Great conjunction on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 A great conjunction is a
A great conjunction is a
 On average, great conjunction seasons occur once every 19.859 Julian years (each of which is 365.25 days). This number can be calculated by the
On average, great conjunction seasons occur once every 19.859 Julian years (each of which is 365.25 days). This number can be calculated by the
 When studying the great conjunction of 1603, Johannes Kepler thought that the
When studying the great conjunction of 1603, Johannes Kepler thought that the
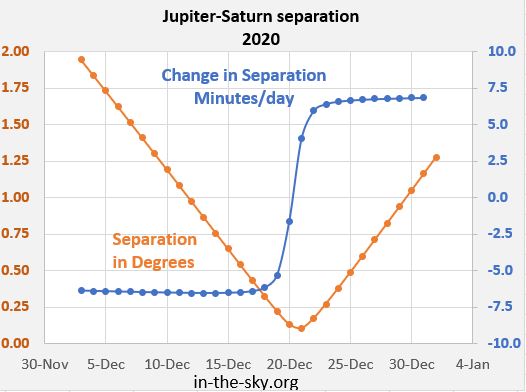 The great conjunction of 2020 was the closest since 1623 and eighth closest of the first three millennia AD, with a minimum separation between the two planets of 6.1 arcminutes. This great conjunction was also the most easily visible close conjunction since 1226 (as the previous close conjunctions in 1563 and 1623 were closer to the Sun and therefore more difficult to see). It occurred seven weeks after the heliocentric conjunction, when Jupiter and Saturn shared the same heliocentric longitude.
The closest separation occurred on 21 December at 18:20 UTC, when Jupiter was 0.1° south of Saturn and 30° east of the Sun. This meant both planets appeared together in the field of view of most small- and medium-sized telescopes (though they were distinguishable from each other without optical aid). During the closest approach, both planets appeared to be a binary object to the naked eye. From mid-northern latitudes, the planets were visible one hour after sunset at less than 15° in altitude above the southwestern horizon in the constellation of
The great conjunction of 2020 was the closest since 1623 and eighth closest of the first three millennia AD, with a minimum separation between the two planets of 6.1 arcminutes. This great conjunction was also the most easily visible close conjunction since 1226 (as the previous close conjunctions in 1563 and 1623 were closer to the Sun and therefore more difficult to see). It occurred seven weeks after the heliocentric conjunction, when Jupiter and Saturn shared the same heliocentric longitude.
The closest separation occurred on 21 December at 18:20 UTC, when Jupiter was 0.1° south of Saturn and 30° east of the Sun. This meant both planets appeared together in the field of view of most small- and medium-sized telescopes (though they were distinguishable from each other without optical aid). During the closest approach, both planets appeared to be a binary object to the naked eye. From mid-northern latitudes, the planets were visible one hour after sunset at less than 15° in altitude above the southwestern horizon in the constellation of
File:Grosse.Konjunktion.P1080051.jpg, Photograph taken two days before closest approach with a separation of approximately 15 arcminutes.
File:Great Conjunction image photographed on December 19, 2020.jpg, Great conjunction photographed on December 19, 2020, with a SCT telescope and color CCD.
File:2020 Great Conjunction simulation by NASA, labeled, 2020-12-21 2215UTC.jpg, Simulated best-case scenario view through a telescope.
File:CodysLab great conjunction clip.gif, Video created using photographs of the event taken over a span of 90 days.
File:Saturn—Jupiter—Conjunction.jpg, Photograph of the great conjunction of 2020 taken two days before closest approach with the four Galilean moons visible around Jupiter. ( Titan can also be seen to the right of Saturn.)
File:KoniunkcjaJS.gif, December 21, 2020, Jupiter and Saturn, 130mm Bresser Messier
File:Grande congiunzione Giove Saturno 22 dicembre 2020ok.jpg, Photograph depicting the great conjunction, taken from Syracuse, Italy.
File:Great conjunction.jpg, Photograph of Jupiter and Saturn with the
Orbital Motion Simulation of Jupiter and Saturn
at GeoGebra
The December 21, 2020 Conjunction of Jupiter and Saturn
The exceptional conjunction of Jupiter and Saturn on December 21, 2020!
Great Conjunctions
{{DEFAULTSORT:Great Conjunction Astrometry Astrological aspects Conjunctions (astronomy and astrology) Jupiter Saturn
 A great conjunction is a
A great conjunction is a conjunction
Conjunction may refer to:
* Conjunction (grammar), a part of speech
* Logical conjunction, a mathematical operator
** Conjunction introduction, a rule of inference of propositional logic
* Conjunction (astronomy), in which two astronomical bodies ...
of the planets Jupiter
Jupiter is the fifth planet from the Sun and the largest in the Solar System. It is a gas giant with a mass more than two and a half times that of all the other planets in the Solar System combined, but slightly less than one-thousandth t ...
and Saturn, when the two planets appear closest together in the sky. Great conjunctions occur approximately every 20 years when Jupiter "overtakes" Saturn in its orbit
In celestial mechanics, an orbit is the curved trajectory of an object such as the trajectory of a planet around a star, or of a natural satellite around a planet, or of an artificial satellite around an object or position in space such as ...
