Hands On Miami on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
A hand is a
 Areas of the human hand include:
* The ''palm'' (Volar), which is the central region of the anterior part of the hand, located superficially to the metacarpus. The skin in this area contains
Areas of the human hand include:
* The ''palm'' (Volar), which is the central region of the anterior part of the hand, located superficially to the metacarpus. The skin in this area contains


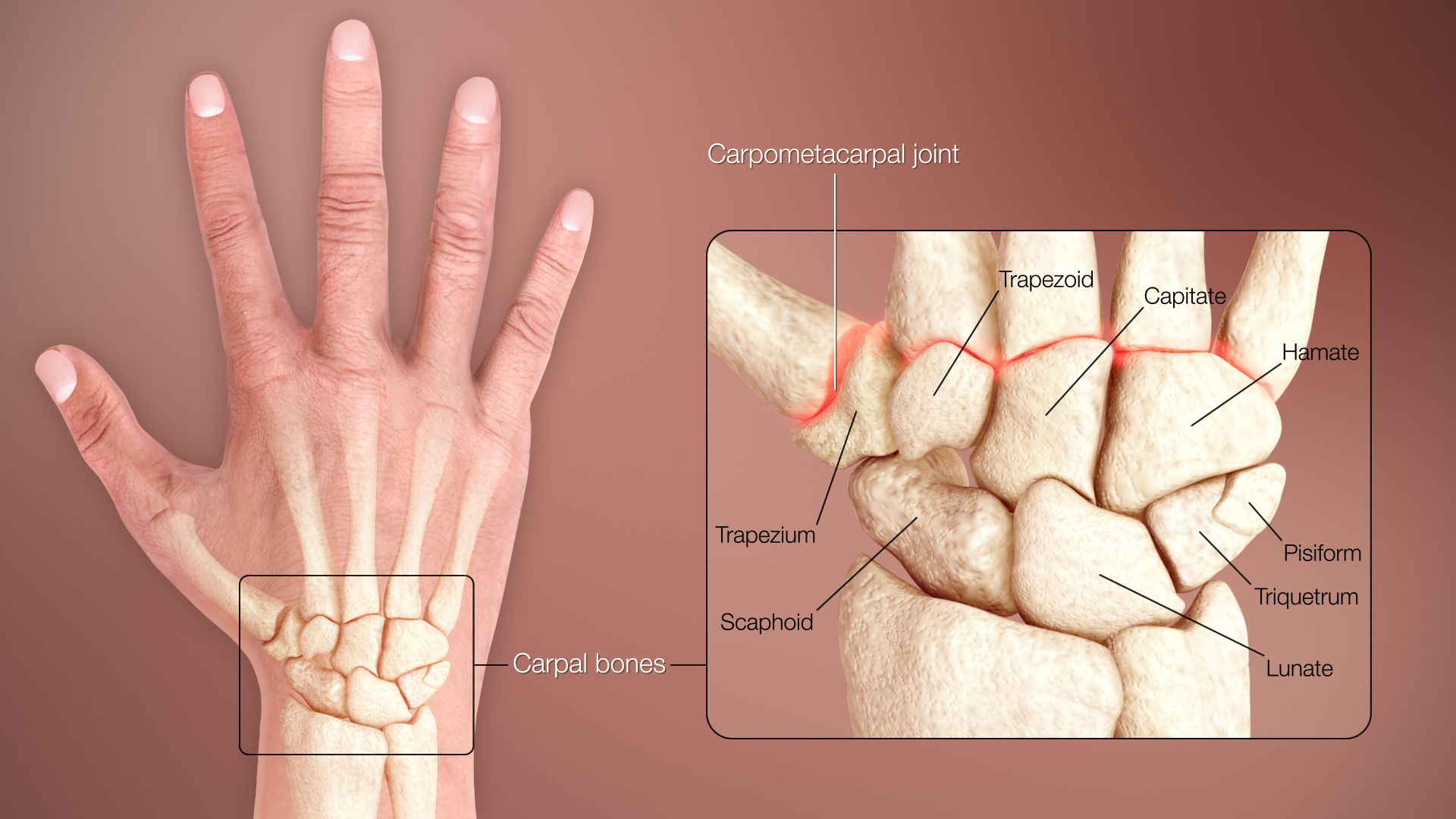 The skeleton of the human hand consists of 27 bones: the eight short carpal bones of the
The skeleton of the human hand consists of 27 bones: the eight short carpal bones of the
 The fixed and mobile parts of the hand adapt to various everyday tasks by forming bony arches: longitudinal arches (the rays formed by the finger bones and their associated metacarpal bones), transverse arches (formed by the carpal bones and distal ends of the metacarpal bones), and oblique arches (between the thumb and four fingers):
Of the longitudinal arches or rays of the hand, that of the thumb is the most mobile (and the least longitudinal). While the ray formed by the little finger and its associated metacarpal bone still offers some mobility, the remaining rays are firmly rigid. The phalangeal joints of the index finger, however, offer some independence to its finger, due to the arrangement of its flexor and extension tendons.
The carpal bones form two transversal rows, each forming an arch concave on the palmar side. Because the proximal arch simultaneously has to adapt to the articular surface of the radius and to the distal carpal row, it is by necessity flexible. In contrast, the capitate, the "keystone" of the distal arch, moves together with the metacarpal bones and the distal arch is therefore rigid. The stability of these arches is more dependent of the ligaments and capsules of the wrist than of the interlocking shapes of the carpal bones, and the wrist is therefore more stable in flexion than in extension. The distal carpal arch affects the function of the CMC joints and the hands, but not the function of the wrist or the proximal carpal arch. The ligaments that maintain the distal carpal arches are the
The fixed and mobile parts of the hand adapt to various everyday tasks by forming bony arches: longitudinal arches (the rays formed by the finger bones and their associated metacarpal bones), transverse arches (formed by the carpal bones and distal ends of the metacarpal bones), and oblique arches (between the thumb and four fingers):
Of the longitudinal arches or rays of the hand, that of the thumb is the most mobile (and the least longitudinal). While the ray formed by the little finger and its associated metacarpal bone still offers some mobility, the remaining rays are firmly rigid. The phalangeal joints of the index finger, however, offer some independence to its finger, due to the arrangement of its flexor and extension tendons.
The carpal bones form two transversal rows, each forming an arch concave on the palmar side. Because the proximal arch simultaneously has to adapt to the articular surface of the radius and to the distal carpal row, it is by necessity flexible. In contrast, the capitate, the "keystone" of the distal arch, moves together with the metacarpal bones and the distal arch is therefore rigid. The stability of these arches is more dependent of the ligaments and capsules of the wrist than of the interlocking shapes of the carpal bones, and the wrist is therefore more stable in flexion than in extension. The distal carpal arch affects the function of the CMC joints and the hands, but not the function of the wrist or the proximal carpal arch. The ligaments that maintain the distal carpal arches are the
 The muscles acting on the hand can be subdivided into two groups: the extrinsic and intrinsic muscle groups. The extrinsic muscle groups are the long flexors and extensors. They are called extrinsic because the muscle belly is located on the forearm.
