History of Cardiff on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 The history of Cardiffa City and County Borough and the capital of
The history of Cardiffa City and County Borough and the capital of
 Mesolithic hunter-gatherers from Central Europe began to migrate northwards from the end of the last
Mesolithic hunter-gatherers from Central Europe began to migrate northwards from the end of the last  In common with the people living all over Great Britain, over the following centuries the people living around what is now known as Cardiff assimilated new immigrants and exchanged ideas of the
In common with the people living all over Great Britain, over the following centuries the people living around what is now known as Cardiff assimilated new immigrants and exchanged ideas of the
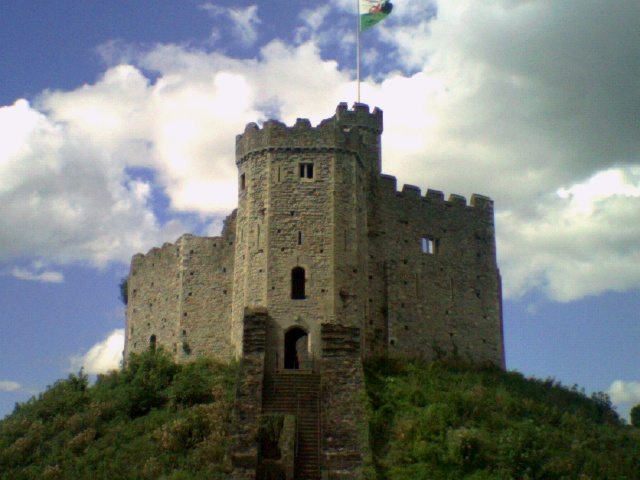
 Excavations from inside Cardiff Castle walls suggest
Excavations from inside Cardiff Castle walls suggest
 In 1091,
In 1091,
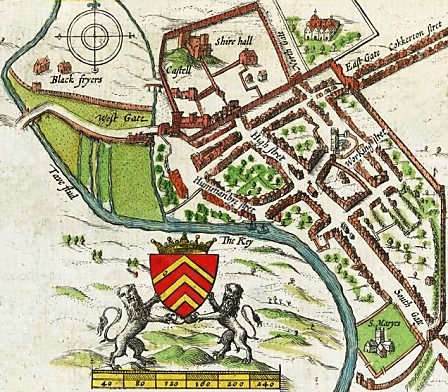
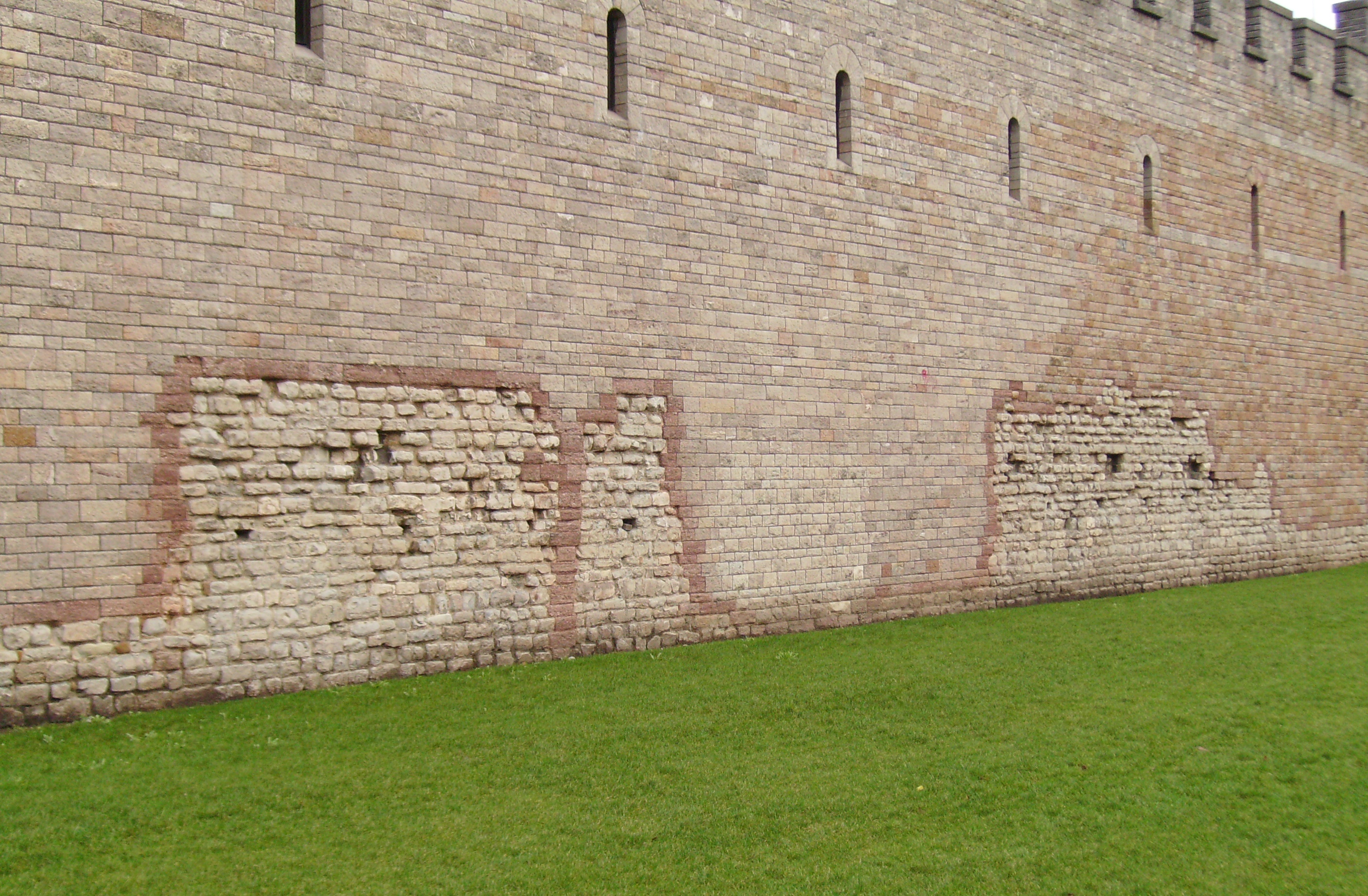
 In 1536, the Act of Union between England and Wales led to the creation of the shire of Glamorgan. Cardiff was made the county town. Around this same time the Herbert family became the most powerful family in the area. In 1538, Henry VIII closed the Dominican and
In 1536, the Act of Union between England and Wales led to the creation of the shire of Glamorgan. Cardiff was made the county town. Around this same time the Herbert family became the most powerful family in the area. In 1538, Henry VIII closed the Dominican and
 In 1793,
In 1793,

Cardiff's Medieval Town Defences
{{DEFAULTSORT:History Of Cardiff
 The history of Cardiffa City and County Borough and the capital of
The history of Cardiffa City and County Borough and the capital of Wales
Wales ( cy, Cymru ) is a country that is part of the United Kingdom. It is bordered by England to the east, the Irish Sea to the north and west, the Celtic Sea to the south west and the Bristol Channel to the south. It had a population in ...
