Guinea (region) on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 Guinea is a traditional name for the region of the
Guinea is a traditional name for the region of the
 The etymology of "Guinea" is uncertain. The English term ''Guinea'' comes directly from the Spanish word ''Guinea'', which in turn derives from the Portuguese word ''Guiné''. The Portuguese term emerged in the mid-15th century to refer to the lands inhabited by the ''Guineus'', a generic term used by the Portuguese to refer to the 'black' African peoples living south of the Senegal River (in contrast to the 'tawny'
The etymology of "Guinea" is uncertain. The English term ''Guinea'' comes directly from the Spanish word ''Guinea'', which in turn derives from the Portuguese word ''Guiné''. The Portuguese term emerged in the mid-15th century to refer to the lands inhabited by the ''Guineus'', a generic term used by the Portuguese to refer to the 'black' African peoples living south of the Senegal River (in contrast to the 'tawny'  A competing theory, first forwarded by Leo Africanus in 1526, claims that 'Guinea' is derived from Djenné (which he refers to as ''Gheneo, Genni'' and ''Ghinea''), the great interior commercial city on the Upper
A competing theory, first forwarded by Leo Africanus in 1526, claims that 'Guinea' is derived from Djenné (which he refers to as ''Gheneo, Genni'' and ''Ghinea''), the great interior commercial city on the Upper
p.20
Other theories try to connect "Guinea" to "Ghana", but this is less certain. The
uinea/nowiki>'' and seized them and all their gold. Another...Castilian voyage to Mina, that of rince/nowiki>'' John.”'' I
''A history of Portuguese overseas expansion, 1400-1668''
Routledge, New York, 2005, p.39,40. Bailey W. Diffie and George D. Winius ''“In a war in which the Castilians were victorious on land and the Portuguese at sea, …”'' i
''Foundations of the Portuguese empire 1415-1580''
volume I, University of Minnesota Press, 1985, p.152. This was the first of many colonial wars among European powers. After the Portuguese and Castilians came the Dutch, French, and British. The extensive trade in ivory,

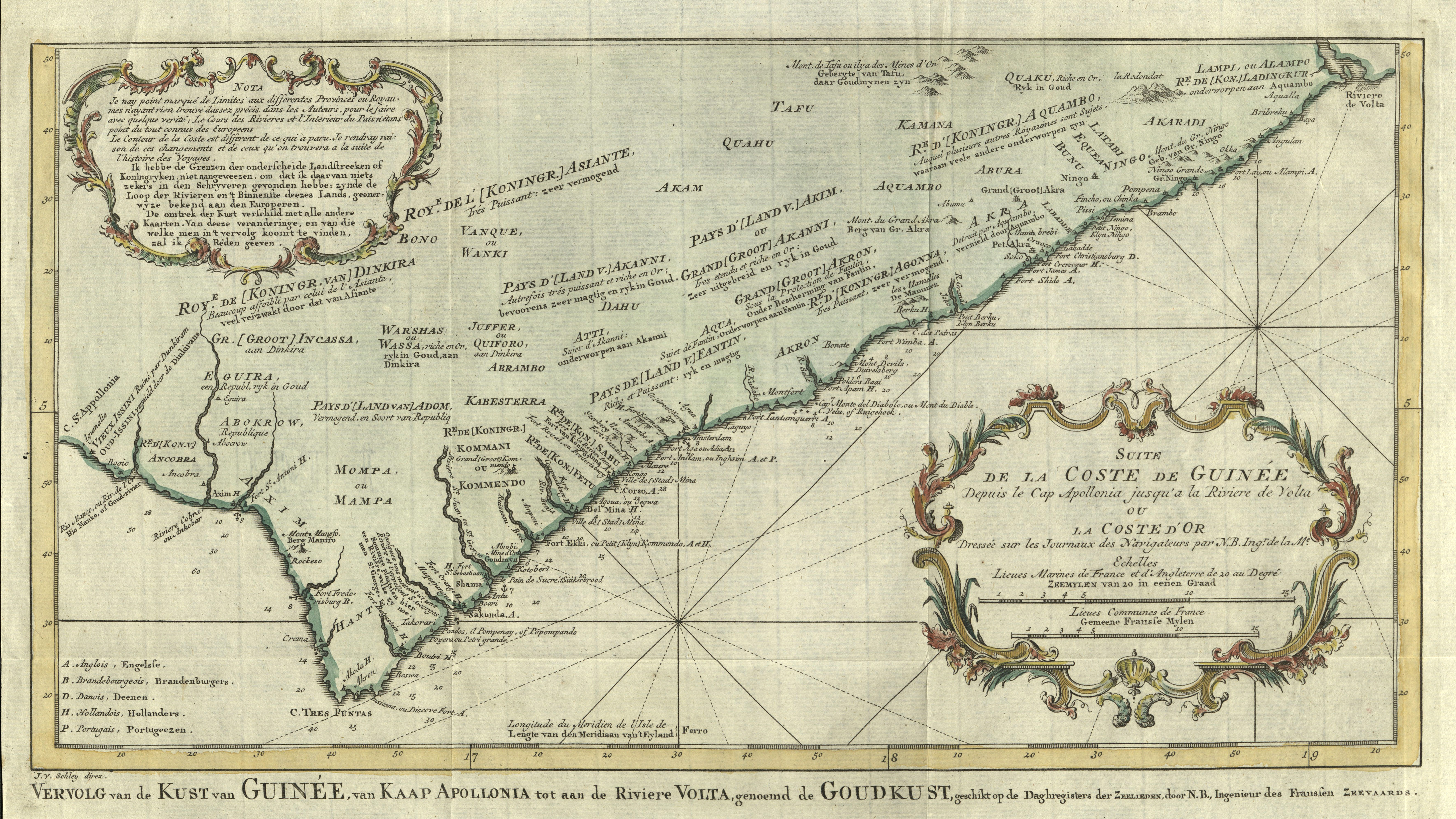 From north to south:
*
From north to south:
*
''Foundations of the Portuguese Empire, 1415-1580''