The muscles acting on the hand can be subdivided into two groups: the extrinsic and intrinsic muscle groups. The extrinsic muscle groups are the long flexors and extensors. They are called extrinsic because the muscle belly is located on the forearm.
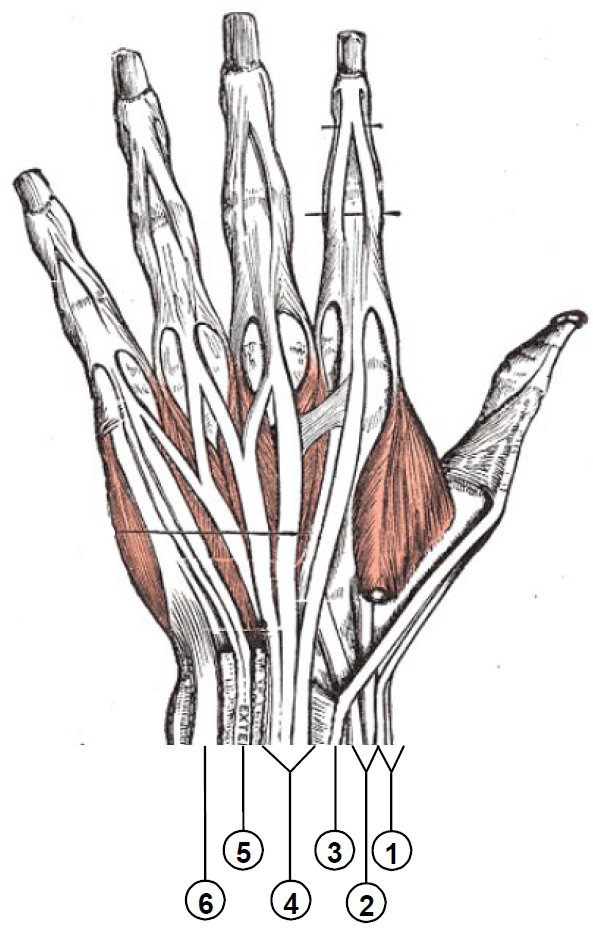 The fingers have two long flexors, located on the underside of the forearm. They insert by tendons to the phalanges of the fingers. The deep flexor attaches to the distal phalanx, and the superficial flexor attaches to the middle phalanx. The flexors allow for the actual bending of the fingers. The thumb has one long flexor and a short flexor in the thenar muscle group. The human thumb also has other muscles in the thenar group ( opponens and abductor brevis muscle), moving the thumb in opposition, making grasping possible.
The extensors are located on the back of the forearm and are connected in a more complex way than the flexors to the dorsum of the fingers. The tendons unite with the interosseous and lumbrical muscles to form the extensorhood mechanism. The primary function of the extensors is to straighten out the digits. The thumb has two extensors in the forearm; the tendons of these form the
The fingers have two long flexors, located on the underside of the forearm. They insert by tendons to the phalanges of the fingers. The deep flexor attaches to the distal phalanx, and the superficial flexor attaches to the middle phalanx. The flexors allow for the actual bending of the fingers. The thumb has one long flexor and a short flexor in the thenar muscle group. The human thumb also has other muscles in the thenar group ( opponens and abductor brevis muscle), moving the thumb in opposition, making grasping possible.
The extensors are located on the back of the forearm and are connected in a more complex way than the flexors to the dorsum of the fingers. The tendons unite with the interosseous and lumbrical muscles to form the extensorhood mechanism. The primary function of the extensors is to straighten out the digits. The thumb has two extensors in the forearm; the tendons of these form the
 The hand is innervated by the
The hand is innervated by the
 The hand is supplied with blood from two arteries, the
The hand is supplied with blood from two arteries, the
 The
The
File:Blausen 0440 HandBones.png, Illustration of hand and wrist bones
File:Gray219.png, Bones of the left hand. Volar surface.
File:Gray220.png, Bones of the left hand. Dorsal surface.
File:HandAnthropometry.JPG, Static adult human physical characteristics of the hand
File:814 Radiograph of Hand.jpg, X-ray showing joints
File:Hand Bone Anatomy by Jason Christian.webm, Hand bone anatomy
Hand anatomy (eMedicine)
Film Board of Canada documentary ''Faces of the Hand''
"The Common Hand"
article in the May 2012 '' National Geographic'' {{Authority control Upper limb anatomy
prehensile
Prehensility is the quality of an appendage or organ that has adapted for grasping or holding. The word is derived from the Latin term ''prehendere'', meaning "to grasp". The ability to grasp is likely derived from a number of different orig ...
, multi-finger
A finger is a limb of the body and a type of digit, an organ of manipulation and sensation found in the hands of most of the Tetrapods, so also with humans and other primates. Most land vertebrates have five fingers ( Pentadactyly). Chambers ...
ed appendage located at the end of the forearm
The forearm is the region of the upper limb between the elbow and the wrist. The term forearm is used in anatomy to distinguish it from the arm, a word which is most often used to describe the entire appendage of the upper limb, but which in ...
or forelimb of primate
Primates are a diverse order of mammals. They are divided into the strepsirrhines, which include the lemurs, galagos, and lorisids, and the haplorhines, which include the tarsiers and the simians ( monkeys and apes, the latter including ...
s such as human
Humans (''Homo sapiens'') are the most abundant and widespread species of primate, characterized by bipedalism and exceptional cognitive skills due to a large and complex brain. This has enabled the development of advanced tools, cultu ...
s, chimpanzees, monkeys, and lemur
Lemurs ( ) (from Latin ''lemures'' – ghosts or spirits) are wet-nosed primates of the superfamily Lemuroidea (), divided into 8 families and consisting of 15 genera and around 100 existing species. They are endemic to the island of Madagas ...
s. A few other vertebrate
Vertebrates () comprise all animal taxa within the subphylum Vertebrata () (chordates with backbones), including all mammals, birds, reptiles, amphibians, and fish. Vertebrates represent the overwhelming majority of the phylum Chordata, with c ...
s such as the koala
The koala or, inaccurately, koala bear (''Phascolarctos cinereus''), is an arboreal herbivorous marsupial native to Australia. It is the only extant representative of the family Phascolarctidae and its closest living relatives are the w ...
