Gytheion on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Gytheio ( el, Γύθειο, ) or Gythio, also the ancient Gythium or Gytheion ( grc, Γύθειον), is a town on the eastern shore of the
Castle Passavas
(now in ruins), which towers over the site of ancient Las. Further west is the historic city of




 The reputed founders of ancient Gythium were
The reputed founders of ancient Gythium were
/ref> The highest officer of the confederacy was the general, who was assisted by a treasurer (''rauias''), while the chief magistrates of the several communities bore the title of
 The province of Gytheio ( el, Επαρχία Γυθείου) was one of the
The province of Gytheio ( el, Επαρχία Γυθείου) was one of the
Mani Peninsula
The Mani Peninsula ( el, Μάνη, Mánē), also long known by its medieval name Maina or Maïna (Μαΐνη), is a geographical and cultural region in Southern Greece that is home to the Maniots (Mανιάτες, ''Maniátes'' in Greek), who cl ...
, and a former municipality in Laconia
Laconia or Lakonia ( el, Λακωνία, , ) is a historical and administrative region of Greece located on the southeastern part of the Peloponnese peninsula. Its administrative capital is Sparta. The word '' laconic''—to speak in a blunt, c ...
, Peloponnese
The Peloponnese (), Peloponnesus (; el, Πελοπόννησος, Pelopónnēsos,(), or Morea is a peninsula and geographic region in southern Greece. It is connected to the central part of the country by the Isthmus of Corinth land bridge which ...
, Greece
Greece,, or , romanized: ', officially the Hellenic Republic, is a country in Southeast Europe. It is situated on the southern tip of the Balkans, and is located at the crossroads of Europe, Asia, and Africa. Greece shares land borders wi ...
. Since the 2011 local government reform it is part of the municipality East Mani
East Mani ( el, Ανατολική Μάνη - ''Anatolikí Máni'') is a municipality in Laconia, Peloponnese, Greece. Its seat of administration is the town Gytheio (before 2011 the small town Kotronas). The municipality covers the southeastern p ...
, of which it is a municipal unit. The municipal unit has an area of 197.313 km2. It was the seaport
A port is a maritime facility comprising one or more wharves or loading areas, where ships load and discharge cargo and passengers. Although usually situated on a sea coast or estuary, ports can also be found far inland, such as ...
of Sparta
Sparta ( Doric Greek: Σπάρτα, ''Spártā''; Attic Greek: Σπάρτη, ''Spártē'') was a prominent city-state in Laconia, in ancient Greece. In antiquity, the city-state was known as Lacedaemon (, ), while the name Sparta referr ...
, some north. Gytheio is the site of ancient Cranae
Cranae or Kranai ( el, Κρανάη ) (also Marathonisi) is an island off the coast of Gytheio (ancient Gythium) connected to the land by a causeway built in 1898.
Etymology
Some believe that the etymology for the name Cranae (Kranai) comes from ...
, a tiny island where according to legend Paris of Troy and Helen
Helen may refer to:
People
* Helen of Troy, in Greek mythology, the most beautiful woman in the world
* Helen (actress) (born 1938), Indian actress
* Helen (given name), a given name (including a list of people with the name)
Places
* Helen, ...
from Sparta
Sparta ( Doric Greek: Σπάρτα, ''Spártā''; Attic Greek: Σπάρτη, ''Spártē'') was a prominent city-state in Laconia, in ancient Greece. In antiquity, the city-state was known as Lacedaemon (, ), while the name Sparta referr ...
spent their first night together before departing for Troy
Troy ( el, Τροία and Latin: Troia, Hittite: 𒋫𒊒𒄿𒊭 ''Truwiša'') or Ilion ( el, Ίλιον and Latin: Ilium, Hittite: 𒃾𒇻𒊭 ''Wiluša'') was an ancient city located at Hisarlik in present-day Turkey, south-west of Ç ...
