Hinduism in Serbia on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 Most of the people of
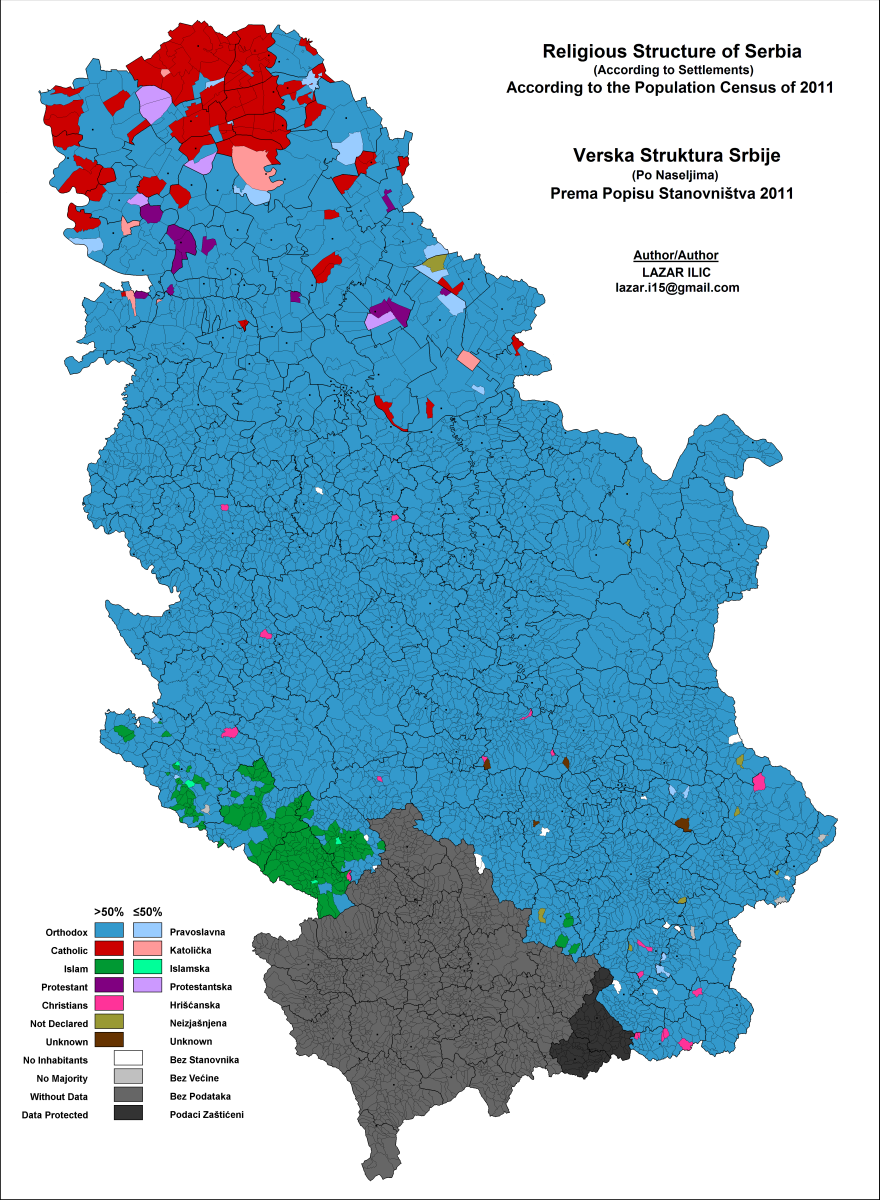
Most of the people of  Eastern Orthodox Christianity predominates throughout most of Serbia, excluding several municipalities and cities near border with neighboring countries where adherents of Islam or Catholicism are more numerous as well as excluding two predominantly Protestant municipalities in Vojvodina. Eastern Orthodoxy also predominates in most of the large cities of Serbia, excluding the cities of Subotica (which is mostly Catholic) and
Eastern Orthodox Christianity predominates throughout most of Serbia, excluding several municipalities and cities near border with neighboring countries where adherents of Islam or Catholicism are more numerous as well as excluding two predominantly Protestant municipalities in Vojvodina. Eastern Orthodoxy also predominates in most of the large cities of Serbia, excluding the cities of Subotica (which is mostly Catholic) and 
 The largest percentage of the Protestant Christians in Serbia on municipal level is in the municipalities of
The largest percentage of the Protestant Christians in Serbia on municipal level is in the municipalities of 
International Religious Freedom Report 2017 Serbia
', US Department of State, Bureau of Democracy, Human Rights, and Labor. The laws of Serbia establish the freedom of religion, forbid the establishment of a state religion, and outlaw religious discrimination. While registration with the government, is not necessary for religious groups to practice, the government confers certain privileges to registered groups. The government maintains a two-tiered system of registered groups, split between "traditional" groups and "nontraditional" groups. Minority groups and independent observers have complained that this system consists of religious discrimination. The government has programs established for the restitution of property confiscated by the government of
Serbian Orthodox ChurchIslamic Community in Serbia
{{DEFAULTSORT:Religion In Serbia

Serbia
Serbia (, ; Serbian: , , ), officially the Republic of Serbia (Serbian: , , ), is a landlocked country in Southeastern and Central Europe, situated at the crossroads of the Pannonian Basin and the Balkans. It shares land borders with Hungar ...
