medical term for the surgical removal of one or both breasts, partially or completely. A mastectomy is usually carried out to treat breast cancer. In some cases, women believed to be at high risk of breast cancer have the operat ...
for breast cancer
Breast cancer is cancer that develops from breast tissue. Signs of breast cancer may include a lump in the breast, a change in breast shape, dimpling of the skin, milk rejection, fluid coming from the nipple, a newly inverted nipple, or a re ...
on a 60-year-old woman named Kan Aiya, using tsūsensan as a general anesthetic
General anaesthetics (or anesthetics, see spelling differences) are often defined as compounds that induce a loss of consciousness in humans or loss of righting reflex in animals. Clinical definitions are also extended to include an induced coma ...
. This is generally regarded today as the first reliable documentation of an operation to be performed under general anesthesia. Hanaoka went on to perform many operations using tsūsensan, including resection of malignant
Malignancy () is the tendency of a medical condition to become progressively worse.
Malignancy is most familiar as a characterization of cancer. A ''malignant'' tumor contrasts with a non-cancerous ''benign'' tumor in that a malignancy is not s ...
tumor
A neoplasm () is a type of abnormal and excessive growth of tissue. The process that occurs to form or produce a neoplasm is called neoplasia. The growth of a neoplasm is uncoordinated with that of the normal surrounding tissue, and persists ...
s, extraction of bladder stones, and extremity amputation
Amputation is the removal of a limb by trauma, medical illness, or surgery. As a surgical measure, it is used to control pain or a disease process in the affected limb, such as malignancy or gangrene. In some cases, it is carried out on indi ...
s. Before his death in 1835, Hanaoka performed more than 150 operations for breast cancer.
Western hemisphere




Friedrich Sertürner
Friedrich Wilhelm Adam Sertürner (19 June 1783 – 20 February 1841) was a German pharmacist and a pioneer of alkaloid chemistry. He is best known for his discovery of morphine in 1804.
Biography
Friedrich Wilhelm Adam Sertürner was born to J ...
(1783–1841) first isolated morphine
Morphine is a strong opiate that is found naturally in opium, a dark brown resin in poppies (''Papaver somniferum''). It is mainly used as a analgesic, pain medication, and is also commonly used recreational drug, recreationally, or to make ...
from opium
Opium (or poppy tears, scientific name: ''Lachryma papaveris'') is dried latex obtained from the seed capsules of the opium poppy ''Papaver somniferum''. Approximately 12 percent of opium is made up of the analgesic alkaloid morphine, which i ...
in 1804; he named it morphine after Morpheus
Morpheus ('Fashioner', derived from the grc, μορφή meaning 'form, shape') is a god associated with sleep and dreams. In Ovid's ''Metamorphoses'' he is the son of Somnus and appears in dreams in human form. From the Middle Ages, the name b ...
, the Greek god of dreams.
Henry Hill Hickman
Henry Hill Hickman (27 January 1800 – 2 April 1830) was an English physician and promoter of anaesthesia.
Life
He was born to tenant farmers at Lady Halton, (near Bromfield, just outside Ludlow, Shropshire). He was the fifth of thirteen c ...
(1800–1830) experimented with the use of carbon dioxide
Carbon dioxide (chemical formula ) is a chemical compound made up of molecules that each have one carbon atom covalently double bonded to two oxygen atoms. It is found in the gas state at room temperature. In the air, carbon dioxide is transpar ...
as an anesthetic in the 1820s. He would make the animal insensible, effectively via almost suffocating it with carbon dioxide, then determine the effects of the gas by amputating one of its limbs. In 1824, Hickman submitted the results of his research to the Royal Society
The Royal Society, formally The Royal Society of London for Improving Natural Knowledge, is a learned society and the United Kingdom's national academy of sciences. The society fulfils a number of roles: promoting science and its benefits, re ...
in a short treatise titled ''Letter on suspended animation: with the view of ascertaining its probable utility in surgical operations on human subjects''. The response was an 1826 article in ''The Lancet
''The Lancet'' is a weekly peer-reviewed general medical journal and one of the oldest of its kind. It is also the world's highest-impact academic journal. It was founded in England in 1823.
The journal publishes original research articles, ...
'' titled "Surgical Humbug" that ruthlessly criticised his work. Hickman died four years later at age 30. Though he was unappreciated at the time of his death, his work has since been positively reappraised and he is now recognised as one of the fathers of anesthesia.
By the late 1830s, Humphry Davy's experiments had become widely publicized within academic circles in the northeastern United States. Wandering lecturers would hold public gatherings, referred to as "ether frolics", where members of the audience were encouraged to inhale diethyl ether or nitrous oxide to demonstrate the mind-altering properties of these agents while providing much entertainment to onlookers. Four notable men participated in these events and witnessed the use of ether in this manner. They were William Edward Clarke (1819–1898), Crawford W. Long (1815–1878), Horace Wells
Horace Wells (January 21, 1815 – January 24, 1848) was an American dentist who pioneered the use of anesthesia in dentistry, specifically the use of nitrous oxide (or laughing gas).
Early life
Wells was the first of three children of H ...
(1815–1848), and William T. G. Morton
William Thomas Green Morton (August 9, 1819 – July 15, 1868) was an American dentist and physician who first publicly demonstrated the use of inhaled ether as a surgical anesthetic in 1846. The promotion of his questionable claim to have been th ...
(1819–1868).
While attending undergraduate school in Rochester, New York, in 1839, classmates Clarke and Morton apparently participated in ether frolics with some regularity. In January 1842, by now a medical student at Berkshire Medical College
Berkshire Medical College (originally the Berkshire Medical Institution, and sometimes referred to as Berkshire Medical College) was a medical school in Pittsfield, Massachusetts. It is notable for establishing the first professorship in mental d ...
