Gunpowder plot on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
The Gunpowder Plot of 1605, in earlier centuries often called the Gunpowder Treason Plot or the Jesuit Treason, was a failed assassination attempt against
 Between 1533 and 1540, King Henry VIII took control of the English Church from Rome, the start of several decades of religious tension in England. English Catholics struggled in a society dominated by the newly separate and increasingly
Between 1533 and 1540, King Henry VIII took control of the English Church from Rome, the start of several decades of religious tension in England. English Catholics struggled in a society dominated by the newly separate and increasingly
 The conspirators' principal aim was to kill King James, but many other important targets would also be present at the State Opening of Parliament, including the monarch's nearest relatives and members of the Privy Council. The senior judges of the English legal system, most of the Protestant aristocracy, and the bishops of the Church of England would all have attended in their capacity as members of the House of Lords, along with the members of the
The conspirators' principal aim was to kill King James, but many other important targets would also be present at the State Opening of Parliament, including the monarch's nearest relatives and members of the Privy Council. The senior judges of the English legal system, most of the Protestant aristocracy, and the bishops of the Church of England would all have attended in their capacity as members of the House of Lords, along with the members of the
 The first meeting between the five conspirators took place on 20 May 1604, probably at the Duck and Drake Inn, just off the Strand, Thomas Wintour's usual residence when staying in London. Catesby, Thomas Wintour, and John Wright were in attendance, joined by Guy Fawkes and Thomas Percy. Alone in a private room, the five plotters swore an oath of secrecy on a prayer book. By coincidence, and ignorant of the plot, Father John Gerard (a friend of Catesby's) was celebrating Mass in another room, and the five men subsequently received the
The first meeting between the five conspirators took place on 20 May 1604, probably at the Duck and Drake Inn, just off the Strand, Thomas Wintour's usual residence when staying in London. Catesby, Thomas Wintour, and John Wright were in attendance, joined by Guy Fawkes and Thomas Percy. Alone in a private room, the five plotters swore an oath of secrecy on a prayer book. By coincidence, and ignorant of the plot, Father John Gerard (a friend of Catesby's) was celebrating Mass in another room, and the five men subsequently received the
 The conspirators returned to London in October 1604, when Robert Keyes, a "desperate man, ruined and indebted", was admitted to the group. His responsibility was to take charge of Catesby's house in Lambeth, where the gunpowder and other supplies were to be stored. Keyes's family had notable connections; his wife's employer was the Catholic Lord Mordaunt. He was tall, with a red beard, and was seen as trustworthy and—like Fawkes—capable of looking after himself. In December Catesby recruited his servant, Thomas Bates, into the plot, after the latter accidentally became aware of it.
It was announced on 24 December that the re-opening of Parliament would be delayed. Concern over the plague meant that rather than sitting in February, as the plotters had originally planned for, Parliament would not sit again until 3 October 1605. The contemporaneous account of the prosecution claimed that during this delay the conspirators were digging a tunnel beneath Parliament. This may have been a government fabrication, as no evidence for the existence of a tunnel was presented by the prosecution, and no trace of one has ever been found. The account of a tunnel comes directly from Thomas Wintour's confession, and Guy Fawkes did not admit the existence of such a scheme until his fifth interrogation. Logistically, digging a tunnel would have proved extremely difficult, especially as none of the conspirators had any experience of mining. If the story is true, by 6 December the Scottish commissioners had finished their work, and the conspirators were busy tunnelling from their rented house to the House of Lords. They ceased their efforts when, during tunnelling, they heard a noise from above. The noise turned out to be the then-tenant's widow, who was clearing out the
The conspirators returned to London in October 1604, when Robert Keyes, a "desperate man, ruined and indebted", was admitted to the group. His responsibility was to take charge of Catesby's house in Lambeth, where the gunpowder and other supplies were to be stored. Keyes's family had notable connections; his wife's employer was the Catholic Lord Mordaunt. He was tall, with a red beard, and was seen as trustworthy and—like Fawkes—capable of looking after himself. In December Catesby recruited his servant, Thomas Bates, into the plot, after the latter accidentally became aware of it.
It was announced on 24 December that the re-opening of Parliament would be delayed. Concern over the plague meant that rather than sitting in February, as the plotters had originally planned for, Parliament would not sit again until 3 October 1605. The contemporaneous account of the prosecution claimed that during this delay the conspirators were digging a tunnel beneath Parliament. This may have been a government fabrication, as no evidence for the existence of a tunnel was presented by the prosecution, and no trace of one has ever been found. The account of a tunnel comes directly from Thomas Wintour's confession, and Guy Fawkes did not admit the existence of such a scheme until his fifth interrogation. Logistically, digging a tunnel would have proved extremely difficult, especially as none of the conspirators had any experience of mining. If the story is true, by 6 December the Scottish commissioners had finished their work, and the conspirators were busy tunnelling from their rented house to the House of Lords. They ceased their efforts when, during tunnelling, they heard a noise from above. The noise turned out to be the then-tenant's widow, who was clearing out the
 In the second week of June Catesby met in London the principal Jesuit in England, Father
In the second week of June Catesby met in London the principal Jesuit in England, Father
 The details of the plot were finalised in October, in a series of taverns across London and
The details of the plot were finalised in October, in a series of taverns across London and
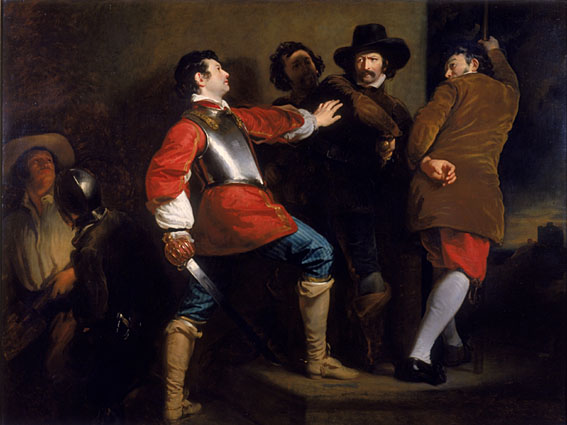 Although two accounts of the number of searches and their timing exist, according to the King's version, the first search of the buildings in and around Parliament was made on Monday 4 November—as the plotters were busy making their final preparations—by Suffolk, Monteagle, and John Whynniard. They found a large pile of firewood in the undercroft beneath the House of Lords, accompanied by what they presumed to be a serving man (Fawkes), who told them that the firewood belonged to his master, Thomas Percy. They left to report their findings, at which time Fawkes also left the building. The mention of Percy's name aroused further suspicion as he was already known to the authorities as a Catholic agitator. The King insisted that a more thorough search be undertaken. Late that night, the search party, headed by Thomas Knyvet, returned to the undercroft. They again found Fawkes, dressed in a cloak and hat, and wearing boots and spurs. He was arrested, whereupon he gave his name as John Johnson. He was carrying a lantern now held in the Ashmolean Museum,
Although two accounts of the number of searches and their timing exist, according to the King's version, the first search of the buildings in and around Parliament was made on Monday 4 November—as the plotters were busy making their final preparations—by Suffolk, Monteagle, and John Whynniard. They found a large pile of firewood in the undercroft beneath the House of Lords, accompanied by what they presumed to be a serving man (Fawkes), who told them that the firewood belonged to his master, Thomas Percy. They left to report their findings, at which time Fawkes also left the building. The mention of Percy's name aroused further suspicion as he was already known to the authorities as a Catholic agitator. The King insisted that a more thorough search be undertaken. Late that night, the search party, headed by Thomas Knyvet, returned to the undercroft. They again found Fawkes, dressed in a cloak and hat, and wearing boots and spurs. He was arrested, whereupon he gave his name as John Johnson. He was carrying a lantern now held in the Ashmolean Museum,
 On 6 November, the Lord Chief Justice, Sir John Popham (a man with a deep-seated hatred of Catholics) questioned Rookwood's servants. By the evening he had learned the names of several of those involved in the conspiracy: Catesby, Rookwood, Keyes, Wynter, John and Christopher Wright, and Grant. "Johnson" meanwhile persisted with his story, and along with the gunpowder he was found with, was moved to the
On 6 November, the Lord Chief Justice, Sir John Popham (a man with a deep-seated hatred of Catholics) questioned Rookwood's servants. By the evening he had learned the names of several of those involved in the conspiracy: Catesby, Rookwood, Keyes, Wynter, John and Christopher Wright, and Grant. "Johnson" meanwhile persisted with his story, and along with the gunpowder he was found with, was moved to the
 Sir Edward Coke was in charge of the interrogations. Over a period of about ten weeks, in the Lieutenant's Lodgings at the Tower of London (now known as the Queen's House) he questioned those who had been implicated in the plot. For the first round of interrogations, no real proof exists that these people were tortured, although on several occasions Salisbury certainly suggested that they should be. Coke later revealed that the threat of torture was in most cases enough to elicit a confession from those caught up in the aftermath of the plot.
Only two confessions were printed in full: Fawkes's confession of 8 November, and Wintour's of 23 November. Having been involved in the conspiracy from the start (unlike Fawkes), Wintour was able to give extremely valuable information to the Privy Council. The handwriting on his testimony is almost certainly that of the man himself, but his signature was markedly different. Wintour had previously only ever signed his name as such, but his confession is signed "Winter", and since he had been shot in the shoulder, the steady hand used to write the signature may indicate some measure of government interference—or it may indicate that writing a shorter version of his name was less painful. Wintour's testimony makes no mention of his brother, Robert. Both were published in the so-called ''King's Book'', a hastily written official account of the conspiracy published in late November 1605.
Henry Percy, Earl of Northumberland, was in a difficult position. His midday dinner with Thomas Percy on 4 November was damning evidence against him, and after Thomas Percy's death there was nobody who could either implicate him or clear him. The Privy Council suspected that Northumberland would have been Princess Elizabeth's protector had the plot succeeded, but there was insufficient evidence to convict him. Northumberland remained in the Tower and on 27 June 1606 was finally charged with contempt. He was stripped of all public offices, fined £30,000 (about £ in ), and kept in the Tower until June 1621. The Lords Mordaunt and Stourton were tried in the Star Chamber. They were condemned to imprisonment in the Tower, where they remained until 1608, when they were transferred to the Fleet Prison. Both were also given significant fines.
Several other people not involved in the conspiracy, but known or related to the conspirators, were also questioned. Northumberland's brothers, Sir Allen and Sir Josceline Percy, were arrested. Lord Montagu had employed Fawkes at an early age, and had also met Catesby on 29 October, and was therefore of interest; he was released several months later.
Sir Edward Coke was in charge of the interrogations. Over a period of about ten weeks, in the Lieutenant's Lodgings at the Tower of London (now known as the Queen's House) he questioned those who had been implicated in the plot. For the first round of interrogations, no real proof exists that these people were tortured, although on several occasions Salisbury certainly suggested that they should be. Coke later revealed that the threat of torture was in most cases enough to elicit a confession from those caught up in the aftermath of the plot.
Only two confessions were printed in full: Fawkes's confession of 8 November, and Wintour's of 23 November. Having been involved in the conspiracy from the start (unlike Fawkes), Wintour was able to give extremely valuable information to the Privy Council. The handwriting on his testimony is almost certainly that of the man himself, but his signature was markedly different. Wintour had previously only ever signed his name as such, but his confession is signed "Winter", and since he had been shot in the shoulder, the steady hand used to write the signature may indicate some measure of government interference—or it may indicate that writing a shorter version of his name was less painful. Wintour's testimony makes no mention of his brother, Robert. Both were published in the so-called ''King's Book'', a hastily written official account of the conspiracy published in late November 1605.
Henry Percy, Earl of Northumberland, was in a difficult position. His midday dinner with Thomas Percy on 4 November was damning evidence against him, and after Thomas Percy's death there was nobody who could either implicate him or clear him. The Privy Council suspected that Northumberland would have been Princess Elizabeth's protector had the plot succeeded, but there was insufficient evidence to convict him. Northumberland remained in the Tower and on 27 June 1606 was finally charged with contempt. He was stripped of all public offices, fined £30,000 (about £ in ), and kept in the Tower until June 1621. The Lords Mordaunt and Stourton were tried in the Star Chamber. They were condemned to imprisonment in the Tower, where they remained until 1608, when they were transferred to the Fleet Prison. Both were also given significant fines.
Several other people not involved in the conspiracy, but known or related to the conspirators, were also questioned. Northumberland's brothers, Sir Allen and Sir Josceline Percy, were arrested. Lord Montagu had employed Fawkes at an early age, and had also met Catesby on 29 October, and was therefore of interest; he was released several months later.
 Thomas Bates confessed on 4 December, providing much of the information that Salisbury needed to link the Catholic clergy to the plot. Bates had been present at most of the conspirators' meetings, and under interrogation he implicated Father Tesimond in the plot. On 13 January 1606, he described how he had visited Garnet and Tesimond on 7 November to inform Garnet of the plot's failure. Bates also told his interrogators of his ride with Tesimond to Huddington, before the priest left him to head for the Habingtons at Hindlip Hall, and of a meeting between Garnet, Gerard, and Tesimond in October 1605.
At about the same time in December, Tresham's health began to deteriorate. He was visited regularly by his wife, a nurse, and his servant William Vavasour—who documented his strangury. Before he died, Tresham had also told of Garnet's involvement with the 1603 mission to Spain, but in his last hours he retracted some of these statements. Nowhere in his confession did he mention the Monteagle letter. He died early on the morning of 23 December, and was buried in the Tower. Nevertheless, he was attainted along with the other plotters; his head was set on a pike either (accounts differ) at Northampton or London Bridge, and his estates confiscated.
On 15 January a proclamation named Father Garnet, Father Gerard, and Father Greenway (Tesimond) as wanted men. Tesimond and Gerard escaped the country and lived out their days in freedom. Several days earlier, on 9 January, Robert Wintour and Stephen Littleton were captured. They had been hiding at
Thomas Bates confessed on 4 December, providing much of the information that Salisbury needed to link the Catholic clergy to the plot. Bates had been present at most of the conspirators' meetings, and under interrogation he implicated Father Tesimond in the plot. On 13 January 1606, he described how he had visited Garnet and Tesimond on 7 November to inform Garnet of the plot's failure. Bates also told his interrogators of his ride with Tesimond to Huddington, before the priest left him to head for the Habingtons at Hindlip Hall, and of a meeting between Garnet, Gerard, and Tesimond in October 1605.
At about the same time in December, Tresham's health began to deteriorate. He was visited regularly by his wife, a nurse, and his servant William Vavasour—who documented his strangury. Before he died, Tresham had also told of Garnet's involvement with the 1603 mission to Spain, but in his last hours he retracted some of these statements. Nowhere in his confession did he mention the Monteagle letter. He died early on the morning of 23 December, and was buried in the Tower. Nevertheless, he was attainted along with the other plotters; his head was set on a pike either (accounts differ) at Northampton or London Bridge, and his estates confiscated.
