HMS Crusader (H60) on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
HMS ''Crusader'' was a C-class destroyer built for the
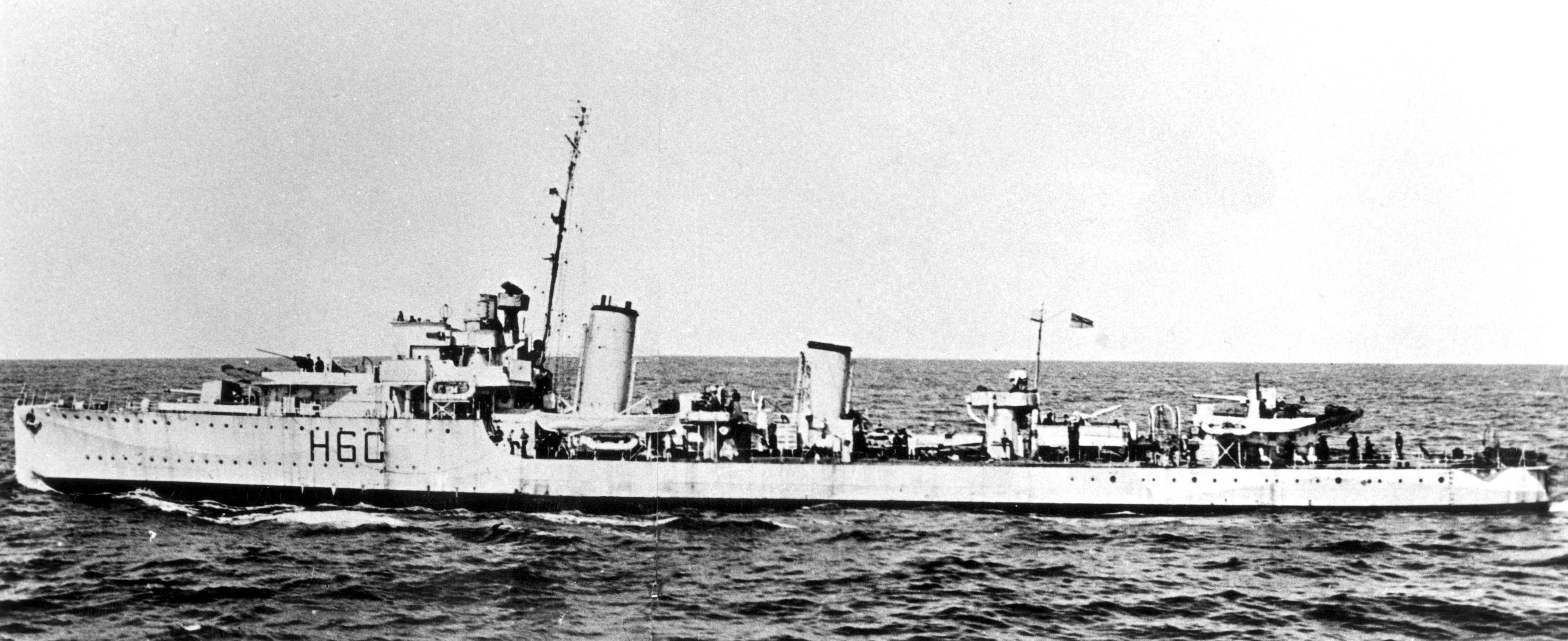 ''Ottawa'' returned to Canada in June 1941 and was assigned to the RCN's Newfoundland Escort Force which covered convoys in the Mid-Atlantic. She was transferred to Escort Group C4 in May 1942. In early September, the ship's captain refused to allow her director-control tower and
''Ottawa'' returned to Canada in June 1941 and was assigned to the RCN's Newfoundland Escort Force which covered convoys in the Mid-Atlantic. She was transferred to Escort Group C4 in May 1942. In early September, the ship's captain refused to allow her director-control tower and
Ottawa on Naval-history.net
{{DEFAULTSORT:Crusader (H60) Ships of the Royal Canadian Navy 1931 ships Canadian River-class destroyers Canadian River-class destroyers converted from C and D-class destroyers Ships built in Portsmouth Ships sunk by German submarines in World War II Shipwrecks of the Newfoundland and Labrador coast World War II shipwrecks in the Atlantic Ocean Maritime incidents in September 1942
Royal Navy
The Royal Navy (RN) is the United Kingdom's naval warfare force. Although warships were used by English and Scottish kings from the early medieval period, the first major maritime engagements were fought in the Hundred Years' War against ...
in the early 1930s. She saw service in the Home and Mediterranean Fleets and spent six months during the Spanish Civil War
The Spanish Civil War ( es, Guerra Civil Española)) or The Revolution ( es, La Revolución, link=no) among Nationalists, the Fourth Carlist War ( es, Cuarta Guerra Carlista, link=no) among Carlists, and The Rebellion ( es, La Rebelión, link ...
in late 1936 in Spanish waters, enforcing the arms blockade imposed by Britain and France on both sides of the conflict. ''Crusader'' was sold to the Royal Canadian Navy
The Royal Canadian Navy (RCN; french: Marine royale canadienne, ''MRC'') is the naval force of Canada. The RCN is one of three environmental commands within the Canadian Armed Forces. As of 2021, the RCN operates 12 frigates, four attack submar ...