(which has two opposable thumbs on each "hand" and fingerprints extremely similar to human fingerprint
A fingerprint is an impression left by the friction ridges of a human finger. The recovery of partial fingerprints from a crime scene is an important method of forensic science. Moisture and grease on a finger result in fingerprints on surfac ...
s) are often described as having "hands" instead of paw
A paw is the soft foot-like part of a mammal, generally a quadruped, that has claws.
Common characteristics
The paw is characterised by thin, pigmented, keratinised, hairless epidermis covering subcutaneous collagenous and adipose tissue, ...
s on their front limbs. The raccoon
The raccoon ( or , ''Procyon lotor''), sometimes called the common raccoon to distinguish it from other species, is a mammal native to North America. It is the largest of the procyonid family, having a body length of , and a body weight of ...
is usually described as having "hands" though opposable thumbs are lacking.
Some evolutionary anatomist
Anatomy () is the branch of biology concerned with the study of the structure of organisms and their parts. Anatomy is a branch of natural science that deals with the structural organization of living things. It is an old science, having it ...
s use the term ''hand'' to refer to the appendage of digits on the forelimb more generally—for example, in the context of whether the three digits of the bird
Birds are a group of warm-blooded vertebrates constituting the class Aves (), characterised by feathers, toothless beaked jaws, the laying of hard-shelled eggs, a high metabolic rate, a four-chambered heart, and a strong yet lightweig ...
hand involved the same homologous loss of two digits as in the dinosaur
Dinosaurs are a diverse group of reptiles of the clade Dinosauria. They first appeared during the Triassic period, between 243 and 233.23 million years ago (mya), although the exact origin and timing of the evolution of dinosaurs is t ...
hand.
The human hand usually has five digits: four finger
A finger is a limb of the body and a type of digit, an organ of manipulation and sensation found in the hands of most of the Tetrapods, so also with humans and other primates. Most land vertebrates have five fingers ( Pentadactyly). Chambers ...
s plus one thumb; these are often referred to collectively as five fingers, however, whereby the thumb is included as one of the fingers. It has 27 bones, not including the sesamoid bone, the number of which varies among people, 14 of which are the phalanges (proximal
Standard anatomical terms of location are used to unambiguously describe the anatomy of animals, including humans. The terms, typically derived from Latin or Greek roots, describe something in its standard anatomical position. This position pro ...
, intermediate and distal) of the fingers and thumb. The metacarpal bones connect the fingers and the carpal bones of the wrist
In human anatomy, the wrist is variously defined as (1) the carpus or carpal bones, the complex of eight bones forming the proximal skeletal segment of the hand; "The wrist contains eight bones, roughly aligned in two rows, known as the carp ...
. Each human hand has five metacarpals
In human anatomy, the metacarpal bones or metacarpus form the intermediate part of the skeletal hand located between the phalanges of the fingers and the carpal bones of the wrist, which forms the connection to the forearm. The metacarpal bones ar ...
and eight carpal bones.
Fingers contain some of the densest areas of nerve endings in the body, and are the richest source of tactile
Tactile may refer to:
* Tactile, related to the sense of touch
* Haptics (disambiguation)
* Tactile (device), a text-to-braille translation device
See also
* Tangibility, in law
* Somatosensory system, where sensations are processed
* CD96
CD ...
feedback. They also have the greatest positioning capability of the body; thus, the sense of touch
In physiology, the somatosensory system is the network of neural structures in the brain and body that produce the perception of touch ( haptic perception), as well as temperature ( thermoception), body position (proprioception), and pain. It ...
is intimately associated with hands. Like other paired organs (eyes, feet, legs) each hand is dominantly controlled by the opposing brain hemisphere
The vertebrate cerebrum (brain) is formed by two cerebral hemispheres that are separated by a groove, the longitudinal fissure. The brain can thus be described as being divided into left and right cerebral hemispheres. Each of these hemispheres ...
, so that handedness—the preferred hand choice for single-handed activities such as writing with a pencil, reflects individual brain functioning.
Among humans, the hands play an important function in body language
Body language is a type of communication in which physical behaviors, as opposed to words, are used to express or convey information. Such behavior includes facial expressions, body posture, gestures, eye movement, touch and the use of space. Th ...
and sign language
Sign languages (also known as signed languages) are languages that use the visual-manual modality to convey meaning, instead of spoken words. Sign languages are expressed through manual articulation in combination with non-manual markers. Sign l ...
. Likewise, the ten digits of two hands and the twelve phalanges of four fingers (touchable by the thumb) have given rise to number systems and calculation techniques.
Structure
Many mammals and otheranimal
Animals are multicellular, eukaryotic organisms in the Kingdom (biology), biological kingdom Animalia. With few exceptions, animals Heterotroph, consume organic material, Cellular respiration#Aerobic respiration, breathe oxygen, are Motilit ...
s have grasping appendages similar in form to a hand such as paw
A paw is the soft foot-like part of a mammal, generally a quadruped, that has claws.
Common characteristics
The paw is characterised by thin, pigmented, keratinised, hairless epidermis covering subcutaneous collagenous and adipose tissue, ...
s, claw
A claw is a curved, pointed appendage found at the end of a toe or finger in most amniotes (mammals, reptiles, birds). Some invertebrates such as beetles and spiders have somewhat similar fine, hooked structures at the end of the leg or tarsus ...
s, and talons, but these are not scientifically considered to be grasping hands. The scientific use of the term ''hand'' in this sense to distinguish the terminations of the front paws from the hind ones is an example of anthropomorphism. The only true grasping hands appear in the mammalian order of primates. Hands must also have opposable thumbs, as described later in the text.
The hand is located at the distal end of each arm. Ape
Apes (collectively Hominoidea ) are a clade of Old World simians native to sub-Saharan Africa and Southeast Asia (though they were more widespread in Africa, most of Asia, and as well as Europe in prehistory), which together with its sister g ...
s and monkeys are sometimes described as having four hands, because the toes are long and the hallux
Toes are the digits (fingers) of the foot of a tetrapod. Animal species such as cats that walk on their toes are described as being '' digitigrade''. Humans, and other animals that walk on the soles of their feet, are described as being '' pl ...
is opposable and looks more like a thumb, thus enabling the feet to be used as hands.
The word "hand" is sometimes used by evolutionary anatomists to refer to the appendage of digits on the forelimb such as when researching the homology between the three digits of the bird
Birds are a group of warm-blooded vertebrates constituting the class Aves (), characterised by feathers, toothless beaked jaws, the laying of hard-shelled eggs, a high metabolic rate, a four-chambered heart, and a strong yet lightweig ...
hand and the dinosaur
Dinosaurs are a diverse group of reptiles of the clade Dinosauria. They first appeared during the Triassic period, between 243 and 233.23 million years ago (mya), although the exact origin and timing of the evolution of dinosaurs is t ...
hand.
