History of Palmyra Atoll on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
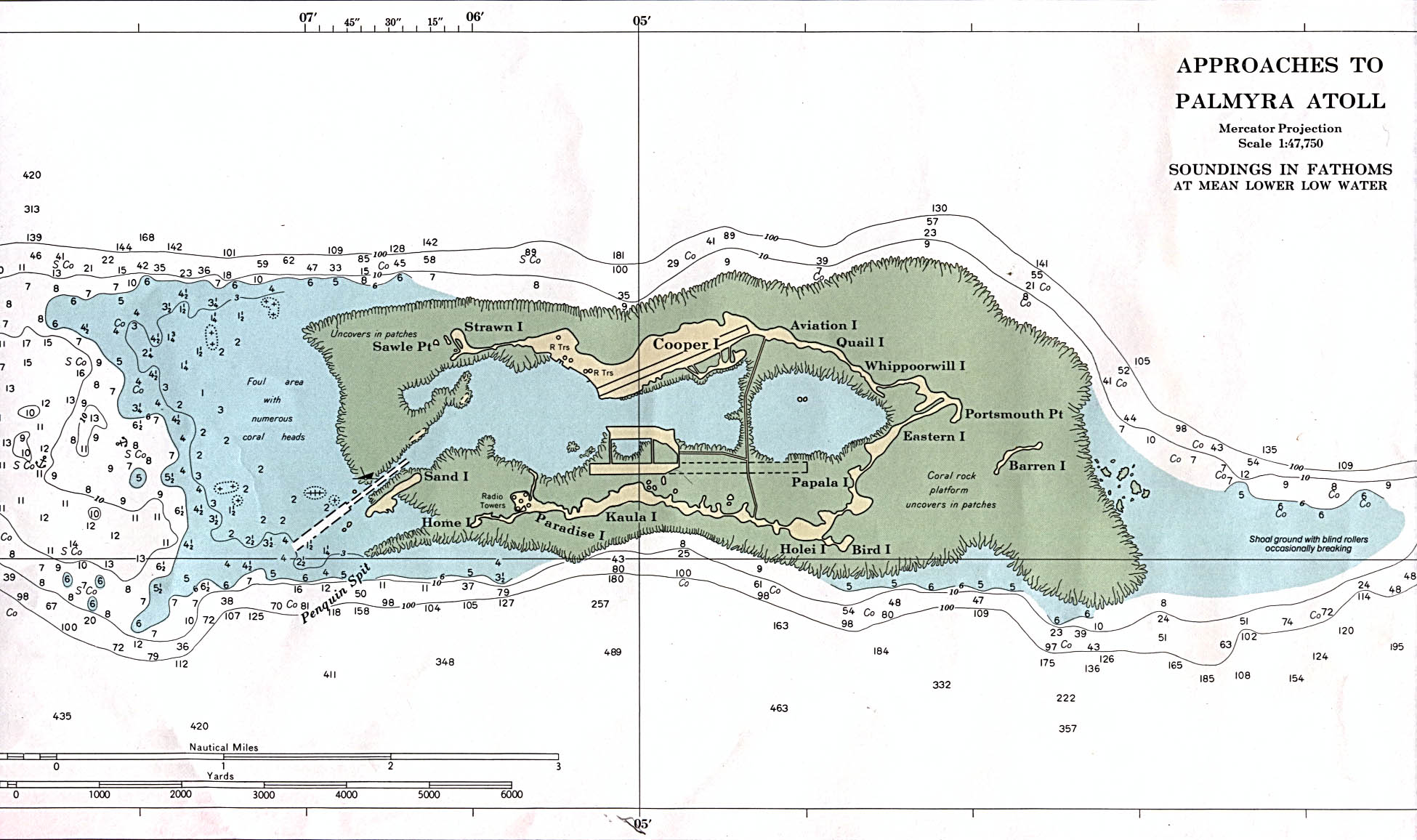
 Palmyra Atoll (), also referred to as Palmyra Island, is one of the Northern Line Islands (southeast of
Palmyra Atoll (), also referred to as Palmyra Island, is one of the Northern Line Islands (southeast of
Territories and Insular Possessions
File:Palmyra Atoll 2010-03-18, EO-1 ALI bands 5-4-3-1, 15m resolution.png, alt=A satellite image, Palmyra Atoll, 2010 satellite image
File:Strawn Island at Palmyra Atoll NWR (5123999194).jpg, alt=Coconut trees overlooking a small inlet, Coconut palms on Strawn Island at Palmyra Atoll

 The first known sighting of Palmyra came in 1798 aboard the American sealing ship ''Betsy'', on a voyage to Asia, according to the
The first known sighting of Palmyra came in 1798 aboard the American sealing ship ''Betsy'', on a voyage to Asia, according to the
/ref> Opening fire at 04:55 Greenwich Civil time, Civil Time, she fired twelve rounds from her deck gun, targeting the atoll's radio station, and hit the United States Army United States Army Corps of Engineers, Corps of Engineers dredge ''Sacramento'', which was anchored in the lagoon, with one shell. A coastal artillery Artillery battery, battery on the atoll returned fire, forcing ''I-75'' to submerge and withdraw. In the lobby of the "Transient Hotel" (built by the Seabees, and used by airmen on their way to the Pacific Ocean theater of World War II, Pacific Theater front), a mural was hung depicting a quiet island scene. It was painted by Academy Award-nominated art director William Glasgow (art director), William Glasgow, who served in the Army from 1943 to 1945, though it is unclear when he painted it and how it ended up on Palmyra. After World War II, much of the Naval Air Station was demolished, with some of the materials piled up and burned on the atoll, dumped into the lagoon, or in the case of unexploded ordnance on some islets, left in place.
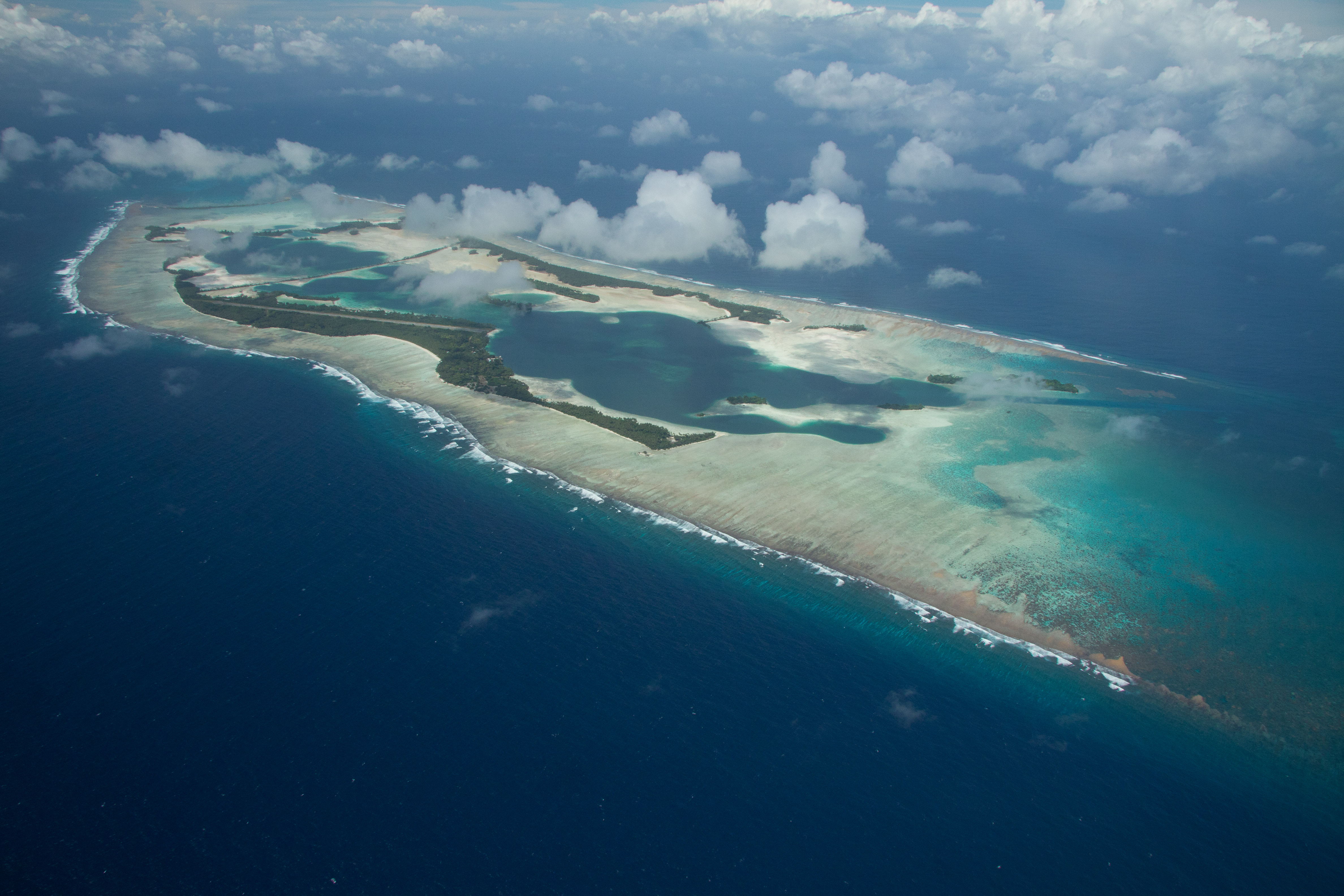 When Hawaii was admitted to the United States in 1959, Palmyra was explicitly separated from the new state, remaining a federal incorporated territory, to be administered by the secretary of the interior under a presidential Executive order (United States), executive order.