(RCN) in 1938 and renamed HMCS ''Ottawa''. She was initially deployed on the Canadian Pacific Coast before World War II
World War II or the Second World War, often abbreviated as WWII or WW2, was a world war that lasted from 1939 to 1945. It involved the vast majority of the world's countries—including all of the great powers—forming two opposing ...
, but was transferred to the Atlantic
The Atlantic Ocean is the second-largest of the world's five oceans, with an area of about . It covers approximately 20% of Earth's surface and about 29% of its water surface area. It is known to separate the " Old World" of Africa, Europe an ...
three months after the war began. She served as a convoy escort during the battle of the Atlantic until sunk by the on 14 September 1942. Together with a British destroyer, she sank an Italian submarine in the North Atlantic in November 1941.
Design and construction
''Crusader'' displaced atstandard Standard may refer to:
Symbols
* Colours, standards and guidons, kinds of military signs
* Standard (emblem), a type of a large symbol or emblem used for identification
Norms, conventions or requirements
* Standard (metrology), an object th ...
load and at deep load
The displacement or displacement tonnage of a ship is its weight. As the term indicates, it is measured indirectly, using Archimedes' principle, by first calculating the volume of water displaced by the ship, then converting that value into wei ...
. The ship had an overall length
The overall length (OAL) of an ammunition cartridge is a measurement from the base of the brass shell casing to the tip of the bullet, seated into the brass casing. Cartridge overall length, or "COL", is important to safe functioning of reloads i ...
of , a beam of and a draught of . She was powered by Parsons
Parsons may refer to:
Places
In the United States:
* Parsons, Kansas, a city
* Parsons, Missouri, an unincorporated community
* Parsons, Tennessee, a city
* Parsons, West Virginia, a town
* Camp Parsons, a Boy Scout camp in the state of Washingt ...
geared steam turbines, driving two shafts, which developed a total of and gave a maximum speed of . Steam for the turbines was provided by three Admiralty 3-drum water-tube boiler
A high pressure watertube boiler (also spelled water-tube and water tube) is a type of boiler in which water circulates in tubes heated externally by the fire. Fuel is burned inside the furnace, creating hot gas which boils water in the steam-gen ...
s. ''Crusader'' carried a maximum of of fuel oil that gave her a range of at . The ship's complement was 145 officers and men.Whitley, p. 26
The ship mounted four 45-calibre
In guns, particularly firearms, caliber (or calibre; sometimes abbreviated as "cal") is the specified nominal internal diameter of the gun barrel bore – regardless of how or where the bore is measured and whether the finished bore match ...
4.7-inch Mk IX guns in single mounts, designated 'A', 'B', 'X', and 'Y' from front to rear. For anti-aircraft (AA) defence, ''Crusader'' had a single QF 3-inch 20 cwt
The QF 3 inch 20 cwt anti-aircraft gun became the standard anti-aircraft gun used in the home defence of the United Kingdom against German airships and bombers and on the Western Front in World War I. It was also common on British warships i ...
"cwt" is the abbreviation for hundredweight
The hundredweight (abbreviation: cwt), formerly also known as the centum weight or quintal, is a British imperial and US customary unit of weight or mass. Its value differs between the US and British imperial systems. The two values are distingu ...
, 30 cwt referring to the weight of the gun. AA gun between her funnel
A funnel is a tube or pipe that is wide at the top and narrow at the bottom, used for guiding liquid or powder into a small opening.
Funnels are usually made of stainless steel, aluminium, glass, or plastic. The material used in its construct ...
s, and two QF 2-pounder Mk II AA guns mounted on the aft end of her forecastle
The forecastle ( ; contracted as fo'c'sle or fo'c's'le) is the upper deck of a sailing ship forward of the foremast, or, historically, the forward part of a ship with the sailors' living quarters. Related to the latter meaning is the phrase " be ...
deck. The AA gun was removed in 1936 and the 2-pounders were relocated to between the funnels. She was fitted with two above-water quadruple torpedo tube
A torpedo tube is a cylindrical device for launching torpedoes.