, thus igniting the Trojan War
In Greek mythology, the Trojan War was waged against the city of Troy by the Achaeans ( Greeks) after Paris of Troy took Helen from her husband Menelaus, king of Sparta. The war is one of the most important events in Greek mythology and ...
.
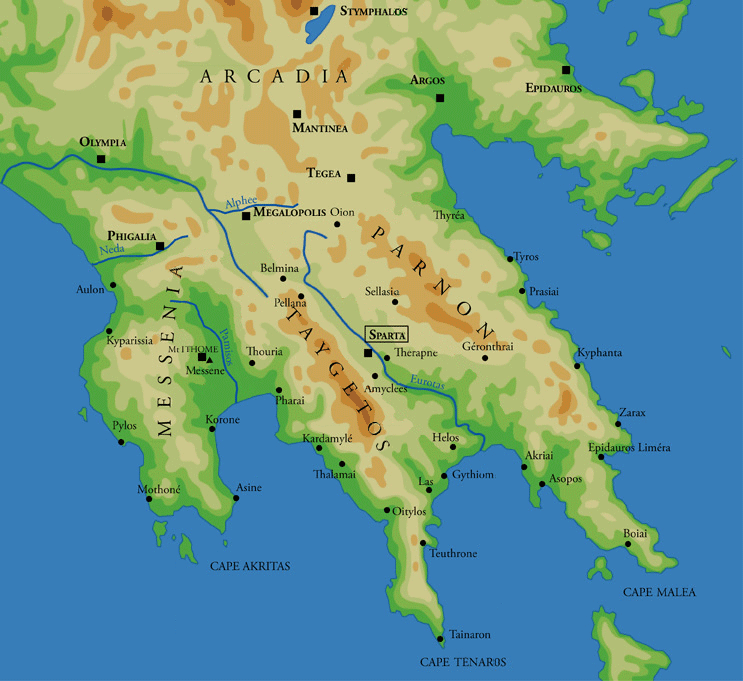
Gytheio used to be an important port until it was destroyed in 4th century AD, possibly by an earthquake. Even thereafter its strategic location gave Gytheio a significant role in Maniot history. Today it is the largest and most important town in Mani
Mani may refer to:
Geography
* Maní, Casanare, a town and municipality in Casanare Department, Colombia
* Mani, Chad, a town and sub-prefecture in Chad
* Mani, Evros, a village in northeastern Greece
* Mani, Karnataka, a village in Dakshina ...
. It is also the seat of the municipality of East Mani.
Historical population
Geography
Gytheio is located in the northeastern corner of the Mani Peninsula and lies on the northwestern end of theLaconian Gulf The Laconian Gulf ( el, Λακωνικός Κόλπος, translit=Lakonikos Kolpos), is a gulf in the south-eastern Peloponnese, in Greece. It is the southernmost gulf in Greece and the largest in the Peloponnese.
In the shape of an inverted "U ...
. Gytheio was built on a hill called Koumaros or Laryssio in one of the most fertile areas in Mani, near the mouth of the Gythium River
Gytheio ( el, Γύθειο, ) or Gythio, also the ancient Gythium or Gytheion ( grc, Γύθειον), is a town on the eastern shore of the Mani Peninsula, and a former municipality in Laconia, Peloponnese, Greece. Since the 2011 local government ...
, which is usually dry and has been nicknamed ''Xerias'' "dry river"; today, most of the Xerias is covered by Ermou Avenue.
Directly north and visible from the harbor is Profitis Ilias, the ultra-prominent
An ultra-prominent peak, or Ultra for short, is a mountain summit with a topographic prominence of or more; it is also called a P1500.
The prominence of a peak is the minimum height of climb to the summit on any route from a higher peak, or ...
peak of Taygetus
The Taygetus, Taugetus, Taygetos or Taÿgetus ( el, Ταΰγετος, Taygetos) is a mountain range on the Peloponnese peninsula in Southern Greece. The highest mountain of the range is Mount Taygetus, also known as "Profitis Ilias", or "Prophet ...
