Henryk Arctowski Polish Antarctic Station on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Henryk Arctowski Polish Antarctic Station (
COMNAP Antarctic Facilities
COMNAP Antarctic Facilities Map

 {{Authority control , additional=Q106092540
Arctowski
Poland and the Antarctic
Research institutes established in 1977
Historic Sites and Monuments of Antarctica
Lighthouses in Antarctica
1977 establishments in Antarctica
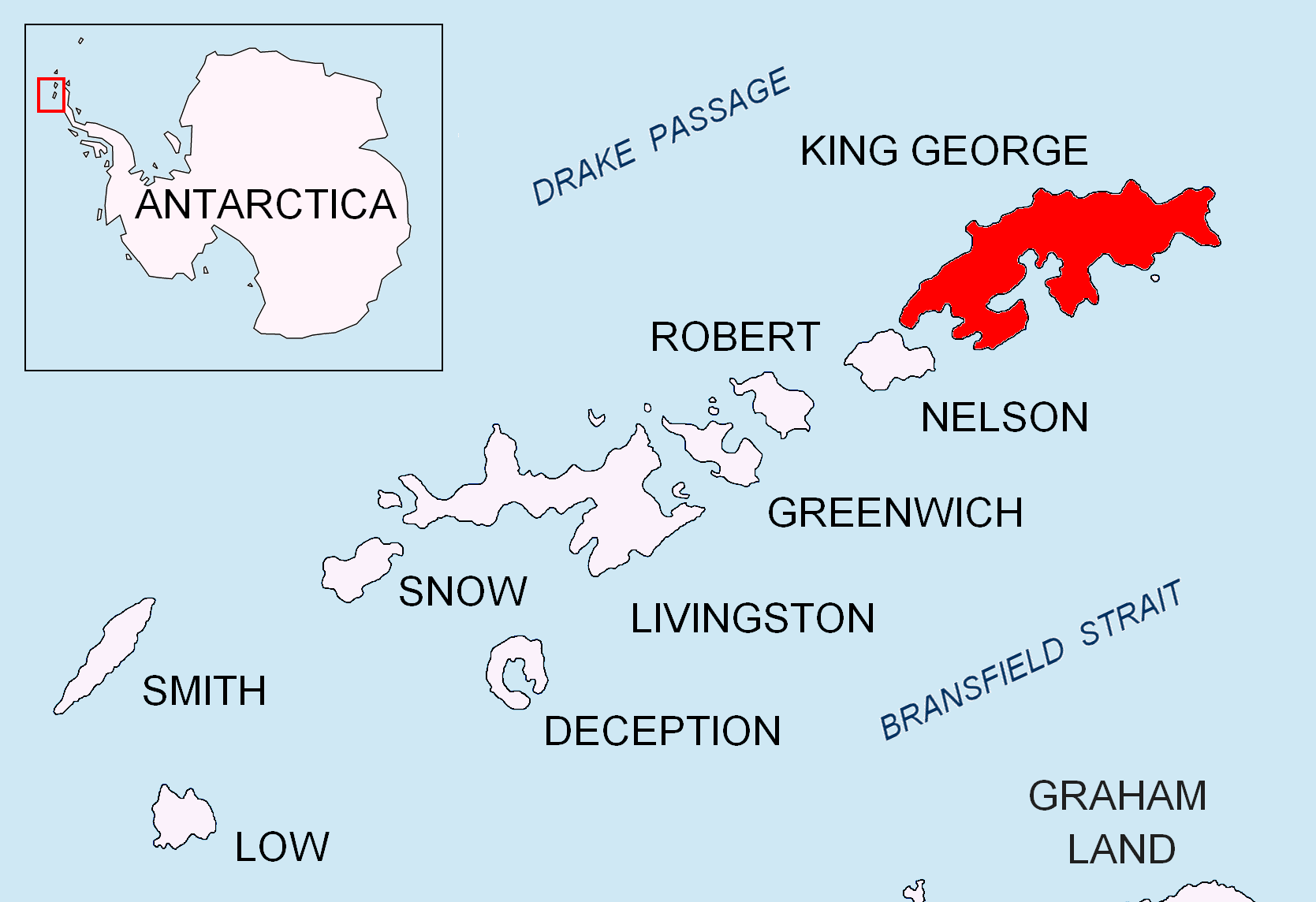
King George Island (South Shetland Islands)
{{Authority control , additional=Q106092540
Arctowski
Poland and the Antarctic
Research institutes established in 1977
Historic Sites and Monuments of Antarctica
Lighthouses in Antarctica
1977 establishments in Antarctica
King George Island (South Shetland Islands)
Polish
Polish may refer to:
* Anything from or related to Poland, a country in Europe
* Polish language
* Poles
Poles,, ; singular masculine: ''Polak'', singular feminine: ''Polka'' or Polish people, are a West Slavic nation and ethnic group, w ...
