History of Hampton Roads on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 The history of
The history of
"Hampton Roads Conference" in ''Encyclopedia Virginia''
/ref> Beginning in 1861, some of the former
 The history of
The history of Hampton Roads
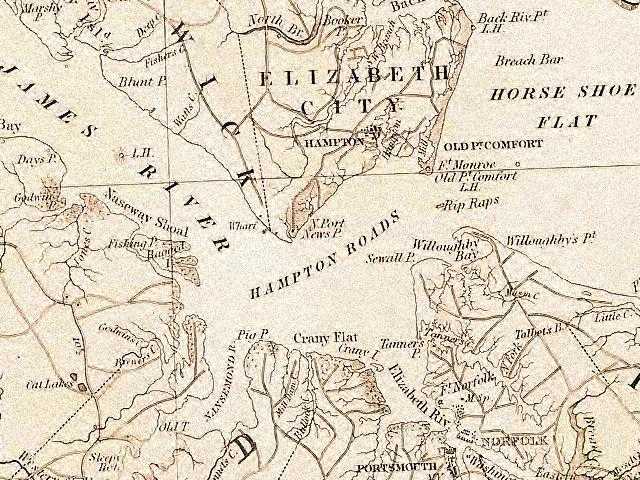
Hampton Roads is the name of both a body of water in the United States that serves as a wide channel for the James, Nansemond and Elizabeth rivers between Old Point Comfort and Sewell's Point where the Chesapeake Bay flows into the Atlantic ...
dates to 1607, when Jamestown was founded. Two wars have taken place in addition to many other historical events.
Colonial era
1607: the English colonists chose Jamestown
The first colonists arrived in 1607 when English Captain Christopher Newport's three ships, hisflagship
A flagship is a vessel used by the commanding officer of a group of naval ships, characteristically a flag officer entitled by custom to fly a distinguishing flag. Used more loosely, it is the lead ship in a fleet of vessels, typically the ...
''Susan Constant
''Susan Constant'', possibly ''Sarah Constant'', captained by Christopher Newport, was the largest of three ships of the English Virginia Company (the others being ''Discovery'' and '' Godspeed'') on the 1606–1607 voyage that resulted in the fo ...
'', the smaller '' Godspeed'', and even smaller ''Discovery'' landed in April 1607 at Cape Henry
Cape Henry is a cape on the Atlantic shore of Virginia located in the northeast corner of Virginia Beach. It is the southern boundary of the entrance to the long estuary of the Chesapeake Bay.
Across the mouth of the bay to the north is Cape Ch ...
along the Atlantic Coast in today's City of Virginia Beach, an event now known as the "First Landing." However, they moved on, under orders from the Virginia Company of London
The London Company, officially known as the Virginia Company of London, was a division of the Virginia Company with responsibility for colonizing the east coast of North America between latitudes 34° and 41° N.
History Origins
The territor ...
, the crews and new colonists sought a more sheltered area up one of the rivers. Their major concern was other European competitors such as the Spanish
Spanish might refer to:
* Items from or related to Spain:
**Spaniards are a nation and ethnic group indigenous to Spain
**Spanish language, spoken in Spain and many Latin American countries
**Spanish cuisine
Other places
* Spanish, Ontario, Can ...
, who had earlier discovered the Chesapeake Bay
The Chesapeake Bay ( ) is the largest estuary in the United States. The Bay is located in the Mid-Atlantic region and is primarily separated from the Atlantic Ocean by the Delmarva Peninsula (including the parts: the Eastern Shore of Maryland / ...
and Virginia's rivers, and had even in 1570 begun a small settlement on the Virginia Peninsula
The Virginia Peninsula is a peninsula in southeast Virginia, USA, bounded by the York River, James River, Hampton Roads and Chesapeake Bay. It is sometimes known as the ''Lower Peninsula'' to distinguish it from two other peninsulas to the n ...
known as the Ajacán Mission, which had failed.
During 18 days of exploring the area, they surely saw the enormous harbor of Hampton Roads
Hampton Roads is the name of both a body of water in the United States that serves as a wide channel for the James, Nansemond and Elizabeth rivers between Old Point Comfort and Sewell's Point where the Chesapeake Bay flows into the Atlantic ...
, and some of the party must have appreciated its possibilities. However, after exploring the James River
The James River is a river in the U.S. state of Virginia that begins in the Appalachian Mountains and flows U.S. Geological Survey. National Hydrography Dataset high-resolution flowline dataThe National Map , accessed April 1, 2011 to Chesap ...
west at least as far as present-day Hopewell, they agreed upon Jamestown Island
Jamestown Island is a island in the James River in Virginia, part of James City County. It is located off Glasshouse Point, to which it is connected via a causeway to the Colonial Parkway. Much of the island is wetland, including both swamp and ...