, the mountain range whose spine juts southward into the Mediterranean Sea
The Mediterranean Sea is a sea connected to the Atlantic Ocean, surrounded by the Mediterranean Basin and almost completely enclosed by land: on the north by Western and Southern Europe and Anatolia, on the south by North Africa, and on ...
and forms the Mani Peninsula.
On the ridgeline running south from Profitis Ilias sits the Monastery of Panayia Yiatrissa
The Monastery of Panayia Yiatrissa is an Orthodox Christian monastery located in the southern Peloponnese of Greece. The monastery was erected on the site of the ruins of an ancient temple of Athena. The conversion of the temple from pagan to ...
overlooking the valley toward Gytheio; the E4 hiking path connects the three, running south from Profitis Ilias, passing by the monastery, and leading to Gytheio.
Northeast of Gytheio is the delta of the Evrotas River
The Eurotas ( grc, Εὐρώτας) or Evrotas (modern Greek: ) is the main river of Laconia and one of the major rivers of the Peloponnese, in Greece. The river's springs are located just northwest of the border between Laconia and Arcadia, at ...
. Offshore are several small islands; the most important of these islands is Cranae
Cranae or Kranai ( el, Κρανάη ) (also Marathonisi) is an island off the coast of Gytheio (ancient Gythium) connected to the land by a causeway built in 1898.
Etymology
Some believe that the etymology for the name Cranae (Kranai) comes from ...
, on which sits the Tzannetakis Tower (now the Historical and Cultural museum of Mani) and a lighthouse built of solid marble. Today Cranae is connected to the mainland by a causeway.
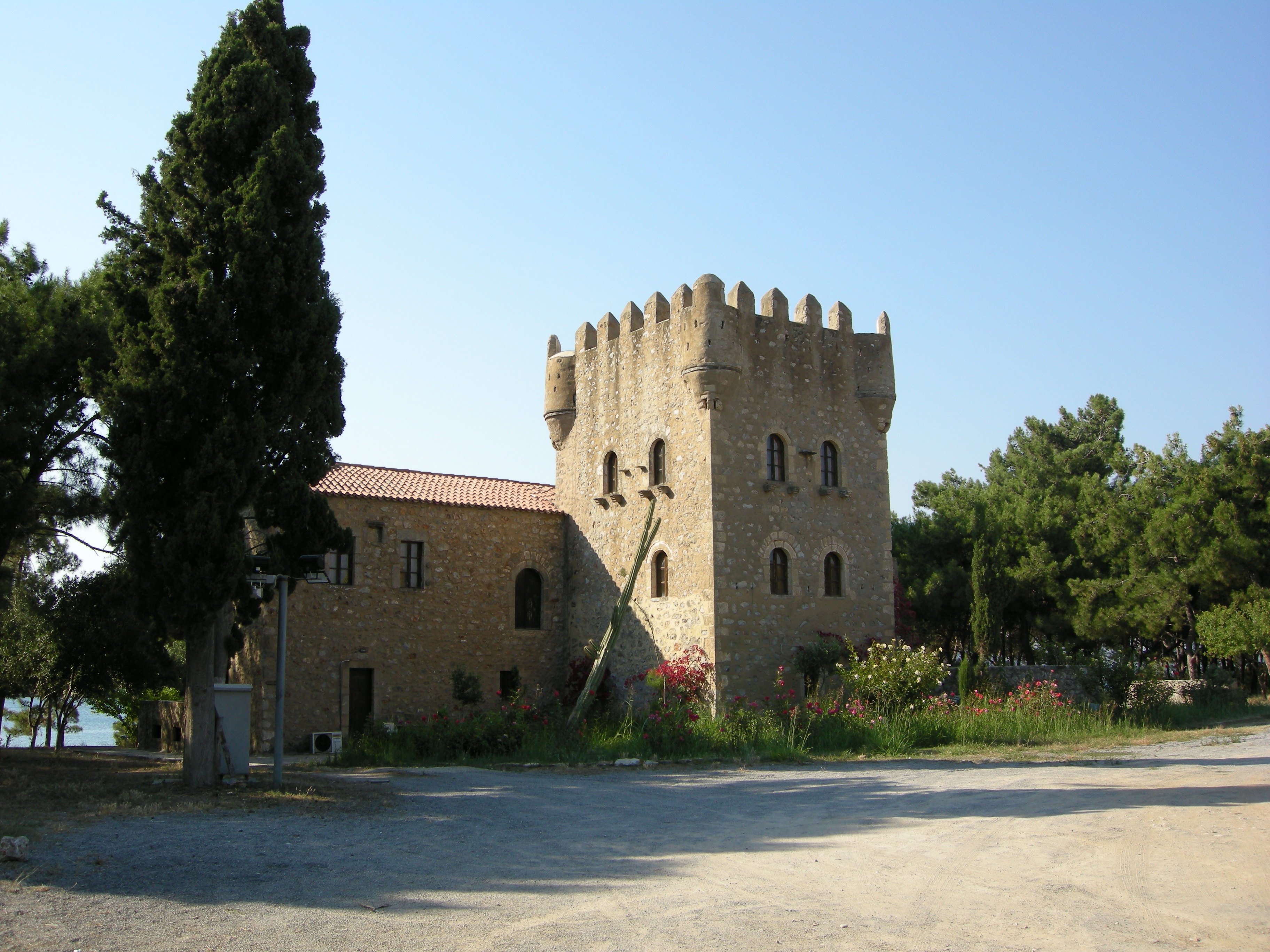
Approximately 5 km (3 mi) southwest is a passageway to the deeper Mani, historically guarded bCastle Passavas
(now in ruins), which towers over the site of ancient Las. Further west is the historic city of
Areopoli
