History of Ancient Egypt on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
The history of ancient Egypt spans the period from the early prehistoric settlements of the northern
 The Nile valley of Egypt was basically uninhabitable until the work of clearing and irrigating the land along the banks was started. However, it appears that this clearance and irrigation was largely under way by the
The Nile valley of Egypt was basically uninhabitable until the work of clearing and irrigating the land along the banks was started. However, it appears that this clearance and irrigation was largely under way by the
 The historical records of ancient Egypt begin with Egypt as a unified state, which occurred sometime around 3150 BC. According to Egyptian tradition, Menes, thought to have unified Upper and Lower Egypt, was the first king. This Egyptian culture, customs, art expression, architecture, and social structure were closely tied to religion, remarkably stable, and changed little over a period of nearly 3000 years.
The historical records of ancient Egypt begin with Egypt as a unified state, which occurred sometime around 3150 BC. According to Egyptian tradition, Menes, thought to have unified Upper and Lower Egypt, was the first king. This Egyptian culture, customs, art expression, architecture, and social structure were closely tied to religion, remarkably stable, and changed little over a period of nearly 3000 years.
 The Old Kingdom is most commonly regarded as spanning the period of time when Egypt was ruled by the Third Dynasty through to the Sixth Dynasty (2686–2181 BCE). The royal capital of Egypt during this period was located at Memphis, where
The Old Kingdom is most commonly regarded as spanning the period of time when Egypt was ruled by the Third Dynasty through to the Sixth Dynasty (2686–2181 BCE). The royal capital of Egypt during this period was located at Memphis, where
Nile
The Nile, , Bohairic , lg, Kiira , Nobiin: Áman Dawū is a major north-flowing river in northeastern Africa. It flows into the Mediterranean Sea. The Nile is the longest river in Africa and has historically been considered the longest riv ...
valley to the Roman conquest of Egypt in 30 BC. The pharaonic period, the period in which Egypt was ruled by a pharaoh
Pharaoh (, ; Egyptian: '' pr ꜥꜣ''; cop, , Pǝrro; Biblical Hebrew: ''Parʿō'') is the vernacular term often used by modern authors for the kings of ancient Egypt who ruled as monarchs from the First Dynasty (c. 3150 BC) until th ...
, is dated from the 32nd century BC, when Upper and Lower Egypt were unified, until the country fell under Macedonian rule in 332 BC.
Chronology
;Note: For alternative 'revisions' to the chronology of Egypt, seeEgyptian chronology
The majority of Egyptologists agree on the outline and many details of the chronology of Ancient Egypt. This scholarly consensus is the so-called Conventional Egyptian chronology, which places the beginning of the Old Kingdom in the 27th centur ...
.
Egypt's history is split into several different periods according to the ruling dynasty
A dynasty is a sequence of rulers from the same family,''Oxford English Dictionary'', "dynasty, ''n''." Oxford University Press (Oxford), 1897. usually in the context of a monarchical system, but sometimes also appearing in republics. A ...
of each pharaoh
Pharaoh (, ; Egyptian: '' pr ꜥꜣ''; cop, , Pǝrro; Biblical Hebrew: ''Parʿō'') is the vernacular term often used by modern authors for the kings of ancient Egypt who ruled as monarchs from the First Dynasty (c. 3150 BC) until th ...
. The dating of events is still a subject of research. The conservative dates are not supported by any reliable absolute date for a span of about three millennia. The following is the list according to conventional Egyptian chronology.
* Prehistoric Egypt (prior to 3100 BC)
* Naqada III ("the protodynastic period", approximately 3100–3000 BC; sometimes referred to as "Dynasty 0")
* Early Dynastic Period ( First–Second
The second (symbol: s) is the unit of time in the International System of Units (SI), historically defined as of a day – this factor derived from the division of the day first into 24 hours, then to 60 minutes and finally to 60 seconds ea ...
Dynasties)
* Old Kingdom
In ancient Egyptian history, the Old Kingdom is the period spanning c. 2700–2200 BC. It is also known as the "Age of the Pyramids" or the "Age of the Pyramid Builders", as it encompasses the reigns of the great pyramid-builders of the Fourth ...
(Third
Third or 3rd may refer to:
Numbers
* 3rd, the ordinal form of the cardinal number 3
* , a fraction of one third
* 1⁄60 of a ''second'', or 1⁄3600 of a ''minute''
Places
* 3rd Street (disambiguation)
* Third Avenue (disambiguation)
* Hi ...
– Sixth Dynasties)
* First Intermediate Period
The First Intermediate Period, described as a 'dark period' in ancient Egyptian history, spanned approximately 125 years, c. 2181–2055 BC, after the end of the Old Kingdom. It comprises the Seventh (although this is mostly considered spuriou ...
( Seventh or Eighth– Eleventh Dynasties)
* Middle Kingdom ( Twelfth–Thirteenth
In music or music theory, a thirteenth is the note thirteen scale degrees from the root of a chord and also the interval between the root and the thirteenth. The interval can be also described as a compound sixth, spanning an octa ...
Dynasties)
* Second Intermediate Period ( Fourteenth– Seventeenth Dynasties)
* New Kingdom
New is an adjective referring to something recently made, discovered, or created.
New or NEW may refer to:
Music
* New, singer of K-pop group The Boyz
Albums and EPs
* ''New'' (album), by Paul McCartney, 2013
* ''New'' (EP), by Regurgitator ...
( Eighteenth– Twentieth Dynasties)
* Third Intermediate Period (also known as the Libyan Period; Twenty-first– Twenty-fifth Dynasties)
* Late Period ( Twenty-sixth– Thirty-first Dynasties)
* Ptolemaic Egypt (305–30 BC)
Neolithic Egypt
Neolithic period
TheNile
The Nile, , Bohairic , lg, Kiira , Nobiin: Áman Dawū is a major north-flowing river in northeastern Africa. It flows into the Mediterranean Sea. The Nile is the longest river in Africa and has historically been considered the longest riv ...
has been the lifeline for Egyptian culture since nomadic hunter-gatherers began living along it during the Pleistocene
The Pleistocene ( , often referred to as the ''Ice age'') is the geological Epoch (geology), epoch that lasted from about 2,580,000 to 11,700 years ago, spanning the Earth's most recent period of repeated glaciations. Before a change was fina ...
. Traces of these early people appear in the form of artefacts and rock carvings along the terraces of the Nile and in the oases.
Along the Nile in the 12th millennium BC, an Upper Paleolithic grain-grinding culture using the earliest type of sickle blades had replaced the culture of hunting
Hunting is the human activity, human practice of seeking, pursuing, capturing, or killing wildlife or feral animals. The most common reasons for humans to hunt are to harvest food (i.e. meat) and useful animal products (fur/hide (skin), hide, ...
, fishing
Fishing is the activity of trying to catch fish. Fish are often caught as wildlife from the natural environment, but may also be caught from fish stocking, stocked bodies of water such as fish pond, ponds, canals, park wetlands and reservoirs. ...
, and hunter-gatherer
A traditional hunter-gatherer or forager is a human living an ancestrally derived lifestyle in which most or all food is obtained by foraging, that is, by gathering food from local sources, especially edible wild plants but also insects, fung ...
s using stone tool
A stone tool is, in the most general sense, any tool made either partially or entirely out of stone. Although stone tool-dependent societies and cultures still exist today, most stone tools are associated with prehistoric (particularly Stone A ...
s. Evidence also indicates human habitation and cattle herding in the southwestern corner of Egypt near the Sudan
Sudan ( or ; ar, السودان, as-Sūdān, officially the Republic of the Sudan ( ar, جمهورية السودان, link=no, Jumhūriyyat as-Sūdān), is a country in Northeast Africa. It shares borders with the Central African Republic t ...
border before the 8th millennium BC
8 (eight) is the natural number following 7 and preceding 9.
In mathematics
8 is:
* a composite number, its proper divisors being , , and . It is twice 4 or four times 2.
* a power of two, being 2 (two cubed), and is the first number of ...
.
Despite this, the idea of an independent bovine domestication event in Africa
Africa is the world's second-largest and second-most populous continent, after Asia in both cases. At about 30.3 million km2 (11.7 million square miles) including adjacent islands, it covers 6% of Earth's total surface area ...
must be abandoned because subsequent evidence gathered over a period of thirty years has failed to corroborate this.
Archaeological evidence has attested that population settlements occurred in Nubia as early as the Late Pleistocene
The Pleistocene ( , often referred to as the ''Ice age'') is the geological Epoch (geology), epoch that lasted from about 2,580,000 to 11,700 years ago, spanning the Earth's most recent period of repeated glaciations. Before a change was fina ...
era and from the 5th millennium BC onwards, whereas there is "no or scanty evidence" of human presence in the Egyptian Nile Valley during these periods, which may be due to problems in site preservation.
The oldest-known domesticated cattle remains in Africa are from the Faiyum c. 4400 BC. Geological evidence and computer climate modeling studies suggest that natural climate changes around the 8th millennium BC began to desiccate the extensive pastoral lands of North Africa
North Africa, or Northern Africa is a region encompassing the northern portion of the African continent. There is no singularly accepted scope for the region, and it is sometimes defined as stretching from the Atlantic shores of Mauritania in ...
, eventually forming the Sahara
, photo = Sahara real color.jpg
, photo_caption = The Sahara taken by Apollo 17 astronauts, 1972
, map =
, map_image =
, location =
, country =
, country1 =
, ...
by the 25th century BC.
Continued desiccation forced the early ancestors of the Egyptians to settle around the Nile more permanently and forced them to adopt a more sedentary lifestyle. However, the period from 9th to the 6th millennium BC
The 6th millennium BC spanned the years 6000 BC to 5001 BC (c. 8 ka to c. 7 ka). It is impossible to precisely date events that happened around the time of this millennium and all dates mentioned here are estimates mostly based on geological an ...
has left very little in the way of archaeological evidence.
Prehistoric Egypt
 The Nile valley of Egypt was basically uninhabitable until the work of clearing and irrigating the land along the banks was started. However, it appears that this clearance and irrigation was largely under way by the
The Nile valley of Egypt was basically uninhabitable until the work of clearing and irrigating the land along the banks was started. However, it appears that this clearance and irrigation was largely under way by the 6th millennium
While the future cannot be predicted with certainty, present understanding in various scientific fields allows for the prediction of some far-future events, if only in the broadest outline. These fields include astrophysics, which studies how ...
. By that time, Nile society was already engaged in organized agriculture and the construction of large buildings.Redford, Donald B. ''Egypt, Canaan, and Israel in Ancient Times.'' (Princeton: University Press, 1992), p. 6.
At this time, Egyptians in the southwestern corner of Egypt were herding cattle and also constructing large buildings. Mortar was in use by the 4th millennium. The people of the valley and the Nile Delta
The Nile Delta ( ar, دلتا النيل, or simply , is the delta formed in Lower Egypt where the Nile River spreads out and drains into the Mediterranean Sea. It is one of the world's largest river deltas—from Alexandria in the west to ...
were self-sufficient and were raising barley
Barley (''Hordeum vulgare''), a member of the grass family, is a major cereal grain grown in temperate climates globally. It was one of the first cultivated grains, particularly in Eurasia as early as 10,000 years ago. Globally 70% of barley p ...
and emmer, an early variety of wheat, and stored it in pits lined with reed mats.Carl Roebuck, ''The World of Ancient Times'', p. 52. They raised cattle, goat
The goat or domestic goat (''Capra hircus'') is a domesticated species of goat-antelope typically kept as livestock. It was domesticated from the wild goat (''C. aegagrus'') of Southwest Asia and Eastern Europe. The goat is a member of the a ...
s and pigs and they wove linen
Linen () is a textile made from the fibers of the flax plant.
Linen is very strong, absorbent, and dries faster than cotton. Because of these properties, linen is comfortable to wear in hot weather and is valued for use in garments. It also ...
and baskets. Prehistory continues through this time, variously held to begin with the Amratian culture.
Between 5500 BC and the 31st century BC
The 31st century BC was a century that lasted from the year 3100 BC to 3001 BC.
Events
*c. 3100 BC: Polo ( mni, Sagol Kangjei) was first played in Manipur state.
*c. 3100 BC?: The Anu Ziggurat and White Temple are built in Uruk.
*c. 3100 BC?: ...
, small settlements flourished along the Nile, whose delta empties into the Mediterranean Sea
The Mediterranean Sea is a sea connected to the Atlantic Ocean, surrounded by the Mediterranean Basin and almost completely enclosed by land: on the north by Western and Southern Europe and Anatolia, on the south by North Africa, and on ...
.
The Tasian culture
The Tasian culture is possibly one of the oldest-known Predynastic culture in Upper Egypt, which evolved around 4500 BC. It is named for the burials found at Deir Tasa, a site on the east bank of the Nile located between Asyut and Akhmim. There i ...
was the next to appear; it existed in Upper Egypt starting about 4500 BC. This group is named for the burials found at Deir Tasa, a site on the east bank of the Nile between Asyut and Akhmim
Akhmim ( ar, أخميم, ; Akhmimic , ; Sahidic/Bohairic cop, ) is a city in the Sohag Governorate of Upper Egypt. Referred to by the ancient Greeks as Khemmis or Chemmis ( grc, Χέμμις) and Panopolis ( grc, Πανὸς πόλις and Π ...
