HMS Britannia (1904) on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
HMS ''Britannia'' was a ''King Edward VII''-class
 Following the development of
Following the development of

 Upon the outbreak of the
Upon the outbreak of the
 On the morning of 9 November 1918, under the command of Captain (naval), Captain Francis Wade Caulfeild, ''Britannia'' was on a voyage in the western entrance to the Strait of Gibraltar when she was torpedoed off
On the morning of 9 November 1918, under the command of Captain (naval), Captain Francis Wade Caulfeild, ''Britannia'' was on a voyage in the western entrance to the Strait of Gibraltar when she was torpedoed off
MaritimeQuest HMS ''Britannia'' pages
{{DEFAULTSORT:Britannia (1904) King Edward VII-class battleships Ships built in Portsmouth 1904 ships World War I battleships of the United Kingdom Maritime incidents in 1910 Maritime incidents in 1915 Maritime incidents in 1918 Ships sunk by German submarines in World War I World War I shipwrecks in the Atlantic Ocean Naval magazine explosions
pre-dreadnought battleship
Pre-dreadnought battleships were sea-going battleships built between the mid- to late- 1880s and 1905, before the launch of in 1906. The pre-dreadnought ships replaced the ironclad battleships of the 1870s and 1880s. Built from steel, protec ...
of the Royal Navy
The Royal Navy (RN) is the United Kingdom's naval warfare force. Although warships were used by English and Scottish kings from the early medieval period, the first major maritime engagements were fought in the Hundred Years' War against ...
. She was named after Britannia
Britannia () is the national personification of Britain as a helmeted female warrior holding a trident and shield. An image first used in classical antiquity, the Latin ''Britannia'' was the name variously applied to the British Isles, Great ...
, the Latin
Latin (, or , ) is a classical language belonging to the Italic branch of the Indo-European languages. Latin was originally a dialect spoken in the lower Tiber area (then known as Latium) around present-day Rome, but through the power of the ...
name of Great Britain under Roman
Roman or Romans most often refers to:
*Rome, the capital city of Italy
*Ancient Rome, Roman civilization from 8th century BC to 5th century AD
*Roman people, the people of ancient Rome
*'' Epistle to the Romans'', shortened to ''Romans'', a lette ...
rule. The ship was built by Portsmouth Dockyard
His Majesty's Naval Base, Portsmouth (HMNB Portsmouth) is one of three operating bases in the United Kingdom for the Royal Navy (the others being HMNB Clyde and HMNB Devonport). Portsmouth Naval Base is part of the city of Portsmouth; it is l ...
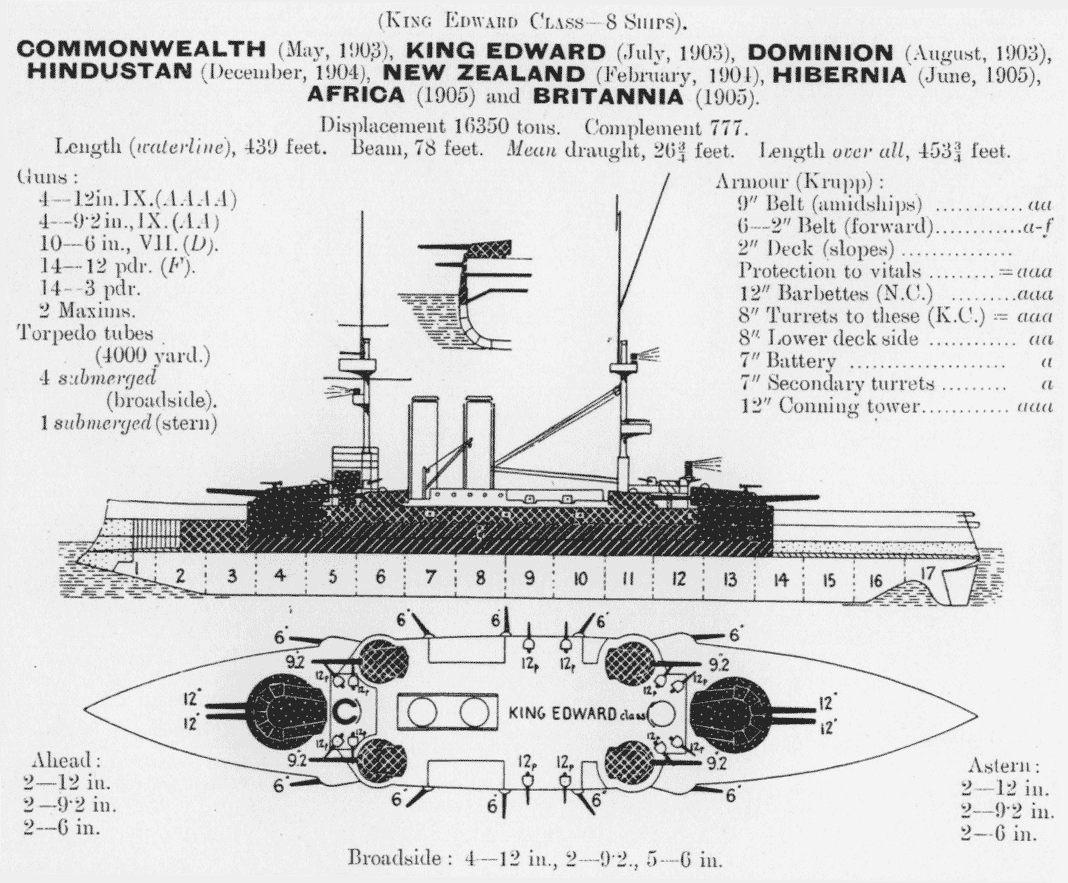