, where they established the first English speaking settlement to survive in the New World
The term ''New World'' is often used to mean the majority of Earth's Western Hemisphere, specifically the Americas."America." ''The Oxford Companion to the English Language'' (). McArthur, Tom, ed., 1992. New York: Oxford University Press, p. ...
on 14 May 1607.
The site was deep enough water for ships to dock but was also easily defendable. But despite the defensive advantages of that location against Spanish attacks, the low and marshy site at Jamestown proved a very poor choice in many other ways. More than five years of fragile existence, disease-carrying insects and high mortality rates followed including the Starving Time of 1609-10 when over 80% of the 500 colonists perished before the future of the Virginia Colony
The Colony of Virginia, chartered in 1606 and settled in 1607, was the first enduring English colony in North America, following failed attempts at settlement on Newfoundland by Sir Humphrey GilbertGilbert (Saunders Family), Sir Humphrey" (histor ...
began to appear more promising. The change came about with the just-in-time arrival of a new Governor, Lord Delaware, and a new colonist with a successful business idea named John Rolfe
John Rolfe (1585 – March 1622) was one of the early English settlers of North America. He is credited with the first successful cultivation of tobacco as an export crop in the Colony of Virginia in 1611.
Biography
John Rolfe is believed ...
.
Values of the harbor: commerce, military control
For centuries, the harbor and rivers of Hampton Roads have been ideal locations for both commerce and for many major shipyards. Some were established as early as the late 17th century such as the Gosport Navy Yard in what is now theCity of Portsmouth
Portsmouth ( ) is a port and city in the ceremonial county of Hampshire in southern England. The city of Portsmouth has been a unitary authority since 1 April 1997 and is administered by Portsmouth City Council.
Portsmouth is the most ...
.
The harbor was also a key point for military control of the region. Even the earliest settlers created fortifications at Old Point Comfort
Old Point Comfort is a point of land located in the independent city of Hampton, Virginia. Previously known as Point Comfort, it lies at the extreme tip of the Virginia Peninsula at the mouth of Hampton Roads in the United States. It was renamed ...
by 1610 against potential attacks by ships of Spanish or other unfriendly European forces.
American Revolutionary War
Important conflicts of theAmerican Revolutionary War
The American Revolutionary War (April 19, 1775 – September 3, 1783), also known as the Revolutionary War or American War of Independence, was a major war of the American Revolution. Widely considered as the war that secured the independence of t ...
involved Norfolk and Craney Island (at the mouth of the Elizabeth River in Portsmouth). It was at Norfolk where the last Royal Governor of the Virginia Colony, Lord Dunmore
Earl of Dunmore is a title in the Peerage of Scotland.
History
The title was created in 1686 for Lord Charles Murray, second son of John Murray, 1st Marquess of Atholl. He was made Lord Murray of Blair, Moulin and Tillimet (or Tullimet) and V ...
, departed mainland Virginia for the last time.
19th Century
War of 1812
The first naval action of theWar of 1812
The War of 1812 (18 June 1812 – 17 February 1815) was fought by the United States of America and its indigenous allies against the United Kingdom and its allies in British North America, with limited participation by Spain in Florida. It be ...
took place on 8 July 1812, when the Bermuda sloop
The Bermuda sloop is a historical type of fore-and-aft rigged single-masted sailing vessel developed on the islands of Bermuda in the 17th century. Such vessels originally had gaff rigs with quadrilateral sails, but evolved to use the Bermuda ri ...
, HMS Whiting, its crew oblivious to the US declaration of war, lowered anchor in Hampton Roads. As its captain was being rowed ashore, the Royal Naval vessel was seized by the American privateer ''Dash'', which happened to be leaving port.
Federal improvements
Under the new United States government, by the 1830s, the entrance fromChesapeake Bay
The Chesapeake Bay ( ) is the largest estuary in the United States. The Bay is located in the Mid-Atlantic region and is primarily separated from the Atlantic Ocean by the Delmarva Peninsula (including the parts: the Eastern Shore of Maryland / ...
was defended by Fort Monroe
Fort Monroe, managed by partnership between the Fort Monroe Authority for the Commonwealth of Virginia, the National Park Service as the Fort Monroe National Monument, and the City of Hampton, is a former military installation in Hampton, Virgi ...
, built by the U.S. Army beginning in 1819 on Old Point Comfort
Old Point Comfort is a point of land located in the independent city of Hampton, Virginia. Previously known as Point Comfort, it lies at the extreme tip of the Virginia Peninsula at the mouth of Hampton Roads in the United States. It was renamed ...