In 1962, the United States Department of Defense, Department of Defense used Palmyra as an observation site during several high-altitude nuclear weapons tests high above Johnston Atoll. A group of about ten men supported the observation posts during this series of tests, while about 40 people carried out the observations.
Alby Mangels, the Australian adventurer and documentary filmmaker of ''World Safari'', visited the atoll during his six-year trip in the 1970s.
In early 1979, the US government began exploring the idea of storing nuclear waste on remote Pacific islands, like Palmyra. Those who knew the island and the region saw no benefit to this idea, commenting on the devastating effects a leak of these storage tanks would create. By 1982 a formal proposal had been written which "analyzes the proposal to store spent nuclear fuel on Palmyra Island, a US territory nearly a thousand miles south of
When Hawaii was admitted to the United States in 1959, Palmyra was explicitly separated from the new state, remaining a federal incorporated territory, to be administered by the secretary of the interior under a presidential Executive order (United States), executive order.
In 1962, the United States Department of Defense, Department of Defense used Palmyra as an observation site during several high-altitude nuclear weapons tests high above Johnston Atoll. A group of about ten men supported the observation posts during this series of tests, while about 40 people carried out the observations.
Alby Mangels, the Australian adventurer and documentary filmmaker of ''World Safari'', visited the atoll during his six-year trip in the 1970s.
In early 1979, the US government began exploring the idea of storing nuclear waste on remote Pacific islands, like Palmyra. Those who knew the island and the region saw no benefit to this idea, commenting on the devastating effects a leak of these storage tanks would create. By 1982 a formal proposal had been written which "analyzes the proposal to store spent nuclear fuel on Palmyra Island, a US territory nearly a thousand miles south of
 On January 18, 2001, Secretary of the Interior Bruce Babbitt issued Secretary's Order No. 3224 designating Palmyra's tidal lands, submerged lands and surrounding waters out to from the water's edge as a National Wildlife Refug
On January 18, 2001, Secretary of the Interior Bruce Babbitt issued Secretary's Order No. 3224 designating Palmyra's tidal lands, submerged lands and surrounding waters out to from the water's edge as a National Wildlife Refug
Subsequently, the Department of the Interior published a regulation providing for the management of the refuge. 66 Fed. Reg. 7660-01 (January 24, 2001). The pertinent part of the regulation states: The conveyance to TNC from the Fullard-Leos in 2000 was subject to a preexisting commercial fishing licence. Then in 2001 the United States Secretary of the Interior, Secretary of the Interior banned commercial fishing near Palmyra but allowed sport fishing, as quoted above. In January 2007, the commercial fishing licensees sued the United States in the Court of Federal Claims alleging that, under the Takings Clause#Eminent domain, Takings Clause, the Interior Department regulation had "directly confiscated, taken, and rendered wholly and completely worthless" their purported property interests. The United States filed a motion to dismiss the lawsuit, and the court granted the motion. On April 9, 2009, the court's decision was affirmed by the Court of Appeals for the Federal Circuit.
In November 2005, TNC established a new research station on Palmyra to study global warming, coral reefs, invasive species and other environmental concerns.
The
The conveyance to TNC from the Fullard-Leos in 2000 was subject to a preexisting commercial fishing licence. Then in 2001 the United States Secretary of the Interior, Secretary of the Interior banned commercial fishing near Palmyra but allowed sport fishing, as quoted above. In January 2007, the commercial fishing licensees sued the United States in the Court of Federal Claims alleging that, under the Takings Clause#Eminent domain, Takings Clause, the Interior Department regulation had "directly confiscated, taken, and rendered wholly and completely worthless" their purported property interests. The United States filed a motion to dismiss the lawsuit, and the court granted the motion. On April 9, 2009, the court's decision was affirmed by the Court of Appeals for the Federal Circuit.
In November 2005, TNC established a new research station on Palmyra to study global warming, coral reefs, invasive species and other environmental concerns.
The
Palmyra Atoll National Wildlife Refuge
Palmyra Atoll photo gallery
by FWS
Overview
from the Department of the Interior
Island Conservation: Palmyra Atoll Restoration Project
The Nature Conservancy in Palmyra Atoll
Palmyra Atoll Research Consortium
{{authority control Palmyra Atoll, 1862 establishments in Hawaii Insular areas of the United States Integral overseas territories Island restoration Pacific islands claimed under the Guano Islands Act National Wildlife Refuges in the United States insular areas Nature Conservancy preserves Pacific Ocean atolls of the United States Pacific Remote Islands Marine National Monument Ramsar sites in the United States Uninhabited Pacific islands of the United States United States Minor Outlying Islands Important Bird Areas of United States Minor Outlying Islands Important Bird Areas of the Line Islands Closed installations of the United States Navy

 Palmyra Atoll (), also referred to as Palmyra Island, is one of the Northern Line Islands (southeast of
Palmyra Atoll (), also referred to as Palmyra Island, is one of the Northern Line Islands (southeast of Kingman Reef
Kingman Reef is a largely submerged, uninhabited, triangle-shaped reef, geologically an atoll, east-west and north-south, in the North Pacific Ocean, roughly halfway between the Hawaiian Islands and American Samoa. It has an area of 3 hectar ...
and north of Kiribati
Kiribati (), officially the Republic of Kiribati ( gil, ibaberikiKiribati),Kiribati
''The Wor ...
). It is located almost due south of the Hawaiian Islands, roughly one-third of the way between ''The Wor ...
Hawaii
Hawaii ( ; haw, Hawaii or ) is a state in the Western United States, located in the Pacific Ocean about from the U.S. mainland. It is the only U.S. state outside North America, the only state that is an archipelago, and the only state ...
and American Samoa
American Samoa ( sm, Amerika Sāmoa, ; also ' or ') is an unincorporated territory of the United States located in the South Pacific Ocean, southeast of the island country of Samoa. Its location is centered on . It is east of the Internationa ...
. North America is about northeast and New Zealand the same distance southwest, placing the atoll
An atoll () is a ring-shaped island, including a coral rim that encircles a lagoon partially or completely. There may be coral islands or cays on the rim. Atolls are located in warm tropical or subtropical oceans and seas where corals can gr ...
at the approximate center of the Pacific Ocean
The Pacific Ocean is the largest and deepest of Earth's five oceanic divisions. It extends from the Arctic Ocean in the north to the Southern Ocean (or, depending on definition, to Antarctica) in the south, and is bounded by the contin ...
. The land area is , with about 9 miles (14 km) of sea-facing coastline and reef. There is one boat anchorage known as West Lagoon, accessible from the sea by a narrow artificial channel.
It is the second-to-northernmost of the Line Islands, and one of three American islands in the archipelago, along with Jarvis Island
Jarvis Island (; formerly known as Bunker Island or Bunker's Shoal) is an uninhabited coral island located in the South Pacific Ocean, about halfway between Hawaii and the Cook Islands. It is an unincorporated, unorganized territory of the Un ...
and Kingman Reef
Kingman Reef is a largely submerged, uninhabited, triangle-shaped reef, geologically an atoll, east-west and north-south, in the North Pacific Ocean, roughly halfway between the Hawaiian Islands and American Samoa. It has an area of 3 hectar ...
. Palmyra Atoll is part of the Pacific Remote Islands Marine National Monument
The Pacific Remote Islands Marine National Monument is a group of unorganized, mostly unincorporated United States Pacific Island territories managed by the United States Fish and Wildlife Service of the United States Department of the Int ...
, the world's largest marine protected area. The atoll is composed of submerged sand flats along with dry land and reefs. It consists of three lagoons separated by coral reefs. The western reef terrace is one of the biggest shelf-reefs, with dimensions of . Over 150 species of coral inhabit Palmyra Atoll, double the number recorded in Hawaii
Hawaii ( ; haw, Hawaii or ) is a state in the Western United States, located in the Pacific Ocean about from the U.S. mainland. It is the only U.S. state outside North America, the only state that is an archipelago, and the only state ...
.
Palmyra Atoll has no permanent population. It is administered as an incorporated unorganized territory, presently the only one of its kind, by the U.S. Fish and Wildlife Service
The United States Fish and Wildlife Service (USFWS or FWS) is an agency within the United States Department of the Interior dedicated to the management of fish, wildlife, and natural habitats. The mission of the agency is "working with othe ...
of the U.S. Department of the Interior
The United States Department of the Interior (DOI) is one of the executive departments of the U.S. federal government headquartered at the Main Interior Building, located at 1849 C Street NW in Washington, D.C. It is responsible for the man ...