spans at least 6,000 years. The area around Cardiff
Cardiff (; cy, Caerdydd ) is the capital and largest city of Wales. It forms a principal area, officially known as the City and County of Cardiff ( cy, Dinas a Sir Caerdydd, links=no), and the city is the eleventh-largest in the United Kingd ...
has been inhabited by modern humans since the Neolithic
The Neolithic period, or New Stone Age, is an Old World archaeological period and the final division of the Stone Age. It saw the Neolithic Revolution, a wide-ranging set of developments that appear to have arisen independently in several p ...
Period. Four Neolithic burial chambers stand within a radius of of Cardiff City Centre, with the St Lythans burial chamber
, alternate_name =
, image = St Lythans burial chamber (4794) (cropped).jpg
, caption =
, alt = a grassy field in which three large upright stones support a stone slab roof
, location = near St Lythans and Barry ()
, region = Vale ...
the nearest, at about to the west. Bronze Age
The Bronze Age is a historic period, lasting approximately from 3300 BC to 1200 BC, characterized by the use of bronze, the presence of writing in some areas, and other early features of urban civilization. The Bronze Age is the second prin ...
tumuli
A tumulus (plural tumuli) is a mound of earth and stones raised over a grave or graves. Tumuli are also known as barrows, burial mounds or ''kurgans'', and may be found throughout much of the world. A cairn, which is a mound of stones built ...
are at the summit of Garth Hill (''The Garth''; cy, Mynydd y Garth), within the county's northern boundary, and four Iron Age
The Iron Age is the final epoch of the three-age division of the prehistory and protohistory of humanity. It was preceded by the Stone Age ( Paleolithic, Mesolithic, Neolithic) and the Bronze Age ( Chalcolithic). The concept has been mostl ...
hillfort
A hillfort is a type of earthwork used as a fortified refuge or defended settlement, located to exploit a rise in elevation for defensive advantage. They are typically European and of the Bronze Age or Iron Age. Some were used in the post-Roma ...
and enclosure
Enclosure or Inclosure is a term, used in English landownership, that refers to the appropriation of "waste" or " common land" enclosing it and by doing so depriving commoners of their rights of access and privilege. Agreements to enclose land ...
sites have been identified within the City and County of Cardiff boundary, including Caerau Hillfort, an enclosed area of . Until the Roman conquest of Britain, Cardiff was part of the territory of an Iron Age Celtic British tribe called the Silures, which included the areas that would become known as Brecknockshire, Monmouthshire and Glamorgan. The Roman fort established by the River Taff
The River Taff ( cy, Afon Taf) is a river in Wales. It rises as two rivers in the Brecon Beacons; the Taf Fechan (''little Taff'') and the Taf Fawr (''great Taff'') before becoming one just north of Merthyr Tydfil. Its confluence with th ...
, which gave its name to the city''Caerdydd'', earlier ''Caerdyf'', from ''caer'' (fort) and ''Taf''was built over an extensive settlement that had been established by the Silures in the 50s AD.
Origins
ice age
An ice age is a long period of reduction in the temperature of Earth's surface and atmosphere, resulting in the presence or expansion of continental and polar ice sheets and alpine glaciers. Earth's climate alternates between ice ages and gre ...
(between 12,000 and 10,000 years before present(BP)). The area that would become known as Wales had become free of glacier
A glacier (; ) is a persistent body of dense ice that is constantly moving under its own weight. A glacier forms where the accumulation of snow exceeds its ablation over many years, often centuries. It acquires distinguishing features, such as ...
s by about 10,250 BP. At that time sea levels were much lower than today, and the shallower parts of what is now the North Sea
The North Sea lies between Great Britain, Norway, Denmark, Germany, the Netherlands and Belgium. An epeiric sea, epeiric sea on the European continental shelf, it connects to the Atlantic Ocean through the English Channel in the south and the ...
were dry land. The east coast of present-day England and the coasts of present-day Denmark, Germany and the Netherlands were connected by the former landmass known as Doggerland
Doggerland was an area of land, now submerged beneath the North Sea, that connected Britain to continental Europe. It was flooded by rising sea levels around 6500–6200 BCE. The flooded land is known as the Dogger Littoral. Geological sur ...
, forming the British Peninsula on the European mainland. The post-glacial rise in sea level separated Wales and Ireland, forming the Irish Sea
The Irish Sea or , gv, Y Keayn Yernagh, sco, Erse Sie, gd, Muir Èireann , Ulster-Scots: ''Airish Sea'', cy, Môr Iwerddon . is an extensive body of water that separates the islands of Ireland and Great Britain. It is linked to the Ce ...