On 15 January a proclamation named Father Garnet, Father Gerard, and Father Greenway (Tesimond) as wanted men. Tesimond and Gerard escaped the country and lived out their days in freedom. Several days earlier, on 9 January, Robert Wintour and Stephen Littleton were captured. They had been hiding at
 By coincidence, on the same day that Garnet was found, the surviving conspirators were
By coincidence, on the same day that Garnet was found, the surviving conspirators were
 Greater freedom for Roman Catholics to worship as they chose seemed unlikely in 1604, but the discovery of such a wide-ranging conspiracy, the capture of those involved, and the subsequent trials, led Parliament to consider introducing new anti-Catholic legislation. The event also destroyed all hope that the Spanish would ever secure tolerance of the Catholics in England. In the summer of 1606, laws against recusancy were strengthened; the Popish Recusants Act returned England to the Elizabethan system of fines and restrictions, introduced a sacramental test, and an Oath of Allegiance, requiring Catholics to abjure as a "heresy" the doctrine that "princes excommunicated by the Pope could be deposed or assassinated".
Greater freedom for Roman Catholics to worship as they chose seemed unlikely in 1604, but the discovery of such a wide-ranging conspiracy, the capture of those involved, and the subsequent trials, led Parliament to consider introducing new anti-Catholic legislation. The event also destroyed all hope that the Spanish would ever secure tolerance of the Catholics in England. In the summer of 1606, laws against recusancy were strengthened; the Popish Recusants Act returned England to the Elizabethan system of fines and restrictions, introduced a sacramental test, and an Oath of Allegiance, requiring Catholics to abjure as a "heresy" the doctrine that "princes excommunicated by the Pope could be deposed or assassinated".
 In January 1606, during the first sitting of Parliament since the plot, the
In January 1606, during the first sitting of Parliament since the plot, the
 In the 2005, ITV programme '' The Gunpowder Plot: Exploding the Legend'', a full-size replica of the House of Lords was built and destroyed with barrels of gunpowder, totalling 1
In the 2005, ITV programme '' The Gunpowder Plot: Exploding the Legend'', a full-size replica of the House of Lords was built and destroyed with barrels of gunpowder, totalling 1
The Gunpowder Plot
The original House of Commons Journal recording the discovery of the plot – Parliamentary Archives catalogue
Digital image of the Original Thanksgiving Act following the Gunpowder Plot from the Parliamentary Archives
Photograph of the Guy Fawkes Search that takes place at the start of a new Parliament – Parliamentary Archives
The Palace of Westminster in 1605 from the Parliamentary Archives
The Gunpowder Plot Society
The story of Guy Fawkes and The Gunpowder Plot from the BBC, with archive video clips
What If the Gunpowder Plot Had Succeeded?
Interactive Guide: Gunpowder Plot
Website of a crew member of ITV's ''Exploding the Legend'' programme, with a photograph of the explosion
* Mark Nicholls, ''The Gunpowder Plot'', Oxford Dictionary of National Biography onlin
History.com – Gunpowder Plot
{{Featured article 17th century in London Anti-Protestantism Conspiracies 1605 in England Attacks on legislatures 17th-century coups d'état and coup attempts Palace of Westminster Military coups in England Failed assassination attempts in the United Kingdom
King James I
James VI and I (James Charles Stuart; 19 June 1566 – 27 March 1625) was King of Scotland as James VI from 24 July 1567 and King of England and Ireland as James I from the union of the Scottish and English crowns on 24 March 1603 until hi ...
by a group of provincial English Catholics led by Robert Catesby
Robert Catesby (c. 1572 – 8 November 1605) was the leader of a group of English Catholics who planned the failed Gunpowder Plot of 1605.
Born in Warwickshire, Catesby was educated in Oxford. His family were prominent recusant Catholics, and ...
who sought to restore the Catholic monarchy to England after decades of persecution against Catholics.
The plan was to blow up the House of Lords
The House of Lords, also known as the House of Peers, is the upper house of the Parliament of the United Kingdom. Membership is by appointment, heredity or official function. Like the House of Commons, it meets in the Palace of Westminste ...
during the State Opening of Parliament on 5 November 1605, as the prelude to a popular revolt in the Midlands during which King James's nine-year-old daughter, Elizabeth
Elizabeth or Elisabeth may refer to:
People
* Elizabeth (given name), a female given name (including people with that name)
* Elizabeth (biblical figure), mother of John the Baptist
Ships
* HMS ''Elizabeth'', several ships
* ''Elisabeth'' (sch ...
, was to be installed as the Catholic head of state. Catesby may have embarked on the scheme after hopes of securing greater religious tolerance under King James I
James VI and I (James Charles Stuart; 19 June 1566 – 27 March 1625) was King of Scotland as James VI from 24 July 1567 and King of England and Ireland as James I from the union of the Scottish and English crowns on 24 March 1603 until hi ...
had faded, leaving many English Catholics disappointed. His fellow contributors were John and Christopher Wright
John (Jack) Wright (January 1568 – 8 November 1605), and Christopher (Kit) Wright (1570? – 8 November 1605), were members of the group of provincial English Catholics who planned the failed Gunpowder Plot of 1605, a conspiracy to assassina ...
, Robert and Thomas Wintour
Robert Wintour (1568 – 30 January 1606) and Thomas Wintour (1571 or 1572 – 31 January 1606), also spelt Winter, were members of the Gunpowder Plot, a failed conspiracy to assassinate King James I. Brothers, they were related to other consp ...
, Thomas Percy, Guy Fawkes
Guy Fawkes (; 13 April 1570 – 31 January 1606), also known as Guido Fawkes while fighting for the Spanish, was a member of a group of provincial English Catholics involved in the failed Gunpowder Plot of 1605. He was born and educated ...
, Robert Keyes, Thomas Bates, John Grant, Ambrose Rookwood, Sir Everard Digby
Sir Everard Digby (c. 1578 – 30 January 1606) was a member of the group of provincial English Catholics who planned the failed Gunpowder Plot of 1605. Although he was raised in a Protestant household, and married a Protestant, Digby and his w ...
and Francis Tresham
Francis Tresham ( 1567 – 23 December 1605), eldest son of
Thomas Tresham and Muriel Throckmorton, was a member of the group of English provincial Catholics who planned the failed Gunpowder Plot of 1605, a conspiracy to assassinate King Jame ...
. Fawkes, who had 10 years of military experience fighting in the Spanish Netherlands
Spanish Netherlands (Spanish: Países Bajos Españoles; Dutch: Spaanse Nederlanden; French: Pays-Bas espagnols; German: Spanische Niederlande.) (historically in Spanish: ''Flandes'', the name "Flanders" was used as a ''pars pro toto'') was the H ...
in the failed suppression of the Dutch Revolt, was given charge of the explosives.
The plot was revealed to the authorities in an anonymous letter sent to William Parker, 4th Baron Monteagle
William Parker, 13th Baron Morley, 4th Baron Monteagle (15751 July 1622), was an English peer, best known for his role in the discovery of the Gunpowder Plot. In 1605 Parker was due to attend the opening of Parliament. He was a member of the Hou ...
, on 26 October 1605. During a search of the House of Lords in the evening on 4 November 1605, Fawkes was discovered guarding 36 barrels of gunpowder
Gunpowder, also commonly known as black powder to distinguish it from modern smokeless powder, is the earliest known chemical explosive. It consists of a mixture of sulfur, carbon (in the form of charcoal) and potassium nitrate (saltpeter). Th ...
—enough to reduce the House of Lords to rubble—and arrested. Most of the conspirators fled from London as they learned that the plot had been discovered, trying to enlist support along the way. Several made a stand against the pursuing Sheriff of Worcester
This is a list of sheriffs and since 1998 high sheriffs of Worcestershire.
The Sheriff is the oldest secular office under the Crown. Formerly the Sheriff was the principal law enforcement officer in the county but over the centuries most of the ...
and his men at Holbeche House
Holbeche House (also, in some texts, Holbeach or Holbeache) is a mansion located approximately north of Kingswinford, now in the Metropolitan Borough of Dudley but historically in Staffordshire.Aikin, L. p.244 Some members of the Gunpowder P ...
; in the ensuing battle Catesby was one of those shot and killed. At their trial on 27 January 1606, eight of the survivors, including Fawkes, were convicted and sentenced to be hanged, drawn and quartered.
Details of the assassination attempt were allegedly known by the principal Jesuit of England, Father Henry Garnet
Henry Garnet (July 1555 – 3 May 1606), sometimes Henry Garnett, was an English Jesuit priest executed for his complicity in the Gunpowder Plot of 1605. Born in Heanor, Derbyshire, he was educated in Nottingham and later at Winchester Colle ...
. Although he was convicted of treason
Treason is the crime of attacking a state authority to which one owes allegiance. This typically includes acts such as participating in a war against one's native country, attempting to overthrow its government, spying on its military, its diplo ...
and sentenced to death, doubt has been cast on how much he really knew of the plot. As its existence was revealed to him through confession
A confession is a statement – made by a person or by a group of persons – acknowledging some personal fact that the person (or the group) would ostensibly prefer to keep hidden. The term presumes that the speaker is providing information th ...
, Garnet was prevented from informing the authorities by the absolute confidentiality of the confessional. Although anti-Catholic legislation was introduced soon after the discovery of the plot, many important and loyal Catholics retained high office during King James I's reign. The thwarting of the Gunpowder Plot was commemorated for many years afterwards by special sermons and other public events such as the ringing of church bells, which evolved into the British variant of Bonfire Night of today.
Background
Religion in England
 Between 1533 and 1540, King Henry VIII took control of the English Church from Rome, the start of several decades of religious tension in England. English Catholics struggled in a society dominated by the newly separate and increasingly
Between 1533 and 1540, King Henry VIII took control of the English Church from Rome, the start of several decades of religious tension in England. English Catholics struggled in a society dominated by the newly separate and increasingly Protestant
Protestantism is a branch of Christianity that follows the theological tenets of the Protestant Reformation, a movement that began seeking to reform the Catholic Church from within in the 16th century against what its followers perceived to b ...
Church of England
The Church of England (C of E) is the established Christian church in England and the mother church of the international Anglican Communion. It traces its history to the Christian church recorded as existing in the Roman province of Britai ...
. Henry's daughter, Queen Elizabeth I
Elizabeth I (7 September 153324 March 1603) was Queen of England and Ireland from 17 November 1558 until her death in 1603. Elizabeth was the last of the five House of Tudor monarchs and is sometimes referred to as the "Virgin Queen".
El ...
, responded to the growing religious divide by introducing the Elizabethan Religious Settlement
The Elizabethan Religious Settlement is the name given to the religious and political arrangements made for England during the reign of Elizabeth I (1558–1603). Implemented between 1559 and 1563, the settlement is considered the end of the ...
, which required anyone appointed to a public or church office to swear allegiance to the monarch as head of the Church and state. The penalties for refusal were severe; fines were imposed for recusancy
Recusancy (from la, recusare, translation=to refuse) was the state of those who remained loyal to the Catholic Church and refused to attend Church of England services after the English Reformation.
The 1558 Recusancy Acts passed in the reign ...
, and repeat offenders risked imprisonment and execution. Catholicism became marginalised, but despite the threat of torture or execution, priests continued to practise their faith in secret.
Succession
Queen Elizabeth, unmarried and childless, steadfastly refused to name an heir. Many Catholics believed that her Catholic cousin,Mary, Queen of Scots
Mary, Queen of Scots (8 December 1542 – 8 February 1587), also known as Mary Stuart or Mary I of Scotland, was Queen of Scotland from 14 December 1542 until her forced abdication in 1567.
The only surviving legitimate child of James V of S ...
, was the legitimate heir to the English throne, but she was executed for treason in 1587. The English Secretary of State, Robert Cecil, negotiated secretly with Mary's son and successor, King James VI of Scotland. In the months before Elizabeth's death on 24 March 1603, Cecil prepared the way for James to succeed her.
Some exiled Catholics favoured Philip II of Spain's daughter, Isabella
Isabella may refer to:
People and fictional characters
* Isabella (given name), including a list of people and fictional characters
* Isabella (surname), including a list of people
Places
United States
* Isabella, Alabama, an unincorpor ...
, as Elizabeth's successor. More moderate Catholics looked to James's and Elizabeth's cousin Arbella Stuart
Lady Arbella Stuart (also Arabella, or Stewart; 1575 – 25 September 1615) was an English noblewoman who was considered a possible successor to Queen Elizabeth I of England. During the reign of King James VI and I (her first cousin), she marri ...
, a woman thought to have Catholic sympathies. As Elizabeth's health deteriorated, the government detained those they considered to be the "principal papists", and the Privy Council grew so worried that Arbella Stuart was moved closer to London to prevent her from being kidnapped by papist
The words Popery (adjective Popish) and Papism (adjective Papist, also used to refer to an individual) are mainly historical pejorative words in the English language for Roman Catholicism, once frequently used by Protestants and Eastern Orthodo ...
s.
Despite competing claims to the English throne, the transition of power following Elizabeth's death went smoothly. James's succession was announced by a proclamation from Cecil on 24 March, which was generally celebrated. Leading papists, rather than causing trouble as anticipated, reacted to the news by offering their enthusiastic support for the new monarch. Jesuit priests, whose presence in England was punishable by death, also demonstrated their support for James, who was widely believed to embody "the natural order of things".
James ordered a ceasefire in the conflict with Spain, and even though the two countries were still technically at war, King Philip III sent his envoy, Don Juan de Tassis, to congratulate James on his accession. In the following year both countries signed the Treaty of London.
For decades, the English had lived under a monarch who refused to provide an heir, but James arrived with a family and a clear line of succession. His wife, Anne of Denmark
Anne of Denmark (; 12 December 1574 – 2 March 1619) was the wife of King James VI and I; as such, she was Queen of Scotland from their marriage on 20 August 1589 and Queen of England and Ireland from the union of the Scottish and Eng ...
, was the daughter of King Frederick II of Denmark. Their eldest child, the nine-year-old Henry
Henry may refer to:
People
*Henry (given name)
* Henry (surname)
* Henry Lau, Canadian singer and musician who performs under the mononym Henry
Royalty
* Portuguese royalty
** King-Cardinal Henry, King of Portugal
** Henry, Count of Portugal, ...
, was considered a handsome and confident boy, and their two younger children, Elizabeth
Elizabeth or Elisabeth may refer to:
People
* Elizabeth (given name), a female given name (including people with that name)
* Elizabeth (biblical figure), mother of John the Baptist
Ships
* HMS ''Elizabeth'', several ships
* ''Elisabeth'' (sch ...
and Charles, were proof that James was able to provide heirs to continue the Protestant monarchy.
Early reign of James I
James's attitude towards Catholics was more moderate than that of his predecessor, perhaps even tolerant. He swore that he would not "persecute any that will be quiet and give an outward obedience to the law", and believed that exile was a better solution thancapital punishment
Capital punishment, also known as the death penalty, is the state-sanctioned practice of deliberately killing a person as a punishment for an actual or supposed crime, usually following an authorized, rule-governed process to conclude that t ...