. The territory hosts a variable transient population of 4–25 staff and scientists employed by various departments of the U.S. government and by The Nature Conservancy
The Nature Conservancy (TNC) is a global environmental organization headquartered in Arlington, Virginia. it works via affiliates or branches in 79 countries and territories, as well as across every state in the US.
Founded in 1951, The Nat ...
, as well as a rotating mix of Palmyra Atoll Research Consortium scholars. Submerged portions of the atoll are administered by the Department of the Interior's Office of Insular Affairs
The Office of Insular Affairs (OIA) is a unit of the United States Department of the Interior that oversees federal administration of several United States insular areas. It is the successor to the Bureau of Insular Affairs of the War Departme ...
.Per U.S. Code
In the law of the United States, the Code of Laws of the United States of America (variously abbreviated to Code of Laws of the United States, United States Code, U.S. Code, U.S.C., or USC) is the official compilation and codification of the ...
Title 48Territories and Insular Possessions
Geography
The atoll consists of an extensivereef
A reef is a ridge or shoal of rock, coral or similar relatively stable material, lying beneath the surface of a natural body of water. Many reefs result from natural, abiotic processes— deposition of sand, wave erosion planing down rock o ...
, three shallow lagoon
A lagoon is a shallow body of water separated from a larger body of water by a narrow landform, such as reefs, barrier islands, barrier peninsulas, or isthmuses. Lagoons are commonly divided into ''coastal lagoons'' (or ''barrier lagoons'') ...
s, and a number of sand and reef-rock islet
An islet is a very small, often unnamed island. Most definitions are not precise, but some suggest that an islet has little or no vegetation and cannot support human habitation. It may be made of rock, sand and/or hard coral; may be permanen ...
s and bars covered with vegetation—mostly coconut palms, '' Scaevola'', and tall ''Pisonia
''Pisonia'' is a genus of flowering plants in the four o'clock flower family, Nyctaginaceae. It was named for Dutch physician and naturalist Willem Piso (1611–1678). Certain species in this genus are known as catchbirdtrees, birdcatcher trees o ...
'' trees.
Many of the islets are connected. Sand Island and the two Home Islets in the west; Quail, Whippoorwill, and Bunker Islands in the north; and Eastern, Fern, Bird and Barren Islands in the east are not. The largest island is Cooper Island in the north, followed by Kaula Island in the south. The northern arch of islets is formed by Strawn Island, Cooper Island (or Cooper-Meng Island since the original Cooper and Meng Islands were joined in 1940), Aviation Island, Quail Island, Whippoorwill Island, Bunker Island, followed in the east by Eastern Island, Papala Island and Pelican Island, and in the south by Bird Island, Holei Island, Engineer Island, Tanager Island, Marine Island, Kaula Island, Paradise Island, the Home Islets, and Sand Island (clockwise).
Palmyra Atoll is in the Samoa Time Zone
250px, SST is UTC-11:00
The Samoa Time Zone or Samoa Standard Time (SST) observes standard time by subtracting eleven hours from Coordinated Universal Time ( UTC-11:00). The clock time in this zone is based on the mean solar time of the 165t ...
(UTC−11:00), the same time zone
A time zone is an area which observes a uniform standard time for legal, commercial and social purposes. Time zones tend to follow the boundaries between countries and their subdivisions instead of strictly following longitude, because it ...
as American Samoa
American Samoa ( sm, Amerika Sāmoa, ; also ' or ') is an unincorporated territory of the United States located in the South Pacific Ocean, southeast of the island country of Samoa. Its location is centered on . It is east of the Internationa ...
, Midway Atoll, Kingman Reef
Kingman Reef is a largely submerged, uninhabited, triangle-shaped reef, geologically an atoll, east-west and north-south, in the North Pacific Ocean, roughly halfway between the Hawaiian Islands and American Samoa. It has an area of 3 hectar ...
and Jarvis Island
Jarvis Island (; formerly known as Bunker Island or Bunker's Shoal) is an uninhabited coral island located in the South Pacific Ocean, about halfway between Hawaii and the Cook Islands. It is an unincorporated, unorganized territory of the Un ...
.
Incorporated in the United States
In ''The Insular Cases'', the Supreme Court held incorporated territories to be integral parts of the United States, as opposed to mere possessions. The incorporated Palmyra Atoll is the southernmost point of the incorporated United States, with its southernmost shore at 5°52'15" Nlatitude
In geography, latitude is a coordinate that specifies the north– south position of a point on the surface of the Earth or another celestial body. Latitude is given as an angle that ranges from –90° at the south pole to 90° at the north pol ...
. U.S.-controlled territories such as American Samoa
American Samoa ( sm, Amerika Sāmoa, ; also ' or ') is an unincorporated territory of the United States located in the South Pacific Ocean, southeast of the island country of Samoa. Its location is centered on . It is east of the Internationa ...
(and the southernmost place, Rose Atoll
Rose Atoll, sometimes called Rose Island or Motu O Manu ("Bird Island") by people of the nearby Manu'a Islands, is an oceanic atoll within the U.S. territory of American Samoa. An uninhabited wildlife refuge, it is the southernmost point bel ...
) are farther south, but they are not incorporated territories.
Climate
Average annual rainfall is approximately per year. Temperatures average year round. The atoll has nearly the highest oceanicity index (i.e. degree to which its climate is affected by the sea) and one of the lowest diurnal and annual temperature variation of any place on earth. Nauru has more consistent nighttime temperatures with every month recording 77 °F (25 C) average, as well as more evenly spread precipitation.Official names
Although Palmyra is acoral atoll
Corals are marine invertebrates within the class Anthozoa of the phylum Cnidaria. They typically form compact colonies of many identical individual polyps. Coral species include the important reef builders that inhabit tropical oceans and secre ...
with several islet
An islet is a very small, often unnamed island. Most definitions are not precise, but some suggest that an islet has little or no vegetation and cannot support human habitation. It may be made of rock, sand and/or hard coral; may be permanen ...
s, not a single island, it has been called ''Palmyra Island'' since the first visit in 1802. More recently it is for some purposes called ''Palmyra Atoll''. The name of the federal territory retained by Congress
A congress is a formal meeting of the representatives of different countries, constituent states, organizations, trade unions, political parties, or other groups. The term originated in Late Middle English to denote an encounter (meeting of ...
since 1959 is ''Palmyra Island'', but the official name of the National Wildlife Refuge within the territory is ''Palmyra Atoll'', as is the corresponding division of the Pacific Remote Islands Marine National Monument
The Pacific Remote Islands Marine National Monument is a group of unorganized, mostly unincorporated United States Pacific Island territories managed by the United States Fish and Wildlife Service of the United States Department of the Int ...
. Formal deeds, leases and federal orders for land there call it ''Palmyra Island''. Further, the islets on the atoll are also named ''island'', such as Kaula Island, Cooper Island, and others.
Political status
Palmyra is anincorporated territory
Territories of the United States are sub-national administrative divisions overseen by the federal government of the United States. The various American territories differ from the U.S. states and tribal reservations as they are not sover ...
of the United States (the only such territory since 1959), meaning that it is subject to all provisions of the U.S. Constitution
The Constitution of the United States is the supreme law of the United States of America. It superseded the Articles of Confederation, the nation's first constitution, in 1789. Originally comprising seven articles, it delineates the nation ...
and is permanently under American sovereignty
Sovereignty is the defining authority within individual consciousness, social construct, or territory. Sovereignty entails hierarchy within the state, as well as external autonomy for states. In any state, sovereignty is assigned to the perso ...
. Palmyra remains an unorganized territory. No Act of Congress since Hawaii statehood
Hawaii ( ; haw, Hawaii or ) is a state in the Western United States, located in the Pacific Ocean about from the U.S. mainland. It is the only U.S. state outside North America, the only state that is an archipelago, and the only state ...
in 1959 has specified how Palmyra is to be governed. Palmyra has no permanent residents. In 2004 accommodations were built to support a small number of temporary inhabitants.
The only relevant federal law
Federal law is the body of law created by the federal government of a country. A federal government is formed when a group of political units, such as states or provinces join in a federation, delegating their individual sovereignty and many po ...
gives the president
President most commonly refers to:
*President (corporate title)
* President (education), a leader of a college or university
* President (government title)
President may also refer to:
Automobiles
* Nissan President, a 1966–2010 Japanese ...
the authority to administer Palmyra as directed, or via the United States District Court for the District of Hawaii
The United States District Court for the District of Hawaii (in case citations, D. Haw.) is the principal trial court of the United States Federal Court System in the state of Hawaii. The court's territorial jurisdiction encompasses the sta ...
(Hawaii Omnibus Act, Pub. L. 86–624, July 12, 1960, 74 Stat. 411). Executive Order 10967, effective 10 October 1961, provided that the Department of the Interior be responsible for all executive, legislative, and judicial authority of its civil administration.