. Doggerland was submerged by the North Sea and, by 8000 BP, the British Peninsula had become the island of Great Britain. John Davies has theorised that the story of ''Cantre'r Gwaelod
, also known as or ( en, The Lowland Hundred), is a legendary ancient sunken kingdom said to have occupied a tract of fertile land lying between Ramsey Island and Bardsey Island in what is now Cardigan Bay to the west of Wales. It has been ...
's'' drowning and tales in the '' Mabinogion'', of the waters between Wales and Ireland being narrower and shallower, may be distant folk memories of this time.
As Great Britain became heavily wooded, movement between different areas was restricted, and travel between what was to become known as Wales and continental Europe became easier by sea, rather than by land. People came to Wales by boat from the Iberian Peninsula
The Iberian Peninsula (),
**
* Aragonese and Occitan: ''Peninsula Iberica''
**
**
* french: Péninsule Ibérique
* mwl, Península Eibérica
* eu, Iberiar penintsula also known as Iberia, is a peninsula in southwestern Europe, def ...
. These Neolithic
The Neolithic period, or New Stone Age, is an Old World archaeological period and the final division of the Stone Age. It saw the Neolithic Revolution, a wide-ranging set of developments that appear to have arisen independently in several p ...
colonists integrated with the indigenous people, gradually changing their lifestyles from a nomadic life of hunting and gathering, to become farmers, some of whom settled in the area that would become Glamorgan. They cleared the forests to establish pasture and to cultivate the land, developed new technologies such as ceramics and textile production, and they brought a tradition of long barrow
Long barrows are a style of monument constructed across Western Europe in the fifth and fourth millennia BCE, during the Early Neolithic period. Typically constructed from earth and either timber or stone, those using the latter material repre ...
construction that began in continental Europe during the 7th millennium BC.
Archaeological evidence from sites in and around Cardiff—the St Lythans burial chamber
, alternate_name =
, image = St Lythans burial chamber (4794) (cropped).jpg
, caption =
, alt = a grassy field in which three large upright stones support a stone slab roof
, location = near St Lythans and Barry ()
, region = Vale ...
, near Wenvoe
Wenvoe ( cy, Gwenfô) is a village, community and electoral ward between Barry and Cardiff in the Vale of Glamorgan, Wales. Nearby are the Wenvoe Transmitter near Twyn-yr-Odyn and the site of the former HTV Wales Television Centre at Culverhouse ...
(about west, southwest of Cardiff City Centre), the Tinkinswood burial chamber, near St. Nicholas, Vale of Glamorgan (about west of Cardiff City Centre), the Cae'rarfau Chambered Tomb
A chamber tomb is a tomb for burial used in many different cultures. In the case of individual burials, the chamber is thought to signify a higher status for the interred than a simple grave. Built from rock or sometimes wood, the chambers could ...
, Creigiau (about northwest of Cardiff City Centre) and the Gwern y Cleppa Long Barrow, near Coedkernew, Newport (about northeast of Cardiff City Centre)—shows that these Neolithic people had settled in the area around Cardiff from at least around 6,000 BP, about 1500 years before either Stonehenge or The Egyptian Great Pyramid of Giza
The Great Pyramid of Giza is the biggest Egyptian pyramid and the tomb of Fourth Dynasty pharaoh Khufu. Built in the early 26th century BC during a period of around 27 years, the pyramid is the oldest of the Seven Wonders of the Ancient Worl ...
was completed.
 In common with the people living all over Great Britain, over the following centuries the people living around what is now known as Cardiff assimilated new immigrants and exchanged ideas of the
In common with the people living all over Great Britain, over the following centuries the people living around what is now known as Cardiff assimilated new immigrants and exchanged ideas of the Bronze Age
The Bronze Age is a historic period, lasting approximately from 3300 BC to 1200 BC, characterized by the use of bronze, the presence of writing in some areas, and other early features of urban civilization. The Bronze Age is the second prin ...
and Iron Age
The Iron Age is the final epoch of the three-age division of the prehistory and protohistory of humanity. It was preceded by the Stone Age ( Paleolithic, Mesolithic, Neolithic) and the Bronze Age ( Chalcolithic). The concept has been mostl ...
Celtic cultures. Together with the approximate areas now known as Breconshire, Monmouthshire and the rest of Glamorgan, the area that would become known as Cardiff was settled by a Celtic British
British may refer to:
Peoples, culture, and language
* British people, nationals or natives of the United Kingdom, British Overseas Territories, and Crown Dependencies.
** Britishness, the British identity and common culture
* British English, ...
tribe called the Silures. There is a group of five tumuli
A tumulus (plural tumuli) is a mound of earth and stones raised over a grave or graves. Tumuli are also known as barrows, burial mounds or ''kurgans'', and may be found throughout much of the world. A cairn, which is a mound of stones built ...
at the top of Mynydd y Garth—near the City and County of Cardiff's northern boundary—thought to be Bronze Age, one of which supports a trig. pillar on its flat top. Several Iron Age sites have been found in the City and County of Cardiff. They are: the Castle Field Camp, east of Graig Llywn, Pontprennau; Craig y Parc enclosure, Pentyrch; Llwynda Ddu Hillfort, Pentyrch; and Caerau Hillfort—an enclosed area of .
The Roman army invaded Great Britain in May AD 43. The area to the south east of the Fosse Way—between modern day Lincoln
Lincoln most commonly refers to:
* Abraham Lincoln (1809–1865), the sixteenth president of the United States
* Lincoln, England, cathedral city and county town of Lincolnshire, England
* Lincoln, Nebraska, the capital of Nebraska, U.S.
