Halogen bulb on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]



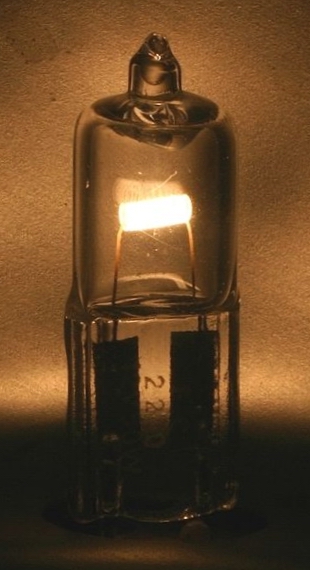 A halogen lamp (also called tungsten halogen, quartz-halogen, and quartz iodine lamp) is an
A halogen lamp (also called tungsten halogen, quartz-halogen, and quartz iodine lamp) is an
PDF
from lutron.com) There are many situations where halogen lamps are dimmed successfully. However, lamp life may not be extended as much as predicted. The life span on dimming depends on lamp construction, the halogen additive used, and whether dimming is normally expected for this type.
 Like all
Like all
 Halogen lamps must run at much higher temperatures than regular incandescent lamps for proper operation. Their small size helps to concentrate the heat on a smaller envelope surface, closer to the filament than a non-halogen incandescent. Because of the very high temperatures, halogen lamps can pose fire and burn hazards. In Australia, numerous house fires each year are attributed to ceiling-mounted halogen downlights. The Western Australia Department of Fire and Emergency Services recommends that homeowners consider instead using cooler-running
Halogen lamps must run at much higher temperatures than regular incandescent lamps for proper operation. Their small size helps to concentrate the heat on a smaller envelope surface, closer to the filament than a non-halogen incandescent. Because of the very high temperatures, halogen lamps can pose fire and burn hazards. In Australia, numerous house fires each year are attributed to ceiling-mounted halogen downlights. The Western Australia Department of Fire and Emergency Services recommends that homeowners consider instead using cooler-running
 Halogen
Halogen
 Fixed-mount lamps are used in indoor and outdoor flood lighting, although improvements in LED systems are displacing halogen lamps. Round spotlights with built-in
Fixed-mount lamps are used in indoor and outdoor flood lighting, although improvements in LED systems are displacing halogen lamps. Round spotlights with built-in



 A halogen lamp (also called tungsten halogen, quartz-halogen, and quartz iodine lamp) is an
A halogen lamp (also called tungsten halogen, quartz-halogen, and quartz iodine lamp) is an incandescent lamp
An incandescent light bulb, incandescent lamp or incandescent light globe is an electric light with a wire filament heated until it glows. The filament is enclosed in a glass bulb with a vacuum or inert gas to protect the filament from oxida ...
consisting of a tungsten filament sealed in a compact transparent envelope that is filled with a mixture of an inert gas
An inert gas is a gas that does not readily undergo chemical reactions with other chemical substances and therefore does not readily form chemical compounds. The noble gases often do not react with many substances and were historically referred to ...
and a small amount of a halogen
The halogens () are a group in the periodic table consisting of five or six chemically related elements: fluorine (F), chlorine (Cl), bromine (Br), iodine (I), astatine (At), and tennessine (Ts). In the modern IUPAC nomenclature, this grou ...
, such as iodine
Iodine is a chemical element with the Symbol (chemistry), symbol I and atomic number 53. The heaviest of the stable halogens, it exists as a semi-lustrous, non-metallic solid at standard conditions that melts to form a deep violet liquid at , ...
or bromine
Bromine is a chemical element with the symbol Br and atomic number 35. It is the third-lightest element in group 17 of the periodic table ( halogens) and is a volatile red-brown liquid at room temperature that evaporates readily to form a simi ...
. The combination of the halogen gas and the tungsten
Tungsten, or wolfram, is a chemical element with the symbol W and atomic number 74. Tungsten is a rare metal found naturally on Earth almost exclusively as compounds with other elements. It was identified as a new element in 1781 and first isol ...
filament produces a halogen-cycle chemical reaction, which redeposits evaporated tungsten on the filament, increasing its life and maintaining the clarity of the envelope. This allows the filament to operate at a higher temperature than a standard incandescent lamp of similar power and operating life; this also produces light with higher luminous efficacy
Luminous efficacy is a measure of how well a light source produces visible light. It is the ratio of luminous flux to power, measured in lumens per watt in the International System of Units (SI). Depending on context, the power can be either the ...
and color temperature
Color temperature is the color of light emitted by an idealized opaque, non-reflective body at a particular temperature measured in kelvins. The color temperature scale is used to categorize the color of light emitted by other light sources ...