The issue of governance is generally a moot point since no permanent population lives there. Cooper Island and ten other land parcels in this atoll are owned by The Nature Conservancy, Inc. (TNC), which manages them as a nature reserve. The southwesternmost islets, including Home, are owned by descendants of former Palmyra owner Henry Ernest Cooper
Henry Ernest Cooper (August 28, 1857 – May 15, 1929) was an American lawyer who moved to the Kingdom of Hawaii and became prominent in Hawaiian politics in the 1890s. He formally deposed Queen Lili'uokalani of Hawaii in 1893, held various offi ...
and others. The rest of Palmyra is federal land and waters under the jurisdiction of the U.S. Fish and Wildlife Service
The United States Fish and Wildlife Service (USFWS or FWS) is an agency within the United States Department of the Interior dedicated to the management of fish, wildlife, and natural habitats. The mission of the agency is "working with othe ...
. Since Palmyra has no state or local government, it is administered directly from Honolulu
Honolulu (; ) is the capital and largest city of the U.S. state of Hawaii, which is in the Pacific Ocean. It is an unincorporated county seat of the consolidated City and County of Honolulu, situated along the southeast coast of the island ...
by the U.S. Fish and Wildlife Service
The United States Fish and Wildlife Service (USFWS or FWS) is an agency within the United States Department of the Interior dedicated to the management of fish, wildlife, and natural habitats. The mission of the agency is "working with othe ...
, except for some submerged tracts administered by the Office of Insular Affairs
The Office of Insular Affairs (OIA) is a unit of the United States Department of the Interior that oversees federal administration of several United States insular areas. It is the successor to the Bureau of Insular Affairs of the War Departme ...
, both in the U.S. Department of the Interior
The United States Department of the Interior (DOI) is one of the executive departments of the U.S. federal government headquartered at the Main Interior Building, located at 1849 C Street NW in Washington, D.C. It is responsible for the man ...
. For all other purposes, Palmyra is counted as one of the U.S. minor outlying islands. They are outside of the customs territory A customs territory is a geographic territory with uniform customs regulations and there are no internal customs or similar taxes within the territory. Customs territories may fall into several types:
* A sovereign state, including a federation
* A ...
of the United States and have no customs duties.
Palmyra land was registered in Hawaii Land Court in 1912. In 1959, the rest of the federal Territory of Hawaii
The Territory of Hawaii or Hawaii Territory ( Hawaiian: ''Panalāʻau o Hawaiʻi'') was an organized incorporated territory of the United States that existed from April 30, 1900, until August 21, 1959, when most of its territory, excluding ...
, excluding Palmyra, became the state of Hawaii. Hawaii Land Court became a state court and lost jurisdiction over Palmyra land. Instead, Palmyra land documents are filed or recorded in federal court in Honolulu.Secretary of the Interior Order No. 2862, ''Palmyra Island Land Recordation'', March 19, 1962. F. R. Doc. 62-2736, , March 22, 1962.
Economy
The only current economic activity on Palmyra is paidecotourism
Ecotourism is a form of tourism involving responsible travel (using sustainable transport) to natural areas, conserving the environment, and improving the well-being of the local people. Its purpose may be to educate the traveler, to provide fund ...
visits by TNC donors. Most of the roads and causeways there were built during World War II
World War II or the Second World War, often abbreviated as WWII or WW2, was a world war that lasted from 1939 to 1945. It involved the vast majority of the world's countries—including all of the great powers—forming two opposing ...
. Most of these are now unserviceable and overgrown, and most causeways and many of the filled areas between islets have washed-away gaps. A unpaved airstrip
An aerodrome ( Commonwealth English) or airdrome (American English) is a location from which aircraft flight operations take place, regardless of whether they involve air cargo, passengers, or neither, and regardless of whether it is for pub ...
on Cooper Island (Palmyra (Cooper) Airport
Palmyra Atoll (), also referred to as Palmyra Island, is one of the Northern Line Islands (southeast of Kingman Reef and north of Kiribati). It is located almost due south of the Hawaiian Islands, roughly one-third of the way between Hawaii a ...
, ICAO code PLPA) was built for the Palmyra Island Naval Air Station before and during World War II.
A construction program in 2004 erected 16 two-person bungalows, a galley/dining area, several maintenance and storage facilities, and a communal block of toilets and showers for the temporary residents. Fresh water is collected from the roof of a 100,000 gallon above-ground concrete cistern in the center of the island. The communal buildings of the area on the southwestern coast of Cooper Island (the only occupied area of the atoll) consist of about a half dozen buildings next to a World War II-era steel ripple wharf, a former seaplane ramp now used as a boat launch ramp, and a more recently built floating dock.
Airport
Palmyra (Cooper) Airport is an unattendedairport
An airport is an aerodrome with extended facilities, mostly for commercial air transport. Airports usually consists of a landing area, which comprises an aerially accessible open space including at least one operationally active surfa ...
on Palmyra Atoll in the Pacific Ocean
The Pacific Ocean is the largest and deepest of Earth's five oceanic divisions. It extends from the Arctic Ocean in the north to the Southern Ocean (or, depending on definition, to Antarctica) in the south, and is bounded by the contin ...
. It is a private-use facility, originally built during World War II
World War II or the Second World War, often abbreviated as WWII or WW2, was a world war that lasted from 1939 to 1945. It involved the vast majority of the world's countries—including all of the great powers—forming two opposing ...
and now owned by The Nature Conservancy
The Nature Conservancy (TNC) is a global environmental organization headquartered in Arlington, Virginia. it works via affiliates or branches in 79 countries and territories, as well as across every state in the US.
Founded in 1951, The Nat ...
. It has one runway
According to the International Civil Aviation Organization (ICAO), a runway is a "defined rectangular area on a land aerodrome prepared for the landing and takeoff of aircraft". Runways may be a man-made surface (often asphalt, concre ...
(6/24) measuring ., effective 2007-08-30 When built, the airport was called Palmyra Atoll Airfield, and later Palmyra Island Naval Air Station as it was a former Naval airfield on the Palmyra Atoll in the Line Islands of the Central Pacific Area
Pacific Ocean Areas was a major Allied military command in the Pacific Ocean theater of World War II. It was one of four major Allied commands during the Pacific War, and one of three United States commands in the Asiatic-Pacific Theater. Admi ...
. The name for the airport comes from Henry Ernest Cooper Sr. (1857–1929) who owned Palmyra from 1911 to 1922.
Preliminary surveys were made by the U.S. Navy in 1938 for an airfield at this location. The first Navy group to begin construction sailed from Honolulu on November 14, 1939. The runway was made from crushed coral and expanded during World War II
World War II or the Second World War, often abbreviated as WWII or WW2, was a world war that lasted from 1939 to 1945. It involved the vast majority of the world's countries—including all of the great powers—forming two opposing ...
. During World War II, the U.S. Naval Construction Battalion dredged a channel so that ships could enter the protected lagoons, and bulldozed coral rubble into a long, unpaved landing strip for refueling transpacific supply planes at the airbase. On January 16, 1942, six Boeing B-17 Flying Fortress bombers from Hawaii were stationed at the airbase, Commanded by Lt. Col. Walter C. Sweeney Jr. as part of Hawaiian Air Force's Task Group 8. Marine Corps VMF-211
Marine Fighter Attack Squadron 211 (VMFA-211) is a United States Marine Corps fighter attack squadron, currently consisting of F-35B Lightning II stealth STOVL strike fighter jets. Known as the "Wake Island Avengers" and the "Bastion Defenders", ...
pilots also used the airfield. During World War II, two other runways were built and used, one on Meng island and one on Sand Island. Both of these runways are now overgrown with plants and returning to jungle. The U.S. Air Force maintained the main airfield until 1961.
The airstrip still exists today but can only be used after prior permission has been obtained or in case of emergency.
History
Discovery

 The first known sighting of Palmyra came in 1798 aboard the American sealing ship ''Betsy'', on a voyage to Asia, according to the
The first known sighting of Palmyra came in 1798 aboard the American sealing ship ''Betsy'', on a voyage to Asia, according to the memoir
A memoir (; , ) is any nonfiction narrative writing based in the author's personal memories. The assertions made in the work are thus understood to be factual. While memoir has historically been defined as a subcategory of biography or autobiog ...
of Captain Edmund Fanning
Edmund Fanning (July 16, 1769 – April 23, 1841) was an American explorer and sea captain, known as the "Pathfinder of the Pacific."