has been traditionally a Christian country since the Christianization of Serbs
The Serbian Orthodox Church ( sr-Cyrl, Српска православна црква, Srpska pravoslavna crkva) is one of the autocephalous (ecclesiastically independent) Eastern Orthodox Christian churches.
The majority of the population in ...
by Clement of Ohrid
Saint Clement of Ohrid ( Bulgarian, Serbian and Macedonian: Свети Климент Охридски, ; el, Ἅγιος Κλήμης τῆς Ἀχρίδας; sk, svätý Kliment Ochridský; – 916) was one of the first medieval Bulgarian ...
and Saint Naum
Saint Naum ( Bulgarian and Macedonian: Свети Наум, ''Sveti Naum''), also known as Naum of Ohrid or Naum of Preslav (c. 830 – December 23, 910) was a medieval Bulgarian writer, enlightener, one of the Seven Apostles of the First Bu ...
in the 9th century. The dominant confession is Eastern Orthodoxy
Eastern Orthodoxy, also known as Eastern Orthodox Christianity, is one of the three main branches of Chalcedonian Christianity, alongside Catholicism and Protestantism.
Like the Pentarchy of the first millennium, the mainstream (or "canonical") ...
of the Serbian Orthodox Church.
During the Ottoman rule of the Balkans
The Balkans ( ), also known as the Balkan Peninsula, is a geographical area in southeastern Europe with various geographical and historical definitions. The region takes its name from the Balkan Mountains that stretch throughout the who ...
, Sunni Islam established itself in the territories of Serbia, mainly in southern regions of Raška (the dominant religion in Raška is Orthodoxy, in Novi Pazar it is Islam) and Preševo Valley
The Preševo Valley ( sr-cyrl, Прешевска долина, Preševska dolina, al, Lugina e Preshevës) is a geopolitical region in southern Serbia, along the border with Kosovo. The valley geographically includes municipalities of Bujanovac ...
, as well as in the disputed territory of Kosovo and Metohija. The Catholic Church
The Catholic Church, also known as the Roman Catholic Church, is the largest Christian church, with 1.3 billion baptized Catholics worldwide . It is among the world's oldest and largest international institutions, and has played a ...
has roots in the country since the presence of Hungarians
Hungarians, also known as Magyars ( ; hu, magyarok ), are a nation and ethnic group native to Hungary () and historical Hungarian lands who share a common culture, history, ancestry, and language. The Hungarian language belongs to the Urali ...
in Vojvodina
Vojvodina ( sr-Cyrl, Војводина}), officially the Autonomous Province of Vojvodina, is an autonomous province that occupies the northernmost part of Serbia. It lies within the Pannonian Basin, bordered to the south by the national capital ...
(mainly in the northern part of the province), while Protestantism
Protestantism is a branch of Christianity that follows the theological tenets of the Protestant Reformation, a movement that began seeking to reform the Catholic Church from within in the 16th century against what its followers perceived to b ...
arrived in the 18th and 19th century with the settlement of Slovaks in Vojvodina.