Areopoli ( el, Αρεόπολη; before 1912 , ) is a town on the Mani Peninsula, Laconia, Greece.
The word ''Areopoli'', which means "city of Ares", the ancient Greek god of war, became the official name in 1912. It was the seat of Oitylo ...
and the Caves of Diros, which are important tourist attractions.
Gytheio is only southeast of Sparti
Sparta ( el, Σπάρτη ) is a city and municipality in Laconia, Greece. It lies at the site of ancient Sparta. The municipality was merged with six nearby municipalities in 2011, for a total population (as of 2011) of 35,259, of whom 17,408 li ...
, connected by Greek National Road 39. The town center is situated around the port. Pine trees are situated in the west and rocky mountains in the north.
Nearest Places
* South: Mavrovouni * Southwest: Castle Passava * West: Rachi * North: Stefania * East:Cranae
Cranae or Kranai ( el, Κρανάη ) (also Marathonisi) is an island off the coast of Gytheio (ancient Gythium) connected to the land by a causeway built in 1898.
Etymology
Some believe that the etymology for the name Cranae (Kranai) comes from ...
History


 The reputed founders of ancient Gythium were
The reputed founders of ancient Gythium were Heracles
Heracles ( ; grc-gre, Ἡρακλῆς, , glory/fame of Hera), born Alcaeus (, ''Alkaios'') or Alcides (, ''Alkeidēs''), was a divine hero in Greek mythology, the son of Zeus and Alcmene, and the foster son of Amphitryon.By his adoptiv ...
and Apollo
Apollo, grc, Ἀπόλλωνος, Apóllōnos, label=genitive , ; , grc-dor, Ἀπέλλων, Apéllōn, ; grc, Ἀπείλων, Apeílōn, label=Arcadocypriot Greek, ; grc-aeo, Ἄπλουν, Áploun, la, Apollō, la, Apollinis, label= ...
, who frequently appear on its coins or in other legends, and Castor and Pollux
Castor; grc, Κάστωρ, Kástōr, beaver. and Pollux. (or Polydeukes). are twin half-brothers in Greek and Roman mythology, known together as the Dioscuri.; grc, Διόσκουροι, Dióskouroi, sons of Zeus, links=no, from ''Dîos'' ('Z ...