. The Tasian culture is notable for producing the earliest blacktop-ware, a type of red and brown pottery painted black on its top and interior.Gardiner (1964), p.388
The Badari culture, named for the Badari site near Deir Tasa, followed the Tasian; however, similarities cause many to avoid differentiating between them at all. The Badari culture continued to produce the kind of pottery called blacktop-ware (although its quality was much improved over previous specimens), and was assigned the sequence dating
Sequence dating, an archaeological relative dating method, allows assemblages to be arranged in a rough serial order, which is then taken to indicate time. Sequence dating is a method of seriation developed by the Egyptologist Sir William Matthew ...
numbers between 21 and 29. The significant difference, however, between the Tasian and Badari, which prevents scholars from completely merging the two, is that Badari sites are Chalcolithic
The Copper Age, also called the Chalcolithic (; from grc-gre, χαλκός ''khalkós'', "copper" and ''líthos'', "Rock (geology), stone") or (A)eneolithic (from Latin ''wikt:aeneus, aeneus'' "of copper"), is an list of archaeologi ...
while the Tasian sites remained Neolithic
The Neolithic period, or New Stone Age, is an Old World archaeological period and the final division of the Stone Age. It saw the Neolithic Revolution, a wide-ranging set of developments that appear to have arisen independently in several pa ...
and are thus considered technically part of the Stone Age
The Stone Age was a broad prehistoric period during which stone was widely used to make tools with an edge, a point, or a percussion surface. The period lasted for roughly 3.4 million years, and ended between 4,000 BC and 2,000 BC, with ...
.Gardiner (1964), p.389
The Amratian culture is named after the site of el-Amreh, about south of Badari. El-Amreh was the first site where this culture was found unmingled with the later Gerzeh culture. However, this period is better attested at Nagada, and so is also referred to as the "Naqada I" culture.Grimal (1988) p.24 Black-topped ware continued to be produced, but white cross-line ware, a type of pottery decorated with close parallel white lines crossed by another set of close parallel white lines, began to be produced during this time. The Amratian period falls between S.D. 30 and 39.Gardiner (1964), 390. Newly excavated objects indicate that trade between Upper and Lower Egypt existed at this time. A stone vase from the north was found at el-Amreh, and copper, which is not present in Egypt, was apparently imported from the Sinai Peninsula
The Sinai Peninsula, or simply Sinai (now usually ) (, , cop, Ⲥⲓⲛⲁ), is a peninsula in Egypt, and the only part of the country located in Asia. It is between the Mediterranean Sea to the north and the Red Sea to the south, and is a ...
or perhaps Nubia
Nubia () ( Nobiin: Nobīn, ) is a region along the Nile river encompassing the area between the first cataract of the Nile (just south of Aswan in southern Egypt) and the confluence of the Blue and White Niles (in Khartoum in central Sud ...
. ObsidianGrimal (1988) p.28 and an extremely small amount of gold
Gold is a chemical element with the symbol Au (from la, aurum) and atomic number 79. This makes it one of the higher atomic number elements that occur naturally. It is a bright, slightly orange-yellow, dense, soft, malleable, and ductile ...
were both definitively imported from Nubia during this time. Trade with the oases was also likely.
Naqada II
The Gerzeh culture ("Naqada II"), named after the site of el-Gerzeh, was the next stage in cultural development, and it was during this time that the foundation for ancient Egypt was laid. The Gerzeh culture was largely an unbroken development out of the Amratian, starting in theNile Delta
The Nile Delta ( ar, دلتا النيل, or simply , is the delta formed in Lower Egypt where the Nile River spreads out and drains into the Mediterranean Sea. It is one of the world's largest river deltas—from Alexandria in the west to ...
and moving south through Upper Egypt
Upper Egypt ( ar, صعيد مصر ', shortened to , , locally: ; ) is the southern portion of Egypt and is composed of the lands on both sides of the Nile that extend upriver from Lower Egypt in the north to Nubia in the south.
In ancient E ...
; however, it failed to dislodge the Amratian in Nubia
Nubia () ( Nobiin: Nobīn, ) is a region along the Nile river encompassing the area between the first cataract of the Nile (just south of Aswan in southern Egypt) and the confluence of the Blue and White Niles (in Khartoum in central Sud ...
.Redford, Donald B. ''Egypt, Canaan, and Israel in Ancient Times.'' (Princeton: University Press, 1992), p. 16. The Gerzeh culture coincided with a significant drop in rainfall and farming produced the vast majority of food. With increased food supplies, the populace adopted a much more sedentary lifestyle, and the larger settlements grew to cities of about 5000 residents. It was in this time that the city dwellers started using adobe
Adobe ( ; ) is a building material made from earth and organic materials. is Spanish for '' mudbrick''. In some English-speaking regions of Spanish heritage, such as the Southwestern United States, the term is used to refer to any kind of ...
to build their cities. Copper instead of stone was increasingly used to make tools and weaponry. Silver
Silver is a chemical element with the symbol Ag (from the Latin ', derived from the Proto-Indo-European ''h₂erǵ'': "shiny" or "white") and atomic number 47. A soft, white, lustrous transition metal, it exhibits the highest electrical ...
, gold
Gold is a chemical element with the symbol Au (from la, aurum) and atomic number 79. This makes it one of the higher atomic number elements that occur naturally. It is a bright, slightly orange-yellow, dense, soft, malleable, and ductile ...
, lapis lazuli (imported from Badakhshan
Badakhshan is a historical region comprising parts of modern-day north-eastern Afghanistan, eastern Tajikistan, and Taxkorgan Tajik Autonomous County in China. Badakhshan Province is one of the 34 provinces of Afghanistan. Much of historic ...
in what is now Afghanistan), and Egyptian faience
Egyptian faience is a sintered- quartz ceramic material from Ancient Egypt. The sintering process "covered he materialwith a true vitreous coating" as the quartz underwent vitrification, creating a bright lustre of various colours "usually i ...
were used ornamentally,Redford, Donald B. ''Egypt, Canaan, and Israel in Ancient Times.'' (Princeton: University Press, 1992), p. 17. and the cosmetic palettes used for eye paint since the Badari culture began to be adorned with relief
Relief is a sculptural method in which the sculpted pieces are bonded to a solid background of the same material. The term '' relief'' is from the Latin verb ''relevo'', to raise. To create a sculpture in relief is to give the impression that th ...
s.Gardiner (1694), p.391
By the 33rd century BC, just before the First Dynasty of Egypt, Egypt was divided into two kingdoms known from later times as Upper Egypt
Upper Egypt ( ar, صعيد مصر ', shortened to , , locally: ; ) is the southern portion of Egypt and is composed of the lands on both sides of the Nile that extend upriver from Lower Egypt in the north to Nubia in the south.
In ancient E ...
to the south and Lower Egypt to the north.Adkins, L. and Adkins, R. (2001) ''The Little Book of Egyptian Hieroglyphics'', p155. London: Hodder and Stoughton. ISBN . The dividing line was drawn roughly in the area of modern Cairo
Cairo ( ; ar, القاهرة, al-Qāhirah, ) is the capital of Egypt and its largest city, home to 10 million people. It is also part of the largest urban agglomeration in Africa, the Arab world and the Middle East: The Greater Cairo metr ...
.
Dynastic Egypt
Early dynastic period
 The historical records of ancient Egypt begin with Egypt as a unified state, which occurred sometime around 3150 BC. According to Egyptian tradition, Menes, thought to have unified Upper and Lower Egypt, was the first king. This Egyptian culture, customs, art expression, architecture, and social structure were closely tied to religion, remarkably stable, and changed little over a period of nearly 3000 years.
The historical records of ancient Egypt begin with Egypt as a unified state, which occurred sometime around 3150 BC. According to Egyptian tradition, Menes, thought to have unified Upper and Lower Egypt, was the first king. This Egyptian culture, customs, art expression, architecture, and social structure were closely tied to religion, remarkably stable, and changed little over a period of nearly 3000 years.
Egyptian chronology
The majority of Egyptologists agree on the outline and many details of the chronology of Ancient Egypt. This scholarly consensus is the so-called Conventional Egyptian chronology, which places the beginning of the Old Kingdom in the 27th centur ...
, which involves regnal year
A regnal year is a year of the reign of a sovereign, from the Latin ''regnum'' meaning kingdom, rule. Regnal years considered the date as an ordinal, not a cardinal number. For example, a monarch could have a first year of rule, a second year ...
s, began around this time. The conventional chronology was accepted during the twentieth century, but it does not include any of the major revision proposals that also have been made in that time. Even within a single work, archaeologists often offer several possible dates, or even several whole chronologies as possibilities. Consequently, there may be discrepancies between dates shown here and in articles on particular rulers or topics related to ancient Egypt. There also are several possible spellings of the names. Typically, Egyptologists divide the history of pharaonic civilization using a schedule laid out first by Manetho's ''Aegyptiaca'', which was written during the Ptolemaic Kingdom in the third century BC.
Prior to the unification of Egypt, the land was settled with autonomous villages. With the early dynasties, and for much of Egypt's history thereafter, the country came to be known as the Two Lands. The pharaoh
Pharaoh (, ; Egyptian: '' pr ꜥꜣ''; cop, , Pǝrro; Biblical Hebrew: ''Parʿō'') is the vernacular term often used by modern authors for the kings of ancient Egypt who ruled as monarchs from the First Dynasty (c. 3150 BC) until th ...
s established a national administration and appointed royal governors.
According to Manetho, the first pharaoh was Menes, but archeological findings support the view that the first ruler to claim to have united the two lands was Narmer, the final king of the Naqada III period. His name is known primarily from the famous Narmer Palette, whose scenes have been interpreted as the act of uniting Upper and Lower Egypt. Menes is now thought to be one of the titles of Hor-Aha, the second pharaoh of the First Dynasty.
Funeral practices for the elite resulted in the construction of mastabas, which later became models for subsequent Old Kingdom
In ancient Egyptian history, the Old Kingdom is the period spanning c. 2700–2200 BC. It is also known as the "Age of the Pyramids" or the "Age of the Pyramid Builders", as it encompasses the reigns of the great pyramid-builders of the Fourth ...
constructions such as the step pyramid, thought to have originated during the Third Dynasty of Egypt
The Third Dynasty of ancient Egypt (Dynasty III) is the first dynasty of the Old Kingdom. Other dynasties of the Old Kingdom include the Fourth, Fifth and Sixth. The capital during the period of the Old Kingdom was at Memphis.
Overview
...
.
Old Kingdom
 The Old Kingdom is most commonly regarded as spanning the period of time when Egypt was ruled by the Third Dynasty through to the Sixth Dynasty (2686–2181 BCE). The royal capital of Egypt during this period was located at Memphis, where
The Old Kingdom is most commonly regarded as spanning the period of time when Egypt was ruled by the Third Dynasty through to the Sixth Dynasty (2686–2181 BCE). The royal capital of Egypt during this period was located at Memphis, where Djoser
Djoser (also read as Djeser and Zoser) was an ancient Egyptian pharaoh of the 3rd Dynasty during the Old Kingdom, and was the founder of that epoch. He is also known by his Hellenized names Tosorthros (from Manetho) and Sesorthos (from Eusebiu ...
(2630–2611 BCE) established his court.
The Old Kingdom is perhaps best known, however, for the large number of pyramid
A pyramid (from el, πυραμίς ') is a structure whose outer surfaces are triangular and converge to a single step at the top, making the shape roughly a pyramid in the geometric sense. The base of a pyramid can be trilateral, quadrilate ...
s, which were constructed at this time as pharaonic burial places. For this reason, this epoch is frequently referred to as "the Age of the Pyramids." The first notable pharaoh of the Old Kingdom was Djoser of the Third Dynasty, who ordered the construction of the first pyramid, the Pyramid of Djoser, in Memphis' necropolis of Saqqara
Saqqara ( ar, سقارة, ), also spelled Sakkara or Saccara in English , is an Egyptian village in Giza Governorate, that contains ancient burial grounds of Egyptian royalty, serving as the necropolis for the ancient Egyptian capital, Memph ...
.
It was in this era that formerly independent states became nomes (districts) ruled solely by the pharaoh. Former local rulers were forced to assume the role of nomarch
A nomarch ( grc, νομάρχης, egy, ḥrj tp ꜥꜣ Great Chief) was a provincial governor in ancient Egypt; the country was divided into 42 provinces, called nomes (singular , plural ). A nomarch was the government official responsib ...
(governor) or work as tax collectors. Egyptians in this era worshiped the pharaoh as a god, believing that he ensured the annual flooding of the Nile that was necessary for their crops.
The Old Kingdom and its royal power reached their zenith under the Fourth Dynasty. Sneferu
Sneferu ( snfr-wj "He has perfected me", from ''Ḥr-nb-mꜣꜥt-snfr-wj'' "Horus, Lord of Maat, has perfected me", also read Snefru or Snofru), well known under his Hellenized name Soris ( grc-koi, Σῶρις by Manetho), was the founding phar ...
, the dynasty's founder, is believed to have commissioned at least three pyramids; while his son and successor Khufu ( Greek ''Cheops'') erected the Great Pyramid of Giza
The Great Pyramid of Giza is the biggest Egyptian pyramid and the tomb of Fourth Dynasty pharaoh Khufu. Built in the early 26th century BC during a period of around 27 years, the pyramid is the oldest of the Seven Wonders of the Ancient Worl ...