, Clarke administered ether to a Miss Hobbie, while Elijah Pope performed a dental extraction
A dental extraction (also referred to as tooth extraction, exodontia, exodontics, or informally, tooth pulling) is the removal of teeth from the dental alveolus (socket) in the alveolar bone. Extractions are performed for a wide variety of reason ...
. In so doing, he became the first to administer an inhaled anesthetic to facilitate the performance of a surgical procedure. Clarke apparently thought little of his accomplishment, and chose neither to publish nor to pursue this technique any further. Indeed, this event is not even mentioned in Clarke's biography.
Crawford W. Long was a physician and pharmacist practicing in Jefferson, Georgia
Jefferson is a city in Jackson County, Georgia, United States. The population was 9,432 at the 2010 census, up from 3,825 at the 2000 census. As of 2019 the estimated population was 12,032. The city is the county seat of Jackson County.
History ...
in the mid-19th century. During his time as a student at the University of Pennsylvania School of Medicine
The Perelman School of Medicine, commonly known as Penn Med, is the medical school of the University of Pennsylvania, a private research university in Philadelphia, Pennsylvania. Founded in 1765, the Perelman School of Medicine is the oldest medi ...
in the late 1830s, he had observed and probably participated in the ether frolics that had become popular at that time. At these gatherings, Long observed that some participants experienced bumps and bruises, but afterward had no recall of what had happened. He postulated that diethyl ether produced pharmacologic effects similar to those of nitrous oxide. On 30 March 1842, he administered diethyl ether by inhalation to a man named James Venable, in order to remove a tumor from the man's neck. Long later removed a second tumor from Venable, again under ether anesthesia. He went on to employ ether as a general anesthetic for limb amputations and parturition
Birth is the act or process of bearing or bringing forth offspring, also referred to in technical contexts as parturition. In mammals, the process is initiated by hormones which cause the muscular walls of the uterus to contract, expelling the f ...
. Long, however, did not publish his experience until 1849, thereby denying himself much of the credit he deserved.
With the beginnings of modern medicine the stage was set for physicians and surgeons to build a paradigm in which anesthesia became useful.
On 10 December 1844, Gardner Quincy Colton
Gardner Quincy Colton (February 7, 1814, Georgia, Vermont – August 10, 1898, Geneva, Switzerland) was an American showman, medicine man, lecturer, and former medical student who pioneered the use of nitrous oxide, or laughing gas, in dentistr ...
held a public demonstration of nitrous oxide in Hartford, Connecticut. One of the participants, Samuel A. Cooley, sustained a significant injury to his leg while under the influence of nitrous oxide without noticing the injury. Horace Wells, a Connecticut dentist present in the audience that day, immediately seized upon the significance of this apparent analgesic effect of nitrous oxide. The following day, Wells underwent a painless dental extraction while under the influence of nitrous oxide administered by Colton. Wells then began to administer nitrous oxide to his patients, successfully performing several dental extractions over the next couple of weeks.
William T. G. Morton, another New England
New England is a region comprising six states in the Northeastern United States: Connecticut, Maine, Massachusetts, New Hampshire, Rhode Island, and Vermont. It is bordered by the state of New York to the west and by the Canadian provinces ...
dentist, was a former student and then-current business partner of Wells. He was also a former acquaintance and classmate of William Edward Clarke (the two had attended undergraduate school together in Rochester, New York). Morton arranged for Wells to demonstrate his technique for dental extraction under nitrous oxide general anesthesia at Massachusetts General Hospital
Massachusetts General Hospital (Mass General or MGH) is the original and largest teaching hospital of Harvard Medical School located in the West End neighborhood of Boston, Massachusetts. It is the third oldest general hospital in the United Stat ...
, in conjunction with the prominent surgeon John Collins Warren
John Collins Warren (August 1, 1778 – May 4, 1856) was an American surgeon. In 1846 he gave permission to William T.G. Morton to provide ether anesthesia while Warren performed a minor surgical procedure. News of this first public demonstrat ...
. This demonstration, which took place on 20 January 1845, ended in failure when the patient cried out in pain in the middle of the operation.
On 30 September 1846, Morton administered diethyl ether to Eben Frost, a music teacher from Boston
Boston (), officially the City of Boston, is the state capital and most populous city of the Commonwealth of Massachusetts, as well as the cultural and financial center of the New England region of the United States. It is the 24th- mo ...
, for a dental extraction. Two weeks later, Morton became the first to publicly demonstrate the use of diethyl ether as a general anesthetic at Massachusetts General Hospital, in what is known today as the Ether Dome
The Ether Dome is a surgical operating amphitheater in the Bulfinch Building at Massachusetts General Hospital in Boston. It served as the hospital's operating room from its opening in 1821 until 1867. It was the site of the first public demonstr ...
. On 16 October 1846, John Collins Warren removed a tumor from the neck of a local printer, Edward Gilbert Abbott
Edward Gilbert Abbott (1825–1855) was the patient upon whom William T. G. Morton first publicly demonstrated the use of ether as a surgical anesthetic. The operation was done in an amphitheater at the Massachusetts General Hospital now known a ...