between 1904 and 1906. Armed with a battery of four and four guns, she and her sister ships marked a significant advance in offensive power compared to earlier British battleship designs that did not carry the 9.2 in guns.
After commissioning in September 1906, she served briefly with the Atlantic Fleet from October to March 1907 before transferring to the Channel Fleet. She then joined the Home Fleet in 1909. In 1912, she, along with her sister ships, was assigned to the 3rd Battle Squadron
The 3rd Battle Squadron was a naval squadron of the British Royal Navy consisting of battleships and other vessels, active from at least 1914 to 1945. The 3rd Battle Squadron was initially part of the Royal Navy's Home Fleet. During the Firs ...
, part of the Home Fleet. That year, the squadron went to the Mediterranean Sea
The Mediterranean Sea is a sea connected to the Atlantic Ocean, surrounded by the Mediterranean Basin and almost completely enclosed by land: on the north by Western and Southern Europe and Anatolia, on the south by North Africa, and on the ...
during the First Balkan War
The First Balkan War ( sr, Први балкански рат, ''Prvi balkanski rat''; bg, Балканска война; el, Αʹ Βαλκανικός πόλεμος; tr, Birinci Balkan Savaşı) lasted from October 1912 to May 1913 and invo ...
as part of an international blockade
A blockade is the act of actively preventing a country or region from receiving or sending out food, supplies, weapons, or communications, and sometimes people, by military force.
A blockade differs from an embargo or sanction, which are leg ...
of Montenegro. In 1913, the ship returned to British waters, where she was reassigned to the Second Division, Home Fleet.
When the First World War
World War I (28 July 1914 11 November 1918), often abbreviated as WWI, was one of the deadliest global conflicts in history. Belligerents included much of Europe, the Russian Empire, the United States, and the Ottoman Empire, with fightin ...
broke out, ''Britannia'' was transferred back to the 3rd Battle Squadron, which was assigned to the Grand Fleet
The Grand Fleet was the main battlefleet of the Royal Navy during the First World War. It was established in August 1914 and disbanded in April 1919. Its main base was Scapa Flow in the Orkney Islands.
History
Formed in August 1914 from the F ...
, the main British fleet during the war. Through 1914 and 1915, the ships frequently went to sea to search for German vessels, but ''Britannia'' saw no action during this period. By the end of the year, the Grand Fleet stopped operating with the older 3rd Battle Squadron ships, and in 1916, she was attached to the 2nd Detached Squadron, then serving in the Adriatic Sea
The Adriatic Sea () is a body of water separating the Italian Peninsula from the Balkan Peninsula. The Adriatic is the northernmost arm of the Mediterranean Sea, extending from the Strait of Otranto (where it connects to the Ionian Sea) to t ...