An adult human male's hand weighs about a pound.
Areas
dermal papillae
The dermis or corium is a layer of skin between the epidermis (with which it makes up the cutis) and subcutaneous tissues, that primarily consists of dense irregular connective tissue and cushions the body from stress and strain. It is divided in ...
to increase friction, such as are also present on the fingers and used for fingerprint
A fingerprint is an impression left by the friction ridges of a human finger. The recovery of partial fingerprints from a crime scene is an important method of forensic science. Moisture and grease on a finger result in fingerprints on surfac ...
s.
* The ''opisthenar'' area (dorsal) is the corresponding area on the posterior part of the hand.
* The ''heel of the hand'' is the area anteriorly to the bases of the metacarpal bones, located in the proximal part of the palm. It is the area that sustains most pressure when using the palm of the hand for support, such as in handstand
__NOTOC__
A handstand is the act of supporting the body in a stable, inverted vertical position by balancing on the hands. In a basic handstand, the body is held straight with arms and legs fully extended, with hands spaced approximately shoulder- ...
.
There are five digits attached to the hand, notably with a nail
Nail or Nails may refer to:
In biology
* Nail (anatomy), toughened protective protein-keratin (known as alpha-keratin, also found in hair) at the end of an animal digit, such as fingernail
* Nail (beak), a plate of hard horny tissue at the tip ...
fixed to the end in place of the normal claw
A claw is a curved, pointed appendage found at the end of a toe or finger in most amniotes (mammals, reptiles, birds). Some invertebrates such as beetles and spiders have somewhat similar fine, hooked structures at the end of the leg or tarsus ...
. The four finger
A finger is a limb of the body and a type of digit, an organ of manipulation and sensation found in the hands of most of the Tetrapods, so also with humans and other primates. Most land vertebrates have five fingers ( Pentadactyly). Chambers ...
s can be folded over the palm which allows the grasping of objects. Each finger, starting with the one closest to the thumb, has a colloquial name to distinguish it from the others:
* index finger
The index finger (also referred to as forefinger, first finger, second finger, pointer finger, trigger finger, digitus secundus, digitus II, and many other terms) is the second digit of a human hand. It is located between the thumb and the mid ...
, pointer finger, forefinger, or 2nd digit
* middle finger
The middle finger, long finger, second finger, third finger, toll finger or tall man is the third digit of the human hand, located between the index finger and the ring finger. It is typically the longest digit. In anatomy, it is also calle ...
or long finger or 3rd digit
* ring finger
The ring finger, third finger, fourth finger, leech finger, or annulary is the fourth digit of the human hand, located between the middle finger and the little finger.
Sometimes the term ring finger only refers to the fourth digit of a left-han ...
or 4th digit
* little finger
The little finger, or pinkie, also known as the baby finger, fifth digit, or pinky finger, is the most ulnar and smallest digit of the human hand, and next to the ring finger.
Etymology
The word "pinkie" is derived from the Dutch word ''p ...
, pinky finger, small finger, baby finger, or 5th digit
The thumb (connected to the first metacarpal bone
The first metacarpal bone or the metacarpal bone of the thumb is the first bone proximal to the thumb. It is connected to the trapezium of the carpus at the first carpometacarpal joint and to the proximal thumb phalanx at the first metacarpophal ...
and trapezium) is located on one of the sides, parallel to the arm. A reliable way of identifying human hands is from the presence of opposable thumbs. Opposable thumbs are identified by the ability to be brought opposite to the fingers, a muscle action known as opposition.
Bones

 The skeleton of the human hand consists of 27 bones: the eight short carpal bones of the
The skeleton of the human hand consists of 27 bones: the eight short carpal bones of the wrist
In human anatomy, the wrist is variously defined as (1) the carpus or carpal bones, the complex of eight bones forming the proximal skeletal segment of the hand; "The wrist contains eight bones, roughly aligned in two rows, known as the carp ...
are organized into a proximal row (scaphoid
The scaphoid bone is one of the carpal bones of the wrist. It is situated between the hand and forearm on the thumb side of the wrist (also called the lateral or radial side). It forms the radial border of the carpal tunnel. The scaphoid bone i ...
, lunate
Lunate is a crescent or moon-shaped microlith. In the specialized terminology of lithic reduction, a lunate flake is a small, crescent-shaped flake removed from a stone tool during the process of pressure flaking.
In the Natufian period, a lun ...
, triquetral
The triquetral bone (; also called triquetrum, pyramidal, three-faced, and formerly cuneiform bone) is located in the wrist on the medial side of the proximal row of the carpus between the lunate and pisiform bones. It is on the ulnar side of the ...
and pisiform
The pisiform bone ( or ), also spelled pisiforme (from the Latin ''pisifomis'', pea-shaped), is a small knobbly, sesamoid bone that is found in the wrist. It forms the ulnar border of the carpal tunnel.
Structure
The pisiform is a sesamoid bone, ...
) which articulates with the bones of the forearm, and a distal row ( trapezium, trapezoid
A quadrilateral with at least one pair of parallel sides is called a trapezoid () in American and Canadian English. In British and other forms of English, it is called a trapezium ().
A trapezoid is necessarily a convex quadrilateral in Eu ...
, capitate
The capitate bone is a bone in the human wrist found in the center of the carpal bone region, located at the distal end of the radius and ulna bones. It articulates with the third metacarpal bone (the middle finger) and forms the third carpomet ...
and hamate
The hamate bone (from Latin hamatus, "hooked"), or unciform bone (from Latin ''uncus'', "hook"), Latin os hamatum and occasionally abbreviated as just hamatum, is a bone in the human wrist readily distinguishable by its wedge shape and a hook-l ...
), which articulates with the bases of the five metacarpal bones of the hand. The heads of the metacarpals will each in turn articulate with the bases of the proximal phalanx
The phalanx ( grc, φάλαγξ; plural phalanxes or phalanges, , ) was a rectangular mass military formation, usually composed entirely of heavy infantry armed with spears, pikes, sarissas, or similar pole weapons. The term is particularly ...
of the fingers and thumb. These articulations with the fingers are the metacarpophalangeal joints
The metacarpophalangeal joints (MCP) are situated between the metacarpal bones and the proximal phalanges of the fingers. These joints are of the condyloid kind, formed by the reception of the rounded heads of the metacarpal bones into shallow ca ...
known as the knuckles. At the palmar aspect of the first metacarpophalangeal joints are small, almost spherical bones called the sesamoid bones. The fourteen phalanges make up the fingers and thumb, and are numbered I-V (thumb to little finger) when the hand is viewed from an anatomical position (palm up). The four fingers each consist of three phalanx bones: proximal, middle, and distal. The thumb only consists of a proximal and distal phalanx.Saladin, Kenneth S. (2007) ''Anatomy & Physiology: The Unity of Form and Function''. New York, NY: McGraw-Hill. Together with the phalanges of the fingers and thumb these metacarpal bones form five rays or poly-articulated chains.