Volume 1, University of Minnesota Press, 1977. * NEWITT, Malyn
''A history of Portuguese overseas expansion, 1400-1668''
Routledge, New York, 2005. {{Regions of Africa Regions of Africa Divided regions
 Guinea is a traditional name for the region of the
Guinea is a traditional name for the region of the Africa
Africa is the world's second-largest and second-most populous continent, after Asia in both cases. At about 30.3 million km2 (11.7 million square miles) including adjacent islands, it covers 6% of Earth's total surface area ...
n coast of West Africa
West Africa or Western Africa is the westernmost region of Africa. The United Nations defines Western Africa as the 16 countries of Benin, Burkina Faso, Cape Verde, The Gambia, Ghana, Guinea, Guinea-Bissau, Ivory Coast, Liberia, Mali ...
which lies along the Gulf of Guinea
The Gulf of Guinea is the northeasternmost part of the tropical Atlantic Ocean from Cape Lopez in Gabon, north and west to Cape Palmas in Liberia. The intersection of the Equator and Prime Meridian (zero degrees latitude and longitude) is i ...
. It is a naturally moist tropical forest or savanna that stretches along the coast and borders the Sahel belt in the north.
Etymology
 The etymology of "Guinea" is uncertain. The English term ''Guinea'' comes directly from the Spanish word ''Guinea'', which in turn derives from the Portuguese word ''Guiné''. The Portuguese term emerged in the mid-15th century to refer to the lands inhabited by the ''Guineus'', a generic term used by the Portuguese to refer to the 'black' African peoples living south of the Senegal River (in contrast to the 'tawny'
The etymology of "Guinea" is uncertain. The English term ''Guinea'' comes directly from the Spanish word ''Guinea'', which in turn derives from the Portuguese word ''Guiné''. The Portuguese term emerged in the mid-15th century to refer to the lands inhabited by the ''Guineus'', a generic term used by the Portuguese to refer to the 'black' African peoples living south of the Senegal River (in contrast to the 'tawny' Sanhaja
The Sanhaja ( ber, Aẓnag, pl. Iẓnagen, and also Aẓnaj, pl. Iẓnajen; ar, صنهاجة, ''Ṣanhaja'' or زناگة ''Znaga'') were once one of the largest Berber tribal confederations, along with the Zanata and Masmuda confederations. Man ...
