Herbert Clark Hoover (August 10, 1874 – October 20, 1964) was an American politician who served as the 31st
president of the United States
The president of the United States (POTUS) is the head of state and head of government of the United States of America. The president directs the Federal government of the United States#Executive branch, executive branch of the Federal gove ...
from 1929 to 1933 and a member of the
Republican Party
Republican Party is a name used by many political parties around the world, though the term most commonly refers to the United States' Republican Party.
Republican Party may also refer to:
Africa
* Republican Party (Liberia)
*Republican Party ...
, holding office during the onset of the
Great Depression in the United States
In the History of the United States, United States, the Great Depression began with the Wall Street Crash of 1929, Wall Street Crash of October 1929 and then spread worldwide. The nadir came in 1931–1933, and recovery came in 1940. The stock m ...
. A self-made man who became rich as a mining engineer, Hoover led the
Commission for Relief in Belgium
The Commission for Relief in Belgium or C.R.B. − known also as just Belgian Relief − was an international (predominantly American) organization that arranged for the supply of food to German-occupied Belgium and northern France during the Wor ...
, served as the director of the
U.S. Food Administration
The United States Food Administration (1917–1920) was an independent Federal agency that controlled the production, distribution and conservation of food in the U.S. during the nation's participation in World War I. It was established to prev ...
, and served as the
U.S. Secretary of Commerce.
Hoover was born to a
Quaker
Quakers are people who belong to a historically Protestant Christian set of denominations known formally as the Religious Society of Friends. Members of these movements ("theFriends") are generally united by a belief in each human's abili ...
family in
West Branch, Iowa, but he grew up in
Oregon
Oregon () is a U.S. state, state in the Pacific Northwest region of the Western United States. The Columbia River delineates much of Oregon's northern boundary with Washington (state), Washington, while the Snake River delineates much of it ...
. He was one of the first graduates of the new
Stanford University
Stanford University, officially Leland Stanford Junior University, is a private research university in Stanford, California. The campus occupies , among the largest in the United States, and enrolls over 17,000 students. Stanford is conside ...
in 1895. He took a position with a London-based mining company working in Australia and China. He rapidly became a wealthy mining engineer. In 1914 at the outbreak of
World War I
World War I (28 July 1914 11 November 1918), often abbreviated as WWI, was List of wars and anthropogenic disasters by death toll, one of the deadliest global conflicts in history. Belligerents included much of Europe, the Russian Empire, ...
, he organized and headed the Commission for Relief in Belgium, an international relief organization that provided food to occupied Belgium. When the U.S. entered the war in 1917, President
Woodrow Wilson
Thomas Woodrow Wilson (December 28, 1856February 3, 1924) was an American politician and academic who served as the 28th president of the United States from 1913 to 1921. A member of the Democratic Party, Wilson served as the president of ...
appointed Hoover to lead the Food Administration. He became famous as his country's "food czar". After the war, Hoover led the
American Relief Administration
American Relief Administration (ARA) was an American relief mission to Europe and later post-revolutionary Russia after World War I. Herbert Hoover, future president of the United States, was the program director.
The ARA's immediate predeces ...
, which provided food to the starving millions in Central and Eastern Europe, especially Russia. Hoover's wartime service made him a favorite of many
progressives
Progressivism holds that it is possible to improve human societies through political action. As a political movement, progressivism seeks to advance the human condition through social reform based on purported advancements in science, techn ...
, and he unsuccessfully sought the Republican nomination in the
1920 presidential election.
Republican President
Warren G. Harding appointed Hoover as Secretary of Commerce in 1920, and he continued to serve under President
Calvin Coolidge
Calvin Coolidge (born John Calvin Coolidge Jr.; ; July 4, 1872January 5, 1933) was the 30th president of the United States from 1923 to 1929. Born in Vermont, Coolidge was a Republican lawyer from New England who climbed up the ladder of Ma ...
after Harding died in 1923. Hoover was an unusually active and visible Cabinet member, becoming known as "Secretary of Commerce and Under-Secretary of all other departments". He was influential in the development of air travel and radio. He led the federal response to the
Great Mississippi Flood of 1927. Hoover won the Republican nomination in the
1928 presidential election, and defeated Democratic candidate
Al Smith
Alfred Emanuel Smith (December 30, 1873 – October 4, 1944) was an American politician who served four terms as Governor of New York and was the Democratic Party's candidate for president in 1928.
The son of an Irish-American mother and a Ci ...
in a landslide. In 1929 Hoover assumed the presidency during a period of widespread economic stability. However, during his first year in office,
the stock market crashed, signaling the onset of the
Great Depression
The Great Depression (19291939) was an economic shock that impacted most countries across the world. It was a period of economic depression that became evident after a major fall in stock prices in the United States. The economic contagio ...
. The Great Depression dominated Hoover's presidency and he responded by pursuing a series of economic policies in an attempt to lift the economy. Hoover scapegoated
Mexicans
Mexicans ( es, mexicanos) are the citizens of the United Mexican States.
The most spoken language by Mexicans is Spanish, but some may also speak languages from 68 different Indigenous linguistic groups and other languages brought to Mexi ...
for the Depression, instituting policies and sponsoring programs of
repatriation and deportation to Mexico.
In the midst of the economic crisis, Hoover was decisively defeated by Democratic nominee
Franklin D. Roosevelt in the
1932 presidential election. Hoover's retirement was over 31 years long, one of the longest presidential retirements. He authored numerous works and became increasingly
conservative
Conservatism is a cultural, social, and political philosophy that seeks to promote and to preserve traditional institutions, practices, and values. The central tenets of conservatism may vary in relation to the culture and civilization in ...
in retirement. He strongly criticized Roosevelt's foreign policy and
New Deal
The New Deal was a series of programs, public work projects, financial reforms, and regulations enacted by President Franklin D. Roosevelt in the United States between 1933 and 1939. Major federal programs agencies included the Civilian Con ...
domestic agenda. In the 1940s and 1950s, public opinion of Hoover improved largely due to his service in various assignments for presidents
Harry S. Truman and
Dwight D. Eisenhower, including chairing the influential
Hoover Commission
The Hoover Commission, officially named the Commission on Organization of the Executive Branch of the Government, was a body appointed by President Harry S. Truman in 1947 to recommend administrative changes in the Federal Government of the Unit ...
. Critical assessments of his presidency by historians and political scientists generally
rank him as a significantly below-average president, although Hoover has received praise for his actions as a humanitarian and public official.
Early life

Herbert Clark Hoover was born on August 10, 1874, in
West Branch, Iowa. His father, Jesse Hoover, was a
blacksmith
A blacksmith is a metalsmith who creates objects primarily from wrought iron or steel, but sometimes from other metals, by forging the metal, using tools to hammer, bend, and cut (cf. tinsmith). Blacksmiths produce objects such as gates, gr ...
and farm implement store owner of German, Swiss, and English ancestry. Hoover's mother, Hulda Randall Minthorn, was raised in
Norwich, Ontario
The Township of Norwich is a municipality located in Oxford County in Southwestern Ontario, Canada. At the centre of the Township of Norwich is the Town of Norwich. The preferred pronunciation of the town name is , which differs from the pronu ...
, Canada, before moving to
Iowa
Iowa () is a U.S. state, state in the Midwestern United States, Midwestern region of the United States, bordered by the Mississippi River to the east and the Missouri River and Big Sioux River to the west. It is bordered by six states: Wiscon ...
in 1859. Like most other citizens of West Branch, Jesse and Hulda were
Quakers
Quakers are people who belong to a historically Protestant Christian set of denominations known formally as the Religious Society of Friends. Members of these movements ("theFriends") are generally united by a belief in each human's abili ...
. Around age two "Bertie", as he was called during that time, contracted a serious bout of
croup
Croup, also known as laryngotracheobronchitis, is a type of respiratory infection that is usually caused by a virus. The infection leads to swelling inside the trachea, which interferes with normal breathing and produces the classic symptoms ...
, and was momentarily thought to have died until resuscitated by his uncle, John Minthorn. As a young child he was often referred to by his father as "my little stick in the mud" when he repeatedly got trapped in the mud crossing the unpaved street. Herbert's family figured prominently in the town's public prayer life, due almost entirely to mother Hulda's role in the church. As a child, Hoover consistently attended schools, but he did little reading on his own aside from the Bible. Hoover's father, noted by the local paper for his "pleasant, sunshiny disposition", died in 1880 at the age of 34 of a sudden
heart attack
A myocardial infarction (MI), commonly known as a heart attack, occurs when blood flow decreases or stops to the coronary artery of the heart, causing damage to the heart muscle. The most common symptom is chest pain or discomfort which ma ...
. Hoover's mother died in 1884 of
typhoid
Typhoid fever, also known as typhoid, is a disease caused by ''Salmonella'' serotype Typhi bacteria. Symptoms vary from mild to severe, and usually begin six to 30 days after exposure. Often there is a gradual onset of a high fever over several d ...
, leaving Hoover, his older brother, Theodore, and his younger sister, May, as orphans. Hoover lived the next 18 months with his uncle Allen Hoover at a nearby farm.

In November 1885, Hoover was sent to
Newberg, Oregon
Newberg is a city in Yamhill County, Oregon, United States. Located in the Portland metropolitan area, the city is home to George Fox University. As of the 2010 census, the city population was 25,138 making it the second most populous city in t ...
, to live with his uncle John Minthorn, a Quaker physician and businessman whose own son had died the year before. The Minthorn household was considered cultured and educational, and imparted a strong work ethic. Much like West Branch, Newberg was a frontier town settled largely by Midwestern Quakers. Minthorn ensured that Hoover received an education, but Hoover disliked the many chores assigned to him and often resented Minthorn. One observer described Hoover as "an orphan
hoseemed to be neglected in many ways". Hoover attended Friends Pacific Academy (now
George Fox University), but dropped out at the age of thirteen to become an office assistant for his uncle's real estate office (Oregon Land Company) in
Salem, Oregon
Salem ( ) is the capital of the U.S. state of Oregon, and the county seat of Marion County. It is located in the center of the Willamette Valley alongside the Willamette River, which runs north through the city. The river forms the boundary bet ...
. Though he did not attend high school, Hoover learned bookkeeping, typing, and mathematics at a night school.
Hoover was a member of the inaugural "Pioneer Class" of
Stanford University
Stanford University, officially Leland Stanford Junior University, is a private research university in Stanford, California. The campus occupies , among the largest in the United States, and enrolls over 17,000 students. Stanford is conside ...
, entering in 1891 despite failing all the
entrance exams except
mathematics
Mathematics is an area of knowledge that includes the topics of numbers, formulas and related structures, shapes and the spaces in which they are contained, and quantities and their changes. These topics are represented in modern mathematics ...
. During his freshman year, he switched his major from
mechanical engineering
Mechanical engineering is the study of physical machines that may involve force and movement. It is an engineering branch that combines engineering physics and mathematics principles with materials science, to design, analyze, manufacture, ...
to
geology
Geology () is a branch of natural science concerned with Earth and other Astronomical object, astronomical objects, the features or rock (geology), rocks of which it is composed, and the processes by which they change over time. Modern geology ...
after working for
John Casper Branner, the chair of Stanford's geology department. During his sophomore year, to reduce his costs, Hoover co-founded the first student housing cooperative at Stanford, "Romero Hall".
Hoover was a mediocre student, and he spent much of his time working in various part-time jobs or participating in campus activities. Though he was initially shy among fellow students, Hoover won election as student treasurer and became known for his distaste for
fraternities and sororities
Fraternities and sororities are social organizations at colleges and universities in North America.
Generally, membership in a fraternity or sorority is obtained as an undergraduate student, but continues thereafter for life. Some accept grad ...
. He served as student manager of both the
baseball
Baseball is a bat-and-ball sport played between two teams of nine players each, taking turns batting and fielding. The game occurs over the course of several plays, with each play generally beginning when a player on the fielding t ...
and
football teams
Football is a family of team sports that involve, to varying degrees, kicking a ball to score a goal. Unqualified, the word ''football'' normally means the form of football that is the most popular where the word is used. Sports commonly ...
, and helped organize the inaugural
Big Game versus the
University of California
The University of California (UC) is a public land-grant research university system in the U.S. state of California. The system is composed of the campuses at Berkeley, Davis, University of California, Irvine, Irvine, University of Califor ...
. During the summers before and after his senior year, Hoover interned under economic geologist
Waldemar Lindgren of the
United States Geological Survey
The United States Geological Survey (USGS), formerly simply known as the Geological Survey, is a scientific agency of the United States government. The scientists of the USGS study the landscape of the United States, its natural resources, ...
; these experiences convinced Hoover to pursue a career as a mining geologist.
Mining engineer
Bewick, Moreing