. The small size of halogen lamps permits their use in compact optical systems for projectors
A projector or image projector is an optical device that projects an image (or moving images) onto a surface, commonly a projection screen. Most projectors create an image by shining a light through a small transparent lens, but some newer types ...
and illumination. The small glass envelope may be enclosed in a much larger outer glass bulb, which has a lower temperature, protects the inner bulb from contamination, and makes the bulb mechanically more similar to a conventional lamp. Source has illustrations of various double-envelope halogen bulbs.
Standard and halogen incandescent bulbs are much less efficient than LED and compact fluorescent lamp
A compact fluorescent lamp (CFL), also called compact fluorescent light, energy-saving light and compact fluorescent tube, is a fluorescent lamp designed to replace an incandescent light bulb; some types fit into light fixtures designed for inca ...
s, and therefore have been or are being phased out in many places.
History
A carbon filament lamp usingchlorine
Chlorine is a chemical element with the symbol Cl and atomic number 17. The second-lightest of the halogens, it appears between fluorine and bromine in the periodic table and its properties are mostly intermediate between them. Chlorine i ...
to prevent darkening of the envelope was patented in 1882, and chlorine-filled "NoVak" lamps were marketed in 1892.
The use of iodine was proposed in a 1933 patent, which also described the cyclic redeposition of tungsten back onto the filament. In 1959, General Electric
General Electric Company (GE) is an American multinational conglomerate founded in 1892, and incorporated in New York state and headquartered in Boston. The company operated in sectors including healthcare, aviation, power, renewable ene ...
patented a practical lamp using iodine.
Phase-out
In 2009, the EU and otherEuropean countries
The list below includes all entities falling even partially under any of the various common definitions of Europe, geographical or political. Fifty generally recognised sovereign states, Kosovo with limited, but substantial, international rec ...
began a phase-out of inefficient bulbs. The production and importation of directional mains-voltage halogen bulbs was banned on 1 September 2016 and non-directional halogen bulbs followed on 1 September 2018. Australia
Australia, officially the Commonwealth of Australia, is a sovereign country comprising the mainland of the Australian continent, the island of Tasmania, and numerous smaller islands. With an area of , Australia is the largest country by ...
banned halogen light bulbs in late 2021 as the original target date of September 2020 to keep the policy in line with the European Union. In June 2021, The UK government also announced plans to end the sale of halogen light bulbs from September, as part of the UK's wider efforts to tackle climate change
In common usage, climate change describes global warming—the ongoing increase in global average temperature—and its effects on Earth's climate system. Climate change in a broader sense also includes previous long-term changes to ...
.
Halogen cycle
In ordinary incandescent lamps, evaporated tungsten mostly deposits onto the inner surface of the bulb, causing the bulb to blacken and the filament to grow increasingly weak until it eventually breaks. The presence of the halogen, however, sets up a reversible chemical reaction cycle with this evaporated tungsten. The halogen cycle keeps the bulb clean and causes the light output to remain almost constant throughout the bulb's life. At moderate temperatures the halogen reacts with the evaporating tungsten, thehalide
In chemistry, a halide (rarely halogenide) is a binary chemical compound, of which one part is a halogen atom and the other part is an element or radical that is less electronegative (or more electropositive) than the halogen, to make a flu ...
formed being moved around in the inert gas filling. At some point, however, it will reach higher temperature regions within the bulb where it then dissociates, releasing tungsten back onto the filament and freeing the halogen to repeat the process. However, the overall bulb envelope temperature must be significantly higher than in conventional incandescent lamps for this reaction to succeed: it is only at temperatures of above on the inside of the glass envelope that the halogen vapor can combine with the tungsten and return it to the filament rather than the tungsten becoming deposited on the glass. A 300 watt tubular halogen bulb operated at full power quickly reaches a temperature of about , while a 500 watt regular incandescent bulb operates at only and a 75 watt regular incandescent at only .
The bulb must be made of fused silica (quartz) or a high-melting-point glass (such as aluminosilicate glass). Since quartz is very strong, the gas pressure can be higher, which reduces the rate of evaporation of the filament, permitting it to run a higher temperature (and so luminous efficacy
Luminous efficacy is a measure of how well a light source produces visible light. It is the ratio of luminous flux to power, measured in lumens per watt in the International System of Units (SI). Depending on context, the power can be either the ...
) for the same average life. The tungsten released in hotter regions does not generally redeposit where it came from, so the hotter parts of the filament eventually thin out and fail.
Quartz iodine lamps, using elemental iodine, were the first commercial halogen lamps launched by GE in 1959. Quite soon, bromine was found to have advantages, but was not used in elemental form. Certain hydrocarbon bromine compounds gave good results. Regeneration of the filament is also possible with fluorine, but its chemical reactivity is so great that other parts of the lamp are attacked.Burgin and Edwards Lighting Research and Technology 1970 2.2. 95–108 The halogen is normally mixed with a noble gas
The noble gases (historically also the inert gases; sometimes referred to as aerogens) make up a class of chemical elements with similar properties; under standard conditions, they are all odorless, colorless, monatomic gases with very low ch ...