. They are named "great" for being by far the rarest of the conjunctions between naked-eye planets (i.e. excluding Uranus
Uranus is the seventh planet from the Sun. Its name is a reference to the Greek god of the sky, Uranus ( Caelus), who, according to Greek mythology, was the great-grandfather of Ares (Mars), grandfather of Zeus (Jupiter) and father of ...
and Neptune).
The spacing between the planets varies from conjunction to conjunction with most events being 0.5 to 1.3 degrees (30 to 78 arcminute
A minute of arc, arcminute (arcmin), arc minute, or minute arc, denoted by the symbol , is a unit of angular measurement equal to of one degree. Since one degree is of a turn (or complete rotation), one minute of arc is of a turn. The n ...
s, or 1 to 2.5 times the width of a full moon
The full moon is the lunar phase when the Moon appears fully illuminated from Earth's perspective. This occurs when Earth is located between the Sun and the Moon (when the ecliptic longitudes of the Sun and Moon differ by 180°). This means ...
). Very close conjunctions happen much less frequently (though the maximum of 1.3° is still close by inner planet
The Solar SystemCapitalization of the name varies. The International Astronomical Union, the authoritative body regarding astronomical nomenclature, specifies capitalizing the names of all individual astronomical objects but uses mixed "Solar S ...
standards): separations of less than 10 arcminutes have only happened four times since 1200, most recently in 2020.
In history
Great conjunctions attracted considerable attention in the past as omens. During the lateMiddle Ages
In the history of Europe, the Middle Ages or medieval period lasted approximately from the late 5th to the late 15th centuries, similar to the post-classical period of global history. It began with the fall of the Western Roman Empire ...
and Renaissance
The Renaissance ( , ) , from , with the same meanings. is a period in European history
The history of Europe is traditionally divided into four time periods: prehistoric Europe (prior to about 800 BC), classical antiquity (800 BC to AD ...
they were a topic broached by the pre-scientific and transitional astronomer-astrologers of the period up to the time of Tycho Brahe
Tycho Brahe ( ; born Tyge Ottesen Brahe; generally called Tycho (14 December 154624 October 1601) was a Danish astronomer, known for his comprehensive astronomical observations, generally considered to be the most accurate of his time. He was ...
and Johannes Kepler, by scholastic thinkers such as Roger Bacon and Pierre d'Ailly
Pierre d'Ailly (; Latin ''Petrus Aliacensis'', ''Petrus de Alliaco''; 13519 August 1420) was a French theologian, astrologer and cardinal of the Roman Catholic Church.
Academic career
D'Ailly was born in Compiègne in 1350 or 1351 of a prospero ...
, and they are mentioned in popular and literary works by authors such as Dante
Dante Alighieri (; – 14 September 1321), probably baptized Durante di Alighiero degli Alighieri and often referred to as Dante (, ), was an Italian people, Italian Italian poetry, poet, writer and philosopher. His ''Divine Comedy'', origin ...
Lope de Vega and Shakespeare
William Shakespeare ( 26 April 1564 – 23 April 1616) was an English playwright, poet and actor. He is widely regarded as the greatest writer in the English language and the world's pre-eminent dramatist. He is often called England's natio ...
. This interest is traced back in Europe to translations of Arabic texts especially Albumasar
Abu Ma'shar al-Balkhi, Latinized as Albumasar (also ''Albusar'', ''Albuxar''; full name ''Abū Maʿshar Jaʿfar ibn Muḥammad ibn ʿUmar al-Balkhī'' ;
, AH 171–272), was an early Persian Muslim astrologer, thought to be the greatest as ...
's book on conjunctions.
Despite mathematical errors and some disagreement among astrologers about when trigons began, belief in the significance of such events generated a stream of publications that grew steadily until the end of the 16th century. As the great conjunction of 1583 was last in the water trigon it was widely supposed to herald apocalyptic changes; a papal bull against divination was issued in 1586 but as nothing significant happened by the feared event of 1603, public interest rapidly died. By the start of the next trigon, modern scientific consensus had long-established astrology
Astrology is a range of divinatory practices, recognized as pseudoscientific since the 18th century, that claim to discern information about human affairs and terrestrial events by studying the apparent positions of celestial objects. Di ...
as pseudoscience, and planetary alignments were no longer perceived as omens.Keith Thomas, ''Religion and the Decline of Magic: Studies in Popular Beliefs in Sixteenth and Seventeenth-Century England'' (Oxford University Press
Oxford University Press (OUP) is the university press of the University of Oxford. It is the largest university press in the world, and its printing history dates back to the 1480s. Having been officially granted the legal right to print books ...