Life
Born in Stonington in the British Crown Colony of Connecticut to Gilbert and Huldah Fanning, from ne ...
of Stonington, Connecticut. Fanning wrote that he had awakened three times during the night before, and after the third time took it as a premonition, ordering ''Betsy'' to heave to
In sailing, heaving to (to heave to and to be hove to) is a way of slowing a sailing vessel's forward progress, as well as fixing the helm and sail positions so that the vessel does not have to be steered. It is commonly used for a "break"; this ...
for the rest of the night. The next morning, ''Betsy'' resumed sailing, but only about a nautical mile further on, he believed that he sighted the reef later known as Palmyra Island. Had the ship continued on her course at night, it might have been wrecked.Thomas, H.F., "Premonition of Danger" in "Connecticut Circle". ''Fate'', March 1953; see also Gaddis, Vincent H. ''Invisible Horizons'' Ace Books, Inc., 1965. Captain Fanning's claim to have discovered Palmyra itself has been challenged, on the view that he had only reached Kingman Reef
Kingman Reef is a largely submerged, uninhabited, triangle-shaped reef, geologically an atoll, east-west and north-south, in the North Pacific Ocean, roughly halfway between the Hawaiian Islands and American Samoa. It has an area of 3 hectar ...
away and could not possibly have seen Palmyra from that distance. On page 3, the Baltimore newspaper ''The Telegraphe and Daily Advertiser'' of July 29, 1803, appears to quote directly from Fanning's journal: "We supposed that we saw land from the masthead to the southward of the shoal (Kingman Reef) but it was so hazy we were not certain." This would stand in conflict with Fanning's book of 1833, in which he, while referring to Kingman Reef, wrote "I went aloft, and with the aid of the glass could plainly see the land over it, far in the south."
On November 7, 1802, the ship ''Palmyra'', under Captain Cornelius Sowle (sometimes spelled "Sawle"), was shipwrecked on the reef, which took the vessel's name. Lacking a navigable boat passage through the reef from the sea, it had never been inhabited. A lack of archaeological surveys on the atoll leave the question of habitation prior to European contact open. As a result, no marae
A ' (in New Zealand Māori, Cook Islands Māori, Tahitian), ' (in Tongan), ' (in Marquesan) or ' (in Samoan) is a communal or sacred place that serves religious and social purposes in Polynesian societies. In all these languages, the term a ...
, basalt
Basalt (; ) is an aphanitic (fine-grained) extrusive igneous rock formed from the rapid cooling of low-viscosity lava rich in magnesium and iron (mafic lava) exposed at or very near the surface of a rocky planet or moon. More than 90 ...
artifacts or evidence of Polynesian, Micronesian or other pre-European native settlements before 1802 have been reported on Palmyra. At the time of his discovery, Captain Sowle wrote:
There are no inhabitants on the island, nor was any fresh water found; but cocoanuts of a very large size, are in great abundance; and fish of various kinds and in large shoals surround the land.
''Esperanza'' treasure
During the 19th and 20th centuries, stories circulated in thePacific
The Pacific Ocean is the largest and deepest of Earth's five oceanic divisions. It extends from the Arctic Ocean in the north to the Southern Ocean (or, depending on definition, to Antarctica) in the south, and is bounded by the contine ...
of a large treasure
Treasure (from la, thesaurus from Greek language ''thēsauros'', "treasure store") is a concentration of wealth — often originating from ancient history — that is considered lost and/or forgotten until rediscovered. Some jurisdictions le ...
of gold
Gold is a chemical element with the symbol Au (from la, aurum) and atomic number 79. This makes it one of the higher atomic number elements that occur naturally. It is a bright, slightly orange-yellow, dense, soft, malleable, and ductile me ...
, silver
Silver is a chemical element with the symbol Ag (from the Latin ', derived from the Proto-Indo-European ''h₂erǵ'': "shiny" or "white") and atomic number 47. A soft, white, lustrous transition metal, it exhibits the highest electrical ...
and precious stones
A gemstone (also called a fine gem, jewel, precious stone, or semiprecious stone) is a piece of mineral crystal which, in cut and polished form, is used to make jewelry or other adornments. However, certain rocks (such as lapis lazuli, opal, a ...
(sometimes described as Inca treasures) that had been looted in the Viceroyalty of Peru
The Viceroyalty of Peru ( es, Virreinato del Perú, links=no) was a Spanish imperial provincial administrative district, created in 1542, that originally contained modern-day Peru and most of the Spanish Empire in South America, governed fro ...
. A crew loaded it in secret onto the ship ''Esperanza'' in Callao harbor, Peru
, image_flag = Flag of Peru.svg
, image_coat = Escudo nacional del Perú.svg
, other_symbol = Great Seal of the State
, other_symbol_type = National seal
, national_motto = "Firm and Happy f ...
, and embarked into the Pacific Ocean
The Pacific Ocean is the largest and deepest of Earth's five oceanic divisions. It extends from the Arctic Ocean in the north to the Southern Ocean (or, depending on definition, to Antarctica) in the south, and is bounded by the contin ...
on January 1, 1816, bound for the Spanish West Indies
The Spanish West Indies or the Spanish Antilles (also known as "Las Antillas Occidentales" or simply "Las Antillas Españolas" in Spanish) were Spanish colonies in the Caribbean. In terms of governance of the Spanish Empire, The Indies was the d ...
.
According to a survivor, seaman James Hines, the ''Esperanza'' was caught in a storm that dismasted and damaged the ship, after which it was attacked and boarded by pirates, who loaded the treasure and surviving crew onto their own ship. The ''Esperanza'' sank, and the pirates and their captives sailed west across the Pacific bound for Macao
Macau or Macao (; ; ; ), officially the Macao Special Administrative Region of the People's Republic of China (MSAR), is a city and special administrative region of China in the western Pearl River Delta by the South China Sea. With a po ...
.
After 43 days, the pirates' ship met a storm, lost course, and struck the coral reef
A coral reef is an underwater ecosystem characterized by reef-building corals. Reefs are formed of colonies of coral polyps held together by calcium carbonate. Most coral reefs are built from stony corals, whose polyps cluster in groups.
C ...
surrounding Palmyra Island, breaking the mast. The 90 men aboard were able to pull the ship closer to land, but it was not serviceable. They offloaded the treasure to the island, distributed some, and buried the rest. They repaired part of their boat and most of the crew shipped away, not to be heard from again. The remaining ten men spent most of a year on Palmyra living on dwindling stores and local food. They spent three months building a small escape boat, upon which six men left Palmyra. Of these, four were washed overboard in a storm and the other two were rescued by an American whaler
A whaler or whaling ship is a specialized vessel, designed or adapted for whaling: the catching or processing of whales.
Terminology
The term ''whaler'' is mostly historic. A handful of nations continue with industrial whaling, and one, Japa ...
bound for San Francisco
San Francisco (; Spanish for " Saint Francis"), officially the City and County of San Francisco, is the commercial, financial, and cultural center of Northern California. The city proper is the fourth most populous in California and 17th ...
. One died en route. The survivor, James Hines, was put in a hospital, but he died 30 days later.
Before Hines died, he wrote letters describing the affair and the location of the treasure, which originally included 1.5 million Spanish gold pesos and an equal value in silver (possibly consisting of precolumbian
In the history of the Americas, the pre-Columbian era spans from the original settlement of North and South America in the Upper Paleolithic period through European colonization, which began with Christopher Columbus's voyage of 1492. Usually, t ...
artworks). Around 1903, over 95 years later, the letters were allegedly deposited for safekeeping with Capt. William R. Foster, the harbormaster of Honolulu
Honolulu (; ) is the capital and largest city of the U.S. state of Hawaii, which is in the Pacific Ocean. It is an unincorporated county seat of the consolidated City and County of Honolulu, situated along the southeast coast of the island ...
, by a sailor who was bound for the Solomon Islands
Solomon Islands is an island country consisting of six major islands and over 900 smaller islands in Oceania, to the east of Papua New Guinea and north-west of Vanuatu. It has a land area of , and a population of approx. 700,000. Its capit ...
but never returned. After holding the letters for 20 years in an iron chest, Foster revealed them to a reporter, who published the details. A conflicting variant of the story was published by Capt. F. D. Walker of Honolulu in 1903 and in 1914. In 1997, William A. Warren filed a federal salvage claim for a ship sunk off the atoll that he claimed had treasure from the ''Esperanza'', but he abandoned his claim after legal objection from the Fullard-Leos, who owned most of Palmyra.
The legend of the ''Esperanza'' and ''Santa Rosa'' (a ship rumored to have recovered the ''Esperanza'' treasure and sailed back to Honolulu) inspired a Jack London
John Griffith Chaney (January 12, 1876 – November 22, 1916), better known as Jack London, was an American novelist, journalist and activist. A pioneer of commercial fiction and American magazines, he was one of the first American authors to ...
story called "The Proud Goat of Aloysius Pankburn", which was published as part of London's David Grief stories in the '' Saturday Evening Post''.
American visits
The atoll was visited by the in 1842 as part of theUnited States Exploring Expedition
The United States Exploring Expedition of 1838–1842 was an exploring and surveying expedition of the Pacific Ocean and surrounding lands conducted by the United States. The original appointed commanding officer was Commodore Thomas ap Catesby ...
, led by Charles Wilkes. This marked the first visit to Palmyra by a scientific expedition. Various live samples of native plants and animals were collected. In his 23rd volume recording the findings of the United States Exploring Expedition, USXX, Wilkes wrote of Palmyra, mentioning some unspecified inhabitants at that time:
This island is inhabited ... It is to be regretted that all these detached islands should not be visited by our national vessels, and friendly intercourse kept up with them. The benefit and assistance that any shipwrecked mariners might derive from their rude inhabitants, would repay the time, trouble, and expense such visits would occasion.In 1859, Palmyra Atoll was claimed for the United States both by Alfred Benson and by Dr. Gerrit P. Judd of the brig ''Josephine'', in accordance with the Guano Islands Act of 1856, but no guano was there to be mined, so the claims were abandoned.