, and by Fort Wool, built as Fort Calhoun in 1829, on a small island called the Rip Raps near the middle of the channel (and now adjacent to one of the manmade islands of the Hampton Roads Bridge-Tunnel
Hampton may refer to:
Places Australia
*Hampton bioregion, an IBRA biogeographic region in Western Australia
*Hampton, New South Wales
*Hampton, Queensland, a town in the Toowoomba Region
*Hampton, Victoria
Canada
*Hampton, New Brunswick
*Hamp ...
). Much work in the building of these fortresses in the early 19th century was done by a 24-year-old engineer in the U.S. Army, a Lieutenant named Robert E. Lee
Robert Edward Lee (January 19, 1807 – October 12, 1870) was a Confederate general during the American Civil War, towards the end of which he was appointed the overall commander of the Confederate States Army. He led the Army of Nor ...
American Civil War, emancipation and education of former slaves
During theAmerican Civil War
The American Civil War (April 12, 1861 – May 26, 1865; also known by Names of the American Civil War, other names) was a civil war in the United States. It was fought between the Union (American Civil War), Union ("the North") and t ...
(1861-1865), the famous Battle of Hampton Roads
The Battle of Hampton Roads, also referred to as the Battle of the ''Monitor'' and ''Virginia'' (rebuilt and renamed from the USS ''Merrimack'') or the Battle of Ironclads, was a naval battle during the American Civil War.
It was fought over t ...
between the first American ironclad warship
An ironclad is a steam engine, steam-propelled warship protected by Wrought iron, iron or steel iron armor, armor plates, constructed from 1859 to the early 1890s. The ironclad was developed as a result of the vulnerability of wooden warships ...
s, the USS ''Monitor'' and the CSS ''Virginia'' (ex-''USS Merrimack'') took place off Sewell's Point
Sewells Point is a peninsula of land in the independent city of Norfolk, Virginia in the United States, located at the mouth of the salt-water port of Hampton Roads. Sewells Point is bordered by water on three sides, with Willoughby Bay to t ...
, on March 8–9, 1862. That battle was inconclusive, but later in 1862, Union forces took control of Hampton Roads, Norfolk, and the lower James River. However, their efforts to take the Confederate capital of Richmond
Richmond most often refers to:
* Richmond, Virginia, the capital of Virginia, United States
* Richmond, London, a part of London
* Richmond, North Yorkshire, a town in England
* Richmond, British Columbia, a city in Canada
* Richmond, Californi ...
via the James River with their vastly superior Navy were thwarted by a strong Confederate battery position high above a bend in the river about below Richmond at Drewry's Bluff
Drewry's Bluff is located in northeastern Chesterfield County, Virginia, in the United States. It was the site of Confederate Fort Darling during the American Civil War. It was named for a local landowner, Confederate Captain Augustus H. Drewry, ...
.
Fort Monroe was the launching place for Union General George McClellan's massive 1862 Peninsula Campaign, a land campaign of many months which began at Fort Monroe and advanced up the Virginia Peninsula
The Virginia Peninsula is a peninsula in southeast Virginia, USA, bounded by the York River, James River, Hampton Roads and Chesapeake Bay. It is sometimes known as the ''Lower Peninsula'' to distinguish it from two other peninsulas to the n ...
, with a Siege at Yorktown and another battle at Williamsburg before the Union Army almost literally reached the gates of Richmond, ending at the Chickahominy River
The Chickahominy is an U.S. Geological Survey. National Hydrography Dataset high-resolution flowline dataThe National Map, accessed April 1, 2011 river in the eastern portion of the U.S. state of Virginia. The river, which serves as the eastern bo ...
within earshot of the city's church bells, according to the journals of Union soldiers. However, the Confederates mounted a credible defense of their capital city, and McClellan's campaign failed to capture Richmond, ending in the Seven Days Battles
The Seven Days Battles were a series of seven battles over seven days from June 25 to July 1, 1862, near Richmond, Virginia, during the American Civil War. Confederate General Robert E. Lee drove the invading Union Army of the Potomac, comman ...
, during which the Union Army withdrew, effectively extending the War for almost three more years.
On February 3, 1865, as the Confederacy was near total collapse, President Abraham Lincoln
Abraham Lincoln ( ; February 12, 1809 – April 15, 1865) was an American lawyer, politician, and statesman who served as the 16th president of the United States from 1861 until his assassination in 1865. Lincoln led the nation throu ...
met with three senior Confederates in an effort to negotiate for peace (the "Hampton Roads Conference
The Hampton Roads Conference was a peace conference held between the United States and representatives of the unrecognized breakaway Confederate States on February 3, 1865, aboard the steamboat ''River Queen'' in Hampton Roads, Virginia, to disc ...