: "I would be glad to have both their heads and their bodies separated from this whole island and transported beyond seas." Some Catholics believed that the martyrdom of James's mother, Mary, Queen of Scots
Mary, Queen of Scots (8 December 1542 – 8 February 1587), also known as Mary Stuart or Mary I of Scotland, was Queen of Scotland from 14 December 1542 until her forced abdication in 1567.
The only surviving legitimate child of James V of S ...
, would encourage James to convert to the Catholic faith, and the Catholic houses of Europe may also have shared that hope.
James received an envoy from Albert VII, ruler of the remaining Catholic territories in the Netherlands after over 30 years of war in the Dutch Revolt by English-supported Protestant rebels. For the Catholic expatriates engaged in that struggle, the restoration by force of a Catholic monarchy was an intriguing possibility, but following the failed Spanish invasion of England
The Spanish Armada (a.k.a. the Enterprise of England, es, Grande y Felicísima Armada, links=no, lit=Great and Most Fortunate Navy) was a Spanish fleet that sailed from Lisbon in late May 1588, commanded by the Duke of Medina Sidonia, an ari ...
in 1588 the papacy had taken a longer-term view on the return of a Catholic monarch to the English throne.
During James I's reign the European wars of religion were intensifying. Protestants and Catholics were engaged in violent persecution of each other across Europe following the Protestant Reformation
The Reformation (alternatively named the Protestant Reformation or the European Reformation) was a major movement within Western Christianity in 16th-century Europe that posed a religious and political challenge to the Catholic Church and ...
. Catholics made several assassination attempts on Protestant rulers in Europe and in England, including plans to poison James I's predecessor, Elizabeth I. In 1589, during the French Wars of Religion
The French Wars of Religion is the term which is used in reference to a period of civil war between French Catholics and Protestants, commonly called Huguenots, which lasted from 1562 to 1598. According to estimates, between two and four mi ...
, the French King Henry III was mortally wounded with a dagger by Jacques Clément
Jacques Clément (1567 – 1 August 1589) was a French conspirator and the assassin of King Henry III.
He was born at Serbonnes, in today's Yonne ''département'', in Burgundy, and became a Dominican lay brother.
During the French Wars of Re ...
, a fanatic member of the Catholic League of France
The Catholic League of France (french: Ligue catholique), sometimes referred to by contemporary (and modern) Catholics as the Holy League (), was a major participant in the French Wars of Religion. The League, founded and led by Henry I, Duke of ...
. Nine years later, the Jesuit Juan de Mariana
Juan de Mariana, , also known as Father Mariana (25 September 1536 – 17 February 1624), was a Spanish Jesuit priest, Scholastic, historian, and member of the Monarchomachs.
Life
Juan de Mariana was born in Talavera, Kingdom of Toledo. He st ...
's 1599 ''On Kings and the Education of Kings'' (''De rege et regis institutione'') argued in support of tyrannicide
Tyrannicide is the killing or assassination of a tyrant or unjust ruler, purportedly for the common good,
and usually by one of the tyrant's subjects. Tyrannicide was legally permitted and encouraged in the Classical period. Often, the term tyra ...
. This work recounted the assassination of Henry III and argued for the legal right to overthrow a tyrant. Perhaps due in part to the publication of ''De rege'', until the 1620s, some English Catholics believed that regicide
Regicide is the purposeful killing of a monarch or sovereign of a polity and is often associated with the usurpation of power. A regicide can also be the person responsible for the killing. The word comes from the Latin roots of ''regis'' ...
was justifiable to remove 'tyrants' from power. Much of the "rather nervous" political writing from James I was "concerned with the threat of Catholic assassination and refutation of the atholicargument that 'faith did not need to be kept with heretics
Heresy is any belief or theory that is strongly at variance with established beliefs or customs, in particular the accepted beliefs of a church or religious organization. The term is usually used in reference to violations of important religi ...
'".
Early plots
In the absence of any sign that James would move to end the persecution of Catholics, as some had hoped for, several members of theclergy
Clergy are formal leaders within established religions. Their roles and functions vary in different religious traditions, but usually involve presiding over specific rituals and teaching their religion's doctrines and practices. Some of the ter ...
(including two anti-Jesuit priests) decided to take matters into their own hands. In what became known as the Bye Plot, the priests William Watson William, Willie, Bill or Billy Watson may refer to:
Entertainment
* William Watson (songwriter) (1794–1840), English concert hall singer and songwriter
* William Watson (poet) (1858–1935), English poet
* Billy Watson (actor) (1923–2022), A ...
and William Clark
William Clark (August 1, 1770 – September 1, 1838) was an American explorer, soldier, Indian agent, and territorial governor. A native of Virginia, he grew up in pre-statehood Kentucky before later settling in what became the state of Miss ...
planned to kidnap James and hold him in the Tower of London
The Tower of London, officially His Majesty's Royal Palace and Fortress of the Tower of London, is a historic castle on the north bank of the River Thames in central London. It lies within the London Borough of Tower Hamlets, which is sep ...
until he agreed to be more tolerant towards Catholics. Cecil received news of the plot from several sources, including the Archpriest George Blackwell
Father George Blackwell (c. 1545 – 12 January 1613) was Roman Catholic Archpriest of England from 1597 to 1608.
Biography
Blackwell was born in Middlesex, England about 1545, perhaps the son of the pewterer Thomas Blackwell. He was admitt ...
, who instructed his priests to have no part in any such schemes. At about the same time, Lord Cobham, Lord Grey de Wilton, Griffin Markham and Walter Raleigh
Sir Walter Raleigh (; – 29 October 1618) was an English statesman, soldier, writer and explorer. One of the most notable figures of the Elizabethan era, he played a leading part in English colonisation of North America, suppressed rebelli ...
hatched what became known as the Main Plot
The Main Plot was an alleged conspiracy of July 1603 by English courtiers to remove King James I from the English throne and to replace him with his cousin Lady Arbella Stuart. The plot was supposedly led by Lord Cobham and funded by the Spanis ...
, which involved removing James and his family and supplanting them with Arbella Stuart
Lady Arbella Stuart (also Arabella, or Stewart; 1575 – 25 September 1615) was an English noblewoman who was considered a possible successor to Queen Elizabeth I of England. During the reign of King James VI and I (her first cousin), she marri ...
. Amongst others, they approached Philip III of Spain
Philip III ( es, Felipe III; 14 April 1578 – 31 March 1621) was King of Spain. As Philip II, he was also King of Portugal, Naples, Sicily and Sardinia and Duke of Milan from 1598 until his death in 1621.
A member of the House of Habsburg, Phi ...
for funding, but were unsuccessful. All those involved in both plots were arrested in July and tried in autumn 1603. George Brooke was executed, but James—keen not to have too bloody a start to his reign—reprieved Cobham, Grey, and Markham while they were at the scaffold. Raleigh, who had watched while his colleagues sweated, had been due to be executed a few days later, but was also pardoned. Arbella Stuart denied any knowledge of the Main Plot. However, the two priests, Watson and Clark—condemned and "very bloodily handled"—were executed.
The Catholic community responded to news of these plots with shock. That the Bye Plot had been revealed by Catholics was instrumental in saving them from further persecution, and James was grateful enough to allow pardons for those recusants who sued for them, as well as postponing payment of their fines for a year.
On 19 February 1604, shortly after he discovered that his wife, Queen Anne, had been sent a rosary from the pope via one of James's spies, Sir Anthony Standen, James denounced the Catholic Church. Three days later, he ordered all Jesuits and all other Catholic priests to leave the country, and reimposed the collection of fines for recusancy.
James changed his focus from the anxieties of English Catholics to the establishment of an Anglo-Scottish union. He also appointed Scottish nobles such as George Home to his court, which proved unpopular with the Parliament of England
The Parliament of England was the legislature of the Kingdom of England from the 13th century until 1707 when it was replaced by the Parliament of Great Britain. Parliament evolved from the great council of bishops and peers that advised ...
. Some Members of Parliament made it clear that, in their view, the "effluxion of people from the Northern parts" was unwelcome, and compared them to "plants which are transported from barren ground into a more fertile one". Even more discontent resulted when the King allowed his Scottish nobles to collect the recusancy fines. There were 5,560 convicted of recusancy in 1605, of whom 112 were landowners. The very few Catholics of great wealth who refused to attend services at their parish church were fined £20 per month. Those of more moderate means had to pay two-thirds of their annual rental income; middle class recusants were fined one shilling a week, although the collection of all these fines was "haphazard and negligent". When James came to power, almost £5,000 a year (equivalent to almost £12 million in 2020) was being raised by these fines.
On 19 March, the King gave his opening speech to his first English Parliament in which he spoke of his desire to secure peace, but only by "profession of the true religion". He also spoke of a Christian union and reiterated his desire to avoid religious persecution. For the Catholics, the King's speech made it clear that they were not to "increase their number and strength in this Kingdom", that "they might be in hope to erect their Religion again". To Father John Gerard
John Gerard (also John Gerarde, c. 1545–1612) was an English herbalist with a large garden in Holborn, now part of London. His 1,484-page illustrated ''Herball, or Generall Historie of Plantes'', first published in 1597, became a popular gard ...
, these words were almost certainly responsible for the heightened levels of persecution the members of his faith now suffered, and for the priest Oswald Tesimond, they were a repudiation of the early claims that the King had made, upon which the papists had built their hopes. A week after James's speech, Lord Edmund Sheffield informed the king of over 900 recusants brought before the Assizes in Normanby, and on 24 April, the Popish Recusants Act 1605
The Popish Recusants Act 1605 (3 Jac.1, c. 4) was an act of the Parliament of England which quickly followed the Gunpowder Plot of the same year, an attempt by English Roman Catholics to assassinate King James I and many of the Parliament.
The ...
was introduced in Parliament which threatened to outlaw all English followers of the Catholic Church.
Plot
 The conspirators' principal aim was to kill King James, but many other important targets would also be present at the State Opening of Parliament, including the monarch's nearest relatives and members of the Privy Council. The senior judges of the English legal system, most of the Protestant aristocracy, and the bishops of the Church of England would all have attended in their capacity as members of the House of Lords, along with the members of the
The conspirators' principal aim was to kill King James, but many other important targets would also be present at the State Opening of Parliament, including the monarch's nearest relatives and members of the Privy Council. The senior judges of the English legal system, most of the Protestant aristocracy, and the bishops of the Church of England would all have attended in their capacity as members of the House of Lords, along with the members of the House of Commons
The House of Commons is the name for the elected lower house of the bicameral parliaments of the United Kingdom and Canada. In both of these countries, the Commons holds much more legislative power than the nominally upper house of parliament. T ...
. Another important objective was the kidnapping of the King's daughter, Elizabeth. Housed at Coombe Abbey near Coventry
Coventry ( or ) is a city in the West Midlands, England. It is on the River Sherbourne. Coventry has been a large settlement for centuries, although it was not founded and given its city status until the Middle Ages. The city is governed b ...
, she lived only ten miles north of Warwick
Warwick ( ) is a market town, civil parish and the county town of Warwickshire in the Warwick District in England, adjacent to the River Avon. It is south of Coventry, and south-east of Birmingham. It is adjoined with Leamington Spa and Whi ...
—convenient for the plotters, most of whom lived in the Midlands. Once the King and his Parliament were dead, the plotters intended to install Elizabeth on the English throne as a titular Queen. The fate of her brothers, Henry and Charles, would be improvised; their role in state ceremonies was, as yet, uncertain. The plotters planned to use Henry Percy, 9th Earl of Northumberland
Henry Percy, 9th Earl of Northumberland, KG (27 April 1564 – 5 November 1632) was an English nobleman. He was a grandee and one of the wealthiest peers of the court of Elizabeth I. Under James I, Northumberland was a long-term prisoner i ...
, as Elizabeth's regent
A regent (from Latin : ruling, governing) is a person appointed to govern a state '' pro tempore'' (Latin: 'for the time being') because the monarch is a minor, absent, incapacitated or unable to discharge the powers and duties of the monarchy ...
, but most likely never informed him of this.
Initial recruitment
Robert Catesby
Robert Catesby (c. 1572 – 8 November 1605) was the leader of a group of English Catholics who planned the failed Gunpowder Plot of 1605.
Born in Warwickshire, Catesby was educated in Oxford. His family were prominent recusant Catholics, and ...
(1573–1605), a man of "ancient, historic and distinguished lineage", was the inspiration behind the plot. He was described by contemporaries as "a good-looking man, about six feet tall, athletic and a good swordsman". Along with several other conspirators, he took part in the Essex Rebellion
Essex's Rebellion was an unsuccessful rebellion led by Robert Devereux, 2nd Earl of Essex, in 1601 against Queen Elizabeth I of England and the court faction led by Sir Robert Cecil to gain further influence at court.
Background
Robert Devereux, ...
in 1601, during which he was wounded and captured. Queen Elizabeth allowed him to escape with his life after fining him 4,000 marks
Marks may refer to:
Business
* Mark's, a Canadian retail chain
* Marks & Spencer, a British retail chain
* Collective trade marks, trademarks owned by an organisation for the benefit of its members
* Marks & Co, the inspiration for the novel ...
(equivalent to more than £6 million in 2008), after which he sold his estate in Chastleton
Chastleton is a village and civil parish in the Cotswold Hills in Oxfordshire, England, about northeast of Stow-on-the-Wold. Chastleton is in the extreme northwest of Oxfordshire, on the boundaries with both Gloucestershire and Warwickshire. T ...
.
In 1603, Catesby helped to organise a mission to the new king of Spain, Philip III, urging Philip to launch an invasion attempt on England, which they assured him would be well supported, particularly by the English Catholics. Thomas Wintour
Robert Wintour (1568 – 30 January 1606) and Thomas Wintour (1571 or 1572 – 31 January 1606), also spelt Winter, were members of the Gunpowder Plot, a failed conspiracy to assassinate King James I. Brothers, they were related to other consp ...
(1571–1606) was chosen as the emissary, but the Spanish king, although sympathetic to the plight of Catholics in England, was intent on making peace with James. Wintour had also attempted to convince the Spanish envoy Don Juan de Tassis that "3,000 Catholics" were ready and waiting to support such an invasion. Concern was voiced by Pope Clement VIII
Pope Clement VIII ( la, Clemens VIII; it, Clemente VIII; 24 February 1536 – 3 March 1605), born Ippolito Aldobrandini, was head of the Catholic Church and ruler of the Papal States from 2 February 1592 to his death in March 1605.
Born ...
that using violence to achieve a restoration of Catholic power in England would result in the destruction of those that remained.
According to contemporary accounts, in February 1604, Catesby invited Thomas Wintour to his house in Lambeth, where they discussed Catesby's plan to re-establish Catholicism in England by blowing up the House of Lords during the State Opening of Parliament. Wintour was known as a competent scholar, able to speak several languages, and he had fought with the English army in the Netherlands. His uncle, Francis Ingleby
Francis Ingleby (c. 1551 – 3 June 1586) was a Roman Catholic martyr executed in York, England during the reign of Elizabeth I.