When Hoover graduated from Stanford in 1895, the country was in the midst of the
Panic of 1893
The Panic of 1893 was an economic depression in the United States that began in 1893 and ended in 1897. It deeply affected every sector of the economy, and produced political upheaval that led to the political realignment of 1896 and the pres ...
, and he initially struggled to find a job. He worked in various low-level mining jobs in the
Sierra Nevada Mountains
The Sierra Nevada () is a mountain range in the Western United States, between the Central Valley of California and the Great Basin. The vast majority of the range lies in the state of California, although the Carson Range spur lies primarily ...
until he convinced prominent mining engineer Louis Janin to hire him. After working as a mine scout for a year, Hoover was hired by Bewick, Moreing & Co., a
London
London is the capital and List of urban areas in the United Kingdom, largest city of England and the United Kingdom, with a population of just under 9 million. It stands on the River Thames in south-east England at the head of a estuary dow ...
-based company that operated
gold mines in
Western Australia
Western Australia (commonly abbreviated as WA) is a state of Australia occupying the western percent of the land area of Australia excluding external territories. It is bounded by the Indian Ocean to the north and west, the Southern Ocean to t ...
. Hoover first went to
Coolgardie, then the center of the
Eastern Goldfields
The Eastern Goldfields is part of the Western Australian Goldfields in the Goldfields-Esperance region of Western Australia, covering the present and former gold-mining area east of Perth.
Extent and name origin
The region encompasses the to ...
. Though Hoover received a $5,000 salary (), conditions were harsh in the goldfields.
Hoover described the
Coolgardie and
Murchison rangeland
Rangelands are grasslands, shrublands, woodlands, wetlands, and deserts that are grazed by domestic livestock or wild animals. Types of rangelands include tallgrass and shortgrass prairies, desert grasslands and shrublands, woodlands, sava ...
s on the edge of the
Great Victoria Desert
The Great Victoria Desert is a sparsely populated desert ecoregion and interim Australian bioregion in Western Australia and South Australia.
History
In 1875, British-born Australian explorer Ernest Giles became the first European to cros ...
as a land of "black flies, red dust and white heat".
Hoover traveled constantly across the
Outback
The Outback is a remote, vast, sparsely populated area of Australia. The Outback is more remote than the bush. While often envisaged as being arid, the Outback regions extend from the northern to southern Australian coastlines and encompass a ...
to evaluate and manage the company's mines. He convinced Bewick, Moreing to purchase the
Sons of Gwalia
Sons of Gwalia was a Western Australian mining company that mined gold, tantalum, spodumene, lithium and tin. It was Australia's third-largest gold producer and also controlled more than half the world's production of tantalum,[Western Australia
Western Australia (commonly abbreviated as WA) is a state of Australia occupying the western percent of the land area of Australia excluding external territories. It is bounded by the Indian Ocean to the north and west, the Southern Ocean to t ...]
. Hoover brought in many
Italian immigrants to cut costs and counter the
labour movement
The labour movement or labor movement consists of two main wings: the trade union movement (British English) or labor union movement (American English) on the one hand, and the political labour movement on the other.
* The trade union movement ...
of the Australian miners.
During his time with the mining company, Hoover became opposed to measures such as a
minimum wage
A minimum wage is the lowest remuneration that employers can legally pay their employees—the price floor below which employees may not sell their labor. Most countries had introduced minimum wage legislation by the end of the 20th century. B ...
and
workers' compensation
Workers' compensation or workers' comp is a form of insurance providing wage replacement and medical benefits to employees injured in the course of employment in exchange for mandatory relinquishment of the employee's right to sue his or her emp ...
, feeling that they were unfair to owners. Hoover's work impressed his employers, and in 1898 he was promoted to junior partner. An open feud developed between Hoover and his boss, Ernest Williams, but company leaders defused the situation by offering Hoover a compelling position in
China
China, officially the People's Republic of China (PRC), is a country in East Asia. It is the world's List of countries and dependencies by population, most populous country, with a Population of China, population exceeding 1.4 billion, slig ...
.
Upon arriving in China, Hoover developed gold mines near
Tianjin
Tianjin (; ; Mandarin: ), alternately romanized as Tientsin (), is a municipality and a coastal metropolis in Northern China on the shore of the Bohai Sea. It is one of the nine national central cities in Mainland China, with a total popu ...
on behalf of Bewick, Moreing, and the Chinese-owned
Chinese Engineering and Mining Company
The Chinese Engineering and Mining Company, Limited, was established with foreign capital around 1879 to mine coal for the steamships of the Chinese Merchants' Steam Navigation Company and the Imperial Chinese Navy. English mining engineer Robert ...
. He became deeply interested in
Chinese history
The earliest known written records of the history of China date from as early as 1250 BC, from the Shang dynasty (c. 1600–1046 BC), during the reign of king Wu Ding. Ancient historical texts such as the ''Book of Documents'' (early chapter ...
, but gave up on learning the
language
Language is a structured system of communication. The structure of a language is its grammar and the free components are its vocabulary. Languages are the primary means by which humans communicate, and may be conveyed through a variety of ...
to
a fluent level. He publicly warned that Chinese workers were inefficient and racially inferior. He made recommendations to improve the lot of the Chinese worker, seeking to end the practice of imposing long-term servitude contracts and to institute reforms for workers based on merit. The
Boxer Rebellion
The Boxer Rebellion, also known as the Boxer Uprising, the Boxer Insurrection, or the Yihetuan Movement, was an Xenophobia, anti-foreign, anti-colonialism, anti-colonial, and Persecution of Christians#China, anti-Christian uprising in China ...
broke out shortly after Hoover arrived in China, trapping the Hoovers and numerous other foreign nationals until a
multi-national military force defeated Boxer forces in the
Battle of Tientsin. Fearing the imminent collapse of the Chinese government, the director of the
Chinese Engineering and Mining Company
The Chinese Engineering and Mining Company, Limited, was established with foreign capital around 1879 to mine coal for the steamships of the Chinese Merchants' Steam Navigation Company and the Imperial Chinese Navy. English mining engineer Robert ...
agreed to establish a new Sino-British venture with Bewick, Moreing. After Hoover and Bewick, Moreing established effective control over the new Chinese mining company, Hoover became the operating partner of Bewick, Moreing in late 1901.
As operating partner, Hoover continually traveled the world on behalf of Bewick, Moreing, visiting mines operated by the company on different continents. Beginning in December 1902, the company faced mounting legal and financial issues after one of the partners admitted to having fraudulently sold stock in a mine. More issues arose in 1904 after the British government formed two separate royal commissions to investigate Bewick, Moreing's labor practices, and financial dealings in Western Australia. After the company lost a suit Hoover began looking for a way to get out of the partnership, and he sold his shares in mid-1908.
Sole proprietor

After leaving Bewick, Moreing, Hoover worked as a London-based independent mining consultant and financier. Though he had risen to prominence as a geologist and mine operator, Hoover focused much of his attention on raising money, restructuring corporate organizations, and financing new ventures. He specialized in rejuvenating troubled mining operations, taking a share of the profits in exchange for his technical and financial expertise. Hoover thought of himself and his associates as "engineering doctors to sick concerns", and he earned a reputation as a "doctor of sick mines". He made investments on every continent and had offices in
San Francisco
San Francisco (; Spanish for " Saint Francis"), officially the City and County of San Francisco, is the commercial, financial, and cultural center of Northern California. The city proper is the fourth most populous in California and 17t ...
;
London
London is the capital and List of urban areas in the United Kingdom, largest city of England and the United Kingdom, with a population of just under 9 million. It stands on the River Thames in south-east England at the head of a estuary dow ...
;
New York City
New York, often called New York City or NYC, is the List of United States cities by population, most populous city in the United States. With a 2020 population of 8,804,190 distributed over , New York City is also the L ...
;
Paris
Paris () is the capital and most populous city of France, with an estimated population of 2,165,423 residents in 2019 in an area of more than 105 km² (41 sq mi), making it the 30th most densely populated city in the world in 2020. Si ...
;
Petrograd
Saint Petersburg ( rus, links=no, Санкт-Петербург, a=Ru-Sankt Peterburg Leningrad Petrograd Piter.ogg, r=Sankt-Peterburg, p=ˈsankt pʲɪtʲɪrˈburk), formerly known as Petrograd (1914–1924) and later Leningrad (1924–1991), i ...
; and
Mandalay
Mandalay ( or ; ) is the second-largest city in Myanmar, after Yangon. Located on the east bank of the Irrawaddy River, 631km (392 miles) (Road Distance) north of Yangon, the city has a population of 1,225,553 (2014 census).
Mandalay was fou ...
,
British Burma
British may refer to:
Peoples, culture, and language
* British people, nationals or natives of the United Kingdom, British Overseas Territories, and Crown Dependencies.
** Britishness, the British identity and common culture
* British English, ...
. By 1914, Hoover was a very wealthy man, with an estimated personal fortune of $4 million (equivalent to $ million in ).
He co-founded the
Zinc Corporation
Consolidated Zinc was an Australian mining company from 1905 to 1962.
History
The company's initial operations focused on extracting zinc from mine tailings of the Broken Hill Ore Deposit at Broken Hill, New South Wales, Australia. The company w ...
to extract
zinc
Zinc is a chemical element with the symbol Zn and atomic number 30. Zinc is a slightly brittle metal at room temperature and has a shiny-greyish appearance when oxidation is removed. It is the first element in group 12 (IIB) of the periodi ...
near the Australian city of
Broken Hill
Broken Hill is an inland mining city in the far west of outback New South Wales, Australia. It is near the border with South Australia on the crossing of the Barrier Highway (A32) and the Silver City Highway (B79), in the Barrier Range. It ...
,
New South Wales
)
, nickname =
, image_map = New South Wales in Australia.svg
, map_caption = Location of New South Wales in AustraliaCoordinates:
, subdivision_type = Country
, subdivision_name = Australia
, established_title = Before federation
, es ...
. The Zinc Corporation developed the
froth flotation
Froth flotation is a process for selectively separating hydrophobic materials from hydrophilic. This is used in mineral processing, paper recycling and waste-water treatment industries. Historically this was first used in the mining industry, wher ...
process to extract zinc from lead-silver ore and operated the world's first selective ore differential flotation plant.
Hoover worked with the Burma Corporation, a British firm that produced silver, lead, and zinc in large quantities at the
Namtu Bawdwin Mine.
He also helped increase
copper production in
Kyshtym
Kyshtym (russian: Кышты́м) is a town in Chelyabinsk Oblast, Russia, located on the eastern slopes of the Southern Ural Mountains northwest of Chelyabinsk, near the town of Ozyorsk. Population: 36,000 (1970).
History
Kyshtym was establ ...
,
Russia
Russia (, , ), or the Russian Federation, is a transcontinental country spanning Eastern Europe and Northern Asia. It is the largest country in the world, with its internationally recognised territory covering , and encompassing one-ei ...
, through the use of pyritic smelting. He also agreed to manage a separate mine in the
Altai Mountains
The Altai Mountains (), also spelled Altay Mountains, are a mountain range in Central and East Asia, where Russia, China, Mongolia and Kazakhstan converge, and where the rivers Irtysh and Ob have their headwaters. The massif merges with the ...
that, according to Hoover, "developed probably the greatest and richest single body of ore known in the world".
[Hoover, Herbert C. (1952). ''The Memoirs of Herbert Hoover Years of Adventure 1874–1920''. London: Hollis & Carter]
In his spare time, Hoover wrote. His lectures at
Columbia
Columbia may refer to:
* Columbia (personification), the historical female national personification of the United States, and a poetic name for America
Places North America Natural features
* Columbia Plateau, a geologic and geographic region i ...
and Stanford universities were published in 1909 as ''Principles of Mining'', which became a standard textbook. The book reflects his move towards
progressive ideals, as Hoover came to endorse
eight-hour workdays and
organized labor
A trade union (labor union in American English), often simply referred to as a union, is an organization of workers intent on "maintaining or improving the conditions of their employment", ch. I such as attaining better wages and benefits (s ...
. Hoover became deeply interested in the
history of science
The history of science covers the development of science from ancient times to the present. It encompasses all three major branches of science: natural, social, and formal.
Science's earliest roots can be traced to Ancient Egypt and Meso ...
, and he was especially drawn to the ''
De re metallica'', an influential 16th century work on mining and metallurgy by
Georgius Agricola. In 1912, Hoover and his wife published the first English translation of ''De re metallica''. Hoover also joined the board of trustees at Stanford, and led a successful campaign to appoint John Branner as the university's president.
Marriage and family
During his senior year at Stanford, Hoover became smitten with a classmate named
Lou Henry, though his financial situation precluded marriage at that time. The daughter of a banker from
Monterey, California
Monterey (; es, Monterrey; Ohlone: ) is a city located in Monterey County on the southern edge of Monterey Bay on the U.S. state of California's Central Coast. Founded on June 3, 1770, it functioned as the capital of Alta California under b ...
, Lou Henry decided to study geology at Stanford after attending a lecture delivered by John Branner. Immediately after earning a promotion in 1898, Hoover cabled Lou Henry, asking her to marry him. After she cabled back her acceptance of the proposal, Hoover briefly returned to the United States for their wedding. They would remain married until Lou Henry Hoover's death in 1944.
Though his Quaker upbringing strongly influenced his career, Hoover rarely attended Quaker meetings during his adult life.
Hoover and his wife had two children:
Herbert Hoover Jr.
Herbert Charles Hoover (August 4, 1903 – July 9, 1969) was an engineer, businessman, and politician who served as United States Under Secretary of State from 1954 to 1957. He was the elder son of President Herbert Hoover.
Biography
Early yea ...
(born in 1903) and
Allan Henry Hoover
Allan Henry Hoover (July 17, 1907 – November 4, 1993) was a British-born American mining engineer, rancher, financier, and the younger son of President Herbert Hoover and First Lady Lou Henry.
Early life and education
Hoover was born in Lon ...
(born in 1907). The Hoover family began living in London in 1902, though they frequently traveled as part of Hoover's career. After 1916, the Hoovers began living in the United States, maintaining homes in
Stanford, California
Stanford is a census-designated place (CDP) in the northwest corner of Santa Clara County, California, United States. It is the home of Stanford University. The population was 21,150 at the 2020 census.
Stanford is an unincorporated area of ...
, and
Washington, D.C.
World War I and aftermath
Relief in Europe