. Upon completion of the procedure, Warren reportedly quipped, "Gentlemen, this is no humbug." News of this event rapidly traveled around the world. Robert Liston
Robert Liston (28 October 1794 – 7 December 1847) was a British surgeon. Liston was noted for his speed and skill in an era prior to anaesthetics, when speed made a difference in terms of pain and survival. He was the first Professor of Cli ...
performed the first amputation in December of that year. Morton published his experience soon after. Harvard University
Harvard University is a private Ivy League research university in Cambridge, Massachusetts. Founded in 1636 as Harvard College and named for its first benefactor, the Puritan clergyman John Harvard, it is the oldest institution of higher le ...
professor Charles Thomas Jackson
Charles Thomas Jackson (June 21, 1805 – August 28, 1880) was an American physician and scientist who was active in medicine, chemistry, mineralogy, and geology.
Life and work
Born at Plymouth, Massachusetts, of a prominent New England fami ...
(1805–1880) later claimed that Morton stole his idea; Morton disagreed and a lifelong dispute began. For many years, Morton was credited as being the pioneer of general anesthesia in the Western hemisphere, despite the fact that his demonstration occurred four years after Long's initial experience. Long later petitioned William Crosby Dawson
William Crosby Dawson (January 4, 1798May 5, 1856) was a lawyer, judge, politician, and soldier from Georgia.
Early life, education and legal career
Dawson was born in Greensboro, Greene County, Georgia, January 4, 1798. His parents were Geo ...
(1798–1856), a United States Senator from Georgia at that time, to support his claim on the floor of the United States Senate
The United States Senate is the upper chamber of the United States Congress, with the House of Representatives being the lower chamber. Together they compose the national bicameral legislature of the United States.
The composition and pow ...
as the first to use ether anesthesia.
In 1847, Scottish obstetrician
Obstetrics is the field of study concentrated on pregnancy, childbirth and the postpartum period. As a medical specialty, obstetrics is combined with gynecology under the discipline known as obstetrics and gynecology (OB/GYN), which is a surgi ...
James Young Simpson
Sir James Young Simpson, 1st Baronet, (7 June 1811 – 6 May 1870) was a Scottish obstetrician and a significant figure in the history of medicine. He was the first physician to demonstrate the anesthetic, anaesthetic properties of chloroform ...
(1811–1870) of Edinburgh
Edinburgh ( ; gd, Dùn Èideann ) is the capital city of Scotland and one of its 32 Council areas of Scotland, council areas. Historically part of the county of Midlothian (interchangeably Edinburghshire before 1921), it is located in Lothian ...
was the first to use chloroform
Chloroform, or trichloromethane, is an organic compound with chemical formula, formula Carbon, CHydrogen, HChlorine, Cl3 and a common organic solvent. It is a colorless, strong-smelling, dense liquid produced on a large scale as a precursor to ...
as a general anesthetic on a human (Robert Mortimer Glover
Dr Robert Mortimer Glover FRSE (1815-1859) was an English physician. In 1838 he co-founded the Paris Medical Society and served as its first Vice President. He won the Medical Society of London’s Fothergill Gold Medal in 1846 for his lecture ...
had written on this possibility in 1842 but only used it on dogs). The use of chloroform anesthesia expanded rapidly thereafter in Europe. Chloroform began to replace ether as an anesthetic in the United States at the beginning of the 20th century. It was soon abandoned in favor of ether when its hepatic
The liver is a major organ only found in vertebrates which performs many essential biological functions such as detoxification of the organism, and the synthesis of proteins and biochemicals necessary for digestion and growth. In humans, it i ...
and cardiac
The heart is a muscular organ in most animals. This organ pumps blood through the blood vessels of the circulatory system. The pumped blood carries oxygen and nutrients to the body, while carrying metabolic waste such as carbon dioxide to t ...
toxicity
Toxicity is the degree to which a chemical substance or a particular mixture of substances can damage an organism. Toxicity can refer to the effect on a whole organism, such as an animal, bacterium, or plant, as well as the effect on a subst ...
, especially its tendency to cause potentially fatal cardiac dysrhythmia
Arrhythmias, also known as cardiac arrhythmias, heart arrhythmias, or dysrhythmias, are irregularities in the heartbeat, including when it is too fast or too slow. A resting heart rate that is too fast – above 100 beats per minute in adults ...
s, became apparent. In fact, the use of chloroform versus ether as the primary anesthetic gas varied by country and region. For instance, Britain and the American South stuck with chloroform while the American North returned to ether. John Snow
John Snow (15 March 1813 – 16 June 1858) was an English physician and a leader in the development of anaesthesia and medical hygiene. He is considered one of the founders of modern epidemiology, in part because of his work in tracing the so ...
quickly became the most experienced British physician working with the new anesthetic gases of ether and chloroform thus becoming, in effect, the first British anesthetist. Through his careful clinical records he was eventually able to convince the elite of London medicine that anesthesia (chloroform) had a rightful place in childbirth. Thus, in 1853 Queen Victoria's accoucheurs invited John Snow to anesthetize the Queen for the birth of her eighth child. From the beginnings of ether and chloroform anesthesia until well into the 20th century, the standard method of administration was the drop mask. A mask was placed over the patient's mouth with some fabric in it and the volatile liquid was dropped onto the mask with the patient spontaneously breathing. Later development of safe endotracheal tubes changed this. Because of the unique social setting of London medicine, anesthesia had become its own speciality there by the end of the nineteenth century, while in the rest of the United Kingdom and most of the world anesthesia remained under the purview of the surgeon who would assign the task to a junior doctor or nurse.
After Austrian diplomat Karl von Scherzer
Karl Ritter von Scherzer (sometimes written Carl; 1 May 1821 in Vienna – 19 February 1903 in Görz) was an Austrian explorer, diplomat and natural scientist.
Biography
He began his working life as a printer. After inheriting a fortune, Scher ...
brought back sufficient quantities of coca leaves from Peru, in 1860 Albert Niemann isolated cocaine, which thus became the first local anesthetic.