: ''Polska Stacja Antarktyczna im. Henryka Arctowskiego'') is a Polish research station
Research stations are facilities where scientific investigation, collection, analysis and experimentation occurs. A research station is a facility that is built for the purpose of conducting scientific research. There are also many types of resea ...
on King George Island, off the coast of Antarctica
Antarctica () is Earth's southernmost and least-populated continent. Situated almost entirely south of the Antarctic Circle and surrounded by the Southern Ocean, it contains the geographic South Pole. Antarctica is the fifth-largest cont ...
.
History
The station is named forHenryk Arctowski
Henryk Arctowski (15 July 1871 – 21 February 1958; ), born Henryk Artzt, was a Polish scientist and explorer. Living in exile for a large part of his life, he was one of the first persons to winter in Antarctica and became an internationally ...
(1871-1959), who as meteorologist had accompanied the Belgian explorer Baron Adrien de Gerlache
Baron Adrien Victor Joseph de Gerlache de Gomery (; 2 August 1866 – 4 December 1934) was a Belgian officer in the Belgian Royal Navy who led the Belgian Antarctic Expedition of 1897–99.
Early years
Born in Hasselt in eastern Belgium as th ...
on the Belgian Antarctic Expedition "Belgica", 1897–1899. This was the first expedition to overwinter in Antarctica. He proposed the original notion of a wind chill factor, arguing that wind could be as damaging to human flesh as cold in harsh climates.
Established on 26 February 1977, the station is managed by the Polish Academy of Sciences
The Polish Academy of Sciences ( pl, Polska Akademia Nauk, PAN) is a Polish state-sponsored institution of higher learning. Headquartered in Warsaw, it is responsible for spearheading the development of science across the country by a society o ...
; its main research areas include marine biology
Biology is the scientific study of life. It is a natural science with a broad scope but has several unifying themes that tie it together as a single, coherent field. For instance, all organisms are made up of cells that process hereditary i ...
, oceanography, geology
Geology () is a branch of natural science concerned with Earth and other astronomical objects, the features or rocks of which it is composed, and the processes by which they change over time. Modern geology significantly overlaps all other Ea ...
, geomorphology, glaciology
Glaciology (; ) is the scientific study of glaciers, or more generally ice and natural phenomena that involve ice.
Glaciology is an interdisciplinary Earth science that integrates geophysics, geology, physical geography, geomorphology, c ...
, meteorology
Meteorology is a branch of the atmospheric sciences (which include atmospheric chemistry and physics) with a major focus on weather forecasting. The study of meteorology dates back millennia, though significant progress in meteorology did no ...
, climatology
Climatology (from Greek , ''klima'', "place, zone"; and , ''-logia'') or climate science is the scientific study of Earth's climate, typically defined as weather conditions averaged over a period of at least 30 years. This modern field of study ...
, seismology
Seismology (; from Ancient Greek σεισμός (''seismós'') meaning "earthquake" and -λογία (''-logía'') meaning "study of") is the scientific study of earthquakes and the propagation of elastic waves through the Earth or through other ...
, magnetism and ecology
Ecology () is the study of the relationships between living organisms, including humans, and their physical environment. Ecology considers organisms at the individual, population, community, ecosystem, and biosphere level. Ecology overl ...