"). Lincoln wanted the states to return to the Union and indicated the Union would pay for the slaves. The Confederates insisted their demand was complete independence, so the 4-hour conference ended in failure.Se"Hampton Roads Conference" in ''Encyclopedia Virginia''
/ref> Beginning in 1861, some of the former
slaves
Slavery and enslavement are both the state and the condition of being a slave—someone forbidden to quit one's service for an enslaver, and who is treated by the enslaver as property. Slavery typically involves slaves being made to perf ...
found refuge near Fort Monroe
Fort Monroe, managed by partnership between the Fort Monroe Authority for the Commonwealth of Virginia, the National Park Service as the Fort Monroe National Monument, and the City of Hampton, is a former military installation in Hampton, Virgi ...
, which remained in Union hands throughout the War. There, the commander, Union Army General Benjamin F. Butler, a lawyer
A lawyer is a person who practices law. The role of a lawyer varies greatly across different legal jurisdictions. A lawyer can be classified as an advocate, attorney, barrister, canon lawyer, civil law notary, counsel, counselor, solicit ...
by training, declared them to be "Contraband of war". On that legal basis, Union forces refused to return them to Confederate owners as would have been the practice even in many "free states" before Virginia seceded and declared itself a foreign power. Soon, word spread, and many slaves were understandably anxious to become "contraband."
Although many of the "contraband" men at Hampton and elsewhere during the War volunteered and became part of the United States Colored Troops
The United States Colored Troops (USCT) were regiments in the United States Army composed primarily of African-American ( colored) soldiers, although members of other minority groups also served within the units. They were first recruited durin ...
(USCT), others and the women and children grew in increasing numbers near Fort Monroe in Elizabeth City County. From the wood and materials salvaged from the remains of the Town of Hampton, which had been burned earlier by retreating Confederates, they built the Grand Contraband Camp The Grand Contraband Camp was located in Elizabeth City County, Virginia, on the Virginia Peninsula near Fort Monroe, during and immediately after the American Civil War. The area was a refuge for escaped slaves who the Union forces refused to r ...
, near, but outside the protective walls of the Army base. It was the first self-contained African American
African Americans (also referred to as Black Americans and Afro-Americans) are an ethnic group consisting of Americans with partial or total ancestry from sub-Saharan Africa. The term "African American" generally denotes descendants of ens ...
community in the United States.
Close by, was (and still is) the Emancipation Oak
Emancipation Oak is a historic tree on the campus of Hampton University in what is now the City of Hampton, Virginia in the United States. The large sprawling southern live oak ('' Quercus virginiana''), which is believed to be over 200 years ...
, on the grounds of the school for them which grew to become Hampton University
Hampton University is a private, historically black, research university in Hampton, Virginia. Founded in 1868 as Hampton Agricultural and Industrial School, it was established by Black and White leaders of the American Missionary Association a ...
. Beginning as a normal school
A normal school or normal college is an institution created to train teachers by educating them in the norms of pedagogy and curriculum. In the 19th century in the United States, instruction in normal schools was at the high school level, turni ...
founded to train teachers, Hampton University was established by church groups and former Union Army
During the American Civil War, the Union Army, also known as the Federal Army and the Northern Army, referring to the United States Army, was the land force that fought to preserve the Union (American Civil War), Union of the collective U.S. st ...
officers. Early educators of the era included Mary Smith Peake
Mary Smith Peake, born Mary Smith Kelsey (1823 – February 22, 1862), was an American teacher, humanitarian and a member of the black elite in Hampton, best known for starting a school for the children of former slaves starting in the fall of ...
and former Union Army General Samuel Chapman Armstrong
Samuel Chapman Armstrong (January 30, 1839 – May 11, 1893) was an American soldier and general during the American Civil War who later became an educator, particularly of non-whites. The son of missionaries in Hawaii, he rose through the Union ...
, who was himself the son of missionaries, and had commanded a USCT force during the War. Among the earlier students was a young former slave named Booker T. Washington
Booker Taliaferro Washington (April 5, 1856November 14, 1915) was an American educator, author, orator, and adviser to several presidents of the United States. Between 1890 and 1915, Washington was the dominant leader in the African-American c ...
, who became a famed African-American
African Americans (also referred to as Black Americans and Afro-Americans) are an ethnic group consisting of Americans with partial or total ancestry from sub-Saharan Africa. The term "African American" generally denotes descendants of ensl ...
educator and was the first head of present-day Tuskegee University
Tuskegee University (Tuskegee or TU), formerly known as the Tuskegee Institute, is a private, historically black land-grant university in Tuskegee, Alabama. It was founded on Independence Day in 1881 by the state legislature.
The campus was de ...
. The Emancipation Oak is part of the official logo of the modern city of Hampton.