:Fermor. ''Mani: Travels in the Southern Peloponesse.'', 302-303 the former of these names may point to the influence of Phoenicia
Phoenicia () was an ancient thalassocratic civilization originating in the Levant region of the eastern Mediterranean, primarily located in modern Lebanon. The territory of the Phoenician city-states extended and shrank throughout their his ...
n traders from Tyre, who, we know, visited the Laconian shores at a very early period. It is thought that Gytheio may have been the center of their purple dye trade because the Laconian Gulf had a plentiful source of murex
''Murex'' is a genus of medium to large sized predatory tropical sea snails. These are carnivorous marine gastropod molluscs in the family Muricidae, commonly called "murexes" or "rock snails".Houart, R.; Gofas, S. (2010). Murex Linnaeus, 175 ...
. In classical times it was a community of ''Perioeci
The Perioeci or Perioikoi (, ) were the second-tier citizens of the '' polis'' of Sparta until 200 BC. They lived in several dozen cities within Spartan territories (mostly Laconia and Messenia), which were dependent on Sparta. The ''perioeci' ...
'', politically dependent on Sparta, though doubtless with a municipal life of its own.
In 455 BC, during the First Peloponnesian War
The First Peloponnesian War (460–445 BC) was fought between Sparta as the leaders of the Peloponnesian League and Sparta's other allies, most notably Thebes, Greece, Thebes, and the Delian League led by Athens with support from Ancient Argos, ...
, it was burned by the Athenian admiral Tolmides Tolmides, (Greek: Τολμίδης), son of Tolmaeus, was a leading Athenian general of the First Peloponnesian War. He rivalled Pericles and Myronides for the military leadership of Athens during the 450s and early 440s BC.
In 455 BC, Tolmides wa ...
who besieged the city with 50 ships and 4,000 hoplites
Hoplites ( ) ( grc, ὁπλίτης : hoplítēs) were citizen-soldiers of Ancient Greek city-states who were primarily armed with spears and shields. Hoplite soldiers used the phalanx formation to be effective in war with fewer soldiers. The f ...
. It was rebuilt and was most probably, the building ground for the Spartan fleet in the Peloponnesian War
The Peloponnesian War (431–404 BC) was an ancient Greek war fought between Athens and Sparta and their respective allies for the hegemony of the Greek world. The war remained undecided for a long time until the decisive intervention of ...
. In 407 BC during the Peloponnesian War, Alcibiades
Alcibiades ( ; grc-gre, Ἀλκιβιάδης; 450 – 404 BC) was a prominent Athenian statesman, orator, and general. He was the last of the Alcmaeonidae, which fell from prominence after the Peloponnesian War. He played a major role in t ...
landed there and saw the thirty triremes the Spartans were building there. In 370 BC, the Thebans
Thebes (; ell, Θήβα, ''Thíva'' ; grc, Θῆβαι, ''Thêbai'' .) is a city in Boeotia, Central Greece. It played an important role in Greek myths, as the site of the stories of Cadmus, Oedipus, Dionysus, Heracles and others. Archaeol ...
under the command of Epaminondas
Epaminondas (; grc-gre, Ἐπαμεινώνδας; 419/411–362 BC) was a Greek general of Thebes and statesman of the 4th century BC who transformed the Ancient Greek city-state, leading it out of Spartan subjugation into a pre-eminent posit ...
besieged the city successfully for three days after ravaging Laconia
Laconia or Lakonia ( el, Λακωνία, , ) is a historical and administrative region of Greece located on the southeastern part of the Peloponnese peninsula. Its administrative capital is Sparta. The word '' laconic''—to speak in a blunt, c ...
. However it was recaptured by the Spartans three days later.
In 219 BC, Philip V of Macedon
Philip V ( grc-gre, Φίλιππος ; 238–179 BC) was king ( Basileus) of Macedonia from 221 to 179 BC. Philip's reign was principally marked by an unsuccessful struggle with the emerging power of the Roman Republic. He would lead Macedon a ...
tried to capture the city but without success. Under Nabis
Nabis ( grc-gre, Νάβις) was the last king of independent Sparta. He was probably a member of the Heracleidae, and he ruled from 207 BC to 192 BC, during the years of the First and Second Macedonian Wars and the eponymous " War against Nab ...