Demographics

Christianity
Eastern Orthodoxy
 Most of the people of
Most of the people of Serbia
Serbia (, ; Serbian: , , ), officially the Republic of Serbia (Serbian: , , ), is a landlocked country in Southeastern and Central Europe, situated at the crossroads of the Pannonian Basin and the Balkans. It shares land borders with Hungar ...
are adherents of the Serbian Orthodox Church, while the Romanian Orthodox Church
The Romanian Orthodox Church (ROC; ro, Biserica Ortodoxă Română, ), or Patriarchate of Romania, is an autocephalous Eastern Orthodox church in full communion with other Eastern Orthodox Christian churches, and one of the nine patriarchates ...
is also present in parts of Vojvodina inhabited by ethnic Romanian
Romanian may refer to:
*anything of, from, or related to the country and nation of Romania
**Romanians, an ethnic group
**Romanian language, a Romance language
*** Romanian dialects, variants of the Romanian language
** Romanian cuisine, tradition ...
minority. Besides Serbs
The Serbs ( sr-Cyr, Срби, Srbi, ) are the most numerous South Slavic ethnic group native to the Balkans in Southeastern Europe, who share a common Serbian ancestry, culture, history and language.
The majority of Serbs live in their na ...
, other Eastern Orthodox Christians include Montenegrins
Montenegrins ( cnr, Црногорци, Crnogorci, or ; lit. "Black Mountain People") are a South Slavic ethnic group that share a common Montenegrin culture, history, and language, identified with the country of Montenegro.
Genetics
Accordi ...
, Romanians
The Romanians ( ro, români, ; dated exonym '' Vlachs'') are a Romance-speaking ethnic group. Sharing a common Romanian culture and ancestry, and speaking the Romanian language, they live primarily in Romania and Moldova. The 2011 Roman ...
, Macedonians, Bulgarians
Bulgarians ( bg, българи, Bǎlgari, ) are a nation and South Slavic ethnic group native to Bulgaria and the rest of Southeast Europe.
Etymology
Bulgarians derive their ethnonym from the Bulgars. Their name is not completely unders ...
and majority of Roma people
The Romani (also spelled Romany or Rromani , ), colloquially known as the Roma, are an Indo-Aryan ethnic group, traditionally nomadic itinerants. They live in Europe and Anatolia, and have diaspora populations located worldwide, with sign ...
.
 Eastern Orthodox Christianity predominates throughout most of Serbia, excluding several municipalities and cities near border with neighboring countries where adherents of Islam or Catholicism are more numerous as well as excluding two predominantly Protestant municipalities in Vojvodina. Eastern Orthodoxy also predominates in most of the large cities of Serbia, excluding the cities of Subotica (which is mostly Catholic) and
Eastern Orthodox Christianity predominates throughout most of Serbia, excluding several municipalities and cities near border with neighboring countries where adherents of Islam or Catholicism are more numerous as well as excluding two predominantly Protestant municipalities in Vojvodina. Eastern Orthodoxy also predominates in most of the large cities of Serbia, excluding the cities of Subotica (which is mostly Catholic) and Novi Pazar
Novi Pazar ( sr-cyr, Нови Пазар, lit. "New Bazaar"; ) is a city located in the Raška District of southwestern Serbia. As of the 2011 census, the urban area has 66,527 inhabitants, while the city administrative area has 100,410 inhabit ...
(which is mostly Muslim).
The identity of ethnic Serbs was historically largely based on Eastern Orthodox Christianity and on the Serbian Orthodox Church, to the extent that there are claims that those who are not its faithful are not Serbs. However, the conversion of the south Slavs from paganism to Christianity took place before the Great Schism, the split between the Greek East and the Latin West. After the Schism, generally speaking, those Christians who lived within the Eastern Orthodox sphere of influence became "Eastern Orthodox" and those who lived within the Catholic sphere of influence, under Rome as the patriarchal see of the West, became "Catholic." Some ethnologists consider that the distinct Serb and Croat identities relate to religion rather than ethnicity. With the arrival of the Ottoman Empire
The Ottoman Empire, * ; is an archaic version. The definite article forms and were synonymous * and el, Оθωμανική Αυτοκρατορία, Othōmanikē Avtokratoria, label=none * info page on book at Martin Luther University) ...
