History of Samos on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
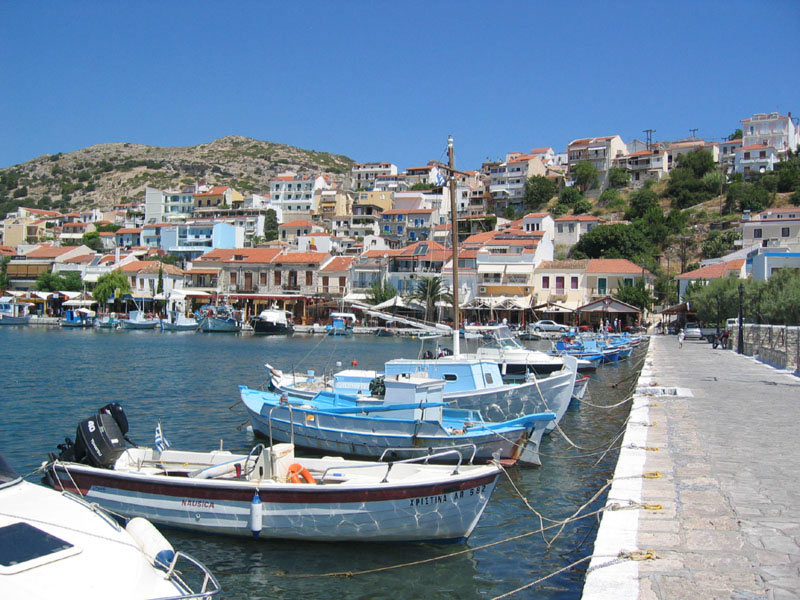
Samos (, also ; el, Σάμος ) is a
 The area of the
The area of the 

 In classical antiquity, the island was a center of Ionian culture and luxury, renowned for its Samian wines and its red pottery (called
In classical antiquity, the island was a center of Ionian culture and luxury, renowned for its Samian wines and its red pottery (called 
 In the 6th century BC, Samos was ruled by the famous
In the 6th century BC, Samos was ruled by the famous
 Perhaps the most famous persons ever connected with classical Samos were the philosopher and mathematician
Perhaps the most famous persons ever connected with classical Samos were the philosopher and mathematician

 As a portion of the
As a portion of the
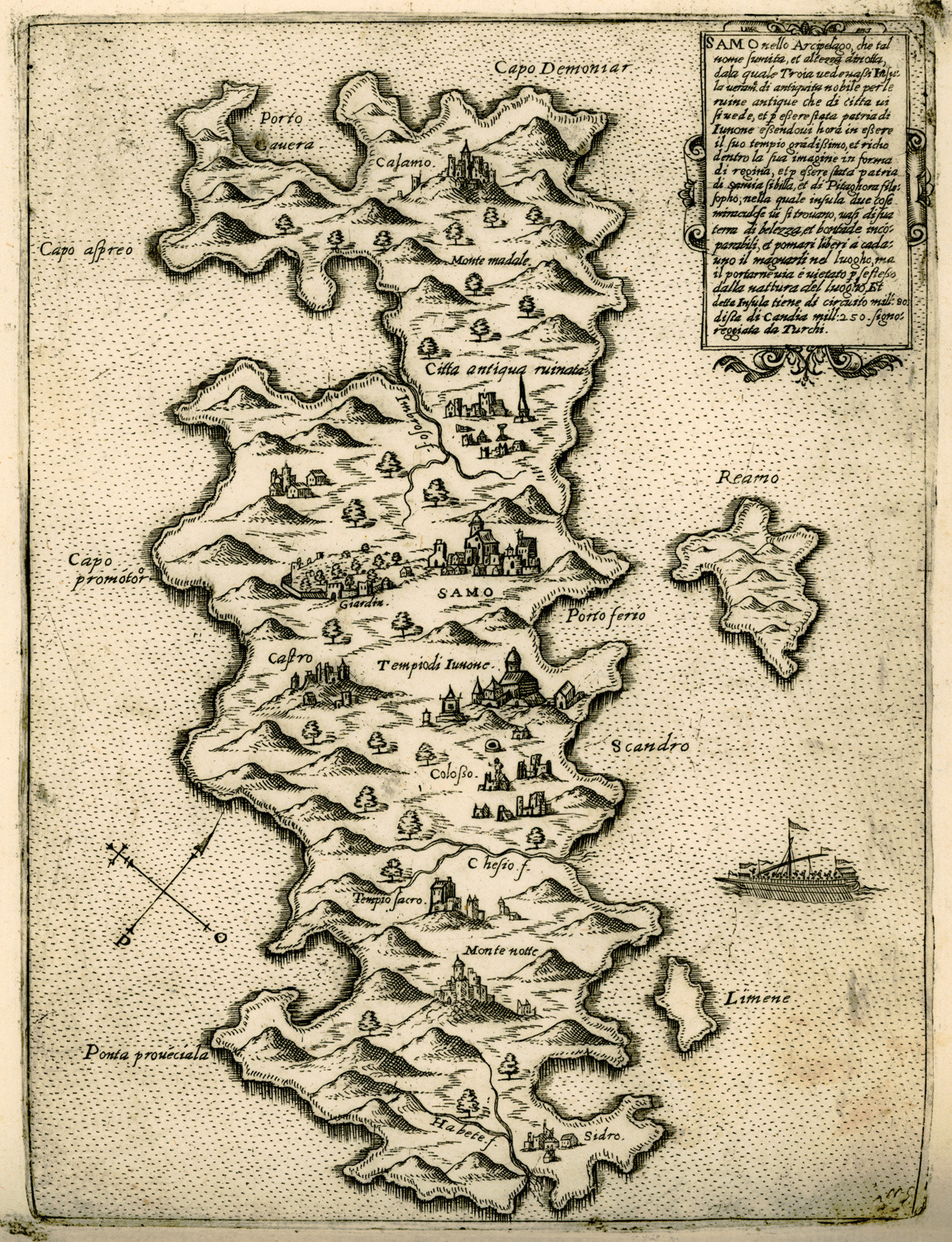 Samos came under Ottoman rule in 1475 or c. 1479/80, at which time the island was practically abandoned due to the effects of piracy and the plague. The island remained desolate for almost a full century before the Ottoman authorities, by now in secure control of the Aegean, undertook a serious effort to repopulate the island.
In 1572/3, the island was granted as a personal domain (''hass'') to Kilic Ali Pasha, the ''
Samos came under Ottoman rule in 1475 or c. 1479/80, at which time the island was practically abandoned due to the effects of piracy and the plague. The island remained desolate for almost a full century before the Ottoman authorities, by now in secure control of the Aegean, undertook a serious effort to repopulate the island.
In 1572/3, the island was granted as a personal domain (''hass'') to Kilic Ali Pasha, the ''

 In March 1821, the Greek War of Independence broke out, and on 18 April, under the leadership of Logothetis and the ''Karmanioloi'', Samos too joined the uprising. In May, a revolutionary government with its own constitution was set up to administer the island, mostly inspired by Logothetis.
The Samians successfully repulsed three Ottoman attempts to recapture the island: in summer 1821, in July 1824; when Greek naval victories off
In March 1821, the Greek War of Independence broke out, and on 18 April, under the leadership of Logothetis and the ''Karmanioloi'', Samos too joined the uprising. In May, a revolutionary government with its own constitution was set up to administer the island, mostly inspired by Logothetis.
