Hamza River on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
The Hamza River (
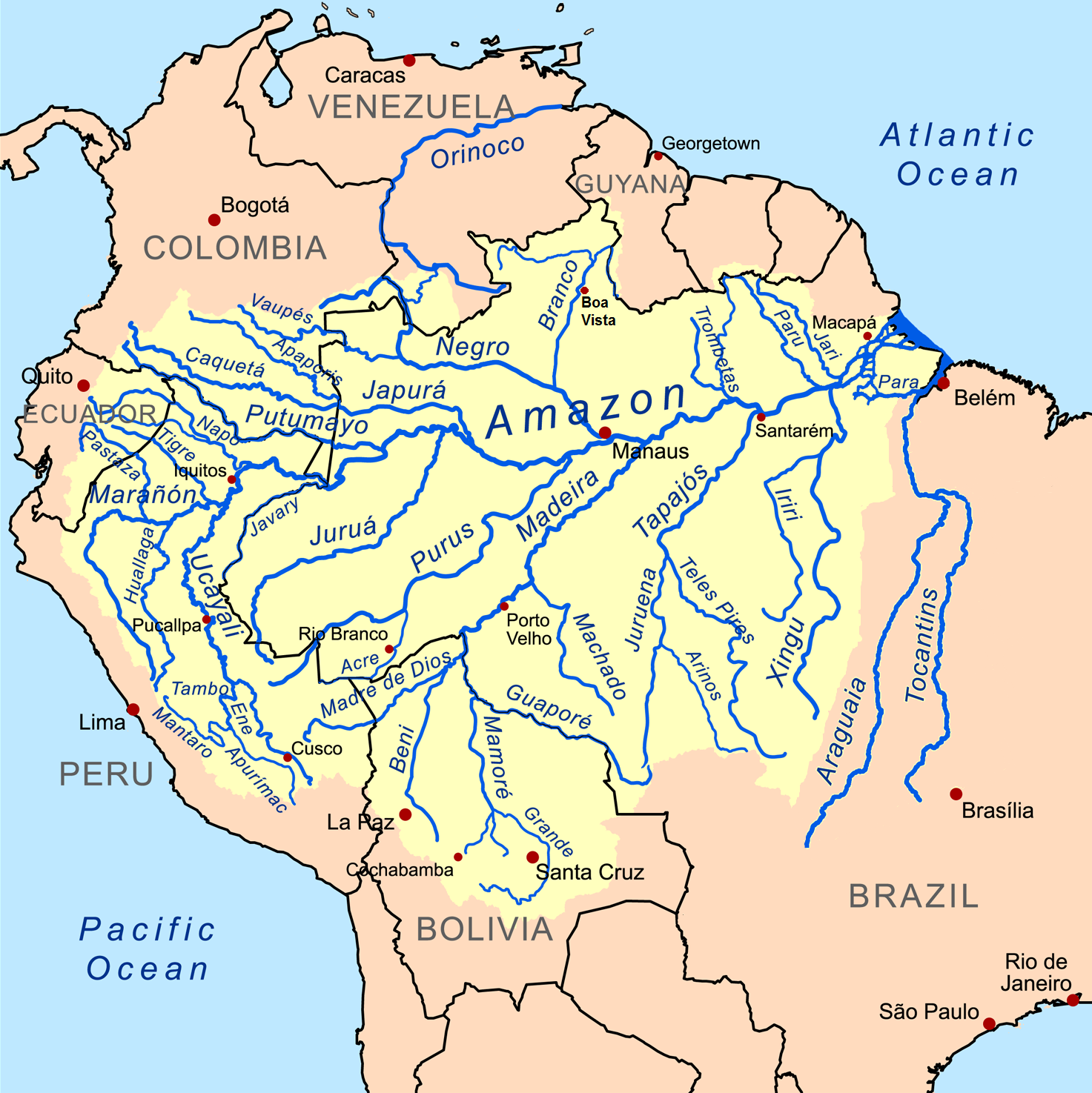 The Hamza and the Amazon are the two main drainage systems for the Amazon Basin. The reported flow rate of the Hamza, at approximately per second, is 3% of the Amazon's. It runs west to east, some below the Earth's surface, and follows roughly the path of the Amazon River. The Hamza is born in the
The Hamza and the Amazon are the two main drainage systems for the Amazon Basin. The reported flow rate of the Hamza, at approximately per second, is 3% of the Amazon's. It runs west to east, some below the Earth's surface, and follows roughly the path of the Amazon River. The Hamza is born in the
Portuguese
Portuguese may refer to:
* anything of, from, or related to the country and nation of Portugal
** Portuguese cuisine, traditional foods
** Portuguese language, a Romance language
*** Portuguese dialects, variants of the Portuguese language
** Portu ...
: ''Rio Hamza'') is an unofficial name for what seems to be a slowly flowing aquifer
An aquifer is an underground layer of water-bearing, permeable rock, rock fractures, or unconsolidated materials ( gravel, sand, or silt). Groundwater from aquifers can be extracted using a water well. Aquifers vary greatly in their characteris ...
in Brazil
Brazil ( pt, Brasil; ), officially the Federative Republic of Brazil (Portuguese: ), is the largest country in both South America and Latin America. At and with over 217 million people, Brazil is the world's fifth-largest country by area ...
and Peru
, image_flag = Flag of Peru.svg
, image_coat = Escudo nacional del Perú.svg
, other_symbol = Great Seal of the State
, other_symbol_type = National seal
, national_motto = "Firm and Happy f ...
, approximately long at a depth of nearly . Its discovery was announced in 2011 at a meeting of the Geophysical Society in Rio de Janeiro
Rio de Janeiro ( , , ; literally 'River of January'), or simply Rio, is the capital of the state of the same name, Brazil's third-most populous state, and the second-most populous city in Brazil, after São Paulo. Listed by the GaWC as a ...
. The unofficial name is in honour of Indian
Indian or Indians may refer to:
Peoples South Asia
* Indian people, people of Indian nationality, or people who have an Indian ancestor
** Non-resident Indian, a citizen of India who has temporarily emigrated to another country
* South Asia ...
scientist Valiya Mannathal Hamza, of Brazil's National Observatory, who has undertaken research on the region for four decades. The Hamza "river" and the Amazon River form a geologically unusual instance of a twin-river system flowing at different levels of the Earth's crust.
Description
 The Hamza and the Amazon are the two main drainage systems for the Amazon Basin. The reported flow rate of the Hamza, at approximately per second, is 3% of the Amazon's. It runs west to east, some below the Earth's surface, and follows roughly the path of the Amazon River. The Hamza is born in the
The Hamza and the Amazon are the two main drainage systems for the Amazon Basin. The reported flow rate of the Hamza, at approximately per second, is 3% of the Amazon's. It runs west to east, some below the Earth's surface, and follows roughly the path of the Amazon River. The Hamza is born in the Andes
The Andes, Andes Mountains or Andean Mountains (; ) are the longest continental mountain range in the world, forming a continuous highland along the western edge of South America. The range is long, wide (widest between 18°S – 20°S ...
and empties in the Atlantic Ocean
The Atlantic Ocean is the second-largest of the world's five oceans, with an area of about . It covers approximately 20% of Earth's surface and about 29% of its water surface area. It is known to separate the " Old World" of Africa, Europe ...
, deep under the surface. Its own water has a high salt content.
It flows from the Andean foothills to the Atlantic coast in a nearly west-to-east direction like the Amazon River. A combination of seismic
Seismology (; from Ancient Greek σεισμός (''seismós'') meaning "earthquake" and -λογία (''-logía'') meaning "study of") is the scientific study of earthquakes and the propagation of elastic waves through the Earth or through other ...
data and anomalous temperature variation with depth measured in 241 inactive oil wells helped locate the aquifer. Except for the flow direction, the Amazon and the Hamza have very different characteristics. The most obvious ones are their width and flow speed. While the Amazon is to wide, the Hamza is to in width. But the flow speed is in the Amazon and less than speed in the Hamza.