Twentieth century
Sewell's Point: Jamestown Exposition and a Navy Base
TheJamestown Exposition
The Jamestown Exposition was one of the many world's fairs and expositions that were popular in the United States in the early part of the 20th century. Commemorating the 300th anniversary of the founding of Jamestown in the Virginia Colony, it ...
for the 300th anniversary of the 1607 founding of Jamestown was held at Sewell's Point
Sewells Point is a peninsula of land in the independent city of Norfolk, Virginia in the United States, located at the mouth of the salt-water port of Hampton Roads. Sewells Point is bordered by water on three sides, with Willoughby Bay to t ...
in a rural section of Norfolk County in 1907.
President Theodore Roosevelt
Theodore Roosevelt Jr. ( ; October 27, 1858 – January 6, 1919), often referred to as Teddy or by his initials, T. R., was an American politician, statesman, soldier, conservationist, naturalist, historian, and writer who served as the 26t ...
arrived by water in the harbor of Hampton Roads, as did other notable persons such as Mark Twain
Samuel Langhorne Clemens (November 30, 1835 – April 21, 1910), known by his pen name Mark Twain, was an American writer, humorist, entrepreneur, publisher, and lecturer. He was praised as the "greatest humorist the United States has pr ...
and Henry Huttleston Rogers, who both arrived aboard the latter's steam yacht ''Kanawha''. A major naval display was featured, and the U.S. Great White Fleet
The Great White Fleet was the popular nickname for the group of United States Navy battleships which completed a journey around the globe from December 16, 1907 to February 22, 1909 by order of President Theodore Roosevelt. Its mission was ...
made an appearance. The leaders of the U.S. Navy apparently did not fail to note the ideal harbor conditions, as was later proved.
Beginning in 1917, as the United States became involved in World War I
World War I (28 July 1914 11 November 1918), often abbreviated as WWI, was List of wars and anthropogenic disasters by death toll, one of the deadliest global conflicts in history. Belligerents included much of Europe, the Russian Empire, ...
under President Woodrow Wilson
Thomas Woodrow Wilson (December 28, 1856February 3, 1924) was an American politician and academic who served as the 28th president of the United States from 1913 to 1921. A member of the Democratic Party, Wilson served as the president of ...
, formerly rural Sewell's Point
Sewells Point is a peninsula of land in the independent city of Norfolk, Virginia in the United States, located at the mouth of the salt-water port of Hampton Roads. Sewells Point is bordered by water on three sides, with Willoughby Bay to t ...
became the site of what grew to become the largest Naval Base in the world which was established by the United States Navy
The United States Navy (USN) is the maritime service branch of the United States Armed Forces and one of the eight uniformed services of the United States. It is the largest and most powerful navy in the world, with the estimated tonnage ...
and is now known as the Naval Station Norfolk
Naval Station Norfolk is a United States Navy base in Norfolk, Virginia, that is the headquarters and home port of the U.S. Navy's Fleet Forces Command. The installation occupies about of waterfront space and of pier and wharf space of the Hampt ...
.
Military use of northern side of the Peninsula
Twice in the 20th century, families of mostlyAfrican American
African Americans (also referred to as Black Americans and Afro-Americans) are an ethnic group consisting of Americans with partial or total ancestry from sub-Saharan Africa. The term "African American" generally denotes descendants of ens ...
heritage were displaced in entire communities when land along the northern side of the Peninsula
A peninsula (; ) is a landform that extends from a mainland and is surrounded by water on most, but not all of its borders. A peninsula is also sometimes defined as a piece of land bordered by water on three of its sides. Peninsulas exist on a ...
primarily in York County west of Yorktown was taken in large tracts for military use during World War I
World War I (28 July 1914 11 November 1918), often abbreviated as WWI, was List of wars and anthropogenic disasters by death toll, one of the deadliest global conflicts in history. Belligerents included much of Europe, the Russian Empire, ...
and World War II
World War II or the Second World War, often abbreviated as WWII or WW2, was a world war that lasted from 1939 to 1945. It involved the World War II by country, vast majority of the world's countries—including all of the great power ...
, creating the present-day U.S. Naval Weapons Station Yorktown, which includes Cheatham Annex, and a former Seabee
, colors =
, mascot = Bumblebee
, battles = Guadalcanal, Bougainville, Cape Gloucester, Los Negros, Guam, Peleliu, Tarawa, Kwajalein, Saipan, Tinian, Iwo Jima, Philippin ...
base which became Camp Peary
Camp Peary is an approximately 9,000 acre U.S. military reservation in York County near Williamsburg, Virginia. Officially referred to as an Armed Forces Experimental Training Activity (AFETA) under the authority of the Department of Defense, ...