Because supination and pronation (rotation about the axis of the forearm) are added to the two axes of movements of the wrist, the ulna
The ulna (''pl''. ulnae or ulnas) is a long bone found in the forearm that stretches from the elbow to the smallest finger, and when in anatomical position, is found on the medial side of the forearm. That is, the ulna is on the same side of t ...
and radius
In classical geometry, a radius ( : radii) of a circle or sphere is any of the line segments from its center to its perimeter, and in more modern usage, it is also their length. The name comes from the latin ''radius'', meaning ray but also the ...
are sometimes considered part of the skeleton of the hand.
There are numerous sesamoid bones in the hand, small ossified
Ossification (also called osteogenesis or bone mineralization) in bone remodeling is the process of laying down new bone material by cells named osteoblasts. It is synonymous with bone tissue formation. There are two processes resulting in t ...
nodes embedded in tendons; the exact number varies between people: whereas a pair of sesamoid bones are found at virtually all thumb metacarpophalangeal joints, sesamoid bones are also common at the interphalangeal joint of the thumb (72.9%) and at the metacarpophalangeal joints of the little finger (82.5%) and the index finger (48%). In rare cases, sesamoid bones have been found in all the metacarpophalangeal joints and all distal interphalangeal joints except that of the long finger.
The articulations are:
*interphalangeal articulations of hand
The interphalangeal joints of the hand are the hinge joints between the phalanges of the fingers that provide flexion towards the palm of the hand.
There are two sets in each finger (except in the thumb, which has only one joint):
* "proximal in ...
(the hinge joints between the bones of the digits)
*metacarpophalangeal joint
The metacarpophalangeal joints (MCP) are situated between the metacarpal bones and the proximal phalanges of the fingers. These joints are of the condyloid kind, formed by the reception of the rounded heads of the metacarpal bones into shallow ca ...
s (where the digits meet the palm)
*intercarpal articulations
The intercarpal joints (joints of the carpal bones of the wrist) can be subdivided into three sets of joints (also called ''articulations''): Those of the proximal row of carpal bones, those of the distal row of carpal bones, and those of the two ...
(where the palm meets the wrist)
*wrist
In human anatomy, the wrist is variously defined as (1) the carpus or carpal bones, the complex of eight bones forming the proximal skeletal segment of the hand; "The wrist contains eight bones, roughly aligned in two rows, known as the carp ...
(may also be viewed as belonging to the forearm
The forearm is the region of the upper limb between the elbow and the wrist. The term forearm is used in anatomy to distinguish it from the arm, a word which is most often used to describe the entire appendage of the upper limb, but which in ...
).
Arches
transverse carpal ligament
The flexor retinaculum (transverse carpal ligament, or anterior annular ligament) is a fibrous band on the palmar side of the hand near the wrist. It arches over the carpal bones of the hands, covering them and forming the carpal tunnel.
Structur ...
and the intercarpal ligaments (also oriented transversally). These ligaments also form the carpal tunnel
In the human body, the carpal tunnel or carpal canal is the passageway on the palmar side of the wrist that connects the forearm to the hand.
The tunnel is bounded by the bones of the wrist and flexor retinaculum from connective tissue. Norma ...
and contribute to the deep
Deep or The Deep may refer to:
Places United States
* Deep Creek (Appomattox River tributary), Virginia
* Deep Creek (Great Salt Lake), Idaho and Utah
* Deep Creek (Mahantango Creek tributary), Pennsylvania
* Deep Creek (Mojave River tributary), ...
and superficial palmar arches. Several muscle tendons attaching to the TCL and the distal carpals also contribute to maintaining the carpal arch.
Compared to the carpal arches, the arch formed by the distal ends of the metacarpal bones is flexible due to the mobility of the peripheral metacarpals (thumb and little finger). As these two metacarpals approach each other, the palmar gutter deepens. The central-most metacarpal (middle finger) is the most rigid. It and its two neighbors are tied to the carpus by the interlocking shapes of the metacarpal bones. The thumb metacarpal only articulates with the trapezium and is therefore completely independent, while the fifth metacarpal (little finger) is semi-independent with the fourth metacarpal (ring finger) which forms a transitional element to the fifth metacarpal.
Together with the thumb, the four fingers form four oblique arches, of which the arch of the index finger functionally is the most important, especially for precision grip, while the arch of the little finger contribute an important locking mechanism for power grip. The thumb is undoubtedly the "master digit" of the hand, giving value to all the other fingers. Together with the index and middle finger, it forms the dynamic tridactyl configuration responsible for most grips not requiring force. The ring and little fingers are more static, a reserve ready to interact with the palm when great force is needed.
Muscles
Intrinsic
The intrinsic muscle groups are the thenar (thumb) andhypothenar
The hypothenar muscles are a group of three muscles of the palm that control the motion of the little finger.
The three muscles are:
* Abductor digiti minimi
* Flexor digiti minimi brevis
* Opponens digiti minimi
Structure
The muscles of hypot ...
(little finger) muscles; the interosseous muscles ( four dorsally and three volarly) originating between the metacarpal bones; and the lumbrical muscles arising from the deep flexor (and are special because they have no bony origin) to insert on the dorsal extensor hood mechanism.
Extrinsic
anatomical snuff box
The anatomical snuff box or snuffbox or foveola radialis is a triangular deepening on the radial, dorsal aspect of the hand—at the level of the carpal bones, specifically, the scaphoid and trapezium bones forming the floor. The name originates ...
. Also, the index finger and the little finger have an extra extensor used, for instance, for pointing. The extensors are situated within 6 separate compartments.
The first four compartments are located in the grooves present on the dorsum of inferior side of radius while the 5th compartment is in between radius and ulna. The 6th compartment is in the groove on the dorsum of inferior side of ulna.
Nerve supply
radial
Radial is a geometric term of location which may refer to:
Mathematics and Direction
* Vector (geometric), a line
* Radius, adjective form of
* Radial distance, a directional coordinate in a polar coordinate system
* Radial set
* A bearing f ...
, median, and ulnar nerves.
; Motor
The radial nerve supplies the finger extensors and the thumb abductor, thus the muscles that extends at the wrist and metacarpophalangeal joints (knuckles); and that abducts and extends the thumb.
The median nerve supplies the flexors of the wrist and digits, the abductors and opponens of the thumb, the first and second lumbrical.
The ulnar nerve supplies the remaining intrinsic muscles of the hand.