* Lincol ...
and Exeter—was under Roman control by 47. British tribes from beyond this new frontier of the Roman Empire
The Roman Empire ( la, Imperium Romanum ; grc-gre, Βασιλεία τῶν Ῥωμαίων, Basileía tôn Rhōmaíōn) was the post- Republican period of ancient Rome. As a polity, it included large territorial holdings around the Mediter ...
resisted the Roman advance and the Silures, along with Caratacus
Caratacus (Brythonic ''*Caratācos'', Middle Welsh ''Caratawc''; Welsh ''Caradog''; Breton ''Karadeg''; Greek ''Καράτακος''; variants Latin ''Caractacus'', Greek ''Καρτάκης'') was a 1st-century AD British chieftain of the ...
( cy, Caradoc), attacked the Romans in 47 and 48. A Roman legion
The Roman legion ( la, legiō, ) was the largest military unit of the Roman army, composed of 5,200 infantry and 300 equites (cavalry) in the period of the Roman Republic (509 BC–27 BC) and of 5,600 infantry and 200 auxilia in the period o ...
(thought to be the Twentieth) was defeated in 52 by the Silures.
Archaeological evidence shows that a settlement had been established by the Silures in central Cardiff in the 50s AD, probably during the period following their victory over the Roman army. The settlement included several large timber-framed buildings of up to by . The extent of the settlement is not known. Until the Romans established their fort, which they built on the earlier Silures settlement, the area that would become known as Cardiff remained outside the control of the Roman province of Britannia
Britannia () is the national personification of Britain as a helmeted female warrior holding a trident and shield. An image first used in classical antiquity, the Latin ''Britannia'' was the name variously applied to the British Isles, Great ...
.
The Roman settlement
 Excavations from inside Cardiff Castle walls suggest
Excavations from inside Cardiff Castle walls suggest Roman legion
The Roman legion ( la, legiō, ) was the largest military unit of the Roman army, composed of 5,200 infantry and 300 equites (cavalry) in the period of the Roman Republic (509 BC–27 BC) and of 5,600 infantry and 200 auxilia in the period o ...
s arrived in the area as early as AD 54–68 during the reign of the Emperor Nero
Nero Claudius Caesar Augustus Germanicus ( ; born Lucius Domitius Ahenobarbus; 15 December AD 37 – 9 June AD 68), was the fifth Roman emperor and final emperor of the Julio-Claudian dynasty, reigning from AD 54 unt ...
. The Romans defeated the Silures and exiled Caratacus
Caratacus (Brythonic ''*Caratācos'', Middle Welsh ''Caratawc''; Welsh ''Caradog''; Breton ''Karadeg''; Greek ''Καράτακος''; variants Latin ''Caractacus'', Greek ''Καρτάκης'') was a 1st-century AD British chieftain of the ...
to Rome. They then established their first fort
A fortification is a military construction or building designed for the defense of territories in warfare, and is also used to establish rule in a region during peacetime. The term is derived from Latin ''fortis'' ("strong") and ''facere'' ...
, built on this strategically important site where the River Taff
The River Taff ( cy, Afon Taf) is a river in Wales. It rises as two rivers in the Brecon Beacons; the Taf Fechan (''little Taff'') and the Taf Fawr (''great Taff'') before becoming one just north of Merthyr Tydfil. Its confluence with th ...
and River Ely enter the Bristol Channel, on a site on which were built timber barracks, stores and workshops.
The Silures were not finally conquered until AD 75, when Sextus Julius Frontinus' long campaign against them began to succeed, and they gained control of the whole of Wales
Wales ( cy, Cymru ) is a country that is part of the United Kingdom. It is bordered by England to the east, the Irish Sea to the north and west, the Celtic Sea to the south west and the Bristol Channel to the south. It had a population in ...
. The Roman fort at Cardiff was rebuilt smaller than before, in the 70s AD on the site of the extensive previous settlement dating from the 50s AD. Another fort was built on the site around 250, with stone walls thick along with an earth bank, to help defend against attacks from Hibernia
''Hibernia'' () is the Classical Latin name for Ireland. The name ''Hibernia'' was taken from Greek geographical accounts. During his exploration of northwest Europe (c. 320 BC), Pytheas of Massalia called the island ''Iérnē'' (written ). ...
. This was used until the Roman army
The Roman army (Latin: ) was the armed forces deployed by the Romans throughout the duration of Ancient Rome, from the Roman Kingdom (c. 500 BC) to the Roman Republic (500–31 BC) and the Roman Empire (31 BC–395 AD), and its medieval contin ...
withdrew from the fort, and from the whole of the province
A province is almost always an administrative division within a country or state. The term derives from the ancient Roman '' provincia'', which was the major territorial and administrative unit of the Roman Empire's territorial possessions ou ...
of Britannia
Britannia () is the national personification of Britain as a helmeted female warrior holding a trident and shield. An image first used in classical antiquity, the Latin ''Britannia'' was the name variously applied to the British Isles, Great ...
, near the start of the 5th century.
The Viking settlement and the Middle Ages
During the early Dark Ages little is known of Cardiff. It is speculated that perhaps for long periods, raiders attacked the area, making Cardiff untenable, By 850 theVikings
Vikings ; non, víkingr is the modern name given to seafaring people originally from Scandinavia (present-day Denmark, Norway and Sweden),
who from the late 8th to the late 11th centuries raided, pirated, traded and ...
attacked the Welsh coast and used Cardiff as a base and later as a port. Street names such as Dumballs Road and Womanby Street come from the Vikings.