.
Communities including "the Reservation", Halstead's Point, Penniman, Bigler's Mill, and Magruder were all absorbed into the large military bases.
Although some left the area entirely, many of the displaced families chose to relocate nearby to Grove, an unincorporated town in southeastern James City County where many generations of some of those families now reside. From a population estimated at only 37 in 1895, Grove had grown to an estimated 1,100 families by the end of the 20th century. (To its north, Grove actually borders the Naval Weapons Station property and on its extreme east, a portion of the U.S. Army's land at Fort Eustis extends across Skiffe's Creek, although there is no direct access to either base).
Colonial Williamsburg
A dream of one Episcopalian priest to save his 18th century church building was to expand to create the world's largestliving museum
A living museum, also known as a living history museum, is a type of museum which recreates historical settings to simulate a past time period, providing visitors with an experiential interpretation of history. It is a type of museum that recrea ...
. Replacing Jamestown and the end of the 17th century, Williamsburg had been capital of the Colony and the new State of Virginia from 1699-1780. After the capital moved to Richmond in 1780, Williamsburg became a quieter and sometimes described as "sleepy" small town. It saw some action during the Battle of Williamsburg
The Battle of Williamsburg, also known as the Battle of Fort Magruder, took place on May 5, 1862, in York County, James City County, and Williamsburg, Virginia, as part of the Peninsula Campaign of the American Civil War. It was the first p ...
of the 1862 Peninsula Campaign during the Civil War. However, it was not located along any major waterway and did not have railroad access until 1881. Perhaps due to the secure inland location originally known as Middle Plantation, for Williamsburg, growth and great expansion of commerce in the 19th century did not occur as rapidly as in many other Virginia cities. The main activities were the College of William and Mary
The College of William & Mary (officially The College of William and Mary in Virginia, abbreviated as William & Mary, W&M) is a public research university in Williamsburg, Virginia. Founded in 1693 by letters patent issued by King William ...
and Eastern State Hospital, each historic institutions in their own right. In addition to the city's historic past, quite a few buildings of antiquity from the 18th century were still extant, although time was taking a toll by the early 20th century.
The Reverend Dr. W.A.R. Goodwin
William Archer Rutherfoord Goodwin (June 18, 1869 – September 7, 1939) (or W.A.R. Goodwin as he preferred or "the Doctor" as commonly used to his annoyance) was an Episcopal priest, historian, and author. As the rector of Bruton Parish Church, ...
of Bruton Parish Church
Bruton Parish Church is located in the restored area of Colonial Williamsburg in Williamsburg, Virginia, United States. It was established in 1674 by the consolidation of two previous parishes in the Virginia Colony, and remains an active Epi ...
initially had wanted merely to save his historic church building. This he accomplished by 1907. He later served in Rochester, New York
Rochester () is a City (New York), city in the U.S. state of New York (state), New York, the county seat, seat of Monroe County, New York, Monroe County, and the fourth-most populous in the state after New York City, Buffalo, New York, Buffalo, ...
for many years. Upon returning to Williamsburg in 1923, he began to realize that many of the other colonial-era buildings also remained, but were in deteriorating condition, and their continued longevity was at risk.
Goodwin dreamed of a much larger restoration along the lines of what he had accomplished with his historic church. A cleric of modest means, he sought support and financing from a number of sources before successfully drawing the interests and major financial support of Standard Oil
Standard Oil Company, Inc., was an American oil production, transportation, refining, and marketing company that operated from 1870 to 1911. At its height, Standard Oil was the largest petroleum company in the world, and its success made its co- ...
heir and philanthropist
Philanthropy is a form of altruism that consists of "private initiatives, for the public good, focusing on quality of life". Philanthropy contrasts with business initiatives, which are private initiatives for private good, focusing on material ...
John D. Rockefeller Jr.
John Davison Rockefeller Jr. (January 29, 1874 – May 11, 1960) was an American financier and philanthropist, and the only son of Standard Oil co-founder John D. Rockefeller.
He was involved in the development of the vast office complex in M ...
and his wife Abby Aldrich Rockefeller
Abigail Greene Aldrich Rockefeller (October 26, 1874 – April 5, 1948) was an American socialite and philanthropist. She was a prominent member of the Rockefeller family through her marriage to financier and philanthropist John D. Rockefeller ...
. The result of their combined efforts was the creation of Colonial Williamsburg
Colonial Williamsburg is a living-history museum and private foundation presenting a part of the historic district in the city of Williamsburg, Virginia, United States. The Colonial Williamsburg Foundation has 7300 employees at this location ...