, Gythium became a major naval arsenal and port. During the Roman-Spartan War, Gythium was captured after a lengthy siege. After the war finished, Gythium was made part of the Union of Free Laconians under Achean protection.Greenhalgh and Eliopoulos. ''Deep into Mani:Journey to the southern tip of Greece.'', 21 Nabis recaptured Gythium three years and the Spartan fleet defeated the Achean fleet outside of Gythium. Gythium was liberated by a Roman fleet under the command of Aulus Atilius Serranus.
Subsequently, Gythium formed the most important of the Union of Free Laconians, a group of twenty-four, later eighteen, communities leagued together to maintain their autonomy against Sparta and declared free by Caesar Augustus
Caesar Augustus (born Gaius Octavius; 23 September 63 BC – 19 August AD 14), also known as Octavian, was the first Roman emperor; he reigned from 27 BC until his death in AD 14. He is known for being the founder of the Roman Pr ...
. Pausaniasbr>3.21.7/ref> The highest officer of the confederacy was the general, who was assisted by a treasurer (''rauias''), while the chief magistrates of the several communities bore the title of
ephors
The ephors were a board of five magistrates in ancient Sparta. They had an extensive range of judicial, religious, legislative, and military powers, and could shape Sparta's home and foreign affairs.
The word "''ephors''" (Ancient Greek ''ép ...
.
In Roman times Gythium remained a major port and it prospered as a member of the Union. As purple dye was popular in Rome
, established_title = Founded
, established_date = 753 BC
, founder = King Romulus ( legendary)
, image_map = Map of comune of Rome (metropolitan city of Capital Rome, region Lazio, Italy).svg
, map_caption ...
, Gythium exported that as well as porphyry and rose antique marble. Evidence of the ancient Gythium prosperity can be found by the fact that the Romans built an ancient theatre which is well preserved today and is still used occasionally. The ancient theatre, as well as the city's Acropolis (west to the location of the theatre) discovered by the archeologist Dimitris Skias in 1891. Some time in the 4th century AD, Gythium was destroyed. What happened to Gythium is not recorded but it is thought to have been either sacked by Alaric and Visigoths
The Visigoths (; la, Visigothi, Wisigothi, Vesi, Visi, Wesi, Wisi) were an early Germanic people who, along with the Ostrogoths, constituted the two major political entities of the Goths within the Roman Empire in late antiquity, or what is k ...
, pillaged by the Slavs
Slavs are the largest European ethnolinguistic group. They speak the various Slavic languages, belonging to the larger Balto-Slavic branch of the Indo-European languages. Slavs are geographically distributed throughout northern Eurasia, main ...
or destroyed by the massive earthquake that struck the area in 375 AD.
After the earthquake Gythium was abandoned. It remained a small village throughout the Byzantine
The Byzantine Empire, also referred to as the Eastern Roman Empire or Byzantium, was the continuation of the Roman Empire primarily in its eastern provinces during Late Antiquity and the Middle Ages, when its capital city was Constantinopl ...
and Ottoman times. Its importance grew when Tzannetos Grigorakis built his tower at Cranae
Cranae or Kranai ( el, Κρανάη ) (also Marathonisi) is an island off the coast of Gytheio (ancient Gythium) connected to the land by a causeway built in 1898.
Etymology
Some believe that the etymology for the name Cranae (Kranai) comes from ...
and more people came and settled at Gytheio. But during the Greek War of Independence
The Greek War of Independence, also known as the Greek Revolution or the Greek Revolution of 1821, was a successful war of independence by Greek revolutionaries against the Ottoman Empire between 1821 and 1829. The Greeks were later assisted by ...
