Greater tubercle on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
The greater tubercle of the humerus is the outward part the upper end of that bone, adjacent to the large rounded prominence of the humerus head. It provides attachment points for the
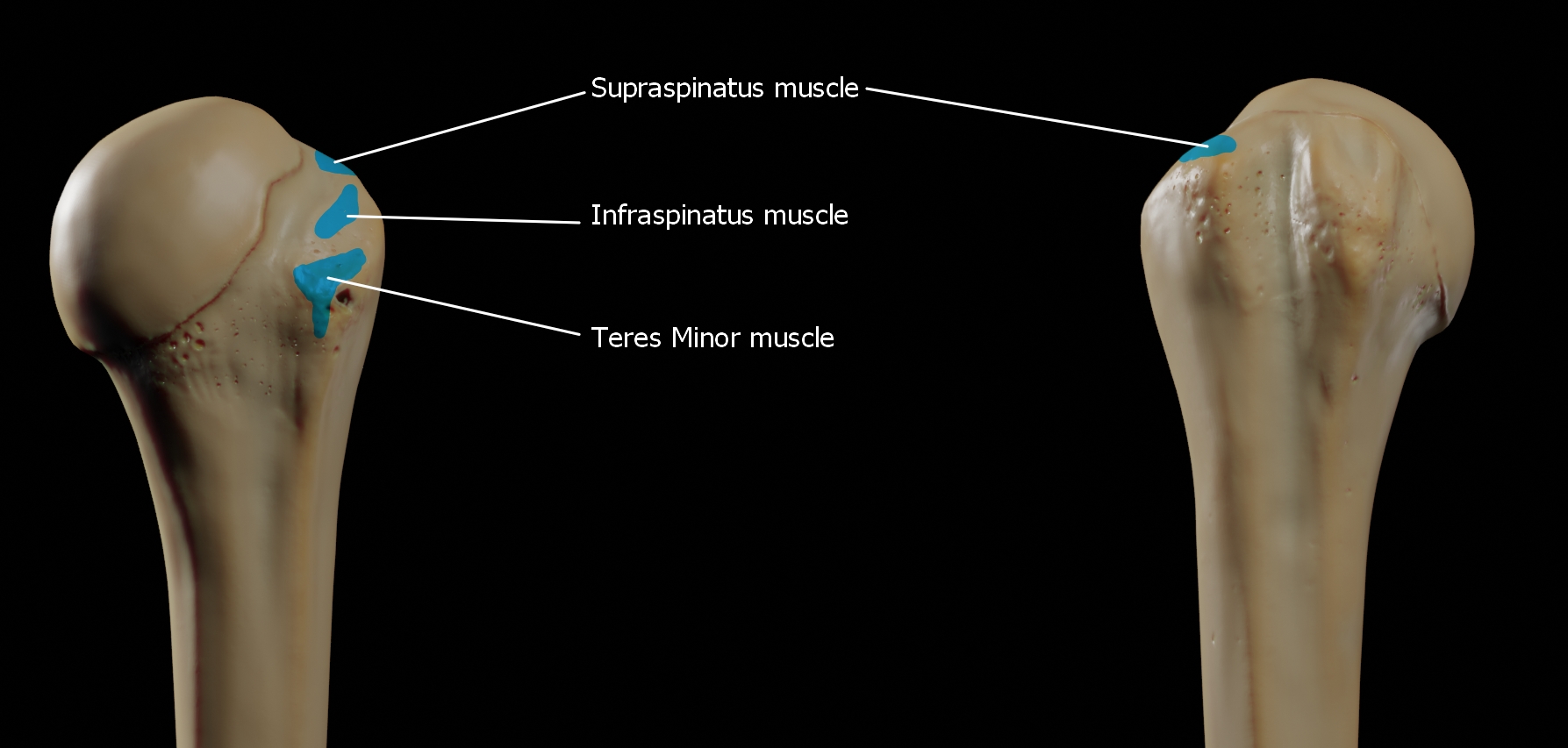 The upper surface of the greater tubercle is rounded, and marked by three flat impressions:
* the highest ("superior facet") gives insertion to the