. After a refit in 1917, she conducted patrol and convoy escort duties in the Atlantic. On 9 November 1918, just two days before the end of the war, she was torpedoed by a German submarine off Cape Trafalgar
Cape Trafalgar (; es, Cabo Trafalgar ) is a headland in the Province of Cádiz in the southwest of Spain. The 1805 naval Battle of Trafalgar, in which the Royal Navy commanded by Admiral Horatio Nelson decisively defeated Napoleon's combined ...
and sank with the loss of 50 men. ''Britannia'' was one of the last British warships to be sunk in the war.
Design
 Following the development of
Following the development of pre-dreadnought
Pre-dreadnought battleships were sea-going battleships built between the mid- to late- 1880s and 1905, before the launch of in 1906. The pre-dreadnought ships replaced the ironclad battleships of the 1870s and 1880s. Built from steel, protec ...
type battleships carrying heavy secondary guns of diameter in the Italian ''Regia Marina
The ''Regia Marina'' (; ) was the navy of the Kingdom of Italy (''Regno d'Italia'') from 1861 to 1946. In 1946, with the birth of the Italian Republic (''Repubblica Italiana''), the ''Regia Marina'' changed its name to ''Marina Militare'' ("M ...
'' and the United States Navy
The United States Navy (USN) is the maritime service branch of the United States Armed Forces and one of the eight uniformed services of the United States. It is the largest and most powerful navy in the world, with the estimated tonnage ...
, the Royal Navy
The Royal Navy (RN) is the United Kingdom's naval warfare force. Although warships were used by English and Scottish kings from the early medieval period, the first major maritime engagements were fought in the Hundred Years' War against ...
decided to build similar ships. Initial proposals called for a battleship equipped with eight guns to support the main battery, though under the direction of William Henry White
Sir William Henry White, (2 February 1845 – 27 February 1913) was a prolific British warship designer and Chief Constructor at the Admiralty.
Biography
White was born in Devonport, the son of Robert White, a currier, and his wife, Jane ...
, the Director of Naval Construction
The Director of Naval Construction (DNC) also known as the Department of the Director of Naval Construction and Directorate of Naval Construction and originally known as the Chief Constructor of the Navy was a senior principal civil officer resp ...
, these were replaced with four guns. The new ships, though based on the general type that had formed the basis of the preceding four battleship designs, marked the first significant change in the series. Like all late pre-dreadnoughts that entered service in the mid-1900s, ''Britannia'' was made almost instantaneously obsolescent by the commissioning of the all-big-gun in December 1906, armed with a battery of ten heavy guns compared to the typical four of most pre-dreadnoughts.
''Britannia'' was long overall
__NOTOC__
Length overall (LOA, o/a, o.a. or oa) is the maximum length of a vessel's hull measured parallel to the waterline. This length is important while docking the ship. It is the most commonly used way of expressing the size of a ship, an ...
, with a beam of and a draft
Draft, The Draft, or Draught may refer to:
Watercraft dimensions
* Draft (hull), the distance from waterline to keel of a vessel
* Draft (sail), degree of curvature in a sail
* Air draft, distance from waterline to the highest point on a vesse ...
of . The ''King Edward VII''-class battleships displaced normally and up to fully loaded. Her crew numbered 777 officers and ratings. The ''King Edward VII''-class ships were powered by a pair of 4-cylinder triple-expansion engine
A compound steam engine unit is a type of steam engine where steam is expanded in two or more stages.
A typical arrangement for a compound engine is that the steam is first expanded in a high-pressure ''(HP)'' cylinder, then having given up he ...
s that drove two screws, with steam provided by sixteen water-tube boiler
A high pressure watertube boiler (also spelled water-tube and water tube) is a type of boiler in which water circulates in tubes heated externally by the fire. Fuel is burned inside the furnace, creating hot gas which boils water in the steam-gen ...
s. The boilers were trunked into two funnels located amidships
This glossary of nautical terms is an alphabetical listing of terms and expressions connected with ships, shipping, seamanship and navigation on water (mostly though not necessarily on the sea). Some remain current, while many date from the 17th ...
. The ''King Edward VII''-class ships had a top speed of from .