, which included a restoration of the Wren Building at the College of William and Mary
The College of William & Mary (officially The College of William and Mary in Virginia, abbreviated as William & Mary, W&M) is a public research university in Williamsburg, Virginia. Founded in 1693 by letters patent issued by King William ...
and a change of much of the downtown Williamsburg area into a Historic Area of restored and replica buildings and surrounds to celebrate the patriots and the early history of America.
By the 1930s, Colonial Williamsburg had become the centerpiece of the Historic Triangle of Colonial Virginia
The Historic Triangle includes three historic colonial communities located on the Virginia Peninsula of the United States and is bounded by the York River on the north and the James River on the south. The points that form the triangle are James ...
. These were, of course, Jamestown, where the colony started, Williamsburg, and Yorktown, where independence from Great Britain
Great Britain is an island in the North Atlantic Ocean off the northwest coast of continental Europe. With an area of , it is the largest of the British Isles, the largest European island and the ninth-largest island in the world. It ...
was won. The three points were joined by the U.S. National Park Service
The National Park Service (NPS) is an agency of the United States federal government within the U.S. Department of the Interior that manages all national parks, most national monuments, and other natural, historical, and recreational properti ...
's Colonial Parkway
Colonial Parkway is a scenic parkway linking the three points of Virginia's Historic Triangle, Jamestown, Williamsburg, and Yorktown. It is part of the National Park Service's Colonial National Historical Park. Virginia's official state c ...
, a remarkable accomplishment built over a period of 27 years. The Historic Triangle area of the Hampton Roads region became one of the largest tourist attractions in the entire world.
In Dr. Goodwin's words: "Williamsburg is Jamestown continued, and Yorktown is Williamsburg vindicated."
Other notable Hampton Roads "firsts"
In 1957, theHampton Roads Bridge-Tunnel
Hampton may refer to:
Places Australia
*Hampton bioregion, an IBRA biogeographic region in Western Australia
*Hampton, New South Wales
*Hampton, Queensland, a town in the Toowoomba Region
*Hampton, Victoria
Canada
*Hampton, New Brunswick
*Hamp ...
was the first bridge-tunnel complex in the world, to be followed by the area's much longer Chesapeake Bay Bridge-Tunnel in 1963.
In the 1960s, the first astronaut
An astronaut (from the Ancient Greek (), meaning 'star', and (), meaning 'sailor') is a person trained, equipped, and deployed by a human spaceflight program to serve as a commander or crew member aboard a spacecraft. Although generally r ...
s of Project Mercury
Project Mercury was the first human spaceflight program of the United States, running from 1958 through 1963. An early highlight of the Space Race, its goal was to put a man into Earth orbit and return him safely, ideally before the Soviet Un ...
trained at the NASA
The National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA ) is an independent agency of the US federal government responsible for the civil space program, aeronautics research, and space research.
NASA was established in 1958, succeedin ...
facility adjacent to Hampton's Langley Air Force Base
Langley Air Force Base is a United States Air Force base located in Hampton, Virginia, adjacent to Newport News. It was one of thirty-two Air Service training camps established after the entry of the United States into World War I in April 1 ...
. Local features including Mercury Boulevard
Mercury Boulevard in the cities of Hampton and Newport News in the Peninsula region of southeastern Virginia carries U.S. Route 258 (US 258) approximately south from Fort Monroe at Old Point Comfort on Hampton Roads to the north end of ...
commemorate this fact.
Defunct shires, counties, cities, towns
As the current communities in the Hampton Roads region were formed and grew from the Colonial period to statehood and modern times, the political structure of many areas inVirginia
Virginia, officially the Commonwealth of Virginia, is a state in the Mid-Atlantic and Southeastern regions of the United States, between the Atlantic Coast and the Appalachian Mountains. The geography and climate of the Commonwealth are ...
changed. Between 1952 and 1976, a wave of consolidations of local governments led to almost the entire southeastern portion of Virginia consisting of a group of adjoining independent cities
An independent city or independent town is a city or town that does not form part of another general-purpose local government entity (such as a province).
Historical precursors
In the Holy Roman Empire, and to a degree in its successor state ...
, eventually numbering eight. Joining the seven major cities of Hampton Roads
Hampton Roads is the name of both a body of water in the United States that serves as a wide channel for the James, Nansemond and Elizabeth rivers between Old Point Comfort and Sewell's Point where the Chesapeake Bay flows into the Atlantic ...
was the comparatively tiny City of Poquoson, which had formerly been an incorporated town
An incorporated town is a town that is a municipal corporation.
Canada
Incorporated towns are a form of local government in Canada, which is a responsibility of provincial rather than federal government.
United Kingdom
United States
An in ...
in York County).
Many incorporated (formally constituted) localities became legally defunct, though mostly not abandoned by their citizens, with the notable exception of Jamestown. For search of genealogical, land, and other historical records, it may be necessary to find these old names.