The Samians successfully repulsed three Ottoman attempts to recapture the island: in summer 1821, in July 1824; when Greek naval victories off
 In 1834, the island of Samos became the territory of the
In 1834, the island of Samos became the territory of the

 The island was united with the
The island was united with the
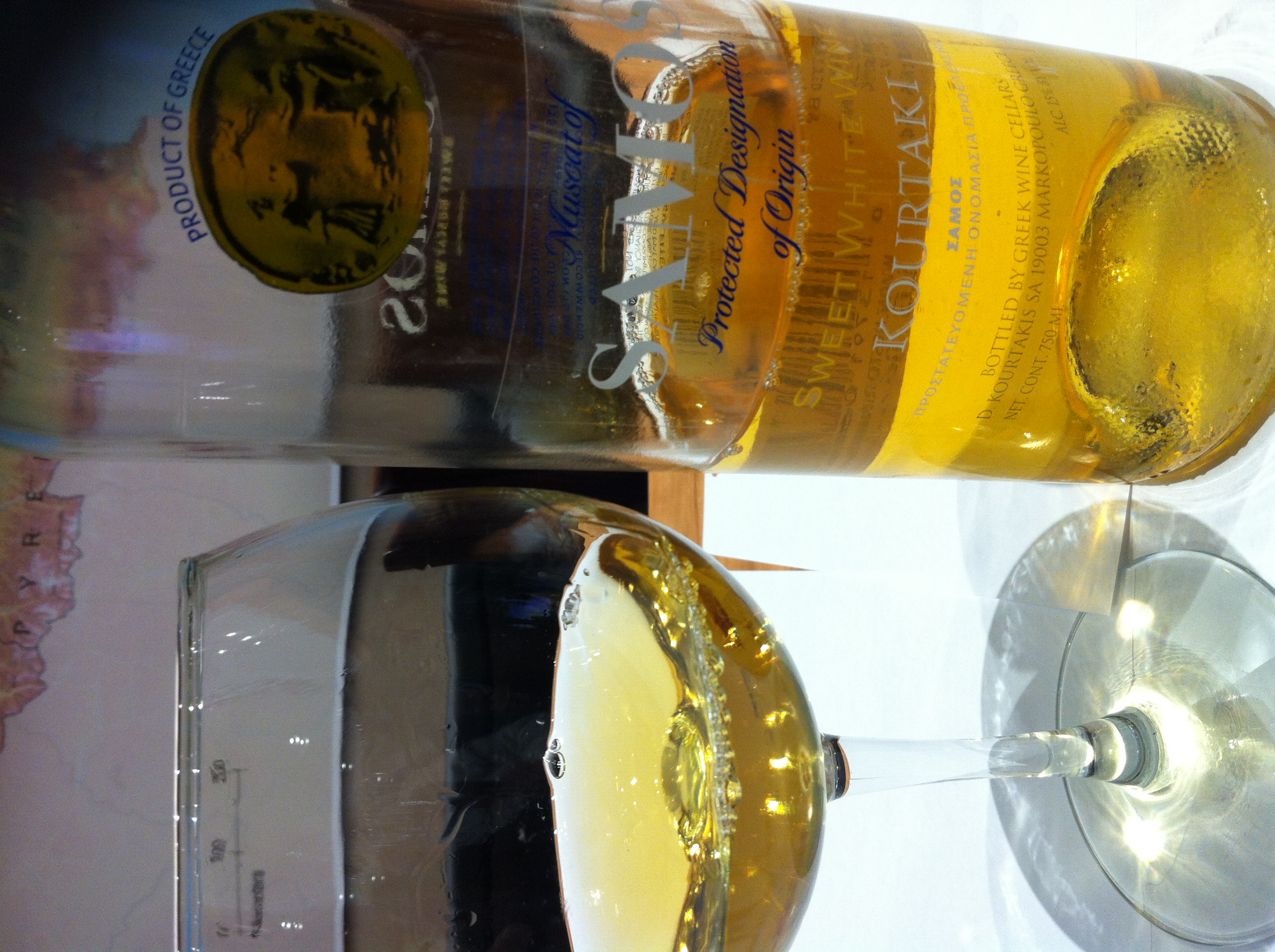

 The Samian economy depends mainly on agriculture and the tourist industry which was growing steadily since the early 1980s and reached a peak at the end of the 1990s. The main agricultural products include
The Samian economy depends mainly on agriculture and the tourist industry which was growing steadily since the early 1980s and reached a peak at the end of the 1990s. The main agricultural products include

 The island is the location of the joint
The island is the location of the joint
File:Samos town - Archaeological museum and Municipal building.jpg, The town hall and the archaeological museum in Vathy
File:Samos town Agios Spyridonas church 01.jpg, St Spyridon, Samos town
File:Former tobacco factory, Samos Town. - panoramio.jpg, Old tobacco factory, Samos town
File:Kokkari Sea Beach.JPG, Kokkari beach
File:FlughafenSamos.jpg, Samos International Airport
Municipality of Samos
Visit Samos
{{Authority control * Ionian League Regional units of the North Aegean Provinces of Greece Islands of Greece Landforms of Samos Islands of the North Aegean Populated places in the ancient Aegean islands Populated places in ancient Ionia Wine regions of Greece
Greek
Greek may refer to:
Greece
Anything of, from, or related to Greece, a country in Southern Europe:
*Greeks, an ethnic group.
*Greek language, a branch of the Indo-European language family.
**Proto-Greek language, the assumed last common ancestor ...
island in the eastern Aegean Sea
The Aegean Sea ; tr, Ege Denizi (Greek: Αιγαίο Πέλαγος: "Egéo Pélagos", Turkish: "Ege Denizi" or "Adalar Denizi") is an elongated embayment of the Mediterranean Sea between Europe and Asia. It is located between the Balkans ...
, south of Chios
Chios (; el, Χίος, Chíos , traditionally known as Scio in English) is the fifth largest Greek island, situated in the northern Aegean Sea. The island is separated from Turkey by the Chios Strait. Chios is notable for its exports of masti ...
, north of Patmos
Patmos ( el, Πάτμος, ) is a Greek island in the Aegean Sea. It is famous as the location where John of Patmos received the visions found in the Book of Revelation of the New Testament, and where the book was written.
One of the northern ...
and the Dodecanese, and off the coast of western Turkey
Turkey ( tr, Türkiye ), officially the Republic of Türkiye ( tr, Türkiye Cumhuriyeti, links=no ), is a transcontinental country located mainly on the Anatolian Peninsula in Western Asia, with a small portion on the Balkan Peninsula in ...
, from which it is separated by the -wide Mycale Strait
The Mycale Strait ( el, Στενό της Μυκάλης; tr, Dilek Geçidi) is a narrow strait separating the island of Samos from Anatolia (Turkey) in the eastern Aegean Sea. At its narrowest point it is only 1.6 km wide; the narrowest betw ...
. It is also a separate regional unit of the North Aegean
The North Aegean Region ( el, Περιφέρεια Βορείου Αιγαίου, translit=Periféria Voríou Eyéou, ) is one of the thirteen administrative regions of Greece, and the smallest of the thirteen by population. It comprises the isla ...
region.
In ancient times
Ancient history is a time period from the beginning of writing and recorded human history to as far as late antiquity. The span of recorded history is roughly 5,000 years, beginning with the Sumerian cuneiform script. Ancient history cov ...
, Samos was an especially rich and powerful city-state
A city-state is an independent sovereign city which serves as the center of political, economic, and cultural life over its contiguous territory. They have existed in many parts of the world since the dawn of history, including cities such as ...
, particularly known for its vineyard
A vineyard (; also ) is a plantation of grape-bearing vines, grown mainly for winemaking, but also raisins, table grapes and non-alcoholic grape juice. The science, practice and study of vineyard production is known as viticulture. Vineya ...
s and wine
Wine is an alcoholic drink typically made from fermented grapes. Yeast consumes the sugar in the grapes and converts it to ethanol and carbon dioxide, releasing heat in the process. Different varieties of grapes and strains of yeasts are m ...
production. It is home to Pythagoreion
The Pythagoreion is the archaeological site of the ancient town of Samos in Samos, Greece. It is located in the area of the modern town of Pythagoreio, from which it has got its modern name. The archaeological site contains ancient Greek and Roma ...
and the Heraion of Samos
The Heraion of Samos was a large sanctuary to the goddess Hera, on the island of Samos, Greece, 6 km southwest of the ancient city of Samos (modern Pythagoreion). It was located in the low, marshy basin of the Imbrasos river, near where it ...
, a UNESCO World Heritage Site
A World Heritage Site is a landmark or area with legal protection by an international convention administered by the United Nations Educational, Scientific and Cultural Organization (UNESCO). World Heritage Sites are designated by UNESCO for ...
that includes the Eupalinian aqueduct
The Tunnel of Eupalinos or Eupalinian aqueduct ( el, Ευπαλίνιον όρυγμα, translit=Efpalinion orygma) is a tunnel of length running through Mount Kastro in Samos, Greece, built in the 6th century BC to serve as an aqueduct. The tunn ...
, a marvel of ancient engineering. Samos is the birthplace of the Greek philosopher
Ancient Greek philosophy arose in the 6th century BC, marking the end of the Greek Dark Ages. Greek philosophy continued throughout the Hellenistic period and the period in which Greece and most Greek-inhabited lands were part of the Roman Empire ...
and mathematician Pythagoras
Pythagoras of Samos ( grc, Πυθαγόρας ὁ Σάμιος, Pythagóras ho Sámios, Pythagoras the Samian, or simply ; in Ionian Greek; ) was an ancient Ionian Greek philosopher and the eponymous founder of Pythagoreanism. His politi ...
, after whom the Pythagorean theorem is named, the philosophers Melissus of Samos and Epicurus, and the astronomer Aristarchus of Samos, the first known individual to propose that the Earth revolves around the sun. Samian wine was well known in antiquity and is still produced on the island.
The island was governed by the semi-autonomous Principality of Samos
The Principality of Samos ( el, Ηγεμονία της Σάμου, ; ota, Sisam İmâreti, script=Latn, italic=yes; tr, Sisam Beyliği) was an autonomous tributary state of the Ottoman Empire from 1834 to 1912. The island of Samos participated ...
under Ottoman suzerainty from 1835 until it joined Greece
Greece,, or , romanized: ', officially the Hellenic Republic, is a country in Southeast Europe. It is situated on the southern tip of the Balkans, and is located at the crossroads of Europe, Asia, and Africa. Greece shares land borders ...
in March 1913.
Etymology
Strabo derived the name from the Phoenician word ''sama'' meaning "high".Geography
 The area of the
The area of the island
An island (or isle) is an isolated piece of habitat that is surrounded by a dramatically different habitat, such as water. Very small islands such as emergent land features on atolls can be called islets, skerries, cays or keys. An island ...
is , and it is long and wide. It is separated from Anatolia
Anatolia, tr, Anadolu Yarımadası), and the Anatolian plateau, also known as Asia Minor, is a large peninsula in Western Asia and the westernmost protrusion of the Asian continent. It constitutes the major part of modern-day Turkey. The ...
by the approximately Mycale Strait
The Mycale Strait ( el, Στενό της Μυκάλης; tr, Dilek Geçidi) is a narrow strait separating the island of Samos from Anatolia (Turkey) in the eastern Aegean Sea. At its narrowest point it is only 1.6 km wide; the narrowest betw ...
. While largely mountainous, Samos has several relatively large and fertile plains.
A great portion of the island is covered with vineyards
A vineyard (; also ) is a plantation of grape-bearing vines, grown mainly for winemaking, but also raisins, table grapes and non-alcoholic grape juice. The science, practice and study of vineyard production is known as viticulture. Vineyards ...
, from which Muscat
Muscat ( ar, مَسْقَط, ) is the capital and most populated city in Oman. It is the seat of the Governorate of Muscat. According to the National Centre for Statistics and Information (NCSI), the total population of Muscat Governorate was ...
wine is made. The most important plains other than the capital, Vathy, in the northeast, are those of Karlovasi
Karlovasi ( el, Καρλόβασι) is a town, a municipal unit, and a former municipality on the island of Samos, North Aegean, Greece. Since the 2019 local government reform it is part of the municipality West Samos, of which it is a municipal u ...