In 1871, the German surgeon Friedrich Trendelenburg
Friedrich Trendelenburg (; 24 May 184415 December 1924) was a German surgeon. He was son of the philosophy, philosopher Friedrich Adolf Trendelenburg, father of the pharmacology, pharmacologist Paul Trendelenburg and grandfather of the pharmaco ...
(1844–1924) published a paper describing the first successful elective human tracheotomy
Tracheotomy (, ), or tracheostomy, is a surgical airway management procedure which consists of making an incision (cut) on the anterior aspect (front) of the neck and opening a direct airway through an incision in the trachea (windpipe). The ...
to be performed for the purpose of administration of general anesthesia.
In 1880, the Scottish surgeon William Macewen
Sir William Macewen, (; 22 June 1848 – 22 March 1924) was a Scottish surgeon. He was a pioneer in modern brain surgery, considered the ''father of neurosurgery'' and contributed to the development of bone graft surgery, the surgical treat ...
(1848–1924) reported on his use of orotracheal intubation as an alternative to tracheotomy to allow a patient with glottic edema to breathe, as well as in the setting of general anesthesia with chloroform
Chloroform, or trichloromethane, is an organic compound with chemical formula, formula Carbon, CHydrogen, HChlorine, Cl3 and a common organic solvent. It is a colorless, strong-smelling, dense liquid produced on a large scale as a precursor to ...
. All previous observations of the glottis and larynx (including those of Manuel García, Wilhelm Hack and Macewen) had been performed under indirect vision (using mirrors) until 23 April 1895, when Alfred Kirstein
Alfred may refer to:
Arts and entertainment
*''Alfred J. Kwak'', Dutch-German-Japanese anime television series
* ''Alfred'' (Arne opera), a 1740 masque by Thomas Arne
* ''Alfred'' (Dvořák), an 1870 opera by Antonín Dvořák
*"Alfred (Interlu ...
(1863–1922) of Germany first described direct visualization of the vocal cords. Kirstein performed the first direct laryngoscopy in Berlin, using an esophagoscope he had modified for this purpose; he called this device an ''autoscope''. The death of Emperor Frederick III (1831–1888) may have motivated Kirstein to develop the autoscope.
20th century
 The 20th century saw the transformation of the practices of tracheotomy,
The 20th century saw the transformation of the practices of tracheotomy, endoscopy
An endoscopy is a procedure used in medicine to look inside the body. The endoscopy procedure uses an endoscope to examine the interior of a hollow organ or cavity of the body. Unlike many other medical imaging techniques, endoscopes are insert ...
and non-surgical tracheal intubation from rarely employed procedures to essential components of the practices of anesthesia, critical care medicine
Intensive care medicine, also called critical care medicine, is a medical specialty that deals with seriously or critically ill patients who have, are at risk of, or are recovering from conditions that may be life-threatening. It includes pro ...
, emergency medicine
Emergency medicine is the medical speciality concerned with the care of illnesses or injuries requiring immediate medical attention. Emergency physicians (often called “ER doctors” in the United States) continuously learn to care for unsche ...
, gastroenterology
Gastroenterology (from the Greek gastḗr- “belly”, -énteron “intestine”, and -logía "study of") is the branch of medicine focused on the digestive system and its disorders. The digestive system consists of the gastrointestinal tract ...
, pulmonology and surgery.
In 1902, Hermann Emil Fischer
Hermann Emil Louis Fischer (; 9 October 1852 – 15 July 1919) was a German chemist and 1902 recipient of the Nobel Prize in Chemistry. He discovered the Fischer esterification. He also developed the Fischer projection, a symbolic way of dra ...
(1852–1919) and Joseph von Mering (1849–1908) discovered that diethylbarbituric acid
Barbital (or barbitone), marketed under the brand names Veronal for the pure acid and Medinal for the sodium salt, was the first commercially available barbiturate. It was used as a sleeping aid ( hypnotic) from 1903 until the mid-1950s. The chem ...
was an effective hypnotic
Hypnotic (from Greek ''Hypnos'', sleep), or soporific drugs, commonly known as sleeping pills, are a class of (and umbrella term for) psychoactive drugs whose primary function is to induce sleep (or surgical anesthesiaWhen used in anesthesia ...
agent. Also called barbital or ''Veronal'' (the trade name
A trade name, trading name, or business name, is a pseudonym used by companies that do not operate under their registered company name. The term for this type of alternative name is a "fictitious" business name. Registering the fictitious name w ...
assigned to it by Bayer Pharmaceuticals
Bayer AG (, commonly pronounced ; ) is a German multinational pharmaceutical and biotechnology company and one of the largest pharmaceutical companies in the world. Headquartered in Leverkusen, Bayer's areas of business include pharmaceutica ...
), this new drug became the first commercially marketed barbiturate
Barbiturates are a class of depressant drugs that are chemically derived from barbituric acid. They are effective when used medically as anxiolytics, hypnotics, and anticonvulsants, but have physical and psychological addiction potential as we ...
; it was used as a treatment for insomnia
Insomnia, also known as sleeplessness, is a sleep disorder in which people have trouble sleeping. They may have difficulty falling asleep, or staying asleep as long as desired. Insomnia is typically followed by daytime sleepiness, low energy, ...
from 1903 until the mid-1950s.
Until 1913, oral and maxillofacial surgery was performed by mask inhalation anesthesia, topical application of local anesthetic
A local anesthetic (LA) is a medication that causes absence of pain sensation. In the context of surgery, a local anesthetic creates an absence of pain in a specific location of the body without a loss of consciousness, as opposed to a general an ...
s to the mucosa
A mucous membrane or mucosa is a membrane that lines various cavities in the body of an organism and covers the surface of internal organs. It consists of one or more layers of epithelial cells overlying a layer of loose connective tissue. It is ...