Born about 1551, he was the fourth son of Sir William Ingleby and Anne Malory of Ripley Castle, North Yorkshi ...
, had been executed for being a Catholic priest in 1586, and Wintour later converted to Catholicism. Also present at the meeting was John Wright, a devout Catholic said to be one of the best swordsmen of his day, and a man who had taken part with Catesby in the Earl of Essex's rebellion three years earlier. Despite his reservations over the possible repercussions should the attempt fail, Wintour agreed to join the conspiracy, perhaps persuaded by Catesby's rhetoric: "Let us give the attempt and where it faileth, pass no further."
Wintour travelled to Flanders
Flanders (, ; Dutch: ''Vlaanderen'' ) is the Flemish-speaking northern portion of Belgium and one of the communities, regions and language areas of Belgium. However, there are several overlapping definitions, including ones related to cultu ...
to enquire about Spanish support. While there, he sought out Guy Fawkes (1570–1606), a committed Catholic who had served as a soldier in the Southern Netherlands
The Southern Netherlands, also called the Catholic Netherlands, were the parts of the Low Countries belonging to the Holy Roman Empire which were at first largely controlled by Habsburg Spain (Spanish Netherlands, 1556–1714) and later by the A ...
under the command of William Stanley, and in 1603 had been recommended for a captaincy. Accompanied by John Wright's brother Christopher, Fawkes had also been a member of the 1603 delegation to the Spanish court pleading for an invasion of England. Wintour told Fawkes that " en-emodeng, label=none, some good frends of his wished his company in Ingland", and that certain gentlemen " en-emodeng, label=none, were uppon a resolution to doe some whatt in Ingland if the pece with Spain healped us nott". The two men returned to England late in April 1604, telling Catesby that Spanish support was unlikely. Thomas Percy, Catesby's friend and John Wright's brother-in-law, was introduced to the plot several weeks later.
Percy had found employment with his kinsman the Earl of Northumberland, and by 1596, was his agent for the family's northern estates. About 1600–1601 he served with his patron in the Low Countries
The term Low Countries, also known as the Low Lands ( nl, de Lage Landen, french: les Pays-Bas, lb, déi Niddereg Lännereien) and historically called the Netherlands ( nl, de Nederlanden), Flanders, or Belgica, is a coastal lowland region in N ...
. At some point during Northumberland's command in the Low Countries, Percy became his agent in his communications with James I. Percy was reputedly a "serious" character who had converted to the Catholic faith. His early years were, according to a Catholic source, marked by a tendency to rely on "his sword and personal courage". Northumberland, although not a Catholic himself, planned to build a strong relationship with James I in order to better the prospects of English Catholics, and to reduce the family disgrace caused by his separation from his wife Martha Wright, a favourite of Elizabeth I.
Thomas Percy's meetings with James seemed to go well. Percy returned with promises of support for the Catholics, and Northumberland believed that James would go so far as to allow Mass
Mass is an intrinsic property of a body. It was traditionally believed to be related to the quantity of matter in a physical body, until the discovery of the atom and particle physics. It was found that different atoms and different eleme ...
in private houses, so as not to cause public offence. Percy, keen to improve his standing, went even further, claiming that the future king would guarantee the safety of English Catholics.
Initial planning
 The first meeting between the five conspirators took place on 20 May 1604, probably at the Duck and Drake Inn, just off the Strand, Thomas Wintour's usual residence when staying in London. Catesby, Thomas Wintour, and John Wright were in attendance, joined by Guy Fawkes and Thomas Percy. Alone in a private room, the five plotters swore an oath of secrecy on a prayer book. By coincidence, and ignorant of the plot, Father John Gerard (a friend of Catesby's) was celebrating Mass in another room, and the five men subsequently received the
The first meeting between the five conspirators took place on 20 May 1604, probably at the Duck and Drake Inn, just off the Strand, Thomas Wintour's usual residence when staying in London. Catesby, Thomas Wintour, and John Wright were in attendance, joined by Guy Fawkes and Thomas Percy. Alone in a private room, the five plotters swore an oath of secrecy on a prayer book. By coincidence, and ignorant of the plot, Father John Gerard (a friend of Catesby's) was celebrating Mass in another room, and the five men subsequently received the Eucharist
The Eucharist (; from Greek , , ), also known as Holy Communion and the Lord's Supper, is a Christian rite that is considered a sacrament in most churches, and as an ordinance in others. According to the New Testament, the rite was instit ...
.
Further recruitment
Following their oath, the plotters left London and returned to their homes. The adjournment of Parliament gave them, they thought, until February 1605 to finalise their plans. On 9 June, Percy's patron, the Earl of Northumberland, appointed him to the Band of Gentlemen Pensioners, a mounted troop of 50 bodyguards to the King. This role gave Percy reason to seek a base in London, and a small property near the Prince's Chamber owned by Henry Ferrers, a tenant of John Whynniard, was chosen. Percy arranged for the use of the house through Northumberland's agents, Dudley Carleton and John Hippisley. Fawkes, using the pseudonym "John Johnson", took charge of the building, posing as Percy's servant. The building was occupied by Scottish commissioners appointed by the King to consider his plans for the unification of England and Scotland, so the plotters hired Catesby's lodgings in Lambeth, on the opposite bank of the Thames, from where their stored gunpowder and other supplies could be conveniently rowed across each night. Meanwhile, King James I continued with his policies against the Catholics, and Parliament pushed through anti-Catholic legislation, until its adjournment on 7 July. The conspirators returned to London in October 1604, when Robert Keyes, a "desperate man, ruined and indebted", was admitted to the group. His responsibility was to take charge of Catesby's house in Lambeth, where the gunpowder and other supplies were to be stored. Keyes's family had notable connections; his wife's employer was the Catholic Lord Mordaunt. He was tall, with a red beard, and was seen as trustworthy and—like Fawkes—capable of looking after himself. In December Catesby recruited his servant, Thomas Bates, into the plot, after the latter accidentally became aware of it.
It was announced on 24 December that the re-opening of Parliament would be delayed. Concern over the plague meant that rather than sitting in February, as the plotters had originally planned for, Parliament would not sit again until 3 October 1605. The contemporaneous account of the prosecution claimed that during this delay the conspirators were digging a tunnel beneath Parliament. This may have been a government fabrication, as no evidence for the existence of a tunnel was presented by the prosecution, and no trace of one has ever been found. The account of a tunnel comes directly from Thomas Wintour's confession, and Guy Fawkes did not admit the existence of such a scheme until his fifth interrogation. Logistically, digging a tunnel would have proved extremely difficult, especially as none of the conspirators had any experience of mining. If the story is true, by 6 December the Scottish commissioners had finished their work, and the conspirators were busy tunnelling from their rented house to the House of Lords. They ceased their efforts when, during tunnelling, they heard a noise from above. The noise turned out to be the then-tenant's widow, who was clearing out the
The conspirators returned to London in October 1604, when Robert Keyes, a "desperate man, ruined and indebted", was admitted to the group. His responsibility was to take charge of Catesby's house in Lambeth, where the gunpowder and other supplies were to be stored. Keyes's family had notable connections; his wife's employer was the Catholic Lord Mordaunt. He was tall, with a red beard, and was seen as trustworthy and—like Fawkes—capable of looking after himself. In December Catesby recruited his servant, Thomas Bates, into the plot, after the latter accidentally became aware of it.
It was announced on 24 December that the re-opening of Parliament would be delayed. Concern over the plague meant that rather than sitting in February, as the plotters had originally planned for, Parliament would not sit again until 3 October 1605. The contemporaneous account of the prosecution claimed that during this delay the conspirators were digging a tunnel beneath Parliament. This may have been a government fabrication, as no evidence for the existence of a tunnel was presented by the prosecution, and no trace of one has ever been found. The account of a tunnel comes directly from Thomas Wintour's confession, and Guy Fawkes did not admit the existence of such a scheme until his fifth interrogation. Logistically, digging a tunnel would have proved extremely difficult, especially as none of the conspirators had any experience of mining. If the story is true, by 6 December the Scottish commissioners had finished their work, and the conspirators were busy tunnelling from their rented house to the House of Lords. They ceased their efforts when, during tunnelling, they heard a noise from above. The noise turned out to be the then-tenant's widow, who was clearing out the undercroft
An undercroft is traditionally a cellar or storage room, often brick-lined and vaulted, and used for storage in buildings since medieval times. In modern usage, an undercroft is generally a ground (street-level) area which is relatively open ...
directly beneath the House of Lords—the room where the plotters eventually stored the gunpowder.
By the time the plotters reconvened at the start of the old style
Old Style (O.S.) and New Style (N.S.) indicate dating systems before and after a calendar change, respectively. Usually, this is the change from the Julian calendar to the Gregorian calendar as enacted in various European countries between 158 ...
new year on Lady Day
In the Western liturgical year, Lady Day is the traditional name in some English-speaking countries of the Feast of the Annunciation, which is celebrated on 25 March, and commemorates the visit of the archangel Gabriel to the Virgin Mary, durin ...
, 25 March, three more had been admitted to their ranks; Robert Wintour
Robert Wintour (1568 – 30 January 1606) and Thomas Wintour (1571 or 1572 – 31 January 1606), also spelt Winter, were members of the Gunpowder Plot, a failed conspiracy to assassinate King James I. Brothers, they were related to other consp ...
, John Grant, and Christopher Wright. The additions of Wintour and Wright were obvious choices. Along with a small fortune, Robert Wintour inherited Huddington Court (a known refuge for priests) near Worcester
Worcester may refer to:
Places United Kingdom
* Worcester, England, a city and the county town of Worcestershire in England
** Worcester (UK Parliament constituency), an area represented by a Member of Parliament
* Worcester Park, London, Engla ...
, and was reputedly a generous and well-liked man. A devout Catholic, he married Gertrude, the daughter of John Talbot of Grafton
Sir John Talbot of Grafton, Worcestershire (1545 – 28 January 1611) was a prominent recusant English Catholic layman of the reigns of Elizabeth I of England and James I of England. He was connected by marriage to one of the Gunpowder Plot conspi ...
, from a prominent Worcestershire family of recusants. Christopher Wright (1568–1605), John's brother, had also taken part in the Earl of Essex's revolt and had moved his family to Twigmore in Lincolnshire
Lincolnshire (abbreviated Lincs.) is a Counties of England, county in the East Midlands of England, with a long coastline on the North Sea to the east. It borders Norfolk to the south-east, Cambridgeshire to the south, Rutland to the south-we ...
, then known as something of a haven for priests. John Grant was married to Wintour's sister, Dorothy, and was lord of the manor
Lord of the Manor is a title that, in Anglo-Saxon England, referred to the landholder of a rural estate. The lord enjoyed manorial rights (the rights to establish and occupy a residence, known as the manor house and demesne) as well as seig ...
of Norbrook near Stratford-upon-Avon. Reputed to be an intelligent, thoughtful man, he sheltered Catholics at his home at Snitterfield
Snitterfield is a village and civil parish in the Stratford on Avon district of Warwickshire, England, less than to the north of the A46 road, from Stratford upon Avon, from Warwick and from Coventry. The population of the civil parish at t ...
, and was another who had been involved in the Essex revolt of 1601.
Undercroft
In addition, 25 March was the day on which the plotters purchased the lease to theundercroft
An undercroft is traditionally a cellar or storage room, often brick-lined and vaulted, and used for storage in buildings since medieval times. In modern usage, an undercroft is generally a ground (street-level) area which is relatively open ...
they had supposedly tunnelled near to, owned by John Whynniard. The Palace of Westminster in the early 17th century was a warren of buildings clustered around the medieval chambers, chapels, and halls of the former royal palace that housed both Parliament and the various royal law courts. The old palace was easily accessible; merchants, lawyers, and others lived and worked in the lodgings, shops and taverns within its precincts. Whynniard's building was along a right-angle to the House of Lords, alongside a passageway called Parliament Place, which itself led to Parliament Stairs and the River Thames
The River Thames ( ), known alternatively in parts as the River Isis, is a river that flows through southern England including London. At , it is the longest river entirely in England and the second-longest in the United Kingdom, after the R ...
. Undercrofts were common features at the time, used to house a variety of materials including food and firewood. Whynniard's undercroft, on the ground floor, was directly beneath the first-floor House of Lords, and may once have been part of the palace's medieval kitchen. Unused and filthy, its location was ideal for what the group planned to do.
 In the second week of June Catesby met in London the principal Jesuit in England, Father
In the second week of June Catesby met in London the principal Jesuit in England, Father Henry Garnet
Henry Garnet (July 1555 – 3 May 1606), sometimes Henry Garnett, was an English Jesuit priest executed for his complicity in the Gunpowder Plot of 1605. Born in Heanor, Derbyshire, he was educated in Nottingham and later at Winchester Colle ...
, and asked him about the morality of entering into an undertaking which might involve the destruction of the innocent, together with the guilty. Garnet answered that such actions could often be excused, but according to his own account later admonished Catesby during a second meeting in July in Essex, showing him a letter from the pope which forbade rebellion. Soon after, the Jesuit priest Oswald Tesimond told Garnet he had taken Catesby's confession, in the course of which he had learnt of the plot. Garnet and Catesby met for a third time on 24 July 1605, at the house of the wealthy catholic Anne Vaux
Anne Vaux (c. 1562 – in or after 1637) was a wealthy Catholic recusant.
Background
Vaux was the third daughter of William Vaux, 3rd Baron Vaux of Harrowden (1535–1595) and his first wife, Elizabeth, daughter of John Beaumont of Grace Die ...
in Enfield Chase
Enfield Chase is an area of Enfield that is named for a former royal hunting ground. Much of the former area of the Chase has been developed, but a large part survives between Cockfosters in the west and Enfield in the east as Trent Country ...
. Garnet decided that Tesimond's account had been given under the seal of the confessional, and that canon law therefore forbade him to repeat what he had heard. Without acknowledging that he was aware of the precise nature of the plot, Garnet attempted to dissuade Catesby from his course, to no avail. Garnet wrote to a colleague in Rome, Claudio Acquaviva
Claudio Acquaviva, SJ (14 September 1543 – 31 January 1615) was an Italian Jesuit priest. Elected in 1581 as the fifth Superior General of the Society of Jesus, he has been referred to as the second founder of the Jesuit order.
Early life a ...
, expressing his concerns about open rebellion in England. He also told Acquaviva that "there is a risk that some private endeavour may commit treason or use force against the King", and urged the pope to issue a public brief against the use of force.
