Historical nuclear weapons stockpiles and nuclear tests by country on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
This article shows various estimates of the
 The United States nuclear stockpile increased rapidly from 1945, peaked in 1966, and declined after that. By 2012, the United States had several times fewer nuclear weapons than it had in 1966.
The Soviet Union developed its first nuclear weapon in 1949 and increased its nuclear stockpile rapidly until it peaked in 1986 under Mikhail Gorbachev. As Cold War tensions decreased, and after the
The United States nuclear stockpile increased rapidly from 1945, peaked in 1966, and declined after that. By 2012, the United States had several times fewer nuclear weapons than it had in 1966.
The Soviet Union developed its first nuclear weapon in 1949 and increased its nuclear stockpile rapidly until it peaked in 1986 under Mikhail Gorbachev. As Cold War tensions decreased, and after the
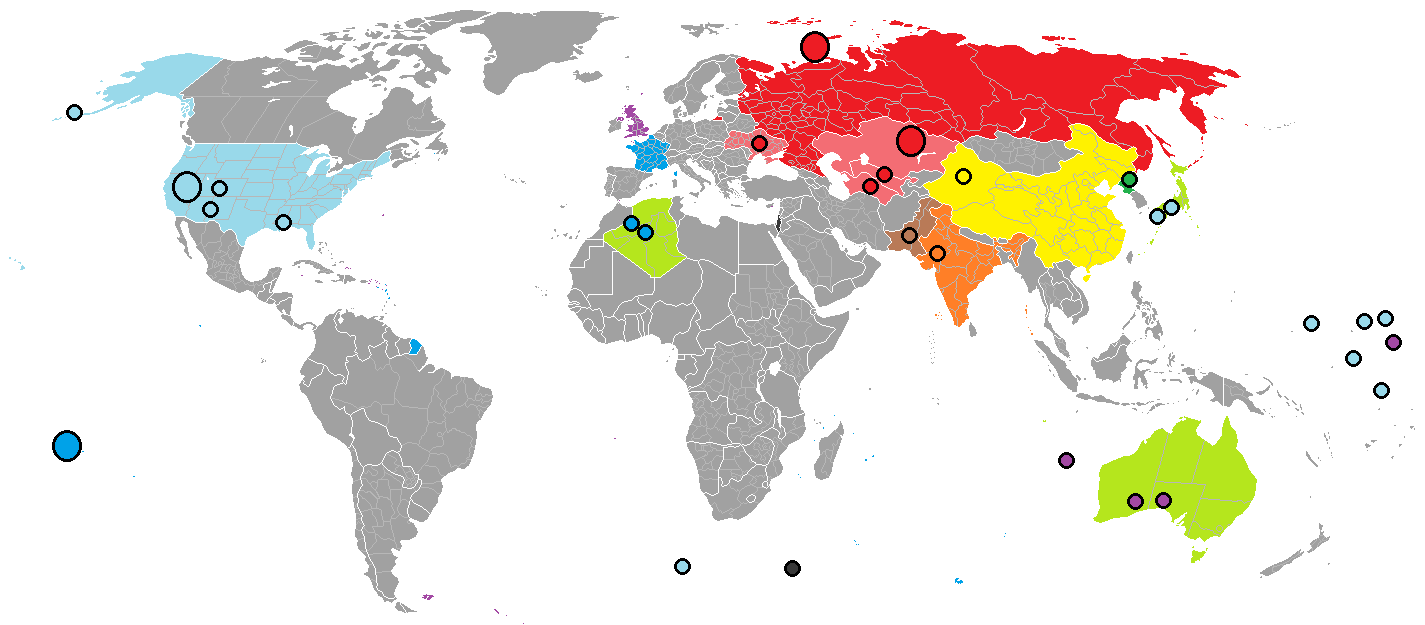 From the first nuclear test in 1945, worldwide nuclear testing increased rapidly until the 1970s, when it peaked. However, there was still a large amount of worldwide nuclear testing until the end of the Cold War in the early 1990s. Afterwards, the
From the first nuclear test in 1945, worldwide nuclear testing increased rapidly until the 1970s, when it peaked. However, there was still a large amount of worldwide nuclear testing until the end of the Cold War in the early 1990s. Afterwards, the
nuclear weapon
A nuclear weapon is an explosive device that derives its destructive force from nuclear reactions, either fission (fission bomb) or a combination of fission and fusion reactions ( thermonuclear bomb), producing a nuclear explosion. Both bom ...
stockpiles of various countries at various points in time. This article also shows the number of nuclear weapons tests
Nuclear weapons tests are experiments carried out to determine nuclear weapons' effectiveness, yield, and explosive capability. Testing nuclear weapons offers practical information about how the weapons function, how detonations are affected b ...
conducted by each country
A country is a distinct part of the world, such as a state, nation, or other political entity. It may be a sovereign state or make up one part of a larger state. For example, the country of Japan is an independent, sovereign state, while ...
at various points in time.