There are two main types of torpedo tube: underwater tubes fitted to submarines and some surface ships, and deck-mounted units (also referred to as torpedo launchers) installed aboa ...
mounts for 21-inch torpedoes. Three depth-charge chutes were fitted, each with a capacity of two depth charges. After World War II began this was increased to 33 depth charges, delivered by one or two rails and two throwers.
The ship was ordered on 15 July 1930 from Portsmouth Dockyard
His Majesty's Naval Base, Portsmouth (HMNB Portsmouth) is one of three operating bases in the United Kingdom for the Royal Navy (the others being HMNB Clyde and HMNB Devonport). Portsmouth Naval Base is part of the city of Portsmouth; it is l ...
under the 1929 Naval Programme. ''Crusader'' was laid down
Laying the keel or laying down is the formal recognition of the start of a ship's construction. It is often marked with a ceremony attended by dignitaries from the shipbuilding company and the ultimate owners of the ship.
Keel laying is one o ...
on 12 September 1930, launched on 30 September 1931,English, p. 45 as the second ship to carry the name, and completed on 2 May 1932.
Service history
''Crusader'' was initially assigned to the2nd Destroyer Flotilla
The British 2nd Destroyer Flotilla (also styled as Second Destroyer Flotilla) was a naval formation of the Royal Navy from 1909 to 1943 and again from 1945 to 1946.
History
The 2nd Destroyer Flotilla originated in early 1907 as a part of a Home ...
of Home Fleet and remained with this flotilla for the next four years. She received her first refit at Portsmouth
Portsmouth ( ) is a port and city in the ceremonial county of Hampshire in southern England. The city of Portsmouth has been a unitary authority since 1 April 1997 and is administered by Portsmouth City Council.
Portsmouth is the most dens ...
from 30 July to 4 September 1934. Following the Italian invasion of Abyssinia in August 1935, ''Crusader'' was sent with the rest of her flotilla to reinforce the Mediterranean Fleet the following month. From October to March 1936 she was deployed in the Red Sea
The Red Sea ( ar, البحر الأحمر - بحر القلزم, translit=Modern: al-Baḥr al-ʾAḥmar, Medieval: Baḥr al-Qulzum; or ; Coptic: ⲫⲓⲟⲙ ⲛ̀ϩⲁϩ ''Phiom Enhah'' or ⲫⲓⲟⲙ ⲛ̀ϣⲁⲣⲓ ''Phiom ǹšari''; ...
to monitor Italian warship movements. Upon her return in April, the ship was refitted at Portsmouth from 27 April to 30 May. During the beginning of the Spanish Civil War
The Spanish Civil War ( es, Guerra Civil Española)) or The Revolution ( es, La Revolución, link=no) among Nationalists, the Fourth Carlist War ( es, Cuarta Guerra Carlista, link=no) among Carlists, and The Rebellion ( es, La Rebelión, link ...
in August–September 1936, the ship evacuated British nationals from Spanish ports on the Bay of Biscay. Crusader was assigned as the plane guard
A plane guard is a warship (commonly a destroyer or frigate) or helicopter tasked to recover the aircrew of planes or helicopters which ditch or crash in the water during aircraft carrier flight operations.
Ships
For ships, the plane guard is po ...
for the aircraft carrier from January 1937 to March 1938, aside from a brief refit between 30 March and 27 April 1937. The ship began a major refit at Sheerness on 28 April 1938 to bring her up to Canadian specifications that included the installation of Type 124 ASDIC
Sonar (sound navigation and ranging or sonic navigation and ranging) is a technique that uses sound propagation (usually underwater, as in submarine navigation) to navigate, measure distances ( ranging), communicate with or detect objects on ...
.
Transfer to the Royal Canadian Navy
The ship was purchased by the Royal Canadian Navy and she was commissioned on 15 June as HMCS ''Ottawa''. The ship was assigned to the Canadian Pacific Coast and arrived atEsquimalt
The Township of Esquimalt is a municipality at the southern tip of Vancouver Island, in British Columbia, Canada. It is bordered to the east by the provincial capital, Victoria, to the south by the Strait of Juan de Fuca, to the west by Esquim ...
on 7 November 1938.English, p. 49 She remained there until she was ordered to Halifax, Nova Scotia on 15 November 1939 where she escorted local convoys, including the convoy carrying half of the 1st Canadian Infantry Division
The 1st Canadian Division (French: ''1re Division du Canada'' ) is a joint operational command and control formation based at CFB Kingston, and falls under Canadian Joint Operations Command. It is a high-readiness unit, able to move on very short ...
to the UK on 10 December. ''Ottawa''s stern was damaged in a collision with the tugboat
A tugboat or tug is a marine vessel that manoeuvres other vessels by pushing or pulling them, with direct contact or a tow line. These boats typically tug ships in circumstances where they cannot or should not move under their own power, su ...