, some Serbs
The Serbs ( sr-Cyr, Срби, Srbi, ) are the most numerous South Slavic ethnic group native to the Balkans in Southeastern Europe, who share a common Serbian ancestry, culture, history and language.
The majority of Serbs live in their na ...
converted to Islam. This was particularly, but not wholly, so in Bosnia. The best known Muslim Serb is probably either Mehmed Paša Sokolović or Meša Selimović
Mehmed "Meša" Selimović (; ; 26 April 1910 – 11 July 1982) was a Yugoslav writer, whose novel '' Death and the Dervish'' is one of the most important literary works in post-World War II Yugoslavia. Some of the main themes in his works are the ...
. Since the second half of the 19th century, some Serbs converted to Protestantism, while historically some Serbs also were Latin Rite Catholic (especially in Dalmatia) or Eastern Catholic.

Catholicism
Catholicism is present mostly in the northern part ofVojvodina
Vojvodina ( sr-Cyrl, Војводина}), officially the Autonomous Province of Vojvodina, is an autonomous province that occupies the northernmost part of Serbia. It lies within the Pannonian Basin, bordered to the south by the national capital ...
, notably in the municipalities with Hungarian ethnic majority (Bačka Topola
Bačka Topola ( sr-Cyrl, Бачка Топола, ; hu, Topolya, ) is a town and municipality located in the North Bačka District of the autonomous province of Vojvodina, Serbia. The municipality is composed of 23 local communities and has a po ...
, Mali Iđoš
Mali Iđoš ( sr-cyrl, Мали Иђош, ; hu, Kishegyes, ) is a village and municipality located in the North Bačka District of the autonomous province Vojvodina, Serbia. The municipality comprises three local communities and has a population ...
, Kanjiža
Kanjiža ( sr-Cyrl, Кањижа, pronounced ) formerly Stara Kanjiža ( sr-cyrl, Стара Кањижа; yi, קניזשא; hu, Magyarkanizsa, formerly ''Kanizsa'') is a town and municipality located in the North Banat District of the autonomou ...
, Senta
Senta ( sr-cyrl, Сента, ; Hungarian: ''Zenta'', ; Romanian: ''Zenta'') is a town and municipality located in the North Banat District of the autonomous province of Vojvodina, Serbia. It is situated on the bank of the Tisa river in the g ...
, Ada
Ada may refer to:
Places
Africa
* Ada Foah, a town in Ghana
* Ada (Ghana parliament constituency)
* Ada, Osun, a town in Nigeria
Asia
* Ada, Urmia, a village in West Azerbaijan Province, Iran
* Ada, Karaman, a village in Karaman Province, ...
, Čoka
Čoka ( sr-Cyrl, Чока, ; hu, Csóka, ; german: Tschoka; sk, Čoka) is a town and municipality located in the North Banat District of the autonomous province of Vojvodina, Serbia. The town has a population of 4,028, while Čoka municipalit ...
) and in the multi-ethnic city of Subotica and multi-ethnic municipality of Bečej
Bečej ( sr-cyrl, Бечеј, ; hu, Óbecse, ) is a town and municipality located in the South Bačka District of the autonomous province of Vojvodina, Serbia. The town has a population of 23,895, while the municipality has 37,351 inhabitants. I ...
. It is represented mainly by the following ethnic groups: Hungarians
Hungarians, also known as Magyars ( ; hu, magyarok ), are a nation and ethnic group native to Hungary () and historical Hungarian lands who share a common culture, history, ancestry, and language. The Hungarian language belongs to the Urali ...
, Croats
The Croats (; hr, Hrvati ) are a South Slavic ethnic group who share a common Croatian ancestry, culture, history and language. They are also a recognized minority in a number of neighboring countries, namely Austria, the Czech Republic, ...
, Bunjevci
Bunjevci ( sh-Latn-Cyrl, separator=" / ", Bunjevci, Буњевци, ; sh-Latn-Cyrl, label=, separator=" / ", Bunjevac, Буњевац, sh-Latn-Cyrl, label=, separator=" / ", Bunjevka, Буњевка) are a South Slavic sub-ethnic group living ...