Berbers, north of it, whom they called ''Azenegues''). The term "Guinea" is extensively used in the 1453 chronicle of Gomes Eanes de Zurara. King John II of Portugal took up the title of ''Senhor da Guiné'' (Lord of Guinea) from 1481.
It is believed the Portuguese borrowed ''Guineus'' from the Berber term ''Ghinawen'' (sometimes Arabized
Arabization or Arabisation ( ar, تعريب, ') describes both the process of growing Arab influence on non-Arab populations, causing a language shift by the latter's gradual adoption of the Arabic language and incorporation of Arab culture, ...
as ''Guinauha'' or ''Genewah'') meaning "the burnt people" (analogous to the Classical Greek
Ancient Greek includes the forms of the Greek language used in ancient Greece and the ancient world from around 1500 BC to 300 BC. It is often roughly divided into the following periods: Mycenaean Greek (), Dark Ages (), the Archaic pe ...
'' Aithiops'', "of the burned face"). The Berber terms "aginaw" and " Akal n-Iguinawen" mean "black" and "land of the blacks", respectively.
 A competing theory, first forwarded by Leo Africanus in 1526, claims that 'Guinea' is derived from Djenné (which he refers to as ''Gheneo, Genni'' and ''Ghinea''), the great interior commercial city on the Upper
A competing theory, first forwarded by Leo Africanus in 1526, claims that 'Guinea' is derived from Djenné (which he refers to as ''Gheneo, Genni'' and ''Ghinea''), the great interior commercial city on the Upper Niger River
The Niger River ( ; ) is the main river of West Africa, extending about . Its drainage basin is in area. Its source is in the Guinea Highlands in south-eastern Guinea near the Sierra Leone border. It runs in a crescent shape through Mal ...
. Djenné dominated the gold and salt trade across West Africa, from the 11th century (fall of Ghana
Ghana (; tw, Gaana, ee, Gana), officially the Republic of Ghana, is a country in West Africa. It abuts the Gulf of Guinea and the Atlantic Ocean to the south, sharing borders with Ivory Coast in the west, Burkina Faso in the north, and Tog ...
) until the 13th century (when the Mali
Mali (; ), officially the Republic of Mali,, , ff, 𞤈𞤫𞤲𞥆𞤣𞤢𞥄𞤲𞤣𞤭 𞤃𞤢𞥄𞤤𞤭, Renndaandi Maali, italics=no, ar, جمهورية مالي, Jumhūriyyāt Mālī is a landlocked country in West Africa. Ma ...
invasion disrupted its routes and redirected trade to Timbuktu, hitherto just a small Djenné outpost). It is during the period of Djenné dominance that the term ''Genewah'' really comes forward into usage in Arab sources (''al-Sudan'' – Arabic for "blacks" – is used more commonly before).W. D. Cooley
William Desborough Cooley (c. 1795 – 1883) was an Irish geographer. Discoveries by European explorers gradually showed that a number of his theories about Central Africa, though strongly held, were incorrect. In other controversies his positio ...
(1841) ''The Negroland of the Arabs examined and explained''p.20
Other theories try to connect "Guinea" to "Ghana", but this is less certain. The
Ghana Empire
The Ghana Empire, also known as Wagadou ( ar, غانا) or Awkar, was a West African empire based in the modern-day southeast of Mauritania and western Mali that existed from c. 300 until 1100. The Empire was founded by the Soninke people, a ...
is named after the Medieval trading city of '' Ghanah'' mentioned already by 11th-century Arab geographers (e.g. al-Bakri
Abū ʿUbayd ʿAbd Allāh ibn ʿAbd al-ʿAzīz ibn Muḥammad ibn Ayyūb ibn ʿAmr al-Bakrī ( ar, أبو عبيد عبد الله بن عبد العزيز بن محمد بن أيوب بن عمرو البكري), or simply al-Bakrī (c. 1040–1 ...