World War I
World War I (28 July 1914 11 November 1918), often abbreviated as WWI, was List of wars and anthropogenic disasters by death toll, one of the deadliest global conflicts in history. Belligerents included much of Europe, the Russian Empire, ...
broke out in August 1914, pitting Germany and its allies against France and its allies. The German plan was a quick victory by marching through neutral Belgium to envelop the French Army east of Paris. That failed but the Germans did control nearly all of Belgium for the entire war. Hoover and other London-based American businessmen established a committee to organize the return of the roughly 100,000 Americans stranded in Europe. Hoover was appointed as the committee's chair and, with the assent of Congress and the
Wilson administration
Woodrow Wilson's tenure as the 28th president of the United States lasted from 4 March 1913 until 4 March 1921. He was largely incapacitated the last year and a half. He became president after winning the 1912 election. Wilson was a Democ ...
, took charge of the distribution of relief to Americans in Europe. Hoover later stated, "I did not realize it at the moment, but on August 3, 1914, my career was over forever. I was on the slippery road of public life." By early October 1914, Hoover's organization had distributed relief to at least 40,000 Americans.
The
German invasion of Belgium in August 1914 set off a food crisis in Belgium, which relied heavily on food imports. The Germans refused to take responsibility for feeding Belgian citizens in captured territory, and the British refused to lift their
blockade
A blockade is the act of actively preventing a country or region from receiving or sending out food, supplies, weapons, or communications, and sometimes people, by military force.
A blockade differs from an embargo or sanction, which are leg ...
of
German-occupied Belgium unless the U.S. government-supervised Belgian food imports as a neutral party in the war. With the cooperation of the Wilson administration and the
CNSA, a Belgian relief organization, Hoover established the
Commission for Relief in Belgium
The Commission for Relief in Belgium or C.R.B. − known also as just Belgian Relief − was an international (predominantly American) organization that arranged for the supply of food to German-occupied Belgium and northern France during the Wor ...
(CRB). The CRB obtained and imported millions of tons of foodstuffs for the CNSA to distribute, and helped ensure that the German army did not appropriate the food. Private donations and government grants supplied the majority of its $11-million-a-month budget, and the CRB became a veritable independent republic of relief, with its own flag, navy, factories, mills, and railroads.
Hoover worked 14-hour days from London, administering the distribution of over two million tons of food to nine million war victims. In an early form of
shuttle diplomacy
In diplomacy and international relations, shuttle diplomacy is the action of an outside party in serving as an intermediary between (or among) principals in a dispute, without direct principal-to-principal contact. Originally and usually, the proc ...
, he crossed the
North Sea
The North Sea lies between Great Britain, Norway, Denmark, Germany, the Netherlands and Belgium. An epeiric sea on the European continental shelf, it connects to the Atlantic Ocean through the English Channel in the south and the Norwegian ...
forty times to meet with German authorities and persuade them to allow food shipments.
He also convinced British
Chancellor of the Exchequer
The chancellor of the Exchequer, often abbreviated to chancellor, is a senior minister of the Crown within the Government of the United Kingdom, and head of HM Treasury, His Majesty's Treasury. As one of the four Great Offices of State, the Ch ...
David Lloyd George
David Lloyd George, 1st Earl Lloyd-George of Dwyfor, (17 January 1863 – 26 March 1945) was Prime Minister of the United Kingdom from 1916 to 1922. He was a Liberal Party (United Kingdom), Liberal Party politician from Wales, known for lea ...
to allow individuals to send money to the people of Belgium, thereby lessening workload of the CRB. At the request of the French government, the CRB began delivering supplies to the people of
German-occupied Northern France in 1915. American diplomat
Walter Page
Walter Sylvester Page (February 9, 1900 – December 20, 1957) was an American jazz multi-instrumentalist and bandleader, best known for his groundbreaking work as a double bass player with Walter Page's Blue Devils and the Count Basie Orchestr ...
described Hoover as "probably the only man living who has privately (i.e., without holding office) negotiated understandings with the British, French, German, Dutch, and Belgian governments".
[ vol 40 p 369.]
U.S. Food Administration
War upon Germany was declared in April 1917, and American food was essential to Allied victory. With the U.S. mobilizing for war, President Wilson appointed Hoover to head the
U.S. Food Administration
The United States Food Administration (1917–1920) was an independent Federal agency that controlled the production, distribution and conservation of food in the U.S. during the nation's participation in World War I. It was established to prev ...
, which was charged with ensuring the nation's food needs during the war. Hoover had hoped to join the administration in some capacity since at least 1916, and he obtained the position after lobbying several members of Congress and Wilson's confidant,
Edward M. House. Earning the appellation of "food czar", Hoover recruited a volunteer force of hundreds of thousands of women and deployed
propaganda
Propaganda is communication that is primarily used to influence or persuade an audience to further an agenda, which may not be objective and may be selectively presenting facts to encourage a particular synthesis or perception, or using loaded ...
in movie theaters, schools, and churches. He carefully selected men to assist in the agency leadership—Alonzo Taylor (technical abilities),
Robert Taft (political associations),
Gifford Pinchot
Gifford Pinchot (August 11, 1865October 4, 1946) was an American forester and politician. He served as the fourth chief of the U.S. Division of Forestry, as the first head of the United States Forest Service, and as the 28th governor of Pennsy ...
(agricultural influence), and Julius Barnes (business acumen).
World War I had created a global food crisis that dramatically increased food prices and caused food riots and starvation in the countries at war. Hoover's chief goal as food czar was to provide supplies to the Allied Powers, but he also sought to stabilize domestic prices and to prevent domestic shortages. Under the broad powers granted by the
Food and Fuel Control Act
The Food and Fuel Control Act, , also called the Lever Act or the Lever Food Act was a World War I era US law that among other things created the United States Food Administration and the United States Fuel Administration.
Legislative history
...
, the Food Administration supervised food production throughout the United States, and the administration made use of its authority to buy, import, store, and sell food. Determined to avoid rationing, Hoover established set days for people to avoid eating specified foods and save them for soldiers' rations:
meatless Mondays, wheatless Wednesdays, and "when in doubt, eat
potato
The potato is a starchy food, a tuber of the plant ''Solanum tuberosum'' and is a root vegetable native to the Americas. The plant is a perennial in the nightshade family Solanaceae.
Wild potato species can be found from the southern Uni ...
es". These policies were dubbed "Hooverizing" by government publicists, in spite of Hoover's continual orders that publicity should not mention him by name. The Food Administration shipped 23 million metric tons of food to the Allied Powers, preventing their collapse and earning Hoover great acclaim. As head of the Food Administration, Hoover gained a following in the United States, especially among progressives who saw in Hoover an expert administrator and symbol of efficiency.
Post-war relief in Europe
World War I came to an end in November 1918, but Europe continued to face a critical food situation; Hoover estimated that as many as 400 million people faced the possibility of starvation. The United States Food Administration became the
American Relief Administration
American Relief Administration (ARA) was an American relief mission to Europe and later post-revolutionary Russia after World War I. Herbert Hoover, future president of the United States, was the program director.
The ARA's immediate predeces ...
(ARA), and Hoover was charged with providing food to Central and Eastern Europe. In addition to providing relief, the ARA rebuilt infrastructure in an effort to rejuvenate the economy of Europe. Throughout the
Paris Peace Conference, Hoover served as a close adviser to President Wilson, and he largely shared Wilson's goals of establishing the
League of Nations
The League of Nations (french: link=no, Société des Nations ) was the first worldwide intergovernmental organisation whose principal mission was to maintain world peace. It was founded on 10 January 1920 by the Paris Peace Conference th ...
, settling borders on the basis of
self-determination
The right of a people to self-determination is a cardinal principle in modern international law (commonly regarded as a '' jus cogens'' rule), binding, as such, on the United Nations as authoritative interpretation of the Charter's norms. It sta ...
, and refraining from inflicting a harsh punishment on the defeated Central Powers. The following year, famed British economist
John Maynard Keynes
John Maynard Keynes, 1st Baron Keynes, ( ; 5 June 1883 – 21 April 1946), was an English economist whose ideas fundamentally changed the theory and practice of macroeconomics and the economic policies of governments. Originally trained in ...
wrote in
The Economic Consequences of the Peace
''The Economic Consequences of the Peace'' (1919) is a book written and published by the British economist John Maynard Keynes. After the First World War, Keynes attended the Paris Peace Conference of 1919 as a delegate of the British Treasu ...
that if Hoover's realism, "knowledge, magnanimity and disinterestedness" had found wider play in the councils of Paris, the world would have had "the Good Peace". After U.S. government funding for the ARA expired in mid-1919, Hoover transformed the ARA into a private organization, raising millions of dollars from private donors. He also established the European Children's Fund, which provided relief to fifteen million children across fourteen countries.
Despite the opposition of Senator
Henry Cabot Lodge
Henry Cabot Lodge (May 12, 1850 November 9, 1924) was an American Republican politician, historian, and statesman from Massachusetts. He served in the United States Senate from 1893 to 1924 and is best known for his positions on foreign polic ...
and other Republicans, Hoover provided aid to the defeated German nation after the war, as well as relief to
famine
A famine is a widespread scarcity of food, caused by several factors including war, natural disasters, crop failure, population imbalance, widespread poverty, an economic catastrophe or government policies. This phenomenon is usually accompan ...
-stricken
Russian Soviet Federative Socialist Republic
The Russian Soviet Federative Socialist Republic, Russian SFSR or RSFSR ( rus, Российская Советская Федеративная Социалистическая Республика, Rossíyskaya Sovétskaya Federatívnaya Soci ...
. Hoover condemned the
Bolsheviks
The Bolsheviks (russian: Большевики́, from большинство́ ''bol'shinstvó'', 'majority'),; derived from ''bol'shinstvó'' (большинство́), "majority", literally meaning "one of the majority". also known in English ...
, but warned President Wilson against an
intervention in the
Russian Civil War
{{Infobox military conflict
, conflict = Russian Civil War
, partof = the Russian Revolution and the aftermath of World War I
, image =
, caption = Clockwise from top left:
{{flatlist,
*Soldiers ...
, as he viewed the
White Russian forces as little better than the Bolsheviks and feared the possibility of a protracted U.S. involvement. The
Russian famine of 1921–22
Russian(s) refers to anything related to Russia, including:
* Russians (, ''russkiye''), an ethnic group of the East Slavic peoples, primarily living in Russia and neighboring countries
*Rossiyane (), Russian language term for all citizens and pe ...
claimed six million people, but the intervention of the ARA likely saved millions of lives. When asked if he was not helping Bolshevism by providing relief, Hoover stated, "twenty million people are starving. Whatever their politics, they shall be fed!" Reflecting the gratitude of many Europeans, in July 1922, Soviet author
Maxim Gorky
Alexei Maximovich Peshkov (russian: link=no, Алексе́й Макси́мович Пешко́в; – 18 June 1936), popularly known as Maxim Gorky (russian: Макси́м Го́рький, link=no), was a Russian writer and social ...
told Hoover that "your help will enter history as a unique, gigantic achievement, worthy of the greatest glory, which will long remain in the memory of millions of Russians whom you have saved from death".
In 1919, Hoover established the
Hoover War Collection at Stanford University. He donated all the files of the Commission for Relief in Belgium, the U.S. Food Administration, and the American Relief Administration, and pledged $50,000 as an endowment (). Scholars were sent to Europe to collect pamphlets, society publications, government documents, newspapers, posters, proclamations, and other ephemeral materials related to the war and the revolutions that followed it. The collection was renamed the Hoover War Library in 1922 and is now known as the
Hoover Institution Library and Archives
The Hoover Institution Library and Archives is a research center and archival repository located at Stanford University, near Palo Alto, California in the United States. Built around a collection amassed by Stanford graduate Herbert Hoover prio ...
. During the post-war period, Hoover also served as the president of the Federated American Engineering Societies.
1920 election
Hoover had been little known among the American public before 1914, but his service in the Wilson administration established him as a contender in the 1920 presidential election. Hoover's wartime push for higher taxes, criticism of Attorney General
A. Mitchell Palmer's actions during the
First Red Scare
The First Red Scare was a period during the early 20th-century history of the United States marked by a widespread fear of far-left movements, including Bolshevism and anarchism, due to real and imagined events; real events included the R ...
, and his advocacy for measures such as the
minimum wage
A minimum wage is the lowest remuneration that employers can legally pay their employees—the price floor below which employees may not sell their labor. Most countries had introduced minimum wage legislation by the end of the 20th century. B ...
, forty-eight-hour workweek, and
elimination of child labor made him appealing to progressives of both parties. Despite his service in the
Democratic administration of Woodrow Wilson, Hoover had never been closely affiliated with either the Democrats or the
Republicans. He initially sought to avoid committing to any party in the 1920 election, hoping that either of the two major parties would draft him for president at their national conventions. In March 1920, he changed strategy and declared himself a Republican; he was motivated in large part by the belief that the Democrats had little chance of winning. Despite his national renown, Hoover's service in the Wilson administration had alienated farmers and the
conservative Old Guard of the GOP, and his presidential candidacy fizzled out after his defeat in the California primary by
favorite son
Favorite son (or favorite daughter) is a political term.
* At the quadrennial American national political party conventions, a state delegation sometimes nominates a candidate from the state, or less often from the state's region, who is not a ...
Hiram Johnson
Hiram Warren Johnson (September 2, 1866August 6, 1945) was an American attorney and politician who served as the 23rd governor of California from 1911 to 1917. Johnson achieved national prominence in the early 20th century. He was elected in 191 ...
. At the
1920 Republican National Convention
The 1920 Republican National Convention nominated Ohio Senator Warren G. Harding for president and Massachusetts Governor Calvin Coolidge for vice president. The convention was held in Chicago, Illinois, at the Chicago Coliseum from June 8 to ...
,
Warren G. Harding emerged as a compromise candidate after the convention became deadlocked between supporters of Johnson,
Leonard Wood
Leonard Wood (October 9, 1860 – August 7, 1927) was a United States Army major general, physician, and public official. He served as the Chief of Staff of the United States Army, Military Governor of Cuba, and Governor-General of the Philipp ...
, and
Frank Orren Lowden. Hoover backed Harding's successful campaign in the general election, and he began laying the groundwork for a future presidential run by building a base of strong supporters in the Republican Party.
Secretary of Commerce (1921–1928)

After his election as president in 1920, Harding rewarded Hoover for his support, offering to appoint him as either
Secretary of the Interior Secretary of the Interior may refer to:
* Secretary of the Interior (Mexico)
* Interior Secretary of Pakistan
* Secretary of the Interior and Local Government (Philippines)
* United States Secretary of the Interior
See also
*Interior ministry
An ...
or
Secretary of Commerce
The United States secretary of commerce (SecCom) is the head of the United States Department of Commerce. The secretary serves as the principal advisor to the president of the United States on all matters relating to commerce. The secretary rep ...
. Secretary of Commerce was considered a minor Cabinet post, with limited and vaguely defined responsibilities, but Hoover decided to accept the position. Hoover's progressive stances, continuing support for the
League of Nations
The League of Nations (french: link=no, Société des Nations ) was the first worldwide intergovernmental organisation whose principal mission was to maintain world peace. It was founded on 10 January 1920 by the Paris Peace Conference th ...
, and recent conversion to the Republican Party aroused opposition to his appointment from many
Senate Republicans. To overcome this opposition, Harding paired Hoover's nomination with that of conservative favorite
Andrew Mellon
Andrew William Mellon (; March 24, 1855 – August 26, 1937), sometimes A. W. Mellon, was an American banker, businessman, industrialist, philanthropist, art collector, and politician. From the wealthy Mellon family of Pittsburgh, Pennsylv ...
as
Secretary of the Treasury
The United States secretary of the treasury is the head of the United States Department of the Treasury, and is the chief financial officer of the federal government of the United States. The secretary of the treasury serves as the principal a ...
, and the nominations of both Hoover and Mellon were confirmed by the Senate. Hoover would serve as Secretary of Commerce from 1921 to 1929, serving under Harding and, after Harding's death in 1923, President
Calvin Coolidge
Calvin Coolidge (born John Calvin Coolidge Jr.; ; July 4, 1872January 5, 1933) was the 30th president of the United States from 1923 to 1929. Born in Vermont, Coolidge was a Republican lawyer from New England who climbed up the ladder of Ma ...
. While some of the most prominent members of the Harding administration, including Attorney General
Harry M. Daugherty
Harry Micajah Daugherty (; January 26, 1860 – October 12, 1941) was an American politician. A key Ohio Republican political insider, he is best remembered for his service as Attorney General of the United States under Presidents Warren G. Hard ...
and Secretary of Interior
Albert B. Fall, were implicated in
major scandals, Hoover emerged largely unscathed from investigations into the Harding administration.
Hoover envisioned the Commerce Department as the hub of the nation's growth and stability. His experience mobilizing the war-time economy convinced him that the federal government could promote efficiency by eliminating waste, increasing production, encouraging the adoption of data-based practices, investing in infrastructure, and conserving natural resources. Contemporaries described Hoover's approach as a "third alternative" between "unrestrained capitalism" and
socialism
Socialism is a left-wing economic philosophy and movement encompassing a range of economic systems characterized by the dominance of social ownership of the means of production as opposed to private ownership. As a term, it describes th ...
, which was becoming increasingly popular in Europe. Hoover sought to foster a balance among labor, capital, and the government, and for this, he has been variously labeled a
corporatist
Corporatism is a collectivist political ideology which advocates the organization of society by corporate groups, such as agricultural, labour, military, business, scientific, or guild associations, on the basis of their common interests. The ...
or an
associationalist. A high priority was economic diplomacy, including promoting the growth of exports, as well as protection against monopolistic practices of foreign governments, especially regarding rubber and coffee.
Hoover demanded and received, authority to coordinate economic affairs throughout the government. He created many sub-departments and committees, overseeing and regulating everything from manufacturing statistics to
air travel. In some instances he "seized" control of responsibilities from other Cabinet departments when he deemed that they were not carrying out their responsibilities well; some began referring to him as the "Secretary of Commerce and Under-Secretary of all other departments". In response to the
Depression of 1920–21
Depression may refer to:
Mental health
* Depression (mood), a state of low mood and aversion to activity
* Mood disorders characterized by depression are commonly referred to as simply ''depression'', including:
** Dysthymia, also known as pe ...
, he convinced Harding to assemble a presidential commission on unemployment, which encouraged local governments to engage in countercyclical infrastructure spending. He endorsed much of Mellon's tax reduction program, but favored a more
progressive tax
A progressive tax is a tax in which the tax rate increases as the taxable amount increases.Sommerfeld, Ray M., Silvia A. Madeo, Kenneth E. Anderson, Betty R. Jackson (1992), ''Concepts of Taxation'', Dryden Press: Fort Worth, TX The term ''progre ...
system and opposed the treasury secretary's efforts to eliminate the
estate tax
An inheritance tax is a tax paid by a person who inherits money or property of a person who has died, whereas an estate tax is a levy on the estate (money and property) of a person who has died.
International tax law distinguishes between an ...
.
Radio regulation and air travel