''Britannia'' had a main battery
A main battery is the primary weapon or group of weapons around which a warship is designed. As such, a main battery was historically a gun or group of guns, as in the broadsides of cannon on a ship of the line. Later, this came to be turreted ...
of four 40-calibre guns mounted in twin-gun turret
A gun turret (or simply turret) is a mounting platform from which weapons can be fired that affords protection, visibility and ability to turn and aim. A modern gun turret is generally a rotatable weapon mount that houses the crew or mechani ...
s fore and aft. These were supported by a heavy secondary battery
A rechargeable battery, storage battery, or secondary cell (formally a type of energy accumulator), is a type of electrical battery which can be charged, discharged into a load, and recharged many times, as opposed to a disposable or pri ...
of four guns in four single turrets, two on each broadside. The ships also mounted ten 6-inch 50 calibre guns mounted in casemates, in addition to fourteen 12-pounder guns and fourteen 3-pounder guns for defence against torpedo boat
A torpedo boat is a relatively small and fast naval ship designed to carry torpedoes into battle. The first designs were steam-powered craft dedicated to ramming enemy ships with explosive spar torpedoes. Later evolutions launched variants of ...
s. As was customary for battleships of the period, she was also equipped with five torpedo tubes submerged in the hull; two were on each broadside, with the fifth in the stern.
''Britannia'' had an armoured belt
Belt armor is a layer of heavy metal armor plated onto or within the outer hulls of warships, typically on battleships, battlecruisers and cruisers, and aircraft carriers.
The belt armor is designed to prevent projectiles from penetrating t ...
that was thick; the transverse bulkheads on the aft end of the belt was thick. The sides of her main battery turrets were also 8 to 12 in thick, atop 12 in barbette
Barbettes are several types of gun emplacement in terrestrial fortifications or on naval ships.
In recent naval usage, a barbette is a protective circular armour support for a heavy gun turret. This evolved from earlier forms of gun protectio ...
s, and the 9.2 turrets had sides. The casemate battery was protected with of armour plate. Her conning tower had 12-inch-thick sides. She was fitted with two armoured decks, thick, respectively.
Service history
Pre-First World War
HMS ''Britannia'' was built atPortsmouth Dockyard
His Majesty's Naval Base, Portsmouth (HMNB Portsmouth) is one of three operating bases in the United Kingdom for the Royal Navy (the others being HMNB Clyde and HMNB Devonport). Portsmouth Naval Base is part of the city of Portsmouth; it is l ...
, and was named for the Latin name for Great Britain
Great Britain is an island in the North Atlantic Ocean off the northwest coast of continental Europe. With an area of , it is the largest of the British Isles, the largest European island and the ninth-largest island in the world. It i ...
under Roman rule. She was laid down
Laying the keel or laying down is the formal recognition of the start of a ship's construction. It is often marked with a ceremony attended by dignitaries from the shipbuilding company and the ultimate owners of the ship.
Keel laying is one o ...
on 4 February 1904, launched on 10 December that year, and completed in September 1906. ''Britannia'' was commissioned into the reserve
Reserve or reserves may refer to:
Places
* Reserve, Kansas, a US city
* Reserve, Louisiana, a census-designated place in St. John the Baptist Parish
* Reserve, Montana, a census-designated place in Sheridan County
* Reserve, New Mexico, a US vi ...
at Portsmouth Dockyard on 6 September 1906. She went into full commission on 2 October 1906 for service in the Atlantic Fleet. She transferred to the Channel Fleet on 4 March 1907. As part of a fleet reorganisation on 24 March 1909, the Channel Fleet became the Second Division, Home Fleet, and ''Britannia'' became a Home Fleet unit in that division, becoming Flagship, Vice Admiral, Second Division, in April 1909. She underwent a refit at Portsmouth from 1909 to 1910. On 14 July 1910, she collided with the barque
A barque, barc, or bark is a type of sailing vessel with three or more masts having the fore- and mainmasts rigged square and only the mizzen (the aftmost mast) rigged fore and aft. Sometimes, the mizzen is only partly fore-and-aft rigged, b ...
''Loch Trool'', suffering slight damage.