, rectal anesthesia, or intravenous
Intravenous therapy (abbreviated as IV therapy) is a medical technique that administers fluids, medications and nutrients directly into a person's vein. The intravenous route of administration is commonly used for rehydration or to provide nutrie ...
anesthesia. While otherwise effective, these techniques did not protect the airway from obstruction and also exposed patients to the risk of pulmonary aspiration of blood and mucus
Mucus ( ) is a slippery aqueous secretion produced by, and covering, mucous membranes. It is typically produced from cells found in mucous glands, although it may also originate from mixed glands, which contain both serous and mucous cells. It is ...
into the tracheobronchial tree. In 1913, Chevalier Jackson
Chevalier Quixote Jackson (November 4, 1865 – August 16, 1958) was an American pioneer in laryngology. He is sometimes known as the "father of endoscopy", although Philipp Bozzini (1773–1809) is also often given this sobriquet. Chevalier Q. Ja ...
(1865–1958) was the first to report a high rate of success for the use of direct laryngoscopy as a means to intubate the trachea. Jackson introduced a new laryngoscope blade that had a light source at the distal tip, rather than the proximal light source used by Kirstein. This new blade incorporated a component that the operator could slide out to allow room for passage of an endotracheal tube or bronchoscope.
Also in 1913, Henry H. Janeway
Henry Harrington Janeway (19 March 1873 – 1 February 1921) was an American physician and pioneer of radiation therapy.
Publications
Janeway's clinical and experimental observations were published in medical journals of his time. His report on ' ...
(1873–1921) published results he had achieved using a laryngoscope he had recently developed. An American anesthesiologist practicing at Bellevue Hospital
Bellevue Hospital (officially NYC Health + Hospitals/Bellevue and formerly known as Bellevue Hospital Center) is a hospital in New York City and the oldest public hospital in the United States. One of the largest hospitals in the United States b ...
in New York City
New York, often called New York City or NYC, is the List of United States cities by population, most populous city in the United States. With a 2020 population of 8,804,190 distributed over , New York City is also the L ...
, Janeway was of the opinion that direct intratracheal insufflation
In religious and magical practice, insufflation and exsufflation are ritual acts of blowing, breathing, hissing, or puffing that signify variously expulsion or renunciation of evil or of the devil (the Evil One), or infilling or blessing with go ...
of volatile anesthetics
An inhalational anesthetic is a chemical compound possessing general anesthetic properties that can be delivered via inhalation. They are administered through a face mask, laryngeal mask airway or tracheal tube connected to an anesthetic vapor ...
would provide improved conditions for otolaryngologic surgery. With this in mind, he developed a laryngoscope designed for the sole purpose of tracheal intubation. Similar to Jackson's device, Janeway's instrument incorporated a distal light source. Unique, however, was the inclusion of batteries within the handle, a central notch in the blade for maintaining the tracheal tube in the midline of the oropharynx during intubation and a slight curve to the distal tip of the blade to help guide the tube through the glottis. The success of this design led to its subsequent use in other types of surgery. Janeway was thus instrumental in popularizing the widespread use of direct laryngoscopy and tracheal intubation in the practice of anesthesiology.
In 1928 Arthur Ernest Guedel introduced the cuffed endotracheal tube, which allowed deep enough anesthesia that completely suppressed spontaneously respirations while the gas and oxygen were delivered via positive pressure ventilation controlled by the anesthesiologist. Also important for the development of modern anesthesia are anesthesia machines. Only three years later Joseph W. Gale developed the technology where the anesthesiologist was able to ventilate only one lung at a time. This allowed the development of thoracic surgery, which had previously been vexed by the pendelluft problem in which the bad lung being operated on inflated with patient exhalation due to the loss of vacuum with the thorax being open to the atmosphere. Eventually by early 1980s double lumen endotracheal tubes made out of clear plastic enabled anesthesiologists to selectively ventilate one lung while using flexible fiberoptic bronchoscopy to block off the diseased lung and prevent cross contamination. One early device, the copper kettle, was developed by Dr. Lucien E. Morris at the University of Wisconsin.
Sodium thiopental
Sodium thiopental, also known as Sodium Pentothal (a trademark of Abbott Laboratories), thiopental, thiopentone, or Trapanal (also a trademark), is a rapid-onset short-acting barbiturate general anesthetic. It is the thiobarbiturate analog of pe ...
, the first intravenous anesthetic, was synthesized in 1934 by Ernest H. Volwiler
Ernest Henry Volwiler (August 22, 1893 – October 3, 1992) was an American chemist. He spent his career at Abbott Laboratories working his way from staff chemist to CEO. He was a pioneer in the field of anesthetic pharmacology, assisting in th ...
(1893–1992) and Donalee L. Tabern (1900–1974), working for Abbott Laboratories
Abbott Laboratories is an American multinational medical devices and health care company with headquarters in Abbott Park, Illinois, United States. The company was founded by Chicago physician Wallace Calvin Abbott in 1888 to formulate known dr ...
. It was first used in humans on 8 March 1934 by Ralph M. Waters in an investigation of its properties, which were short-term anesthesia and surprisingly little analgesia. Three months later, John Silas Lundy started a clinical trial of thiopental at the Mayo Clinic
The Mayo Clinic () is a nonprofit American academic medical center focused on integrated health care, education, and research. It employs over 4,500 physicians and scientists, along with another 58,400 administrative and allied health staff, ...
at the request of Abbott Laboratories. Volwiler and Tabern were awarded U.S. Patent No. 2,153,729 in 1939 for the discovery of thiopental, and they were inducted into the National Inventors Hall of Fame in 1986.