, often krypton
Krypton (from grc, κρυπτός, translit=kryptos 'the hidden one') is a chemical element with the symbol Kr and atomic number 36. It is a colorless, odorless, tasteless noble gas that occurs in trace amounts in the atmosphere and is of ...
or xenon
Xenon is a chemical element with the symbol Xe and atomic number 54. It is a dense, colorless, odorless noble gas found in Earth's atmosphere in trace amounts. Although generally unreactive, it can undergo a few chemical reactions such as the ...
. The first lamps used only tungsten for filament supports, but some designs use molybdenum
Molybdenum is a chemical element with the symbol Mo and atomic number 42 which is located in period 5 and group 6. The name is from Neo-Latin ''molybdaenum'', which is based on Ancient Greek ', meaning lead, since its ores were confused with lead ...
– an example being the molybdenum shield in the H4 twin filament headlight
A headlamp is a lamp attached to the front of a vehicle to illuminate the road ahead. Headlamps are also often called headlights, but in the most precise usage, ''headlamp'' is the term for the device itself and ''headlight'' is the term for ...
for the European Asymmetric Passing Beam.
For a fixed power and life, the luminous efficacy
Luminous efficacy is a measure of how well a light source produces visible light. It is the ratio of luminous flux to power, measured in lumens per watt in the International System of Units (SI). Depending on context, the power can be either the ...
of all incandescent lamps is greatest at a particular design voltage. Halogen lamps made for 12 to 24 volt operation have good light outputs, and the very compact filaments are particularly beneficial for optical control (see picture). The ranges
of multifaceted reflector
A multifaceted reflector (often abbreviated MR) light bulb is a reflector housing format for halogen as well as some LED and fluorescent lamps. MR lamps were originally designed for use in slide projectors, but see use in residential lighting ...
"MR" lamps of 20–50 watts were originally conceived for the projection of 8 mm film
8 (eight) is the natural number following 7 and preceding 9.
In mathematics
8 is:
* a composite number, its proper divisors being , , and . It is twice 4 or four times 2.
* a power of two, being 2 (two cubed), and is the first number of t ...
, but are now widely used for display lighting and in the home. More recently, wider beam versions have become available designed for direct use on supply voltages of 120 or .
Effect of voltage on performance
Tungsten halogen lamps behave in a similar manner to other incandescent lamps when run on a different voltage. However the light output is reported as proportional to , and theluminous efficacy
Luminous efficacy is a measure of how well a light source produces visible light. It is the ratio of luminous flux to power, measured in lumens per watt in the International System of Units (SI). Depending on context, the power can be either the ...
proportional to . The normal relationship regarding the lifetime is that it is proportional to . For example, a bulb operated at 5% higher than its design voltage would produce about 15% more light, and the luminous efficacy
Luminous efficacy is a measure of how well a light source produces visible light. It is the ratio of luminous flux to power, measured in lumens per watt in the International System of Units (SI). Depending on context, the power can be either the ...
would be about 6.5% higher, but would be expected to have only half the rated life.
Halogen lamps are manufactured with enough halogen to match the rate of tungsten evaporation at their design voltage. Increasing the applied voltage increases the rate of evaporation, so at some point, there may be insufficient halogen and the lamp goes black. Over-voltage operation is not generally recommended. With a reduced voltage, the evaporation is lower and there may be too much halogen, which can lead to abnormal failure. At much lower voltages, the bulb temperature may be too low to support the halogen cycle, but by this time the evaporation rate is too low for the bulb to blacken significantly. If the bulbs do blacken, it is recommended to run the lamps at the rated voltage to restart the cycle. (Also available as from lutron.com) There are many situations where halogen lamps are dimmed successfully. However, lamp life may not be extended as much as predicted. The life span on dimming depends on lamp construction, the halogen additive used, and whether dimming is normally expected for this type.
Spectrum
incandescent light bulb
An incandescent light bulb, incandescent lamp or incandescent light globe is an electric light with a wire filament heated until it glows. The filament is enclosed in a glass bulb with a vacuum or inert gas to protect the filament from oxi ...
s, a halogen lamp produces a continuous spectrum of light, from near ultraviolet to deep into the infrared. Since the lamp filament can operate at a higher temperature than a non-halogen lamp, the spectrum is shifted toward blue, producing light with a higher effective color temperature
Color temperature is the color of light emitted by an idealized opaque, non-reflective body at a particular temperature measured in kelvins. The color temperature scale is used to categorize the color of light emitted by other light sources ...
and higher power efficiency. This makes halogen lamps the only option for consumer light source with black-body radiation
Black-body radiation is the thermal electromagnetic radiation within, or surrounding, a body in thermodynamic equilibrium with its environment, emitted by a black body (an idealized opaque, non-reflective body). It has a specific, continuous spe ...
spectrum similar to that of the Sun
The Sun is the star at the center of the Solar System. It is a nearly perfect ball of hot plasma, heated to incandescence by nuclear fusion reactions in its core. The Sun radiates this energy mainly as light, ultraviolet, and infrared radi ...
and most suitable for the eyes. Alternatively, multi-component glasses can be used, which have a natural UV-block. These glasses belong to the family of the aluminosilicate-glasses.