Under a fleet reorganisation in May 1912, ''Britannia'' and all seven of her sisters (, , , , , , and ) were assigned to form the 3rd Battle Squadron
The 3rd Battle Squadron was a naval squadron of the British Royal Navy consisting of battleships and other vessels, active from at least 1914 to 1945. The 3rd Battle Squadron was initially part of the Royal Navy's Home Fleet. During the Firs ...
, assigned to the First Fleet, Home Fleet. The squadron was detached to the Mediterranean in November because of the First Balkan War
The First Balkan War ( sr, Први балкански рат, ''Prvi balkanski rat''; bg, Балканска война; el, Αʹ Βαλκανικός πόλεμος; tr, Birinci Balkan Savaşı) lasted from October 1912 to May 1913 and invo ...
(October 1912 – May 1913); it arrived at Malta
Malta ( , , ), officially the Republic of Malta ( mt, Repubblika ta' Malta ), is an island country in the Mediterranean Sea. It consists of an archipelago, between Italy and Libya, and is often considered a part of Southern Europe. It lies ...
on 27 November and subsequently participated in a blockade
A blockade is the act of actively preventing a country or region from receiving or sending out food, supplies, weapons, or communications, and sometimes people, by military force.
A blockade differs from an embargo or sanction, which are leg ...
by an international force of Montenegro
)
, image_map = Europe-Montenegro.svg
, map_caption =
, image_map2 =
, capital = Podgorica
, coordinates =
, largest_city = capital
, official_languages = M ...
and in an occupation of Scutari. The squadron returned to the United Kingdom in 1913 and rejoined the Home Fleet on 27 June , after which ''Britannia'' left the squadron to return to the Second Division, Home Fleet.
First World War
With the Grand Fleet

 Upon the outbreak of the
Upon the outbreak of the First World War
World War I (28 July 1914 11 November 1918), often abbreviated as WWI, was one of the deadliest global conflicts in history. Belligerents included much of Europe, the Russian Empire, the United States, and the Ottoman Empire, with fightin ...
in August 1914, the 3rd Battle Squadron, at the time under the command of Vice-Admiral Edward Bradford Edward Bradford may refer to:
* Edward Bradford (1798–1871), founderof Pine Hill Plantation in Leon County, Florida.
* Edward Green Bradford (1819–1884), Delaware politician and United States federal judge
*Sir Edward Bradford, 1st Baronet (183 ...
, was assigned to the Grand Fleet and based at Rosyth
Rosyth ( gd, Ros Fhìobh, "headland of Fife") is a town on the Firth of Forth, south of the centre of Dunfermline. According to the census of 2011, the town has a population of 13,440.
The new town was founded as a Garden city-style suburb ...
, where it was reinforced with the five s, It was used to supplement the Grand Fleet's cruisers on the Northern Patrol
The Northern Patrol, also known as Cruiser Force B and the Northern Patrol Force, was an operation of the British Royal Navy during the First World War and Second World War. The Patrol was part of the British "distant" blockade of Germany. Its ma ...
. On 6 August, the day after Britain declared war on Germany, elements of the Grand Fleet sortied to inspect the coast of Norway in search of a German naval base violating Norwegian neutrality. ''Britannia'' and the rest of the 3rd Battle Squadron provided distant support to the operation. No such base was found, and the ships returned to port the next day. On 14 August, the ships of the Grand Fleet went to sea for battle practice before conducting a sweep into the North Sea
The North Sea lies between Great Britain, Norway, Denmark, Germany, the Netherlands and Belgium. An epeiric sea, epeiric sea on the European continental shelf, it connects to the Atlantic Ocean through the English Channel in the south and the ...
later that day and into 15 August. During sweeps by the fleet, she and her sisters often steamed at the heads of divisions of the far more valuable dreadnought
The dreadnought (alternatively spelled dreadnaught) was the predominant type of battleship in the early 20th century. The first of the kind, the Royal Navy's , had such an impact when launched in 1906 that similar battleships built after her ...
s, where they could protect the dreadnoughts by watching for mines or by being the first to strike them. On 2 November 1914, the squadron was detached to reinforce the Channel Fleet and was rebased at Portland
Portland most commonly refers to:
* Portland, Oregon, the largest city in the state of Oregon, in the Pacific Northwest region of the United States
* Portland, Maine, the largest city in the state of Maine, in the New England region of the northeas ...