, Sneferu had more stone and brick moved than any other pharaoh. Khufu, his son Khafre (Greek ''Chephren''), and his grandson Menkaure
Menkaure (also Menkaura, Egyptian transliteration ''mn-k3w-Rˁ''), was an ancient Egyptian king ( pharaoh) of the fourth dynasty during the Old Kingdom, who is well known under his Hellenized names Mykerinos ( gr, Μυκερῖνος) (by He ...
(Greek ''Mycerinus'') all achieved lasting fame in the construction of the Giza pyramid complex
The Giza pyramid complex ( ar, مجمع أهرامات الجيزة), also called the Giza necropolis, is the site on the Giza Plateau in Greater Cairo, Egypt that includes the Great Pyramid of Giza, the Pyramid of Khafre, and the Pyramid of Me ...
.
To organize and feed the manpower needed to create these pyramids required a centralized government with extensive powers, and Egyptologists believe the Old Kingdom at this time demonstrated this level of sophistication. Recent excavations near the pyramids led by Mark Lehner have uncovered a large city that seems to have housed, fed and supplied the pyramid workers. Although it was once believed that slaves built these monuments, a theory based on The Exodus
The Exodus (Hebrew: יציאת מצרים, ''Yeẓi’at Miẓrayim'': ) is the founding myth of the Israelites whose narrative is spread over four books of the Torah (or Pentateuch, corresponding to the first five books of the Bible), namely E ...
narrative of the Hebrew Bible
The Hebrew Bible or Tanakh (;"Tanach"
'' corvée of
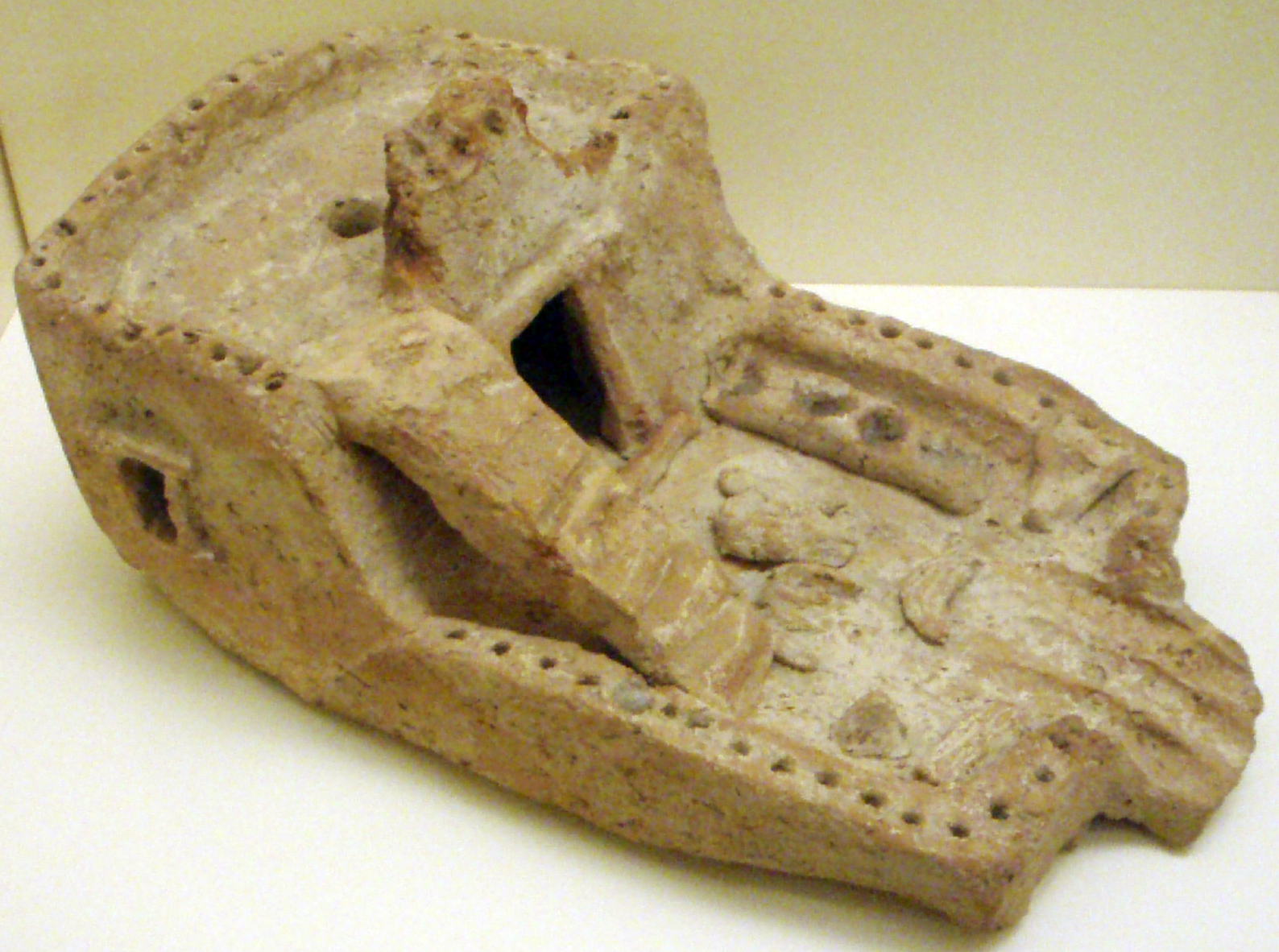 After the fall of the Old Kingdom came a roughly 200-year stretch of time known as the First Intermediate Period, which is generally thought to include a relatively obscure set of pharaohs running from the end of the Sixth to the Tenth and most of the Eleventh Dynasties. Most of these were likely local monarchs who did not hold much power outside of their nome. There are a number of texts known as "Lamentations" from the early period of the subsequent Middle Kingdom that may shed some light on what happened during this period. Some of these texts reflect on the breakdown of rule, others allude to invasion by "Asiatic bowmen". In general, the stories focus on a society where the natural order of things in both society and nature was overthrown.
It is also highly likely that it was during this period that all of the pyramid and tomb complexes were looted. Further lamentation texts allude to this fact, and by the beginning of the Middle Kingdom
After the fall of the Old Kingdom came a roughly 200-year stretch of time known as the First Intermediate Period, which is generally thought to include a relatively obscure set of pharaohs running from the end of the Sixth to the Tenth and most of the Eleventh Dynasties. Most of these were likely local monarchs who did not hold much power outside of their nome. There are a number of texts known as "Lamentations" from the early period of the subsequent Middle Kingdom that may shed some light on what happened during this period. Some of these texts reflect on the breakdown of rule, others allude to invasion by "Asiatic bowmen". In general, the stories focus on a society where the natural order of things in both society and nature was overthrown.
It is also highly likely that it was during this period that all of the pyramid and tomb complexes were looted. Further lamentation texts allude to this fact, and by the beginning of the Middle Kingdom
 The Middle Kingdom is the period in the history of ancient Egypt stretching from the 39th regnal year of Mentuhotep II of the
The Middle Kingdom is the period in the history of ancient Egypt stretching from the 39th regnal year of Mentuhotep II of the
 The Second Intermediate Period marks a period when Egypt once again fell into disarray between the end of the Middle Kingdom and the start of the
The Second Intermediate Period marks a period when Egypt once again fell into disarray between the end of the Middle Kingdom and the start of the
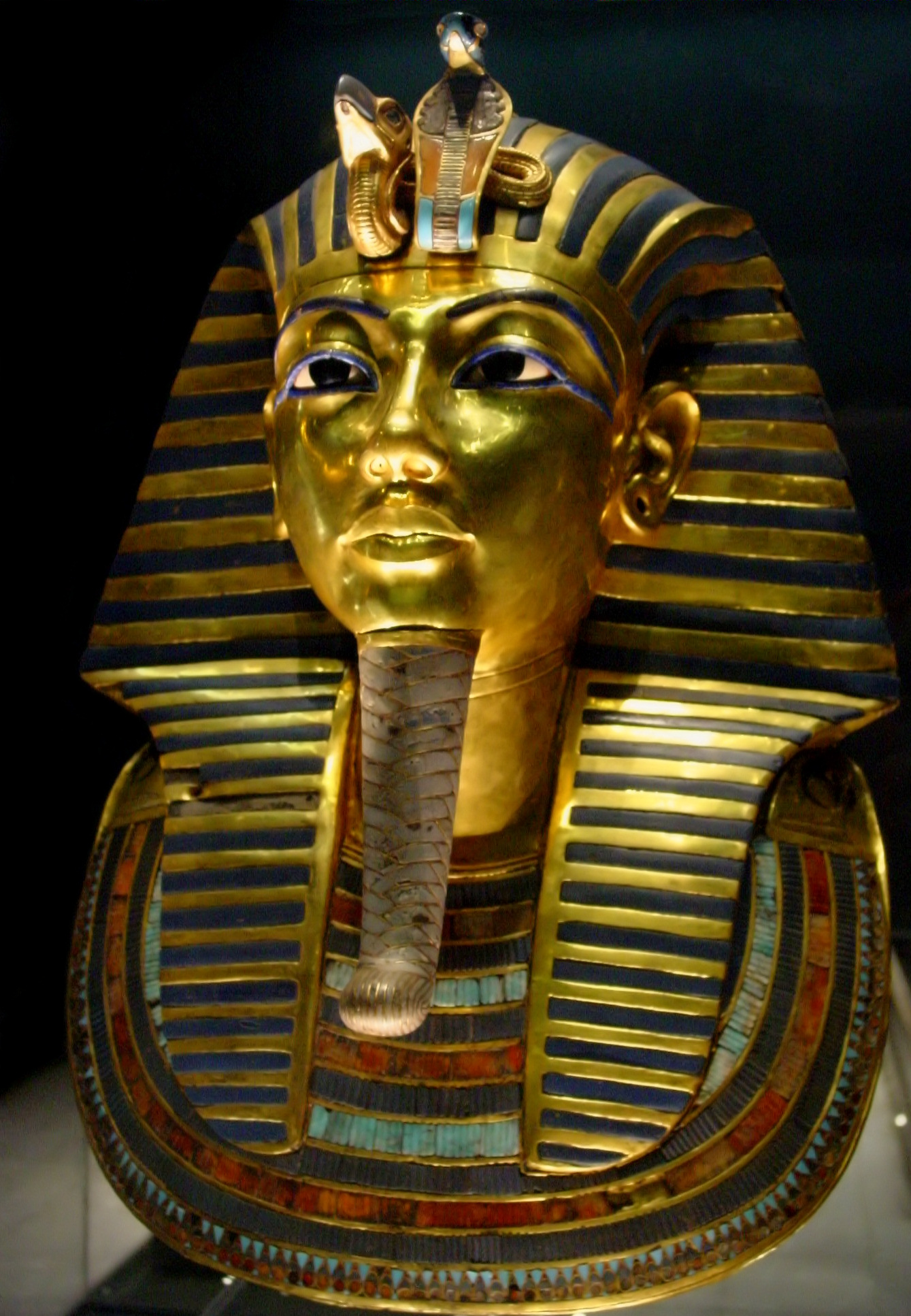 This was a time of great wealth and power for Egypt. Some of the most important and best-known pharaohs ruled at this time, such as Hatshepsut. Hatshepsut is unusual as she was a female pharaoh, a rare occurrence in Egyptian history. She was an ambitious and competent leader, extending Egyptian trade south into present-day
This was a time of great wealth and power for Egypt. Some of the most important and best-known pharaohs ruled at this time, such as Hatshepsut. Hatshepsut is unusual as she was a female pharaoh, a rare occurrence in Egyptian history. She was an ambitious and competent leader, extending Egyptian trade south into present-day
 Ramesses I reigned for two years and was succeeded by his son
Ramesses I reigned for two years and was succeeded by his son
 After the death of Ramesses XI, his successor
After the death of Ramesses XI, his successor  After the withdrawal of Egypt from
After the withdrawal of Egypt from
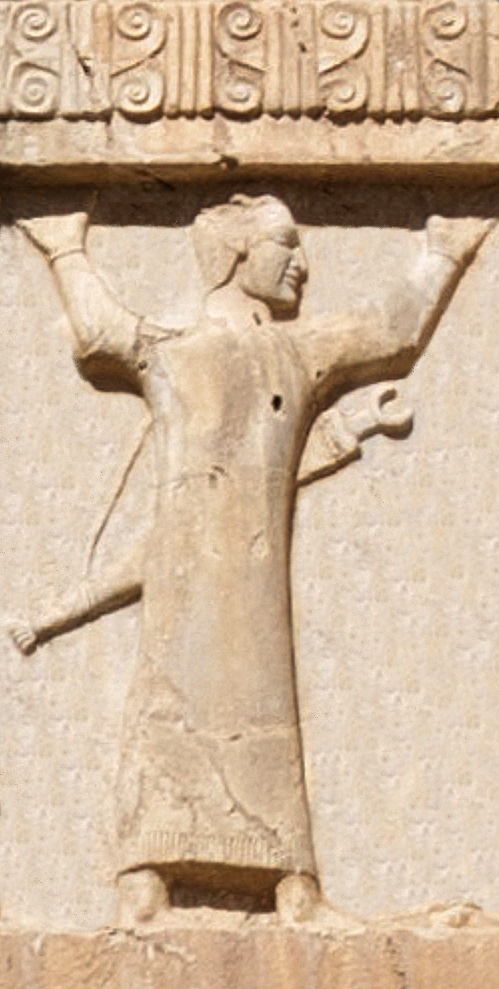 Achaemenid Egypt can be divided into three eras: the first period of Persian occupation, 525–404 BC (when Egypt became a
Achaemenid Egypt can be divided into three eras: the first period of Persian occupation, 525–404 BC (when Egypt became a
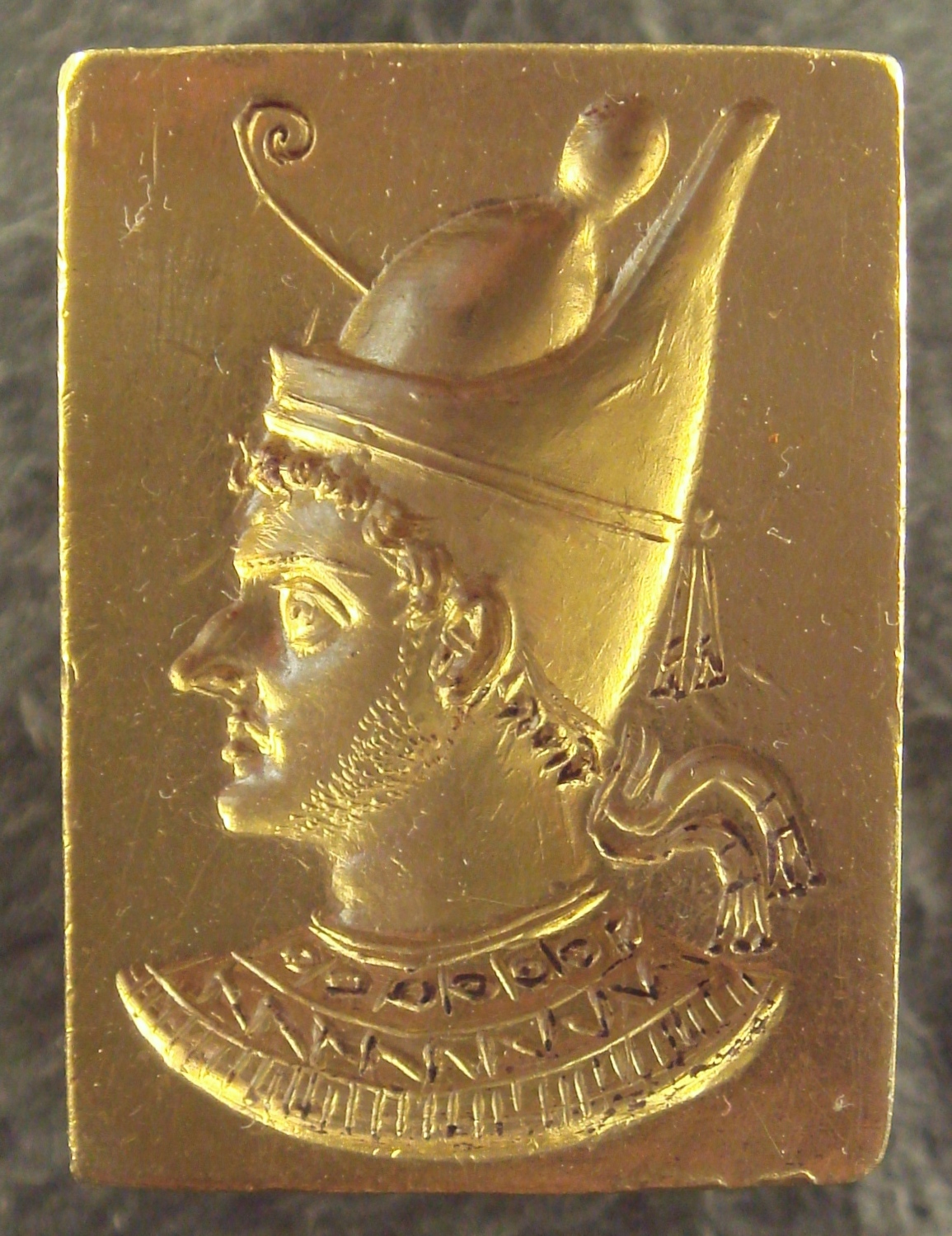 Following Alexander's death in
Following Alexander's death in
The Ancient Egypt Site
* ttps://books.google.com/books?vid=ISBN9004130489&id=qeApebusL_0C&dq=PtahHotep&as_brr=1&hl=nl Texts from the Pyramid Age Door Nigel C. Strudwick, Ronald J. Leprohon, 2005, Brill Academic Publishers
Ancient Egyptian Science: A Source Book Door Marshall Clagett, 1989
{{DEFAULTSORT:History Of Ancient Egypt *
'' corvée of
peasant
A peasant is a pre-industrial agricultural laborer or a farmer with limited land-ownership, especially one living in the Middle Ages under feudalism and paying rent, tax, fees, or services to a landlord. In Europe, three classes of peasa ...
s drawn from across Egypt. They apparently worked while the annual flood covered their fields, as well as a very large crew of specialists, including stonecutters, painters, mathematicians and priests.
The Fifth Dynasty began with Userkaf
Userkaf (known in Ancient Greek as , ) was a pharaoh of ancient Egypt and the founder of the Fifth Dynasty. He reigned for seven to eight years in the early 25th century BC, during the Old Kingdom period. He probably belonged to a branch of t ...
c. 2495 BC and was marked by the growing importance of the cult of the sun god Ra. Consequently, less effort was devoted to the construction of pyramid complexes than during the Fourth Dynasty and more to the construction of sun temples in Abusir
Abusir ( ar, ابو صير ; Egyptian ''pr wsjr'' cop, ⲃⲟⲩⲥⲓⲣⲓ ' "the House or Temple of Osiris"; grc, Βούσιρις) is the name given to an Egyptian archaeological locality – specifically, an extensive necropolis ...
. The decoration of pyramid complexes grew more elaborate during the dynasty and its last king, Unas
Unas or Wenis, also spelled Unis ( egy, wnjs, hellenized form Oenas or Onnos), was a pharaoh, the ninth and last ruler of the Fifth Dynasty of Egypt during the Old Kingdom. Unas reigned for 15 to 30 years in the mid- 24th century BC (circ ...
, was the first to have the Pyramid Texts
The Pyramid Texts are the oldest ancient Egyptian funerary texts, dating to the late Old Kingdom. They are the earliest known corpus of ancient Egyptian religious texts. Written in Old Egyptian, the pyramid texts were carved onto the subterran ...
inscribed in his pyramid.