), but it is used distinctly from ''Genewah'' by Arab sources (e.g. they would say "Ghanah in the country of Genewah"). Conversely, it remains possible that both Ghana and Djenné themselves owe their original city names to the Berber appellation for the blacks that lived there. A possible reconciliation of the theories is that the Berber ''Ghinawen'' (blacks) was the source of the ''Djenné'' (city), which in turn gave rise to the Arabic ''Genewah'' (land dominated by that city), which finally made it into the Portuguese ''Guiné''.Cooley (1841) endorses the theory (p.18n) that Djenné, rather than blacks, was the source of the Arabic term Genewah (and thus Portuguese Guiné), but at the same time (p.20n) recognizes that Djenné itself might originally come from the Berber Ghinawen (blacks).
History
In 1478 (during the War of the Castilian Succession), a Castilian armada of thirty-five caravels and a Portuguese fleet fought thebattle of Guinea
The Battle of Guinea took place on the Gulf of Guinea, in western Africa, 1478, between a Portuguese fleet and a Castilian fleet in the context of the War of the Castilian Succession.
The outcome of the battle of Guinea was decisive for Portu ...
in the waters off Elmina
Elmina, also known as Edina by the local Fante, is a town and the capital of the Komenda/Edina/Eguafo/Abirem District on the south coast of Ghana in the Central Region, situated on a bay on the Atlantic Ocean, west of Cape Coast. Elmina wa ...
, for the hegemony of the Guinea trade (gold, ivory and black pepper). The war ended both with a Portuguese naval victory and the official recognition by the Catholic Monarchs of the Portuguese sovereignty over most of the African territories in dispute (Treaty of Alcáçovas
The Treaty of Alcáçovas (also known as Treaty or Peace of Alcáçovas-Toledo) was signed on 4 September 1479 between the Catholic Monarchs of Castile and Aragon on one side and Afonso V and his son, Prince John of Portugal, on the other side ...
, 1479).Historian Malyn Newitt: ''“However, in 1478 the Portuguese surprised thirty-five Castilian ships returning from Mina ''Eustache de la Fosse
Tassin or Eustache de la Fosse (also spelled Delafosse) (ca. 1451 - 23 April 1523) was a Flemish-speaking sailor and merchant from Tournai, who traveled with Portuguese sailors from Palos to territories of West Africa (1479–80) in what are now ...
, was intercepted ... in 1480. (...) All things considered, it is not surprising that the Portuguese emerged victorious from this first maritime colonial war. They were far better organised than the Castilians, were able to raise money for the preparation and supply of their fleets, and had clear central direction from ... ''''A history of Portuguese overseas expansion, 1400-1668''
Routledge, New York, 2005, p.39,40.
''Foundations of the Portuguese empire 1415-1580''
volume I, University of Minnesota Press, 1985, p.152. This was the first of many colonial wars among European powers. After the Portuguese and Castilians came the Dutch, French, and British. The extensive trade in ivory,
gold
Gold is a chemical element with the symbol Au (from la, aurum) and atomic number 79. This makes it one of the higher atomic number elements that occur naturally. It is a bright, slightly orange-yellow, dense, soft, malleable, and ductile ...
, and slaves made the region wealthy, with a number of centralized kingdoms developing in the 18th and 19th centuries. These were much smaller than the large states of the wide-open Sahel, but they had far higher population densities and were more centralized politically. The cohesion of these kingdoms caused the region to show more resistance to European incursions than other areas of Africa. Such resistance, combined with a disease
A disease is a particular abnormal condition that negatively affects the structure or function of all or part of an organism, and that is not immediately due to any external injury. Diseases are often known to be medical conditions that a ...
environment hostile to Europeans, meant that much of Guinea was not colonised by Europeans until the very end of the 19th century.
Subdivisions
Guinea is often subdivided into " Lower Guinea" and " Upper Guinea". Lower Guinea is one of the most densely populated regions of Africa, covering southernNigeria
Nigeria ( ), , ig, Naìjíríyà, yo, Nàìjíríà, pcm, Naijá , ff, Naajeeriya, kcg, Naijeriya officially the Federal Republic of Nigeria, is a country in West Africa. It is situated between the Sahel to the north and the Gulf o ...