. It returned to the Grand Fleet on 13 November 1914.
On 14 December, the 1st Battlecruiser Squadron, 2nd Battle Squadron
The 2nd Battle Squadron was a naval squadron of the British Royal Navy consisting of battleships. The 2nd Battle Squadron was initially part of the Royal Navy's Grand Fleet. After World War I the Grand Fleet was reverted to its original name, ...
, and accompanying cruisers and destroyers left port to intercept the German forces preparing to raid Scarborough, Hartlepool and Whitby. On the first reports of contact with German units on the morning of 16 December, the Grand Fleet commander, Admiral John Jellicoe
Admiral of the Fleet John Rushworth Jellicoe, 1st Earl Jellicoe, (5 December 1859 – 20 November 1935) was a Royal Navy officer. He fought in the Anglo-Egyptian War and the Boxer Rebellion and commanded the Grand Fleet at the Battle of Jutlan ...
, ordered Bradford to take the 3rd Battle Squadron to support the ships in contact at 10:00. Four hours later, they met the 1st and 4th Battle Squadron
The 4th Battle Squadron was a squadron of the British Royal Navy consisting of battleships. The 4th Battle Squadron was initially part of the Royal Navy's Home Fleet (1912–14) and then the Grand Fleet after the outbreak of the First World War ...
s, en route from Scapa Flow, though they failed to reach the German High Seas Fleet
The High Seas Fleet (''Hochseeflotte'') was the battle fleet of the German Imperial Navy and saw action during the First World War. The formation was created in February 1907, when the Home Fleet (''Heimatflotte'') was renamed as the High Seas ...
before the latter withdrew. The Grand Fleet remained at sea until late on 17 December, at which point the 3rd Battle Squadron was ordered back to Rosyth. ''Britannia'' and the rest of the squadron joined the Grand Fleet for another sweep into the North Sea on 25 December. The fleet returned to its ports two days later, having failed to locate any German vessels.
The 3rd Battle Squadron went to sea on 12 January 1915 for gunnery training, steaming north and passing to the west of Orkney on the night of 13–14 January. After completing training on the 14th, they returned to Rosyth on 15 January. On 23 January, the 1st and 2nd Battlecruiser Squadrons sortied to ambush the German I Scouting Group
The I Scouting Group (german: I. Aufklärungsgruppe) was a special reconnaissance unit within the German Kaiserliche Marine. The unit was famously commanded by Admiral Franz von Hipper during World War I. The I Scouting Group was one of the most ...
in what resulted in the Battle of Dogger Bank the following day. Later on the 23rd, the rest of the Grand Fleet, including ''Britannia'', sortied to support the battlecruisers. The 3rd Squadron ships left first and steamed at full speed to reach ships of the Harwich Force
The Harwich Force originally called Harwich Striking Force was a squadron of the Royal Navy, formed during the First World War and based in Harwich. It played a significant role in the war.
History
After the outbreak of the First World War, a ...
, which had reported contact with German vessels. The battlecruisers intervened first, and ''Britannia'' and her sisters arrived around 14:00, by which time the battlecruisers had sunk the armoured cruiser and the surviving German ships had fled. The 3rd Battle Squadron patrolled the area with the rest of the Grand Fleet over the night before being detached at 08:00 on 25 January to steam to Rosyth. While steaming in the Firth of Forth off Inchkeith
Inchkeith (from the gd, Innis Cheith) is an island in the Firth of Forth, Scotland, administratively part of the Fife council area.
Inchkeith has had a colourful history as a result of its proximity to Edinburgh and strategic location for u ...
the next day, ''Britannia'' ran aground. She was stranded for 36 hours but was refloated; having suffered extensive damage, the ship required lengthy repairs at the Devonport Dockyard.
Later operations
On 29 April 1916, the 3rd Battle Squadron was rebased at Sheerness, and on 3 May it was separated from the Grand Fleet, being transferred to theNore Command
The Commander-in-Chief, The Nore, was an operational commander of the Royal Navy. His subordinate units, establishments, and staff were sometimes informally known as the Nore Station or Nore Command. The Nore is a sandbank at the mouth of the Th ...