According to Fawkes, 20 barrels of gunpowder were brought in at first, followed by 16 more on 20 July. The supply of gunpowder was theoretically controlled by the government, but it was easily obtained from illicit sources. On 28 July, the ever-present threat of the plague again delayed the opening of Parliament, this time until Tuesday 5 November. Fawkes left the country for a short time. The King, meanwhile, spent much of the summer away from the city, hunting. He stayed wherever was convenient, including on occasion at the houses of prominent Catholics. Garnet, convinced that the threat of an uprising had receded, travelled the country on a pilgrimage
A pilgrimage is a journey, often into an unknown or foreign place, where a person goes in search of new or expanded meaning about their self, others, nature, or a higher good, through the experience. It can lead to a personal transformation, aft ...
.
It is uncertain when Fawkes returned to England, but he was back in London by late August, when he and Wintour discovered that the gunpowder stored in the undercroft had decayed. More gunpowder was brought into the room, along with firewood to conceal it. The final three conspirators were recruited in late 1605. At Michaelmas
Michaelmas ( ; also known as the Feast of Saints Michael, Gabriel, and Raphael, the Feast of the Archangels, or the Feast of Saint Michael and All Angels) is a Christian festival observed in some Western liturgical calendars on 29 September, ...
, Catesby persuaded the staunchly Catholic Ambrose Rookwood to rent Clopton House
Clopton House is a 17th-century country mansion near Stratford upon Avon, Warwickshire, now converted into residential apartments. It is a Grade II* listed building.
The Manor of Clopton was granted to the eponymous family in the 13th century and ...
near Stratford-upon-Avon. Rookwood was a young man with recusant connections, whose stable of horses at Coldham Hall
Coldham Hall is a Grade I listed building, built in 1574, that is located in the parish of Bradfield Combust with Stanningfield in Suffolk. The Hall is very close to the village of Lawshall, and part of the Coldham estate is located within this ...
in Stanningfield, Suffolk was an important factor in his enlistment. His parents, Robert Rookwood and Dorothea Drury
Dorothea (also spelled Dorothée, Dorotea or other variants) is a female given name from Greek (Dōrothéa) meaning "God's Gift". It may refer to:
People
* Dorothea Binz (1920–1947), German concentration camp officer executed for war cri ...
, were wealthy landowners, and had educated their son at a Jesuit school near Calais. Everard Digby
Sir Everard Digby (c. 1578 – 30 January 1606) was a member of the group of provincial English Catholics who planned the failed Gunpowder Plot of 1605. Although he was raised in a Protestant household, and married a Protestant, Digby and his w ...
was a young man who was generally well liked, and lived at Gayhurst House
Gayhurst House (now known as Gayhurst Court) is a late-Elizabethan country house in Buckinghamshire. It is located near the village of Gayhurst, several kilometres north of Milton Keynes. The earliest house dates from the 1520s. In 1597 it was ...
in Buckinghamshire. He had been knighted by the King in April 1603, and was converted to Catholicism by Gerard. Digby and his wife, Mary Mulshaw
Mary may refer to:
People
* Mary (name), a feminine given name (includes a list of people with the name)
Religious contexts
* New Testament people named Mary, overview article linking to many of those below
* Mary, mother of Jesus, also calle ...
, had accompanied the priest on his pilgrimage, and the two men were reportedly close friends. Digby was asked by Catesby to rent Coughton Court
Coughton Court () is an English Tudor country house, situated on the main road between Studley and Alcester in Warwickshire. It is a Grade I listed building.
The house has a long crenellated façade directly facing the main road, at the cen ...
near Alcester
Alcester () is a market town and civil parish of Roman origin at the junction of the River Alne and River Arrow in the Stratford-on-Avon District in Warwickshire, England, approximately west of Stratford-upon-Avon, and 7 miles south of Reddit ...
. Digby also promised £1,500 after Percy failed to pay the rent due for the properties he had taken in Westminster. Finally, on 14 October Catesby invited Francis Tresham
Francis Tresham ( 1567 – 23 December 1605), eldest son of
Thomas Tresham and Muriel Throckmorton, was a member of the group of English provincial Catholics who planned the failed Gunpowder Plot of 1605, a conspiracy to assassinate King Jame ...
into the conspiracy. Tresham was the son of the Catholic Thomas Tresham, and a cousin to Robert Catesby; the two had been raised together. He was also the heir to his father's large fortune, which had been depleted by recusant fines, expensive tastes, and by Francis and Catesby's involvement in the Essex revolt.
Catesby and Tresham met at the home of Tresham's brother-in-law and cousin, Lord Stourton. In his confession, Tresham claimed that he had asked Catesby if the plot would damn their souls, to which Catesby had replied it would not, and that the plight of England's Catholics required that it be done. Catesby also apparently asked for £2,000, and the use of Rushton Hall in Northamptonshire
Northamptonshire (; abbreviated Northants.) is a county in the East Midlands of England. In 2015, it had a population of 723,000. The county is administered by
two unitary authorities: North Northamptonshire and West Northamptonshire. It is ...
. Tresham declined both offers (although he did give £100 to Thomas Wintour), and told his interrogators that he had moved his family from Rushton to London in advance of the plot; hardly the actions of a guilty man, he claimed.
Monteagle letter
 The details of the plot were finalised in October, in a series of taverns across London and
The details of the plot were finalised in October, in a series of taverns across London and Daventry
Daventry ( , historically ) is a market town and civil parish in the West Northamptonshire unitary authority in Northamptonshire, England, close to the border with Warwickshire. At the 2021 Census Daventry had a population of 28,123, making ...
. Fawkes would be left to light the fuse and then escape across the Thames, while simultaneously a revolt in the Midlands would help to ensure the capture of the King's daughter, Elizabeth. Fawkes would leave for the continent, to explain events in England to the European Catholic powers.
The wives of those involved and Anne Vaux
Anne Vaux (c. 1562 – in or after 1637) was a wealthy Catholic recusant.
Background
Vaux was the third daughter of William Vaux, 3rd Baron Vaux of Harrowden (1535–1595) and his first wife, Elizabeth, daughter of John Beaumont of Grace Die ...
(a friend of Garnet who often shielded priests at her home) became increasingly concerned by what they suspected was about to happen. Several of the conspirators expressed worries about the safety of fellow Catholics who would be present in Parliament on the day of the planned explosion. Percy was concerned for his patron, Northumberland, and the young Earl of Arundel
Earl of Arundel is a title of nobility in England, and one of the oldest extant in the English peerage. It is currently held by the Duke of Norfolk, and is used (along with the Earl of Surrey) by his heir apparent as a courtesy title. The ...
's name was brought up; Catesby suggested that a minor wound might keep him from the chamber on that day. The Lords Vaux, Montagu, Monteagle, and Stourton were also mentioned. Keyes suggested warning Lord Mordaunt, his wife's employer, to derision from Catesby.
On Saturday 26 October, Monteagle (Tresham's brother-in-law) arranged a meal in a long-disused house at Hoxton
Hoxton is an area in the London Borough of Hackney, England. As a part of Shoreditch, it is often considered to be part of the East End – the historic core of wider East London. It was historically in the county of Middlesex until 1889. It li ...
. Suddenly a servant appeared saying he had been handed a letter for Lord Monteagle from a stranger in the road. Monteagle ordered it to be read aloud to the company.
Uncertain of the letter's meaning, Monteagle promptly rode to Whitehall
Whitehall is a road and area in the City of Westminster, Central London. The road forms the first part of the A3212 road from Trafalgar Square to Chelsea. It is the main thoroughfare running south from Trafalgar Square towards Parliament Sq ...
and handed it to Cecil (then Earl of Salisbury
Earl of Salisbury is a title that has been created several times in English and British history. It has a complex history, and is now a subsidiary title to the marquessate of Salisbury.
Background
The title was first created for Patrick de S ...
). Salisbury informed the Earl of Worcester
Earl of Worcester is a title that has been created five times in the Peerage of England.
Five creations
The first creation came in 1138 in favour of the Norman noble Waleran de Beaumont. He was the son of Robert de Beaumont, 1st Earl of Leice ...
, considered to have recusant sympathies, and the suspected Catholic Henry Howard, 1st Earl of Northampton
Henry Howard, Earl of Northampton, KG (25 February 154015 June 1614), was an important English aristocrat and courtier. He was suspect as a crypto-Catholic throughout his life, and went through periods of royal disfavour, in which his reputati ...
, but kept news of the plot from the King, who was busy hunting in Cambridgeshire
Cambridgeshire (abbreviated Cambs.) is a county in the East of England, bordering Lincolnshire to the north, Norfolk to the north-east, Suffolk to the east, Essex and Hertfordshire to the south, and Bedfordshire and Northamptonshire to the ...
and not expected back for several days. Monteagle's servant, Thomas Ward, had family connections with the Wright brothers, and sent a message to Catesby about the betrayal. Catesby, who had been due to go hunting with the King, suspected that Tresham was responsible for the letter, and with Thomas Wintour confronted the recently recruited conspirator. Tresham managed to convince the pair that he had not written the letter, but urged them to abandon the plot. Salisbury was already aware of certain stirrings before he received the letter, but did not yet know the exact nature of the plot, or who exactly was involved. He therefore elected to wait, to see how events unfolded.
Discovery
The letter was shown to the King on Friday 1 November following his arrival back in London. Upon reading it, James immediately seized upon the word "blow" and felt that it hinted at "some strategem of fire and powder", perhaps an explosion exceeding in violence the one that killed his father,Lord Darnley
Lord Darnley is a noble title associated with a Scottish Lordship of Parliament, first created in 1356 for the family of Stewart of Darnley and tracing a descent to the Dukedom of Richmond in England. The title's name refers to Darnley in Sco ...
, at Kirk o' Field
The Collegiate Church of St Mary in the Fields (commonly known as Kirk o' Field) was a pre-Reformation collegiate church in Edinburgh, Scotland. Likely founded in the 13th century and secularised at the Reformation, the church's site is now covered ...
in 1567. Keen not to seem too intriguing, and wanting to allow the King to take the credit for unveiling the conspiracy, Salisbury feigned ignorance. The following day members of the Privy Council visited the King at the Palace of Whitehall and informed him that, based on the information that Salisbury had given them a week earlier, on Monday the Lord Chamberlain
The Lord Chamberlain of the Household is the most senior officer of the Royal Household of the United Kingdom, supervising the departments which support and provide advice to the Sovereign of the United Kingdom while also acting as the main c ...
Thomas Howard, 1st Earl of Suffolk
Thomas Howard, 1st Earl of Suffolk, (24 August 156128 May 1626) of Audley End House in the parish of Saffron Walden in Essex, and of Suffolk House near Westminster, a member of the House of Howard, was the second son of Thomas Howard, 4th ...
would undertake a search of the Houses of Parliament, "both above and below". On Sunday 3 November, Percy, Catesby and Wintour had a final meeting, where Percy told his colleagues that they should "abide the uttermost triall", and reminded them of their ship waiting at anchor on the Thames.
By 4 November, Digby was ensconced with a "hunting party" at Dunchurch
Dunchurch is a large village and civil parish on the south-western outskirts of Rugby in Warwickshire, England, approximately southwest of central Rugby. The civil parish which also includes the nearby hamlet of Toft, had a population of 4,12 ...
, ready to abduct Elizabeth. The same day, Percy visited the Earl of Northumberland
The title of Earl of Northumberland has been created several times in the Peerage of England and of Great Britain, succeeding the title Earl of Northumbria. Its most famous holders are the House of Percy (''alias'' Perci), who were the most po ...
—who was uninvolved in the conspiracy—to see if he could discern what rumours surrounded the letter to Monteagle. Percy returned to London and assured Wintour, John Wright, and Robert Keyes that they had nothing to be concerned about, and returned to his lodgings on Gray's Inn Road. That same evening Catesby, likely accompanied by John Wright and Bates, set off for the Midlands. Fawkes visited Keyes, and was given a pocket watch
A pocket watch (or pocketwatch) is a watch that is made to be carried in a pocket, as opposed to a wristwatch, which is strapped to the wrist.
They were the most common type of watch from their development in the 16th century until wristw ...
left by Percy, to time the fuse, and an hour later Rookwood received several engraved swords from a local cutler.
 Although two accounts of the number of searches and their timing exist, according to the King's version, the first search of the buildings in and around Parliament was made on Monday 4 November—as the plotters were busy making their final preparations—by Suffolk, Monteagle, and John Whynniard. They found a large pile of firewood in the undercroft beneath the House of Lords, accompanied by what they presumed to be a serving man (Fawkes), who told them that the firewood belonged to his master, Thomas Percy. They left to report their findings, at which time Fawkes also left the building. The mention of Percy's name aroused further suspicion as he was already known to the authorities as a Catholic agitator. The King insisted that a more thorough search be undertaken. Late that night, the search party, headed by Thomas Knyvet, returned to the undercroft. They again found Fawkes, dressed in a cloak and hat, and wearing boots and spurs. He was arrested, whereupon he gave his name as John Johnson. He was carrying a lantern now held in the Ashmolean Museum,
Although two accounts of the number of searches and their timing exist, according to the King's version, the first search of the buildings in and around Parliament was made on Monday 4 November—as the plotters were busy making their final preparations—by Suffolk, Monteagle, and John Whynniard. They found a large pile of firewood in the undercroft beneath the House of Lords, accompanied by what they presumed to be a serving man (Fawkes), who told them that the firewood belonged to his master, Thomas Percy. They left to report their findings, at which time Fawkes also left the building. The mention of Percy's name aroused further suspicion as he was already known to the authorities as a Catholic agitator. The King insisted that a more thorough search be undertaken. Late that night, the search party, headed by Thomas Knyvet, returned to the undercroft. They again found Fawkes, dressed in a cloak and hat, and wearing boots and spurs. He was arrested, whereupon he gave his name as John Johnson. He was carrying a lantern now held in the Ashmolean Museum, Oxford
Oxford () is a city in England. It is the county town and only city of Oxfordshire. In 2020, its population was estimated at 151,584. It is north-west of London, south-east of Birmingham and north-east of Bristol. The city is home to the ...
, and a search of his person revealed a pocket watch, several slow match
Slow match, also called match cord, is the slow-burning cord or twine fuse used by early gunpowder musketeers, artillerymen, and soldiers to ignite matchlock muskets, cannons, shells, and petards. Slow matches were most suitable for use aroun ...
es and touchwood. 36 barrels of gunpowder were discovered hidden under piles of faggots and coal. Fawkes was taken to the King early on the morning of 5 November.
Flight
As news of "John Johnson's" arrest spread among the plotters still in London, most fled northwest, alongWatling Street
Watling Street is a historic route in England that crosses the River Thames at London and which was used in Classical Antiquity, Late Antiquity, and throughout the Middle Ages. It was used by the ancient Britons and paved as one of the main ...
. Christopher Wright and Thomas Percy left together. Rookwood left soon after, and managed to cover 30 miles in two hours on one horse. He overtook Keyes, who had set off earlier, then Wright and Percy at Little Brickhill
Little Brickhill is a village and civil parish in the unitary authority area of the City of Milton Keynes, Buckinghamshire, England. Located immediately to the west of the A5, it is just outside and overlooking the Milton Keynes urban area, ab ...