In 1939, the search for a synthetic substitute for atropine culminated serendipitously in the discovery of meperidine, the first opiate with a structure altogether different from that of morphine. This was followed in 1947 by the widespread introduction of methadone, another structurally unrelated compound with pharmacological properties similar to those of morphine.
After World War I
World War I (28 July 1914 11 November 1918), often abbreviated as WWI, was one of the deadliest global conflicts in history. Belligerents included much of Europe, the Russian Empire, the United States, and the Ottoman Empire, with fightin ...
, further advances were made in the field of intratracheal anesthesia. Among these were those made by Sir Ivan Whiteside Magill (1888–1986). Working at the Queen's Hospital for Facial and Jaw Injuries in Sidcup
Sidcup is an area of south-east London, England, primarily in the London Borough of Bexley. It is south-east of Charing Cross, bordering the London Boroughs of London Borough of Bromley, Bromley and Royal Borough of Greenwich, Greenwich. Before ...
with plastic surgeon Sir Harold Gillies
Sir Harold Delf Gillies (17 June 1882 – 10 September 1960) was a New Zealand otolaryngologist and father of modern plastic surgery.
Early life
Gillies was born in Dunedin, New Zealand, the son of Member of Parliament in Otago, Robert Gillies ...
(1882–1960) and anesthetist E. Stanley Rowbotham (1890–1979), Magill developed the technique of awake blind nasotracheal intubation. Magill devised a new type of angulated forceps (the Magill forceps
Magill forceps are angled forceps used to guide a tracheal tube into the larynx or a nasogastric tube into the esophagus under direct vision. Other devices invented by Magill include the Magill laryngoscope blade, as well as several apparatuses for the administration of volatile anesthetic agents. The Magill curve of an endotracheal tube is also named for Magill.
The first hospital anesthesia department was established at the Massachusetts General Hospital in 1936, under the leadership of
 The "digital revolution" of the 21st century has brought newer technology to the art and science of tracheal intubation. Several manufacturers have developed video laryngoscopes which employ
The "digital revolution" of the 21st century has brought newer technology to the art and science of tracheal intubation. Several manufacturers have developed video laryngoscopes which employ
Wood Library-Museum of Anesthesiology
The most comprehensive educational, scientific and archival resources in anesthesiology.
An article at University of Bristol providing interesting facts about chloroform.
* ttps://web.archive.org/web/20051219095333/http://www.rcoa.ac.uk/index.asp?PageID=69 Royal College of Anaesthetists Patient Information page
''Turning the Pages''
a virtual reconstruction of Hanaoka's ''Surgical Casebook'', c. 1825. From the
Die Geschichte der Anästhesie
"Anesthesia as a specialty: Past, present and future"
Presentation by Prof. Janusz Andres. {{DEFAULTSORT:History Of General Anesthesia General anesthetics
Henry K. Beecher
Henry Knowles Beecher (February 4, 1904 – July 25, 1976) was a pioneering American anesthesiologist, medical ethicist, and investigator of the placebo effect at Harvard Medical School.
An article by Beecher's in 1966 on unethical medical exp ...
(1904–1976). Beecher, who received his training in surgery, had no previous experience in anesthesia.
Although initially used to reduce the sequelae of spasticity associated with electro-shock therapy for psychiatric disease, curare
Curare ( /kʊˈrɑːri/ or /kjʊˈrɑːri/; ''koo-rah-ree'' or ''kyoo-rah-ree'') is a common name for various alkaloid arrow poisons originating from plant extracts. Used as a paralyzing agent by indigenous peoples in Central and South ...
found use in the operating rooms at Bellvue by E.M. Papper and Stuart Cullen in the 1940s using preparations made by Squibb. This neuromuscular blockade permitted complete paralysis of the diaphragm and enabled control of ventilation via positive pressure ventilation. Mechanical ventilation
Mechanical ventilation, assisted ventilation or intermittent mandatory ventilation (IMV), is the medical term for using a machine called a ventilator to fully or partially provide artificial ventilation. Mechanical ventilation helps move air ...
first became common place with the polio epidemics of the 1950s, most notably in Denmark where an outbreak in 1952 lead to the creation of critical care medicine out of anesthesia. At first anesthesiologists hesitated to bring the ventilator into the operating theater unless necessary, but by the 1960s it became standard operating room equipment.
Sir Robert Macintosh
Sir Robert Reynolds Macintosh (17 October 1897, Timaru, New Zealand – 28 August 1989, Oxford, England) was a New Zealand-born British anaesthetist. He was the first professor of anaesthetics outside the United States.
Early life
Macintosh w ...
(1897–1989) achieved significant advances in techniques for tracheal intubation when he introduced his new curved laryngoscope blade in 1943. The Macintosh blade remains to this day the most widely used laryngoscope blade for orotracheal intubation. In 1949, Macintosh published a case report describing the novel use of a gum elastic urinary catheter
In urinary catheterization a latex, polyurethane, or silicone tube known as a urinary catheter is inserted into the bladder through the urethra to allow urine to drain from the bladder for collection. It may also be used to inject liquids used ...
as an endotracheal tube introducer to facilitate difficult tracheal intubation. Inspired by Macintosh's report, P. Hex Venn (who was at that time the anesthetic advisor to the British firm Eschmann Bros. & Walsh, Ltd.) set about developing an endotracheal tube introducer based on this concept. Venn's design was accepted in March 1973, and what became known as the Eschmann endotracheal tube introducer went into production later that year. The material of Venn's design was different from that of a gum elastic bougie in that it had two layers: a core of tube woven from polyester
Polyester is a category of polymers that contain the ester functional group in every repeat unit of their main chain. As a specific material, it most commonly refers to a type called polyethylene terephthalate (PET). Polyesters include natural ...
threads and an outer resin
In polymer chemistry and materials science, resin is a solid or highly viscous substance of plant or synthetic origin that is typically convertible into polymers. Resins are usually mixtures of organic compounds. This article focuses on natu ...
layer. This provided more stiffness but maintained the flexibility and the slippery surface. Other differences were the length (the new introducer was , which is much longer than the gum elastic bougie) and the presence of a 35° curved tip, permitting it to be steered around obstacles.