, refugees flooded into Mani
Mani may refer to:
Geography
* Maní, Casanare, a town and municipality in Casanare Department, Colombia
* Mani, Chad, a town and sub-prefecture in Chad
* Mani, Evros, a village in northeastern Greece
* Mani, Karnataka, a village in Dakshina ...
and made Gytheio a major town.Saïtis. ''Mani.'', 46-47.
The modern Gytheio opened a port in the 1960s. Ferries sail from Gytheio to Kythira
Kythira (, ; el, Κύθηρα, , also transliterated as Cythera, Kythera and Kithira) is an island in Greece lying opposite the south-eastern tip of the Peloponnese peninsula. It is traditionally listed as one of the seven main Ionian Islands ...
almost daily and also to Crete
Crete ( el, Κρήτη, translit=, Modern: , Ancient: ) is the largest and most populous of the Greek islands, the 88th largest island in the world and the fifth largest island in the Mediterranean Sea, after Sicily, Sardinia, Cyprus, ...
twice a week. It is the See of the Diocese
In church governance, a diocese or bishopric is the ecclesiastical district under the jurisdiction of a bishop.
History
In the later organization of the Roman Empire, the increasingly subdivided provinces were administratively associ ...
of Gytheion and Oitylo
Oitylo ( el, Οίτυλο, pronounced Ítilo), known as "Βίτσουλο", pronounced Vitsoulo, in the native Maniot dialect, is a village and a former municipality in Laconia, Peloponnese, Greece. Since the 2011 local government reform it is part ...
, headed by a Metropolitan bishop
In Christian churches with episcopal polity, the rank of metropolitan bishop, or simply metropolitan (alternative obsolete form: metropolite), pertains to the diocesan bishop or archbishop of a metropolis.
Originally, the term referred to the ...
of the Orthodox Church of Greece
The Church of Greece ( el, Ἐκκλησία τῆς Ἑλλάδος, Ekklēsía tē̂s Helládos, ), part of the wider Greek Orthodox Church, is one of the autocephalous churches which make up the communion of Eastern Orthodox Christianity. It ...
. Gytheio is the largest and most important town in Mani. Most of the ruins of ancient Gythium are now submerged in the Laconian Gulf.
Some walls' remains can be seen today on the sandy beach of Valtaki and in the shallow waters, where the well known Dimitrios shipwreck lies stranded. It is also the capital of the municipality of Gytheio.
Province
 The province of Gytheio ( el, Επαρχία Γυθείου) was one of the
The province of Gytheio ( el, Επαρχία Γυθείου) was one of the provinces
A province is almost always an administrative division within a country or state. The term derives from the ancient Roman '' provincia'', which was the major territorial and administrative unit of the Roman Empire's territorial possessions ou ...
of the Laconia Prefecture. Its territory corresponded with that of the current municipal units Gytheio and East Mani
East Mani ( el, Ανατολική Μάνη - ''Anatolikí Máni'') is a municipality in Laconia, Peloponnese, Greece. Its seat of administration is the town Gytheio (before 2011 the small town Kotronas). The municipality covers the southeastern p ...
. It was abolished in 2006.
Persons
*Alexandros Othonaios
Alexandros Othonaios ( el, Αλέξανδρος Οθωναίος, Gytheio, 1879 – Athens, 20 September 1970) was a distinguished Greek general, who became briefly the acting Prime Minister of Greece, heading an emergency government during an ab ...
(1879–1970), general and former Prime Minister of Greece
The prime minister of the Hellenic Republic ( el, Πρωθυπουργός της Ελληνικής Δημοκρατίας, Prothypourgós tis Ellinikís Dimokratías), colloquially referred to as the prime minister of Greece ( el, Πρωθυ� ...
*Tzannis Tzannetakis
Tzannis Tzannetakis ( el, Τζαννής Τζαννετάκης) (13 September 1927 – 1 April 2010) was a Greek politician who was briefly Prime Minister of Greece during the political crisis of 1989.
Biography
Tzannetakis was born in Gythe ...