Annexation by the Kingdom of Hawaii (1862)
On February 26, 1862, King Kamehameha IV of Kingdom of Hawaii, Hawaii commissioned Captain Zenas Bent and Johnson Beswick Wilkinson, both Hawaiian citizens, to take possession of the atoll. On April 15, 1862, it was formally annexed to the Kingdom of Hawaii, while Bent and Wilkinson became joint owners. Over the next century, ownership passed through various hands. Bent sold his rights to Wilkinson on December 25, 1862. Palmyra later passed to Kalama Wilkinson (Johnson's widow). In 1885, it was divided among her four heirs, two of whom sold their rights to William Luther Wilcox who, in turn, sold them to the Pacific Navigation Company. In 1897, this company was liquidated, and its interests were sold first to William Ansel Kinney, and then to Fred Wundenberg, all of Honolulu. On June 12, 1911, Wundenberg's widow sold his two-thirds undivided interest in Palmyra as a tenant in common to JudgeHenry Ernest Cooper
Henry Ernest Cooper (August 28, 1857 – May 15, 1929) was an American lawyer who moved to the Kingdom of Hawaii and became prominent in Hawaiian politics in the 1890s. He formally deposed Queen Lili'uokalani of Hawaii in 1893, held various offi ...
(1857–1929).
A further Wilkinson heir left her share to her son William Ringer Sr., who also bought his great-uncle's share, giving Ringer a one-third undivided share as a tenant in common.
Meanwhile, in 1889, Commander Nichols of claimed Palmyra for the United Kingdom, unaware of the prior claim made by Hawaii.
Part of the U.S. Territory of Hawaii (1900–1959)
In 1898, the United States by the Newlands Resolution annexed the Republic of Hawaii, formerly the Provisional Government of Hawaii, and Palmyra with it. An Act of Congress made all of Hawaii, including Palmyra, into an "incorporated territory" of the United States at that time. (''Act'' of April 30, 1900, ch. 339, §§ 4–5.) On June 14, 1900, Palmyra became part of the new U.S.Territory of Hawaii
The Territory of Hawaii or Hawaii Territory ( Hawaiian: ''Panalāʻau o Hawaiʻi'') was an organized incorporated territory of the United States that existed from April 30, 1900, until August 21, 1959, when most of its territory, excluding ...
.
With the imminent opening of the Panama Canal, Palmyra became strategically important. Britain had established a submarine communications cable, submarine cable station for the All Red Line on nearby Tabuaeran, Fanning Island. The United States Navy, U.S. Navy sent to Palmyra, where on February 21, 1912, American sovereignty was formally reaffirmed.
William Ringer Sr. died in 1909, survived by his wife and three minor daughters. In 1912, Henry Ernest Cooper
Henry Ernest Cooper (August 28, 1857 – May 15, 1929) was an American lawyer who moved to the Kingdom of Hawaii and became prominent in Hawaiian politics in the 1890s. He formally deposed Queen Lili'uokalani of Hawaii in 1893, held various offi ...
bought the daughters' inherited rights from their legal guardian and petitioned to register Torrens title to all of Palmyra for himself. After a challenge in court, Cooper's ownership of the atoll was held by the Supreme Court of Hawaii to be subject to rights sold by Ringer's widow to Henry Maui and Joseph Clarke. Maui's and Clarke's interests, noted by the U.S. Supreme Court, US Supreme Court in 1947, were divided one-third to Bella Jones of Honolulu in 1912 and the rest passed to their heirs.
Cooper visited the island in July 1913 with scientists Charles Montague Cooke Jr. and Joseph F. Rock, who wrote a scientific description of the atoll. Botanist Rock discovered unusual coconut palms in 1913, which palms expert Odoardo Beccari identified as ''Cocos nucifera palmyrensis'' (Becc.), the coconut type with the largest, longest and most triangular (in cross-section) fruits in the world, existing only at Palmyra. (The apparently closest ''Cocos nucifera'' relative occurs only in the distant Nicobar Islands in the Indian Ocean.) The "mammoth coconuts" were put on display in Honolulu in 1914 along with paintings of Palmyra by Hawaiian artist D. Howard Hitchcock, who had accompanied Cooper to the island.
In September 1921, as part of a national push to better document the coastal and outlying areas owned by the United States, a small naval detachment was sent to Palmyra to conduct the first aerial surveys of the atoll. The events of that trip were recorded by a naval Pharmacist Mate, M. L. Steele, who wrote:
During our visit the weather was delightful. The detachment remained at these islands two days and they were perfect for flying, affording an opportunity to take wonderful aerial pictures. The commanding officer and the aviators made a number of flights and the official photographer was in his element.At the time, Palmyra was occupied by three Americans: Colonel William Meng, his wife, and Edwin Benner Jr. While there, the USS ''Eagle-class patrol craft, Eagle Boat 40'', which had transported aircraft and photographic equipment to the islands, made a very rare exception to naval regulation and took aboard the wife, Mrs. Meng, to return her to Honolulu for medical aid as she was not handling the isolation and trying physical conditions of Palmyra well. On August 19, 1922, Cooper sold his interest in the atoll except two minor islets to Leslie and Ellen Fullard-Leo for $15,000 (). They established the Palmyra Copra Company to harvest the coconuts growing on the atoll. Their three sons, including actor Leslie Vincent, continued as the owners afterwards, subject to a period of military administration and construction by the Navy before and during
World War II
World War II or the Second World War, often abbreviated as WWII or WW2, was a world war that lasted from 1939 to 1945. It involved the vast majority of the world's countries—including all of the great powers—forming two opposing ...
from 1939 through 1945. In 2000, The Nature Conservancy
The Nature Conservancy (TNC) is a global environmental organization headquartered in Arlington, Virginia. it works via affiliates or branches in 79 countries and territories, as well as across every state in the US.
Founded in 1951, The Nat ...
acquired the majority of Palmyra Atoll from the Fullard-Leo family for $30 million ().
U.S. Navy occupation (1939–1959)
A number of memoirs, reports and unofficial documents in the decades since World War II, have stated Palmyra was placed under naval jurisdiction in 1934, as part of Executive order (United States), Executive Order 6935. However, Palmyra is not mentioned in this order, in any capacity. The first official mention of Palmyra under Naval Jurisdiction comes from a 1939 letter from the Homer Stille Cummings, US Attorney General, mentioned in a 1997 Insular Areas report, concluding "Palmyra was U.S. public land and that the Fullard-Leo claim was invalid. S. Rep. No. 83-886 at 37." Soon after this determination, Franklin D. Roosevelt, President Roosevelt issued Executive Order 8616, officially, "Placing Palmyra Island, Territory of Hawaii, Under the Control and Jurisdiction of the Secretary of the Navy". Starting in 1937, the Fullard-Leo family began attempts to lease Palmyra to the U.S. Navy. During negotiations, the government filed a quiet title action against the Fullard-Leos andHenry Ernest Cooper
Henry Ernest Cooper (August 28, 1857 – May 15, 1929) was an American lawyer who moved to the Kingdom of Hawaii and became prominent in Hawaiian politics in the 1890s. He formally deposed Queen Lili'uokalani of Hawaii in 1893, held various offi ...
's six surviving children, claiming property at Palmyra had never been privately owned under the Kingdom of Hawaii or later. The case reached the US Supreme Court. The Insular Areas report goes on to state, "While the suit was pending during World War II, the Navy occupied Palmyra and built a runway and several buildings." The Fullard-Leos and Coopers finally won their case in ''United States v. Fullard-Leo et al.'', 331 U.S. 256 (1947), which quieted good land title against the federal government in favor of private landowners. The opinion acknowledged certain of Henry Maui's and Joseph Clarke's interests (331 U.S. 256 at 278) but their heirs and their successor Mrs. Bella Jones were not made parties to the case., descendants of Henry Cooper still owned two small Home islets in the southwestern tip that were not sold in 1922.