Egypt's expanding interests in trade goods such as ebony, incense such as myrrh
Myrrh (; from Semitic, but see '' § Etymology'') is a gum-resin extracted from a number of small, thorny tree species of the genus '' Commiphora''. Myrrh resin has been used throughout history as a perfume, incense and medicine. Myrrh m ...
and frankincense
Frankincense (also known as olibanum) is an aromatic resin used in incense and perfumes, obtained from trees of the genus '' Boswellia'' in the family Burseraceae. The word is from Old French ('high-quality incense').
There are several species ...
, gold, copper and other useful metals compelled the ancient Egyptians to navigate the open seas. Evidence from the pyramid of Sahure, second king of the dynasty, shows that a regular trade existed with the Syrian coast to procure cedar wood. Pharaohs also launched expeditions to the famed Land of Punt, possibly the Horn of Africa
The Horn of Africa (HoA), also known as the Somali Peninsula, is a large peninsula and geopolitical region in East Africa.Robert Stock, ''Africa South of the Sahara, Second Edition: A Geographical Interpretation'', (The Guilford Press; 2004 ...
, for ebony, ivory and aromatic resins.
During the Sixth Dynasty (2345–2181 BCE), the power of pharaohs gradually weakened in favor of powerful nomarch
A nomarch ( grc, νομάρχης, egy, ḥrj tp ꜥꜣ Great Chief) was a provincial governor in ancient Egypt; the country was divided into 42 provinces, called nomes (singular , plural ). A nomarch was the government official responsib ...
s. These no longer belonged to the royal family and their charge became hereditary, thus creating local dynasties largely independent from the central authority of the pharaoh. Internal disorders set in during the incredibly long reign of Pepi II Neferkare (2278–2184 BCE) towards the end of the dynasty. His death, certainly well past that of his intended heirs, might have created succession struggles and the country slipped into civil wars mere decades after the close of Pepi II
Pepi II Neferkare (2284 BC – after 2247 BC, probably either 2216 or 2184 BC) was a pharaoh of the Sixth Dynasty in Egypt's Old Kingdom who reigned from 2278 BC. His second name, Neferkare (''Nefer-ka-Re''), means "Beautiful ...
's reign. The final blow came when the 4.2 kiloyear event
The 4.2-kiloyear (thousand years) BP aridification event (long-term drought) was one of the most severe climatic events of the Holocene epoch. It defines the beginning of the current Meghalayan age in the Holocene epoch.
Starting around 2200& ...
struck the region in the 22nd century BC, producing consistently low Nile flood levels. The result was the collapse of the Old Kingdom followed by decades of famine and strife.
First Intermediate Period
 After the fall of the Old Kingdom came a roughly 200-year stretch of time known as the First Intermediate Period, which is generally thought to include a relatively obscure set of pharaohs running from the end of the Sixth to the Tenth and most of the Eleventh Dynasties. Most of these were likely local monarchs who did not hold much power outside of their nome. There are a number of texts known as "Lamentations" from the early period of the subsequent Middle Kingdom that may shed some light on what happened during this period. Some of these texts reflect on the breakdown of rule, others allude to invasion by "Asiatic bowmen". In general, the stories focus on a society where the natural order of things in both society and nature was overthrown.
It is also highly likely that it was during this period that all of the pyramid and tomb complexes were looted. Further lamentation texts allude to this fact, and by the beginning of the Middle Kingdom
After the fall of the Old Kingdom came a roughly 200-year stretch of time known as the First Intermediate Period, which is generally thought to include a relatively obscure set of pharaohs running from the end of the Sixth to the Tenth and most of the Eleventh Dynasties. Most of these were likely local monarchs who did not hold much power outside of their nome. There are a number of texts known as "Lamentations" from the early period of the subsequent Middle Kingdom that may shed some light on what happened during this period. Some of these texts reflect on the breakdown of rule, others allude to invasion by "Asiatic bowmen". In general, the stories focus on a society where the natural order of things in both society and nature was overthrown.
It is also highly likely that it was during this period that all of the pyramid and tomb complexes were looted. Further lamentation texts allude to this fact, and by the beginning of the Middle Kingdom mummies
A mummy is a dead human or an animal whose soft tissues and organs have been preserved by either intentional or accidental exposure to chemicals, extreme cold, very low humidity, or lack of air, so that the recovered body does not decay furt ...
are found decorated with magical spells that were once exclusive to the pyramid of the kings of the Sixth Dynasty.
By 2160 BC, a new line of pharaohs, the Ninth and Tenth Dynasties, consolidated Lower Egypt from their capital in Heracleopolis Magna. A rival line, the Eleventh Dynasty
The Eleventh Dynasty of ancient Egypt (notated Dynasty XI) is a well-attested group of rulers. Its earlier members before Pharaoh Mentuhotep II are grouped with the four preceding dynasties to form the First Intermediate Period, whereas the lat ...
based at Thebes, reunited Upper Egypt
Upper Egypt ( ar, صعيد مصر ', shortened to , , locally: ; ) is the southern portion of Egypt and is composed of the lands on both sides of the Nile that extend upriver from Lower Egypt in the north to Nubia in the south.
In ancient E ...
, and a clash between the rival dynasties was inevitable. Around 2055 BC, the Theban forces defeated the Heracleopolitan pharaohs and reunited the Two Lands. The reign of its first pharaoh, Mentuhotep II
Mentuhotep II ( egy, Mn- ṯw- ḥtp, meaning " Mentu is satisfied"), also known under his prenomen Nebhepetre ( egy, Nb- ḥpt- Rˁ, meaning "The Lord of the rudder is Ra"), was an ancient Egyptian pharaoh, the sixth ruler of the Eleventh ...
, marks the beginning of the Middle Kingdom.
Middle Kingdom
 The Middle Kingdom is the period in the history of ancient Egypt stretching from the 39th regnal year of Mentuhotep II of the
The Middle Kingdom is the period in the history of ancient Egypt stretching from the 39th regnal year of Mentuhotep II of the Eleventh Dynasty
The Eleventh Dynasty of ancient Egypt (notated Dynasty XI) is a well-attested group of rulers. Its earlier members before Pharaoh Mentuhotep II are grouped with the four preceding dynasties to form the First Intermediate Period, whereas the lat ...
to the end of the Thirteenth Dynasty, roughly between 2030 and 1650 BC. The period comprises two phases, the Eleventh Dynasty, which ruled from Thebes, and then the Twelfth Dynasty, whose capital was Lisht. These two dynasties were originally considered the full extent of this unified kingdom, but some historians now consider the first part of the Thirteenth Dynasty to belong to the Middle Kingdom.
The earliest pharaohs of the Middle Kingdom traced their origin to two nomarchs of Thebes, Intef the Elder
Intef, whose name is commonly accompanied by epithets such as the Elder, the Great (= ''Intef-aa'') or born of Iku, was a Theban nomarch during the First Intermediate Period c. 2150 BC and later considered a founding figure of the 11th Dynasty, wh ...