For over a hundred years the mainstay of inhalational anesthetics remained ether
In organic chemistry, ethers are a class of compounds that contain an ether group—an oxygen atom connected to two alkyl or aryl groups. They have the general formula , where R and R′ represent the alkyl or aryl groups. Ethers can again be c ...
with cyclopropane
Cyclopropane is the cycloalkane with the molecular formula (CH2)3, consisting of three methylene groups (CH2) linked to each other to form a ring. The small size of the ring creates substantial ring strain in the structure. Cyclopropane itself ...
, which had been introduced in the 1930s. In 1956 halothane
Halothane, sold under the brand name Fluothane among others, is a general anaesthetic. It can be used to induce or maintain anaesthesia. One of its benefits is that it does not increase the production of saliva, which can be particularly useful i ...
was introduced which had the significant advantage of not being flammable. This reduced the risk of operating room fires. In the sixties the halogenated ether
A halogenated ether is a subcategory of a larger group of chemicals known as ethers. An ether is an organic chemical that contains an ether group—an oxygen atom connected to two (substituted) alkyl groups. A good example of an ether is t ...
s superseded Halothane
Halothane, sold under the brand name Fluothane among others, is a general anaesthetic. It can be used to induce or maintain anaesthesia. One of its benefits is that it does not increase the production of saliva, which can be particularly useful i ...
due to the rare, but significant side effects of cardiac arrhythmias and liver toxicity. The first two halogenated ethers were methoxyflurane
Methoxyflurane, sold under the brand name Penthrox among others, is an inhaled medication primarily used to reduce pain following trauma. It may also be used for short episodes of pain as a result of medical procedures. Onset of pain relief is ...
and enflurane
Enflurane (2-chloro-1,1,2-trifluoroethyl difluoromethyl ether) is a halogenated ether. Developed by Ross Terrell in 1963, it was first used clinically in 1966. It was increasingly used for inhalational anesthesia during the 1970s and 1980s but is ...
. These in turn were replaced by the current standards of isoflurane
Isoflurane, sold under the brand name Forane among others, is a general anesthetic. It can be used to start or maintain anesthesia; however, other medications are often used to start anesthesia rather than isoflurane, due to airway irritation w ...
, sevoflurane
Sevoflurane, sold under the brand name Sevorane, among others, is a sweet-smelling, nonflammable, highly fluorinated methyl isopropyl ether used as an inhalational anaesthetic for induction and maintenance of general anesthesia. After desflura ...
, and desflurane
Desflurane (1,2,2,2-tetrafluoroethyl difluoromethyl ether) is a highly fluorinated methyl ethyl ether used for maintenance of general anesthesia. Like halothane, enflurane, and isoflurane, it is a racemic mixture of (''R'') and (''S'') optical i ...
in the eighties and nineties although methoxyflurane
Methoxyflurane, sold under the brand name Penthrox among others, is an inhaled medication primarily used to reduce pain following trauma. It may also be used for short episodes of pain as a result of medical procedures. Onset of pain relief is ...
remains in use for prehospital anesthesia in Australia as Penthrox. Halothane
Halothane, sold under the brand name Fluothane among others, is a general anaesthetic. It can be used to induce or maintain anaesthesia. One of its benefits is that it does not increase the production of saliva, which can be particularly useful i ...
remains in common place throughout much of the developing world.
Many new intravenous and inhalational anesthetics were developed and brought into clinical use during the second half of the 20th century. Paul Janssen
Paul Adriaan Jan, Baron Janssen (12 September 1926 - 11 November 2003) was a Belgian physician. He was the founder of Janssen Pharmaceutica, a pharmaceutical company with over 20,000 employees which is now a subsidiary of Johnson & Johnson.
Ea ...
(1926–2003), the founder of Janssen Pharmaceutica
Janssen Pharmaceuticals is a pharmaceutical company headquartered in Beerse, Belgium, and wholly-owned by Johnson & Johnson. It was founded in 1953 by Paul Janssen.
In 1961, Janssen Pharmaceuticals was purchased by New Jersey-based American ...
, is credited with the development of over 80 pharmaceutical compounds. Janssen synthesized nearly all of the butyrophenone
Butyrophenone is an organic compound with the formula C6H5C(O)C3H7. It is a colorless liquid.
The butyrophenone structure—a ketone flanked by a phenyl ring and a butyl chain—forms the basis for many other chemicals containing various sub ...
class of antipsychotic
Antipsychotics, also known as neuroleptics, are a class of Psychiatric medication, psychotropic medication primarily used to manage psychosis (including delusions, hallucinations, paranoia or disordered thought), principally in schizophrenia but ...
agents, beginning with haloperidol
Haloperidol, sold under the brand name Haldol among others, is a typical antipsychotic medication. Haloperidol is used in the treatment of schizophrenia, tics in Tourette syndrome, mania in bipolar disorder, delirium, agitation, acute psychosi ...