In July 1938, United States Secretary of the Interior, Secretary of the Interior Harold L. Ickes wrote a letter to Franklin D. Roosevelt, President Roosevelt, imploring him not to turn Palmyra over to the US Navy for use as a military base. Quoting his letter, he writes,
... the Navy Department has plans for the acquisition and development of the island as an air base. Our representatives have studied conditions at Palmyra and other islands in the south Pacific, and they report that use of this small land area as an air base for Navy Department purposes would undoubtedly destroy much, if not all, that makes the island one of our most scientifically and scenically unique possessions.The letter was unsuccessful, and plans for the base proceeded. On February 14, 1941, Roosevelt issued Executive Order 8682 to create naval defenses areas in the central Pacific territories. The proclamation established "Palmyra Island Naval Defensive Sea Area" which encompassed the territorial waters between the extreme high-water marks and the three-mile marine boundaries surrounding the atoll. "Palmyra Island Naval Airspace Reservation" was also established to restrict access to the airspace over the area. Only U.S. government ships and aircraft were permitted to enter the naval defense areas at Palmyra Atoll unless authorized by the United States Secretary of the Navy, Secretary of the Navy. The Navy took over the atoll for use as the Palmyra Island Naval Air Station on August 15, 1941. From November 1939 through 1947, the atoll had resident Federal Government representatives, the island commanders. The atoll was Shelling of Johnston and Palmyra, shelled by a Japanese submarine in 1941, with no significant damage or injuries. The government made extensive alterations to the land forms. It blasted and dredged a ship channel from the open sea into the West Lagoon, which had been completely enclosed by islands and reef and was non-navigable until the channel reached the lagoon on May 15, 1941. It joined islands with causeway roads, built new islands and extended existing islands with dredged coral spoil, including the main runway on Cooper Island, an emergency landing strip called Sand Island joined by a causeway to Home Island, and two artificial runway islands that were not completed. These alterations blocked the water flow through the atoll and are believed to have severely harmed the natural ecology of the lagoons. During
World War II
World War II or the Second World War, often abbreviated as WWII or WW2, was a world war that lasted from 1939 to 1945. It involved the vast majority of the world's countries—including all of the great powers—forming two opposing ...
, the Imperial Japanese Navy submarine ''Japanese submarine I-175, I-75'' bombarded the naval air station on December 24, 1941.I-175 ijnsubsite.com November 25, 2018 Accessed 6 May 2022/ref> Opening fire at 04:55 Greenwich Civil time, Civil Time, she fired twelve rounds from her deck gun, targeting the atoll's radio station, and hit the United States Army United States Army Corps of Engineers, Corps of Engineers dredge ''Sacramento'', which was anchored in the lagoon, with one shell. A coastal artillery Artillery battery, battery on the atoll returned fire, forcing ''I-75'' to submerge and withdraw. In the lobby of the "Transient Hotel" (built by the Seabees, and used by airmen on their way to the Pacific Ocean theater of World War II, Pacific Theater front), a mural was hung depicting a quiet island scene. It was painted by Academy Award-nominated art director William Glasgow (art director), William Glasgow, who served in the Army from 1943 to 1945, though it is unclear when he painted it and how it ended up on Palmyra. After World War II, much of the Naval Air Station was demolished, with some of the materials piled up and burned on the atoll, dumped into the lagoon, or in the case of unexploded ordnance on some islets, left in place.
U.S. Territory of Palmyra Island (1959–present)
 When Hawaii was admitted to the United States in 1959, Palmyra was explicitly separated from the new state, remaining a federal incorporated territory, to be administered by the secretary of the interior under a presidential Executive order (United States), executive order.
In 1962, the United States Department of Defense, Department of Defense used Palmyra as an observation site during several high-altitude nuclear weapons tests high above Johnston Atoll. A group of about ten men supported the observation posts during this series of tests, while about 40 people carried out the observations.
Alby Mangels, the Australian adventurer and documentary filmmaker of ''World Safari'', visited the atoll during his six-year trip in the 1970s.
In early 1979, the US government began exploring the idea of storing nuclear waste on remote Pacific islands, like Palmyra. Those who knew the island and the region saw no benefit to this idea, commenting on the devastating effects a leak of these storage tanks would create. By 1982 a formal proposal had been written which "analyzes the proposal to store spent nuclear fuel on Palmyra Island, a US territory nearly a thousand miles south of
When Hawaii was admitted to the United States in 1959, Palmyra was explicitly separated from the new state, remaining a federal incorporated territory, to be administered by the secretary of the interior under a presidential Executive order (United States), executive order.
In 1962, the United States Department of Defense, Department of Defense used Palmyra as an observation site during several high-altitude nuclear weapons tests high above Johnston Atoll. A group of about ten men supported the observation posts during this series of tests, while about 40 people carried out the observations.
Alby Mangels, the Australian adventurer and documentary filmmaker of ''World Safari'', visited the atoll during his six-year trip in the 1970s.
In early 1979, the US government began exploring the idea of storing nuclear waste on remote Pacific islands, like Palmyra. Those who knew the island and the region saw no benefit to this idea, commenting on the devastating effects a leak of these storage tanks would create. By 1982 a formal proposal had been written which "analyzes the proposal to store spent nuclear fuel on Palmyra Island, a US territory nearly a thousand miles south of Hawaii
Hawaii ( ; haw, Hawaii or ) is a state in the Western United States, located in the Pacific Ocean about from the U.S. mainland. It is the only U.S. state outside North America, the only state that is an archipelago, and the only state ...
. The proposal has military, political, social, and technical implications." The idea was abandoned soon after the proposal, and no such storage facilities were built.
''Sea Wind'' murder
In 1974, Palmyra was the site of a murder, and possible double murder, of a wealthy San Diego couple, Malcolm "Mac" Graham and his wife, Eleanor "Muff" Graham. The mysterious deaths, including the murder conviction of Duane ("Buck") Walker (a.k.a. Wesley G. Walker) for Eleanor Graham's murder, and the acquittal of his girlfriend, Stephanie Stearns, made headlines worldwide, and became the subject of a true crime book, ''And the Sea Will Tell'', written by Bruce Henderson (author), Bruce Henderson and Vincent Bugliosi, Stearns's defense attorney. The book led to a CBS television miniseries of the same name, starring James Brolin, Rachel Ward, Deidre Hall, and Hart Bochner; Richard Crenna played lawyer Vincent Bugliosi, Bugliosi. The story was retold in ''The FBI Files''. Walker and Stearns were arrested in Honolulu in 1974 after returning from Palmyra aboard ''Sea Wind'', the yacht stolen from the Grahams. Because no bodies were found at the time, Walker and Stearns were convicted only for the theft of the yacht. Six years later, a partially-buried, corroded chest was found in a lagoon at Palmyra, containing Eleanor Graham's remains. Walker and Stearns were arrested in Arizona for murder, and Walker was convicted in 1985. Stearns was acquitted in 1986 after her defense argued that Walker had committed the murders without Stearns's knowledge. Because no body or other evidence of Malcolm Graham's death has been discovered, his murder was never formally alleged. Walker served 22 years in the United States Penitentiary, Victorville, California before receiving parole in 2007. He wrote an 895-page book about his experiences, and life on Palmyra Island, in which he denied killing Eleanor Graham. It states they had sexual relations, her husband Malcolm Graham caught them and shot at them in anger, inadvertently killing her. The two men had a gunfight the next day, and Malcolm Graham consequently died from a rifle wound. Walker accused author Vincent Bugliosi – Stearns' lawyer – of vainglory and exploiting class prejudice against him, and wrote that his own lawyer Earle Partington was incompetent. Walker did not implicate Stearns in any killing. Walker died in a nursing home, on April 26, 2010, following a stroke.Sovereignty challenges (1997–1999)
In the late 1990s, Rachel Lahela Kekoa Bolt, a native Hawaiian heir of Henry Maui, and some of her descendants filed federal lawsuits claiming her inherited interest in Palmyra and challenging the legality of the Newlands Resolution that annexed Hawaii. The lawsuits Hawaiian sovereignty movement, challenged American sovereignty over both the State of Hawaii and the United States Territory of Palmyra Island. On similar grounds they Intervention (law), intervened in a federal marine salvage claim for a sunkentreasure
Treasure (from la, thesaurus from Greek language ''thēsauros'', "treasure store") is a concentration of wealth — often originating from ancient history — that is considered lost and/or forgotten until rediscovered. Some jurisdictions le ...
ship at Palmyra. The cases were dismissed on procedural grounds before trial.
National Wildlife Refuge and National Monument
In December 2000,The Nature Conservancy
The Nature Conservancy (TNC) is a global environmental organization headquartered in Arlington, Virginia. it works via affiliates or branches in 79 countries and territories, as well as across every state in the US.
Founded in 1951, The Nat ...
(TNC) bought most of Palmyra Atoll from the three Fullard-Leo brothers for coral reef
A coral reef is an underwater ecosystem characterized by reef-building corals. Reefs are formed of colonies of coral polyps held together by calcium carbonate. Most coral reefs are built from stony corals, whose polyps cluster in groups.
C ...
conservation biology, conservation and research. In 2003, a scientific study was published about fossilized coral that was washing up on Palmyra. This fossilized coral was examined for evidence of the behavior of the effect of El Niño on the tropical Pacific Ocean
The Pacific Ocean is the largest and deepest of Earth's five oceanic divisions. It extends from the Arctic Ocean in the north to the Southern Ocean (or, depending on definition, to Antarctica) in the south, and is bounded by the contin ...
over the past 1,000 years.