, in the northwest, Pythagoreio
Pythagoreio ( el, Πυθαγόρειο) is a town and municipal unit on the island of Samos, North Aegean, Greece. Before the 2011 local government reform, Pythagoreio was a municipality. Since 2019, it is a municipal unit of East Samos. In 2011, ...
, in the southeast, and Marathokampos
Marathokampos ( el, Μαραθόκαμπος) is a town, municipal unit, and a former municipality on the island of Samos, North Aegean, Greece. Since the 2019 local government reform it is part of the municipality West Samos, of which it is a muni ...
in the southwest. The island's population is 33,814, which makes it the 9th most populous of the Greek islands. The Samian climate is typically Mediterranean, with mild rainy winters, and warm rainless summers.
Samos's relief is dominated by two large mountains, Ampelos and Kerkis (anc. Kerketeus). The Ampelos massif (colloquially referred to as "Karvounis") is the larger of the two and occupies the center of the island, rising to . Mt. Kerkis, though smaller in area, is the taller of the two, and its summit is the island's highest point, at . The mountains are a continuation of the Mycale
Mycale (). also Mykale and Mykali ( grc, Μυκάλη, ''Mykálē''), called Samsun Dağı and Dilek Dağı (Dilek Peninsula) in modern Turkey, is a mountain on the west coast of central Anatolia in Turkey, north of the mouth of the Maeander an ...
range on the Anatolian mainland.
Fauna
Samos is home to many species including thegolden jackal
The golden jackal (''Canis aureus''), also called common jackal, is a wolf-like canid that is native to Southeast Europe, Southwest Asia, South Asia, and regions of Southeast Asia. The golden jackal's coat varies in color from a pale creamy ...
, stone marten
The beech marten (''Martes foina''), also known as the stone marten, house marten or white breasted marten, is a species of marten native to much of Europe and Central Asia, though it has established a feral population in North America. It is li ...
, wild boar
The wild boar (''Sus scrofa''), also known as the wild swine, common wild pig, Eurasian wild pig, or simply wild pig, is a suid native to much of Eurasia and North Africa, and has been introduced to the Americas and Oceania. The species is ...
, flamingos
Flamingos or flamingoes are a type of wading bird in the family Phoenicopteridae, which is the only extant family in the order Phoenicopteriformes. There are four flamingo species distributed throughout the Americas (including the Caribbea ...
and monk seal
Monk seals are earless seals of the tribe Monachini. They are the only earless seals found in tropical climates. The two genera of monk seals, ''Monachus'' and ''Neomonachus'', comprise three species: the Mediterranean monk seal, ''Monachus mona ...
.
Climate
Samos has aMediterranean climate
A Mediterranean climate (also called a dry summer temperate climate ''Cs'') is a temperate climate sub-type, generally characterized by warm, dry summers and mild, fairly wet winters; these weather conditions are typically experienced in the ...
(Köppen Köppen is a German surname. Notable people with the surname include:
* Bernd Köppen (born 1951), German pianist and composer
* Carl Köppen (1833-1907), German military advisor in Meiji era Japan
* Edlef Köppen (1893–1939), German author and ...
: ''Csa''), with mild winters and hot summers.
History
Early and Classical Antiquity

Samian ware
Terra sigillata is a term with at least three distinct meanings: as a description of medieval medicinal earth; in archaeology, as a general term for some of the fine red Ancient Roman pottery with glossy surface slips made in specific areas of t ...
by the Romans). Its most famous building was the Ionic order archaic Temple of goddess Hera—the Heraion.
Concerning the earliest history of Samos, literary tradition is singularly defective. At the time of the great migrations, it received an Ionian population which traced its origin to Epidaurus in Argolis
Argolis or Argolida ( el, Αργολίδα , ; , in ancient Greek and Katharevousa) is one of the regional units of Greece. It is part of the region of Peloponnese, situated in the eastern part of the Peloponnese peninsula and part of the ...
: Samos became one of the twelve members of the Ionian League
The Ionian League ( grc, Ἴωνες, ''Íōnes''; , ''koinón Iōnōn''; or , ''koinē sýnodos Iōnōn''; Latin: ''commune consilium''), also called the Panionic League, was a confederation formed at the end of the Meliac War in the mid-7th ce ...
. By the 7th century BC, it had become one of the leading commercial centers of Greece. This early prosperity of the Samians seems largely due to the island's position near trade routes, which facilitated the importation of textiles from inner Asia Minor, but the Samians also developed an extensive oversea commerce. They helped to open up trade with the population that lived around the Black Sea as well as with Egypt, Cyrene (Libya), Corinth, and Chalcis. Among the colonies
In modern parlance, a colony is a territory subject to a form of foreign rule. Though dominated by the foreign colonizers, colonies remain separate from the administration of the original country of the colonizers, the '' metropolitan state'' ...
the Samians founded, most of them in the sixth century BCE, were Bisanthe, Perinthus
Perinthus or Perinthos ( grc, ἡ Πέρινθος) was a great and flourishing town of ancient Thrace, situated on the Propontis. According to John Tzetzes, it bore at an early period the name of Mygdonia (Μυγδονία). It lay 22 miles wes ...
, and Samothrace
Samothrace (also known as Samothraki, el, Σαμοθράκη, ) is a Greek island in the northern Aegean Sea. It is a municipality within the Evros regional unit of Thrace. The island is long and is in size and has a population of 2,859 (2011 ...
(northern Aegean Sea
The Aegean Sea ; tr, Ege Denizi (Greek: Αιγαίο Πέλαγος: "Egéo Pélagos", Turkish: "Ege Denizi" or "Adalar Denizi") is an elongated embayment of the Mediterranean Sea between Europe and Asia. It is located between the Balkans ...
), Cydonia
Cydonia may refer to:
Music
* ''Cydonia'' (album), a 2001 album by The Orb
* "Cydonia", a track by heavy metal band Crimson Glory from '' Astronomica''
Places and jurisdictions
* Kydonia or Cydonia, an ancient city state on Crete, at modern ...
(Crete), Nagidos
Nagidos ( grc, Νάγιδος; la, Nagidus) was an ancient city of Cilicia. In ancient times it was located between Anemurion to the west and Arsinoe to the east. Today its ruins are found on the hill named ''Paşabeleni'' at the mouth of the ...
and Kelenderis (southern Anatolia
Anatolia, tr, Anadolu Yarımadası), and the Anatolian plateau, also known as Asia Minor, is a large peninsula in Western Asia and the westernmost protrusion of the Asian continent. It constitutes the major part of modern-day Turkey. The ...
), Dicaearchia (Italy), and Oasis Polis Oasis Polis (Greek: Ὄασις Πόλις; literally “Oasis City”) is said by Herodotus (''Histories'', III.26.1-3) to be an ancient Greek colony from Samos in the Egyptian Desert.
The oasis that would fit in with Herodotus's story here (the ...
(Egypt). The trade caused them to become bitter rivals with Miletus. Samos was able to become so prominent despite the growing power of the Persian empire because of the alliance they had with the Egyptians and their powerful fleet. The Samians are also credited with having been the first Greeks to reach the Straits of Gibraltar.
The feud between Miletus and Samos broke out into open strife during the Lelantine War
The Lelantine War was a military conflict between the two ancient Greek city states Chalcis and Eretria in Euboea which took place in the early Archaic period, between c. 710 and 650 BC. The reason for war was, according to tradition, the struggl ...
(7th century BC), with which a Samian innovation in Greek naval warfare may be connected, the use of the trireme
A trireme( ; derived from Latin: ''trirēmis'' "with three banks of oars"; cf. Greek ''triērēs'', literally "three-rower") was an ancient vessel and a type of galley that was used by the ancient maritime civilizations of the Mediterranean S ...
. The result of this conflict was to confirm the supremacy of the Milesians in eastern waters for the time being; but in the 6th century, the insular position of Samos preserved it from those aggressions at the hands of Asiatic kings to which Miletus was henceforth exposed. About 535 BC, when the existing oligarchy was overturned by the tyrant Polycrates
Polycrates (; grc-gre, Πολυκράτης), son of Aeaces, was the tyrant of Samos from the 540s BC to 522 BC. He had a reputation as both a fierce warrior and an enlightened tyrant.
Sources
The main source for Polycrates' life and activit ...
, Samos reached the height of its prosperity. Its navy not only protected it from invasion but also ruled supreme in Aegean waters. The city was beautified with public works, and its school of sculptors, metal-workers and engineers achieved high repute.

Eupalinian aqueduct
tyrant
A tyrant (), in the modern English usage of the word, is an absolute ruler who is unrestrained by law, or one who has usurped a legitimate ruler's sovereignty. Often portrayed as cruel, tyrants may defend their positions by resorting to re ...
Polycrates
Polycrates (; grc-gre, Πολυκράτης), son of Aeaces, was the tyrant of Samos from the 540s BC to 522 BC. He had a reputation as both a fierce warrior and an enlightened tyrant.
Sources
The main source for Polycrates' life and activit ...
. During his reign, two working groups under the leadership of the engineer Eupalinos
Eupalinos ( grc, Εὐπαλῖνος) or Eupalinus of Megara was an ancient Greek engineer who built the Tunnel of Eupalinos on Samos Island in the 6th century BC.
The tunnel, presumably completed between 550 and 530 BC, is the second known tu ...
dug a tunnel through Mount Kastro to build an aqueduct to supply the ancient capital of Samos with fresh water, as this was of the utmost defensive importance (since being underground, it was not easily detected by an enemy who could otherwise cut off the supply). Eupalinos's tunnel is particularly notable because it is the second earliest tunnel in history to be dug from both ends in a methodical manner. With a length of over , Eupalinos's subterranean aqueduct is today regarded as one of the masterpieces of ancient engineering. The aqueduct is now part of the UNESCO
The United Nations Educational, Scientific and Cultural Organization is a specialized agency of the United Nations (UN) aimed at promoting world peace and security through international cooperation in education, arts, sciences and culture. It ...