, before catching Catesby, John Wright, and Bates on the same road. Reunited, the group continued northwest to Dunchurch, using horses provided by Digby. Keyes went to Mordaunt's house at Drayton. Meanwhile, Thomas Wintour stayed in London, and even went to Westminster to see what was happening. When he realised the plot had been uncovered, he took his horse and made for his sister's house at Norbrook, before continuing to Huddington Court.
The group of six conspirators stopped at Ashby St Ledgers
Ashby St Ledgers is a village in the West Northamptonshire district of Northamptonshire, England.OS Explorer Map Map 223 - Northampton & Market Harborough (1:25 000) The post town is Rugby in Warwickshire. The population of the civil parish at ...
at about 6 pm, where they met Robert Wintour and updated him on their situation. They then continued on to Dunchurch, and met with Digby. Catesby convinced him that despite the plot's failure, an armed struggle was still a real possibility. He announced to Digby's "hunting party" that the King and Salisbury were dead, before the fugitives moved west to Warwick.
In London, news of the plot was spreading, and the authorities set extra guards on the city gates
A city gate is a gate which is, or was, set within a city wall. It is a type of fortified gateway.
Uses
City gates were traditionally built to provide a point of controlled access to and departure from a walled city for people, vehicles, good ...
, closed the ports, and protected the house of the Spanish Ambassador, which was surrounded by an angry mob. An arrest warrant was issued against Thomas Percy, and his patron, the Earl of Northumberland, was placed under house arrest. In "John Johnson's" initial interrogation he revealed nothing other than the name of his mother, and that he was from Yorkshire
Yorkshire ( ; abbreviated Yorks), formally known as the County of York, is a historic county in northern England and by far the largest in the United Kingdom. Because of its large area in comparison with other English counties, functions have ...
. A letter to Guy Fawkes was discovered on his person, but he claimed that name was one of his aliases. Far from denying his intentions, "Johnson" stated that it had been his purpose to destroy the King and Parliament. Nevertheless, he maintained his composure and insisted that he had acted alone. His unwillingness to yield so impressed the King that he described him as possessing "a Roman resolution".
Investigation
 On 6 November, the Lord Chief Justice, Sir John Popham (a man with a deep-seated hatred of Catholics) questioned Rookwood's servants. By the evening he had learned the names of several of those involved in the conspiracy: Catesby, Rookwood, Keyes, Wynter, John and Christopher Wright, and Grant. "Johnson" meanwhile persisted with his story, and along with the gunpowder he was found with, was moved to the
On 6 November, the Lord Chief Justice, Sir John Popham (a man with a deep-seated hatred of Catholics) questioned Rookwood's servants. By the evening he had learned the names of several of those involved in the conspiracy: Catesby, Rookwood, Keyes, Wynter, John and Christopher Wright, and Grant. "Johnson" meanwhile persisted with his story, and along with the gunpowder he was found with, was moved to the Tower of London
The Tower of London, officially His Majesty's Royal Palace and Fortress of the Tower of London, is a historic castle on the north bank of the River Thames in central London. It lies within the London Borough of Tower Hamlets, which is sep ...
, where the King had decided that "Johnson" would be torture
Torture is the deliberate infliction of severe pain or suffering on a person for reasons such as punishment, extracting a confession, interrogational torture, interrogation for information, or intimidating third parties. definitions of tortur ...
d. The use of torture was forbidden, except by royal prerogative or a body such as the Privy Council or Star Chamber. In a letter of 6 November James wrote: "The gentler tortours orturesare to be first used unto him, nd thus by steps extended to the bottom depths and so God speed your good work." "Johnson" may have been placed in manacles
Handcuffs are restraint devices designed to secure an individual's wrists in proximity to each other. They comprise two parts, linked together by a chain, a hinge, or rigid bar. Each cuff has a rotating arm which engages with a ratchet that ...
and hung from the wall, but he was almost certainly subjected to the horrors of the rack
Rack or racks may refer to:
Storage and installation
* Amp rack, short for amplifier rack, a piece of furniture in which amplifiers are mounted
* Bicycle rack, a frame for storing bicycles when not in use
* Bustle rack, a type of storage bi ...
. On 7 November his resolve was broken; he confessed late that day, and again over the following two days.
Last stand
On 6 November, with Fawkes maintaining his silence, the fugitives raidedWarwick Castle
Warwick Castle is a medieval castle developed from a wooden fort, originally built by William the Conqueror during 1068. Warwick is the county town of Warwickshire, England, situated on a meander of the River Avon. The original wooden motte-an ...
for supplies, then continued to Norbrook to collect weapons. From there they continued their journey to Huddington. Bates left the group and travelled to Coughton Court
Coughton Court () is an English Tudor country house, situated on the main road between Studley and Alcester in Warwickshire. It is a Grade I listed building.
The house has a long crenellated façade directly facing the main road, at the cen ...
to deliver a letter from Catesby, to Father Garnet and the other priests, informing them of what had transpired, and asking for their help in raising an army. Garnet replied by begging Catesby and his followers to stop their "wicked actions", before himself fleeing. Several priests set out for Warwick, worried about the fate of their colleagues. They were caught, and then imprisoned in London. Catesby and the others arrived at Huddington early in the afternoon, and were met by Thomas Wintour. They received practically no support or sympathy from those they met, including family members, who were terrified at the prospect of being associated with treason. They continued on to Holbeche House
Holbeche House (also, in some texts, Holbeach or Holbeache) is a mansion located approximately north of Kingswinford, now in the Metropolitan Borough of Dudley but historically in Staffordshire.Aikin, L. p.244 Some members of the Gunpowder P ...
on the border of Staffordshire, the home of Stephen Littleton, a member of their ever-decreasing band of followers. Whilst there, Stephen Littleton and Thomas Wintour went to Pepperhill, the Shropshire
Shropshire (; alternatively Salop; abbreviated in print only as Shrops; demonym Salopian ) is a landlocked historic county in the West Midlands region of England. It is bordered by Wales to the west and the English counties of Cheshire to ...
residence at Boningale of Robert Wintour's father-in-law John Talbot, to gain support, but to no avail. Tired and desperate, they spread out some of the now-soaked gunpowder in front of the fire, to dry out. Although gunpowder does not explode unless physically contained, a spark from the fire landed on the powder and the resultant flames engulfed Catesby, Rookwood, Grant, and a man named Morgan, who was a member of the hunting party.
Thomas Wintour and Littleton, on their way from Huddington to Holbeche House, were told by a messenger that Catesby had died. At that point, Littleton left, but Thomas arrived at the house to find Catesby alive, albeit scorched. John Grant was not so lucky, and had been blinded by the fire. Digby, Robert Wintour and his half-brother John, and Thomas Bates, had all left. Of the plotters, only the singed figures of Catesby and Grant, the Wright brothers, Rookwood, and Percy remained. The fugitives resolved to stay in the house and wait for the arrival of the King's men.
Richard Walsh (Sheriff of Worcestershire
This is a list of sheriffs and since 1998 high sheriffs of Worcestershire.
The Sheriff is the oldest secular office under the Crown. Formerly the Sheriff was the principal law enforcement officer in the county but over the centuries most of the ...
) and his company of 200 men besieged Holbeche House on the morning of 8 November. Thomas Wintour was hit in the shoulder while crossing the courtyard. John Wright was shot, followed by his brother, and then Rookwood. Catesby and Percy were reportedly killed by a single lucky shot. The attackers rushed the property, and stripped the dead or dying defenders of their clothing. Grant, Morgan, Rookwood, and Wintour were arrested.
Reaction
Bates and Keyes were captured shortly after Holbeche House was taken. Digby, who had intended to give himself up, was caught by a small group of pursuers. Tresham was arrested on 12 November, and taken to the Tower three days later. Montague, Mordaunt, and Stourton (Tresham's brother-in-law) were also imprisoned in the Tower. The Earl of Northumberland joined them on 27 November. Meanwhile, the government used the revelation of the plot to accelerate its persecution of Catholics. The home ofAnne Vaux
Anne Vaux (c. 1562 – in or after 1637) was a wealthy Catholic recusant.
Background
Vaux was the third daughter of William Vaux, 3rd Baron Vaux of Harrowden (1535–1595) and his first wife, Elizabeth, daughter of John Beaumont of Grace Die ...
at Enfield Chase
Enfield Chase is an area of Enfield that is named for a former royal hunting ground. Much of the former area of the Chase has been developed, but a large part survives between Cockfosters in the west and Enfield in the east as Trent Country ...
was searched, revealing the presence of trap doors and hidden passages. A terrified servant then revealed that Garnet, who had often stayed at the house, had recently given a Mass there. Father John Gerard
John Gerard (also John Gerarde, c. 1545–1612) was an English herbalist with a large garden in Holborn, now part of London. His 1,484-page illustrated ''Herball, or Generall Historie of Plantes'', first published in 1597, became a popular gard ...
was secreted at the home of Elizabeth Vaux, in Harrowden. Vaux was taken to London for interrogation. There she was resolute; she had never been aware that Gerard was a priest, she had presumed he was a "Catholic gentleman", and she did not know of his whereabouts. The homes of the conspirators were searched, and looted; Mary Digby's household was ransacked, and she was made destitute. Some time before the end of November, Garnet moved to Hindlip Hall
Hindlip Hall is a stately home in Hindlip, Worcestershire, England. The first major hall was built before 1575, and it played a significant role in both the Babington and the Gunpowder plots, where it hid four people in priest holes. It was Hump ...
near Worcester
Worcester may refer to:
Places United Kingdom
* Worcester, England, a city and the county town of Worcestershire in England
** Worcester (UK Parliament constituency), an area represented by a Member of Parliament
* Worcester Park, London, Engla ...
, the home of the Habingtons, where he wrote a letter to the Privy Council protesting his innocence.
The foiling of the Gunpowder Plot initiated a wave of national relief at the delivery of the King and his sons, and inspired in the ensuing parliament a mood of loyalty and goodwill, which Salisbury astutely exploited to extract higher subsidies for the King than any (bar one) granted in Elizabeth I's reign. Walter Raleigh, who was languishing in the Tower owing to his involvement in the Main Plot
The Main Plot was an alleged conspiracy of July 1603 by English courtiers to remove King James I from the English throne and to replace him with his cousin Lady Arbella Stuart. The plot was supposedly led by Lord Cobham and funded by the Spanis ...
, and whose wife was a first cousin of Lady Catesby, declared he had had no knowledge of the conspiracy. The Bishop of Rochester gave a sermon at St. Paul's Cross, in which he condemned the plot. In his speech to both Houses on 9 November, James expounded on two emerging preoccupations of his monarchy: the divine right of kings and the Catholic question. He insisted that the plot had been the work of only a few Catholics, not of the English Catholics as a whole, and he reminded the assembly to rejoice at his survival, since kings were divinely appointed and he owed his escape to a miracle. Salisbury wrote to his English ambassadors abroad, informing them of what had occurred, and also reminding them that the King bore no ill will to his Catholic neighbours. The foreign powers largely distanced themselves from the plotters, calling them atheists and Protestant heretics.
Interrogations
 Sir Edward Coke was in charge of the interrogations. Over a period of about ten weeks, in the Lieutenant's Lodgings at the Tower of London (now known as the Queen's House) he questioned those who had been implicated in the plot. For the first round of interrogations, no real proof exists that these people were tortured, although on several occasions Salisbury certainly suggested that they should be. Coke later revealed that the threat of torture was in most cases enough to elicit a confession from those caught up in the aftermath of the plot.
Only two confessions were printed in full: Fawkes's confession of 8 November, and Wintour's of 23 November. Having been involved in the conspiracy from the start (unlike Fawkes), Wintour was able to give extremely valuable information to the Privy Council. The handwriting on his testimony is almost certainly that of the man himself, but his signature was markedly different. Wintour had previously only ever signed his name as such, but his confession is signed "Winter", and since he had been shot in the shoulder, the steady hand used to write the signature may indicate some measure of government interference—or it may indicate that writing a shorter version of his name was less painful. Wintour's testimony makes no mention of his brother, Robert. Both were published in the so-called ''King's Book'', a hastily written official account of the conspiracy published in late November 1605.
Henry Percy, Earl of Northumberland, was in a difficult position. His midday dinner with Thomas Percy on 4 November was damning evidence against him, and after Thomas Percy's death there was nobody who could either implicate him or clear him. The Privy Council suspected that Northumberland would have been Princess Elizabeth's protector had the plot succeeded, but there was insufficient evidence to convict him. Northumberland remained in the Tower and on 27 June 1606 was finally charged with contempt. He was stripped of all public offices, fined £30,000 (about £ in ), and kept in the Tower until June 1621. The Lords Mordaunt and Stourton were tried in the Star Chamber. They were condemned to imprisonment in the Tower, where they remained until 1608, when they were transferred to the Fleet Prison. Both were also given significant fines.
Several other people not involved in the conspiracy, but known or related to the conspirators, were also questioned. Northumberland's brothers, Sir Allen and Sir Josceline Percy, were arrested. Lord Montagu had employed Fawkes at an early age, and had also met Catesby on 29 October, and was therefore of interest; he was released several months later.
Sir Edward Coke was in charge of the interrogations. Over a period of about ten weeks, in the Lieutenant's Lodgings at the Tower of London (now known as the Queen's House) he questioned those who had been implicated in the plot. For the first round of interrogations, no real proof exists that these people were tortured, although on several occasions Salisbury certainly suggested that they should be. Coke later revealed that the threat of torture was in most cases enough to elicit a confession from those caught up in the aftermath of the plot.
Only two confessions were printed in full: Fawkes's confession of 8 November, and Wintour's of 23 November. Having been involved in the conspiracy from the start (unlike Fawkes), Wintour was able to give extremely valuable information to the Privy Council. The handwriting on his testimony is almost certainly that of the man himself, but his signature was markedly different. Wintour had previously only ever signed his name as such, but his confession is signed "Winter", and since he had been shot in the shoulder, the steady hand used to write the signature may indicate some measure of government interference—or it may indicate that writing a shorter version of his name was less painful. Wintour's testimony makes no mention of his brother, Robert. Both were published in the so-called ''King's Book'', a hastily written official account of the conspiracy published in late November 1605.
Henry Percy, Earl of Northumberland, was in a difficult position. His midday dinner with Thomas Percy on 4 November was damning evidence against him, and after Thomas Percy's death there was nobody who could either implicate him or clear him. The Privy Council suspected that Northumberland would have been Princess Elizabeth's protector had the plot succeeded, but there was insufficient evidence to convict him. Northumberland remained in the Tower and on 27 June 1606 was finally charged with contempt. He was stripped of all public offices, fined £30,000 (about £ in ), and kept in the Tower until June 1621. The Lords Mordaunt and Stourton were tried in the Star Chamber. They were condemned to imprisonment in the Tower, where they remained until 1608, when they were transferred to the Fleet Prison. Both were also given significant fines.