Between 1923 and 1929, the number of families with radios grew from 300,000 to 10 million, and Hoover's tenure as Secretary of Commerce heavily influenced radio use in the United States. In the early and mid-1920s, Hoover's radio conferences played a key role in the organization, development, and regulation of
radio broadcasting
Radio broadcasting is transmission of audio (sound), sometimes with related metadata, by radio waves to radio receivers belonging to a public audience. In terrestrial radio broadcasting the radio waves are broadcast by a land-based radio ...
. Hoover also helped pass the
Radio Act of 1927, which allowed the government to intervene and abolish
radio stations
Radio broadcasting is transmission of audio (sound), sometimes with related metadata, by radio waves to radio receivers belonging to a public audience. In terrestrial radio broadcasting the radio waves are broadcast by a land-based radio sta ...
that were deemed "non-useful" to the public. Hoover's attempts at regulating radio were not supported by all congressmen, and he received much opposition from the Senate and from radio station owners.
Hoover was also influential in the early development of air travel, and he sought to create a thriving private industry boosted by indirect government subsidies. He encouraged the development of emergency landing fields, required all runways to be equipped with lights and radio beams, and encouraged farmers to make use of planes for
crop dusting. He also established the federal government's power to inspect planes and license pilots, setting a precedent for the later
Federal Aviation Administration
The Federal Aviation Administration (FAA) is the largest transportation agency of the U.S. government and regulates all aspects of civil aviation in the country as well as over surrounding international waters. Its powers include air traffic ...
.
As Commerce Secretary, Hoover hosted national conferences on street traffic collectively known as the National Conference on Street and Highway Safety. Hoover's chief objective was to address the growing casualty toll of
traffic accidents, but the scope of the conferences grew and soon embraced motor vehicle standards, rules of the road, and urban traffic control. He left the invited interest groups to negotiate agreements among themselves, which were then presented for adoption by states and localities. Because automotive trade associations were the best organized, many of the positions taken by the conferences reflected their interests. The conferences issued a model Uniform Vehicle Code for adoption by the states and a Model Municipal Traffic Ordinance for adoption by cities. Both were widely influential, promoting greater uniformity between jurisdictions and tending to promote the automobile's priority in city streets.
Hoover's image building
Phillips Payson O'Brien argues that Hoover had a Britain problem. He had spent so many years living in Britain and Australia, as an employee of British companies, there was a risk that he would be labeled a British tool. There were three solutions, all of which he tried in close collaboration with the media, which greatly admired him. First came the image of the dispassionate scientist, emotionally uninvolved but always committed to finding and implementing the best possible solution. The second solution was to gain the reputation of a humanitarian, deeply concerned with the world's troubles, such as famine in Belgium, as well as specific American problems which he had solved as food commissioner during the world war. The third solution to was to fall back on that old tactic of twisting the British tail. He employed that solution in 1925–1926 in the worldwide rubber crisis. The
American auto industry consumed 70% of the world's output, but British investors controlled much of the supply. Their plan was to drastically cut back on output from
British Malaya
The term "British Malaya" (; ms, Tanah Melayu British) loosely describes a set of states on the Malay Peninsula and the island of Singapore that were brought under British hegemony or control between the late 18th and the mid-20th century. ...
, which had the effect of tripling rubber prices. Hoover energetically gave a series of speeches and interviews denouncing the
monopolistic practice, and demanding that it be ended. The American State Department wanted no such crisis and compromised the issue in 1926. By then Hoover had solved his image problem, and during his 1928 campaign he successfully squelched attacks that alleged he was too close to British interests.
Other initiatives

With the goal of encouraging wise business investments, Hoover made the Commerce Department a clearinghouse of information. He recruited numerous academics from various fields and tasked them with publishing reports on different aspects of the economy, including
steel production and films. To eliminate waste, he encouraged
standardization
Standardization or standardisation is the process of implementing and developing technical standards based on the consensus of different parties that include firms, users, interest groups, standards organizations and governments. Standardizatio ...
of products like
automobile tires and baby bottle nipples. Other efforts at eliminating waste included reducing labor losses from trade disputes and seasonal fluctuations, reducing industrial losses from accident and injury, and reducing the amount of
crude oil
Petroleum, also known as crude oil, or simply oil, is a naturally occurring yellowish-black liquid mixture of mainly hydrocarbons, and is found in geological formations. The name ''petroleum'' covers both naturally occurring unprocessed crude ...
spilled during extraction and shipping. He promoted international trade by opening overseas offices to advise businessmen. Hoover was especially eager to promote Hollywood films overseas. His "Own Your Own Home" campaign was a collaboration to promote ownership of single-family dwellings, with groups such as the Better Houses in America movement, the Architects' Small House Service Bureau, and the Home Modernizing Bureau. He worked with bankers and the
savings and loan
Wealth is the abundance of valuable financial assets or physical possessions which can be converted into a form that can be used for transactions. This includes the core meaning as held in the originating Old English word , which is from an ...
industry to promote the new long-term home mortgage, which dramatically stimulated home construction. Other accomplishments included winning the agreement of
U.S. Steel to adopt an eight-hour workday, and the fostering of the
Colorado River Compact, a
water rights compact among
Southwestern states.
Mississippi flood
The
Great Mississippi Flood of 1927 broke the banks and
levee
A levee (), dike (American English), dyke (Commonwealth English), embankment, floodbank, or stop bank is a structure that is usually earthen and that often runs parallel to the course of a river in its floodplain or along low-lying coastli ...
s of the
lower Mississippi River
The Lower Mississippi River is the portion of the Mississippi River downstream of Cairo, Illinois. From the confluence of the Ohio River and Upper Mississippi River at Cairo, the Lower flows just under 1000 miles (1600 km) to the Gulf of ...
in early 1927, resulting in the flooding of millions of acres and leaving 1.5 million people displaced from their homes. Although disaster response did not fall under the duties of the
Commerce Department, the governors of six states along the Mississippi River specifically asked President Coolidge to appoint Hoover to coordinate the response to the flood. Believing that disaster response was not the domain of the federal government, Coolidge initially refused to become involved, but he eventually acceded to political pressure and appointed Hoover to chair a special committee to help the region. Hoover established over one hundred
tent cities
A tent city is a temporary housing facility made using tents or other temporary structures.
State governments or military organizations set up tent cities to house evacuees, refugees, or soldiers. UNICEF's Supply Division supplies expandable te ...
and a fleet of more than six hundred vessels, and raised $17 million (equivalent to $ million in ). In large part due to his leadership during the flood crisis, by 1928, Hoover had begun to overshadow President Coolidge himself. Though Hoover received wide acclaim for his role in the crisis, he ordered the suppression of reports of mistreatment of
African Americans
African Americans (also referred to as Black Americans and Afro-Americans) are an ethnic group consisting of Americans with partial or total ancestry from sub-Saharan Africa. The term "African American" generally denotes descendants of ens ...
in
refugee camp
A refugee camp is a temporary settlement built to receive refugees and people in refugee-like situations. Refugee camps usually accommodate displaced people who have fled their home country, but camps are also made for internally displaced peo ...
s. He did so with the cooperation of African-American leader
Robert Russa Moton
Robert Russa Moton (August 26, 1867 – May 31, 1940) was an American educator and author. He served as an administrator at Hampton Institute. In 1915 he was named principal of Tuskegee Institute, after the death of founder Booker T. Washington, ...
, who was promised unprecedented influence once Hoover became president.
['Robert Moton and the Colored Advisory Commission'](_blank)
PBS.org
Presidential election of 1928
Hoover quietly built up support for a future presidential bid throughout the 1920s, but he carefully avoided alienating Coolidge, who possibly could have run for another term in the
1928 presidential election. Along with the rest of the nation, he was surprised when Coolidge announced in August 1927 that he would not seek another term. With the impending retirement of Coolidge, Hoover immediately emerged as the front-runner for the 1928 Republican nomination, and he quickly put together a strong campaign team led by
Hubert Work
Hubert Work (July 3, 1860December 14, 1942) was a U.S. administrator and physician. He served as the United States Postmaster General from 1922 until 1923 during the presidency of Warren G. Harding. He served as the United States Secretary of th ...
,
Will H. Hays
William Harrison Hays Sr. (; November 5, 1879 – March 7, 1954) was an American Republican politician.
As chairman of the Republican National Committee from 1918–1921, Hays managed the successful 1920 presidential campaign of Warren G. H ...
, and
Reed Smoot
Reed Smoot (January 10, 1862February 9, 1941) was an American politician, businessman, and apostle of the Church of Jesus Christ of Latter-day Saints (LDS Church). First elected by the Utah State Legislature to the U.S. Senate in 1902, he serv ...
. Coolidge was unwilling to anoint Hoover as his successor; on one occasion he remarked that, "for six years that man has given me unsolicited advice—all of it bad". Despite his lukewarm feelings towards Hoover, Coolidge had no desire to split the party by publicly opposing the popular Commerce Secretary's candidacy.
Many wary Republican leaders cast about for an alternative candidate, such as Treasury Secretary Andrew Mellon or former secretary of state
Charles Evans Hughes
Charles Evans Hughes Sr. (April 11, 1862 – August 27, 1948) was an American statesman, politician and jurist who served as the 11th Chief Justice of the United States from 1930 to 1941. A member of the Republican Party, he previously was the ...
.
However, Hughes and Mellon declined to run, and other potential contenders like
Frank Orren Lowden and Vice President
Charles G. Dawes
Charles Gates Dawes (August 27, 1865 – April 23, 1951) was an American banker, general, diplomat, composer, and Republican politician who was the 30th vice president of the United States from 1925 to 1929 under Calvin Coolidge. He was a co-rec ...
failed to garner widespread support. Hoover won the presidential nomination on the first ballot of the
1928 Republican National Convention
The 1928 Republican National Convention was held at Convention Hall in Kansas City, Missouri, from June 12 to June 15, 1928.
Because President Coolidge had announced unexpectedly he would not run for re-election in 1928, Commerce Secretary H ...
. Convention delegates considered re-nominating Vice President Charles Dawes to be Hoover's
running mate
A running mate is a person running together with another person on a joint ticket during an election. The term is most often used in reference to the person in the subordinate position (such as the vice presidential candidate running with a p ...
, but Coolidge, who hated Dawes, remarked that this would be "a personal affront" to him. The convention instead selected
Senator
A senate is a deliberative assembly, often the upper house or chamber of a bicameral legislature. The name comes from the ancient Roman Senate (Latin: ''Senatus''), so-called as an assembly of the senior (Latin: ''senex'' meaning "the el ...
Charles Curtis
Charles Curtis (January 25, 1860 – February 8, 1936) was an American attorney and Republican politician from Kansas who served as the 31st vice president of the United States from 1929 to 1933 under Herbert Hoover. He had served as the Sena ...
of Kansas. Hoover accepted the nomination at
Stanford Stadium
Stanford Stadium is an outdoor college football stadium on the west coast of the United States, located on the campus of Stanford University in Stanford, California. It is the home of the Stanford Cardinal and hosts the university's commencemen ...
, telling a huge crowd that he would continue the policies of the Harding and Coolidge administrations. The Democrats nominated New York governor
Al Smith
Alfred Emanuel Smith (December 30, 1873 – October 4, 1944) was an American politician who served four terms as Governor of New York and was the Democratic Party's candidate for president in 1928.
The son of an Irish-American mother and a Ci ...
, who became the first
Catholic
The Catholic Church, also known as the Roman Catholic Church, is the largest Christian church, with 1.3 billion baptized Catholics worldwide . It is among the world's oldest and largest international institutions, and has played a ...
major party nominee for president.

Hoover centered his campaign around the Republican record of peace and prosperity, as well as his own reputation as a successful engineer and public official. Averse to giving political speeches, Hoover largely stayed out of the fray and left the campaigning to Curtis and other Republicans. Smith was more charismatic and gregarious than Hoover, but his campaign was damaged by
anti-Catholicism
Anti-Catholicism is hostility towards Catholics or opposition to the Catholic Church, its clergy, and/or its adherents. At various points after the Reformation, some majority Protestant states, including England, Prussia, Scotland, and the Uni ...
and his overt opposition to Prohibition. Hoover had never been a strong proponent of Prohibition, but he accepted the Republican Party's plank in favor of it and issued an ambivalent statement calling Prohibition "a great social and economic experiment, noble in motive and far-reaching in purpose". In the South, Hoover and the national party pursued a "
lily-white" strategy, removing black Republicans from leadership positions in an attempt to curry favor with white Southerners.
Hoover maintained polling leads throughout the 1928 campaign, and he decisively defeated Smith on election day, taking 58 percent of the popular vote and 444 of the 531 electoral votes. Historians agree that Hoover's national reputation and the booming economy, combined with deep splits in the Democratic Party over religion and Prohibition, guaranteed his landslide victory. Hoover's appeal to Southern white voters succeeded in cracking the "
Solid South
The Solid South or Southern bloc was the electoral voting bloc of the states of the Southern United States for issues that were regarded as particularly important to the interests of Democrats in those states. The Southern bloc existed especial ...
", and he won five Southern states. Hoover's victory was positively received by newspapers; one wrote that Hoover would "drive so forcefully at the tasks now before the nation that the end of his eight years as president will find us looking back on an era of prodigious achievement".
Hoover's detractors wondered why he did not do anything to
reapportion congress after the
1920 United States Census which saw an increase in urban and immigrant populations. The 1920 Census was the first and only Decennial Census where the results were not used to reapportion Congress, which ultimately influenced the 1928 Electoral College and impacted the Presidential Election.
Presidency (1929–1933)

Hoover saw the presidency as a vehicle for improving the conditions of all Americans by encouraging public-private cooperation—what he termed "volunteerism". He tended to oppose governmental coercion or intervention, as he thought they infringed on American ideals of individualism and self-reliance.
The first major bill that he signed, the
Agricultural Marketing Act of 1929
The Agricultural Marketing Act of 1929, under the administration of Herbert Hoover, established the Federal Farm Board from the Federal Farm Loan Board established by the Federal Farm Loan Act of 1916 with a revolving fund of half a billion dolla ...
, established the
Federal Farm Board in order to stabilize farm prices. Hoover made extensive use of commissions to study issues and propose solutions, and many of those commissions were sponsored by private donors rather than by the government. One of the commissions started by Hoover, the Research Committee on Social Trends, was tasked with surveying the entirety of American society. He appointed a Cabinet consisting largely of wealthy, business-oriented conservatives, including Secretary of the Treasury Andrew Mellon. Lou Henry Hoover was an activist First Lady. She typified the
new woman
The New Woman was a feminist ideal that emerged in the late 19th century and had a profound influence well into the 20th century. In 1894, Irish writer Sarah Grand (1854–1943) used the term "new woman" in an influential article, to refer to ...
of the
post–World War I era: intelligent, robust, and aware of multiple female possibilities.
Great Depression