All muscles of the hand are innervated by the brachial plexus
The brachial plexus is a network () of nerves formed by the anterior rami of the lower four cervical nerves and first thoracic nerve ( C5, C6, C7, C8, and T1). This plexus extends from the spinal cord, through the cervicoaxillary canal in t ...
(C5–T1) and can be classified by innervation:
; Sensory
The radial nerve supplies the skin on the back of the hand from the thumb to the ring finger and the dorsal aspects of the index, middle, and half ring fingers as far as the proximal interphalangeal joints.
The median nerve supplies the palmar side of the thumb, index, middle, and half ring fingers. Dorsal branches innervates the distal phalanges of the index, middle, and half ring fingers.
The ulnar nerve supplies the ulnar third of the hand, both at the palm and the back of the hand, and the little and half ring fingers.
There is a considerable variation to this general pattern, except for the little finger and volar surface of the index finger. For example, in some individuals, the ulnar nerve supplies the entire ring finger and the ulnar side of the middle finger, whilst, in others, the median nerve supplies the entire ring finger.
Blood supply
ulnar artery
The ulnar artery is the main blood vessel, with oxygenated blood, of the medial aspects of the forearm. It arises from the brachial artery and terminates in the superficial palmar arch, which joins with the superficial branch of the radial ar ...
and the radial artery
In human anatomy, the radial artery is the main artery of the lateral aspect of the forearm.
Structure
The radial artery arises from the bifurcation of the brachial artery in the antecubital fossa. It runs distally on the anterior part of th ...
. These arteries form three arches over the dorsal and palmar aspects of the hand, the dorsal carpal arch
The dorsal carpal arch (dorsal carpal network, posterior carpal arch) is an anatomical term for the combination ( anastomosis) of dorsal carpal branch of the radial artery and the dorsal carpal branch of the ulnar artery near the back of the wris ...
(across the back of the hand), the deep palmar arch, and the superficial palmar arch. Together these three arches and their anastomoses
An anastomosis (, plural anastomoses) is a connection or opening between two things (especially cavities or passages) that are normally diverging or branching, such as between blood vessels, leaf veins, or streams. Such a connection may be norm ...
provide oxygenated blood to the palm, the fingers, and the thumb.
The hand is drained by the dorsal venous network of the hand with deoxygenated blood leaving the hand via the cephalic vein
In human anatomy, the cephalic vein is a superficial vein in the arm. It originates from the radial end of the dorsal venous network of hand, and ascends along the radial (lateral) side of the arm before emptying into the axillary vein. At the e ...
and the basilic vein
The basilic vein is a large superficial vein of the upper limb that helps drain parts of the hand and forearm. It originates on the medial (ulnar) side of the dorsal venous network of the hand and travels up the base of the forearm, where its c ...
.
Skin
Theglabrous
Glabrousness (from the Latin '' glaber'' meaning "bald", "hairless", "shaved", "smooth") is the technical term for a lack of hair, down, setae, trichomes or other such covering. A glabrous surface may be a natural characteristic of all or part of ...
(hairless) skin on the front of the hand, the palm, is relatively thick and can be bent along the hand's flexure lines where the skin is tightly bound to the underlying tissue and bones. Compared to the rest of the body's skin, the hands' palms (as well as the soles of the feet
The foot ( : feet) is an anatomical structure found in many vertebrates. It is the terminal portion of a limb which bears weight and allows locomotion. In many animals with feet, the foot is a separate organ at the terminal part of the leg made ...
) are usually lighter—and even much lighter in dark-skinned individuals, compared to the other side of the hand. Indeed, genes specifically expressed in the dermis of palmoplantar skin inhibit melanin
Melanin (; from el, μέλας, melas, black, dark) is a broad term for a group of natural pigments found in most organisms. Eumelanin is produced through a multistage chemical process known as melanogenesis, where the oxidation of the amino ...
production and thus the ability to tan
Tan or TAN may refer to:
Businesses and organisations
* Black and Tans, a nickname for British special constables during the Irish War of Independence. By extension "Tans" can now also colloquially refer to English or British people in general, es ...
, and promote the thickening of the stratum lucidum
The stratum lucidum (Latin, 'clear layer') is a thin, clear layer of dead skin cells in the epidermis named for its translucent appearance under a microscope. It is readily visible by light microscopy only in areas of thick skin, which are found ...
and stratum corneum layers of the epidermis. All parts of the skin involved in grasping are covered by papillary ridges (fingerprint
A fingerprint is an impression left by the friction ridges of a human finger. The recovery of partial fingerprints from a crime scene is an important method of forensic science. Moisture and grease on a finger result in fingerprints on surfac ...
s) acting as friction pads. In contrast, the hairy skin on the dorsal side is thin, soft, and pliable, so that the skin can recoil when the fingers are stretched. On the dorsal side, the skin can be moved across the hand up to ; an important input the cutaneous mechanoreceptors.
The web of the hand is a "fold of skin which connects the digits". These webs, located between each set of digits, are known as skin folds (interdigital folds or plica interdigitalis). They are defined as "one of the folds of skin, or rudimentary web, between the fingers and toes".
Variation
The ratio of the length of the index finger to the length of the ring finger in adults is affected by the level of exposure to malesex hormones
Sex hormones, also known as sex steroids, gonadocorticoids and gonadal steroids, are steroid hormones that interact with vertebrate steroid hormone receptors. The sex hormones include the androgens, estrogens, and progestogens. Their effects a ...
of the embryo in utero
''In Utero'' is the third and final studio album by American rock band Nirvana. It was released on September 21, 1993, by DGC Records. After breaking into the mainstream with their second album, ''Nevermind'' (1991), Nirvana hired Steve Albin ...
. This digit ratio is below 1 for both sexes but it is lower in males than in females on average.
Clinical significance
A number ofgenetic disorder
A genetic disorder is a health problem caused by one or more abnormalities in the genome. It can be caused by a mutation in a single gene (monogenic) or multiple genes (polygenic) or by a chromosomal abnormality. Although polygenic disorders ...
s affect the hand. Polydactyly
Polydactyly or polydactylism (), also known as hyperdactyly, is an anomaly in humans and animals resulting in supernumerary fingers and/or toes. Polydactyly is the opposite of oligodactyly (fewer fingers or toes).
Signs and symptoms
In human ...
is the presence of more than the usual number of fingers. One of the disorders that can cause this is Catel-Manzke syndrome. The fingers may be fused in a disorder known as syndactyly
Syndactyly is a condition wherein two or more digits are fused together. It occurs normally in some mammals, such as the siamang and diprotodontia, but is an unusual condition in humans. The term is from Greek σύν, ''syn'' 'together' and δά� ...
