HM Fort Roughs on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
HM Fort Roughs was one of several
 As a contemporary historical society notes, Fort Roughs or the "Rough Towers" was "the first of originally four naval forts designed by G. Maunsell to protect the Thames Estuary." The artificial sea fort was constructed in dry dock at Red Lion Wharf, Gravesend, in the year preceding and into 1942.
This artificial naval installation is similar in some respects to early "fixed" offshore
As a contemporary historical society notes, Fort Roughs or the "Rough Towers" was "the first of originally four naval forts designed by G. Maunsell to protect the Thames Estuary." The artificial sea fort was constructed in dry dock at Red Lion Wharf, Gravesend, in the year preceding and into 1942.
This artificial naval installation is similar in some respects to early "fixed" offshore
 British government official entities used Roughs Tower for a variety of purposes until 1956 when all full-time personnel were finally removed. Roughs Tower remained identified by name on buoys placed in position by the Ministry of Defence which are maintained under an arrangement with
British government official entities used Roughs Tower for a variety of purposes until 1956 when all full-time personnel were finally removed. Roughs Tower remained identified by name on buoys placed in position by the Ministry of Defence which are maintained under an arrangement with
World War II
World War II or the Second World War, often abbreviated as WWII or WW2, was a world war that lasted from 1939 to 1945. It involved the vast majority of the world's countries—including all of the great powers—forming two opposing ...
installations that were designed by Guy Maunsell and known collectively as ''His Majesty's Forts'' or as '' Maunsell Sea Forts''; its purpose was to guard the port of Harwich, Essex
Essex () is a county in the East of England. One of the home counties, it borders Suffolk and Cambridgeshire to the north, the North Sea to the east, Hertfordshire to the west, Kent across the estuary of the River Thames to the south, and Grea ...
, and more broadly, the Thames estuary. This 4,500 ton artificial naval installation is similar in some respects to "fixed" offshore oil platforms
An oil platform (or oil rig, offshore platform, oil production platform, and similar terms) is a large structure with facilities to extract and process petroleum and natural gas that lie in rock formations beneath the seabed. Many oil platfor ...
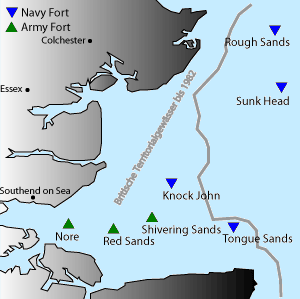
. It is situated on Rough Sands, a sandbar
In oceanography, geomorphology, and geoscience, a shoal is a natural submerged ridge, bank, or bar that consists of, or is covered by, sand or other unconsolidated material and rises from the bed of a body of water to near the surface. ...
located approximately from the coast of Suffolk and from the coast of Essex. Today it is the location and de facto capital of the unrecognised state of the Principality of Sealand
The Principality of Sealand () is an unrecognized micronation that claims HM Fort Roughs (also known as Roughs Tower), an offshore platform in the North Sea approximately off the coast of Suffolk, as its territory. Roughs Tower is a Mauns ...
.
History
1942: Construction, positioning, occupation
oil platforms
An oil platform (or oil rig, offshore platform, oil production platform, and similar terms) is a large structure with facilities to extract and process petroleum and natural gas that lie in rock formations beneath the seabed. Many oil platfor ...
. It consisted of a rectangular reinforced concrete pontoon base with a support superstructure of two tall, diameter hollow reinforced concrete towers, walls roughly thick; overall weight is estimated to have been approximately 4,500 tons. The twin concrete supporting towers were divided into seven floors, four for crew quarters; the remainder provided dining, operational, and storage areas, e.g., for several generators, and for fresh water tanks and antiaircraft munitions. There was a steel framework at one end supporting a landing jetty and crane which was used to hoist supplies aboard; the wooden landing stage itself became known as a "dolphin".
The towers were joined above the eventual waterline by a steel platform deck upon which other structures could be added; this became a gun deck, on which an upper deck and a central tower unit were constructed. QF 3.7 inch anti-aircraft guns were positioned at each end of this main deck, with a further two Bofors 40 mm anti-aircraft guns and the central tower radar installations atop a central living area that contained a galley, medical, and officers quarters.