On taking office, Hoover said that "given the chance to go forward with the policies of the last eight years, we shall soon with the help of God, be in sight of the day when poverty will be banished from this nation". Having seen the fruits of prosperity brought by technological progress, many shared Hoover's optimism, and the already bullish stock market climbed even higher on Hoover's accession. This optimism concealed several threats to sustained U.S. economic growth, including a persistent
farm crisis
A farm crisis describes times of agricultural recession, low crop prices and low farm incomes. The most recent US farm crisis occurred during the 1980s.
Crisis of the 1920s and 1930s
A farm crisis began in the 1920s, commonly believed to be ...
, a saturation of
consumer goods
A final good or consumer good is a final product ready for sale that is used by the consumer to satisfy current wants or needs, unlike a intermediate good, which is used to produce other goods. A microwave oven or a bicycle is a final good, b ...
like
automobiles
A car or automobile is a motor vehicle with wheels. Most definitions of ''cars'' say that they run primarily on roads, seat one to eight people, have four wheels, and mainly transport people instead of goods.
The year 1886 is regarded ...
, and growing
income inequality
There are wide varieties of economic inequality, most notably income inequality measured using the distribution of income (the amount of money people are paid) and wealth inequality measured using the distribution of wealth (the amount of we ...
. Most dangerous of all to the economy was excessive
speculation
In finance, speculation is the purchase of an asset (a commodity, goods, or real estate) with the hope that it will become more valuable shortly. (It can also refer to short sales in which the speculator hopes for a decline in value.)
Many ...
that had raised
stock prices far beyond their value. Some regulators and bankers had warned Coolidge and Hoover that a failure to curb speculation would lead to "one of the greatest financial catastrophes that this country has ever seen," but both presidents were reluctant to become involved with the workings of the
Federal Reserve System
The Federal Reserve System (often shortened to the Federal Reserve, or simply the Fed) is the central banking system of the United States of America. It was created on December 23, 1913, with the enactment of the Federal Reserve Act, after ...
, which regulated banks.
In late October 1929, the
Stock Market Crash of 1929
The Wall Street Crash of 1929, also known as the Great Crash, was a major American stock market crash that occurred in the autumn of 1929. It started in September and ended late in October, when share prices on the New York Stock Exchange colla ...
occurred, and the worldwide economy began to spiral downward into the
Great Depression
The Great Depression (19291939) was an economic shock that impacted most countries across the world. It was a period of economic depression that became evident after a major fall in stock prices in the United States. The economic contagio ...
. The
causes of the Great Depression
The causes of the Great Depression in the early 20th century in the United States have been extensively discussed by economists and remain a matter of active debate. They are part of the larger debate about economic crises and recessions. The sp ...
remain a matter of debate, but Hoover viewed a lack of confidence in the financial system as the fundamental economic problem facing the nation. He sought to avoid direct federal intervention, believing that the best way to bolster the economy was through the strengthening of businesses such as banks and railroads. He also feared that allowing individuals on the "
dole" would permanently weaken the country. Instead, Hoover strongly believed that local governments and private giving should address the needs of individuals.
Early policies

Though he attempted to put a positive spin on
Black Tuesday
The Wall Street Crash of 1929, also known as the Great Crash, was a major American stock market crash that occurred in the autumn of 1929. It started in September and ended late in October, when share prices on the New York Stock Exchange coll ...
, Hoover moved quickly to address the
stock market collapse. In the days following Black Tuesday, Hoover gathered business and labor leaders, asking them to avoid wage cuts and work stoppages while the country faced what he believed would be a short recession similar to the Depression of 1920–21. Hoover also convinced railroads and public utilities to increase spending on construction and maintenance, and the
Federal Reserve
The Federal Reserve System (often shortened to the Federal Reserve, or simply the Fed) is the central banking system of the United States of America. It was created on December 23, 1913, with the enactment of the Federal Reserve Act, after a ...
announced that it would cut
interest rate
An interest rate is the amount of interest due per period, as a proportion of the amount lent, deposited, or borrowed (called the principal sum). The total interest on an amount lent or borrowed depends on the principal sum, the interest rate, t ...
s. In early 1930, Hoover acquired from Congress an additional $100 million to continue the
Federal Farm Board lending and purchasing policies. These actions were collectively designed to prevent a cycle of
deflation
In economics, deflation is a decrease in the general price level of goods and services. Deflation occurs when the inflation rate falls below 0% (a negative inflation rate). Inflation reduces the value of currency over time, but sudden deflatio ...
and provide a
fiscal stimulus
In economics, stimulus refers to attempts to use monetary policy or fiscal policy (or stabilization policy in general) to stimulate the economy. Stimulus can also refer to monetary policies such as lowering interest rates and quantitative easin ...
. At the same time, Hoover opposed congressional proposals to provide federal relief to the unemployed, as he believed that such programs were the responsibility of state and local governments and philanthropic organizations.
Hoover had taken office hoping to raise agricultural tariffs in order to help farmers reeling from the farm crisis of the 1920s, but his attempt to raise agricultural tariffs became connected with a bill that broadly raised tariffs. Hoover refused to become closely involved in the congressional debate over the tariff, and Congress produced a tariff bill that raised rates for many goods. Despite the widespread unpopularity of the bill, Hoover felt that he could not reject the main legislative accomplishment of the Republican-controlled
71st Congress. Over the objection of many economists, Hoover signed the
Smoot–Hawley Tariff Act
The Tariff Act of 1930 (codified at ), commonly known as the Smoot–Hawley Tariff or Hawley–Smoot Tariff, was a law that implemented protectionist trade policies in the United States. Sponsored by Senator Reed Smoot and Representative Willi ...
into law in June 1930. Canada, France, and other nations retaliated by raising tariffs, resulting in a contraction of international trade and a worsening of the economy. Progressive Republicans such as Senator William E. Borah of Idaho were outraged when Hoover signed the tariff act, and Hoover's relations with that wing of the party never recovered.
Later policies

By the end of 1930, the Unemployment in the United States, national unemployment rate had reached 11.9 percent, but it was not yet clear to most Americans that the economic downturn would be worse than the Depression of 1920–1921, Depression of 1920–21. A series of bank failures in late 1930 heralded a larger Economic collapse, collapse of the economy in 1931. While other countries left the gold standard, Hoover refused to abandon it; he derided any other monetary system as "Collectivism and individualism, collectivism". Hoover viewed the weak Economy of Europe, European economy as a major cause of economic troubles in the United States. In response to the collapse of the Economy of Germany, German economy, Hoover marshaled congressional support behind a one-year moratorium on European war debts. The Hoover Moratorium was warmly received in Europe and the United States, but Germany remained on the brink of Default (finance), defaulting on its loans. As the worldwide economy worsened, democratic governments fell; in Germany, Nazi Party leader Adolf Hitler assumed power and dismantled the Weimar Republic.
By mid-1931, the unemployment rate had reached 15 percent, giving rise to growing fears that the country was experiencing a depression far worse than recent economic downturns. A reserved man with a fear of public speaking, Hoover allowed his opponents in the Democratic Party to define him as cold, incompetent, reactionary, and out-of-touch. Hoover's opponents developed defamatory epithets to discredit him, such as "Hooverville" (the shanty towns and homeless encampments), "Hoover leather" (cardboard used to cover holes in the soles of shoes), and "Hoover blanket" (old newspaper used to cover oneself from the cold). While Hoover continued to resist direct federal relief efforts, Governor
Franklin D. Roosevelt of New York launched the Federal Emergency Relief Administration, Temporary Emergency Relief Administration to provide aid to the unemployed. Democrats positioned the program as a kinder alternative to Hoover's alleged apathy towards the unemployed, despite Hoover's belief that such programs were the responsibility of state and local governments.
The economy continued to worsen, with unemployment rates nearing 23 percent in early 1932, and Hoover finally heeded calls for more direct federal intervention. In January 1932, he convinced Congress to authorize the establishment of the Reconstruction Finance Corporation (RFC), which would provide government-secured loans to financial institutions, railroads, and local governments. The RFC saved numerous businesses from failure, but it failed to stimulate commercial lending as much as Hoover had hoped, partly because it was run by conservative bankers unwilling to make riskier loans. The same month the RFC was established, Hoover signed the Federal Home Loan Bank Act, establishing 12 district banks overseen by a Federal Home Loan Bank Board in a manner similar to the Federal Reserve System. He also helped arrange passage of the Glass–Steagall Act of 1932, emergency banking legislation designed to expand banking credit by expanding the collateral on which Federal Reserve banks were authorized to lend. As these measures failed to stem the economic crisis, Hoover signed the Emergency Relief and Construction Act, a $2 billion public works bill, in July 1932.
Budget policy
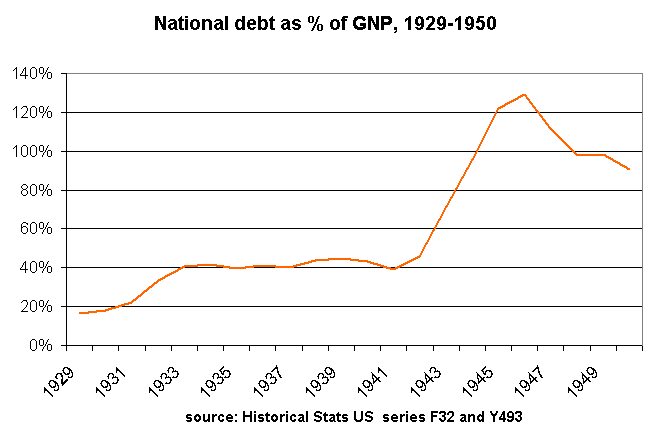
After a decade of budget surpluses, the federal government experienced a Budget deficits, budget deficit in 1931. Though some economists, like William Trufant Foster, favored deficit spending to address the Great Depression, most politicians and economists believed in the necessity of keeping a balanced budget. In late 1931, Hoover proposed a tax plan to increase tax revenue by 30 percent, resulting in the passage of the Revenue Act of 1932. The act increased taxes across the board, rolling back much of the tax cut reduction program Mellon had presided over during the 1920s. Top earners were taxed at 63 percent on their net income, the highest rate since the early 1920s. The act also doubled the top Estate tax in the United States, estate tax rate, cut Income tax in the United States, personal income tax exemptions, eliminated the Corporate tax in the United States, corporate income tax exemption, and raised corporate tax rates. Despite the passage of the Revenue Act, the federal government continued to run a budget deficit.
Civil rights and Mexican Repatriation

Hoover seldom mentioned Civil rights movement (1896–1954), civil rights while he was president. He believed that
African Americans
African Americans (also referred to as Black Americans and Afro-Americans) are an ethnic group consisting of Americans with partial or total ancestry from sub-Saharan Africa. The term "African American" generally denotes descendants of ens ...
and other races could improve themselves with education and individual initiative. Hoover appointed more African Americans to federal positions than Harding and Coolidge combined, but many African-American leaders condemned various aspects of the Hoover administration, including Hoover's unwillingness to push for a federal Anti-lynching movement, anti-lynching law. Hoover also continued to pursue the lily-white strategy, removing African Americans from positions of leadership in the Republican Party in an attempt to end the Democratic Party's Solid South, dominance in the South. Though Robert Russa Moton, Robert Moton and some other black leaders accepted the lily-white strategy as a temporary measure, most African-American leaders were outraged. Hoover further alienated black leaders by nominating conservative Southern judge John J. Parker to the Supreme Court of the United States, Supreme Court; Parker's nomination ultimately failed in the Senate due to opposition from the NAACP and organized labor. Many black voters switched to the Democratic Party in the 1932 election, and African Americans would later become an important part of Franklin Roosevelt's New Deal coalition.
As part of his efforts to limit unemployment, Hoover sought to cut immigration to the United States, and in 1930 he promulgated an executive order requiring individuals to have employment before migrating to the United States. The Hoover Administration began a campaign to prosecute Illegal immigration to the United States, illegal immigrants in the United States, which most strongly affected
Mexicans
Mexicans ( es, mexicanos) are the citizens of the United Mexican States.
The most spoken language by Mexicans is Spanish, but some may also speak languages from 68 different Indigenous linguistic groups and other languages brought to Mexi ...
, especially those living in Southern California. During the 1930s, between 355,000 and one million Mexicans and Mexican Americans were repatriated or deported to Mexico; an estimated forty to sixty percent of whom were Birthright citizenship in the United States, birthright citizens - overwhelmingly children.
Some scholars contend that the unprecedented number of repatriations between 1929 and 1933 were part of an “explicit Hoover administration policy".
While supported and encouraged by the federal government, most deportations and repatriations were organized by local and state governments, often with support from local private entities. Voluntary repatriation was far more common than formal deportation, with 34,000 people deported to Mexico by the federal government between 1930 and 1933.
According to legal professor Kevin R. Johnson, the repatriation campaigns were a form of ethnic cleansing against an ethnic minority.
He reorganized the Bureau of Indian Affairs to limit exploitation of Native Americans.
Prohibition
On taking office, Hoover urged Americans to obey the Eighteenth Amendment to the United States Constitution, Eighteenth Amendment and the Volstead Act, which had established Prohibition in the United States, Prohibition across the United States. To make public policy recommendations regarding Prohibition, he created the Wickersham Commission. Hoover had hoped that the commission's public report would buttress his stance in favor of Prohibition, but the report criticized the enforcement of the Volstead Act and noted the growing public opposition to Prohibition. After the Wickersham Report was published in 1931, Hoover rejected the advice of some of his closest allies and refused to endorse any revision of the Volstead Act or the Eighteenth Amendment, as he feared doing so would undermine his support among Prohibition advocates. As public opinion increasingly turned against Prohibition, more and more people flouted the law, and a grassroots movement began working in earnest for Prohibition's repeal. In January 1933, a constitutional amendment repealing the Eighteenth Amendment was approved by Congress and submitted to the states for ratification. By December 1933, it had been ratified by the requisite number of states to become the Twenty-first Amendment to the United States Constitution, Twenty-first Amendment.
Foreign relations
According to Leuchtenburg, Hoover was "the last American president to take office with no conspicuous need to pay attention to the rest of the world". Nevertheless, during Hoover's term, the world order established in the immediate aftermath of World War I began to crumble. As president, Hoover largely made good on his pledge made prior to assuming office not to interfere in Latin America's internal affairs. In 1930, he released the Clark Memorandum, a rejection of the Roosevelt Corollary and a move towards non-interventionism in Latin America. Hoover did not completely refrain from the use of the military in Latin America–United States relations, Latin American affairs; he thrice threatened intervention in the Dominican Republic, and he sent warships to El Salvador to support the government against a left-wing revolution. Notwithstanding those actions, he wound down the Banana Wars, ending the United States occupation of Nicaragua, occupation of Nicaragua and nearly bringing an end to the United States occupation of Haiti, occupation of Haiti.
Hoover placed a priority on disarmament, which he hoped would allow the United States to shift money from the military to domestic needs. Hoover and Secretary of State Henry L. Stimson focused on extending the 1922 Washington Naval Treaty, which sought to prevent a naval arms race. As a result of Hoover's efforts, the United States and other major naval powers signed the 1930 London Naval Treaty. The treaty represented the first time that the naval powers had agreed to cap their tonnage of Auxiliary ship, auxiliary vessels, as previous agreements had only affected capital ships.
At the 1932 World Disarmament Conference, Hoover urged further cutbacks in armaments and the outlawing of tanks and bombers, but his proposals were not adopted.
In 1931, Japan Japanese invasion of Manchuria, invaded Manchuria, defeating the Republic of China (1912–1949), Republic of China's National Revolutionary Army and establishing Manchukuo, a puppet state. The Hoover administration deplored the invasion, but also sought to avoid antagonizing the Japanese, fearing that taking too strong a stand would weaken the moderate forces in the Japanese government and alienate a potential ally against the Soviet Union, which he saw as a much greater threat. In response to the Japanese invasion, Hoover and Secretary of State Stimson outlined the Stimson Doctrine, which held that the United States would not recognize territories gained by force.
Bonus Army
Thousands of World War I veterans and their families demonstrated and camped out in Washington, DC, during June 1932, calling for immediate payment of bonuses that had been promised by the World War Adjusted Compensation Act in 1924; the terms of the act called for payment of the bonuses in 1945. Although offered money by Congress of the United States, Congress to return home, some members of the "Bonus Army" remained. Washington police attempted to disperse the demonstrators, but they were outnumbered and unsuccessful. Shots were fired by the police in a futile attempt to attain order, and two protesters were killed while many officers were injured. Hoover sent U.S. Army forces led by General Douglas MacArthur to the protests. MacArthur, believing he was fighting a Communist revolution, chose to clear out the camp with military force. Though Hoover had not ordered MacArthur's clearing out of the protesters, he endorsed it after the fact. The incident proved embarrassing for the Hoover administration and hurt his bid for re-election.
1932 re-election campaign