, Germans
, native_name_lang = de
, region1 =
, pop1 = 72,650,269
, region2 =
, pop2 = 534,000
, region3 =
, pop3 = 157,000
3,322,405
, region4 =
, pop4 = ...
, Slovenes
The Slovenes, also known as Slovenians ( sl, Slovenci ), are a South Slavic ethnic group native to Slovenia, and adjacent regions in Italy, Austria and Hungary. Slovenes share a common ancestry, culture, history and speak Slovene as their na ...
, Czechs
The Czechs ( cs, Češi, ; singular Czech, masculine: ''Čech'' , singular feminine: ''Češka'' ), or the Czech people (), are a West Slavic ethnic group and a nation native to the Czech Republic in Central Europe, who share a common ancestry, ...
, etc. A smaller number of Roma people
The Romani (also spelled Romany or Rromani , ), colloquially known as the Roma, are an Indo-Aryan ethnic group, traditionally nomadic itinerants. They live in Europe and Anatolia, and have diaspora populations located worldwide, with sign ...
, Slovaks and Serbs
The Serbs ( sr-Cyr, Срби, Srbi, ) are the most numerous South Slavic ethnic group native to the Balkans in Southeastern Europe, who share a common Serbian ancestry, culture, history and language.
The majority of Serbs live in their na ...
are also Catholic. The ethnic Rusyns
Rusyns (), also known as Carpatho-Rusyns (), or Rusnaks (), are an East Slavic ethnic group from the Eastern Carpathians in Central Europe. They speak Rusyn, an East Slavic language variety, treated variously as either a distinct langu ...
and a smaller part of the ethnic Ukrainians
Ukrainians ( uk, Українці, Ukraintsi, ) are an East Slavic ethnic group native to Ukraine. They are the seventh-largest nation in Europe. The native language of the Ukrainians is Ukrainian. The majority of Ukrainians are Eastern Ort ...
are primarily Eastern Rite Catholics.
Protestantism
Bački Petrovac
Bački Petrovac ( sr-cyrl, Бачки Петровац; sk, Báčsky Petrovec; hu, Petrőc) is a town and municipality located in the South Bačka District of the autonomous province of Vojvodina, Serbia. The town has a population of 7,452, whil ...
and Kovačica
Kovačica ( sr-cyrl, Ковачица, ; sk, Kovačica; hu, Antalfalva; ro, Covăcița) is a town and municipality located in the South Banat District of the autonomous province of Vojvodina, Serbia. According to the 2011 census, the town has ...
, where the absolute or relative majority of the population are ethnic Slovaks (most of whom are adherents of Protestant Christianity). Some members of other ethnic groups (especially Serbs
The Serbs ( sr-Cyr, Срби, Srbi, ) are the most numerous South Slavic ethnic group native to the Balkans in Southeastern Europe, who share a common Serbian ancestry, culture, history and language.
The majority of Serbs live in their na ...
in absolute terms and Hungarians
Hungarians, also known as Magyars ( ; hu, magyarok ), are a nation and ethnic group native to Hungary () and historical Hungarian lands who share a common culture, history, ancestry, and language. The Hungarian language belongs to the Urali ...
and Germans
, native_name_lang = de
, region1 =
, pop1 = 72,650,269
, region2 =
, pop2 = 534,000
, region3 =
, pop3 = 157,000
3,322,405
, region4 =
, pop4 = ...
in proportional terms) are also adherents of various forms of Protestant Christianity.
There are various neo-Protestant groups in the country, including Methodists, Seventh-day Adventists
The Seventh-day Adventist Church is an Adventist Protestant Christian denomination which is distinguished by its observance of Saturday, the seventh day of the week in the Christian (Gregorian) and the Hebrew calendar, as the Sabbath, and i ...
, Evangelical Baptists (Nazarene), and others. Many of these groups are situated in the culturally diverse province of Vojvodina. Prior to end of World War II number of Protestants in the region was larger.