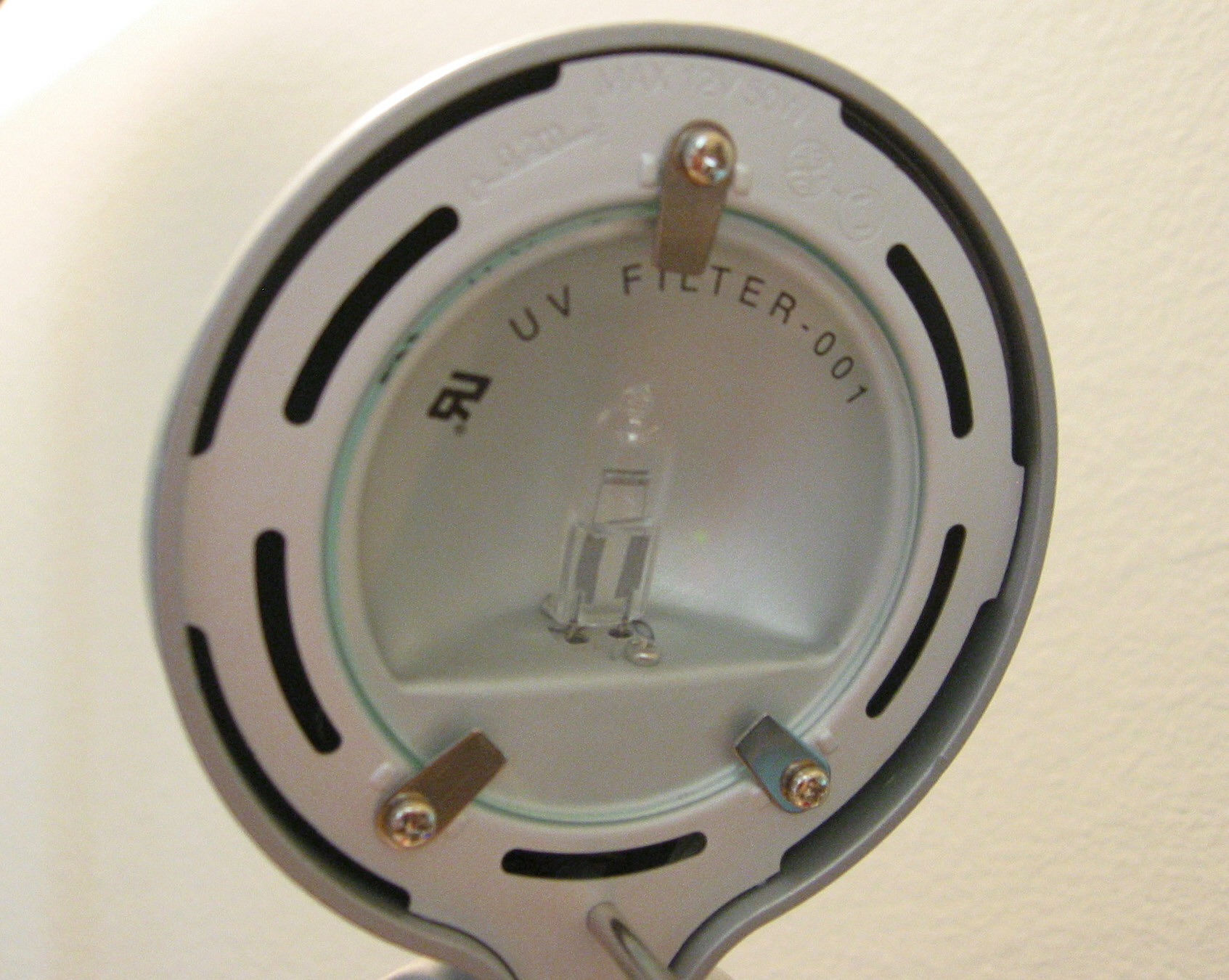
High-temperature filaments emit some energy in the UV region. Small amounts of other elements can be mixed into the quartz, so that the ''doped'' quartz (or selective optical coating) blocks harmful UV radiation. Hard glass blocks UV and has been used extensively for the bulbs of car headlights. Alternatively, the halogen lamp can be mounted inside an outer bulb, similar to an ordinary incandescent lamp, which also reduces the risks from the high bulb temperature. Undoped quartz halogen lamps are used in some scientific, medical, and dental instruments as a UV-B source.