By mid-1931 few observers thought that Hoover had much hope of winning a second term in the midst of the ongoing economic crisis. The Republican expectations were so bleak that Hoover faced no serious opposition for re-nomination at the 1932 Republican National Convention. Coolidge and other prominent Republicans all passed on the opportunity to challenge Hoover. Franklin D. Roosevelt won the presidential nomination on the fourth ballot of the 1932 Democratic National Convention, defeating the 1928 Democratic nominee, Al Smith. The Democrats attacked Hoover as the cause of the Great Depression, and for being indifferent to the suffering of millions. As Governor of New York, Roosevelt had called on the New York legislature to provide aid for the needy, establishing Roosevelt's reputation for being more favorable toward government interventionism during the economic crisis. The Democratic Party, including Al Smith and other national leaders, coalesced behind Roosevelt, while progressive Republicans like George Norris and Robert M. La Follette Jr., Robert La Follette Jr. deserted Hoover. Prohibition was increasingly unpopular and wets offered the argument that states and localities needed the tax money. Hoover proposed a new constitutional amendment that was vague on particulars. Roosevelt's platform promised repeal of the 18th Amendment.

Hoover originally planned to make only one or two major speeches and to leave the rest of the campaigning to proxies, as sitting presidents had traditionally done. However, encouraged by Republican pleas and outraged by Democratic claims, Hoover entered the public fray. In his nine major radio addresses Hoover primarily defended his administration and his Political philosophy, philosophy of government, urging voters to hold to the "foundations of experience" and reject the notion that government interventionism could save the country from the Depression. In his campaign trips around the country, Hoover was faced with perhaps the most hostile crowds ever seen by a sitting president. Besides having his train and motorcades pelted with eggs and rotten fruit, he was often heckled while speaking, and on several occasions, the United States Secret Service, Secret Service halted attempts to hurt Hoover, including capturing one man nearing Hoover carrying sticks of dynamite, and another already having removed several spikes from the rails in front of the president's train.
Hoover's attempts to vindicate his administration fell on deaf ears, as much of the public blamed his administration for the depression. In the electoral vote, Hoover lost 59–472, carrying six states. Hoover won 39.7 percent of the popular vote, a plunge of 26 percentage points from his result in the 1928 election.
Post-presidency (1933–1964)
Roosevelt administration
Opposition to New Deal

Hoover departed from Washington in March 1933, bitter at his election loss and continuing unpopularity. As Coolidge, Harding, Wilson, and Taft had all died during the 1920s or early 1930s and Roosevelt died in office, Hoover was the Lifespan timeline of presidents of the United States, sole living ex-president from 1933 to 1953. He and his wife lived in Palo Alto until her death in 1944, at which point Hoover began to live permanently at the Waldorf Astoria New York, Waldorf Astoria hotel in New York City. During the 1930s, Hoover increasingly self-identified as a Conservatism in the United States, conservative. He closely followed national events after leaving public office, becoming a constant critic of Franklin Roosevelt. In response to continued attacks on his character and presidency, Hoover wrote more than two dozen books, including ''The Challenge to Liberty'' (1934), which harshly criticized Roosevelt's
New Deal
The New Deal was a series of programs, public work projects, financial reforms, and regulations enacted by President Franklin D. Roosevelt in the United States between 1933 and 1939. Major federal programs agencies included the Civilian Con ...
. Hoover described the New Deal's National Recovery Administration and Agricultural Adjustment Act, Agricultural Adjustment Administration as "fascistic", and he called the 1933 Banking Act a "move to gigantic socialism".
Only 58 when he left office, Hoover held out hope for another term as president throughout the 1930s. At the 1936 Republican National Convention, Hoover's speech attacking the New Deal was well received, but the nomination went to Kansas Governor Alf Landon. In 1936 United States presidential election, the general election, Hoover delivered numerous well-publicized speeches on behalf of Landon, but Landon was defeated by Roosevelt. Though Hoover was eager to oppose Roosevelt at every turn, Senator Arthur Vandenberg and other Republicans urged the still-unpopular Hoover to remain out of the fray during the debate over Roosevelt's proposed Judicial Procedures Reform Bill of 1937, Judiciary Reorganization Bill of 1937. At the 1940 Republican National Convention, he again hoped for the presidential nomination, but it went to the internationalist Wendell Willkie, who lost to Roosevelt in the general election.
World War II
During a 1938 trip to Europe, Hoover met with Adolf Hitler and stayed at Hermann Göring's hunting lodge. He expressed dismay at the persecution of Jews in Germany and believed that Hitler was mad, but did not present a threat to the U.S. Instead, Hoover believed that Roosevelt posed the biggest threat to peace, holding that Roosevelt's policies provoked Japan and discouraged France and the United Kingdom from reaching an "accommodation" with Germany.
After the September 1939 invasion of Poland by Germany, Hoover opposed U.S. involvement in World War II, including the Lend-Lease policy. He was active in the United States non-interventionism, isolationist America First Committee. He rejected Roosevelt's offers to help coordinate relief in Europe, but, with the help of old friends from the CRB, helped establish the Commission for Polish Relief. After the beginning of the German occupation of Belgium during World War II, occupation of Belgium in 1940, Hoover provided aid for Belgian civilians, though this aid was described as unnecessary by German broadcasts.
In December 1939, sympathetic Americans led by Hoover formed the Finnish Relief Fund to donate money to aid Finland, Finnish civilians and refugees after the Soviet Union had started the Winter War by attacking Finland, which had outraged Americans. By the end of January, it had already sent more than two million dollars to the Finns.
During a radio broadcast on June 29, 1941, one week after the Nazi invasion of the Soviet Union, Hoover disparaged any "tacit alliance" between the U.S. and the USSR, stating, "if we join the war and Stalin wins, we have aided him to impose more communism on Europe and the world... War alongside Stalin to impose freedom is more than a travesty. It is a tragedy." Much to his frustration, Hoover was not called upon to serve after the Military history of the United States during World War II, United States entered World War II due to his differences with Roosevelt and his continuing unpopularity. He did not pursue the presidential nomination at the 1944 Republican National Convention, and, at the request of Republican nominee Thomas E. Dewey, refrained from campaigning during the general election. In 1945, Hoover advised President Harry S. Truman to drop the United States' demand for the unconditional surrender of Japan because of the high projected casualties of the Operation Downfall, planned invasion of Japan, although Hoover was unaware of the Manhattan Project and the Nuclear weapons of the United States, atomic bomb.
Post–World War II

Following World War II, Hoover befriended President
Harry S. Truman despite their ideological differences. Because of Hoover's experience with Germany at the end of World War I, in 1946 Truman selected the former president to tour Allied-occupied Germany and Rome, Italy to ascertain the food needs of the occupied nations. After touring Germany, Hoover produced The President's Economic Mission to Germany and Austria, a number of reports critical of U.S. occupation policy. He stated in one report that "there is the illusion that the New Germany left after the Historical Eastern Germany#Potsdam Conference, annexations can be reduced to a 'Morgenthau Plan, pastoral state.' It cannot be done unless we genocide, exterminate or move 25,000,000 people out of it." On Hoover's initiative, a school meals program in the Bizone, American and British occupation zones of Germany was begun on April 14, 1947; the program served 3,500,000 children.
Even more important, in 1947 Truman appointed Hoover to lead the Hoover Commission, Commission on Organization of the Executive Branch of the Government a new high level study. Truman accepted some of the recommendations of the "Hoover Commission" for eliminating waste, fraud, and inefficiency, consolidating agencies, and strengthening White House control of policy. Though Hoover had opposed Roosevelt's concentration of power in the 1930s, he believed that a stronger presidency was required with the advent of the Atomic Age. During the 1948 United States presidential election, 1948 presidential election, Hoover supported Republican nominee Thomas E. Dewey, Thomas Dewey's unsuccessful campaign against Truman, but he remained on good terms with Truman. Hoover favored the United Nations in principle, but he opposed granting membership to the Soviet Union and other Communist states. He viewed the Soviet Union to be as morally repugnant as Nazi Germany and supported the efforts of Richard Nixon and others to expose Communists in the United States.
In 1949, New York Governor Thomas E. Dewey offered Hoover the Senate seat vacated by Robert F. Wagner. It was a matter of being senator for only two months and he declined.