World Heritage Site
A World Heritage Site is a landmark or area with legal protection by an international convention administered by the United Nations Educational, Scientific and Cultural Organization (UNESCO). World Heritage Sites are designated by UNESCO for h ...
, the Pythagoreion
The Pythagoreion is the archaeological site of the ancient town of Samos in Samos, Greece. It is located in the area of the modern town of Pythagoreio, from which it has got its modern name. The archaeological site contains ancient Greek and Roma ...
.
Persian Wars and Persian rule
After Polycrates's death, Samos suffered a severe blow when the Persian Achaemenid Empire conquered and partly depopulated the island. It had regained much of its power when in 499 BC it joined the general revolt of the Ionian city-states against Persia; but owing to its long-standing jealousy of Miletus, it rendered indifferent service, and at the decisive battle of Lade (494 BC), part of its contingent of sixty ships was guilty of outright treachery. In 479BC, the Samians led the revolt against Persia, during the Battle of Mycale, which was part of the offensive by the Delian League (led by Cimon).Samian War
In the Delian League, Samos held a position of special privilege and remained actively loyal to Athens until 440 BC, when a dispute with Miletus, which the Athenians had decided against them, induced them to secede. With a fleet of sixty ships, they held their own for some time against a large Athenian fleet led byPericles
Pericles (; grc-gre, Περικλῆς; c. 495 – 429 BC) was a Greek politician and general during the Golden Age of Athens. He was prominent and influential in Athenian politics, particularly between the Greco-Persian Wars and the Pelo ...
himself, but after a protracted siege, they were forced to capitulate. Samos was punished, but Thucydides
Thucydides (; grc, , }; BC) was an Athenian historian and general. His '' History of the Peloponnesian War'' recounts the fifth-century BC war between Sparta and Athens until the year 411 BC. Thucydides has been dubbed the father of " scienti ...
tells readers not as harshly as other states which rebelled against Athens. Most in the past had been forced to pay tribute, but Samos was only told to repay the damages that the rebellion had cost the Athenians: 1,300 talents, to pay back in installments of 50 talents per annum.
Peloponnesian War
During the Peloponnesian War (431–404 BC), Samos took the side ofAthens
Athens ( ; el, Αθήνα, Athína ; grc, Ἀθῆναι, Athênai (pl.) ) is both the capital and largest city of Greece. With a population close to four million, it is also the seventh largest city in the European Union. Athens dominates ...
against Sparta
Sparta ( Doric Greek: Σπάρτα, ''Spártā''; Attic Greek: Σπάρτη, ''Spártē'') was a prominent city-state in Laconia, in ancient Greece. In antiquity, the city-state was known as Lacedaemon (, ), while the name Sparta referre ...
, providing their port to the Athenian fleet
Fleet may refer to:
Vehicles
*Fishing fleet
*Naval fleet
*Fleet vehicles, a pool of motor vehicles
*Fleet Aircraft, the aircraft manufacturing company
Places
Canada
* Fleet, Alberta, Canada, a hamlet
England
* The Fleet Lagoon, at Chesil Beach ...
. At the end of the Peloponnesian War, Samos appears as one of the most loyal dependencies of Athens, serving as a base for the naval war against the Peloponnesians and as a temporary home of the Athenian democracy during the revolution of the Four Hundred at Athens (411 BC), and in the last stage of the war was rewarded with the Athenian franchise. This friendly attitude towards Athens was the result of a series of political revolutions, which ended in the establishment of a democracy. After the downfall of Athens, Samos was besieged by Lysander
Lysander (; grc-gre, Λύσανδρος ; died 395 BC) was a Spartan military and political leader. He destroyed the Athenian fleet at the Battle of Aegospotami in 405 BC, forcing Athens to capitulate and bringing the Peloponnesian War to an en ...
and again placed under an oligarchy.
In 394 BC, the withdrawal of the Spartan navy induced the island to declare its independence and reestablish a democracy, but by the peace of Antalcidas (387 BC), it fell again under Persian dominion. It was recovered by the Athenians in 366 after a siege of eleven months, and received a strong body of military settlers, the cleruchs
A cleruchy (, ''klēroukhia'') in Classical Greece, was a specialized type of colony established by Athens. The term comes from the Greek word , ''klērouchos'', literally "lot-holder".
History
Normally, Greek colonies were politically independen ...
, which proved vital in the Social War (357-355 BC). After the Lamian War
The Lamian War, or the Hellenic War (323–322 BC) was fought by a coalition of cities including Athens and the Aetolian League against Macedon and its ally Boeotia. The war broke out after the death of the King of Macedon, Alexander the Great, ...
(322 BC), when Athens was deprived of Samos, the vicissitudes of the island can no longer be followed.
Famous Samians of Antiquity
 Perhaps the most famous persons ever connected with classical Samos were the philosopher and mathematician
Perhaps the most famous persons ever connected with classical Samos were the philosopher and mathematician Pythagoras
Pythagoras of Samos ( grc, Πυθαγόρας ὁ Σάμιος, Pythagóras ho Sámios, Pythagoras the Samian, or simply ; in Ionian Greek; ) was an ancient Ionian Greek philosopher and the eponymous founder of Pythagoreanism. His politi ...
and the fabulist Aesop
Aesop ( or ; , ; c. 620–564 BCE) was a Greek fabulist and storyteller credited with a number of fables now collectively known as ''Aesop's Fables''. Although his existence remains unclear and no writings by him survive, numerous tales c ...
. In 1955, the town of Tigani was renamed Pythagoreio in honor of the philosopher.
Other notable personalities include the philosophers Melissus of Samos and Epicurus, who were of Samian birth, and the astronomer
An astronomer is a scientist in the field of astronomy who focuses their studies on a specific question or field outside the scope of Earth. They observe astronomical objects such as stars, planets, moons, comets and galaxies – in either ...
Aristarchus of Samos, whom history credits with the first recorded heliocentric model
Heliocentrism (also known as the Heliocentric model) is the astronomical model in which the Earth and planets revolve around the Sun at the center of the universe. Historically, heliocentrism was opposed to geocentrism, which placed the Earth a ...
of the Solar System
The Solar System Capitalization of the name varies. The International Astronomical Union, the authoritative body regarding astronomical nomenclature, specifies capitalizing the names of all individual astronomical objects but uses mixed "Solar ...
. The historian Herodotus
Herodotus ( ; grc, , }; BC) was an ancient Greek historian and geographer
A geographer is a physical scientist, social scientist or humanist whose area of study is geography, the study of Earth's natural environment and human society ...
, known by his Histories, resided in Samos for a while.
There was a school of sculptors and architects that included Rhoecus Rhoecus (or Rhaecus, Rhœcus, Rhæcus, Rhoikos) ( grc, Ῥοῖκός) was a Samian sculptor of the 6th century BCE. He and his son Theodorus were especially noted for their work in bronze. Herodotus says that Rhoecus built the temple of Hera at ...
, the architect of the Temple of Hera (Olympia), and the great sculptor and inventor Theodorus, who is said to have invented with Rhoecus Rhoecus (or Rhaecus, Rhœcus, Rhæcus, Rhoikos) ( grc, Ῥοῖκός) was a Samian sculptor of the 6th century BCE. He and his son Theodorus were especially noted for their work in bronze. Herodotus says that Rhoecus built the temple of Hera at ...
the art of casting statues in bronze.
The vases of Samos were among the most characteristic products of Ionian pottery in the 6th century.
Hellenistic and Roman Eras
For some time (about 275–270 BC), Samos served as a base for the Egyptian fleet of the Ptolemies; at other periods, it recognized the overlordship ofSeleucid
The Seleucid Empire (; grc, Βασιλεία τῶν Σελευκιδῶν, ''Basileía tōn Seleukidōn'') was a Greek state in West Asia that existed during the Hellenistic period from 312 BC to 63 BC. The Seleucid Empire was founded by the ...
Syria. In 189 BC, it was transferred by the Romans to their vassal, the Attalid
The Kingdom of Pergamon or Attalid kingdom was a Greek state during the Hellenistic period that ruled much of the Western part of Asia Minor from its capital city of Pergamon. It was ruled by the Attalid dynasty (; grc-x-koine, Δυναστ� ...
dynasty's Hellenistic kingdom of Pergamon
Pergamon or Pergamum ( or ; grc-gre, Πέργαμον), also referred to by its modern Greek form Pergamos (), was a rich and powerful ancient Greek city in Mysia. It is located from the modern coastline of the Aegean Sea on a promontory on th ...
, in Asia Minor
Anatolia, tr, Anadolu Yarımadası), and the Anatolian plateau, also known as Asia Minor, is a large peninsula in Western Asia and the westernmost protrusion of the Asian continent. It constitutes the major part of modern-day Turkey. The re ...
.
Enrolled from 133 in the Roman province of Asia Minor, Samos sided with Aristonicus (132) and Mithridates (88) against its overlord, and consequently forfeited its autonomy, which it only temporarily recovered between the reigns of Augustus
Caesar Augustus (born Gaius Octavius; 23 September 63 BC – 19 August AD 14), also known as Octavian, was the first Roman emperor; he reigned from 27 BC until his death in AD 14. He is known for being the founder of the Roman Pr ...
and Vespasian
Vespasian (; la, Vespasianus ; 17 November AD 9 – 23/24 June 79) was a Roman emperor who reigned from AD 69 to 79. The fourth and last emperor who reigned in the Year of the Four Emperors, he founded the Flavian dynasty that ruled the Empi ...
. Nevertheless, Samos remained comparatively flourishing and was able to contest with Smyrna
Smyrna ( ; grc, Σμύρνη, Smýrnē, or , ) was a Greek city located at a strategic point on the Aegean coast of Anatolia. Due to its advantageous port conditions, its ease of defence, and its good inland connections, Smyrna rose to promi ...
and Ephesus the title "first city of lonia"; it was chiefly noted as a health resort and for the manufacture of pottery. Since Emperor Diocletian's Tetrarchy
The Tetrarchy was the system instituted by Roman emperor Diocletian in 293 AD to govern the ancient Roman Empire by dividing it between two emperors, the ''augusti'', and their juniors colleagues and designated successors, the '' caesares'' ...