Safety
 Halogen lamps must run at much higher temperatures than regular incandescent lamps for proper operation. Their small size helps to concentrate the heat on a smaller envelope surface, closer to the filament than a non-halogen incandescent. Because of the very high temperatures, halogen lamps can pose fire and burn hazards. In Australia, numerous house fires each year are attributed to ceiling-mounted halogen downlights. The Western Australia Department of Fire and Emergency Services recommends that homeowners consider instead using cooler-running
Halogen lamps must run at much higher temperatures than regular incandescent lamps for proper operation. Their small size helps to concentrate the heat on a smaller envelope surface, closer to the filament than a non-halogen incandescent. Because of the very high temperatures, halogen lamps can pose fire and burn hazards. In Australia, numerous house fires each year are attributed to ceiling-mounted halogen downlights. The Western Australia Department of Fire and Emergency Services recommends that homeowners consider instead using cooler-running compact fluorescent lamp
A compact fluorescent lamp (CFL), also called compact fluorescent light, energy-saving light and compact fluorescent tube, is a fluorescent lamp designed to replace an incandescent light bulb; some types fit into light fixtures designed for inca ...
s or light emitting diode lamps. Halogen torchères have been banned in some places, such as dormitories
A dormitory (originated from the Latin word ''dormitorium'', often abbreviated to dorm) is a building primarily providing sleeping and residential quarters for large numbers of people such as boarding school, high school, college or university s ...
, because of the large numbers of fires they have caused. They were held responsible by the US Consumer Product Safety Commission
The United States Consumer Product Safety Commission (USCPSC, CPSC, or commission) is an independent agency of the United States government. The CPSC seeks to promote the safety of consumer products by addressing “unreasonable risks” of in ...
for 100 fires and 10 deaths between 1992 and 1997. Halogen bulbs operate at high temperature
Temperature is a physical quantity that expresses quantitatively the perceptions of hotness and coldness. Temperature is measured with a thermometer.
Thermometers are calibrated in various temperature scales that historically have relied o ...
s and the tall height of the lamps brings them near flammable
A combustible material is something that can burn (i.e., ''combust'') in air. A combustible material is flammable if it ignites easily at ambient temperatures. In other words, a combustible material ignites with some effort and a flammable mat ...
materials, such as curtain
A curtain is a piece of cloth
Textile is an umbrella term that includes various fiber-based materials, including fibers, yarns, filaments, threads, different fabric types, etc. At first, the word "textiles" only referred to woven fa ...
s. Some safety codes require halogen bulbs to be protected by a grid or grille, especially for high-power (1–2 kW) bulbs used in theatre
Theatre or theater is a collaborative form of performing art that uses live performers, usually actors or actresses, to present the experience of a real or imagined event before a live audience in a specific place, often a stage. The perfor ...
, or by the glass and metal housing of the fixture, to prevent ignition of draperies or flammable objects in contact with the lamp.
To reduce unintentional ultraviolet
Ultraviolet (UV) is a form of electromagnetic radiation with wavelength from 10 nm (with a corresponding frequency around 30 PHz) to 400 nm (750 THz), shorter than that of visible light, but longer than X-rays. UV radiation ...
(UV) exposure, and to contain hot bulb fragments in the event of explosive bulb failure, general-purpose lamps usually have a UV-absorbing glass filter over or around the bulb. Alternatively, lamp bulbs may be doped or coated to filter
Filter, filtering or filters may refer to:
Science and technology
Computing
* Filter (higher-order function), in functional programming
* Filter (software), a computer program to process a data stream
* Filter (video), a software component tha ...
out the UV radiation. With adequate filtering, a halogen lamp exposes users to less UV than a standard incandescent lamp producing the same effective level of illumination without filtering.
Any surface contamination, notably the oil from human fingertips, can damage the quartz envelope when it is heated. Contaminants, because they absorb more light and heat than the glass does, will create a hot spot on the bulb surface when the lamp is turned on. This extreme, localized heat causes the quartz to change from its vitreous
Vitreous may refer to:
Materials
* Glass, an amorphous solid material
** Vitreous enamel, a material made by fusing powdered glass to a substrate by firing
* Vitreous lustre, a glassy luster or sheen on a mineral surface
Biology
* Vitreous bod ...
form into a weaker, crystalline
A crystal or crystalline solid is a solid material whose constituents (such as atoms, molecules, or ions) are arranged in a highly ordered microscopic structure, forming a crystal lattice that extends in all directions. In addition, macros ...
form that leaks gas. This weakening may also cause the bulb to form a bubble, weakening it and leading to its explosion.