Several other people not involved in the conspiracy, but known or related to the conspirators, were also questioned. Northumberland's brothers, Sir Allen and Sir Josceline Percy, were arrested. Lord Montagu had employed Fawkes at an early age, and had also met Catesby on 29 October, and was therefore of interest; he was released several months later. Agnes Wenman
Agnes, Viscountess Wenman (died 1617) was an English Roman Catholic woman, under suspicion of involvement at the time of the Gunpowder Plot of 1605. She is correctly referred to either as Agnes Wenman or as Lady Wenman.
Life
She was the eldest sur ...
was from a Catholic family, and related to Elizabeth Vaux. She was examined twice but the charges against her were eventually dropped. Percy's secretary and later the controller of Northumberland's household, Dudley Carleton, had leased the vault where the gunpowder was stored, and consequently he was imprisoned in the Tower. Salisbury believed his story, and authorised his release.
Jesuits
 Thomas Bates confessed on 4 December, providing much of the information that Salisbury needed to link the Catholic clergy to the plot. Bates had been present at most of the conspirators' meetings, and under interrogation he implicated Father Tesimond in the plot. On 13 January 1606, he described how he had visited Garnet and Tesimond on 7 November to inform Garnet of the plot's failure. Bates also told his interrogators of his ride with Tesimond to Huddington, before the priest left him to head for the Habingtons at Hindlip Hall, and of a meeting between Garnet, Gerard, and Tesimond in October 1605.
At about the same time in December, Tresham's health began to deteriorate. He was visited regularly by his wife, a nurse, and his servant William Vavasour—who documented his strangury. Before he died, Tresham had also told of Garnet's involvement with the 1603 mission to Spain, but in his last hours he retracted some of these statements. Nowhere in his confession did he mention the Monteagle letter. He died early on the morning of 23 December, and was buried in the Tower. Nevertheless, he was attainted along with the other plotters; his head was set on a pike either (accounts differ) at Northampton or London Bridge, and his estates confiscated.
On 15 January a proclamation named Father Garnet, Father Gerard, and Father Greenway (Tesimond) as wanted men. Tesimond and Gerard escaped the country and lived out their days in freedom. Several days earlier, on 9 January, Robert Wintour and Stephen Littleton were captured. They had been hiding at
Thomas Bates confessed on 4 December, providing much of the information that Salisbury needed to link the Catholic clergy to the plot. Bates had been present at most of the conspirators' meetings, and under interrogation he implicated Father Tesimond in the plot. On 13 January 1606, he described how he had visited Garnet and Tesimond on 7 November to inform Garnet of the plot's failure. Bates also told his interrogators of his ride with Tesimond to Huddington, before the priest left him to head for the Habingtons at Hindlip Hall, and of a meeting between Garnet, Gerard, and Tesimond in October 1605.
At about the same time in December, Tresham's health began to deteriorate. He was visited regularly by his wife, a nurse, and his servant William Vavasour—who documented his strangury. Before he died, Tresham had also told of Garnet's involvement with the 1603 mission to Spain, but in his last hours he retracted some of these statements. Nowhere in his confession did he mention the Monteagle letter. He died early on the morning of 23 December, and was buried in the Tower. Nevertheless, he was attainted along with the other plotters; his head was set on a pike either (accounts differ) at Northampton or London Bridge, and his estates confiscated.
On 15 January a proclamation named Father Garnet, Father Gerard, and Father Greenway (Tesimond) as wanted men. Tesimond and Gerard escaped the country and lived out their days in freedom. Several days earlier, on 9 January, Robert Wintour and Stephen Littleton were captured. They had been hiding at Hagley
Hagley is a large village and civil parish in Worcestershire, England. It is on the boundary of the West Midlands and Worcestershire counties between the Metropolitan Borough of Dudley and Kidderminster. Its estimated population was 7,162 in 2 ...
, the home of Humphrey Littleton
Humphrey Littleton, or Humphrey Lyttelton, died on 7 April 1606 at Red Hill outside Worcester. A member of the Lyttelton family, he was executed for his involvement in the Gunpowder plot. Robert Wintour and Stephen Littleton who had escaped ...
, brother of MP John Littleton, imprisoned for treason in 1601 for his part in the Essex revolt. They were betrayed by a cook, who grew suspicious of the amount of food sent up for his master's consumption. Humphrey denied the presence of the two fugitives, but another servant led the authorities to their hiding place. On 20 January, the local Justice of the Peace and his retainers arrived at Thomas Habington's home, Hindlip Hall
Hindlip Hall is a stately home in Hindlip, Worcestershire, England. The first major hall was built before 1575, and it played a significant role in both the Babington and the Gunpowder plots, where it hid four people in priest holes. It was Hump ...
, to arrest the Jesuits. Despite Thomas Habington's protests, the men spent the next four days searching the house. On 24 January, starving, two priests left their hiding places and were discovered. Humphrey Littleton, who had escaped from the authorities at Hagley, got as far as Prestwood
Prestwood is a village in Buckinghamshire, England. It is located in the Chiltern Hills, about two miles west of Great Missenden and six miles north of High Wycombe.
History
Early history and creation of parish
The village name is Anglo Sax ...
in Staffordshire before he was captured. He was imprisoned, and then condemned to death at Worcester
Worcester may refer to:
Places United Kingdom
* Worcester, England, a city and the county town of Worcestershire in England
** Worcester (UK Parliament constituency), an area represented by a Member of Parliament
* Worcester Park, London, Engla ...
. On 26 January, in exchange for his life, he told the authorities where they could find Father Garnet. Worn down by hiding for so long, Garnet, accompanied by another priest, emerged from his priest hole
A priest hole is a hiding place for a priest built into many of the principal Catholic houses of England, Wales and Ireland during the period when Catholics were persecuted by law. When Queen Elizabeth I came to the throne in 1558, there were se ...
the next day.
Trials
 By coincidence, on the same day that Garnet was found, the surviving conspirators were
By coincidence, on the same day that Garnet was found, the surviving conspirators were arraigned
Arraignment is a formal reading of a criminal charging document in the presence of the defendant, to inform them of the charges against them. In response to arraignment, the accused is expected to enter a plea. Acceptable pleas vary among jurisdi ...
in Westminster Hall
The Palace of Westminster serves as the meeting place for both the House of Commons and the House of Lords, the two houses of the Parliament of the United Kingdom. Informally known as the Houses of Parliament, the Palace lies on the north bank ...
. Seven of the prisoners were taken from the Tower to the Star Chamber by barge. Bates, who was considered lower class, was brought from the Gatehouse Prison
Gatehouse Prison was a prison in Westminster, built in 1370 as the gatehouse of Westminster Abbey. It was first used as a prison by the Abbot, a powerful churchman who held considerable power over the precincts and sanctuary. It was one of the pri ...
. Some of the prisoners were reportedly despondent, but others were nonchalant, even smoking tobacco
Tobacco is the common name of several plants in the genus '' Nicotiana'' of the family Solanaceae, and the general term for any product prepared from the cured leaves of these plants. More than 70 species of tobacco are known, but the ...
. The King and his family, hidden from view, were among the many who watched the trial. The Lords Commissioners present were the Earls of Suffolk, Worcester, Northampton, Devonshire
Devon ( , historically known as Devonshire , ) is a ceremonial county, ceremonial and non-metropolitan county, non-metropolitan counties of England, county in South West England. The most populous settlement in Devon is the city of Plymouth, ...
, and Salisbury. Sir John Popham was Lord Chief Justice
Lord is an appellation for a person or deity who has authority, control, or power over others, acting as a master, chief, or ruler. The appellation can also denote certain persons who hold a title of the peerage in the United Kingdom, or are ...
, Sir Thomas Fleming was Lord Chief Baron of the Exchequer
The Chief Baron of the Exchequer was the first "baron" (meaning judge) of the English Exchequer of Pleas. "In the absence of both the Treasurer of the Exchequer or First Lord of the Treasury, and the Chancellor of the Exchequer, it was he who ...
, and two Justices, Sir Thomas Walmsley and Sir Peter Warburton, sat as Justices of the Common Pleas
A judge is a person who presides over court proceedings, either alone or as a part of a panel of judges. A judge hears all the witnesses and any other evidence presented by the barristers or solicitors of the case, assesses the credibility an ...
. The list of traitors' names was read aloud, beginning with those of the priests: Garnet, Tesimond, and Gerard.
The first to speak was the Speaker of the House of Commons Speaker of the House of Commons is a political leadership position found in countries that have a House of Commons, where the membership of the body elects a speaker to lead its proceedings.
Systems that have such a position include:
* Speaker of ...
(later Master of the Rolls
The Keeper or Master of the Rolls and Records of the Chancery of England, known as the Master of the Rolls, is the President of the Civil Division of the Court of Appeal of England and Wales and Head of Civil Justice. As a judge, the Master of ...
), Sir Edward Philips, who described the intent behind the plot in lurid detail. He was followed by the Attorney-General
In most common law jurisdictions, the attorney general or attorney-general (sometimes abbreviated AG or Atty.-Gen) is the main legal advisor to the government. The plural is attorneys general.
In some jurisdictions, attorneys general also have exec ...
Sir Edward Coke, who began with a long speech—the content of which was heavily influenced by Salisbury—that included a denial that the King had ever made any promises to the Catholics. Monteagle's part in the discovery of the plot was welcomed, and denunciations of the 1603 mission to Spain featured strongly. Fawkes's protestations that Gerard knew nothing of the plot were omitted from Coke's speech. The foreign powers, when mentioned, were accorded due respect, but the priests were accursed, their behaviour analysed and criticised wherever possible. There was little doubt, according to Coke, that the plot had been invented by the Jesuits. Garnet's meeting with Catesby, at which the former was said to have absolved the latter of any blame in the plot, was proof enough that the Jesuits were central to the conspiracy; according to Coke the Gunpowder Plot would always be known as the Jesuit Treason. Coke spoke with feeling of the probable fate of the Queen and the rest of the King's family, and of the innocents who would have been caught up in the explosion.
Each of the condemned, said Coke, would be drawn backwards to his death, by a horse, his head near the ground. He was to be "put to death halfway between heaven and earth as unworthy of both". His genitals would be cut off and burnt before his eyes, and his bowels and heart then removed. Then he would be decapitated, and the dismembered parts of his body displayed so that they might become "prey for the fowls of the air". Confessions and declarations from the prisoners were then read aloud, and finally the prisoners were allowed to speak. Rookwood claimed that he had been drawn into the plot by Catesby, "whom he loved above any worldy man". Thomas Wintour begged to be hanged for himself and his brother, so that his brother might be spared. Fawkes explained his not guilty plea as ignorance of certain aspects of the indictment. Keyes appeared to accept his fate, Bates and Robert Wintour begged for mercy, and Grant explained his involvement as "a conspiracy intended but never effected". Only Digby, tried on a separate indictment, pleaded guilty, insisting that the King had reneged upon promises of toleration for Catholics, and that affection for Catesby and love of the Catholic cause mitigated his actions. He sought death by the axe
Decapitation or beheading is the total separation of the head from the body. Such an injury is invariably fatal to humans and most other animals, since it deprives the brain of oxygenated blood, while all other organs are deprived of the i ...
and begged mercy from the King for his young family. His defence was in vain; his arguments were rebuked by Coke and Northumberland, and along with his seven co-conspirators, he was found guilty by the jury
A jury is a sworn body of people (jurors) convened to hear evidence and render an impartial verdict (a finding of fact on a question) officially submitted to them by a court, or to set a penalty or judgment.
Juries developed in England du ...
of high treason
Treason is the crime of attacking a state authority to which one owes allegiance. This typically includes acts such as participating in a war against one's native country, attempting to overthrow its government, spying on its military, its diplo ...
. Digby shouted "If I may but hear any of your lordships say, you forgive me, I shall go more cheerfully to the gallows." The response was short: "God forgive you, and we do."
Garnet may have been questioned on as many as 23 occasions. His response to the threat of the rack was " hreats are only for boys, and he denied having encouraged Catholics to pray for the success of the "Catholic Cause". His interrogators resorted to the forgery of correspondence between Garnet and other Catholics, but to no avail. His jailers then allowed him to talk with another priest in a neighbouring cell, with eavesdroppers listening to every word. Eventually Garnet let slip a crucial piece of information, that there was only one man who could testify that he had any knowledge of the plot. Under torture Garnet admitted that he had heard of the plot from fellow Jesuit Oswald Tesimond, who had learnt of it in confession from Catesby. Garnet was charged with high treason and tried in the Guildhall
A guildhall, also known as a "guild hall" or "guild house", is a historical building originally used for tax collecting by municipalities or merchants in Great Britain and the Low Countries. These buildings commonly become town halls and in som ...
on 28 March, in a trial lasting from 8 am until 7 pm. According to Coke, Garnet instigated the plot: " arnethath many gifts and endowments of nature, by art learned, a good linguist and, by profession, a Jesuit and a Superior as indeed he is Superior to all his predecessors in devilish treason, a Doctor of Dissimulation, Deposing of Princes, Disposing of Kingdoms, Daunting and deterring of subjects, and Destruction." Garnet refuted all the charges against him, and explained the Catholic position on such matters, but he was nevertheless found guilty and sentenced to death.
Executions
Although Catesby and Percy escaped the executioner, their bodies were exhumed and decapitated, and their heads exhibited on spikes outside the House of Lords. On a cold 30 January, Everard Digby, Robert Wintour, John Grant, and Thomas Bates were tied to hurdles—wooden panels—and dragged through the crowded streets of London toSt Paul's Churchyard
St Paul's Churchyard is an area immediately around St Paul's Cathedral in the City of London. It included St Paul's Cross and Paternoster Row. It became one of the principal marketplaces in London. St Paul's Cross was an open-air pulpit from whi ...
. Digby, the first to mount the scaffold, asked the spectators for forgiveness, and refused the attentions of a Protestant clergyman. He was stripped of his clothing, and wearing only a shirt, climbed the ladder to place his head through the noose. He was quickly cut down, and while still fully conscious was castrated
Castration is any action, surgical, chemical, or otherwise, by which an individual loses use of the testicles: the male gonad. Surgical castration is bilateral orchiectomy (excision of both testicles), while chemical castration uses pharmac ...
, disembowelled
Disembowelment or evisceration is the removal of some or all of the organs of the gastrointestinal tract (the bowels, or viscera), usually through a horizontal incision made across the abdominal area. Disembowelment may result from an accident ...
, and then quartered, along with the three other prisoners. The following day, Thomas Wintour, Ambrose Rookwood, Robert Keyes, and Guy Fawkes were hanged, drawn and quartered, opposite the building they had planned to blow up, in the Old Palace Yard
Old Palace Yard is a paved open space in the City of Westminster in Central London, England. It lies between the Palace of Westminster to its north and east and Westminster Abbey to its west. It is known as the site of executions, including those ...
at Westminster. Keyes did not wait for the hangman's command and jumped from the gallows, but he survived the drop and was led to the quartering block. Although weakened by his torture, Fawkes managed to jump from the gallows and break his neck, thus avoiding the agony of the gruesome latter part of his execution.