(1927–2010), politician and former Prime Minister of Greece
The prime minister of the Hellenic Republic ( el, Πρωθυπουργός της Ελληνικής Δημοκρατίας, Prothypourgós tis Ellinikís Dimokratías), colloquially referred to as the prime minister of Greece ( el, Πρωθυ� ...
International relations
Twin towns – Sister cities
Gytheio is twinned with: *Villeneuve-lès-Avignon
Villeneuve-lès-Avignon (; Provençal: ''Vilanòva d’Avinhon'') is a commune in the Gard department in southern France. It can also be spelled ''Villeneuve-lez-Avignon''.
History
In the 6th century the Benedictine abbey of St André was foun ...
, France
France (), officially the French Republic ( ), is a country primarily located in Western Europe. It also comprises of Overseas France, overseas regions and territories in the Americas and the Atlantic Ocean, Atlantic, Pacific Ocean, Pac ...
Notes
Inline Citations
References
Primary Sources
*Livy
Titus Livius (; 59 BC – AD 17), known in English as Livy ( ), was a Roman historian. He wrote a monumental history of Rome and the Roman people, titled , covering the period from the earliest legends of Rome before the traditional founding in ...
, translated by Henry Bettison, (1976). Rome and the Mediterranean. London: Penguin Classics. .
* Pausanias, translated by W.H.S Jones, (1918). Pausanias Description of Greece. London: Harvard University Press. .
* Polybius
Polybius (; grc-gre, Πολύβιος, ; ) was a Greek historian of the Hellenistic period. He is noted for his work , which covered the period of 264–146 BC and the Punic Wars in detail.
Polybius is important for his analysis of the mixed ...
, translated by Frank W. Walbank, (1979). The Rise of the Roman Empire. New York: Penguin Classics. .
Secondary Sources
* Collitz-Bechtel, Sammlung d. griech. Dialekt-Inschriften, iii. Nos. 4562-4573; British School Annual, x. 179 foll. *Paul Cartledge
Paul Anthony Cartledge (born 24 March 1947)"CARTLEDGE, Prof. Paul Anthony", ''Who's Who 2010'', A & C Black, 2010online edition/ref> is a British ancient historian and academic. From 2008 to 2014 he was the A. G. Leventis Professor of Greek C ...
and Antony Spawforth, (2002). Hellenistic and Roman Sparta: A tale of two cities. London: Routledge.
* E. Curtius, Peloponnesos, ii. 267 foll. Inscriptions: Le Bas-Foucart, Voyage archéologique, ii. Nos. 238-248 f.
* Patrick Leigh Fermor
Sir Patrick Michael Leigh Fermor (11 February 1915 – 10 June 2011) was an English writer, scholar, soldier and polyglot. He played a prominent role in the Cretan resistance during the Second World War, and was widely seen as Britain's great ...
, (1984). '' Mani: Travels in the Southern Peloponnese''. London: Penguin.
* Peter Greenhalgh and Edward Eliopoulos, (1985). Deep into Mani:Journey to the southern tip of Greece. London: Trinity Press
* Peter Green, (1990). Alexander to Actium: The Historical Evolution of the Hellenistic Age, (2nd edition). Los Angeles: University of California Press. .
* Rosemary Hall, Paul Hellander, Corinne Simcock and David Willet. Lonely Planet: Greece. Singapore: SNP Printing Pte Ltd.
* Kyriakos Kassis, (1979). Mani's History. Athens: Presoft
* William Leake
William Leake, father (died 1633) and son (died 1681), were London publishers and booksellers of the late sixteenth and the seventeenth centuries. They were responsible for a range of texts in English Renaissance drama and poetry, including work ...
, Travels in the Morea, i. 244 foll.
* Maria Mavromataki, (2001). 8,500 Years of Civilization: Greece: Between Legend and History. Athens: Haïtalis.
*
* G. Weber, De Gytheo et Lacedaemoniorum rebus navalibus (Heidelberg, 1833)
{{Authority control
Cities in ancient Peloponnese
Populated places in Laconia
Mediterranean port cities and towns in Greece
Populated places in the Mani Peninsula
Provinces of Greece
East Mani