, who served a Heracleopolitan pharaoh of the Tenth Dynasty, and his successor, Mentuhotep I. The successor of the latter, Intef I, was the first Theban nomarch to claim a Horus name
The Horus name is the oldest known and used crest of ancient Egyptian rulers. It belongs to the " great five names" of an Egyptian pharaoh. However, modern Egyptologists and linguists are starting to prefer the more neutral term: the "serekh na ...
and thus the throne of Egypt. He is considered the first pharaoh of the Eleventh Dynasty. His claims brought the Thebans into conflict with the rulers of the Tenth Dynasty. Intef I and his brother Intef II undertook several campaigns northwards and finally captured the important nome of Abydos Abydos may refer to:
*Abydos, a progressive metal side project of German singer Andy Kuntz
*Abydos (Hellespont), an ancient city in Mysia, Asia Minor
* Abydos (''Stargate''), name of a fictional planet in the ''Stargate'' science fiction universe ...
. Warfare continued intermittently between the Thebean and Heracleapolitan dynasties until the 39th regnal year
A regnal year is a year of the reign of a sovereign, from the Latin ''regnum'' meaning kingdom, rule. Regnal years considered the date as an ordinal, not a cardinal number. For example, a monarch could have a first year of rule, a second year ...
of Mentuhotep II
Mentuhotep II ( egy, Mn- ṯw- ḥtp, meaning " Mentu is satisfied"), also known under his prenomen Nebhepetre ( egy, Nb- ḥpt- Rˁ, meaning "The Lord of the rudder is Ra"), was an ancient Egyptian pharaoh, the sixth ruler of the Eleventh ...
, second successor of Intef II. At this point, the Herakleopolitans were defeated and the Theban dynasty consolidated their rule over Egypt. Mentuhotep II is known to have commanded military campaigns south into Nubia, which had gained its independence during the First Intermediate Period. There is also evidence for military actions against the Southern Levant. The king reorganized the country and placed a vizier
A vizier (; ar, وزير, wazīr; fa, وزیر, vazīr), or wazir, is a high-ranking political advisor or minister in the near east. The Abbasid caliphs gave the title ''wazir'' to a minister formerly called '' katib'' (secretary), who was ...
at the head of civil administration for the country. Mentuhotep II was succeeded by his son, Mentuhotep III
Sankhkare Mentuhotep III (also Montuhotep III) of the Eleventh Dynasty was Pharaoh of Egypt during the Middle Kingdom. He was assigned a reign of 12 years in the Turin Canon.
Reign
Mentuhotep III succeeded his father Mentuhotep II to th ...
, who organized an expedition to Punt. His reign saw the realization of some of the finest Egyptian carvings. Mentuhotep III was succeeded by Mentuhotep IV, the final pharaoh of this dynasty. Despite being absent from various lists of pharaohs, his reign is attested from a few inscriptions in Wadi Hammamat that record expeditions to the Red Sea
The Red Sea ( ar, البحر الأحمر - بحر القلزم, translit=Modern: al-Baḥr al-ʾAḥmar, Medieval: Baḥr al-Qulzum; or ; Coptic: ⲫⲓⲟⲙ ⲛ̀ϩⲁϩ ''Phiom Enhah'' or ⲫⲓⲟⲙ ⲛ̀ϣⲁⲣⲓ ''Phiom ǹšari''; ...
coast and to quarry stone for the royal monuments.
The leader of this expedition was his vizier Amenemhat, who is widely assumed to be the future Pharaoh Amenemhat I, the first pharaoh of the Twelfth Dynasty. Amenemhat is therefore assumed by some Egyptologists to have either usurped the throne or assumed power after Mentuhotep IV died childless. Amenemhat I built a new capital for Egypt, Itjtawy, thought to be located near the present-day Lisht, although Manetho claims the capital remained at Thebes. Amenemhat forcibly pacified internal unrest, curtailed the rights of the nomarchs, and is known to have launched at least one campaign into Nubia. His son Senusret I
Senusret I (Middle Egyptian: z-n-wsrt; /suʀ nij ˈwas.ɾiʔ/) also anglicized as Sesostris I and Senwosret I, was the second pharaoh of the Twelfth Dynasty of Egypt. He ruled from 1971 BC to 1926 BC (1920 BC to 1875 BC), and was one of the mos ...
continued the policy of his father to recapture Nubia and other territories lost during the First Intermediate Period. The Libu were subdued under his forty-five year reign and Egypt's prosperity and security were secured. Senusret III (1878–1839 BC) was a warrior king, leading his troops deep into Nubia, and built a series of massive forts throughout the country to establish Egypt's formal boundaries with the unconquered areas of its territory. Amenemhat III (1860–1815 BC) is considered the last great pharaoh of the Middle Kingdom.
Egypt's population began to exceed food production levels during the reign of Amenemhat III, who then ordered the exploitation of the Faiyum and increased mining operations in the Sinai Peninsula
The Sinai Peninsula, or simply Sinai (now usually ) (, , cop, Ⲥⲓⲛⲁ), is a peninsula in Egypt, and the only part of the country located in Asia. It is between the Mediterranean Sea to the north and the Red Sea to the south, and is a ...
. He also invited settlers from Western Asia
Western Asia, West Asia, or Southwest Asia, is the westernmost subregion of the larger geographical region of Asia, as defined by some academics, UN bodies and other institutions. It is almost entirely a part of the Middle East, and includes A ...
to Egypt to labor on Egypt's monuments. Late in his reign, the annual flooding of the Nile began to fail, further straining the resources of the government. The Thirteenth Dynasty and Fourteenth Dynasty
The Fourteenth Dynasty of Egypt was a series of rulers reigning during the Second Intermediate Period over the Nile Delta region of Egypt. It lasted between 75 (ca. 1725–1650 BC) and 155 years (ca. 1805–1650 BC), depending on the sc ...
witnessed the slow decline of Egypt into the Second Intermediate Period, in which some of the settlers invited by Amenemhat III would seize power as the Hyksos
Hyksos (; Egyptian '' ḥqꜣ(w)- ḫꜣswt'', Egyptological pronunciation: ''hekau khasut'', "ruler(s) of foreign lands") is a term which, in modern Egyptology, designates the kings of the Fifteenth Dynasty of Egypt (fl. c. 1650–1550 BC).
T ...
.
Second Intermediate Period and the Hyksos
 The Second Intermediate Period marks a period when Egypt once again fell into disarray between the end of the Middle Kingdom and the start of the
The Second Intermediate Period marks a period when Egypt once again fell into disarray between the end of the Middle Kingdom and the start of the New Kingdom
New is an adjective referring to something recently made, discovered, or created.
New or NEW may refer to:
Music
* New, singer of K-pop group The Boyz
Albums and EPs
* ''New'' (album), by Paul McCartney, 2013
* ''New'' (EP), by Regurgitator ...
. This period is best known as the time the Hyksos
Hyksos (; Egyptian '' ḥqꜣ(w)- ḫꜣswt'', Egyptological pronunciation: ''hekau khasut'', "ruler(s) of foreign lands") is a term which, in modern Egyptology, designates the kings of the Fifteenth Dynasty of Egypt (fl. c. 1650–1550 BC).
T ...
made their appearance in Egypt, the reigns of its kings comprising the Fifteenth Dynasty.
The Thirteenth Dynasty proved unable to hold onto the long land of Egypt, and a provincial family of Levantine descent located in the marshes of the eastern Delta at Avaris broke away from the central authority to form the Fourteenth Dynasty
The Fourteenth Dynasty of Egypt was a series of rulers reigning during the Second Intermediate Period over the Nile Delta region of Egypt. It lasted between 75 (ca. 1725–1650 BC) and 155 years (ca. 1805–1650 BC), depending on the sc ...
. The splintering of the land most likely happened shortly after the reigns of the powerful Thirteenth Dynasty Pharaohs Neferhotep I and Sobekhotep IV c. 1720 BC.
While the Fourteenth Dynasty was Levantine, the Hyksos first appeared in Egypt c. 1650 BC when they took control of Avaris and rapidly moved south to Memphis, thereby ending the Thirteenth and Fourteenth Dynasties. The outlines of the traditional account of the "invasion" of the land by the Hyksos is preserved in the ''Aegyptiaca'' of Manetho, who records that during this time the Hyksos overran Egypt, led by Salitis, the founder of the Fifteenth Dynasty. More recently, however, the idea of a simple migration, with little or no violence involved, has gained some support. Under this theory, the Egyptian rulers of the Thirteenth and Fourteenth dynasties were unable to stop these new migrants from traveling to Egypt from the Levant because their kingdoms were struggling to cope with various domestic problems, including possibly famine and plague. Be it military or peaceful, the weakened state of the Thirteenth and Fourteenth Dynasty kingdoms could explain why they rapidly fell to the emerging Hyksos power.
The Hyksos princes and chieftains ruled in the eastern Delta with their local Egyptian vassals. The Fifteenth Dynasty rulers established their capital and seat of government at Memphis and their summer residence at Avaris. The Hyksos kingdom was centered in the eastern Nile Delta
The Nile Delta ( ar, دلتا النيل, or simply , is the delta formed in Lower Egypt where the Nile River spreads out and drains into the Mediterranean Sea. It is one of the world's largest river deltas—from Alexandria in the west to ...
and central Egypt but relentlessly pushed south for the control of central and Upper Egypt. Around the time Memphis fell to the Hyksos, the native Egyptian ruling house in Thebes declared its independence and set itself up as the Sixteenth Dynasty. Another short lived dynasty might have done the same in central Egypt, profiting from the power vacuum created by the fall of the Thirteenth Dynasty and forming the Abydos Dynasty.Kim Ryholt
Kim Steven Bardrum Ryholt (born 19 June 1970) is a professor of Egyptology at the University of Copenhagen and a specialist on Egyptian history and literature. He is director of the research centeCanon and Identity Formation in the Earliest Litera ...
: ''The Political Situation in Egypt during the Second Intermediate Period'', Museum Tusculanum Press, (1997) By 1600 BC, the Hyksos had successfully moved south in central Egypt, eliminating the Abydos Dynasty and directly threatening the Sixteenth Dynasty. The latter was to prove unable to resist and Thebes fell to the Hyksos for a very short period c. 1580 BC. The Hyksos rapidly withdrew to the north and Thebes regained some independence under the Seventeenth Dynasty
The Seventeenth Dynasty of Egypt (notated Dynasty XVII, alternatively 17th Dynasty or Dynasty 17) was a dynasty of pharaohs that ruled in Upper Egypt during the late Second Intermediate Period, approximately from 1580 to 1550 BC. Its mainly Theb ...
. From then on, Hyksos relations with the south seem to have been mainly of a commercial nature, although Theban princes appear to have recognized the Hyksos rulers and may possibly have provided them with tribute
A tribute (; from Latin ''tributum'', "contribution") is wealth, often in kind, that a party gives to another as a sign of submission, allegiance or respect. Various ancient states exacted tribute from the rulers of land which the state conq ...
for a period.
The Seventeenth Dynasty was to prove the salvation of Egypt and would eventually lead the war of liberation that drove the Hyksos back into Asia. The two last kings of this dynasty were Seqenenre Tao
Seqenenre Tao (also Seqenera Djehuty-aa or Sekenenra Taa, called 'the Brave') ruled over the last of the local kingdoms of the Theban region of Egypt in the Seventeenth Dynasty during the Second Intermediate Period. He probably was the son and ...
and Kamose. Ahmose I completed the conquest and expulsion of the Hyksos from the Nile Delta, restored Theban rule over the whole of Egypt and successfully reasserted Egyptian power in its formerly subject territories of Nubia
Nubia () ( Nobiin: Nobīn, ) is a region along the Nile river encompassing the area between the first cataract of the Nile (just south of Aswan in southern Egypt) and the confluence of the Blue and White Niles (in Khartoum in central Sud ...
and the Southern Levant.Grimal, Nicolas. ''A History of Ancient Egypt'' p. 194. Librairie Arthéme Fayard, 1988. His reign marks the beginning of the Eighteenth Dynasty and the New Kingdom
New is an adjective referring to something recently made, discovered, or created.
New or NEW may refer to:
Music
* New, singer of K-pop group The Boyz
Albums and EPs
* ''New'' (album), by Paul McCartney, 2013
* ''New'' (EP), by Regurgitator ...
.
New Kingdom
Possibly as a result of the foreign rule of theHyksos
Hyksos (; Egyptian '' ḥqꜣ(w)- ḫꜣswt'', Egyptological pronunciation: ''hekau khasut'', "ruler(s) of foreign lands") is a term which, in modern Egyptology, designates the kings of the Fifteenth Dynasty of Egypt (fl. c. 1650–1550 BC).
T ...
during the Second Intermediate Period, the New Kingdom saw Egypt attempt to create a buffer between the Levant and Egypt, and attain its greatest territorial extent. It expanded far south into Nubia
Nubia () ( Nobiin: Nobīn, ) is a region along the Nile river encompassing the area between the first cataract of the Nile (just south of Aswan in southern Egypt) and the confluence of the Blue and White Niles (in Khartoum in central Sud ...
and held wide territories in the Near East. Egyptian armies fought Hittite armies for control of modern-day Syria
Syria ( ar, سُورِيَا or سُورِيَة, translit=Sūriyā), officially the Syrian Arab Republic ( ar, الجمهورية العربية السورية, al-Jumhūrīyah al-ʻArabīyah as-Sūrīyah), is a Western Asian country loc ...