Geology
Several geological factors have played a vital role in the formation and existence of these subterranean water bodies. Theporous
Porosity or void fraction is a measure of the void (i.e. "empty") spaces in a material, and is a fraction of the volume of voids over the total volume, between 0 and 1, or as a percentage between 0% and 100%. Strictly speaking, some tests measure ...
and permeable
Permeability, permeable, and semipermeable may refer to:
Chemistry
*Semipermeable membrane, a membrane which will allow certain molecules or ions to pass through it by diffusion
*Vascular permeability, the movement of fluids and molecules betwe ...
sedimentary rock
Sedimentary rocks are types of rock that are formed by the accumulation or deposition of mineral or organic particles at Earth's surface, followed by cementation. Sedimentation is the collective name for processes that cause these particles ...
s behave as conduits for the water to sink to greater depths. East–west trending faults and the karst topography present along the northern border of the Amazon basin may have some role in supplying water to the "river". If the impermeable rocks stop the vertical flow, the west-to-east gradient of the topography directs it to flow towards the Atlantic Ocean.
Unlike the Hamza, the 153 km-long underground river in Mexico's Yucatán Peninsula
The Yucatán Peninsula (, also , ; es, Península de Yucatán ) is a large peninsula in southeastern Mexico and adjacent portions of Belize and Guatemala. The peninsula extends towards the northeast, separating the Gulf of Mexico to the north ...
and the 8.2 km-long Cabayugan River in the Puerto Princesa Subterranean River National Park in the Philippines
The Philippines (; fil, Pilipinas, links=no), officially the Republic of the Philippines ( fil, Republika ng Pilipinas, links=no),
* bik, Republika kan Filipinas
* ceb, Republika sa Pilipinas
* cbk, República de Filipinas
* hil, Republ ...
have come into being thanks to the karst topography. Water in these places has dissolved the carbonate rock to form extensive underground river systems.
Research status and debate
The Hamza was discovered by a team of scientists led by Valiya Hamza usingthermal
A thermal column (or thermal) is a rising mass of buoyant air, a convective current in the atmosphere, that transfers heat energy vertically. Thermals are created by the uneven heating of Earth's surface from solar radiation, and are an example ...
data collected from 241 inactive oil wells in the area, drilled in the 1970s and 1980s, by the Petrobras oil company. Calculations from the data showed that a larger flow should exist. Direct observation of water movement at a very low rate can be difficult. The speed of flow is slower than that of an average glacier
A glacier (; ) is a persistent body of dense ice that is constantly moving under its own weight. A glacier forms where the accumulation of snow exceeds its ablation over many years, often centuries. It acquires distinguishing features, such as ...
, and Hamza himself says that the team uses the term ‘river’ in a general sense, not in the conventional sense. In the title to the original paper, the word ‘river’ appears in quotation marks.
The evidence was presented at the 12th International Congress of the Brazilian Geophysical Society in Rio de Janeiro and as of August 2011 has not yet been published, although the research team noted that the techniques used to predict the flowing aquifer's presence are not unusual for earth science. Scientists have explained that the research results are preliminary, and that the definite scientific validation of the existence of the flowing aquifer is to be expected in a few years.
See also
* Valiya Hamza *Hydrogeology
Hydrogeology (''hydro-'' meaning water, and ''-geology'' meaning the study of the Earth) is the area of geology that deals with the distribution and movement of groundwater in the soil and rocks of the Earth's crust (commonly in aqui ...
* Amazon River
* Apurimac River
References
{{Aquifers Aquifers of South America Amazon basin Aquifers in Brazil Geology of Brazil