. ''Britannia'' remained there with the squadron until August, when she began a refit at Portsmouth Dockyard. On completion of her refit in September, ''Britannia'' transferred out of the 3rd Battle Squadron for service in the 2nd Detached Squadron, which had been organised in 1915 to reinforce the Italian Navy against the Austro-Hungarian Navy in the Adriatic Sea
The Adriatic Sea () is a body of water separating the Italian Peninsula from the Balkan Peninsula. The Adriatic is the northernmost arm of the Mediterranean Sea, extending from the Strait of Otranto (where it connects to the Ionian Sea) to t ...
. Admiral Paolo Thaon di Revel
Paolo Camillo Thaon, Marquess of Revel (10 June 1859 – 24 March 1948), latterly titled with the honorary title of 1st Duke of the Sea, was an Italian admiral of the ''Regia Marina'' during World War I and later a politician.
Early life an ...
, the Italian naval chief of staff, believed that the threat from Austro-Hungarian submarines and naval mines in the narrow waters of the Adriatic was too serious for him to use the fleet for active operations. Instead, Revel decided to implement a blockade at the relatively safer southern end of the Adriatic with the main fleet, while smaller vessels, such as the MAS boats, conducted raids on Austro-Hungarian ships and installations.
She underwent a refit at Gibraltar
)
, anthem = " God Save the King"
, song = " Gibraltar Anthem"
, image_map = Gibraltar location in Europe.svg
, map_alt = Location of Gibraltar in Europe
, map_caption = United Kingdom shown in pale green
, mapsize =
, image_map2 = Gib ...
in February–March 1917, and on its completion was attached to the 9th Cruiser Squadron to serve on the Atlantic Patrol (United Kingdom), Atlantic Patrol and on convoy escort duty, based mainly at Sierra Leone. She relieved the armoured cruiser as flagship of the 9th Cruiser Squadron in March and underwent a refit at Bermuda in May, during which her 6-inch guns were removed and replaced by four 6-inch guns in shielded pivot mounts on her shelter deck, in place of where the 12-pounder guns had been located.
Loss
 On the morning of 9 November 1918, under the command of Captain (naval), Captain Francis Wade Caulfeild, ''Britannia'' was on a voyage in the western entrance to the Strait of Gibraltar when she was torpedoed off
On the morning of 9 November 1918, under the command of Captain (naval), Captain Francis Wade Caulfeild, ''Britannia'' was on a voyage in the western entrance to the Strait of Gibraltar when she was torpedoed off Cape Trafalgar
Cape Trafalgar (; es, Cabo Trafalgar ) is a headland in the Province of Cádiz in the southwest of Spain. The 1805 naval Battle of Trafalgar, in which the Royal Navy commanded by Admiral Horatio Nelson decisively defeated Napoleon's combined ...
by the German submarine SM UB-50, ''UB-50''. After the first explosion, the ship angle of list, listed ten degrees to port. A few minutes later, a second explosion started a fire in a 9.2-inch magazine (artillery), magazine, which in turn caused a cordite explosion in the magazine. Darkness below decks made it virtually impossible to find the flooding valves for the magazines, and those the crew did find were poorly located and therefore hard to turn, and the resulting failure to properly flood the burning magazine probably doomed the ship. ''Britannia'' held her 10-degree list for 2 and a half hours before sinking, allowing most of the crew to be taken off. Most of the men who were lost were killed by toxic smoke from burning cordite; 50 men died and 80 were injured. In total, 39 officers and 673 men were saved.
''Britannia'' was sunk only two days before the First Armistice at Compiègne, Armistice ending the First World War was signed on 11 November 1918. She was one of the last British warships lost in the war.
Notes
References
* * * * * * * * *Further reading
* * * * *External links
MaritimeQuest HMS ''Britannia'' pages
{{DEFAULTSORT:Britannia (1904) King Edward VII-class battleships Ships built in Portsmouth 1904 ships World War I battleships of the United Kingdom Maritime incidents in 1910 Maritime incidents in 1915 Maritime incidents in 1918 Ships sunk by German submarines in World War I World War I shipwrecks in the Atlantic Ocean Naval magazine explosions