(1958) and droperidol
Droperidol (Inapsine, Droleptan, Dridol, Xomolix, Innovar ombination with fentanyl">fentanyl.html" ;"title="ombination with fentanyl">ombination with fentanyl is an antidopaminergic medication, drug used as an antiemetic (that is, to prevent o ...
(1961). These agents were rapidly integrated into the practice of anesthesia. In 1960, Janssen's team synthesized fentanyl
Fentanyl, also spelled fentanil, is a very potent synthetic opioid used as a pain medication. Together with other drugs, fentanyl is used for anesthesia. It is also used illicitly as a recreational drug, sometimes mixed with heroin, cocaine ...
, the first of the piperidinone-derived opioids. Fentanyl was followed by sufentanil
Sufentanil, sold under the brand names Dsuvia and Sufenta, is a synthetic opioid analgesic drug approximately 5 to 10 times as potent as its parent drug, fentanyl, and 500 times as potent as morphine. Structurally, sufentanil differs from fen ...
(1974), alfentanil
Alfentanil (R-39209, trade name Alfenta, Rapifen in Australia) is a potent but short-acting synthetic opioid analgesic drug, used for anaesthesia in surgery. It is an analogue of fentanyl with around one-fourth to one-tenth the potency, one-third ...
(1976), carfentanil
Carfentanil or carfentanyl, sold under the brand name Wildnil, is a very potent opioid analgesic which is used in veterinary medicine to anesthetize large animals such as elephants and rhinoceroses. It is typically administered in this context ...
(1976), and lofentanil
Lofentanil is one of the most potent opioid analgesics known and is an analogue of fentanyl, which was developed in 1960. It is most similar to the highly potent opioid carfentanil (4-carbomethoxyfentanyl), only slightly more potent. Lofentanil ...
(1980). Janssen and his team also developed etomidate
Etomidate (USAN, INN, BAN; marketed as Amidate) is a short-acting intravenous anaesthetic agent used for the induction of general anaesthesia and sedation for short procedures such as reduction of dislocated joints, tracheal intubation, cardiove ...
(1964), a potent intravenous anesthetic induction agent.
The concept of using a fiberoptic endoscope for tracheal intubation was introduced by Peter Murphy, an English anesthetist, in 1967. By the mid-1980s, the flexible fiberoptic bronchoscope had become an indispensable instrument within the pulmonology
Pulmonology (, , from Latin ''pulmō, -ōnis'' "lung" and the Greek suffix "study of"), pneumology (, built on Greek πνεύμων "lung") or pneumonology () is a medical specialty that deals with diseases involving the respiratory tract. ...
and anesthesia communities.
21st century
 The "digital revolution" of the 21st century has brought newer technology to the art and science of tracheal intubation. Several manufacturers have developed video laryngoscopes which employ
The "digital revolution" of the 21st century has brought newer technology to the art and science of tracheal intubation. Several manufacturers have developed video laryngoscopes which employ digital technology Digital technology may refer to:
* Application of digital electronics
* Any significant piece of knowledge from information technology
Information technology (IT) is the use of computers to create, process, store, retrieve, and exchange a ...
such as the CMOS
Complementary metal–oxide–semiconductor (CMOS, pronounced "sea-moss", ) is a type of metal–oxide–semiconductor field-effect transistor (MOSFET) fabrication process that uses complementary and symmetrical pairs of p-type and n-type MOSFE ...
active pixel sensor
An active-pixel sensor (APS) is an image sensor where each pixel sensor unit cell has a photodetector (typically a pinned photodiode) and one or more active transistors. In a metal–oxide–semiconductor (MOS) active-pixel sensor, MOS field-effec ...
(APS) to generate a view of the glottis so that the trachea may be intubated. The Glidescope video laryngoscope is one example of such a device.
Xenon
Xenon is a chemical element with the symbol Xe and atomic number 54. It is a dense, colorless, odorless noble gas found in Earth's atmosphere in trace amounts. Although generally unreactive, it can undergo a few chemical reactions such as the ...
has recently been approved in some jurisdictions as an anaesthetic agent which does not act as a greenhouse gas.
See also
References
Further reading
* * * * * * * * * Arashiro Toshiaki, ''Ryukyu-Okinawa Rekishi Jinbutsuden'', Okinawajijishuppan, 2006 p66 * "Reevaluation of surgical achievements by Tokumei Takamine". Matsuki A. Masui. November 2000; 49(11):1285-9. Japanese. * "The secret anesthetic used in the repair of a hare-lip performed by Tokumei Takamine in Ryukyu". Matsuki A. ''Nippon Ishigaku Zasshi''. October 1985 31(4):463-89. Japanese.External links
Wood Library-Museum of Anesthesiology
The most comprehensive educational, scientific and archival resources in anesthesiology.
An article at University of Bristol providing interesting facts about chloroform.
* ttps://web.archive.org/web/20051219095333/http://www.rcoa.ac.uk/index.asp?PageID=69 Royal College of Anaesthetists Patient Information page
''Turning the Pages''
a virtual reconstruction of Hanaoka's ''Surgical Casebook'', c. 1825. From the
U.S. National Library of Medicine
The United States National Library of Medicine (NLM), operated by the United States federal government, is the world's largest medical library.
Located in Bethesda, Maryland, the NLM is an institute within the National Institutes of Health. Its ...
*Die Geschichte der Anästhesie
"Anesthesia as a specialty: Past, present and future"
Presentation by Prof. Janusz Andres. {{DEFAULTSORT:History Of General Anesthesia General anesthetics
General anesthesia
General anaesthesia (UK) or general anesthesia (US) is a medically induced loss of consciousness that renders the patient unarousable even with painful stimuli. This effect is achieved by administering either intravenous or inhalational general ...
Drug discovery