''Bansurf'' in April 1940, and repairs took two months to complete.
On 27 August 1940, ''Ottawa'' was sailed to Greenock, Scotland
Scotland (, ) is a Countries of the United Kingdom, country that is part of the United Kingdom. Covering the northern third of the island of Great Britain, mainland Scotland has a Anglo-Scottish border, border with England to the southeast ...
, and assigned to the 10th Escort Group of the Western Approaches Command
Commander-in-Chief, Western Approaches was the commander of a major operational command of the Royal Navy during World War II. The admiral commanding, and his forces, sometimes informally known as 'Western Approaches Command,' were responsibl ...
upon her arrival on 4 September for convoy escort duties. In October, the ship's rear torpedo tube mount was exchanged for a 12-pounder AA gun. On 24–26 September, she rescued survivors of two British merchant ships; 55 from that had been sunk by and 60 from that had been sunk by . ''Ottawa'' assisted the British destroyer in sinking the on 7 November. By mid-November, ''Ottawa'' had been fitted with a Type 286M short-range surface-search radar
Radar is a detection system that uses radio waves to determine the distance ('' ranging''), angle, and radial velocity of objects relative to the site. It can be used to detect aircraft, ships, spacecraft, guided missiles, motor vehicles, we ...
, adapted from the Royal Air Force
The Royal Air Force (RAF) is the United Kingdom's air and space force. It was formed towards the end of the First World War on 1 April 1918, becoming the first independent air force in the world, by regrouping the Royal Flying Corps (RFC) an ...
's ASV radar. This early model, however, could only scan directly forward and had to be aimed by turning the entire ship. On 23 November, she rescued 29 survivors of the grain carrier which had been sunk by .
 ''Ottawa'' returned to Canada in June 1941 and was assigned to the RCN's Newfoundland Escort Force which covered convoys in the Mid-Atlantic. She was transferred to Escort Group C4 in May 1942. In early September, the ship's captain refused to allow her director-control tower and
''Ottawa'' returned to Canada in June 1941 and was assigned to the RCN's Newfoundland Escort Force which covered convoys in the Mid-Atlantic. She was transferred to Escort Group C4 in May 1942. In early September, the ship's captain refused to allow her director-control tower and rangefinder
A rangefinder (also rangefinding telemeter, depending on the context) is a device used to measure distances to remote objects. Originally optical devices used in surveying, they soon found applications in other fields, such as photography an ...
to be removed in exchange for a Type 271 target indication radar
Radar is a detection system that uses radio waves to determine the distance ('' ranging''), angle, and radial velocity of objects relative to the site. It can be used to detect aircraft, ships, spacecraft, guided missiles, motor vehicles, we ...
. On 14 September, while escorting Convoy ON 127
Convoy ON 127 was a trade convoy of merchant ships during the second World War. It was the 127th of the numbered series of ON convoys Outbound from the British Isles to North America and the only North Atlantic trade convoy of 1942 or 1943 wher ...
east of St. John's, Newfoundland
St. John's is the capital and largest city of the Canadian province of Newfoundland and Labrador, located on the eastern tip of the Avalon Peninsula on the island of Newfoundland.
The city spans and is the easternmost city in North America ...
, ''Ottawa'' was torpedoed by ''U-91''. Ten minutes later, unable to manoeuvre, she was hit by a second torpedo. She sank ten minutes later; 114 crewmen lost their lives, including the commanding officer, while nearby vessels rescued 69 survivors.
The armament changes undergone by the ship during the war are not entirely clear. Photographic evidence shows that four Oerlikon 20 mm AA guns were added, one pair to her searchlight
A searchlight (or spotlight) is an apparatus that combines an extremely bright source (traditionally a carbon arc lamp) with a mirrored parabolic reflector to project a powerful beam of light of approximately parallel rays in a particular direc ...
platform and the other pair on the bridge
A bridge is a structure built to span a physical obstacle (such as a body of water, valley, road, or rail) without blocking the way underneath. It is constructed for the purpose of providing passage over the obstacle, which is usually somethi ...
wings, although ''Ottawa'' retained her 2-pounder guns even after the Oerlikons were added. The 'Y' gun was also removed to allow her depth charge stowage to be increased to at least 60 depth charges.Friedman, p. 237
Trans-Atlantic convoys escorted
Notes
Footnotes
References
* * * * * * *External links
Ottawa on Naval-history.net
{{DEFAULTSORT:Crusader (H60) Ships of the Royal Canadian Navy 1931 ships Canadian River-class destroyers Canadian River-class destroyers converted from C and D-class destroyers Ships built in Portsmouth Ships sunk by German submarines in World War II Shipwrecks of the Newfoundland and Labrador coast World War II shipwrecks in the Atlantic Ocean Maritime incidents in September 1942