 In 1091,
In 1091, Robert Fitzhamon
Robert Fitzhamon (died March 1107), or Robert FitzHamon (literally, 'Robert, son of Hamon'), Seigneur de Creully in the Calvados region and Torigny in the Manche region of Normandy, was the first Norman feudal baron of Gloucester and the Nor ...
the Lord of Glamorgan, began work on the castle keep within the walls of the old Roman fort and by 1111, Cardiff town walls
Cardiff's town walls were a Medieval defensive wall enclosing much of the present day centre of Cardiff, the capital city of Wales, which included Cardiff Castle. It measured 1280 paces or in circumference and had an average thickness of betwe ...
had also been built and this was recorded by Caradoc of Llancarfan in his book ''Brut y Tywysogion
''Brut y Tywysogion'' ( en, Chronicle of the Princes) is one of the most important primary sources for Welsh history. It is an annalistic chronicle that serves as a continuation of Geoffrey of Monmouth’s ''Historia Regum Britanniae''. ''Brut ...
'' (''Chronicle of the Princes''). Cardiff Castle has been at the heart of the city ever since. Soon a little town grew up in the shadow of the castle, made up primarily of settlers from England. Cardiff had a population of between 1,500 and 2,000 in the Middle Ages, a relatively normal size for a Welsh town in this period. Robert Fitzhamon died in 1107, later his daughter Mabel, married Robert, 1st Earl of Gloucester
Robert FitzRoy, 1st Earl of Gloucester (c. 1090 – 31 October 1147David Crouch, 'Robert, first earl of Gloucester (b. c. 1090, d. 1147)’, Oxford Dictionary of National Biography, Oxford University Press, 2004; online edn, May 200Retrieved ...
, the illegitimate
Legitimacy, in traditional Western common law, is the status of a child born to parents who are legally married to each other, and of a child conceived before the parents obtain a legal divorce. Conversely, ''illegitimacy'', also known as '' ...
son of King Henry I of England. He built the first stone keep in Cardiff Castle, and he used it to imprison Robert II, Duke of Normandy
Robert Curthose, or Robert II of Normandy ( 1051 – 3 February 1134, french: Robert Courteheuse / Robert II de Normandie), was the eldest son of William the Conqueror and succeeded his father as Duke of Normandy in 1087, reigning until 1106. ...
from 1126 until his death in 1134, by order of King Henry I, who was the Duke's younger brother. During the same period Ralph "Prepositus de Kardi" ("Provost of Cardiff") took up office as the first Mayor of Cardiff. During this period after the Norman conquest they usually referred the leading figure by the Latin name of prepositus ( en, provost) meaning "leading man". Robert (Earl of Gloucester) died in 1147 and was succeeded by his son William, 2nd Earl of Gloucester who died without male heir in 1183. The lordship of Cardiff then passed to Prince John, later King John through his marriage to Isabel, Countess of Gloucester
Isabella, Countess of Gloucester (1173/1174 – 14 October 1217), was an English noblewoman who was married to King John prior to his accession.
Lineage
Isabella was the daughter of William Fitz Robert, 2nd Earl of Gloucester, and his wife Hawi ...
, William's daughter. John divorced Isabel but retained the lordship until her second marriage; to Geoffrey FitzGeoffrey de Mandeville, 2nd Earl of Essex
Earl of Essex is a title in the Peerage of England which was first created in the 12th century by King Stephen of England. The title has been recreated eight times from its original inception, beginning with a new first Earl upon each new cre ...
in 1214 until 1216 when the lordship passed to Gilbert de Clare, 5th Earl of Hertford
Gilbert de Clare, 4th Earl of Hertford, 5th Earl of Gloucester, 1st Lord of Glamorgan, 7th Lord of Clare (1180 – 25 October 1230) was the son of Richard de Clare, 3rd Earl of Hertford (c. 1153–1217), from whom he inherited the Clare estat ...
.
Between 1158 and 1316 Cardiff was attacked on several occasions. Amongst the various attackers of the castle were Ifor Bach
Ifor Bach (meaning Ivor the Short) (fl. 1158) also known as Ifor ap Meurig and in anglicised form Ivor Bach, Lord of Senghenydd, was a twelfth-century resident in and a leader of the Welsh in south Wales.
Welsh Lord of Senghenydd
At this perio ...
, who captured the Earl of Gloucester
The title of Earl of Gloucester was created several times in the Peerage of England. A fictional earl is also a character in William Shakespeare's play ''King Lear.''
Earls of Gloucester, 1st Creation (1121)
*Robert, 1st Earl of Gloucester (1100� ...
who at the time held the castle. Morgan ap Maredudd apparently attacked the settlement during the revolt of Madog ap Llywelyn
Madog ap Llywelyn (died after 1312) was the leader of the Welsh revolt of 1294–95 against English rule in Wales and proclaimed "Prince of Wales". The revolt was surpassed in longevity only by the revolt of Owain Glyndŵr in the 15th century. Ma ...
in 1294. In 1316 Llywelyn Bren
Llywelyn Bren (), or Llywelyn ap Gruffudd ap Rhys / Llywelyn ap Rhys (also Llewelyn) or in en, Llywelyn of the Woods. He was a nobleman who led a 1316 revolt in Wales in the reign of King Edward II of England. It marked the last serious challen ...
, Ifor Bach's great-grandson, also attacked Cardiff Castle as part of a revolt. He was illegally executed in the town in 1318 on the order of Hugh Despenser the Younger
Hugh le Despenser, 1st Baron le Despenser (c. 1287/1289 – 24 November 1326), also referred to as "the Younger Despenser", was the son and heir of Hugh le Despenser, Earl of Winchester (the Elder Despenser), by his wife Isabella de Beaucham ...
.
By the end of the 13th century, Cardiff was the only town in Wales with a population exceeding 2,000, but it was relatively small compared to most other notable towns in the Kingdom of England
The Kingdom of England (, ) was a sovereign state on the island of Great Britain from 12 July 927, when it emerged from various History of Anglo-Saxon England, Anglo-Saxon kingdoms, until 1 May 1707, when it united with Kingdom of Scotland, ...