The following is a partial listing of defunct political subdivisions in the Hampton Roads area with approximate formation and dissolution dates. Note: Former towns which grew to become cities of the same name are not listed separately, nor are unincorporated towns. More information about dates and dispositions may be found in most individual articles by following the links.
In order of date founded:
*Jamestown, Virginia
The Jamestown settlement in the Colony of Virginia was the first permanent English settlement in the Americas. It was located on the northeast bank of the James (Powhatan) River about southwest of the center of modern Williamsburg. It was ...
(1607) largely abandoned as a Town after 1699
*Kecoughtan, Virginia In the seventeenth century, Kecoughtan was the name of the settlement now known as Hampton, Virginia, In the early twentieth century, it was also the name of a town nearby in Elizabeth City County. It was annexed into the City of Newport News in 19 ...
(1610), became part of Town and City of Hampton
* James Cittie (sic) (1619-1624)
*Elizabeth Cittie Elizabeth City (or Elizabeth Cittie as it was then called) was one of four incorporations established in the Virginia Colony in 1619 by the proprietor, the Virginia Company of London, acting in accordance with instructions issued by Sir George Yeard ...
(sic) (1619-1624)
* Middle Plantation (1632-1699), (changed name to Williamsburg in 1699, chartered as city in 1722)
* Elizabeth River Shire (1634-1643)
* Warwick River Shire (1634-1643)
* Charles River Shire (1634-1643)
* James City Shire (1634-1643)
*Warrosquyoake Shire
Warrosquoake Shire (with numerous variant spellings, including Warrascoyack, Warrascocke and "Warwick Squeak") was officially formed in 1634 in the Virginia colony, but had already been known as "Warascoyack County" before this. It was named for ...
(1634-1637)
*New Norfolk County New Norfolk County is a long-extinct county which was located in colonial Virginia from 1636 until 1637.
It was formed in 1636 from Elizabeth City Shire, one of the eight original shires (or counties) formed in 1634 in the colony of Virginia by di ...
(1636-1637)
*Lower Norfolk County Lower Norfolk County is a long-extinct county which was organized in colonial Virginia, operating from 1637 until 1691.
New Norfolk County was formed in 1636 from Elizabeth City Shire, one of the eight original shires (or counties) formed in 1634 ...
(1637-1691)
* Upper Norfolk County (1637-1646)
*Norfolk County, Virginia
Norfolk County was a county of the South Hampton Roads in eastern Virginia in the United States that was created in 1691. After the American Civil War, for a period of about 100 years, portions of Norfolk County were lost and the territory of th ...
(1691-1963)
*Princess Anne County
County of Princess Anne is a former county in the British Colony of Virginia and the Commonwealth of Virginia in the United States, first incorporated in 1691. The county was merged into the city of Virginia Beach
on January 1, 1963, ceasing to ...
(1691-1963)
* Elizabeth City County (1643-1952)
*Nansemond County
Nansemond is an extinct jurisdiction that was located south of the James River in Virginia Colony and in the Commonwealth of Virginia (after statehood) in the United States, from 1646 until 1974. It was known as Nansemond County until 1972. From ...
(1646-1972)
* Warwick County (aka Warwick River County) (1643-1952)
* City of South Norfolk (1922-1963)
* Town of Berkley incorporated town until 1906 when annexed by City of Norfolk
* Town of Phoebus(1900-1952) (earlier known as unincorporated towns of Millwood, Roseland Farms and Chesapeake City)
*City of Warwick
The City of Warwick was a local government area administering the regional centre of Warwick in the Darling Downs region of Queensland. The City covered an area of , and existed as a local government entity from 1861 until 1994, when it was dis ...
(1952-1958)
* City of Nansemond (1972-1974)
See also
* Timeline of Hampton, Virginia *History of Norfolk, Virginia
The history of Norfolk, Virginia as a modern settlement begins in 1636. The city formally was incorporated in 1736. The city was burned by orders of the outgoing Virginia governor Lord Dunmore in 1776 during the second year of the American Re ...
and Timeline
A timeline is a display of a list of events in chronological order. It is typically a graphic design showing a long bar labelled with dates paralleling it, and usually contemporaneous events.
Timelines can use any suitable scale represen ...
*History of Virginia Beach
The history of Virginia Beach, Virginia, goes back to the Native Americans who lived in the area for thousands of years before the English colonists landed at Cape Henry in April 1607 and established their first permanent settlement at Jamestown ...
and Timeline of Virginia Beach, Virginia, Timeline
*History of Williamsburg, Virginia
References
{{Hampton Roads Hampton Roads History of Virginia Maritime history of Virginia