.
Eighteenth Dynasty
 This was a time of great wealth and power for Egypt. Some of the most important and best-known pharaohs ruled at this time, such as Hatshepsut. Hatshepsut is unusual as she was a female pharaoh, a rare occurrence in Egyptian history. She was an ambitious and competent leader, extending Egyptian trade south into present-day
This was a time of great wealth and power for Egypt. Some of the most important and best-known pharaohs ruled at this time, such as Hatshepsut. Hatshepsut is unusual as she was a female pharaoh, a rare occurrence in Egyptian history. She was an ambitious and competent leader, extending Egyptian trade south into present-day Somalia
Somalia, , Osmanya script: 𐒈𐒝𐒑𐒛𐒐𐒘𐒕𐒖; ar, الصومال, aṣ-Ṣūmāl officially the Federal Republic of SomaliaThe ''Federal Republic of Somalia'' is the country's name per Article 1 of thProvisional Constitut ...
and north into the Mediterranean. She ruled for twenty years through a combination of widespread propaganda and deft political skill. Her co-regent and successor Thutmose III ("the Napoleon
Napoleon Bonaparte ; it, Napoleone Bonaparte, ; co, Napulione Buonaparte. (born Napoleone Buonaparte; 15 August 1769 – 5 May 1821), later known by his regnal name Napoleon I, was a French military commander and political leader wh ...
of Egypt") expanded Egypt's army and wielded it with great success. However, late in his reign, he ordered her name hacked out from her monuments. He fought against Asiatic people and was the most successful of Egyptian pharaohs. Amenhotep III built extensively at the temple of Karnak
The Karnak Temple Complex, commonly known as Karnak (, which was originally derived from ar, خورنق ''Khurnaq'' "fortified village"), comprises a vast mix of decayed temples, pylons, chapels, and other buildings near Luxor, Egypt. Constru ...
including the Luxor Temple, which consisted of two pylons
Pylon may refer to:
Structures and boundaries
* Pylon (architecture), the gateway to the inner part of an Ancient Egyptian temple or Christian cathedral
* Pylon, a support tower structure for suspension bridges or highways
* Pylon, an orange mar ...
, a colonnade behind the new temple entrance, and a new temple to the goddess Maat
Maat or Maʽat ( Egyptian:
mꜣꜥt /ˈmuʀʕat/, Coptic: ⲙⲉⲓ) refers to the ancient Egyptian concepts of truth, balance, order, harmony, law, morality, and justice. Ma'at was also the goddess who personified these concepts, and r ...
.
During the reign of Thutmose III (c. 1479–1425 BC), pharaoh
Pharaoh (, ; Egyptian: '' pr ꜥꜣ''; cop, , Pǝrro; Biblical Hebrew: ''Parʿō'') is the vernacular term often used by modern authors for the kings of ancient Egypt who ruled as monarchs from the First Dynasty (c. 3150 BC) until th ...
, originally referring to the king's palace, became a form of address for the person who was king.
One of the best-known 18th Dynasty pharaohs is Amenhotep IV, who changed his name to Akhenaten
Akhenaten (pronounced ), also spelled Echnaton, Akhenaton, ( egy, ꜣḫ-n-jtn ''ʾŪḫə-nə-yātəy'', , meaning "Effective for the Aten"), was an ancient Egyptian pharaoh reigning or 1351–1334 BC, the tenth ruler of the Eighteenth D ...
in honor of the god Aten. His exclusive worship of the Aten, sometimes called Atenism, is often seen as history's first instance of monotheism
Monotheism is the belief that there is only one deity, an all-supreme being that is universally referred to as God. Cross, F.L.; Livingstone, E.A., eds. (1974). "Monotheism". The Oxford Dictionary of the Christian Church (2 ed.). Oxford: Oxfo ...
. Atenism and several changes that accompanied it seriously disrupted Egyptian society. Akhenaten built a new capital at the site of Amarna
Amarna (; ar, العمارنة, al-ʿamārnah) is an extensive Egyptian archaeological site containing the remains of what was the capital city of the late Eighteenth Dynasty. The city was established in 1346 BC, built at the direction of the Ph ...
, which gives his reign and the few that followed their modern name, the Amarna Period
The Amarna Period was an era of Egyptian history during the later half of the Eighteenth Dynasty when the royal residence of the pharaoh and his queen was shifted to Akhetaten ('Horizon of the Aten') in what is now Amarna. It was marked by the ...
. Amarna art
Amarna art, or the Amarna style, is a style adopted in the Amarna Period during and just after the reign of Akhenaten (r. 1351–1334 BC) in the late Eighteenth Dynasty, during the New Kingdom. Whereas Ancient Egyptian art was famously slow t ...
diverged significantly from the previous conventions of Egyptian art. Under a series of successors, of whom the longest reigning were Tutankhamun
Tutankhamun (, egy, twt-ꜥnḫ-jmn), Egyptological pronunciation Tutankhamen () (), sometimes referred to as King Tut, was an Egyptian pharaoh who was the last of his royal family to rule during the end of the Eighteenth Dynasty (ruled ...
and Horemheb
Horemheb, also spelled Horemhab or Haremhab ( egy, ḥr-m-ḥb, meaning " Horus is in Jubilation") was the last pharaoh of the 18th Dynasty of Egypt (1550–1295 BC). He ruled for at least 14 years between 1319 BC and 1292 BC. ...
. Under them, worship of the old gods was revived and much of the art and monuments that were created during Akhenaten's reign was defaced or destroyed. When Horemheb died without an heir, he named as his successor Ramesses I
Menpehtyre Ramesses I (or Ramses) was the founding pharaoh of ancient Egypt's 19th Dynasty. The dates for his short reign are not completely known but the time-line of late 1292–1290 BC is frequently cited as well as 1295–1294 BC. While R ...
, founder of the Nineteenth Dynasty.
Nineteenth Dynasty

Seti I
Menmaatre Seti I (or Sethos I in Greek) was the second pharaoh of the Nineteenth Dynasty of Egypt during the New Kingdom period, ruling c.1294 or 1290 BC to 1279 BC. He was the son of Ramesses I and Sitre, and the father of Ramesses II.
The ...
. Seti I carried on the work of Horemheb
Horemheb, also spelled Horemhab or Haremhab ( egy, ḥr-m-ḥb, meaning " Horus is in Jubilation") was the last pharaoh of the 18th Dynasty of Egypt (1550–1295 BC). He ruled for at least 14 years between 1319 BC and 1292 BC. ...
in restoring power, control, and respect to Egypt. He also was responsible for creating the temple complex at Abydos.
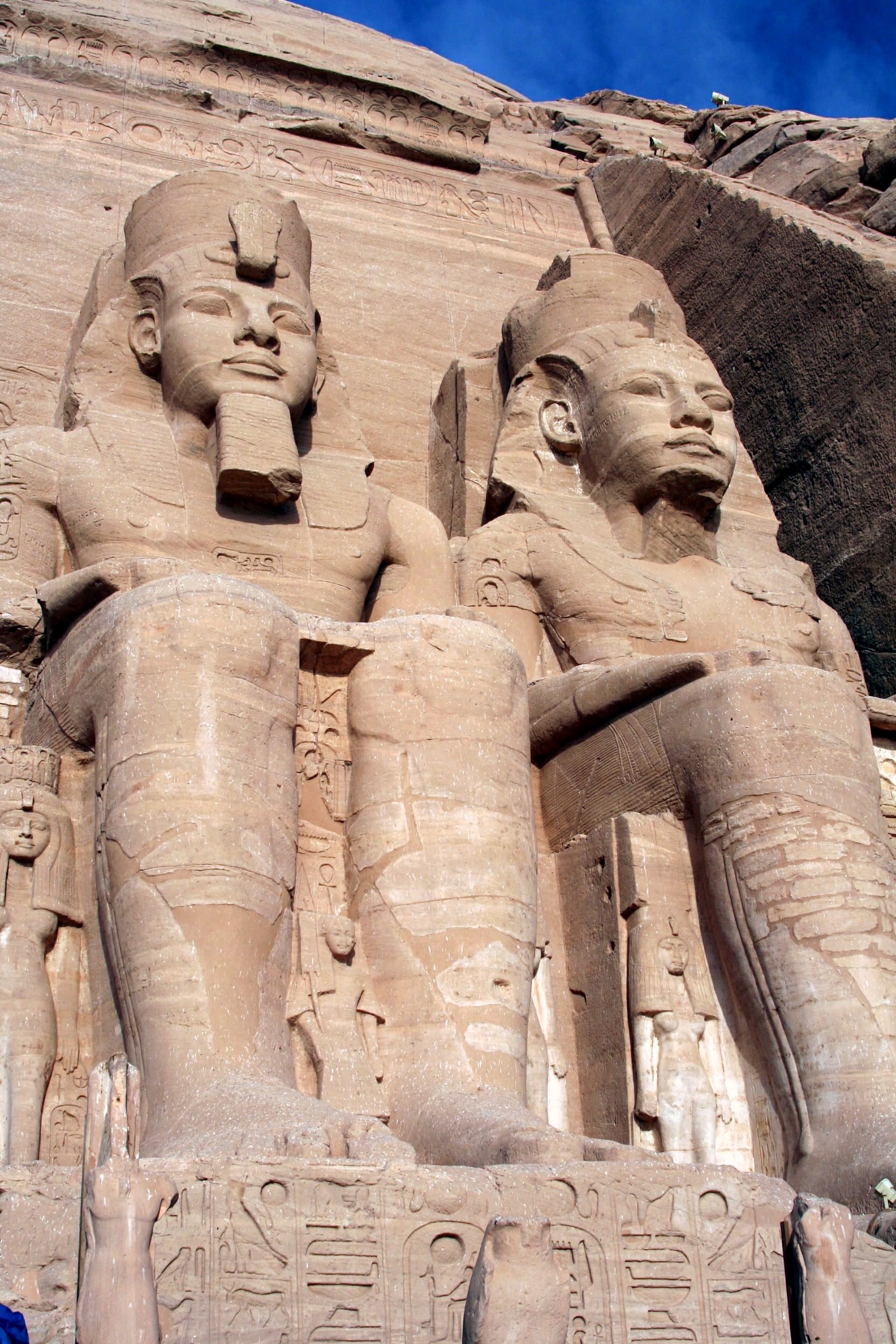
Arguably Ancient Egypt's power as a nation-state peaked during the reign of Ramesses II
Ramesses II ( egy, rꜥ-ms-sw ''Rīʿa-məsī-sū'', , meaning "Ra is the one who bore him"; ), commonly known as Ramesses the Great, was the third pharaoh of the Nineteenth Dynasty of Egypt. Along with Thutmose III he is often regarded a ...
("the Great") of the Nineteenth Dynasty. He reigned for 67 years from the age of 18 and carried on his father Seti I's work and created many more splendid temples, such as that of Abu Simbel temples on the Nubian border. He sought to recover territories in the Levant that had been held by the Eighteenth Dynasty. His campaigns of reconquest culminated in the Battle of Kadesh
The Battle of Kadesh or Battle of Qadesh took place between the forces of the New Kingdom of Egypt under Ramesses II and the Hittite Empire under Muwatalli II at the city of Kadesh on the Orontes River, just upstream of Lake Homs near the ...
in 1274 BC, where he led Egyptian armies against those of the Hittite king Muwatalli II and was caught in history's first recorded military ambush.
Ramesses II was famed for the huge number of children he sired by his various wives and concubines
Concubinage is an interpersonal and sexual relationship between a man and a woman in which the couple does not want, or cannot enter into a full marriage. Concubinage and marriage are often regarded as similar but mutually exclusive.
Concubi ...
; the tomb
A tomb ( grc-gre, τύμβος ''tumbos'') is a repository for the remains of the dead. It is generally any structurally enclosed interment space or burial chamber, of varying sizes. Placing a corpse into a tomb can be called ''immureme ...
he built for his sons (many of whom he outlived) in the Valley of the Kings
The Valley of the Kings ( ar, وادي الملوك ; Late Coptic: ), also known as the Valley of the Gates of the Kings ( ar, وادي أبوا الملوك ), is a valley in Egypt where, for a period of nearly 500 years from the 16th to 11th ...
has proven to be the largest funerary complex in Egypt.
His immediate successors continued the military campaigns, though an increasingly troubled court complicated matters. Ramesses II was succeeded by his son Merneptah and then by Merenptah's son Seti II
Seti II (or Sethos II) was the fifth pharaoh of the Nineteenth Dynasty of Egypt and reigned from 1203 BC to 1197 BC. His throne name, Userkheperure Setepenre, means "Powerful are the manifestations of Re, the chosen one of Re." H ...
. Seti II's throne seems to have been disputed by his half-brother Amenmesse
Amenmesse (also Amenmesses or Amenmose) was the fifth pharaoh of the Nineteenth Dynasty in Ancient Egypt, possibly the son of Merneptah and Queen Takhat. Others consider him to be one of the innumerable sons of Ramesses II. Very little is kn ...
, who may have temporarily ruled from Thebes.