Nuclear weapons stockpiles
collapse of the Soviet Union
The dissolution of the Soviet Union, also negatively connoted as rus, Разва́л Сове́тского Сою́за, r=Razvál Sovétskogo Soyúza, ''Ruining of the Soviet Union''. was the process of internal disintegration within the Sov ...
, the Soviet and Russian nuclear stockpile decreased by over 80% between 1986 and 2012.
The U.S. and Russian nuclear weapons stockpiles are projected to continue decreasing over the next decade.
The United Kingdom became a nuclear power in 1952, and its nuclear arsenal peaked at just under 500 nuclear weapons in 1981. France became a nuclear power in 1960, and French nuclear stockpiles peaked at just over 500 nuclear weapons in 1992. China developed its first nuclear weapon in 1964; its nuclear stockpile increased until the early 1980s, when it stabilized at between 200 and 260. India became a nuclear power in 1974, while Pakistan developed its first nuclear weapon in the 1980s. India and Pakistan currently have around one hundred nuclear weapons each. Pakistan's nuclear stockpile has increased rapidly, and it is speculated that Pakistan might have more nuclear weapons than the United Kingdom within a decade.
South Africa
South Africa, officially the Republic of South Africa (RSA), is the Southern Africa, southernmost country in Africa. It is bounded to the south by of coastline that stretch along the Atlantic Ocean, South Atlantic and Indian Oceans; to the ...
successfully built six nuclear weapons in the 1980s, but dismantled all of them in the early 1990s, shortly before the fall of the apartheid
Apartheid (, especially South African English: , ; , "aparthood") was a system of institutionalised racial segregation that existed in South Africa and South West Africa (now Namibia) from 1948 to the early 1990s. Apartheid was ...
system. So far it is the only nuclear-capable country to give up nuclear weapons, although several members of the Soviet Union did so during the collapse of the Soviet regime.
North Korea joined the nuclear club in 2006 or before. A United States Defense Intelligence Agency report from 1999 projected that both Iran
Iran, officially the Islamic Republic of Iran, and also called Persia, is a country located in Western Asia. It is bordered by Iraq and Turkey to the west, by Azerbaijan and Armenia to the northwest, by the Caspian Sea and Turkmeni ...
and Iraq
Iraq,; ku, عێراق, translit=Êraq officially the Republic of Iraq, '; ku, کۆماری عێراق, translit=Komarî Êraq is a country in Western Asia. It is bordered by Turkey to the north, Iran to the east, the Persian Gulf and K ...
would join the nuclear club and have 10-20 nuclear weapons in 2020. However, it is worth pointing out that this report was written before the overthrow of Iraqi dictator Saddam Hussein
Saddam Hussein ( ; ar, صدام حسين, Ṣaddām Ḥusayn; 28 April 1937 – 30 December 2006) was an Iraqi politician who served as the fifth president of Iraq from 16 July 1979 until 9 April 2003. A leading member of the revolutio ...
and before information was released indicating that Iraq had already given up its nuclear weapons program. Even before the U.S. started the nuclear club
Eight sovereign states have publicly announced successful detonation of nuclear weapons. United Nations Security Council#Permanent members, Five are considered to be nuclear-weapon states (NWS) under the terms of the Treaty on the Non-Prolifera ...
in 1945, some states (most notably Germany
Germany,, officially the Federal Republic of Germany, is a country in Central Europe. It is the second most populous country in Europe after Russia, and the most populous member state of the European Union. Germany is situated betwe ...
) unsuccessfully attempted to build nuclear weapons.
Nuclear weapon tests
 From the first nuclear test in 1945, worldwide nuclear testing increased rapidly until the 1970s, when it peaked. However, there was still a large amount of worldwide nuclear testing until the end of the Cold War in the early 1990s. Afterwards, the
From the first nuclear test in 1945, worldwide nuclear testing increased rapidly until the 1970s, when it peaked. However, there was still a large amount of worldwide nuclear testing until the end of the Cold War in the early 1990s. Afterwards, the Comprehensive Test Ban Treaty
The Comprehensive Nuclear-Test-Ban Treaty (CTBT) is a multilateral treaty to ban nuclear weapons test explosions and any other nuclear explosions, for both civilian and military purposes, in all environments. It was adopted by the United Nat ...
was signed and ratified by the major nuclear weapons powers, and the number of worldwide nuclear tests decreased rapidly. India and Pakistan conducted nuclear tests in 1998, but afterwards only North Korea conducted nuclear tests-- in 2006, 2009, 2013, twice in 2016, and in 2017.
References
{{DEFAULTSORT:List Of States With Nuclear Weapons * Nuclear weapons Nuclear weapons policy Nuclear proliferation States With Nuclear Weapons Cold War