 On January 18, 2001, Secretary of the Interior Bruce Babbitt issued Secretary's Order No. 3224 designating Palmyra's tidal lands, submerged lands and surrounding waters out to from the water's edge as a National Wildlife Refug
On January 18, 2001, Secretary of the Interior Bruce Babbitt issued Secretary's Order No. 3224 designating Palmyra's tidal lands, submerged lands and surrounding waters out to from the water's edge as a National Wildlife RefugSubsequently, the Department of the Interior published a regulation providing for the management of the refuge. 66 Fed. Reg. 7660-01 (January 24, 2001). The pertinent part of the regulation states:
We will close the refuge to commercial fishing but will permit a low level of compatible recreational fishing for bonefishing and deep water sportfishing under programs that we will carefully manage to ensure compatibility with refuge purposes. ... Management actions will include protection of the refuge waters and wildlife from commercial fishing activities.In March 2003, TNC conveyed of the emergent land of Palmyra to the United States to be included in the refuge. In 2005, it added 28 acres to the conveyance. TNC and
Henry Ernest Cooper
Henry Ernest Cooper (August 28, 1857 – May 15, 1929) was an American lawyer who moved to the Kingdom of Hawaii and became prominent in Hawaiian politics in the 1890s. He formally deposed Queen Lili'uokalani of Hawaii in 1893, held various offi ...
's descendants kept their remaining private land tracts.
 The conveyance to TNC from the Fullard-Leos in 2000 was subject to a preexisting commercial fishing licence. Then in 2001 the United States Secretary of the Interior, Secretary of the Interior banned commercial fishing near Palmyra but allowed sport fishing, as quoted above. In January 2007, the commercial fishing licensees sued the United States in the Court of Federal Claims alleging that, under the Takings Clause#Eminent domain, Takings Clause, the Interior Department regulation had "directly confiscated, taken, and rendered wholly and completely worthless" their purported property interests. The United States filed a motion to dismiss the lawsuit, and the court granted the motion. On April 9, 2009, the court's decision was affirmed by the Court of Appeals for the Federal Circuit.
In November 2005, TNC established a new research station on Palmyra to study global warming, coral reefs, invasive species and other environmental concerns.
The
The conveyance to TNC from the Fullard-Leos in 2000 was subject to a preexisting commercial fishing licence. Then in 2001 the United States Secretary of the Interior, Secretary of the Interior banned commercial fishing near Palmyra but allowed sport fishing, as quoted above. In January 2007, the commercial fishing licensees sued the United States in the Court of Federal Claims alleging that, under the Takings Clause#Eminent domain, Takings Clause, the Interior Department regulation had "directly confiscated, taken, and rendered wholly and completely worthless" their purported property interests. The United States filed a motion to dismiss the lawsuit, and the court granted the motion. On April 9, 2009, the court's decision was affirmed by the Court of Appeals for the Federal Circuit.
In November 2005, TNC established a new research station on Palmyra to study global warming, coral reefs, invasive species and other environmental concerns.
The Pacific Remote Islands Marine National Monument
The Pacific Remote Islands Marine National Monument is a group of unorganized, mostly unincorporated United States Pacific Island territories managed by the United States Fish and Wildlife Service of the United States Department of the Int ...
, comprising Palmyra Atoll, Baker Island, Howland Island, Jarvis Island
Jarvis Island (; formerly known as Bunker Island or Bunker's Shoal) is an uninhabited coral island located in the South Pacific Ocean, about halfway between Hawaii and the Cook Islands. It is an unincorporated, unorganized territory of the Un ...
, Johnston Atoll, and Kingman Reef
Kingman Reef is a largely submerged, uninhabited, triangle-shaped reef, geologically an atoll, east-west and north-south, in the North Pacific Ocean, roughly halfway between the Hawaiian Islands and American Samoa. It has an area of 3 hectar ...
, was established on January 6, 2009, by proclamation of President George W. Bush. This National Monument, national monument extends offshore and is managed by the U.S. Fish and Wildlife Service
The United States Fish and Wildlife Service (USFWS or FWS) is an agency within the United States Department of the Interior dedicated to the management of fish, wildlife, and natural habitats. The mission of the agency is "working with othe ...
and National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration.
Conservation and restoration
In 2011, Fish and Wildlife Service, TNC and Island Conservation began an extensive program to eradicate the horde of non-native rats that had arrived on Palmyra during World War II. As many as 30,000 rats once roamed the atoll, eating the eggs of native seabirds and destroying the seedlings of one of the largest remaining Pacific stands of ''pisonia grandis'' trees. The rats were eliminated in 2012; however, fifty-one animal samples representing 15 species of birds, fish, reptiles and invertebrates were collected for residue analysis during systematic searches or as nontarget mortalities. Brodifacoum residues (the toxicant employed during the project) were detected in most (84.3%) of the samples analyzed with unknown long-term and sublethal effects. One side effect was the demise of the island's population of Aedes albopictus, Asian tiger mosquitoes. This was claimed to be the first time that killing off one unwanted species resulted in the removal of a second unwanted species. The other mosquito species on the island, ''Culex quinquefasciatus,'' has a preference for feeding on birds and was not affected by the elimination of rats. Post-rat-eradication monitoring documented a notable recruitment event for ''pisonia grandis'', a dominant tree species that is important throughout the Pacific region. However, by five years post-eradication, a 13-fold increase in recruitment of the range-expanding coconut palm ''Cocos nucifera'' was found. Beginning in 2019, TNC worked in partnership with Island Conservation and the Fish and Wildlife Service to restore the native rainforest at Palmyra Atoll by removing dominant ''C. nucifera'' coconut palms, which the conservancy says are the result of former copra plantations and military activity. Other trees provide habitat for 11 seabird species, and the conservancy wrote that their re-establishment across the atoll would encourage coral growth and might lessen the local impact of a rise in sea-level. As of December 2019, half a million coconut sprouts had been removed, and tracking begun of the ecosystem's response. Palmyra Atoll's location in the Pacific Ocean, where the southern and northern currents meet, litters its beaches with trash and debris. Plastic mooring buoys and plastic bottles are plentiful.Tourism
Tourists are allowed to visit Palmyra Atoll (unlike most of the U.S. minor outlying islands, which are closed to the public). Palmyra Atoll is difficult to access, and few visit. Visitors must obtain prior approval from the U.S. Fish and Wildlife Service orThe Nature Conservancy
The Nature Conservancy (TNC) is a global environmental organization headquartered in Arlington, Virginia. it works via affiliates or branches in 79 countries and territories, as well as across every state in the US.
Founded in 1951, The Nat ...
. A statement by the U.S. Fish and Wildlife Service is as follows:
"Public access to Palmyra Atoll is self-limiting due to the very high expense of traveling to such a remote destination. The Nature Conservancy owns and operates the only airplane runway on Palmyra, and by boat it's a 5–7 day sailing trip from Honolulu. There are four ways the public may gain access to the refuge: (1) Working for, contracting with, or volunteering for The Nature Conservancy or Fish and Wildlife Service; (2) Conducting scientific research via Fish and Wildlife Service Special Use Permits; (3) Invitation through The Nature Conservancy sponsored donor trip; (4) Visitation by private recreational sailboat or motorboat."
Amateur radio (DX) visitors
Since the 1940s, Palmyra's most consistent visitors have been members of DXpedition, distance expedition (DXing#Amateur radio DX, DX) teams, as the atoll is a popular spot for these amateur radio operators. To date, more than 25 expeditions have arrived. Once on the islands, the hams set up radios and antennas and make as many two-way radio contacts with other hams as possible. Former N. California DXing#DX Clubs, DX Club president Richard Malcolm Crouch became a Palmyra landowner. In June 1974 the KP6PA Palmyra Atoll DXpedition, KP6PA DXpedition team helped rescue a couple whose ship had run aground on the reefs. The man, Buck Walker, was later convicted of homicide in the much publicized And the Sea Will Tell, ''Sea Wind'' murder case. Two members of the 1980 team were injured severely enough to need an airlift back to Honolulu. The first incident resulted from injuries sustained in a plane crash as their pilot underestimated wind conditions and the poor state of the landing strip. The second injury, to a surgeon, happened when he fell and cut his hands on broken glass. The surgeon then sued the atoll's owners, as he was no longer able to practice surgery, and the atoll was closed to visitors for most of the 1980s while cleanup activities were undertaken.See also
* List of Guano Island claims *Naval Base SamoaReferences
Further reading
* Vincent Bugliosi and Bruce B. Henderson (1991/1992), ''And the Sea Will Tell'', reprint, New York: Ballantine Books.External links
Palmyra Atoll National Wildlife Refuge
Palmyra Atoll photo gallery
by FWS
Overview
from the Department of the Interior
Island Conservation: Palmyra Atoll Restoration Project
The Nature Conservancy in Palmyra Atoll
Palmyra Atoll Research Consortium
{{authority control Palmyra Atoll, 1862 establishments in Hawaii Insular areas of the United States Integral overseas territories Island restoration Pacific islands claimed under the Guano Islands Act National Wildlife Refuges in the United States insular areas Nature Conservancy preserves Pacific Ocean atolls of the United States Pacific Remote Islands Marine National Monument Ramsar sites in the United States Uninhabited Pacific islands of the United States United States Minor Outlying Islands Important Bird Areas of United States Minor Outlying Islands Important Bird Areas of the Line Islands Closed installations of the United States Navy