The small glass envelope may be enclosed in a much larger outer glass bulb, which provides several advantages if small size is not required:
* the outer jacket will be at a much lower, safer, temperature, protecting objects or people that might touch it
* the hot-running inner envelope is protected from contamination, and the bulb may be handled without damaging it
* surroundings are protected from possible shattering of the inner capsule
* the jacket may filter out UV radiation
* when a halogen bulb is used to replace a normal incandescent in a fitting, the larger jacket makes it mechanically similar to the bulb replaced
* the inner and outer envelope can be at different pressures, reducing heat dissipation by conduction or convection in order to optimize the trade-off between luminous efficacy and lifetime
Form factors
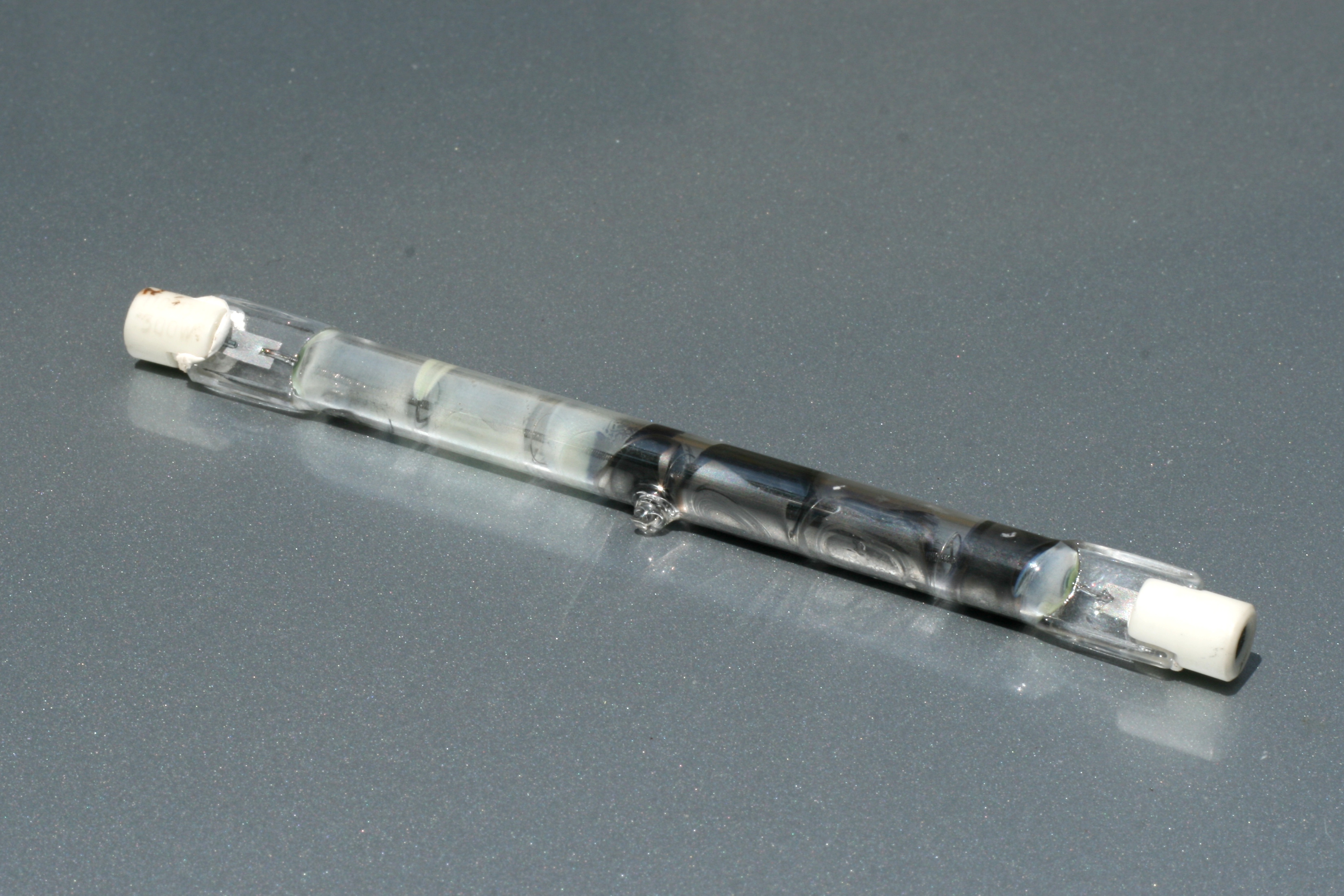
Halogen lamps are available in a series of different shapes and sizes, and are designated according to a coding system that specifies the diameter of the bulb as well as whether or not the bulb has a built-in infrared-transparent dichroic reflector. Many such lamps have designations that begin with the letter "T" to indicate that they are "tubular" followed by a number indicating the diameter of the tube in eighths of an inch: a T3 bulb, then is a tubular halogen bulb that is in diameter.However, a T-3, T ''hyphen'' 3, is a halogen "tube" lamp that is 3/8 of an inch in diameter with a single bi-pin base rather than a T3 ''cylindrical'' tube 3/8 of an inch in diameter with electrodes at ''opposite ends.'' The designation ''MR'' means "Multifaceted Reflector
A multifaceted reflector (often abbreviated MR) light bulb is a reflector housing format for halogen as well as some LED and fluorescent lamps. MR lamps were originally designed for use in slide projectors, but see use in residential lighting ...