The upper surface of the greater tubercle is rounded, and marked by three flat impressions:
* the highest ("superior facet") gives insertion to the 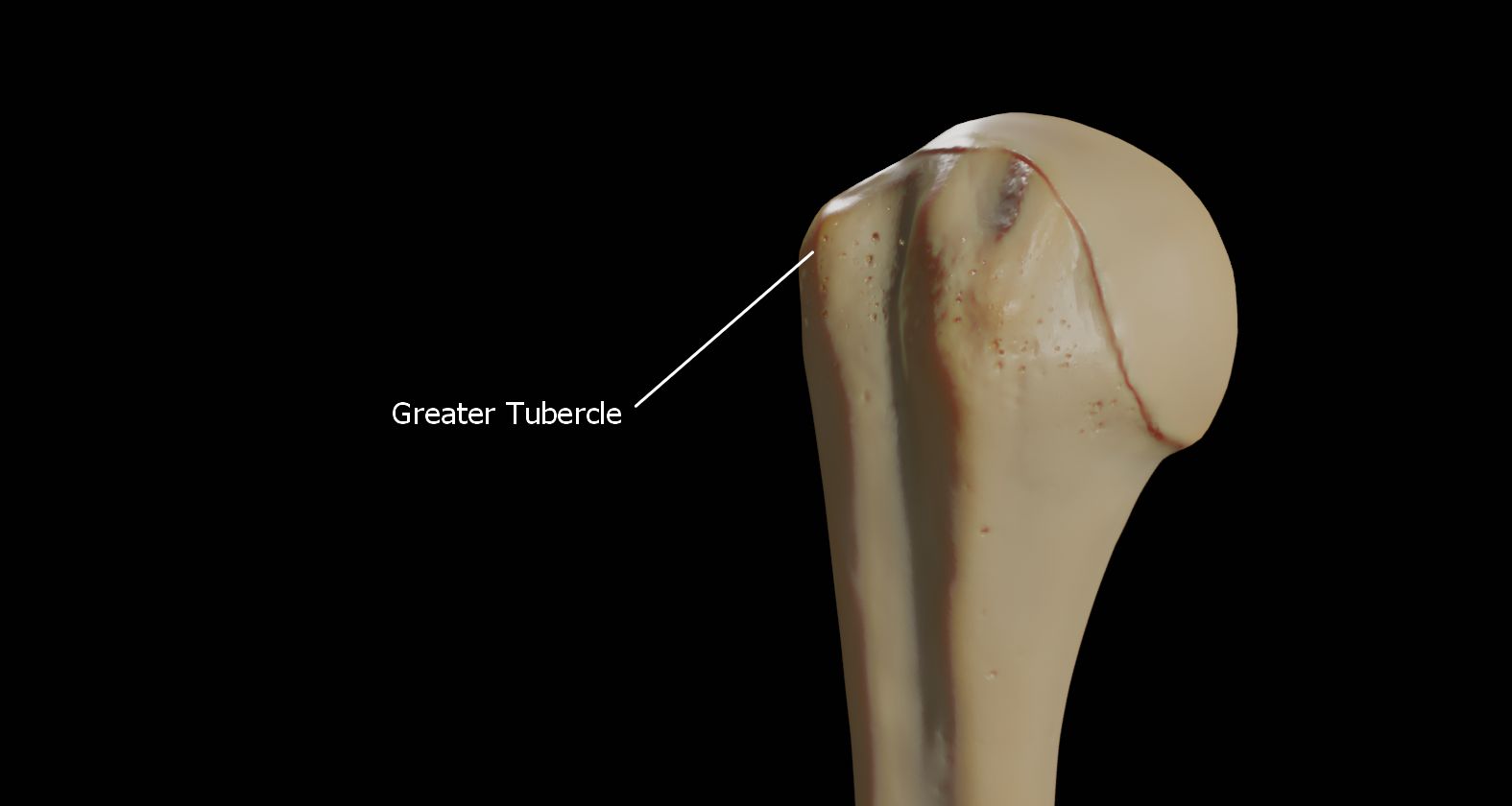
File:Human arm bones diagram.svg, Human arm bones diagram
supraspinatus
The supraspinatus (plural ''supraspinati'') is a relatively small muscle of the upper back that runs from the supraspinous fossa superior portion of the scapula (shoulder blade) to the greater tubercle of the humerus. It is one of the four rotat ...