According to the 2011 census, the largest Protestant communities were recorded in the municipalities of Kovačica
Kovačica ( sr-cyrl, Ковачица, ; sk, Kovačica; hu, Antalfalva; ro, Covăcița) is a town and municipality located in the South Banat District of the autonomous province of Vojvodina, Serbia. According to the 2011 census, the town has ...
(11,349) and Bački Petrovac
Bački Petrovac ( sr-cyrl, Бачки Петровац; sk, Báčsky Petrovec; hu, Petrőc) is a town and municipality located in the South Bačka District of the autonomous province of Vojvodina, Serbia. The town has a population of 7,452, whil ...
(8,516), as well as in Stara Pazova
Stara Pazova (, ; hu, Ópazova) is a town and municipality located in the Srem District of the autonomous province of Vojvodina, Serbia. The town has a population of 64792, while Stara Pazova municipality has 65,792 inhabitants. The entrance into ...
(4,940) and the second largest Serbian city Novi Sad
Novi Sad ( sr-Cyrl, Нови Сад, ; hu, Újvidék, ; german: Neusatz; see below for other names) is the second largest city in Serbia and the capital of the autonomous province of Vojvodina. It is located in the southern portion of the Pan ...
(8,499), which are predominantly Eastern Orthodox. While Protestants from Kovačica, Bački Petrovac and Stara Pazova are mostly Slovaks, members of Slovak Evangelical Church of the Augsburg Confession in Serbia
The Slovak Evangelical Church of the Augsburg Confession in Serbia (Slovak: Slovenská evanjelická augsburského vyznania cirkev v Srbsku, abbreviated SEAVC) is a Lutheranism, Lutheran church in Serbia.
This, the largest Protestant church in form ...
, services in most of the Protestant churches in Novi Sad are performed in the Serbian language
Serbian (, ) is the standardized variety of the Serbo-Croatian language mainly used by Serbs. It is the official and national language of Serbia, one of the three official languages of Bosnia and Herzegovina and co-official in Montenegro and K ...
.
Protestantism (mostly in its Nazarene form) started to spread among Serbs in Vojvodina
The Serbs of Vojvodina are the largest ethnic group in this northern province of Serbia. For centuries, Vojvodina was ruled by several European powers, but Vojvodina Serbs never assimilated into cultures of those countries. Thus, they have consi ...
in the last decades of the 19th century. Although the percentage of Protestants among Serbs is not large, it is the only religious form besides Eastern Orthodoxy, which is today widespread among Serbs.

Islam
Islam is mostly present in the southwest of Serbia in the region ofSandžak
Sandžak (; sh, / , ; sq, Sanxhaku; ota, سنجاق, Sancak), also known as Sanjak, is a historical geo-political region in Serbia and Montenegro. The name Sandžak derives from the Sanjak of Novi Pazar, a former Ottoman administrative dis ...
or Raška (notably in the city of Novi Pazar
Novi Pazar ( sr-cyr, Нови Пазар, lit. "New Bazaar"; ) is a city located in the Raška District of southwestern Serbia. As of the 2011 census, the urban area has 66,527 inhabitants, while the city administrative area has 100,410 inhabit ...
and municipalities of Tutin
Tutin may refer to:
Places
*Tutin, Serbia, town in Serbia
Surname
*Arthur Tutin (1907–1961), English footballer
*Dorothy Tutin (1930–2001), English actress
*Mary Tutin, maiden name of Mary Gillick (1881–1965), English sculptor
*Tom Tutin (1 ...
and Sjenica
Sjenica ( sr-cyr, Сјеница, ) is a town and municipality located in the Zlatibor District of southwestern Serbia. The population of the town, according to 2011 census, is 14,060 inhabitants, while the municipality has 26,392.
Sjenica is si ...
), as well as in parts of southern Serbia (municipalities of Preševo and Bujanovac). Ethnic groups whose members are mostly adherents of Islam are: Bosniaks, ethnic Muslims
Muslims ( Serbo-Croatian Latin and sl, Muslimani, Serbo-Croatian Cyrillic and mk, Муслимани) is a designation for a Serbo-Croatian speaking Muslims, inhabiting mostly the territory of the former Yugoslav republics. The term, adopted ...