Steven Littleton was executed at Stafford. His cousin Humphrey, despite his co-operation with the authorities, met his end at Red Hill near Worcester. Henry Garnet's execution took place on 3 May 1606.
Aftermath
 Greater freedom for Roman Catholics to worship as they chose seemed unlikely in 1604, but the discovery of such a wide-ranging conspiracy, the capture of those involved, and the subsequent trials, led Parliament to consider introducing new anti-Catholic legislation. The event also destroyed all hope that the Spanish would ever secure tolerance of the Catholics in England. In the summer of 1606, laws against recusancy were strengthened; the Popish Recusants Act returned England to the Elizabethan system of fines and restrictions, introduced a sacramental test, and an Oath of Allegiance, requiring Catholics to abjure as a "heresy" the doctrine that "princes excommunicated by the Pope could be deposed or assassinated".
Greater freedom for Roman Catholics to worship as they chose seemed unlikely in 1604, but the discovery of such a wide-ranging conspiracy, the capture of those involved, and the subsequent trials, led Parliament to consider introducing new anti-Catholic legislation. The event also destroyed all hope that the Spanish would ever secure tolerance of the Catholics in England. In the summer of 1606, laws against recusancy were strengthened; the Popish Recusants Act returned England to the Elizabethan system of fines and restrictions, introduced a sacramental test, and an Oath of Allegiance, requiring Catholics to abjure as a "heresy" the doctrine that "princes excommunicated by the Pope could be deposed or assassinated". Catholic emancipation
Catholic emancipation or Catholic relief was a process in the kingdoms of Great Britain and Ireland, and later the combined United Kingdom in the late 18th century and early 19th century, that involved reducing and removing many of the restricti ...
took another 200 years, but many important and loyal Catholics retained high office during King James I's reign. Although there was no "golden time" of "toleration" of Catholics, which Father Garnet had hoped for, James's reign was nevertheless a period of relative leniency for Catholics, and few were subject to prosecution.
The playwright William Shakespeare
William Shakespeare ( 26 April 1564 – 23 April 1616) was an English playwright, poet and actor. He is widely regarded as the greatest writer in the English language and the world's pre-eminent dramatist. He is often called England's nation ...
had already used the family history of Northumberland's family in his '' Henry IV'' series of plays, and the events of the Gunpowder Plot seem to have featured alongside the earlier Gowrie conspiracy
John Ruthven, 3rd Earl of Gowrie (c. 1577 – 5 August 1600), was a Scottish nobleman who died in mysterious circumstances, referred to as the "Gowrie Conspiracy", in which he and/or his brother Alexander were attempting to kill or kidnap King ...
in '' Macbeth'', written some time between 1603 and 1607. Interest in the demonic was heightened by the Gunpowder Plot. The King had become engaged in the great debate about other-worldly powers in writing his ''Daemonologie
''Daemonologie''—in full ''Daemonologie, In Forme of a Dialogue, Divided into three Books: By the High and Mighty Prince, James &c.''—was first published in 1597 by King James VI of Scotland (later also James I of England) as a philosophi ...
'' in 1599, before he became King of England as well as Scotland. Inversions seen in such lines as "fair is foul and foul is fair" are used frequently, and another possible reference to the plot relates to the use of equivocation; Garnet's ''A Treatise of Equivocation'' was found on one of the plotters. Another writer influenced by the plot was John Milton, who in 1626 wrote what one commentator has called a "critically vexing poem", '' In Quintum Novembris''. Reflecting "partisan public sentiment on an English-Protestant national holiday", in the published editions of 1645 and 1673, the poem is preceded by five epigrams on the subject of the Gunpowder Plot, apparently written by Milton in preparation for the larger work. The plot may also have influenced his later work, '' Paradise Lost''.
The Gunpowder Plot was commemorated for years by special sermons and other public acts, such as the ringing of church bells. It added to an increasingly full calendar of Protestant celebrations that contributed to the national and religious life of 17th-century England, and has evolved into the Bonfire Night
Bonfire Night is a name given to various annual celebrations characterised by bonfires and fireworks. The event celebrates different traditions on different dates, depending on the country. Some of the most popular instances include Guy Fawkes ...
of today. In ''What If the Gunpowder Plot Had Succeeded?'' historian Ronald Hutton
Ronald Edmund Hutton (born 19 December 1953) is an English historian who specialises in Early Modern Britain, British folklore, pre-Christian religion and Contemporary Paganism. He is a professor at the University of Bristol, has written 14 b ...
considered the events which might have followed a successful implementation of the plot; the destruction of the House of Lords and all those within it. He concluded that a severe backlash against suspected Catholics would have followed, and that without foreign assistance a successful rebellion would have been unlikely; despite differing religious convictions, most Englishmen were loyal to the institution of the monarchy. England might have become a more "Puritan absolute monarchy", as "existed in Sweden, Denmark, Saxony
Saxony (german: Sachsen ; Upper Saxon: ''Saggsn''; hsb, Sakska), officially the Free State of Saxony (german: Freistaat Sachsen, links=no ; Upper Saxon: ''Freischdaad Saggsn''; hsb, Swobodny stat Sakska, links=no), is a landlocked state of ...
, and Prussia
Prussia, , Old Prussian: ''Prūsa'' or ''Prūsija'' was a German state on the southeast coast of the Baltic Sea. It formed the German Empire under Prussian rule when it united the German states in 1871. It was ''de facto'' dissolved by an ...
in the seventeenth century", rather than following the path of parliamentary and civil reform that it did.
Accusations of state conspiracy
Many at the time felt that Salisbury had been involved in the plot to gain favour with the King and enact more stridently anti-Catholic legislation. Suchconspiracy theories
A conspiracy theory is an explanation for an event or situation that invokes a conspiracy by sinister and powerful groups, often political in motivation, when other explanations are more probable.Additional sources:
*
*
*
* The term has a nega ...
alleged that Salisbury had either actually invented the plot or allowed it to continue when his agents had already infiltrated it, for the purposes of propaganda. The Popish Plot of 1678 sparked renewed interest in the Gunpowder Plot, resulting in a book by Thomas Barlow, Bishop of Lincoln, which refuted "a bold and groundless surmise that all this was a contrivance of Secretary Cecil".
In 1897 Father John Gerard of Stonyhurst College, namesake of John Gerard
John Gerard (also John Gerarde, c. 1545–1612) was an English herbalist with a large garden in Holborn, now part of London. His 1,484-page illustrated ''Herball, or Generall Historie of Plantes'', first published in 1597, became a popular gard ...
(who, following the plot's discovery, had evaded capture), wrote an account called ''What was the Gunpowder Plot?'', alleging Salisbury's culpability. This prompted a refutation later that year by Samuel Gardiner, who argued that Gerard had gone too far in trying to "wipe away the reproach" which the plot had exacted on generations of English Catholics. Gardiner portrayed Salisbury as guilty of nothing more than opportunism. Subsequent attempts to prove Salisbury's involvement, such as Francis Edwards's 1969 work ''Guy Fawkes: the real story of the gunpowder plot?'', have similarly foundered on the lack of any clear evidence.
The cellars under the Houses of Parliament continued to be leased out to private individuals until 1678, when news of the Popish Plot broke. It was then considered prudent to search the cellars on the day before each State Opening of Parliament, a ritual that survives to this day.
Bonfire Night
 In January 1606, during the first sitting of Parliament since the plot, the
In January 1606, during the first sitting of Parliament since the plot, the Observance of 5th November Act 1605
The Observance of 5th November Act 1605, also known as the Thanksgiving Act, was an act of the Parliament of England passed in 1606 in the aftermath of the Gunpowder Plot.
The originating bill was drafted and introduced on 23 January 1606 (New ...
was passed, making services and sermons commemorating the event an annual feature of English life; the act remained in force until 1859. The tradition of marking the day with the ringing of church bells and bonfires started soon after the Plot's discovery, and fireworks
Fireworks are a class of low explosive pyrotechnic devices used for aesthetic and entertainment purposes. They are most commonly used in fireworks displays (also called a fireworks show or pyrotechnics), combining a large number of devices ...
were included in some of the earliest celebrations. In Britain, 5 November is variously called Bonfire Night, Fireworks Night, or Guy Fawkes Night.
5 November firework displays and bonfire parties are common throughout Britain, both in major public displays and in private gardens. Traditionally, in the weeks running up to the 5th, children made "guys"—effigies
An effigy is an often life-size sculptural representation of a specific person, or a prototypical figure. The term is mostly used for the makeshift dummies used for symbolic punishment in political protests and for the figures burned in certai ...
supposedly of Fawkes—usually made from old clothes stuffed with newspaper, and fitted with a grotesque mask, to be burnt on 5 November bonfire. These "guys" were exhibited in the street to collect money for fireworks, although this custom has become less common. The word ''guy'', in the 19th century, thus came to mean an oddly dressed person and, in the 20th and 21st centuries, to mean any male person.
According to the biographer Esther Forbes
Esther Louise Forbes (; June 28, 1891 – August 12, 1967) was an American novelist, historian and children's writer who received the Pulitzer Prize and the Newbery Medal. She was the first woman elected to membership in the American Antiqu ...
, the Guy Fawkes Day celebration in the pre-revolutionary American colonies was a very popular holiday. In Boston
Boston (), officially the City of Boston, is the state capital and most populous city of the Commonwealth of Massachusetts, as well as the cultural and financial center of the New England region of the United States. It is the 24th- mo ...
, the revelry on "Pope Night
Pope Night (also called Pope's Night, Pope Day, or Pope's Day) was an anti-Catholic holiday celebrated annually on November 5 in the colonial United States. It evolved from the British Guy Fawkes Night, which commemorates the failure of the Gunpo ...
" took on anti-authoritarian overtones, and often became so dangerous that many would not venture out of their homes.
Reconstructing the explosion
 In the 2005, ITV programme '' The Gunpowder Plot: Exploding the Legend'', a full-size replica of the House of Lords was built and destroyed with barrels of gunpowder, totalling 1
In the 2005, ITV programme '' The Gunpowder Plot: Exploding the Legend'', a full-size replica of the House of Lords was built and destroyed with barrels of gunpowder, totalling 1 tonne
The tonne ( or ; symbol: t) is a unit of mass equal to 1000 kilograms. It is a non-SI unit accepted for use with SI. It is also referred to as a metric ton to distinguish it from the non-metric units of the short ton ( United State ...
of explosives. The experiment was conducted on the Advantica-owned Spadeadam test site and demonstrated that the explosion—if the gunpowder had been in good order—would have killed all those in the building. The power of the explosion was such that of the deep concrete walls making up the undercroft (replicating how archives suggest the walls of the old House of Lords were constructed), the end wall where the barrels were placed, under the throne, was reduced to rubble, and the adjacent surviving portions of wall were shoved away. Measuring devices placed in the chamber to calculate the force of the blast were recorded as going off the scale just before their destruction by the explosion; a piece of the head of the dummy representing King James, which had been placed on a throne inside the chamber—surrounded by courtiers, peers and bishops—was found a considerable distance from its initial location. According to the findings of the programme, no one within of the blast could have survived, and all of the stained glass windows in Westminster Abbey
Westminster Abbey, formally titled the Collegiate Church of Saint Peter at Westminster, is an historic, mainly Gothic church in the City of Westminster, London, England, just to the west of the Palace of Westminster. It is one of the Unite ...
would have shattered, as would all of the windows in the vicinity of the Palace. The explosion would have been seen from miles away and heard from further away still. Even if only half of the gunpowder had gone off—which Fawkes was apparently prepared for—everyone in the House of Lords and its environs would have been killed instantly.
The programme also disproved claims that some deterioration in the quality of the gunpowder would have prevented the explosion. A portion of deliberately deteriorated gunpowder, of such low quality as to make it unusable in firearms, when placed in a heap and ignited, still managed to create a large explosion. The impact of even deteriorated gunpowder would have been magnified by its containment in wooden barrels, compensating for the quality of the contents. The compression would have created a cannon effect, with the powder first blowing up from the top of the barrel before, a millisecond later, blowing out. Calculations showed that Fawkes, who was skilled in the use of gunpowder, had deployed double the amount needed. In a test detonation of all of period-accurate gunpowder available in the UK inside the same size of barrel Fawkes had used, the experts for the project were surprised at how much more powerful an effect compression had in creating an explosion.
Some of the gunpowder guarded by Fawkes may have survived. In March 2002, workers cataloguing archives of diarist John Evelyn
John Evelyn (31 October 162027 February 1706) was an English writer, landowner, gardener, courtier and minor government official, who is now best known as a diarist. He was a founding Fellow of the Royal Society.
John Evelyn's diary, or ...
at the British Library
The British Library is the national library of the United Kingdom and is one of the largest libraries in the world. It is estimated to contain between 170 and 200 million items from many countries. As a legal deposit library, the British ...
found a box containing a number of gunpowder samples, including a compressed bar with a note in Evelyn's handwriting stating that it had belonged to Guy Fawkes. A further note, written in the 19th century, confirmed this provenance, although in 1952 the document acquired a new comment: "but there was none left!"
See also
*Nicholas Owen (Jesuit)
Nicholas Owen, S.J., (c. 1562 – 1/2 March 1606) was an English Jesuit lay brother who was the principal builder of priest holes during the reigns of Queen Elizabeth I and James I of England. Owen built many priest holes in the buildings ...
* List of attacks on legislatures
The following is a list of attacks on state or national legislature
A legislature is an assembly with the authority to make laws for a political entity such as a country or city. They are often contrasted with the executive and judicial ...
References
Notes Footnotes Bibliography * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * *External links
The Gunpowder Plot
The original House of Commons Journal recording the discovery of the plot – Parliamentary Archives catalogue
Digital image of the Original Thanksgiving Act following the Gunpowder Plot from the Parliamentary Archives
Photograph of the Guy Fawkes Search that takes place at the start of a new Parliament – Parliamentary Archives
The Palace of Westminster in 1605 from the Parliamentary Archives
The Gunpowder Plot Society
The story of Guy Fawkes and The Gunpowder Plot from the BBC, with archive video clips
What If the Gunpowder Plot Had Succeeded?
Interactive Guide: Gunpowder Plot
Guardian Unlimited
TheGuardian.com, formerly known as Guardian.co.uk and ''Guardian Unlimited'', is a British news and media website owned by the Guardian Media Group. It contains nearly all of the content of the newspapers ''The Guardian'' and ''The Observer'', ...
Website of a crew member of ITV's ''Exploding the Legend'' programme, with a photograph of the explosion
* Mark Nicholls, ''The Gunpowder Plot'', Oxford Dictionary of National Biography onlin
History.com – Gunpowder Plot
{{Featured article 17th century in London Anti-Protestantism Conspiracies 1605 in England Attacks on legislatures 17th-century coups d'état and coup attempts Palace of Westminster Military coups in England Failed assassination attempts in the United Kingdom