Upon his death, Seti II's son Siptah, who may have been afflicted with poliomyelitis
Poliomyelitis, commonly shortened to polio, is an infectious disease caused by the poliovirus. Approximately 70% of cases are asymptomatic; mild symptoms which can occur include sore throat and fever; in a proportion of cases more severe sym ...
during his life, was appointed to the throne by Chancellor Bay, a West Asian commoner who served as vizier behind the scenes. At Siptah's early death, the throne was assumed by Twosret, the queen dowager
A queen dowager or dowager queen (compare: princess dowager or dowager princess) is a title or status generally held by the widow of a king. In the case of the widow of an emperor, the title of empress dowager is used. Its full meaning is clear ...
of Seti II and possibly Amenmesse's sister.
A period of anarchy at the end of Twosret's short reign saw a native reaction to foreign control leading to the execution of Bay and the enthronement of Setnakhte, establishing the Twentieth Dynasty.
Twentieth Dynasty
The last "great" pharaoh from the New Kingdom is widely consideredRamesses III
Usermaatre Meryamun Ramesses III (also written Ramses and Rameses) was the second Pharaoh of the Twentieth Dynasty in Ancient Egypt. He is thought to have reigned from 26 March 1186 to 15 April 1155 BC and is considered to be the last great mona ...
, the son of Setnakhte who reigned three decades after the time of Ramesses II
Ramesses II ( egy, rꜥ-ms-sw ''Rīʿa-məsī-sū'', , meaning "Ra is the one who bore him"; ), commonly known as Ramesses the Great, was the third pharaoh of the Nineteenth Dynasty of Egypt. Along with Thutmose III he is often regarded a ...
(c.1279–1213 BC). In Year 8 of his reign, the Sea People invaded Egypt by land and sea. Ramesses III defeated them in two great land and sea battles. He claimed that he incorporated them as subject people and settled them in Southern Canaan, although there is evidence that they forced their way into Canaan
Canaan (; Phoenician: 𐤊𐤍𐤏𐤍 – ; he, כְּנַעַן – , in pausa – ; grc-bib, Χανααν – ;The current scholarly edition of the Greek Old Testament spells the word without any accents, cf. Septuaginta : id est Vetus T ...
. Their presence in Canaan may have contributed to the formation of new states in this region such as Philistia after the collapse of the Egyptian Empire. He was also compelled to fight invading Libyan tribesmen in two major campaigns in Egypt's Western Delta in his Year 6 and Year 11 respectively.
The heavy cost of these battles slowly exhausted Egypt's treasury and contributed to the gradual decline of the Egyptian Empire in Asia. The severity of these difficulties is stressed by the fact that the first known strike action
Strike action, also called labor strike, labour strike, or simply strike, is a work stoppage caused by the mass refusal of employees to work. A strike usually takes place in response to employee grievances. Strikes became common during the ...
in recorded history occurred during Year 29 of Ramesses III's reign, when the food rations for the Egypt's favoured and elite royal tomb-builders and artisans in the village of Deir el-Medina
Deir el-Medina ( arz, دير المدينة), or Dayr al-Madīnah, is an ancient Egyptian workmen's village which was home to the artisans who worked on the tombs in the Valley of the Kings during the 18th to 20th Dynasties of the New Kingdom ...
could not be provisioned. Something in the air prevented much sunlight from reaching the ground and also arrested global tree growth for almost two full decades until 1140 BC. One proposed cause is the Hekla 3 eruption
The Hekla 3 eruption (H-3) circa 1000 BC is considered the most severe eruption of Hekla during the Holocene. It threw about 7.3 km3 of volcanic rock into the atmosphere, placing its Volcanic Explosivity Index (VEI) at 5. This would have c ...
in Iceland
Iceland ( is, Ísland; ) is a Nordic island country in the North Atlantic Ocean and in the Arctic Ocean. Iceland is the most sparsely populated country in Europe. Iceland's capital and largest city is Reykjavík, which (along with its ...
, but the dating of that event remains in dispute.
Following Ramesses III's death, there was endless bickering between his heirs. Three of his sons would go on to assume power as Ramesses IV, Ramesses VI and Ramesses VIII
Usermaatre Akhenamun Ramesses VIII (also written Ramses and Rameses) or Ramesses Sethherkhepshef Meryamun ('Set is his Strength, beloved of Amun') (reigned 1130–1129 BC, or 1130 BC), was the seventh Pharaoh of the Twentieth Dynasty of the New ...
, respectively. However, at this time Egypt was also increasingly beset by a series of droughts, below-normal flooding levels of the Nile, famine, civil unrest and official corruption. The power of the last pharaoh, Ramesses XI, grew so weak that in the south the Theban High Priests of Amun became the effective de facto rulers of Upper Egypt, while Smendes
Hedjkheperre Setepenre Smendes was the founder of the Twenty-first Dynasty of Egypt and succeeded to the throne after burying Ramesses XI in Lower Egypt – territory which he controlled. His Egyptian nomen or birth name was actually Nesba ...
controlled Lower Egypt even before Ramesses XI's death. Smendes would eventually found the Twenty-first Dynasty at Tanis
Tanis ( grc, Τάνις or Τανέως ) or San al-Hagar ( ar, صان الحجر, Ṣān al-Ḥaǧar; egy, ḏꜥn.t ; ; cop, ϫⲁⲛⲓ or or ) is the Greek name for ancient Egyptian ''ḏꜥn.t'', an important archaeological site in the ...
.
Third Intermediate Period
 After the death of Ramesses XI, his successor
After the death of Ramesses XI, his successor Smendes
Hedjkheperre Setepenre Smendes was the founder of the Twenty-first Dynasty of Egypt and succeeded to the throne after burying Ramesses XI in Lower Egypt – territory which he controlled. His Egyptian nomen or birth name was actually Nesba ...
ruled from the city of Tanis
Tanis ( grc, Τάνις or Τανέως ) or San al-Hagar ( ar, صان الحجر, Ṣān al-Ḥaǧar; egy, ḏꜥn.t ; ; cop, ϫⲁⲛⲓ or or ) is the Greek name for ancient Egyptian ''ḏꜥn.t'', an important archaeological site in the ...
in the north, while the High Priests of Amun at Thebes had effective rule of the south of the country, whilst still nominally recognizing Smendes as king. In fact, this division was less significant than it seems, since both priests and pharaohs came from the same family. Piankh, assumed control of Upper Egypt, ruling from Thebes, with the northern limit of his control ending at Al-Hibah. (The High Priest Herihor had died before Ramesses XI, but also was an all-but-independent ruler in the latter days of the king's reign.) The country was once again split into two parts with the priests in Thebes and the pharaohs at Tanis. Their reign seems without other distinction, and they were replaced without any apparent struggle by the Libyan kings of the Twenty-Second Dynasty.
Egypt has long had ties with Libya
Libya (; ar, ليبيا, Lībiyā), officially the State of Libya ( ar, دولة ليبيا, Dawlat Lībiyā), is a country in the Maghreb region in North Africa. It is bordered by the Mediterranean Sea to the north, Egypt to the east, Suda ...
, and the first king of the new dynasty, Shoshenq I
Hedjkheperre Setepenre Shoshenq I ( Egyptian ''ššnq''; reigned c. 943–922 BC)—also known as Shashank or Sheshonk or Sheshonq Ifor discussion of the spelling, see Shoshenq—was a pharaoh of ancient Egypt and the founder of the Twenty-sec ...
, was a Meshwesh
The Meshwesh (often abbreviated in ancient Egyptian as Ma) was an ancient Libyan Berber tribe, along with other groups like Libu and Tehenou/Tehenu.
Early records of the Meshwesh date back to the Eighteenth Dynasty of Egypt from the reign of ...
Libyan, who served as the commander of the armies under the last ruler of the Twenty-First Dynasty, Psusennes II. He unified the country, putting control of the Amun clergy
Clergy are formal leaders within established religions. Their roles and functions vary in different religious traditions, but usually involve presiding over specific rituals and teaching their religion's doctrines and practices. Some of the ter ...
under his own son as the High Priest of Amun, a post that was previously a hereditary appointment. The scant and patchy nature of the written records from this period suggest that it was unsettled. There appear to have been many subversive groups, which eventually led to the creation of the Twenty-Third Dynasty, which ran concurrent with the latter part of the Twenty-Second Dynasty.
The country was reunited by the Twenty-Second Dynasty founded by Shoshenq I
Hedjkheperre Setepenre Shoshenq I ( Egyptian ''ššnq''; reigned c. 943–922 BC)—also known as Shashank or Sheshonk or Sheshonq Ifor discussion of the spelling, see Shoshenq—was a pharaoh of ancient Egypt and the founder of the Twenty-sec ...
in 945 BC (or 943 BC), who descended from Meshwesh
The Meshwesh (often abbreviated in ancient Egyptian as Ma) was an ancient Libyan Berber tribe, along with other groups like Libu and Tehenou/Tehenu.
Early records of the Meshwesh date back to the Eighteenth Dynasty of Egypt from the reign of ...
immigrants, originally from Ancient Libya. This brought stability to the country for well over a century. After the reign of Osorkon II the country had again splintered into two states with Shoshenq III of the Twenty-Second Dynasty controlling Lower Egypt by 818 BC while Takelot II and his son (the future Osorkon III) ruled Middle and Upper Egypt.
 After the withdrawal of Egypt from
After the withdrawal of Egypt from Nubia
Nubia () ( Nobiin: Nobīn, ) is a region along the Nile river encompassing the area between the first cataract of the Nile (just south of Aswan in southern Egypt) and the confluence of the Blue and White Niles (in Khartoum in central Sud ...
at the end of the New Kingdom, a native dynasty took control of Nubia. Under king Piye, the Nubian founder of Twenty-Fifth Dynasty
The Twenty-fifth Dynasty of Egypt (notated Dynasty XXV, alternatively 25th Dynasty or Dynasty 25), also known as the Nubian Dynasty, the Kushite Empire, the Black Pharaohs, or the Napatans, after their capital Napata, was the last dynasty of t ...
, the Nubians pushed north in an effort to crush his Libyan opponents ruling in the Delta. Piye managed to attain power as far as Memphis. His opponent Tefnakhte
Shepsesre Tefnakht (in grc, Τνέφαχθος, translit=Tnephachthos) was a prince of Sais and founder of the relatively short Twenty-fourth Dynasty of Egypt; he rose to become a Chief of the Ma in his home city. He is thought to have reigned ...
ultimately submitted to him, but he was allowed to remain in power in Lower Egypt and founded the short-lived Twenty-Fourth Dynasty at Sais. The Kushite kingdom to the south took full advantage of this division and political instability and defeated the combined might of several native-Egyptian rulers such as Peftjauawybast
PeftjauawybastKneeling statuette of King Peftjauawybast'. Museum of Fine Arts, Boston. or Peftjaubast was an ancient Egyptian ruler ("king") of Herakleopolis Magna during the 25th Dynasty.
Biography
He was likely installed as governor of the town ...
, Osorkon IV of Tanis, and Tefnakht of Sais. Piye was succeeded first by his brother, Shabaka, and then by his two sons Shebitku and Taharqa. Taharqa reunited the Two Lands of Northern and Southern Egypt and created an empire that was as large as it had been since the New Kingdom
New is an adjective referring to something recently made, discovered, or created.
New or NEW may refer to:
Music
* New, singer of K-pop group The Boyz
Albums and EPs
* ''New'' (album), by Paul McCartney, 2013
* ''New'' (EP), by Regurgitator ...
. Pharaohs such as Taharqa built or restored temples and monuments throughout the Nile valley, including at Memphis, Karnak, Kawa, and Jebel Barkal. It was during the 25th Dynasty that the Nile valley saw the first widespread construction of pyramids (many in modern Sudan) since the Middle Kingdom.
The international prestige of Egypt declined considerably by this time. The country's international allies had fallen under the sphere of influence of Assyria
Assyria ( Neo-Assyrian cuneiform: , romanized: ''māt Aššur''; syc, ܐܬܘܪ, ʾāthor) was a major ancient Mesopotamian civilization which existed as a city-state at times controlling regional territories in the indigenous lands of the A ...
and from about 700 BC the question became when, not if, there would be war between the two states. Taharqa's reign and that of his successor, Tantamani, were filled with constant conflict with the Assyrians against whom there were numerous victories, but ultimately Thebes was occupied and Memphis sacked.
Late Period
From 671 BC on, Memphis and the Delta region became the target of many attacks from theAssyria
Assyria ( Neo-Assyrian cuneiform: , romanized: ''māt Aššur''; syc, ܐܬܘܪ, ʾāthor) was a major ancient Mesopotamian civilization which existed as a city-state at times controlling regional territories in the indigenous lands of the A ...
ns, who expelled the Nubians and handed over power to client kings of the Twenty-Sixth Dynasty. Psamtik I was the first recognized as the king of the whole of Egypt, and he brought increased stability to the country during a 54-year reign from the new capital of Sais. Four successive Saite kings continued guiding Egypt successfully and peacefully from 610–526 BC, keeping the Babylonia
Babylonia (; Akkadian: , ''māt Akkadī'') was an ancient Akkadian-speaking state and cultural area based in the city of Babylon in central-southern Mesopotamia (present-day Iraq and parts of Syria). It emerged as an Amorite-ruled state c ...
ns in certain measures away with the help of Greek mercenaries.
However, during this period Babylonian emperor Nebuchadnezzar II
Nebuchadnezzar II (Babylonian cuneiform: ''Nabû-kudurri-uṣur'', meaning "Nabu, watch over my heir"; Biblical Hebrew: ''Nəḇūḵaḏneʾṣṣar''), also spelled Nebuchadrezzar II, was the second king of the Neo-Babylonian Empire, ruling ...