, Albanians, and Gorani. A significant number of Roma people
The Romani (also spelled Romany or Rromani , ), colloquially known as the Roma, are an Indo-Aryan ethnic group, traditionally nomadic itinerants. They live in Europe and Anatolia, and have diaspora populations located worldwide, with sign ...
are also adherents of Islam.
Adherents belong to one of two communities – Islamic Community of Serbia or the Islamic Community in Serbia.
Judaism
As of 2011, out of 787 declaredJews
Jews ( he, יְהוּדִים, , ) or Jewish people are an ethnoreligious group and nation originating from the Israelites Israelite origins and kingdom: "The first act in the long drama of Jewish history is the age of the Israelites""The ...
in Serbia
Serbia (, ; Serbian: , , ), officially the Republic of Serbia (Serbian: , , ), is a landlocked country in Southeastern and Central Europe, situated at the crossroads of the Pannonian Basin and the Balkans. It shares land borders with Hungar ...
578 stated their religion as Judaism, mostly in the cities of Belgrade (286), Novi Sad
Novi Sad ( sr-Cyrl, Нови Сад, ; hu, Újvidék, ; german: Neusatz; see below for other names) is the second largest city in Serbia and the capital of the autonomous province of Vojvodina. It is located in the southern portion of the Pan ...
(84), Subotica (75) and Pančevo (31). The only remaining functioning synagogue in Serbia is the Belgrade Synagogue
Sukkat Shalom Synagogue or Belgrade Synagogue (Serbian: Београдска синагога / Beogradska sinagoga) is currently the only fully active Jewish place of worship in Serbian capital Belgrade, as other synagogues citywide are not activ ...
. There are also small numbers of Jews in Zrenjanin and Sombor, with isolated families scattered throughout the rest of Serbia.
Irreligion
About 1.1% of Serbian population is atheist. Religiosity was lowest inNovi Beograd
New Belgrade ( sr, / , ) is a municipality of the city of Belgrade. It is a planned city, built since 1948 in a previously uninhabited area on the left bank of the Sava river, opposite old Belgrade. In recent years, it has become the central bu ...
, with 3.5% of population being atheists (compare to whole Belgrade's and Novi Sad's 1.5%) and highest in rural parts of the country, where atheism in most municipalities went below 0.01%.
In a 2009 Gallup poll, 44% of respondents in Serbia answered 'no' to the question "Is religion an important part of your daily life?"
A Pew Research Center poll, conducted from June 2015 to July 2016, found that 2% of Serbia
Serbia (, ; Serbian: , , ), officially the Republic of Serbia (Serbian: , , ), is a landlocked country in Southeastern and Central Europe, situated at the crossroads of the Pannonian Basin and the Balkans. It shares land borders with Hungar ...
were atheists, while 10% stated that they "Do not believe in God".
Role of the religion in public life
Public schools allow religious teaching in cooperation with religious communities having agreements with the state, but attendance is not mandated. Religion classes ( sr, verska nastava) are organized in public elementary and secondary schools, most commonly coordinated with the Serbian Orthodox Church, but also with the Catholic Church and Islamic community. The public holidays in Serbia also include thereligious festival
A religious festival is a time of special importance marked by adherents to that religion. Religious festivals are commonly celebrated on recurring cycles in a calendar year or lunar calendar. The science of religious rites and festivals is known ...
s of Eastern Orthodox Christmas and Eastern Orthodox Easter, as well as Saint Sava
Saint Sava ( sr, Свети Сава, Sveti Sava, ; Old Church Slavonic: ; gr, Άγιος Σάββας; 1169 or 1174 – 14 January 1236), known as the Enlightener, was a Serbian prince and Orthodox monk, the first Archbishop of the autocephalou ...
Day which is a working holiday and is celebrated as a Day of Spirituality as well as Day of Education. Believers of other faiths are legally allowed to celebrate their religious holidays.