. Cardiff had an established port in the Middle Ages and by 1327, it was declared a Staple port. The town had weekly markets and after 1340, Cardiff also had 2 annual fairs, which drew traders from all around Glamorgan.
In 1404, Owain Glyndŵr burned Cardiff and took Cardiff Castle. As the town was still very small, most of the buildings were made of wood and the town was reduced to ashes. However, the town was rebuilt not long after and began to flourish once again.
County town of Glamorganshire

 In 1536, the Act of Union between England and Wales led to the creation of the shire of Glamorgan. Cardiff was made the county town. Around this same time the Herbert family became the most powerful family in the area. In 1538, Henry VIII closed the Dominican and
In 1536, the Act of Union between England and Wales led to the creation of the shire of Glamorgan. Cardiff was made the county town. Around this same time the Herbert family became the most powerful family in the area. In 1538, Henry VIII closed the Dominican and Franciscan
, image = FrancescoCoA PioM.svg
, image_size = 200px
, caption = A cross, Christ's arm and Saint Francis's arm, a universal symbol of the Franciscans
, abbreviation = OFM
, predecessor =
, ...
friaries in Cardiff, the remains of which were used as building materials. A writer around this period described Cardiff: "The River Taff runs under the walls of his honours castle and from the north part of the town to the south part where there is a fair quay and a safe harbour for shipping."
In 1542, Cardiff gained representation in the House of Commons
The House of Commons is the name for the elected lower house of the bicameral parliaments of the United Kingdom and Canada. In both of these countries, the Commons holds much more legislative power than the nominally upper house of parliament. T ...
for the first time. The next year, the English militia
A militia () is generally an army or some other fighting organization of non-professional soldiers, citizens of a country, or subjects of a state, who may perform military service during a time of need, as opposed to a professional force of r ...
system was introduced. In 1551, William Herbert, Earl of Pembroke was created first Baron Herbert of Cardiff.
Cardiff had become a Free Borough in 1542. In 1573, it was made a head port for collection of customs duties. In 1581, Elizabeth I
Elizabeth I (7 September 153324 March 1603) was List of English monarchs, Queen of England and List of Irish monarchs, Ireland from 17 November 1558 until her death in 1603. Elizabeth was the last of the five House of Tudor monarchs and is ...
granted Cardiff its first royal charter
A royal charter is a formal grant issued by a monarch under royal prerogative as letters patent. Historically, they have been used to promulgate public laws, the most famous example being the English Magna Carta (great charter) of 1215, but s ...
. By 1602 Pembrokeshire historian George Owen described Cardiff as "the fayrest towne in Wales yett not the welthiest. The town gained a second Royal charter
A royal charter is a formal grant issued by a monarch under royal prerogative as letters patent. Historically, they have been used to promulgate public laws, the most famous example being the English Magna Carta (great charter) of 1215, but s ...
in 1608. During the Second English Civil War
The Second English Civil War took place between February to August 1648 in Kingdom of England, England and Wales. It forms part of the series of conflicts known collectively as the 1639-1651 Wars of the Three Kingdoms, which include the 1641� ...
, St. Fagans just to the west of the town, played host to the Battle of St Fagans. The battle, between a Royalist
A royalist supports a particular monarch as head of state for a particular kingdom, or of a particular dynastic claim. In the abstract, this position is royalism. It is distinct from monarchism, which advocates a monarchical system of governm ...
rebellion and a New Model Army detachment, was a decisive victory for the Parliamentarians and allowed Oliver Cromwell
Oliver Cromwell (25 April 15993 September 1658) was an English politician and military officer who is widely regarded as one of the most important statesmen in English history. He came to prominence during the 1639 to 1651 Wars of the Three K ...
to conquer Wales. It is the last major battle to occur in Wales, with a total death toll of about 200 (mostly Royalist) soldiers killed.
In the ensuing century Cardiff was at peace. In 1766, John Stuart, 1st Marquess of Bute
John Stuart, 1st Marquess of Bute PC, FRS (30 June 1744 – 16 November 1814), styled Lord Mount Stuart until 1792 and known as The Earl of Bute between 1792 and 1794, was a British nobleman, coalfield owner, diplomat and politician who sat in ...
married into the Herbert family and was later created Baron Cardiff. In 1778, he began renovations on Cardiff Castle. In the 1790s, a race track
A race track (racetrack, racing track or racing circuit) is a facility built for racing of vehicles, athletes, or animals (e.g. horse racing or greyhound racing). A race track also may feature grandstands or concourses. Race tracks are also use ...
, printing press
A printing press is a mechanical device for applying pressure to an inked surface resting upon a print medium (such as paper or cloth), thereby transferring the ink. It marked a dramatic improvement on earlier printing methods in which the ...
, bank and coffee room all opened, and Cardiff gained a stagecoach service to London. Despite these improvements, Cardiff's position in the Welsh urban hierarchy
The urban hierarchy ranks each city based on the size of population residing within the nationally defined statistical urban area. Because urban population depends on how governments define their metropolitan areas, urban hierarchies are convention ...
had declined over the 18th century. Iolo Morganwg
Edward Williams, better known by his bardic name Iolo Morganwg (; 10 March 1747 – 18 December 1826), was a Welsh antiquarian, poet and collector.Jones, Mary (2004)"Edward Williams/Iolo Morganwg/Iolo Morgannwg" From ''Jones' Celtic Encyclop ...
called it "an obscure and inconsiderable place", and the 1801 census found the population to be only 1,870, making Cardiff only the twenty-fifth largest town in Wales, well behind Merthyr Tydfil and Swansea.The Welsh Academy Encyclopedia of Wales. Cardiff: University of Wales Press 2008.