Hoover backed conservative leader Robert A. Taft at the 1952 Republican National Convention, but the party's presidential nomination instead went to
Dwight D. Eisenhower, who went on to win the 1952 United States presidential election, 1952 election. Though Eisenhower appointed Hoover to another presidential commission, Hoover disliked Eisenhower, faulting the latter's failure to roll back the New Deal. Hoover's public work helped to rehabilitate his reputation, as did his use of self-deprecating humor; he occasionally remarked that "I am the only person of distinction who's ever had a depression named after him." In 1958, Congress passed the Former Presidents Act, offering a $25,000 yearly pension () to each former president.
Hoover took the pension even though he did not need the money, possibly to avoid embarrassing Truman, whose precarious financial status played a role in the law's enactment. In the early 1960s, President John F. Kennedy offered Hoover various positions; Hoover declined the offers but defended Kennedy after the Bay of Pigs Invasion, Bay of Pigs invasion and was personally distraught by assassination of John F. Kennedy, Kennedy's assassination in 1963.
Hoover wrote several books during his retirement, including ''The Ordeal of Woodrow Wilson'', in which he strongly defended Wilson's actions at the Paris Peace Conference. In 1944, he began working on ''Freedom Betrayed'', which he often referred to as his "magnum opus". In ''Freedom Betrayed'', Hoover strongly critiques Foreign policy of the Franklin D. Roosevelt administration, Roosevelt's foreign policy, especially Roosevelt's decision to recognize the Soviet Union in order to provide aid to that country during World War II. The book was published in 2012 after being edited by historian George H. Nash.
Death
Hoover faced three major illnesses during the last two years of his life, including an August 1962 operation in which a growth on his large intestine was removed.
He died on October 20, 1964, in New York City following massive internal bleeding.
Though Hoover's last spoken words are unknown, his last known written words were a get well message to his friend Harry Truman, six days before his death, after he heard that Truman had sustained injuries from slipping in a bathroom: "Bathtubs are a menace to ex-presidents for as you may recall a bathtub rose up and Fractured vertebra, fractured my vertebrae when I was in Venezuela on your world famine mission in 1946. My warmest sympathy and best wishes for your recovery." Two months earlier, on August 10, Hoover reached the age of 90, only the second U.S. president (after John Adams) to do so. When asked how he felt on reaching the milestone, Hoover replied, "Too old."
[ At the time of his death, Hoover had been out of office for over 31 years ( days all together). This was the longest retirement in presidential history until Jimmy Carter broke that record in September 2012.
Hoover was honored with a state funeral in which he lying in state#United States, lay in state in the United States Capitol rotunda. President Lyndon Johnson and First Lady Ladybird Johnson attended, along with former presidents Truman and Eisenhower. Then, on October 25, he was buried in West Branch, Iowa, near his Presidential library system, presidential library and birthplace on the grounds of the Herbert Hoover National Historic Site. Afterwards, Hoover's wife, Lou Henry Hoover, who had been buried in Palo Alto, California, following her death in 1944, was re-interred beside him. Hoover was the last surviving member of the Harding and Coolidge Cabinets. John Nance Garner (he was Speaker of the House during the second half of Hoover's term) was the only person in Hoover's United States presidential line of succession he did not outlive.
]
Legacy
Historical reputation
Hoover was extremely unpopular when he left office after the 1932 election, and his historical reputation would not begin to recover until the 1970s. According to Professor David E. Hamilton, historians have credited Hoover for his genuine belief in voluntarism and cooperation, as well as the innovation of some of his programs. However, Hamilton also notes that Hoover was politically inept and failed to recognize the severity of the Great Depression.American Relief Administration
American Relief Administration (ARA) was an American relief mission to Europe and later post-revolutionary Russia after World War I. Herbert Hoover, future president of the United States, was the program director.
The ARA's immediate predeces ...
, said of him "Many statesmen occupy a prominent place in history for having sent millions to their death; Herbert Hoover, maligned for his performance as President, and soon forgotten in Russia, has the rare distinction of having saved millions."
Views of race
Racist remarks and racial humor was common at the time, but Hoover never indulged in them while President and deliberate discrimination was anathema to him; he thought of himself as a friend to blacks and an advocate for their progress. W. E. B. Du Bois described him as an "undemocratic racist who saw blacks as a species of 'sub-men.
Memorials
The Herbert Hoover Presidential Library and Museum is located in West Branch, Iowa next to the Herbert Hoover National Historic Site. The library is one of thirteen Presidential library system, presidential libraries run by the National Archives and Records Administration. The Hoover–Minthorn House, where Hoover lived from 1885 to 1891, is located in Newberg, Oregon, Newberg, Oregon
Oregon () is a U.S. state, state in the Pacific Northwest region of the Western United States. The Columbia River delineates much of Oregon's northern boundary with Washington (state), Washington, while the Snake River delineates much of it ...
. His Rapidan Camp, Rapidan fishing camp in Virginia, which he donated to the government in 1933, is now a National Historic Landmark within the Shenandoah National Park. The Lou Henry Hoover House, Lou Henry and Herbert Hoover House, built in 1919 in Stanford, California
Stanford is a census-designated place (CDP) in the northwest corner of Santa Clara County, California, United States. It is the home of Stanford University. The population was 21,150 at the 2020 census.
Stanford is an unincorporated area of ...
, is now the official residence of the president of Stanford University, and a National Historic Landmark. Also located at Stanford is the Hoover Institution, a think tank and research institution started by Hoover.
Hoover has been memorialized in the names of several things, including the Hoover Dam on the Colorado River and numerous Elementary school, elementary, Middle school, middle, and High school (North America), high schools across the United States. Two minor planets, 932 Hooveria and 1363 Herberta, are named in his honor. The Polish capital of Warsaw has a square named after Hoover, and the historic townsite of Gwalia, Western Australia contains the Hoover House Bed and Breakfast, where Hoover resided while managing and visiting the mine during the first decade of the twentieth century. A medicine ball game known as Hooverball is named for Hoover; it was invented by White House physician Admiral Joel T. Boone to help Hoover keep fit while serving as president.
Other honors
Hoover was inducted into the National Mining Hall of Fame in 1988 (inaugural class). His wife was inducted into the hall in 1990.
Hoover was inducted into the Australian Prospectors and Miners' Hall of Fame in the category Directors and Management.
Hoover was awarded an Honorary degree, honorary doctorate by the Charles University in Prague and University of Helsinki in March 1938.
See also
* Great Depression in the United States
In the History of the United States, United States, the Great Depression began with the Wall Street Crash of 1929, Wall Street Crash of October 1929 and then spread worldwide. The nadir came in 1931–1933, and recovery came in 1940. The stock m ...
* List of presidents of the United States
* Progressive Era
* Roaring Twenties
Explanatory notes
References
Citations
Works cited
* Originally published as
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
* Book 1 in The Life of Herbert Hoover Series.
*
*
*
*
*
Further reading
Biographical
* Best, Gary Dean. ''The Politics of American Individualism: Herbert Hoover in Transition, 1918–1921'' (1975)
* Best, Gary Dean. ''The Life of Herbert Hoover: Keeper of the Torch, 1933–1964.'' Palgrave Macmillan, 2013.
* Clements, Kendrick A. ''The Life of Herbert Hoover: Imperfect Visionary, 1918–1928'' (2010).
* Edwards, Barry C. "Putting Hoover on the Map: Was the 31st President a Progressive?" ''Congress & the Presidency'' 41#1 (2014) pp 49–83
* Hatfield, Mark. ed. ''Herbert Hoover Reassessed'' (2002)
* .
* Jeansonne, Glen. ''The Life of Herbert Hoover: Fighting Quaker, 1928–1933.'' Palgrave Macmillan; 2012.
* Lloyd, Craig. ''Aggressive Introvert: A Study of Herbert Hoover and Public Relations Management, 1912–1932'' (1973).
* George H. Nash, Nash, George H. ''The Life of Herbert Hoover: The Engineer 1874–1914'' (1983); in-depth scholarly study
** .
** .
* Nash, Lee, ed. ''Understanding Herbert Hoover: Ten Perspectives'' (1987); essays by scholars
* Smith, Richard Norton. ''An Uncommon Man: The Triumph of Herbert Hoover'', (1987), biography concentrating on post 1932.
* Walch, Timothy. ed. ''Uncommon Americans: The Lives and Legacies of Herbert and Lou Henry Hoover'' Praeger, 2003.
* West, Hal Elliott. ''Hoover, the Fishing President: Portrait of the Man and his Life Outdoors'' (2005).
Scholarly studies
* Arnold, Peri E. "The 'Great Engineer' as Administrator: Herbert Hoover and Modern Bureaucracy." ''Review of Politics'' 42.3 (1980): 329–348. .
* Barber, William J. ''From New Era to New Deal: Herbert Hoover, the Economists, and American Economic Policy, 1921–1933''. (1985)
*
* Brandes, Joseph. ''Herbert Hoover and Economic Diplomacy: Department of Commerce Policy, 1921–1928.'' (U of Pittsburgh Press, 1970).
* Britten, Thomas A. "Hoover and the Indians: the Case for Continuity in Federal Indian Policy, 1900–1933" ''Historian'' 1999 61(3): 518–538. .
* Clements, Kendrick A. ''Hoover, Conservation, and Consumerism: Engineering the Good Life''. University Press of Kansas, 2000
* Dodge, Mark M., ed. ''Herbert Hoover and the Historians''. (1989)
* Fausold Martin L. and George Mazuzan, eds. ''The Hoover Presidency: A Reappraisal'' (1974)
* Goodman, Mark, and Mark Gring
"The Radio Act of 1927: progressive ideology, epistemology, and praxis"
''Rhetoric & Public Affairs'' 3.3 (2000): 397–418.
* Hawley, Ellis."Herbert Hoover and the Historians—Recent Developments: A Review Essay" ''Annals of Iowa'' 78#1 (2018) pp. 75–86
* Hawley, Ellis
"Herbert Hoover, the Commerce Secretariat, and the Vision of an 'Associative State', 1921–1928"
. ''Journal of American History'', (June 1974) 61#1: 116–140.
* Jansky Jr, C. M. "The contribution of Herbert Hoover to broadcasting." ''Journal of Broadcasting & Electronic Media'' 1.3 (1957): 241–249.
* Lee, David D. "Herbert Hoover and the Development of Commercial Aviation, 1921–1926." ''Business History Review'' 58.1 (1984): 78–102.
* Lichtman, Allan J. ''Prejudice and the Old Politics: The Presidential Election of 1928'' (1979)
* Lisio, Donald J. ''The President and Protest: Hoover, MacArthur, and the Bonus Riot'', 2d ed. (1994)
* Lisio, Donald J. ''Hoover, Blacks, and Lily-whites: A Study of Southern Strategies'' (1985)
* Parafianowicz,Halina
'Herbert C. Hoover and Poland: 1919–1933. Between Myth and Reality'
* Polsky, Andrew J., and Olesya Tkacheva. "Legacies Versus Politics: Herbert Hoover, Partisan Conflict, and the Symbolic Appeal of Associationalism in the 1920s." ''International Journal of Politics, Culture, and Society'' 16.2 (2002): 207–235
online
* Short, Brant. "The Rhetoric of the Post-Presidency: Herbert Hoover's Campaign against the New Deal, 1934–1936" ''Presidential Studies Quarterly'' (1991) 21#2 pp. 333–35
online
* Sibley, Katherine A.S., ed. ''A Companion to Warren G. Harding, Calvin Coolidge, and Herbert Hoover'' (2014); 616pp; essays by scholars stressing historiography
* Wueschner, Silvano A. ''Charting Twentieth-Century Monetary Policy: Herbert Hoover and Benjamin Strong, 1917–1927''. Greenwood, 1999
Primary sources
* Myers, William Starr; Walter H. Newton, eds. (1936). ''The Hoover Administration; a documented narrative''.
* Hawley, Ellis, ed. (1974–1977). ''Herbert Hoover: Containing the Public Messages, Speeches, and Statements of the President'', 4 vols.
* .
* .
* .
* .
* .
* .
* .
* .
*
* .
* .
External links
*
*
Herbert Hoover Presidential Library and Museum
Herbert Hoover National Historic Site
National Park Service
*
*
*
{{DEFAULTSORT:Hoover, Herbert
Herbert Hoover,
1874 births
1964 deaths
19th-century American people
19th-century Quakers
20th-century American politicians
20th-century presidents of the United States
20th-century Quakers
American expatriates in Australia
American expatriates in China
American geologists
American humanitarians
American male non-fiction writers
American memoirists
American mining engineers
American non-fiction outdoors writers
American people of Canadian descent
American people of English descent
American people of German descent
American people of Irish descent
American people of Swiss descent
American political writers
American Quakers
Articles containing video clips
Belgian relief in World War I
Burials in Iowa
California Republicans
Candidates in the 1920 United States presidential election
Candidates in the 1928 United States presidential election
Candidates in the 1932 United States presidential election
Candidates in the 1936 United States presidential election
Candidates in the 1940 United States presidential election
Coolidge administration cabinet members
Deaths from bleeding
Engineers from California
Engineers from Iowa
Engineers from New York (state)
George Fox University alumni
Harding administration cabinet members
Hoover family
John Fritz Medal recipients
Members of the United States National Academy of Sciences
People from Newberg, Oregon
People from Stanford, California
People from West Branch, Iowa
Presidents of the United States
Republican Party (United States) presidential nominees
Republican Party presidents of the United States
Sons of the American Revolution
Stanford University alumni
Stanford University trustees
United States Secretaries of Commerce
Writers from California
Writers from Iowa
Writers from New York City
American expatriates in the United Kingdom
 Herbert Clark Hoover was born on August 10, 1874, in West Branch, Iowa. His father, Jesse Hoover, was a
Herbert Clark Hoover was born on August 10, 1874, in West Branch, Iowa. His father, Jesse Hoover, was a  In November 1885, Hoover was sent to
In November 1885, Hoover was sent to  When Hoover graduated from Stanford in 1895, the country was in the midst of the
When Hoover graduated from Stanford in 1895, the country was in the midst of the  After leaving Bewick, Moreing, Hoover worked as a London-based independent mining consultant and financier. Though he had risen to prominence as a geologist and mine operator, Hoover focused much of his attention on raising money, restructuring corporate organizations, and financing new ventures. He specialized in rejuvenating troubled mining operations, taking a share of the profits in exchange for his technical and financial expertise. Hoover thought of himself and his associates as "engineering doctors to sick concerns", and he earned a reputation as a "doctor of sick mines". He made investments on every continent and had offices in
After leaving Bewick, Moreing, Hoover worked as a London-based independent mining consultant and financier. Though he had risen to prominence as a geologist and mine operator, Hoover focused much of his attention on raising money, restructuring corporate organizations, and financing new ventures. He specialized in rejuvenating troubled mining operations, taking a share of the profits in exchange for his technical and financial expertise. Hoover thought of himself and his associates as "engineering doctors to sick concerns", and he earned a reputation as a "doctor of sick mines". He made investments on every continent and had offices in 
 After his election as president in 1920, Harding rewarded Hoover for his support, offering to appoint him as either
After his election as president in 1920, Harding rewarded Hoover for his support, offering to appoint him as either  Between 1923 and 1929, the number of families with radios grew from 300,000 to 10 million, and Hoover's tenure as Secretary of Commerce heavily influenced radio use in the United States. In the early and mid-1920s, Hoover's radio conferences played a key role in the organization, development, and regulation of
Between 1923 and 1929, the number of families with radios grew from 300,000 to 10 million, and Hoover's tenure as Secretary of Commerce heavily influenced radio use in the United States. In the early and mid-1920s, Hoover's radio conferences played a key role in the organization, development, and regulation of  With the goal of encouraging wise business investments, Hoover made the Commerce Department a clearinghouse of information. He recruited numerous academics from various fields and tasked them with publishing reports on different aspects of the economy, including steel production and films. To eliminate waste, he encouraged
With the goal of encouraging wise business investments, Hoover made the Commerce Department a clearinghouse of information. He recruited numerous academics from various fields and tasked them with publishing reports on different aspects of the economy, including steel production and films. To eliminate waste, he encouraged  Hoover saw the presidency as a vehicle for improving the conditions of all Americans by encouraging public-private cooperation—what he termed "volunteerism". He tended to oppose governmental coercion or intervention, as he thought they infringed on American ideals of individualism and self-reliance. The first major bill that he signed, the
Hoover saw the presidency as a vehicle for improving the conditions of all Americans by encouraging public-private cooperation—what he termed "volunteerism". He tended to oppose governmental coercion or intervention, as he thought they infringed on American ideals of individualism and self-reliance. The first major bill that he signed, the  On taking office, Hoover said that "given the chance to go forward with the policies of the last eight years, we shall soon with the help of God, be in sight of the day when poverty will be banished from this nation". Having seen the fruits of prosperity brought by technological progress, many shared Hoover's optimism, and the already bullish stock market climbed even higher on Hoover's accession. This optimism concealed several threats to sustained U.S. economic growth, including a persistent
On taking office, Hoover said that "given the chance to go forward with the policies of the last eight years, we shall soon with the help of God, be in sight of the day when poverty will be banished from this nation". Having seen the fruits of prosperity brought by technological progress, many shared Hoover's optimism, and the already bullish stock market climbed even higher on Hoover's accession. This optimism concealed several threats to sustained U.S. economic growth, including a persistent  Though he attempted to put a positive spin on
Though he attempted to put a positive spin on  By the end of 1930, the Unemployment in the United States, national unemployment rate had reached 11.9 percent, but it was not yet clear to most Americans that the economic downturn would be worse than the Depression of 1920–1921, Depression of 1920–21. A series of bank failures in late 1930 heralded a larger Economic collapse, collapse of the economy in 1931. While other countries left the gold standard, Hoover refused to abandon it; he derided any other monetary system as "Collectivism and individualism, collectivism". Hoover viewed the weak Economy of Europe, European economy as a major cause of economic troubles in the United States. In response to the collapse of the Economy of Germany, German economy, Hoover marshaled congressional support behind a one-year moratorium on European war debts. The Hoover Moratorium was warmly received in Europe and the United States, but Germany remained on the brink of Default (finance), defaulting on its loans. As the worldwide economy worsened, democratic governments fell; in Germany, Nazi Party leader Adolf Hitler assumed power and dismantled the Weimar Republic.