Religious freedom
The government ofSerbia
Serbia (, ; Serbian: , , ), officially the Republic of Serbia (Serbian: , , ), is a landlocked country in Southeastern and Central Europe, situated at the crossroads of the Pannonian Basin and the Balkans. It shares land borders with Hungar ...
does not keep records of religiously motivated violence, and reporting from individual religious organization is sparse.International Religious Freedom Report 2017 Serbia
', US Department of State, Bureau of Democracy, Human Rights, and Labor. The laws of Serbia establish the freedom of religion, forbid the establishment of a state religion, and outlaw religious discrimination. While registration with the government, is not necessary for religious groups to practice, the government confers certain privileges to registered groups. The government maintains a two-tiered system of registered groups, split between "traditional" groups and "nontraditional" groups. Minority groups and independent observers have complained that this system consists of religious discrimination. The government has programs established for the restitution of property confiscated by the government of
Yugoslavia
Yugoslavia (; sh-Latn-Cyrl, separator=" / ", Jugoslavija, Југославија ; sl, Jugoslavija ; mk, Југославија ;; rup, Iugoslavia; hu, Jugoszlávia; rue, label=Pannonian Rusyn, Югославия, translit=Juhoslavija ...
after World War II
World War II or the Second World War, often abbreviated as WWII or WW2, was a world war that lasted from 1939 to 1945. It involved the vast majority of the world's countries—including all of the great powers—forming two opposing ...
, and for property lost in the Holocaust
The Holocaust, also known as the Shoah, was the genocide of European Jews during World War II. Between 1941 and 1945, Nazi Germany and its collaborators systematically murdered some six million Jews across German-occupied Europe; ...
.
The media and individual members of parliament have been criticized for using disparaging language when referring to non-traditional groups. Antisemitic literature is commonly available in bookstores, and is prevalent online.
Although religious freedom was largely respected by the government of the Kingdom of Yugoslavia
The Kingdom of Yugoslavia ( sh-Latn-Cyrl, separator=" / ", Kraljevina Jugoslavija, Краљевина Југославија; sl, Kraljevina Jugoslavija) was a state in Southeast and Central Europe that existed from 1918 until 1941. From 1918 ...
and Serbia's constitutions through its various incarnations as either an independent state or as part of Yugoslavia have nominally upheld religious freedom, it was also the site of significant religiously and ethnically-motivated war crimes during World War IITomasevich, Jozo (2001). War and Revolution in Yugoslavia: 1941–1945. p744. Stanford University Press. . and the Yugoslav Wars
The Yugoslav Wars were a series of separate but related Naimark (2003), p. xvii. ethnic conflicts, wars of independence, and insurgencies that took place in the SFR Yugoslavia from 1991 to 2001. The conflicts both led up to and resulted from ...
.
See also
*Religion in Vojvodina
The dominant religion in Vojvodina is Orthodox Christianity, mainly represented by the Serbian Orthodox Church, while other important religions of the region are Catholic Christianity, Protestant Christianity, Islam, and Judaism.
Demographics ...
References
Sources
* Kuburić, Z., 2010. Verske zajednice u Srbiji i verska distanca. CEIR—Centar za empirijska istraživanja religije. * * Radisavljević-Ćiparizović, D., 2002. Religija i svakodnevni život: vezanost ljudi za religiju i crkvu u Srbiji krajem devedesetih. Srbija krajem milenijuma: Razaranje društva, promene i svakodnevni život. * Radulović, L.B., 2012. Religija ovde i sada: revitalizacije religije u Srbiji. Srpski geneaološki centar, Odeljenje za etnologiju i antropologiju Filozofskog fakulteta. * Blagojević, M., 2011. „Aktuelna religioznost građana Srbije “, u A. Mladenović (prir.). Religioznost u Srbiji 2010, pp. 43–72. * Đorđević, D.B., 2005. Religije i veroispovesti nacionalnih manjina u Srbiji. Sociologija, 47(3), pp. 193–212. * Đukić, V., 2008. Religije Srbije–mreža dijaloga i saradnje. * Ilić, A., 2013. Odnos religije i društva u današnjoj Srbiji. Religija i Tolerancija, 1(3). * Kuburić, Z. and Gavrilović, D., 2013. Verovanje i pripadanje u savremenoj Srbiji. Religija i Tolerancija, (1).External links
Serbian Orthodox Church
{{DEFAULTSORT:Religion In Serbia