Building of the docks to modern Cardiff
 In 1793,
In 1793, John Crichton-Stuart, 2nd Marquess of Bute
John Crichton-Stuart, 2nd Marquess of Bute, KT, FRS (10 August 1793 – 18 March 1848), styled Lord Mount Stuart between 1794 and 1814, was a wealthy aristocrat and industrialist in Georgian and early Victorian Britain. He developed the coal ...
was born. He would spend his life building the Cardiff docks and would later be called "the creator of modern Cardiff". In 1815, a boat service between Cardiff and Bristol
Bristol () is a city, ceremonial county and unitary authority in England. Situated on the River Avon, it is bordered by the ceremonial counties of Gloucestershire to the north and Somerset to the south. Bristol is the most populous city in ...
was established, running twice weekly. In 1821, the Cardiff Gas Works was established.
The town grew rapidly from the 1830s onwards, when the Marquess of Bute built a dock which eventually linked to the Taff Vale Railway
The Taff Vale Railway (TVR) was a standard gauge railway in South Wales, built by the Taff Vale Railway Company to serve the iron and coal industries around Merthyr Tydfil and to connect them with docks in Cardiff. It was opened in st ...
. Cardiff became the main port for exports of coal from the Cynon, Rhondda
Rhondda , or the Rhondda Valley ( cy, Cwm Rhondda ), is a former coal mining, coalmining area in South Wales, historically in the county of Glamorgan. It takes its name from the River Rhondda, and embraces two valleys – the larger Rhondda Fa ...
, and Rhymney valleys, and grew at a rate of nearly 80% per decade between 1840 and 1870. Much of the growth was due to migration
Migration, migratory, or migrate may refer to: Human migration
* Human migration, physical movement by humans from one region to another
** International migration, when peoples cross state boundaries and stay in the host state for some minimum le ...
from within and outside Wales: in 1851, a quarter of Cardiff's population were English-born and more than 10% had been born in Ireland. By the 1881 census, Cardiff had overtaken both Merthyr and Swansea to become the largest town in Wales. Cardiff's new status as the premier town in South Wales was confirmed when it was chosen as the site of the University College South Wales and Monmouthshire in 1893.
Cardiff developed municipal slaughterhouses from 1835, one of the first cities in the United Kingdom to do so, and by the early twentieth century there were no private slaughterhouses.
Cardiff faced a challenge in the 1880s when David Davies of Llandinam and the Barry Railway Company promoted the development of rival docks at Barry. Barry docks had the advantage of being accessible in all tide
Tides are the rise and fall of sea levels caused by the combined effects of the gravitational forces exerted by the Moon (and to a much lesser extent, the Sun) and are also caused by the Earth and Moon orbiting one another.
Tide tables ...
s, and David Davies claimed that his venture would cause "grass to grow in the streets of Cardiff". From 1901 coal exports from Barry surpassed those from Cardiff, but the administration of the coal trade remained centred on Cardiff, in particular its Coal Exchange
The Coal Exchange (also known as the Exchange Building) is an historic building in Cardiff, Wales. It is designed in Renaissance Revival style. Built in 1888 as the Coal and Shipping Exchange to be used as a market floor and office building for ...
, where the price of coal on the British market was determined and the first million-pound deal was struck in 1907. The city also strengthened its industrial base with the decision of Guest, Keen and Nettlefolds
GKN Ltd is a British multinational automotive and aerospace components business headquartered in Redditch, England. It is a long-running business known for many decades as Guest, Keen and Nettlefolds. It can trace its origins back to 1759 an ...
, owners of the Dowlais Ironworks
The Dowlais Ironworks was a major ironworks and steelworks located at Dowlais near Merthyr Tydfil, in Wales. Founded in the 18th century, it operated until the end of the 20th, at one time in the 19th century being the largest steel producer in ...
in Merthyr, to build a new steelworks close to the docks at East Moors in 1890. The metalworks at nearby Port Talbot
Port Talbot (, ) is a town and community in the county borough of Neath Port Talbot, Wales, situated on the east side of Swansea Bay, approximately from Swansea. The Port Talbot Steelworks covers a large area of land which dominates the south ...
also helped developed the industrial base of Glamorgan.
City and capital city status

King Edward VII
Edward VII (Albert Edward; 9 November 1841 – 6 May 1910) was King of the United Kingdom of Great Britain and Ireland and Emperor of India, from 22 January 1901 until his death in 1910.
The second child and eldest son of Queen Victoria a ...
granted Cardiff city status City status is a symbolic and legal designation given by a national or subnational government. A municipality may receive city status because it already has the qualities of a city, or because it has some special purpose.
Historically, city status ...
on 28 October 1905, and the city acquired a Roman Catholic
Roman or Romans most often refers to:
*Rome, the capital city of Italy
* Ancient Rome, Roman civilization from 8th century BC to 5th century AD
* Roman people, the people of ancient Rome
*'' Epistle to the Romans'', shortened to ''Romans'', a let ...
Cathedral
A cathedral is a church that contains the '' cathedra'' () of a bishop, thus serving as the central church of a diocese, conference, or episcopate. Churches with the function of "cathedral" are usually specific to those Christian denominatio ...
in 1916.The ancient Llandaff Cathedral was outside the city boundaries until 1922 In subsequent years an increasing number of national institutions were located in the city, including the National Museum of Wales
National may refer to:
Common uses
* Nation or country
** Nationality – a ''national'' is a person who is subject to a nation, regardless of whether the person has full rights as a citizen
Places in the United States
* National, Maryland, c ...
, Welsh national war memorial
A war memorial is a building, monument, statue, or other edifice to celebrate a war or victory, or (predominating in modern times) to commemorate those who died or were injured in a war.
Symbolism
Historical usage
It has ...