(605–562 BC) campaigned against the Egyptians and drove them back over the Sinai. In 567 BC he went to war with Pharaoh Amasis, and briefly invaded Egypt
Egypt ( ar, مصر , ), officially the Arab Republic of Egypt, is a List of transcontinental countries, transcontinental country spanning the North Africa, northeast corner of Africa and Western Asia, southwest corner of Asia via a land bridg ...
itself.
By the end of this period a new power was growing in the Near East: Persia
Iran, officially the Islamic Republic of Iran, and also called Persia, is a country located in Western Asia. It is bordered by Iraq and Turkey to the west, by Azerbaijan and Armenia to the northwest, by the Caspian Sea and Turkmeni ...
. The Pharaoh Psamtik III
Psamtik III ( Ancient Egyptian: , pronounced ), known by the Graeco-Romans as Psammetichus or Psammeticus ( Ancient Greek: ), or Psammenitus ( Ancient Greek: ), was the last Pharaoh of the Twenty-sixth Dynasty of Egypt from 526 BC to 525 BC. Most ...
had to face the might of Persia at Pelusium; he was defeated and briefly escaped to Memphis, but ultimately was captured and then executed.
Persian domination
 Achaemenid Egypt can be divided into three eras: the first period of Persian occupation, 525–404 BC (when Egypt became a
Achaemenid Egypt can be divided into three eras: the first period of Persian occupation, 525–404 BC (when Egypt became a satrap
A satrap () was a governor of the provinces of the ancient Median and Achaemenid Empires and in several of their successors, such as in the Sasanian Empire and the Hellenistic empires.
The satrap served as viceroy to the king, though with cons ...
y), followed by an interval of independence, and the second and final period of occupation, 343–332 BC.
The Persian king Cambyses assumed the formal title of Pharaoh, called himself Mesuti-Re ("Re has given birth"), and sacrificed to the Egyptian gods. He founded the Twenty-seventh Dynasty
The Twenty-seventh Dynasty of Egypt (notated Dynasty XXVII, alternatively 27th Dynasty or Dynasty 27), also known as the First Egyptian Satrapy (), was effectively a province (Satrapy) of the Achaemenid Persian Empire between 525 BC and 404 BC. ...
. Egypt
Egypt ( ar, مصر , ), officially the Arab Republic of Egypt, is a List of transcontinental countries, transcontinental country spanning the North Africa, northeast corner of Africa and Western Asia, southwest corner of Asia via a land bridg ...
was then joined with Cyprus
Cyprus ; tr, Kıbrıs (), officially the Republic of Cyprus,, , lit: Republic of Cyprus is an island country located south of the Anatolian Peninsula in the eastern Mediterranean Sea. Its continental position is disputed; while it is ...
and Phoenicia
Phoenicia () was an ancient thalassocratic civilization originating in the Levant region of the eastern Mediterranean, primarily located in modern Lebanon. The territory of the Phoenician city-states extended and shrank throughout their his ...
in the sixth satrapy of the Achaemenid Empire
The Achaemenid Empire or Achaemenian Empire (; peo, 𐎧𐏁𐏂, , ), also called the First Persian Empire, was an ancient Iranian empire founded by Cyrus the Great in 550 BC. Based in Western Asia, it was contemporarily the largest em ...
.
Cambyses' successors Darius I the Great and Xerxes pursued a similar policy, visited the country, and warded off an Athenian
Athens ( ; el, Αθήνα, Athína ; grc, Ἀθῆναι, Athênai (pl.) ) is both the capital and largest city of Greece. With a population close to four million, it is also the seventh largest city in the European Union. Athens dominates a ...
attack. It is likely that Artaxerxes I
Artaxerxes I (, peo, 𐎠𐎼𐎫𐎧𐏁𐏂𐎠 ; grc-gre, Ἀρταξέρξης) was the fifth King of Kings of the Achaemenid Empire, from 465 to December 424 BC. He was the third son of Xerxes I.
He may have been the " Artas ...
and Darius II
Darius II ( peo, 𐎭𐎠𐎼𐎹𐎺𐎢𐏁 ; grc-gre, Δαρεῖος ), also known by his given name Ochus ( ), was King of Kings of the Achaemenid Empire from 423 BC to 405 or 404 BC.
Artaxerxes I, who died in 424 BC, was followed by h ...
visited the country as well, although it is not attested, and did not prevent the Egyptians from feeling unhappy.
During the war of succession after the reign of Darius II, which broke out in 404 BC, they revolted under Amyrtaeus and regained their independence. This sole ruler of the Twenty-eighth Dynasty died in 399, and power went to the Twenty-ninth Dynasty. The Thirtieth Dynasty was established in 380 BC and lasted until 343 BC. Nectanebo II was the last native king to rule Egypt.
Artaxerxes III (358–338 BC) reconquered the Nile valley for a brief period (343–332 BC).
In 332 BC, Mazaces handed over the country to Alexander the Great
Alexander III of Macedon ( grc, Ἀλέξανδρος, Alexandros; 20/21 July 356 BC – 10/11 June 323 BC), commonly known as Alexander the Great, was a king of the ancient Greek kingdom of Macedon. He succeeded his father Philip II to ...
without a fight. The Achaemenid empire had ended, and for a while Egypt was a satrapy in Alexander's empire. Later the Ptolemies
The Ptolemaic dynasty (; grc, Πτολεμαῖοι, ''Ptolemaioi''), sometimes referred to as the Lagid dynasty (Λαγίδαι, ''Lagidae;'' after Ptolemy I's father, Lagus), was a Macedonian Greek royal dynasty which ruled the Ptolemaic ...
and then the Romans successively ruled the Nile valley.
Ptolemaic dynasty
In 332 BC, Alexander III of Macedon conquered Egypt with little resistance from thePersians
The Persians are an Iranian ethnic group who comprise over half of the population of Iran. They share a common cultural system and are native speakers of the Persian language as well as of the languages that are closely related to Persian. ...
. He visited Memphis, and went on a pilgrimage to the oracle of Amun
Amun (; also ''Amon'', ''Ammon'', ''Amen''; egy, jmn, reconstructed as ( Old Egyptian and early Middle Egyptian) → (later Middle Egyptian) → ( Late Egyptian), cop, Ⲁⲙⲟⲩⲛ, Amoun) romanized: ʾmn) was a major ancient Egypt ...
at the Siwa Oasis. The oracle declared him the son of Amun
Amun (; also ''Amon'', ''Ammon'', ''Amen''; egy, jmn, reconstructed as ( Old Egyptian and early Middle Egyptian) → (later Middle Egyptian) → ( Late Egyptian), cop, Ⲁⲙⲟⲩⲛ, Amoun) romanized: ʾmn) was a major ancient Egypt ...
. He conciliated the Egyptians by the respect he showed for their religion, but he appointed Greeks to virtually all the senior posts in the country, and founded a new Greek city, Alexandria
Alexandria ( or ; ar, ٱلْإِسْكَنْدَرِيَّةُ ; grc-gre, Αλεξάνδρεια, Alexándria) is the second largest city in Egypt, and the largest city on the Mediterranean coast. Founded in by Alexander the Great, Alexandri ...
, to be the new capital. The wealth of Egypt could now be harnessed for Alexander's conquest of the rest of the Persian Empire. Early in 331 BC, he led his forces away to Phoenicia, never returning to Egypt.
 Following Alexander's death in
Following Alexander's death in Babylon
''Bābili(m)''
* sux, 𒆍𒀭𒊏𒆠
* arc, 𐡁𐡁𐡋 ''Bāḇel''
* syc, ܒܒܠ ''Bāḇel''
* grc-gre, Βαβυλών ''Babylṓn''
* he, בָּבֶל ''Bāvel''
* peo, 𐎲𐎠𐎲𐎡𐎽𐎢 ''Bābiru''
* elx, 𒀸𒁀𒉿𒇷 ''Babi ...
in 323 BC, a succession crisis erupted among his generals. Perdiccas
Perdiccas ( el, Περδίκκας, ''Perdikkas''; 355 BC – 321/320 BC) was a general of Alexander the Great. He took part in the Macedonian campaign against the Achaemenid Empire, and, following Alexander's death in 323 BC, rose to becom ...
ruled the empire as regent for Alexander's half-brother Arrhidaeus
Arrhidaeus or Arrhidaios ( el, Ἀρριδαῖoς lived 4th century BC), one of Alexander the Great's generals, was entrusted by Ptolemy to bring Alexander's body to Egypt in 323 BC, contrary to the wishes of Perdiccas who wanted the body sent t ...
, who became Philip III of Macedon
Philip III Arrhidaeus ( grc-gre, Φίλιππος Ἀρριδαῖος ; c. 359 BC – 25 December 317 BC) reigned as king of Macedonia an Ancient Greek Kingdom in northern Greece from after 11 June 323 BC until his death. He was a son of King P ...
, and Alexander's infant son Alexander IV of Macedon
Alexander IV (Greek: ; 323/322– 309 BC), sometimes erroneously called Aegus in modern times, was the son of Alexander the Great (Alexander III of Macedon) and Princess Roxana of Bactria.
Birth
Alexander IV was the son of Alexander th ...
. Perdiccas appointed Ptolemy
Claudius Ptolemy (; grc-gre, Πτολεμαῖος, ; la, Claudius Ptolemaeus; AD) was a mathematician, astronomer, astrologer, geographer, and music theorist, who wrote about a dozen scientific treatises, three of which were of importanc ...
, one of Alexander's closest companions, to rule Egypt in the name of the joint kings. However, as Alexander's empire disintegrated, Ptolemy soon established himself as ruler in his own right. Ptolemy successfully defended Egypt against an invasion by Perdiccas in 321 BC and consolidated his position in Egypt and the surrounding areas during the Wars of the Diadochi
The Wars of the Diadochi ( grc, Πόλεμοι τῶν Διαδόχων, '), or Wars of Alexander's Successors, were a series of conflicts that were fought between the generals of Alexander the Great, known as the Diadochi, over who would rule ...
(322–301 BC). In 305 BC, Ptolemy took the title of Pharaoh. As Ptolemy I Soter
Ptolemy I Soter (; gr, Πτολεμαῖος Σωτήρ, ''Ptolemaîos Sōtḗr'' "Ptolemy the Savior"; c. 367 BC – January 282 BC) was a Macedonian Greek general, historian and companion of Alexander the Great from the Kingdom of Macedo ...
("Saviour"), he founded the Ptolemaic dynasty
The Ptolemaic dynasty (; grc, Πτολεμαῖοι, ''Ptolemaioi''), sometimes referred to as the Lagid dynasty (Λαγίδαι, ''Lagidae;'' after Ptolemy I's father, Lagus), was a Macedonian Greek royal dynasty which ruled the Ptolemaic ...
that was to rule Egypt for nearly 300 years.
The later Ptolemies took on Egyptian traditions by marrying their siblings, had themselves portrayed on public monuments in Egyptian style and dress, and participated in Egyptian religious life.Stanwick (2003) Hellenistic culture thrived in Egypt well after the Muslim conquest. The Egyptians soon accepted the Ptolemies as the successors to the pharaohs of independent Egypt. Ptolemy's family ruled Egypt until the Roman conquest of 30 BC.
All the male rulers of the dynasty took the name, Ptolemy. Ptolemaic queens regnant, some of whom were the sisters of their husbands, were usually called Cleopatra, Arsinoe or Berenice. The most famous member of the line was the last queen, Cleopatra VII
Cleopatra VII Philopator ( grc-gre, Κλεοπάτρα Φιλοπάτωρ}, "Cleopatra the father-beloved"; 69 BC10 August 30 BC) was Queen of the Ptolemaic Kingdom of Egypt from 51 to 30 BC, and its last active ruler.She was also a ...
, known for her role in the Roman political battles between Julius Caesar
Gaius Julius Caesar (; ; 12 July 100 BC – 15 March 44 BC), was a Roman general and statesman. A member of the First Triumvirate, Caesar led the Roman armies in the Gallic Wars before defeating his political rival Pompey in a civil war, an ...
and Pompey
Gnaeus Pompeius Magnus (; 29 September 106 BC – 28 September 48 BC), known in English as Pompey or Pompey the Great, was a leading Roman general and statesman. He played a significant role in the transformation of ...
, and later between Octavian and Mark Antony
Marcus Antonius (14 January 1 August 30 BC), commonly known in English as Mark Antony, was a Roman politician and general who played a critical role in the transformation of the Roman Republic from a constitutional republic into the au ...
. Her apparent suicide at the conquest by Rome marked the end of Ptolemaic rule in Egypt.
See also
* Ancient Egypt * History of Egypt * Population history of EgyptReferences
Further reading
Pharaonic Egypt
* * * * * * * * * * * * * * Herodotus ii. 55 and vii. 134 * * * * * * * * * * * * * * *Ptolemaic Egypt
* * *External links
The Ancient Egypt Site
* ttps://books.google.com/books?vid=ISBN9004130489&id=qeApebusL_0C&dq=PtahHotep&as_brr=1&hl=nl Texts from the Pyramid Age Door Nigel C. Strudwick, Ronald J. Leprohon, 2005, Brill Academic Publishers
Ancient Egyptian Science: A Source Book Door Marshall Clagett, 1989
{{DEFAULTSORT:History Of Ancient Egypt *