", with the number following this still corresponding to eighths of an inch in diameter of the overall bulb.Thus, an MR11 is a multifaceted reflector bulb that is 11/8 or 1 3/8 inches in diameter If a lamp has a "G" code,"G" stands for "glass" this will mean the lamp is a bipin shape and the number following the G will indicate the distance in millimeters between the pins, usually either 4, 6.35 or 10; if the G is followed by a letter "Y", then the lamp's pins are thicker than normal— thus, a G6.35 has pins that are 1 mm in diameter but a GY6.35 has pins that are 1.3 mm in diameter. If there is a "C" code, this represents the number of coils in the filament. The length (sometimes also referred to as "height") of any two-ended cylindrical bulb must be specified separately from its form factor code, usually in millimeters, as must the lamp's voltage and wattage— hence, T3 120 V 150 W 118 mm means a double-ended tube-shaped bulb with a diameter of that operates at 120 V and is 150 W and that is also 118 mm long.
An R7S is a double ended, Recessed Single Contact (RSC) linear halogen lamp, usually measuring a length of either 118 mm or 78 mm. Some less common lengths are 189 mm, 254 mm and 331 mm. These lamps have a T3 shape on an RSC/R7S base. These can also be known as J type and T type lamps.
Applications
headlamp
A headlamp is a lamp attached to the front of a vehicle to illuminate the road ahead. Headlamps are also often called headlights, but in the most precise usage, ''headlamp'' is the term for the device itself and ''headlight'' is the term for ...
s are used in many automobiles. Halogen floodlights for outdoor lighting systems as well as for watercraft
Any vehicle used in or on water as well as underwater, including boats, ships, hovercraft and submarines, is a watercraft, also known as a water vessel or waterborne vessel. A watercraft usually has a propulsive capability (whether by sai ...
are also manufactured for commercial and recreational use. They are now also used in desktop lamps.
Tungsten-halogen lamps are frequently used as a near-infrared light source in Infrared spectroscopy
Infrared spectroscopy (IR spectroscopy or vibrational spectroscopy) is the measurement of the interaction of infrared radiation with matter by absorption, emission, or reflection. It is used to study and identify chemical substances or functi ...
.
Halogen lamps were used on the Times Square Ball
The Times Square Ball is a time ball located in New York City's Times Square. Located on the roof of One Times Square, the ball is a prominent part of a New Year's Eve celebration in Times Square commonly referred to as the ball drop, where the ...
from 1999 to 2006. However, from 2007 onward, the halogen lamps were replaced with LEDs
A light-emitting diode (LED) is a semiconductor device that emits light when current flows through it. Electrons in the semiconductor recombine with electron holes, releasing energy in the form of photons. The color of the light (cor ...
, due to the much longer lifespan, about ten times longer for LED over incandescent. The 'New Year' numerals that light up when the Times Square Ball reaches the base used halogen lighting for the last time for the 2009 ball drop.
Heating
Halogen lamps are the heating-elements in halogen ovens, infrared heaters and ceramiccooktop
A cooktop (American English), stovetop (American English) or hob (British English), is a device commonly used for cooking that is commonly found in kitchens and used to apply heat to the base of pans or pots. Cooktops are often found integrated ...
s.
Low wattage halogen lamp arrays are widely used by monitor lizard
Monitor lizards are lizards in the genus ''Varanus,'' the only extant genus in the family Varanidae. They are native to Africa, Asia, and Oceania, and one species is also found in the Americas as an invasive species. About 80 species are rec ...
keepers. Two or three small halogen lamps can produce all the heat needed in an enclosure and are recognized by the animals as sources of heat preventing curious individuals from attempting to touch them. Halogen lamps' thick glass lenses are safe to use inside high humidity reptile enclosures.