, it became part of the Provincia Insularum, in the diocese of ''Asiana'' in the eastern empire's pretorian prefecture of ''Oriens''.
Byzantine and Genoese Eras

 As a portion of the
As a portion of the Byzantine Empire
The Byzantine Empire, also referred to as the Eastern Roman Empire or Byzantium, was the continuation of the Roman Empire primarily in its eastern provinces during Late Antiquity and the Middle Ages, when its capital city was Constantinopl ...
, Samos became part of the namesake theme. After the 13th century, it passed through much the same changes of government as Chios
Chios (; el, Χίος, Chíos , traditionally known as Scio in English) is the fifth largest Greek island, situated in the northern Aegean Sea. The island is separated from Turkey by the Chios Strait. Chios is notable for its exports of masti ...
, and, like the latter island, became the property of the Genoese firm of Giustiniani (1346–1566; 1475 interrupted by an Ottoman period). It was also ruled by Tzachas
Tzachas ( gr, Τζαχᾶς, Tzachás), also known as Chaka Bey ( tr, Çaka Bey)"Tzachas" is the Hellenized form of a Turkish name which does not appear in any historical documents, but was likely "Chaka", "Chagha", or "Chaqan". The name "Chak ...
between 1081–1091.
Ottoman rule
 Samos came under Ottoman rule in 1475 or c. 1479/80, at which time the island was practically abandoned due to the effects of piracy and the plague. The island remained desolate for almost a full century before the Ottoman authorities, by now in secure control of the Aegean, undertook a serious effort to repopulate the island.
In 1572/3, the island was granted as a personal domain (''hass'') to Kilic Ali Pasha, the ''
Samos came under Ottoman rule in 1475 or c. 1479/80, at which time the island was practically abandoned due to the effects of piracy and the plague. The island remained desolate for almost a full century before the Ottoman authorities, by now in secure control of the Aegean, undertook a serious effort to repopulate the island.
In 1572/3, the island was granted as a personal domain (''hass'') to Kilic Ali Pasha, the ''Kapudan Pasha
The Kapudan Pasha ( ota, قپودان پاشا, modern Turkish: ), was the Grand Admiral of the navy of the Ottoman Empire. He was also known as the ( ota, قپودان دریا, links=no, modern: , "Captain of the Sea"). Typically, he was bas ...
'' (the Ottoman Navy's chief admiral). Settlers, including Greeks and Arvanites
Arvanites (; Arvanitika: , or , ; Greek: , ) are a bilingual population group in Greece of Albanian origin. They traditionally speak Arvanitika, an Albanian language variety, along with Greek. Their ancestors were first recorded as settl ...
from the Peloponnese and the Ionian Islands, as well as the descendants of the original inhabitants who had fled to Chios
Chios (; el, Χίος, Chíos , traditionally known as Scio in English) is the fifth largest Greek island, situated in the northern Aegean Sea. The island is separated from Turkey by the Chios Strait. Chios is notable for its exports of masti ...
, were attracted through the concession of certain privileges such as a seven-year tax exemption, a permanent exemption from the tithe
A tithe (; from Old English: ''teogoþa'' "tenth") is a one-tenth part of something, paid as a contribution to a religious organization or compulsory tax to government. Today, tithes are normally voluntary and paid in cash or cheques or more ...
in exchange for a lump annual payment of 45,000 piastres
The piastre or piaster () is any of a number of units of currency. The term originates from the Italian for "thin metal plate". The name was applied to Spanish and Hispanic American pieces of eight, or pesos, by Venetian traders in the Levant ...
, and a considerable autonomy in local affairs. The island recovered gradually, reaching a population of some 10,000 in the 17th century, which was still concentrated mostly in the interior. It was not until the mid-18th century that the coast began to be densely settled as well.
Under Ottoman rule, Samos ( Ottoman Turkish: سيسام ''Sisam'') came under the administration of the ''Kapudan Pasha''s Eyalet of the Archipelago
The Eyalet of the Archipelago ( ota, ایالت جزایر بحر سفید, ''Eyālet-i Cezāyir-i Baḥr-i Sefīd'', "Eyalet of the Islands of the White Sea") was a first-level province (eyalet) of the Ottoman Empire. From its inception until the ...
, usually as part of the Sanjak of Rhodes
The Sanjak of Rodos or Rhodes (Ottoman Turkish: ''Sancak-i/Liva-i Rodos''; el, λιβάς/σαντζάκι Ρόδου) was a second-level Ottoman province (''sanjak'' or '' liva'') encompassing the Dodecanese or Southern Sporades islands, with R ...
rather than as a distinct province. Locally, the Ottoman authorities were represented by a ''voevoda
Voivode (, also spelled ''voievod'', ''voevod'', ''voivoda'', ''vojvoda'' or ''wojewoda'') is a title denoting a military leader or warlord in Central, Southeastern and Eastern Europe since the Early Middle Ages. It primarily referred to the me ...
'', who was in charge of the fiscal administration, the '' kadi'' (judge), the island's Orthodox bishop and four notables representing the four districts of the island ( Vathy, Chora, Karlovasi
Karlovasi ( el, Καρλόβασι) is a town, a municipal unit, and a former municipality on the island of Samos, North Aegean, Greece. Since the 2019 local government reform it is part of the municipality West Samos, of which it is a municipal u ...
and Marathokampos
Marathokampos ( el, Μαραθόκαμπος) is a town, municipal unit, and a former municipality on the island of Samos, North Aegean, Greece. Since the 2019 local government reform it is part of the municipality West Samos, of which it is a muni ...
). Ottoman rule was interrupted during the Russo-Turkish War of 1768–1774, when the island came under Russian control in 1771–1774.
The Treaty of Küçük Kaynarca
The Treaty of Küçük Kaynarca ( tr, Küçük Kaynarca Antlaşması; russian: Кючук-Кайнарджийский мир), formerly often written Kuchuk-Kainarji, was a peace treaty signed on 21 July 1774, in Küçük Kaynarca (today Kayn ...
that concluded the war contained clauses that enabled a great expansion of the commercial activities of the Ottoman Empire's Greek Orthodox population. Samian merchants also took advantage of this, and an urban mercantile class based on commerce and shipping began to grow. The Samian merchants' voyages across the Mediterranean, as well as the settlement of Greeks from the Ionian Islands (which in 1797 had passed from Venice to the French Republic), introduced to Samos the progressive ideas of the Age of Enlightenment
The Age of Enlightenment or the Enlightenment; german: Aufklärung, "Enlightenment"; it, L'Illuminismo, "Enlightenment"; pl, Oświecenie, "Enlightenment"; pt, Iluminismo, "Enlightenment"; es, La Ilustración, "Enlightenment" was an intel ...
and of the French Revolution
The French Revolution ( ) was a period of radical political and societal change in France that began with the Estates General of 1789 and ended with the formation of the French Consulate in coup of 18 Brumaire, November 1799. Many of its ...
, and led to the formation of two rival political parties, the progressive-radical ''Karmanioloi'' ("Carmagnoles", named after the French Revolutionary song ''Carmagnole
"La Carmagnole" is the title of a French song created and made popular during the French Revolution, accompanied by a wild dance of the same name that may have also been brought into France by the Piedmontese. It was first sung in August 1792 and ...
'') and the reactionary ''Kallikantzaroi'' ("goblins
A goblin is a small, grotesque, monstrous creature that appears in the folklore of multiple European cultures. First attested in stories from the Middle Ages, they are ascribed conflicting abilities, temperaments, and appearances depending on t ...
") who represented mostly the traditional land-holding elites. Under the leadership of Lykourgos Logothetis
Lykourgos Logothetis ( el, Λυκούργος Λογοθέτης, 10 February 1772 – 25 May 1850 (O.S.)), born Georgios Paplomatas, was a Samian who became the island's leader during the Greek War of Independence.
The son of a wealthy mercha ...
, in 1807 the ''Karmanioloi'' gained power in the island, introducing liberal and democratic principles and empowering the local popular assembly at the expense of the land-holding notables. Their rule lasted until 1812, when they were overthrown by the Ottoman authorities and their leaders expelled from the island.
Greek Revolution
Samos
Samos (, also ; el, Σάμος ) is a Greece, Greek island in the eastern Aegean Sea, south of Chios, north of Patmos and the Dodecanese, and off the coast of western Turkey, from which it is separated by the -wide Mycale Strait. It is also a se ...
and at Gerontas averted the threat of an invasion, and again in summer 1826. In 1828, the island became formally incorporated into the Hellenic State under Governor Ioannis Kapodistrias
Count Ioannis Antonios Kapodistrias (10 or 11 February 1776 – 9 October 1831), sometimes anglicized as John Capodistrias ( el, Κόμης Ιωάννης Αντώνιος Καποδίστριας, Komis Ioannis Antonios Kapodistrias; russian: � ...
, as part of the province of the Eastern Sporades
Eastern Sporades (Greek: ''Ανατολικές Σποράδες'') or Eastern Islands (Greek: ''Ανατολικοί Νήσοι'') was the name of one of the thirteen divisions (administrative districts) created in 1828 with the administrative div ...
, but the London Protocol of 1830
The 1830 Protocol of London was a treaty signed between the Kingdom of France, the Russian Empire, and the United Kingdom of Great Britain and Ireland on February 3, 1830. It was the first official, international diplomatic act recognizing Greec ...
excluded Samos from the borders of the independent Greek state.