By mid-1931, the unemployment rate had reached 15 percent, giving rise to growing fears that the country was experiencing a depression far worse than recent economic downturns. A reserved man with a fear of public speaking, Hoover allowed his opponents in the Democratic Party to define him as cold, incompetent, reactionary, and out-of-touch. Hoover's opponents developed defamatory epithets to discredit him, such as "Hooverville" (the shanty towns and homeless encampments), "Hoover leather" (cardboard used to cover holes in the soles of shoes), and "Hoover blanket" (old newspaper used to cover oneself from the cold). While Hoover continued to resist direct federal relief efforts, Governor Franklin D. Roosevelt of New York launched the Federal Emergency Relief Administration, Temporary Emergency Relief Administration to provide aid to the unemployed. Democrats positioned the program as a kinder alternative to Hoover's alleged apathy towards the unemployed, despite Hoover's belief that such programs were the responsibility of state and local governments.
The economy continued to worsen, with unemployment rates nearing 23 percent in early 1932, and Hoover finally heeded calls for more direct federal intervention. In January 1932, he convinced Congress to authorize the establishment of the Reconstruction Finance Corporation (RFC), which would provide government-secured loans to financial institutions, railroads, and local governments. The RFC saved numerous businesses from failure, but it failed to stimulate commercial lending as much as Hoover had hoped, partly because it was run by conservative bankers unwilling to make riskier loans. The same month the RFC was established, Hoover signed the Federal Home Loan Bank Act, establishing 12 district banks overseen by a Federal Home Loan Bank Board in a manner similar to the Federal Reserve System. He also helped arrange passage of the Glass–Steagall Act of 1932, emergency banking legislation designed to expand banking credit by expanding the collateral on which Federal Reserve banks were authorized to lend. As these measures failed to stem the economic crisis, Hoover signed the Emergency Relief and Construction Act, a $2 billion public works bill, in July 1932.
By the end of 1930, the Unemployment in the United States, national unemployment rate had reached 11.9 percent, but it was not yet clear to most Americans that the economic downturn would be worse than the Depression of 1920–1921, Depression of 1920–21. A series of bank failures in late 1930 heralded a larger Economic collapse, collapse of the economy in 1931. While other countries left the gold standard, Hoover refused to abandon it; he derided any other monetary system as "Collectivism and individualism, collectivism". Hoover viewed the weak Economy of Europe, European economy as a major cause of economic troubles in the United States. In response to the collapse of the Economy of Germany, German economy, Hoover marshaled congressional support behind a one-year moratorium on European war debts. The Hoover Moratorium was warmly received in Europe and the United States, but Germany remained on the brink of Default (finance), defaulting on its loans. As the worldwide economy worsened, democratic governments fell; in Germany, Nazi Party leader Adolf Hitler assumed power and dismantled the Weimar Republic.
By mid-1931, the unemployment rate had reached 15 percent, giving rise to growing fears that the country was experiencing a depression far worse than recent economic downturns. A reserved man with a fear of public speaking, Hoover allowed his opponents in the Democratic Party to define him as cold, incompetent, reactionary, and out-of-touch. Hoover's opponents developed defamatory epithets to discredit him, such as "Hooverville" (the shanty towns and homeless encampments), "Hoover leather" (cardboard used to cover holes in the soles of shoes), and "Hoover blanket" (old newspaper used to cover oneself from the cold). While Hoover continued to resist direct federal relief efforts, Governor Franklin D. Roosevelt of New York launched the Federal Emergency Relief Administration, Temporary Emergency Relief Administration to provide aid to the unemployed. Democrats positioned the program as a kinder alternative to Hoover's alleged apathy towards the unemployed, despite Hoover's belief that such programs were the responsibility of state and local governments.
The economy continued to worsen, with unemployment rates nearing 23 percent in early 1932, and Hoover finally heeded calls for more direct federal intervention. In January 1932, he convinced Congress to authorize the establishment of the Reconstruction Finance Corporation (RFC), which would provide government-secured loans to financial institutions, railroads, and local governments. The RFC saved numerous businesses from failure, but it failed to stimulate commercial lending as much as Hoover had hoped, partly because it was run by conservative bankers unwilling to make riskier loans. The same month the RFC was established, Hoover signed the Federal Home Loan Bank Act, establishing 12 district banks overseen by a Federal Home Loan Bank Board in a manner similar to the Federal Reserve System. He also helped arrange passage of the Glass–Steagall Act of 1932, emergency banking legislation designed to expand banking credit by expanding the collateral on which Federal Reserve banks were authorized to lend. As these measures failed to stem the economic crisis, Hoover signed the Emergency Relief and Construction Act, a $2 billion public works bill, in July 1932.
 After a decade of budget surpluses, the federal government experienced a Budget deficits, budget deficit in 1931. Though some economists, like William Trufant Foster, favored deficit spending to address the Great Depression, most politicians and economists believed in the necessity of keeping a balanced budget. In late 1931, Hoover proposed a tax plan to increase tax revenue by 30 percent, resulting in the passage of the Revenue Act of 1932. The act increased taxes across the board, rolling back much of the tax cut reduction program Mellon had presided over during the 1920s. Top earners were taxed at 63 percent on their net income, the highest rate since the early 1920s. The act also doubled the top Estate tax in the United States, estate tax rate, cut Income tax in the United States, personal income tax exemptions, eliminated the Corporate tax in the United States, corporate income tax exemption, and raised corporate tax rates. Despite the passage of the Revenue Act, the federal government continued to run a budget deficit.
After a decade of budget surpluses, the federal government experienced a Budget deficits, budget deficit in 1931. Though some economists, like William Trufant Foster, favored deficit spending to address the Great Depression, most politicians and economists believed in the necessity of keeping a balanced budget. In late 1931, Hoover proposed a tax plan to increase tax revenue by 30 percent, resulting in the passage of the Revenue Act of 1932. The act increased taxes across the board, rolling back much of the tax cut reduction program Mellon had presided over during the 1920s. Top earners were taxed at 63 percent on their net income, the highest rate since the early 1920s. The act also doubled the top Estate tax in the United States, estate tax rate, cut Income tax in the United States, personal income tax exemptions, eliminated the Corporate tax in the United States, corporate income tax exemption, and raised corporate tax rates. Despite the passage of the Revenue Act, the federal government continued to run a budget deficit.
 Hoover seldom mentioned Civil rights movement (1896–1954), civil rights while he was president. He believed that
Hoover seldom mentioned Civil rights movement (1896–1954), civil rights while he was president. He believed that  By mid-1931 few observers thought that Hoover had much hope of winning a second term in the midst of the ongoing economic crisis. The Republican expectations were so bleak that Hoover faced no serious opposition for re-nomination at the 1932 Republican National Convention. Coolidge and other prominent Republicans all passed on the opportunity to challenge Hoover. Franklin D. Roosevelt won the presidential nomination on the fourth ballot of the 1932 Democratic National Convention, defeating the 1928 Democratic nominee, Al Smith. The Democrats attacked Hoover as the cause of the Great Depression, and for being indifferent to the suffering of millions. As Governor of New York, Roosevelt had called on the New York legislature to provide aid for the needy, establishing Roosevelt's reputation for being more favorable toward government interventionism during the economic crisis. The Democratic Party, including Al Smith and other national leaders, coalesced behind Roosevelt, while progressive Republicans like George Norris and Robert M. La Follette Jr., Robert La Follette Jr. deserted Hoover. Prohibition was increasingly unpopular and wets offered the argument that states and localities needed the tax money. Hoover proposed a new constitutional amendment that was vague on particulars. Roosevelt's platform promised repeal of the 18th Amendment.
By mid-1931 few observers thought that Hoover had much hope of winning a second term in the midst of the ongoing economic crisis. The Republican expectations were so bleak that Hoover faced no serious opposition for re-nomination at the 1932 Republican National Convention. Coolidge and other prominent Republicans all passed on the opportunity to challenge Hoover. Franklin D. Roosevelt won the presidential nomination on the fourth ballot of the 1932 Democratic National Convention, defeating the 1928 Democratic nominee, Al Smith. The Democrats attacked Hoover as the cause of the Great Depression, and for being indifferent to the suffering of millions. As Governor of New York, Roosevelt had called on the New York legislature to provide aid for the needy, establishing Roosevelt's reputation for being more favorable toward government interventionism during the economic crisis. The Democratic Party, including Al Smith and other national leaders, coalesced behind Roosevelt, while progressive Republicans like George Norris and Robert M. La Follette Jr., Robert La Follette Jr. deserted Hoover. Prohibition was increasingly unpopular and wets offered the argument that states and localities needed the tax money. Hoover proposed a new constitutional amendment that was vague on particulars. Roosevelt's platform promised repeal of the 18th Amendment.
 Hoover departed from Washington in March 1933, bitter at his election loss and continuing unpopularity. As Coolidge, Harding, Wilson, and Taft had all died during the 1920s or early 1930s and Roosevelt died in office, Hoover was the Lifespan timeline of presidents of the United States, sole living ex-president from 1933 to 1953. He and his wife lived in Palo Alto until her death in 1944, at which point Hoover began to live permanently at the Waldorf Astoria New York, Waldorf Astoria hotel in New York City. During the 1930s, Hoover increasingly self-identified as a Conservatism in the United States, conservative. He closely followed national events after leaving public office, becoming a constant critic of Franklin Roosevelt. In response to continued attacks on his character and presidency, Hoover wrote more than two dozen books, including ''The Challenge to Liberty'' (1934), which harshly criticized Roosevelt's
Hoover departed from Washington in March 1933, bitter at his election loss and continuing unpopularity. As Coolidge, Harding, Wilson, and Taft had all died during the 1920s or early 1930s and Roosevelt died in office, Hoover was the Lifespan timeline of presidents of the United States, sole living ex-president from 1933 to 1953. He and his wife lived in Palo Alto until her death in 1944, at which point Hoover began to live permanently at the Waldorf Astoria New York, Waldorf Astoria hotel in New York City. During the 1930s, Hoover increasingly self-identified as a Conservatism in the United States, conservative. He closely followed national events after leaving public office, becoming a constant critic of Franklin Roosevelt. In response to continued attacks on his character and presidency, Hoover wrote more than two dozen books, including ''The Challenge to Liberty'' (1934), which harshly criticized Roosevelt's  Following World War II, Hoover befriended President Harry S. Truman despite their ideological differences. Because of Hoover's experience with Germany at the end of World War I, in 1946 Truman selected the former president to tour Allied-occupied Germany and Rome, Italy to ascertain the food needs of the occupied nations. After touring Germany, Hoover produced The President's Economic Mission to Germany and Austria, a number of reports critical of U.S. occupation policy. He stated in one report that "there is the illusion that the New Germany left after the Historical Eastern Germany#Potsdam Conference, annexations can be reduced to a 'Morgenthau Plan, pastoral state.' It cannot be done unless we genocide, exterminate or move 25,000,000 people out of it." On Hoover's initiative, a school meals program in the Bizone, American and British occupation zones of Germany was begun on April 14, 1947; the program served 3,500,000 children.
Even more important, in 1947 Truman appointed Hoover to lead the Hoover Commission, Commission on Organization of the Executive Branch of the Government a new high level study. Truman accepted some of the recommendations of the "Hoover Commission" for eliminating waste, fraud, and inefficiency, consolidating agencies, and strengthening White House control of policy. Though Hoover had opposed Roosevelt's concentration of power in the 1930s, he believed that a stronger presidency was required with the advent of the Atomic Age. During the 1948 United States presidential election, 1948 presidential election, Hoover supported Republican nominee Thomas E. Dewey, Thomas Dewey's unsuccessful campaign against Truman, but he remained on good terms with Truman. Hoover favored the United Nations in principle, but he opposed granting membership to the Soviet Union and other Communist states. He viewed the Soviet Union to be as morally repugnant as Nazi Germany and supported the efforts of Richard Nixon and others to expose Communists in the United States.
In 1949, New York Governor Thomas E. Dewey offered Hoover the Senate seat vacated by Robert F. Wagner. It was a matter of being senator for only two months and he declined.
Following World War II, Hoover befriended President Harry S. Truman despite their ideological differences. Because of Hoover's experience with Germany at the end of World War I, in 1946 Truman selected the former president to tour Allied-occupied Germany and Rome, Italy to ascertain the food needs of the occupied nations. After touring Germany, Hoover produced The President's Economic Mission to Germany and Austria, a number of reports critical of U.S. occupation policy. He stated in one report that "there is the illusion that the New Germany left after the Historical Eastern Germany#Potsdam Conference, annexations can be reduced to a 'Morgenthau Plan, pastoral state.' It cannot be done unless we genocide, exterminate or move 25,000,000 people out of it." On Hoover's initiative, a school meals program in the Bizone, American and British occupation zones of Germany was begun on April 14, 1947; the program served 3,500,000 children.
Even more important, in 1947 Truman appointed Hoover to lead the Hoover Commission, Commission on Organization of the Executive Branch of the Government a new high level study. Truman accepted some of the recommendations of the "Hoover Commission" for eliminating waste, fraud, and inefficiency, consolidating agencies, and strengthening White House control of policy. Though Hoover had opposed Roosevelt's concentration of power in the 1930s, he believed that a stronger presidency was required with the advent of the Atomic Age. During the 1948 United States presidential election, 1948 presidential election, Hoover supported Republican nominee Thomas E. Dewey, Thomas Dewey's unsuccessful campaign against Truman, but he remained on good terms with Truman. Hoover favored the United Nations in principle, but he opposed granting membership to the Soviet Union and other Communist states. He viewed the Soviet Union to be as morally repugnant as Nazi Germany and supported the efforts of Richard Nixon and others to expose Communists in the United States.
In 1949, New York Governor Thomas E. Dewey offered Hoover the Senate seat vacated by Robert F. Wagner. It was a matter of being senator for only two months and he declined.
 Hoover backed conservative leader Robert A. Taft at the 1952 Republican National Convention, but the party's presidential nomination instead went to Dwight D. Eisenhower, who went on to win the 1952 United States presidential election, 1952 election. Though Eisenhower appointed Hoover to another presidential commission, Hoover disliked Eisenhower, faulting the latter's failure to roll back the New Deal. Hoover's public work helped to rehabilitate his reputation, as did his use of self-deprecating humor; he occasionally remarked that "I am the only person of distinction who's ever had a depression named after him." In 1958, Congress passed the Former Presidents Act, offering a $25,000 yearly pension () to each former president. Hoover took the pension even though he did not need the money, possibly to avoid embarrassing Truman, whose precarious financial status played a role in the law's enactment. In the early 1960s, President John F. Kennedy offered Hoover various positions; Hoover declined the offers but defended Kennedy after the Bay of Pigs Invasion, Bay of Pigs invasion and was personally distraught by assassination of John F. Kennedy, Kennedy's assassination in 1963.
Hoover wrote several books during his retirement, including ''The Ordeal of Woodrow Wilson'', in which he strongly defended Wilson's actions at the Paris Peace Conference. In 1944, he began working on ''Freedom Betrayed'', which he often referred to as his "magnum opus". In ''Freedom Betrayed'', Hoover strongly critiques Foreign policy of the Franklin D. Roosevelt administration, Roosevelt's foreign policy, especially Roosevelt's decision to recognize the Soviet Union in order to provide aid to that country during World War II. The book was published in 2012 after being edited by historian George H. Nash.
Hoover backed conservative leader Robert A. Taft at the 1952 Republican National Convention, but the party's presidential nomination instead went to Dwight D. Eisenhower, who went on to win the 1952 United States presidential election, 1952 election. Though Eisenhower appointed Hoover to another presidential commission, Hoover disliked Eisenhower, faulting the latter's failure to roll back the New Deal. Hoover's public work helped to rehabilitate his reputation, as did his use of self-deprecating humor; he occasionally remarked that "I am the only person of distinction who's ever had a depression named after him." In 1958, Congress passed the Former Presidents Act, offering a $25,000 yearly pension () to each former president. Hoover took the pension even though he did not need the money, possibly to avoid embarrassing Truman, whose precarious financial status played a role in the law's enactment. In the early 1960s, President John F. Kennedy offered Hoover various positions; Hoover declined the offers but defended Kennedy after the Bay of Pigs Invasion, Bay of Pigs invasion and was personally distraught by assassination of John F. Kennedy, Kennedy's assassination in 1963.
Hoover wrote several books during his retirement, including ''The Ordeal of Woodrow Wilson'', in which he strongly defended Wilson's actions at the Paris Peace Conference. In 1944, he began working on ''Freedom Betrayed'', which he often referred to as his "magnum opus". In ''Freedom Betrayed'', Hoover strongly critiques Foreign policy of the Franklin D. Roosevelt administration, Roosevelt's foreign policy, especially Roosevelt's decision to recognize the Soviet Union in order to provide aid to that country during World War II. The book was published in 2012 after being edited by historian George H. Nash.