Banks of powerful tubular halogen lamps were used to simulate the heat of re-entry
Atmospheric entry is the movement of an object from outer space into and through the gases of an atmosphere of a planet, dwarf planet, or natural satellite. There are two main types of atmospheric entry: ''uncontrolled entry'', such as the entr ...
of space vehicles.Raymond Kane, Heinz Sell, ''Revolution in Lamps: A Chronicle of 50 Years of Progress, Second Edition'', 2001 The Fairmount Press, pp. 72-74
General lighting
 Fixed-mount lamps are used in indoor and outdoor flood lighting, although improvements in LED systems are displacing halogen lamps. Round spotlights with built-in
Fixed-mount lamps are used in indoor and outdoor flood lighting, although improvements in LED systems are displacing halogen lamps. Round spotlights with built-in multifaceted reflector
A multifaceted reflector (often abbreviated MR) light bulb is a reflector housing format for halogen as well as some LED and fluorescent lamps. MR lamps were originally designed for use in slide projectors, but see use in residential lighting ...
lamps are widely used in residential and commercial lighting. Tubular halogen lamps provide a large quantity of light from a small source and so can be used to produce powerful flood lamps for architectural lighting effects, or for lighting large areas outdoors.
Low voltage lamps use the GU5.3 and similar bi-pin bases, whereas mains voltage lamps use the same caps as normal mains tungsten filament lamps, or a special GU10/GZ10 base. The GU10/GZ10 bases are shaped to prevent dichroic reflector lamps being used in luminaires intended for aluminised reflector lamps, which could cause overheating of the fitting. Higher efficiency LED versions of all of these lamps are now available.
Tubular lamps with electrical contacts at each end are now being used in standalone lamps and household fixtures. These come in various lengths and power ratings (50–300 W). More powerful lamps are used as portable work lights, with bulbs rated 250 or 500 watts.
Stage lighting
Tungsten halogen lamps are used in the majority of theatrical and studio (film and television) fixtures, includingEllipsoidal reflector spotlight
Ellipsoidal reflector spot (abbreviated to ERS, or colloquially ellipsoidal or ellipse) is the name for a type of stage lighting instrument, named for the ellipsoidal reflector used to collect and direct the light through a barrel that contai ...
s, Source Four
The Electronic Theatre Controls (ETC) Source Four (also known unofficially as Source 4 or S4) is an ellipsoidal reflector spotlight (ERS) used in stage lighting. First released in 1992, the Source Four was invented by David Cunningham and featur ...
, and Fresnels. PAR Cans are also predominantly tungsten halogen.
Specialized
Projection lamps are used inmotion-picture
A film also called a movie, motion picture, moving picture, picture, photoplay or (slang) flick is a work of visual art that simulates experiences and otherwise communicates ideas, stories, perceptions, feelings, beauty, or atmosphere ...
and slide projectors
A slide projector is an opto-mechanical device for showing photographic slides.
35 mm slide projectors, direct descendants of the larger-format magic lantern, first came into widespread use during the 1950s as a form of occasional home ...
for homes and small office or school use. The compact size of the halogen lamp permits a reasonable size for portable projectors, although heat-absorbing filters must be placed between the lamp and the film to prevent melting. Halogen lamps are sometimes used for inspection lights and microscope stage illuminators. Halogen lamps were used for early flat-screen LCD backlighting
A backlight is a form of illumination used in liquid crystal displays (LCDs). As LCDs do not produce light by themselves—unlike, for example, cathode ray tube (CRT), plasma (PDP) or OLED displays—they need illumination ( ambient light or a sp ...
, but other types of lamps such as CCFL
A fluorescent lamp, or fluorescent tube, is a low-pressure mercury-vapor gas-discharge lamp that uses fluorescence to produce visible light. An electric current in the gas excites mercury vapor, which produces short-wave ultraviolet ligh ...
and now LED are used.
Disposal
Halogen lamps do not contain any mercury.General Electric
General Electric Company (GE) is an American multinational conglomerate founded in 1892, and incorporated in New York state and headquartered in Boston. The company operated in sectors including healthcare, aviation, power, renewable ene ...
says that their quartz halogen lamps would not be classified as hazardous waste.
See also
*Bi-pin connector
A bipin or bi-pin (sometimes referred to as two-pin, bipin cap or bipin socket) is a type of lamp fitting. They are included in the IEC standard "IEC 60061 Lamp caps and holders together with gauges for the control of interchangeability and safe ...
for base designations GY6.35, G8, etc.
* FEL lamp
* Lightbulb socket
A lightbulb socket, lightbulb holder, light socket, lamp socket or lamp holder is a device which mechanically supports and provides electrical connections for a compatible electric lamp base. Sockets allow lamps to be safely and conveniently re ...
for other bases
* List of light sources
This is a list of sources of light, the visible part of the electromagnetic spectrum. Light sources produce photons from another energy source, such as heat, chemical reactions, or conversion of mass or a different frequency of electromagnetic ener ...
Notes
References
External links
* {{DEFAULTSORT:Halogen Lamp Types of lamp Incandescent light bulbs de:Glühlampe#Sonderformen