, Benin
Benin ( , ; french: Bénin , ff, Benen), officially the Republic of Benin (french: République du Bénin), and formerly Dahomey, is a country in West Africa. It is bordered by Togo to the west, Nigeria to the east, Burkina Faso to the nort ...
, Togo
Togo (), officially the Togolese Republic (french: République togolaise), is a country in West Africa. It is bordered by Ghana to the west, Benin to the east and Burkina Faso to the north. It extends south to the Gulf of Guinea, where its c ...
and stretching into Ghana
Ghana (; tw, Gaana, ee, Gana), officially the Republic of Ghana, is a country in West Africa. It abuts the Gulf of Guinea and the Atlantic Ocean to the south, sharing borders with Ivory Coast in the west, Burkina Faso in the north, and Tog ...
. It includes the coastal regions as well as the interior. Upper Guinea is far less densely populated and stretches from Côte d'Ivoire to Senegal
Senegal,; Wolof: ''Senegaal''; Pulaar: 𞤅𞤫𞤲𞤫𞤺𞤢𞥄𞤤𞤭 (Senegaali); Arabic: السنغال ''As-Sinighal'') officially the Republic of Senegal,; Wolof: ''Réewum Senegaal''; Pulaar : 𞤈𞤫𞤲𞤣𞤢𞥄𞤲𞤣𞤭 ...
.
Within the Republic of Guinea, Lower Guinea refers to the country's coastal plain, while Upper Guinea refers to the country's interior.
European traders in the region subdivided the region based on its main exports. The eastern portion around Benin and Nigeria was named the Slave Coast. What is now Ghana was called the (British) Gold Coast, a name later given to a British colony in the area which ultimately absorbed earlier European colonies. West of this was the Ivory Coast, still the name of the nation in that region. Farthest west, the area around modern Liberia and Sierra Leone
Sierra Leone,)]. officially the Republic of Sierra Leone, is a country on the southwest coast of West Africa. It is bordered by Liberia to the southeast and Guinea surrounds the northern half of the nation. Covering a total area of , Sierr ...
was referred to as either the Pepper Coast or the Grain Coast.
Countries in the Guinea region

 From north to south:
*
From north to south:
* Senegal
Senegal,; Wolof: ''Senegaal''; Pulaar: 𞤅𞤫𞤲𞤫𞤺𞤢𞥄𞤤𞤭 (Senegaali); Arabic: السنغال ''As-Sinighal'') officially the Republic of Senegal,; Wolof: ''Réewum Senegaal''; Pulaar : 𞤈𞤫𞤲𞤣𞤢𞥄𞤲𞤣𞤭 ...
(formerly French)
* The Gambia
The Gambia,, ff, Gammbi, ar, غامبيا officially the Republic of The Gambia, is a country in West Africa. It is the smallest country within mainland AfricaHoare, Ben. (2002) ''The Kingfisher A-Z Encyclopedia'', Kingfisher Publicatio ...
* Guinea-Bissau
Guinea-Bissau ( ; pt, Guiné-Bissau; ff, italic=no, 𞤘𞤭𞤲𞤫 𞤄𞤭𞤧𞤢𞥄𞤱𞤮, Gine-Bisaawo, script=Adlm; Mandinka: ''Gine-Bisawo''), officially the Republic of Guinea-Bissau ( pt, República da Guiné-Bissau, links=no ) ...
(formerly Portuguese Guinea
Portuguese Guinea ( pt, Guiné), called the Overseas Province of Guinea from 1951 until 1972 and then State of Guinea from 1972 until 1974, was a West African colony of Portugal from 1588 until 10 September 1974, when it gained independence as G ...
)
* Guinea (formerly French Guinea)
* Sierra Leone
Sierra Leone,)]. officially the Republic of Sierra Leone, is a country on the southwest coast of West Africa. It is bordered by Liberia to the southeast and Guinea surrounds the northern half of the nation. Covering a total area of , Sierr ...