. Or there may be an absence of one or more central fingers—a condition known as ectrodactyly
Ectrodactyly, split hand, or cleft hand (derived from Greek ''ektroma'' 'abortion' and ''daktylos'' 'finger') involves the deficiency or absence of one or more central digits of the hand or foot and is also known as split hand/split foot malformat ...
. Additionally, some people are born without one or both hands ( amelia). Hereditary multiple exostoses
Hereditary multiple osteochondromas (HMO), also known as hereditary multiple exostoses, is a disorder characterized by the development of multiple benign osteocartilaginous masses ( exostoses) in relation to the ends of long bones of the lower li ...
of the forearm—also known as hereditary multiple osteochondromas—is another cause of hand and forearm deformity in children and adults.
There are several cutaneous condition
A skin condition, also known as cutaneous condition, is any medical condition that affects the integumentary system—the organ system that encloses the body and includes skin, nails, and related muscle and glands. The major function of thi ...
s that can affect the hand including the nail
Nail or Nails may refer to:
In biology
* Nail (anatomy), toughened protective protein-keratin (known as alpha-keratin, also found in hair) at the end of an animal digit, such as fingernail
* Nail (beak), a plate of hard horny tissue at the tip ...
s.
The autoimmune disease rheumatoid arthritis
Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) is a long-term autoimmune disorder that primarily affects joints. It typically results in warm, swollen, and painful joints. Pain and stiffness often worsen following rest. Most commonly, the wrist and hands are invol ...
can affect the hand, particularly the joint
A joint or articulation (or articular surface) is the connection made between bones, ossicles, or other hard structures in the body which link an animal's skeletal system into a functional whole.Saladin, Ken. Anatomy & Physiology. 7th ed. McGraw- ...
s of the fingers.
Some conditions can be treated by hand surgery. These include carpal tunnel syndrome
Carpal tunnel syndrome (CTS) is the collection of symptoms and signs associated with median neuropathy at the carpal tunnel. Most CTS is related to idiopathic
An idiopathic disease is any disease with an unknown cause or mechanism of apparen ...
, a painful condition of the hand and fingers caused by compression of the median nerve
The median nerve is a nerve in humans and other animals in the upper limb. It is one of the five main nerves originating from the brachial plexus.
The median nerve originates from the lateral and medial cords of the brachial plexus, and has cont ...
, and Dupuytren's contracture
Dupuytren's contracture (also called Dupuytren's disease, Morbus Dupuytren, Viking disease, palmar fibromatosis and Celtic hand) is a condition in which one or more fingers become progressively bent in a flexed position. It is named after Guill ...
, a condition in which fingers bend towards the palm and cannot be straightened. Similarly, injury to the ulnar nerve may result in a condition in which some of the fingers cannot be flexed.
A common fracture of the hand is a scaphoid fracture
A scaphoid fracture is a break of the scaphoid bone in the wrist. Symptoms generally includes pain at the base of the thumb which is worse with use of the hand. The anatomic snuffbox is generally tender and swelling may occur. Complications may ...
—a fracture of the scaphoid bone
The scaphoid bone is one of the carpal bones of the wrist. It is situated between the hand and forearm on the thumb side of the wrist (also called the lateral or radial side). It forms the radial border of the carpal tunnel. The scaphoid bone is ...
, one of the carpal bones. This is the commonest carpal bone
The carpal bones are the eight small bones that make up the wrist (or carpus) that connects the hand to the forearm. The term "carpus" is derived from the Latin carpus and the Greek καρπός (karpós), meaning "wrist". In human anatomy, t ...
fracture and can be slow to heal due to a limited blood flow to the bone. There are various types of fracture to the base of the thumb; these are known as Rolando fractures, Bennet's fracture, and Gamekeeper's thumb. Another common fracture, known as Boxer's fracture, is to the neck of a metacarpal. One can also have a broken finger.
Evolution
 The
The prehensile
Prehensility is the quality of an appendage or organ that has adapted for grasping or holding. The word is derived from the Latin term ''prehendere'', meaning "to grasp". The ability to grasp is likely derived from a number of different orig ...
hands and feet of primate
Primates are a diverse order of mammals. They are divided into the strepsirrhines, which include the lemurs, galagos, and lorisids, and the haplorhines, which include the tarsiers and the simians ( monkeys and apes, the latter including ...
s evolved
Evolution is change in the heritable characteristics of biological populations over successive generations. These characteristics are the expressions of genes, which are passed on from parent to offspring during reproduction. Variation ...
from the mobile hands of semi-arboreal
Arboreal locomotion is the locomotion of animals in trees. In habitats in which trees are present, animals have evolved to move in them. Some animals may scale trees only occasionally, but others are exclusively arboreal. The habitats pose nu ...
tree shrew
The treeshrews (or tree shrews or banxrings) are small mammals native to the tropical forests of South and Southeast Asia. They make up the entire order Scandentia, which split into two families: the Tupaiidae (19 species, "ordinary" treeshrews ...
s that lived about . This development has been accompanied by important changes in the brain and the relocation of the eyes to the front of the face, together allowing the muscle control and stereoscopic vision
Stereopsis () is the component of depth perception retrieved through binocular vision.
Stereopsis is not the only contributor to depth perception, but it is a major one. Binocular vision happens because each eye receives a different image becaus ...
necessary for controlled grasping. This grasping, also known as power grip, is supplemented by the precision grip between the thumb and the distal finger pads made possible by the opposable thumbs. '' Hominidae'' (great apes including humans) acquired an erect bipedal
Bipedalism is a form of terrestrial locomotion where an organism moves by means of its two rear limbs or legs. An animal or machine that usually moves in a bipedal manner is known as a biped , meaning 'two feet' (from Latin ''bis'' 'double' ...
posture about , which freed the hands from the task of locomotion and paved the way for the precision and range of motion in human hands. Functional analyses of the features unique to the hand of modern humans have shown that they are consistent with the stresses and requirements associated with the effective use of paleolithic stone tools. It is possible that the refinement of the bipedal posture in the earliest hominids evolved to facilitate the use of the trunk as leverage in accelerating the hand.
While the human hand has unique anatomical features, including a longer thumb and fingers that can be controlled individually to a higher degree, the hands of other primates are anatomically similar and the dexterity of the human hand can not be explained solely on anatomical factors. The neural machinery underlying hand movements is a major contributing factor; primates have evolved direct connections between neurons in cortical motor areas and spinal motoneuron
A motor neuron (or motoneuron or efferent neuron) is a neuron whose cell body is located in the motor cortex, brainstem or the spinal cord, and whose axon (fiber) projects to the spinal cord or outside of the spinal cord to directly or indirectly ...
s, giving the cerebral cortex monosynaptic control over the motoneurons of the hand muscles; placing the hands "closer" to the brain. The recent evolution of the human hand is thus a direct result of the development of the central nervous system
The central nervous system (CNS) is the part of the nervous system consisting primarily of the brain and spinal cord. The CNS is so named because the brain integrates the received information and coordinates and influences the activity of all p ...