.
Because it is readily accessible, and the Polish staffers are friendly,Society Expeditions, "Expedition Log, EX 1929", Seattle: Society Expeditions, 1990, pp. 26-27 it is one of the most-visited scientific stations in Antarctica. The beaches near the station have numerous whale bones, relics of the time when the site was used to process whales killed nearby.
The station is near colonies of three different types of ''Pygoscelis
The genus ''Pygoscelis'' ("rump-legged") contains three living species of penguins collectively known as "brush-tailed penguins".
Taxonomy
Mitochondrial and nuclear DNA evidence suggests the genus split from other penguins around 38 millio ...
'' penguins ( Adelies, chinstraps, and gentoos), and has been designated a site of Special Scientific Interest (SSI) as provided by the Antarctic Treaty
russian: link=no, Договор об Антарктике es, link=no, Tratado Antártico
, name = Antarctic Treaty System
, image = Flag of the Antarctic Treaty.svgborder
, image_width = 180px
, caption ...
.
Historic site
The grave of Polish wildlife photographer Włodzimierz Puchalski, surmounted by an iron cross, stands on a hill to the south of the station. Puchalski died on 19 January 1979 in the course of filming a nature documentary in the vicinity of the station. The location of the grave and cross has been designated a Historic Site or Monument (HSM 51), following a proposal by Poland to the Antarctic Treaty Consultative Meeting.See also
* List of Antarctic research stations *List of Antarctic field camps
Many Antarctic research stations support satellite field camps which are, in general, seasonal camps. The type of field camp can vary – some are permanent structures used during the annual Antarctic summer, whereas others are little more than te ...
* A.B. Dobrowolski Polar Station
A.B. Dobrowolski Polar Station ( pl, Stacja im. A.B. Dobrowolskiego) is an occasionally active Polish polar research station in Antarctica. It is located at the edge of the Algae Lake, Bunger Hills region in the Wilkes Land and was originally c ...
References
Further reading
* ''Antarctica''. Sydney:Reader's Digest
''Reader's Digest'' is an American general-interest family magazine, published ten times a year. Formerly based in Chappaqua, New York, it is now headquartered in midtown Manhattan. The magazine was founded in 1922 by DeWitt Wallace and his wif ...
, 1985, pp. 130–133, 300.
* Child, Jack. ''Antarctica and South American Geopolitics: Frozen Lebensraum''. New York: Praeger Publishers
Greenwood Publishing Group, Inc. (GPG), also known as ABC-Clio/Greenwood (stylized ABC-CLIO/Greenwood), is an educational and academic publisher (middle school through university level) which is today part of ABC-Clio. Established in 1967 as Gr ...
, 1988, p. 12.
* Lonely Planet
Lonely Planet is a travel guide book publisher. Founded in Australia in 1973, the company has printed over 150 million books.
History Early years
Lonely Planet was founded by married couple Maureen and Tony Wheeler. In 1972, they embarke ...
, ''Antarctica: a Lonely Planet Travel Survival Kit'', Oakland, CA: Lonely Planet Publications, 1996, p. 273.
* Stewart, Andrew, ''Antarctica: An Encyclopedia''. London: McFarland & Company, 1990 (2 volumes, p. 37.
* U.S. National Science Foundation, ''Geographic Names of the Antarctic'', Fred G. Alberts, ed. Washington: NSF, 1980.
External links
*COMNAP Antarctic Facilities
COMNAP Antarctic Facilities Map

 {{Authority control , additional=Q106092540
Arctowski
Poland and the Antarctic
Research institutes established in 1977
Historic Sites and Monuments of Antarctica
Lighthouses in Antarctica
1977 establishments in Antarctica
King George Island (South Shetland Islands)
{{Authority control , additional=Q106092540
Arctowski
Poland and the Antarctic
Research institutes established in 1977
Historic Sites and Monuments of Antarctica
Lighthouses in Antarctica
1977 establishments in Antarctica
King George Island (South Shetland Islands)