(British part of the Pepper Coast, originally Province of Freedom)
* Liberia (from U.S. settlements for ex-slaves on the Pepper Coast)
* Ivory Coast or Côte d'Ivoire
* Ghana
Ghana (; tw, Gaana, ee, Gana), officially the Republic of Ghana, is a country in West Africa. It abuts the Gulf of Guinea and the Atlantic Ocean to the south, sharing borders with Ivory Coast in the west, Burkina Faso in the north, and Tog ...
(formerly the Gold Coast; Danish Guinea, Dutch Guinea, Portuguese Gold Coast
The Portuguese Gold Coast was a Portuguese colony on the West African Gold Coast (present-day Ghana) along the Gulf of Guinea. Established in 1482, the colony was officially incorporated into Dutch territory in 1642 following Portugal’s def ...
(the first), Prussian Gold Coast
The Brandenburger Gold Coast, later Prussian Gold Coast, was a part of the Gold Coast. The Brandenburg colony existed from 1682 to 1721, when King Frederick William I of Prussia sold it for 7200 ducats to the Dutch Republic.
Brandenburger Go ...
and Swedish Guinea all ended up absorbed by the British Gold Coast)
* Togo
Togo (), officially the Togolese Republic (french: République togolaise), is a country in West Africa. It is bordered by Ghana to the west, Benin to the east and Burkina Faso to the north. It extends south to the Gulf of Guinea, where its c ...
(formerly Togoland
Togoland was a German Empire protectorate in West Africa from 1884 to 1914, encompassing what is now the nation of Togo and most of what is now the Volta Region of Ghana, approximately 90,400 km2 (29,867 sq mi) in size. During the period ...
)
* Benin
Benin ( , ; french: Bénin , ff, Benen), officially the Republic of Benin (french: République du Bénin), and formerly Dahomey, is a country in West Africa. It is bordered by Togo to the west, Nigeria to the east, Burkina Faso to the nort ...
( Dahomey)
* Southern Nigeria
Nigeria ( ), , ig, Naìjíríyà, yo, Nàìjíríà, pcm, Naijá , ff, Naajeeriya, kcg, Naijeriya officially the Federal Republic of Nigeria, is a country in West Africa. It is situated between the Sahel to the north and the Gulf o ...
* Western Cameroon
Cameroon (; french: Cameroun, ff, Kamerun), officially the Republic of Cameroon (french: République du Cameroun, links=no), is a country in west-central Africa. It is bordered by Nigeria to the west and north; Chad to the northeast; the ...
(formerly Kamerun)
* Equatorial Guinea (formerly Spanish Guinea
Spanish Guinea (Spanish: ''Guinea Española'') was a set of insular and continental territories controlled by Spain from 1778 in the Gulf of Guinea and on the Bight of Bonny, in Central Africa. It gained independence in 1968 as Equatorial ...
)
See also
* Lower Guinean forests *Upper Guinean forests
The Upper Guinean forests is a tropical seasonal forest region of West Africa. The Upper Guinean forests extend from Guinea and Sierra Leone in the west through Liberia, Côte d'Ivoire and Ghana to Togo in the east, and a few hundred kilometers in ...
* West Africa
West Africa or Western Africa is the westernmost region of Africa. The United Nations defines Western Africa as the 16 countries of Benin, Burkina Faso, Cape Verde, The Gambia, Ghana, Guinea, Guinea-Bissau, Ivory Coast, Liberia, Mali ...
* New Guinea
New Guinea (; Hiri Motu: ''Niu Gini''; id, Papua, or , historically ) is the world's second-largest island with an area of . Located in Oceania in the southwestern Pacific Ocean, the island is separated from Australia by the wide Torres ...
*Guineaman
Slave ships were large cargo ships specially built or converted from the 17th to the 19th century for transporting slaves. Such ships were also known as "Guineamen" because the trade involved human trafficking to and from the Guinea coast i ...
, a ship used to transport slaves from the region of Guinea
Notes
References
Books * DIFFIE, Bailey W. and WINIUS, George D.''Foundations of the Portuguese Empire, 1415-1580''
Volume 1, University of Minnesota Press, 1977. * NEWITT, Malyn
''A history of Portuguese overseas expansion, 1400-1668''
Routledge, New York, 2005. {{Regions of Africa Regions of Africa Divided regions