, infraspinatus
In human anatomy, the infraspinatus muscle is a thick triangular muscle, which occupies the chief part of the infraspinatous fossa.''Gray's Anatomy'', see infobox. As one of the four muscles of the rotator cuff, the main function of the infraspin ...
, and teres minor
The teres minor (Latin ''teres'' meaning 'rounded') is a narrow, elongated muscle of the rotator cuff. The muscle originates from the lateral border and adjacent posterior surface of the corresponding right or left scapula and inserts at both the ...
muscles, three of the four muscles of the rotator cuff
The rotator cuff is a group of muscles and their tendons that act to stabilize the human shoulder and allow for its extensive range of motion. Of the seven scapulohumeral muscles, four make up the rotator cuff. The four muscles are the supraspi ...
, a muscle group that stabilizes the shoulder joint
The shoulder joint (or glenohumeral joint from Greek ''glene'', eyeball, + -''oid'', 'form of', + Latin ''humerus'', shoulder) is structurally classified as a synovial ball-and-socket joint and functionally as a diarthrosis and multiaxial joint ...
. In doing so the tubercle acts as a location for the transfer of forces from the rotator cuff muscles to the humerus.
Structure
 The upper surface of the greater tubercle is rounded, and marked by three flat impressions:
* the highest ("superior facet") gives insertion to the
The upper surface of the greater tubercle is rounded, and marked by three flat impressions:
* the highest ("superior facet") gives insertion to the supraspinatus muscle
The supraspinatus (plural ''supraspinati'') is a relatively small muscle of the upper back that runs from the supraspinous fossa superior portion of the scapula (shoulder blade) to the greater tubercle of the humerus. It is one of the four rota ...
.
* the middle ("middle facet") gives insertion to the infraspinatus muscle
In human anatomy, the infraspinatus muscle is a thick triangular muscle, which occupies the chief part of the infraspinatous fossa.''Gray's Anatomy'', see infobox. As one of the four muscles of the rotator cuff, the main function of the infraspin ...
.
* the lowest ("inferior facet"), and the body of the bone for about 2.5 cm, gives insertion to the teres minor muscle
The teres minor (Latin ''teres'' meaning 'rounded') is a narrow, elongated muscle of the rotator cuff. The muscle originates from the lateral border and adjacent posterior surface of the corresponding right or left scapula and inserts at both the ...
.
The lateral surface of the greater tubercle is convex, rough, and continuous with the lateral surface of the body of the humerus. It can be described as having a cranial and a caudal part.
Between the greater tubercle and the lesser tubercle is the bicipital groove (intertubercular sulcus).

Function
All three of the muscles that attach to the greater tubercle are part of therotator cuff
The rotator cuff is a group of muscles and their tendons that act to stabilize the human shoulder and allow for its extensive range of motion. Of the seven scapulohumeral muscles, four make up the rotator cuff. The four muscles are the supraspi ...
, a muscle group that stabilizes the shoulder joint
The shoulder joint (or glenohumeral joint from Greek ''glene'', eyeball, + -''oid'', 'form of', + Latin ''humerus'', shoulder) is structurally classified as a synovial ball-and-socket joint and functionally as a diarthrosis and multiaxial joint ...
. The greater tubercle therefore acts as a location for the transfer of forces from the rotator cuff muscles to the humerus.
The fourth muscle of the rotator cuff (subscapularis muscle
The subscapularis is a large triangular muscle which fills the subscapular fossa and inserts into the lesser tubercle of the humerus and the front of the capsule of the shoulder-joint.
Structure
It arises from its medial two-thirds and
So ...
) does not attach to the greater tubercle, but instead attaches to the lesser tubercle.
Clinical significance
The greater tubercle is usually the easiest part of the humerus topalpate
Palpation is the process of using one's hands to check the body, especially while perceiving/diagnosing a disease or illness. Usually performed by a health care practitioner, it is the process of feeling an object in or on the body to determine ...
. It can be a useful surface landmark during surgery.
Additional images
References
External links
* * * * {{Authority control Bones of the upper limb Humerus