, and the hand, therefore, is a direct tool of our consciousness—the main source of differentiated tactile sensations—and a precise working organ enabling gestures—the expressions of our personalities.
There are nevertheless several primitive features left in the human hand, including pentadactyly (having five fingers), the hairless skin of the palm and fingers, and the ''os centrale
An accessory bone or supernumerary bone is a bone that is not normally present in the body, but can be found as a anatomical variation, variant in a significant number of people. It poses a risk of being misdiagnosis, misdiagnosed as bone fracture ...
'' found in human embryos, prosimians, and apes. Furthermore, the precursors of the intrinsic muscles of the hand are present in the earliest fishes, reflecting that the hand evolved from the pectoral fin and thus is much older than the arm in evolutionary terms.
The proportions of the human hand are plesiomorphic (shared by both ancestors and extant primate species); the elongated thumbs and short hands more closely resemble the hand proportions of Miocene
The Miocene ( ) is the first epoch (geology), geological epoch of the Neogene Period and extends from about (Ma). The Miocene was named by Scottish geologist Charles Lyell; the name comes from the Greek words (', "less") and (', "new") and mea ...
apes than those of extant primates. Humans did not evolve from knuckle-walking apes, and chimpanzees and gorilla
Gorillas are herbivorous, predominantly ground-dwelling great apes that inhabit the tropical forests of equatorial Africa. The genus ''Gorilla'' is divided into two species: the eastern gorilla and the western gorilla, and either four or fi ...
s independently acquired elongated metacarpals as part of their adaptation to their modes of locomotion. Several primitive hand features most likely present in the chimpanzee-human last common ancestor (CHLCA) and absent in modern humans are still present in the hands of ''Australopithecus
''Australopithecus'' (, ; ) is a genus of early hominins that existed in Africa during the Late Pliocene and Early Pleistocene. The genus ''Homo'' (which includes modern humans) emerged within ''Australopithecus'', as sister to e.g. ''Austral ...
'', '' Paranthropus'', and ''Homo floresiensis
''Homo floresiensis'' also known as "Flores Man"; nicknamed "Hobbit") is an extinct species of small archaic human that inhabited the island of Flores, Indonesia, until the arrival of modern humans about 50,000 years ago.
The remains of an in ...
''. This suggests that the derived changes in modern humans and Neanderthal
Neanderthals (, also ''Homo neanderthalensis'' and erroneously ''Homo sapiens neanderthalensis''), also written as Neandertals, are an extinct species or subspecies of archaic humans who lived in Eurasia until about 40,000 years ago. While the ...
s did not evolve until or after the appearance of the earliest Acheulian stone tools, and that these changes are associated with tool-related tasks beyond those observed in other hominins. The thumbs of ''Ardipithecus ramidus
''Ardipithecus ramidus'' is a species of australopithecine from the Afar region of Early Pliocene Ethiopia 4.4 million years ago (mya). ''A. ramidus'', unlike modern hominids, has adaptations for both walking on two legs ( bipedality) and life i ...
'', an early hominin, are almost as robust as in humans, so this may be a primitive trait, while the palms of other extant higher primates are elongated to the extent that some of the thumb's original function has been lost (most notably in highly arboreal primates such as the spider monkey
Spider monkeys are New World monkeys belonging to the genus ''Ateles'', part of the subfamily Atelinae, family Atelidae. Like other atelines, they are found in tropical forests of Central and South America, from southern Mexico to Brazil. The ...
). In humans, the big toe
Toes are the digits (fingers) of the foot of a tetrapod. Animal species such as cats that walk on their toes are described as being '' digitigrade''. Humans, and other animals that walk on the soles of their feet, are described as being '' pl ...
is thus more derived than the thumb.
There is a hypothesis suggesting the form of the modern human hand is especially conducive to the formation of a compact fist, presumably for fighting purposes. The fist is compact and thus effective as a weapon. It also provides protection for the fingers. However, this is not widely accepted to be one of the primary selective pressures acting on hand morphology throughout human evolution, with tool use and production being thought to be far more influential.
Additional images
See also
* Dactylonomy *Dermatoglyphics
Dermatoglyphics (from Ancient Greek ''derma'', "skin", and ''glyph'', "carving") is the scientific study of fingerprints, lines, mounts and shapes of hands, as distinct from the superficially similar pseudoscience of palmistry.
Dermatoglyphics a ...
* Finger-counting
Finger-counting, also known as dactylonomy, is the act of counting using one's fingers. There are multiple different systems used across time and between cultures, though many of these have seen a decline in use because of the spread of Arabic n ...
* Finger tracking
In the field of gesture recognition and image processing, finger tracking is a high-resolution technique developed in 1969 that is employed to know the consecutive position of the fingers of the user and hence represent objects in 3D.
In additio ...
* Handstand
__NOTOC__
A handstand is the act of supporting the body in a stable, inverted vertical position by balancing on the hands. In a basic handstand, the body is held straight with arms and legs fully extended, with hands spaced approximately shoulder- ...
* Hand strength
* Hand walking
Hand walking is an unusual form of human locomotion in which a person travels in a vertically inverted orientation with all body weight resting on the hands.
It can be executed with legs fully extended or with variations such as stag, straddle or ...
* Human skeletal changes due to bipedalism
The evolution of human bipedalism, which began in primates approximately four million years ago, or as early as seven million years ago with '' Sahelanthropus'', or approximately twelve million years ago with ''Danuvius guggenmosi'', has led to m ...
* Knuckle-walking
Knuckle-walking is a form of quadrupedal walking in which the forelimbs hold the fingers in a partially flexed posture that allows body weight to press down on the ground through the knuckles. Gorillas, bonobos, and chimpanzees use this style o ...
* Palmistry
Palmistry is the pseudoscientific practice of fortune-telling through the study of the palm. Also known as palm reading, chiromancy, chirology or cheirology, the practice is found all over the world, with numerous cultural variations. Those who ...
—fortune-telling based on lines in hand palms.
* Manus (anatomy)
The manus (Latin for ''hand'', plural manus) is the zoological term for the distal portion of the fore limb of an animal. In tetrapods, it is the part of the pentadactyl limb that includes the metacarpals and digits (phalanges). During evolution ...
* Mudra—Hindu term for hand gestures.
References
External links
Hand anatomy (eMedicine)
Film Board of Canada documentary ''Faces of the Hand''
"The Common Hand"
article in the May 2012 '' National Geographic'' {{Authority control Upper limb anatomy