The fort was towed from the degaussing
Degaussing is the process of decreasing or eliminating a remnant magnetic field. It is named after the gauss, a unit of magnetism, which in turn was named after Carl Friedrich Gauss. Due to magnetic hysteresis, it is generally not possible to red ...
station at Tilbury docks by four tugs"Dapper", "Crested Cock", "King Lear" and "Lady Brassey". Although setting off from Tilbury docks on the morning of 9 February 1942, an eventful journey meant that it didn't reach its final destination until 16:00 on 11 February 1942. Held in place by the tug "Dapper", its base was then intentionally flooded so that it sank in about of water, coming to rest on the sandbar at 16:45. Its location on Rough Sands, approximately 10 miles off the Harwich seafront, was at the time situated in international waters although the superstructure of the vessel above the waterline remained visible from the coast of England.
HM Fort Roughs was in operation within 30 minutes of being launched: the crew had been aboard during the fitting out in harbour and were well acquainted with the fort's equipment. Approximately 100 men were assigned to the barge before deployment on Rough Sands; thereafter, the fort was occupied by 150–300 Royal Navy personnel, which continued throughout World War II. At the conclusion of hostilities all original personnel were evacuated from HM Fort Roughs.
1956: Removal of full-time HMG personnel
 British government official entities used Roughs Tower for a variety of purposes until 1956 when all full-time personnel were finally removed. Roughs Tower remained identified by name on buoys placed in position by the Ministry of Defence which are maintained under an arrangement with
British government official entities used Roughs Tower for a variety of purposes until 1956 when all full-time personnel were finally removed. Roughs Tower remained identified by name on buoys placed in position by the Ministry of Defence which are maintained under an arrangement with Trinity House
"Three In One"
, formation =
, founding_location = Deptford, London, England
, status = Royal Charter corporation and registered charity
, purpose = Maintenance of lighthouses, buoys and beacons
, he ...
. Their purpose is to warn vessels of this obstacle, especially in time of fog because busy shipping lanes criss-cross the area with vessels going to and from the container Port of Felixstowe
Felixstowe ( ) is a port town in Suffolk, England. The estimated population in 2017 was 24,521. The Port of Felixstowe is the largest Containerization, container port in the United Kingdom. Felixstowe is approximately 116km (72 miles) northea ...
, Suffolk, and the Port of Harwich, Essex. UK Ordnance Survey
Ordnance Survey (OS) is the national mapping agency for Great Britain. The agency's name indicates its original military purpose (see ordnance and surveying), which was to map Scotland in the wake of the Jacobite rising of 1745. There was a ...
now identify the former sea barge fort as Roughs Tower on their charts.
1966: Occupation
In 1966 Paddy Roy Bates, who operated Radio Essex, andRonan O'Rahilly
Aodogán Ronan O'Rahilly (21 May 1940 – 20 April 2020) was an Irish businessman best known for the creation of the offshore radio station, Radio Caroline and the band Sheep On Drugs. He also became manager of George Lazenby, who played James ...
, who operated Radio Caroline
Radio Caroline is a British radio station founded in 1964 by Ronan O'Rahilly and Alan Crawford initially to circumvent the record companies' control of popular music broadcasting in the United Kingdom and the BBC's radio broadcasting monopoly ...
, landed on and occupied Fort Roughs. After disagreements, Bates seized the tower as his own. O'Rahilly attempted to storm the fort in 1967 but Bates thwarted the attack with guns and petrol bombs. As a result the British Royal Marines went to the fort and ordered Bates to surrender and received warning shots fired by Bates' son Michael. The pair were arrested and charged with weapons offences but the court threw the case out as it did not have jurisdiction beyond the territorial waters of Britain. Bates took this as ''de facto'' recognition of his country and seven years later issued a constitution, flag, and national anthem, among other things, for the Principality of Sealand
The Principality of Sealand () is an unrecognized micronation that claims HM Fort Roughs (also known as Roughs Tower), an offshore platform in the North Sea approximately off the coast of Suffolk, as its territory. Roughs Tower is a Mauns ...
(founded on 2 September 1967). In 1978, a German businessman, along with some other Germans and Dutchmen invaded Roughs Tower but Bates recaptured it and finally released them, after a visit by a diplomat from the German embassy in London.
Location
According to the Admiralty chart the fort's location is at 51°53.71′N 1°28.83′E. The structure is marked by east and west cardinal buoys. Other references (taken from land-based maps) areOrdnance Survey
Ordnance Survey (OS) is the national mapping agency for Great Britain. The agency's name indicates its original military purpose (see ordnance and surveying), which was to map Scotland in the wake of the Jacobite rising of 1745. There was a ...
, and on OpenStreetMap within 200 meters of the chart location .
References
{{Royal Navy shore establishments Fort Roughs Forts in Essex Roughs Fort Roughs Fort Roughs Fort Roughs Coastal Essex Sea forts World War II sites in England