The Samians refused to accept their re-subordination to the Sultan, and Logothetis declared Samos to be an independent state, governed as before under the provisions of the 1821 constitution. Finally, due to the pressure of the Great Powers, Samos was declared an autonomous, tributary principality under Ottoman suzerainty. The Samians still refused to accept this decision until an Ottoman fleet enforced it in May 1834, forcing the revolutionary leadership and a part of the population to flee to independent Greece, where they settled near Chalkis
Chalcis ( ; Ancient Greek & Katharevousa: , ) or Chalkida, also spelled Halkida (Modern Greek: , ), is the chief town of the island of Euboea or Evia in Greece, situated on the Euripus Strait at its narrowest point. The name is preserved from ...
.
Autonomous Principality
Principality of Samos
The Principality of Samos ( el, Ηγεμονία της Σάμου, ; ota, Sisam İmâreti, script=Latn, italic=yes; tr, Sisam Beyliği) was an autonomous tributary state of the Ottoman Empire from 1834 to 1912. The island of Samos participated ...
, a semi-independent state tributary to Ottoman Turkey, paying the annual sum of £2,700. It was governed by a Christian of Greek descent though nominated by the Porte, who bore the title of "Prince." The prince was assisted in his function as chief executive by a 4-member senate. These were chosen by him out of eight candidates nominated by the four districts of the island: Vathy, Chora, Marathokampos, and Karlovasi. The legislative power belonged to a chamber of 36 deputies, presided over by the Greek Orthodox Metropolitan. The seat of the government was the port of Vathý.
The modern capital of the island was, until the early 20th century, at Chora, about from the sea and from the site of the ancient city.
After reconsidering political conditions, the capital was moved to Vathy, at the head of a deep bay on the North coast. This became the residence of the prince and the seat of government.
Since then a new town has grown, with a harbour.
Modern era

Kingdom of Greece
The Kingdom of Greece ( grc, label= Greek, Βασίλειον τῆς Ἑλλάδος ) was established in 1832 and was the successor state to the First Hellenic Republic. It was internationally recognised by the Treaty of Constantinople, wh ...
in March 1913, five months after the outbreak of the First Balkan War
The First Balkan War ( sr, Први балкански рат, ''Prvi balkanski rat''; bg, Балканска война; el, Αʹ Βαλκανικός πόλεμος; tr, Birinci Balkan Savaşı) lasted from October 1912 to May 1913 and invo ...
. Although other Aegean islands had been quickly captured by the Greek Navy
The Hellenic Navy (HN; el, Πολεμικό Ναυτικό, Polemikó Naftikó, War Navy, abbreviated ΠΝ) is the naval force of Greece, part of the Hellenic Armed Forces. The modern Greek navy historically hails from the naval forces of vari ...
, Samos was initially left to its existing ''status quo'' out of a desire not to upset the Italians in the nearby Dodecanese. The Greek fleet landed troops on the island in March 1913. The clashes with the Ottoman garrison were short-lived as the Ottomans withdrew to the Anatolian mainland, so that the island was securely in Greek hands by 16th March.
King George II visited Samos in 1937 during the 4th of August Regime
The 4th of August Regime ( el, Καθεστώς της 4ης Αυγούστου, Kathestós tis tetártis Avgoústou), commonly also known as the Metaxas regime (, ''Kathestós Metaxá''), was a totalitarian regime under the leadership of Gener ...
.
During World War II
World War II or the Second World War, often abbreviated as WWII or WW2, was a world war that lasted from 1939 to 1945. It involved the vast majority of the world's countries—including all of the great powers—forming two opposing ...
, the island was occupied
' (Norwegian: ') is a Norwegian political thriller TV series that premiered on TV2 on 5 October 2015. Based on an original idea by Jo Nesbø, the series is co-created with Karianne Lund and Erik Skjoldbjærg. Season 2 premiered on 10 October ...
by the Italians in May 1941, with the 6th Infantry Division "Cuneo" being stationed on the island. During the winter of 1941–42 Samos was affected by the Great Famine which killed 2,000 Samiots and forced thousands more to flee the island for the Middle East. In December 1942, local communists founded a branch of ELAS
The Greek People's Liberation Army ( el, Ελληνικός Λαϊκός Απελευθερωτικός Στρατός (ΕΛΑΣ), ''Ellinikós Laïkós Apeleftherotikós Stratós'' (ELAS) was the military arm of the left-wing National Liberat ...
resistance organization, the following month the resistance came into contact with the British military who provided them with material support. In spring 1943, the Cuneo Division launched an unsuccessful, two-month-long counter-insurgency operation in Karvouni. In June 1943, ELAS came into contact with the anti-fascist organization within the Cuneo Division resulting in an unofficial two-month truce between the two sides. After the Fall of the Fascist regime in Italy on 25 July, Pietro Badoglio
Pietro Badoglio, 1st Duke of Addis Abeba, 1st Marquess of Sabotino (, ; 28 September 1871 – 1 November 1956), was an Italian general during both World Wars and the first viceroy of Italian East Africa. With the fall of the Fascist regime ...
replaced division commander Mario Soldarelli with Lieutenant General Pierola and reinforced the Samos garrison with 1,500 Blackshirts
The Voluntary Militia for National Security ( it, Milizia Volontaria per la Sicurezza Nazionale, MVSN), commonly called the Blackshirts ( it, Camicie Nere, CCNN, singular: ) or (singular: ), was originally the paramilitary wing of the Nation ...
. Pierola then launched another counter-insurgency operation in Kerkis, which resulted in the death of 40 resistance members. Following the Italian surrender in September 1943, the Cuneo Division joined forces with ELAS in arresting local collaborationists and freeing jailed resistance fighters. Samos was briefly taken over by the Sacred Band and British forces, but following the Allied defeat in the Battle of Leros
The Battle of Leros was the central event of the Dodecanese campaign of the Second World War, and is widely used as an alternate name for the whole campaign. After the Armistice of Cassibile the Italian garrison on the Greek island Leros was str ...
and a fierce aerial bombardment of Vathy and Tigani, the island was abandoned by most of the ELAS members, the anti-fascist Italians and the Allied troops and taken over by Germans without a fight. The Germans then destroyed the harbors of Karlovasos and Ormos Marathokampos with explosives. On 15 September 1944, an Allied aerial bombardment destroyed the German ship "Aslan" along with three support ships in the Vathy harbor. Upon the departure of the Germans, ELAS and a 120-man unit of the Sacred Band forced the remaining 1,000 Blackshirts to surrender; ending the island's occupation on 5 October 1944.
Many of the Samiot ELAS members that abandoned the island following its occupation by the Germans, enlisted in the Greek Armed Forces in the Middle East After the fall of Greece to the Axis powers in April–May 1941, elements of the Greek Armed Forces managed to escape to the British-controlled Middle East. There they were placed under the Greek government in exile, and continued the fight alongsi ...
, participated in the communist-led 1944 Greek naval mutiny and were subsequently imprisoned in British prison camps. Approximately 4,500 of them returned to the island after the end of the war. The anti-communist persecutions that came in the aftermath of the Treaty of Varkiza
The Treaty of Varkiza ( el, Συμφωνία της Βάρκιζας, also known as the Varkiza Pact or the Varkiza Peace Agreement) was signed in Varkiza (near Athens) on February 12, 1945 between the Greek Minister of Foreign Affairs and the Sec ...
led many former ELAS members to create self-defense militias which gradually evolved into the Samos branch of the Democratic Army of Greece
The Democratic Army of Greece (DAG; el, Δημοκρατικός Στρατός Ελλάδας - ΔΣΕ, Dimokratikós Stratós Elládas - DSE) was the army founded by the Communist Party of Greece during the Greek Civil War (1946–1949). At ...
(DSE). The Samiot DSE drew manpower from nearby Icaria
Icaria, also spelled Ikaria ( el, Ικαρία), is a Greek island in the Aegean Sea, 10 nautical miles (19 km) southwest of Samos. According to tradition, it derives its name from Icarus, the son of Daedalus in Greek mythology, who was be ...
which was a notable place of internal exile for Greek communists, it was also able to capture large quantities of weapons and ammunition abandoned by the Italians during World War II. During the course of the Greek Civil War
The Greek Civil War ( el, ο Eμφύλιος �όλεμος}, ''o Emfýlios'' 'Pólemos'' "the Civil War") took place from 1946 to 1949. It was mainly fought against the established Kingdom of Greece, which was supported by the United Kingdom and ...
, Samos became one of the biggest centers of DSE resistance outside of the Greek mainland. The last DSE unit surrendered in Kerkis on 26 August 1949, the defeat of the communist resistance was followed by a celebratory visit of the Greek royal family
The Greek royal family (Greek: Ελληνική Βασιλική Οικογένεια) is a branch of the Danish royal family, itself a branch of the House of Glücksburg, that reigned in Greece from 1863 to 1924 and again from 1935 to 1973. It ...
on 15 October 1949. A total of 197 Samiot DSE fighters were killed during the course of the civil war.
On August 3, 1989, a Short 330
The Short 330 (also SD3-30) is a small turboprop transport aircraft produced by Short Brothers. It seats up to 30 people and was relatively inexpensive and had low maintenance costs at the time of its introduction in 1976. The 330 was based on ...
aircraft of the Olympic Airways (now Olympic Airlines
Olympic Airlines ( el, Ολυμπιακές Αερογραμμές, ''Olympiakés Aerogrammés'' – OA), formerly named Olympic Airways for at least four decades, was the flag carrier airline of Greece. The airline's head office was located ...
) crashed near Samos Airport; 31 passengers and the crew died.
A substantial migrant camp has been developed on the island at the site of a Greek military camp at Vathy to cope with the influx of migrants crossing the strait between the island and the Turkish mainland. It is estimated that in April 2020 the Vathy camp held 6,800 migrants, ten times the number it was originally designed for. The presence of large numbers of migrants on the Greek islands has caused tensions and some civil unrest on the part of island residents and migrants being kept in camps. In 2020, the Greek government announced a new closed reception centre will be built near the village of Zervou to replace the current temporary open camps by 2021.