, and the University of Wales
, latin_name =
, image =
, caption = Coat of Arms
, motto = cy, Goreu Awen Gwirionedd
, mottoeng = The Best Inspiration is Truth
, established =
,
, type = Confederal, non-member ...
registry – although it was denied the National Library of Wales, partly because the library's founder, Sir John Williams, considered Cardiff to have "a non-Welsh population".Encyclopedia of Wales
After a brief post-war boom, Cardiff docks entered a prolonged decline in the interwar period. By 1936, their trade was less than half its value in 1913, reflecting the slump in demand for Welsh coal. Bomb damage during the Cardiff Blitz in World War II
World War II or the Second World War, often abbreviated as WWII or WW2, was a world war that lasted from 1939 to 1945. It involved the vast majority of the world's countries—including all of the great powers—forming two opposing ...
included the devastation of Llandaff Cathedral, and in the immediate postwar years the city's link with the Bute family came to an end.
The city was proclaimed capital city of Wales on 20 December 1955, by a written reply by the Home Secretary
The secretary of state for the Home Department, otherwise known as the home secretary, is a senior minister of the Crown in the Government of the United Kingdom. The home secretary leads the Home Office, and is responsible for all national s ...
Gwilym Lloyd George. Caernarfon had also vied for this title. Cardiff therefore celebrated two important anniversaries
An anniversary is the date on which an event took place or an institution was founded in a previous year, and may also refer to the commemoration or celebration of that event. The word was first used for Catholic feasts to commemorate saints. ...
in 2005. The Encyclopedia of Wales notes that the decision to recognise the city as the capital of Wales "had more to do with the fact that it contained marginal Conservative
Conservatism is a cultural, social, and political philosophy that seeks to promote and to preserve traditional institutions, practices, and values. The central tenets of conservatism may vary in relation to the culture and civilization in ...
constituencies than any reasoned view of what functions a Welsh capital should have". Although the city hosted the Commonwealth Games
The Commonwealth Games, often referred to as the Friendly Games or simply the Comm Games, are a quadrennial international multi-sport event among athletes from the Commonwealth of Nations. The event was first held in 1930, and, with the exce ...
in 1958, Cardiff only became a centre of national administration with the establishment of the Welsh Office
The Welsh Office ( cy, Swyddfa Gymreig) was a department in the Government of the United Kingdom with responsibilities for Wales. It was established in April 1965 to execute government policy in Wales, and was headed by the Secretary of State f ...
in 1964, which later prompted the creation of various other public bodies such as the Arts Council of Wales and the Welsh Development Agency
Welsh Development Agency (WDA; cy, Awdurdod Datblygu Cymru) was an executive agency (or QUANGO) and later designated an Assembly Sponsored Public Body (ASPB). Established in 1976, it was tasked with rescuing the ailing Welsh economy by encour ...
, most of which were headquartered in Cardiff.
The East Moors Steelworks closed in 1978 and Cardiff lost population during the 1980s, consistent with a wider pattern of counter urbanisation in Britain. However, it recovered and was one of the few cities (outside London) where population grew during the 1990s. During this period the Cardiff Bay Development Corporation was promoting the redevelopment
Redevelopment is any new construction on a site that has pre-existing uses. It represents a process of land development uses to revitalize the physical, economic and social fabric of urban space.
Description
Variations on redevelopment include: ...
of south Cardiff; an evaluation of the regeneration of Cardiff Bay published in 2004 concluded that the project had "reinforced the competitive position of Cardiff" and "contributed to a massive improvement in the quality of the built environment", although it had failed "to attract the major inward investors originally anticipated".
In the 1997 devolution referendum, Cardiff voters rejected the establishment of the National Assembly for Wales
The Senedd (; ), officially known as the Welsh Parliament in English and () in Welsh, is the devolved, unicameral legislature of Wales. A democratically elected body, it makes laws for Wales, agrees certain taxes and scrutinises the Welsh Go ...
by 55.4% to 44.2% on a 47% turnout, which Denis Balsom partly ascribed to a general preference in Cardiff and some other parts of Wales for a 'British' rather than exclusively 'Welsh' identity. The relative lack of support for the Assembly locally, and difficulties between the Welsh Office and Cardiff Council in acquiring the original preferred venue, Cardiff City Hall, encouraged other local authorities to bid to house the Assembly. However, the Assembly eventually located at Crickhowell House in Cardiff Bay in 1999; in 2005, a new debating chamber on an adjacent site, designed by Richard Rogers, was opened.
The city was county town of Glamorgan until the council reorganisation in 1974 paired Cardiff and the now Vale of Glamorgan
The Vale of Glamorgan ( cy, Bro Morgannwg ), often referred to as The Vale, is a county borough in the south-east of Wales. It borders Bridgend County Borough to the west, Cardiff to the east, Rhondda Cynon Taf to the north, and the Bristol ...
together as the new county of South Glamorgan
, Government= South Glamorgan County Council
, Status= Non-metropolitan county (1974–1996) Preserved county (1996–)
, Start= 1974
, End= 1996
, Arms=
, HQ= ...
. Further local government restructuring in 1996 resulted in Cardiff city's district
A district is a type of administrative division that, in some countries, is managed by the local government. Across the world, areas known as "districts" vary greatly in size, spanning regions or county, counties, several municipality, municipa ...
council becoming a unitary authority
A unitary authority is a local authority responsible for all local government functions within its area or performing additional functions that elsewhere are usually performed by a higher level of sub-national government or the national governmen ...
, the City and County of Cardiff, with the addition of Creigiau and Pentyrch.
On 1 March 2004, Cardiff was granted Fairtrade City status.
See also
*History of Wales
The history of what is now Wales () begins with evidence of a Neanderthal presence from at least 230,000 years ago, while ''Homo sapiens'' arrived by about 31,000 BC. However, continuous habitation by modern humans dates from the period after ...
* Timeline of Cardiff history
* Tiger Bay
Notes
References
External links
Cardiff's Medieval Town Defences
{{DEFAULTSORT:History Of Cardiff