On October 30 2020, a magnitude 7.0 earthquake struck offshore near the island, triggering a tsunami. Samos recorded two deaths with some churches and buildings in Ano Vathy and Karlovasi
Karlovasi ( el, Καρλόβασι) is a town, a municipal unit, and a former municipality on the island of Samos, North Aegean, Greece. Since the 2019 local government reform it is part of the municipality West Samos, of which it is a municipal u ...
damaged, however, neighbouring Turkey suffered 117 deaths.
Government
Samos is a separate regional unit of theNorth Aegean
The North Aegean Region ( el, Περιφέρεια Βορείου Αιγαίου, translit=Periféria Voríou Eyéou, ) is one of the thirteen administrative regions of Greece, and the smallest of the thirteen by population. It comprises the isla ...
region, and since 2019 it consists of two municipalities
A municipality is usually a single administrative division having corporate status and powers of self-government or jurisdiction as granted by national and regional laws to which it is subordinate.
The term ''municipality'' may also mean the go ...
: East Samos and West Samos
West Samos ( el, Δυτική Σάμος ''Dytiki Samos'') is a municipality on the island of Samos in the North Aegean region in Greece. The municipality was formed at the 2019 local government reform, when the pre-existing municipality of Samos ...
. Between the 2011 Kallikratis government reform and 2019, there was one single municipality on the island: Samos, created out of the 4 former municipalities on the island. At the same reform, the regional unit Samos was created out of part of the former Samos Prefecture
Samos Prefecture ( el, Νομός Σάμου) was a prefecture in Greece, consisting of the islands of Samos, Ikaria and the smaller islands of Fournoi Korseon. In 2011 the prefecture was abolished and the territory is now covered by the regional ...
.
The municipality of East Samos consists of the following municipal units (former municipalities):
*Pythagoreio
Pythagoreio ( el, Πυθαγόρειο) is a town and municipal unit on the island of Samos, North Aegean, Greece. Before the 2011 local government reform, Pythagoreio was a municipality. Since 2019, it is a municipal unit of East Samos. In 2011, ...
* Vathy
The municipality of West Samos consists of the following municipal units:
*Karlovasi
Karlovasi ( el, Καρλόβασι) is a town, a municipal unit, and a former municipality on the island of Samos, North Aegean, Greece. Since the 2019 local government reform it is part of the municipality West Samos, of which it is a municipal u ...
*Marathokampos
Marathokampos ( el, Μαραθόκαμπος) is a town, municipal unit, and a former municipality on the island of Samos, North Aegean, Greece. Since the 2019 local government reform it is part of the municipality West Samos, of which it is a muni ...
Samos has a sister town called Samo
Samo (–) founded the first recorded political union of Slavic tribes, known as Samo's Empire (''realm'', ''kingdom'', or ''tribal union''), stretching from Silesia to present-day Slovakia, ruling from 623 until his death in 658. According to ...
, which is located in Calabria, Italy
Italy ( it, Italia ), officially the Italian Republic, ) or the Republic of Italy, is a country in Southern Europe. It is located in the middle of the Mediterranean Sea, and its territory largely coincides with the homonymous geographical ...
.
Province
The province of Samos ( el, Επαρχία Σάμου) was one of theprovinces
A province is almost always an administrative division within a country or state. The term derives from the ancient Roman '' provincia'', which was the major territorial and administrative unit of the Roman Empire's territorial possessions ou ...
of the Samos Prefecture. It had the same territory as the present regional unit. It was abolished in 2006.
Economy

 The Samian economy depends mainly on agriculture and the tourist industry which was growing steadily since the early 1980s and reached a peak at the end of the 1990s. The main agricultural products include
The Samian economy depends mainly on agriculture and the tourist industry which was growing steadily since the early 1980s and reached a peak at the end of the 1990s. The main agricultural products include grapes
A grape is a fruit, botanically a berry, of the deciduous woody vines of the flowering plant genus ''Vitis''. Grapes are a non- climacteric type of fruit, generally occurring in clusters.
The cultivation of grapes began perhaps 8,000 years ago, ...
, honey
Honey is a sweet and viscous substance made by several bees, the best-known of which are honey bees. Honey is made and stored to nourish bee colonies. Bees produce honey by gathering and then refining the sugary secretions of plants (primar ...
, olives
The olive, botanical name ''Olea europaea'', meaning 'European olive' in Latin, is a species of small tree or shrub in the family Oleaceae, found traditionally in the Mediterranean Basin. When in shrub form, it is known as ''Olea europaea'' 'M ...
, olive oil, citrus
''Citrus'' is a genus of flowering trees and shrubs in the rue family, Rutaceae. Plants in the genus produce citrus fruits, including important crops such as oranges, lemons, grapefruits, pomelos, and limes. The genus ''Citrus'' is native to ...
fruit, dried figs
The fig is the edible fruit of ''Ficus carica'', a species of small tree in the flowering plant family Moraceae. Native to the Mediterranean and western Asia, it has been cultivated since ancient times and is now widely grown throughout the world ...
, almonds and flowers. The Muscat grape
The Muscat family of grapes includes over 200 grape varieties belonging to the ''Vitis vinifera'' species that have been used in wine production and as raisin and table grapes around the globe for many centuries. Their Wine color, colors range ...
is the main crop used for wine production. Samian wine is also exported under several other appellations.
Cuisine
Local specialities: *''Bourekia'' (Börek
Börek or burek are a family of pastries or pies found in the Balkans, Middle East and Central Asia. The pastry is made of a thin flaky dough such as filo with a variety of fillings, such as meat, cheese, spinach or potatoes. Boreks are mainly ...
)
*''Katimeria''
*'' Armogalo'' cheese
*''Katádes'' (dessert)
*''Moustalevria
Mustalevria ( el, μουσταλευριά) or must jelly (also mustpie and mustcake) is a traditional Greek kind of pudding made of grape must mixed with flour and boiled until thick. Moustokouloura, must biscuits or must cookies is the biscuit (c ...
'' (dessert)
*''Muscat of Samos'' (wine)
*''Tiganites'' (pancakes)
UNESCO

UNESCO
The United Nations Educational, Scientific and Cultural Organization is a specialized agency of the United Nations (UN) aimed at promoting world peace and security through international cooperation in education, arts, sciences and culture. It ...
World Heritage Site
A World Heritage Site is a landmark or area with legal protection by an international convention administered by the United Nations Educational, Scientific and Cultural Organization (UNESCO). World Heritage Sites are designated by UNESCO for h ...
s of the Heraion of Samos
The Heraion of Samos was a large sanctuary to the goddess Hera, on the island of Samos, Greece, 6 km southwest of the ancient city of Samos (modern Pythagoreion). It was located in the low, marshy basin of the Imbrasos river, near where it ...
and the Pythagoreion
The Pythagoreion is the archaeological site of the ancient town of Samos in Samos, Greece. It is located in the area of the modern town of Pythagoreio, from which it has got its modern name. The archaeological site contains ancient Greek and Roma ...
which were inscribed in UNESCO's World Heritage list in 1992.
Notable people
Ancient
*Aegles
Aegles (Ancient Greek
Ancient Greek includes the forms of the Greek language used in ancient Greece and the ancient world from around 1500 BC to 300 BC. It is often roughly divided into the following periods: Mycenaean Greek (), Dark ...
, athlete
*Aeschrion of Samos
Aeschrion ( Gr. ) was an iambic poet, and a native of Samos. He is mentioned by Athenaeus, who has preserved some choliambic verses of his, in which he defends the Samian Philaenis, claiming that the popular sex manual attributed to her was real ...
, poet
*Aesop
Aesop ( or ; , ; c. 620–564 BCE) was a Greek fabulist and storyteller credited with a number of fables now collectively known as ''Aesop's Fables''. Although his existence remains unclear and no writings by him survive, numerous tales c ...
, storyteller
* Aethlius (writer)
*Agatharchus
Agatharchus or Agatharch ( grc, Ἀγάθαρχος) was a self-taught painter from Samos, who lived in the 5th century BC. His father was named Eudemos (Εὔδημος).
He is said by Vitruvius to have invented scenic painting, and to have pain ...
, painter
* Agathocles (writer)
* Aristarchus of Samos (3rd century BC), astronomer and mathematician, the first known individual to propose that the Earth revolves around the Sun.
*Asclepiades of Samos Asclepiades of Samos (Sicelidas) ( el, Ἀσκληπιάδης ὁ Σάμιος; born c. 320 BC) was an ancient Greek epigrammatist and lyric poet who flourished around 270 BC. He was a friend of Hedylus and possibly of Theocritus. He may have bee ...
, epigrammist and poet
* Asius of Samos, poet
*Conon of Samos
Conon of Samos ( el, Κόνων ὁ Σάμιος, ''Konōn ho Samios''; c. 280 – c. 220 BC) was a Greek astronomer and mathematician. He is primarily remembered for naming the constellation Coma Berenices.
Life and work
Conon was born on Samos ...
, astronomer and mathematician
* Creophylus of Samos, legendary singer
*Duris of Samos
Duris of Samos (or Douris) ( grc-gre, Δοῦρις ὁ Σάμιος; BCafter 281BC) was a Greek historian and was at some period tyrant of Samos. Duris was the author of a narrative history of events in Greece and Macedonia from 371BC to 281BC, ...
(4th-3rd century BC), historian
* Epicurus (4th century BC), philosopher, founder of the Epicurean school of philosophy
* Melissus of Samos, philosopher
*Nicaenetus of Samos Nicaenetus of Samos ( el, Νικαίνετος ο Σάμιος) was a Greek epic and epigrammatic poet of the 3rd century BC. He was either an Abderite who lived in Samos
Samos (, also ; el, Σάμος ) is a Greece, Greek island in the easte ...
, poet
*Philaenis
Philaenis of Samos was supposedly the author of a famous ancient sex manual. According to a surviving fragment of a treatise which claims to have been written by her, she was from Samos, and her father was called Ocymenes. However, many modern s ...
(4th-3rd century BC), courtesan and writer
*Polycrates
Polycrates (; grc-gre, Πολυκράτης), son of Aeaces, was the tyrant of Samos from the 540s BC to 522 BC. He had a reputation as both a fierce warrior and an enlightened tyrant.
Sources
The main source for Polycrates' life and activit ...
(6th century BC), tyrant of Samos
*Pythagoras
Pythagoras of Samos ( grc, Πυθαγόρας ὁ Σάμιος, Pythagóras ho Sámios, Pythagoras the Samian, or simply ; in Ionian Greek; ) was an ancient Ionian Greek philosopher and the eponymous founder of Pythagoreanism. His politi ...
(6th century BC), philosopher, mathematician, and religious leader, after whom the Pythagorean theorem is named.
*Telauges
Telauges ( el, Τηλαύγης; fl. c. 500 BC) was a Samian Pythagorean philosopher and, according to tradition, the son of Pythagoras and Theano. Little is known about his life and works other than a scattering of remarks from much later writer ...
, philosopher
*Pythagoras (sculptor)
Pythagoras of Samos or Pythagoras of Rhegion (Ancient Greek: , fl. 5th century BC) was a sculptor from Samos whom Pliny the Elder expressly distinguishes from the more renowned Pythagoras the mathematician, from Rhegium. Pliny does however say th ...
*Rhoecus Rhoecus (or Rhaecus, Rhœcus, Rhæcus, Rhoikos) ( grc, Ῥοῖκός) was a Samian sculptor of the 6th century BCE. He and his son Theodorus were especially noted for their work in bronze. Herodotus says that Rhoecus built the temple of Hera at ...
(6th century BC), sculptor
* Telesarchus of Samos (6th century BC), aristocrat
* Theodorus (6th century BC), sculptor and architect
* Theon of Samos, painter
Modern
*Lykourgos Logothetis
Lykourgos Logothetis ( el, Λυκούργος Λογοθέτης, 10 February 1772 – 25 May 1850 (O.S.)), born Georgios Paplomatas, was a Samian who became the island's leader during the Greek War of Independence.
The son of a wealthy mercha ...
(1772–1850), leader of the Samians during the revolution of 1821
*Ion Ghica
Ion Ghica (; 12 August 1816 – 7 May 1897) was a Romanian statesman, mathematician, diplomat and politician, who was Prime Minister of Romania five times. He was a full member of the Romanian Academy and its president many times (1876–1882, ...
(1816–1897), Romanian revolutionary, mathematician, diplomat, prime minister of Romania, first president of the Romanian Academy, prince of Samos
*Themistoklis Sofoulis
Themistoklis Sofoulis or Sophoulis (; 24 November 1860 – 24 June 1949) was a prominent centrist and liberal Greek politician from Samos Island, who served three times as Prime Minister of Greece, with the Liberal Party, which he led for many ...
(1860–1949), politician, Prime Minister of Greece
*Kostas Roukounas
Konstantinos (Kostas) Roukounas ( el, Κώστας Ρούκουνας) (Principality of Samos, 1903 – Athens, 11 March 1984) was a Greek singer. His repertoire included both "traditional" (''δημοτικά'') and "popular" songs (''λαϊκά' ...
(1903-1984), singer of Rebetika
Rebetiko ( el, ρεμπέτικο, ), plural rebetika ( ), occasionally transliterated as rembetiko or rebetico, is a term used today to designate originally disparate kinds of urban Greek music which have come to be grouped together since the s ...
* Nikos Stavridis (1910–1987), actor
*Nerses Ounanian
Nerses Ounanian ( hy, Ներսէս Ունանեան) (1 August 1924 in Samos
Samos (, also ; el, Σάμος ) is a Greece, Greek island in the eastern Aegean Sea, south of Chios, north of Patmos and the Dodecanese, and off the coast of western ...
(1924-1957), Armenian-Uruguayan sculptor
Gallery
See also
* 1904 Samos earthquake *Xenophon
Xenophon of Athens (; grc, Ξενοφῶν ; – probably 355 or 354 BC) was a Greek military leader, philosopher, and historian, born in Athens. At the age of 30, Xenophon was elected commander of one of the biggest Greek mercenary armies o ...
*Ancient regions of Anatolia
The following is a list of regions of Ancient Anatolia, also known as "Asia Minor," in the present day Anatolia region of Turkey in Western Asia.
Late Bronze Age regions (circa 1200 BC)
* Alasiya / Alashiya (later Cyprus in the Classical Age, ...
Notes
References
;Attribution * *Further reading
; Ancient sources *Herodotus, especially book iii. *Strabo xiv. pp. 636–639 *Thucydides, especially books i. and viii. *Xenophon, Hellenica, books i. ii. ;Modern texts *A. Agelarakis, "Anthropologic Results: The Geometric Period Necropolis at Pythagoreion". ''Archival Report''. Samos Island Antiquities Authority, Greece, (2003). *J. P. Barron, ''The Silver Coins of Samos'' (London, 1966). *J. Boehlau, ''Aus ionischen and italischen Nekropolen'' (Leipzig, 1898). (E. H. B.; M. 0. B. C.; E. Ga.). *C. Curtius, ''Urkunden zur Geschichte von Samos'' (Wesel, 1873). *P. Gardner, ''Samos and Samian Coins'' (London, 1882). *V. Guérin, ''Description de l'île de Patmos et de l'île de Samos'' (Paris, 1856). *K. Hallof and A. P. Matthaiou (eds), ''Inscriptiones Chii et Sami cum Corassiis Icariaque'' (Inscriptiones Graecae, xii. 6. 1–2). 2 vols. (Berolini–Novi Eboraci: de Gruyter, 2000; 2004). *B. V. Head, ''Historia Numorum'' (Oxford, 1887), pp. 515–518. *L. E. Hicks and G. F. Hill, ''Greek Historical Inscriptions'' (Oxford, 1901), No. 81. *H. Kyrieleis, ''Führer durch das Heraion von Samos'' (Athen, 1981). *T. Panofka, ''Res Samiorum'' (Berlin, 1822). *Pauly-Wissowa (in German, on Antiquity) *T. J. Quinn, ''Athens and Samos, Chios and Lesbos'' (Manchester, 1981). *G. Shipley, ''A History of Samos 800–188 BC'' (Oxford, 1987). *R. Tölle-Kastenbein, ''Herodot und Samos'' (Bochum, 1976). *H. F. Tozer, ''Islands of the Aegean'' (London, 1890). *K. Tsakos, ''Samos: A Guide to the History and Archaeology'' (Athens, 2003). *H. Walter, ''Das Heraion von Samos'' (München, 1976). *Westermann, ''Großer Atlas zur Weltgeschichte'' (in German) ;Volumes of the ''Samos'' series of archaeological reports published by the Deutsches Archäologisches Institut. *1. V. Milojčić, ''Die prähistorische Siedlung unter dem Heraion'' (Bonn, 1961). *2. R. C. S. Felsch, ''Das Kastro Tigani'' (Bonn, 1988). *3. A. E. Furtwängler, ''Der Nordbau im Heraion von Samos'' (Bonn, 1989). *4. H. P. Isler, ''Das archaische Nordtor und seine Umgebung im Heraion von Samos'' (Bonn, 1978). *5. H. Walter, ''Frühe samische Gefäße'' (Bonn, 1968). *6.1. E. Walter-Karydi, ''Samische Gefäße des 6. Jahrhunderts v. Chr.'' (Bonn, 1973). *7. G. Schmidt, ''Kyprische Bildwerke aus dem Heraion von Samos'' (Bonn, 1968). *8. U. Jantzen, ''Ägyptische und orientalische Bronzen aus dem Heraion von Samos'' (Bonn, 1972). *9. U. Gehrikg, with G. Schneider, ''Die Greifenprotomen aus dem Heraion von Samos'' (Bonn, 2004). *10. H. Kyrieleis, ''Der große Kuros von Samos'' (Bonn, 1996). *11. B. Freyer-Schauenburg, ''Bildwerke der archaischen Zeit und des strengen Stils'' (Bonn, 1974). *12. R. Horn, ''Hellenistische Bildwerke auf Samos'' (Bonn, 1972). *14. R. Tölle-Kastenbein, ''Das Kastro Tigani'' (Bonn, 1974). *15. H. J. Kienast, ''Die Stadtmauer von Samos'' (Bonn, 1978). *16. W. Martini, ''Das Gymnasium von Samos'' (Bonn, 1984). *17. W. Martini and C. Streckner, ''Das Gymnasium von Samos: das frühbyzantinische Klostergut'' (Bonn, 1993). *18. V. Jarosch, ''Samische Tonfiguren aus dem Heraion von Samos'' (Bonn, 1994). *19. H. J. Kienast, ''Die Wasserleitung des Eupalinos auf Samos'' (Bonn, 1995). *20. U. Jantzen with W. Hautumm, W.-R. Megow, M. Weber, and H. J. Kienast, ''Die Wasserleitung des Eupalinos: die Funde'' (Bonn, 2004). *22. B. Kreuzer, ''Die attisch schwarzfigurige Keramik aus dem Heraion von Samos'' (Bonn, 1998). *24.1. T. Schulz with H. J. Kienast, ''Die römischen Tempel im Heraion von Samos: die Prostyloi'' (Bonn, 2002). *25. C. Hendrich, ''Die Säulenordnung des ersten Dipteros von Samos'' (Bonn, 2007).External links
*Municipality of Samos
Visit Samos
{{Authority control * Ionian League Regional units of the North Aegean Provinces of Greece Islands of Greece Landforms of Samos Islands of the North Aegean Populated places in the ancient Aegean islands Populated places in ancient Ionia Wine regions of Greece