, 1971) p. 414-415,
Celestial mechanics
 On average, great conjunction seasons occur once every 19.859 Julian years (each of which is 365.25 days). This number can be calculated by the
On average, great conjunction seasons occur once every 19.859 Julian years (each of which is 365.25 days). This number can be calculated by the synodic period
The orbital period (also revolution period) is the amount of time a given astronomical object takes to complete one orbit around another object. In astronomy, it usually applies to planets or asteroids orbiting the Sun, moons orbiting planets, ...
formula
:
in which and are the orbital period
The orbital period (also revolution period) is the amount of time a given astronomical object takes to complete one orbit around another object. In astronomy, it usually applies to planets or asteroids orbiting the Sun, moons orbiting planets ...
s of Jupiter (4332.59 days) and Saturn (10759.22 days), respectively. This is about 52 days less than 20 years, but in practice, Earth's orbit size can cause great conjunctions to reoccur anytime between 18 years 10 months and 20 years 8 months after the previous one. (See table below.) Since the equivalent periods of other naked-eye planet pairs are all under 900 days, this makes great conjunctions the rarest.
Occasionally there is more than one great conjunction in a season, which happens whenever they're close enough to opposition
Opposition may refer to:
Arts and media
* ''Opposition'' (Altars EP), 2011 EP by Christian metalcore band Altars
* The Opposition (band), a London post-punk band
* '' The Opposition with Jordan Klepper'', a late-night television series on Com ...
: this is called a triple conjunction
A triple conjunction is an astronomical event when two planets or a planet and a star appear to meet each other three times during a brief period, either in opposition or at the time of inferior conjunction, if an inferior planet is involved. Th ...
(which is not exclusive to great conjunctions). In this scenario, Jupiter and Saturn will occupy the same right ascension on three occasions or same ecliptic longitude
The ecliptic coordinate system is a celestial coordinate system commonly used for representing the apparent positions, orbits, and pole orientations of Solar System objects. Because most planets (except Mercury) and many small Solar System b ...
on three occasions, depending on which definition of "conjunction" one uses (this is due to apparent retrograde motion and happens within months). The most recent triple conjunction occurred in 1980–81 and the next will be in 2238–39.
The most recent great conjunction occurred on 21 December 2020, and the next will occur on 4 November 2040. During the 2020 great conjunction, the two planets were separated in the sky by 6 arcminutes at their closest point, which was the closest distance between the two planets since 1623. The closeness is the result of the conjunction occurring in the vicinity of one of the two longitudes
Longitude (, ) is a geographic coordinate that specifies the east–west position of a point on the surface of the Earth, or another celestial body. It is an angular measurement, usually expressed in degrees and denoted by the Greek letter ...
where the two orbits appear to intersect when viewed from the Sun (which has a point of view similar to Earth).
Because 19.859 years is equal to 1.674 Jupiter orbits and 0.674 Saturn orbits, three of these periods come close to a whole number of revolutions. This is why the longitude cycle, as shown in the diagram to the right, has a triangular pattern. The three points of the triangle revolve in the same direction as the planets at the rate of approximately one-sixth of a revolution per four centuries thus creating especially close conjunctions on an approximately four-century cycle. Currently the longitudes of close great conjunctions are about 307.4 and 127.4 degrees, in the constellations Capricornus
Capricornus is one of the constellations of the zodiac. Its name is Latin for "horned goat" or "goat horn" or "having horns like a goat's", and it is commonly represented in the form of a sea goat: a mythical creature that is half goat, half f ...
and Cancer
Cancer is a group of diseases involving abnormal cell growth with the potential to invade or spread to other parts of the body. These contrast with benign tumors, which do not spread. Possible signs and symptoms include a lump, abnormal b ...
respectively. The position of Earth in its orbit, however, can make the planets appear up to about 10 degrees ahead of or behind their heliocentric longitude.
Saturn's orbit plane is inclined 2.485 degrees relative to Earth's, and Jupiter's is inclined 1.303 degrees. The ascending node
An orbital node is either of the two points where an orbit intersects a plane of reference to which it is inclined. A non-inclined orbit, which is contained in the reference plane, has no nodes.
Planes of reference
Common planes of refere ...
s of both planets are similar (100.6 degrees for Jupiter and 113.7 degrees for Saturn), meaning if Saturn is above or below Earth's orbital plane Jupiter usually is too. Because these nodes align so well it would be expected that no closest approach will ever be much worse than the difference between the two inclinations. Indeed, between year 1 and 3000, the maximum conjunction distances were 1.3 degrees in 1306 and 1940. Conjunctions in both years occurred when the planets were tilted most out of the plane: longitude 206 degrees (therefore above the plane) in 1306, and longitude 39 degrees (therefore below the plane) in 1940.
List of great conjunctions (1200 to 2400)
The following table details great conjunctions in between 1200 and 2400. The dates are given for the conjunctions in right ascension (the dates for conjunctions in ecliptic longitude can differ by several days). Dates before 1582 are in theJulian calendar
The Julian calendar, proposed by Roman consul Julius Caesar in 46 BC, was a reform of the Roman calendar. It took effect on , by edict. It was designed with the aid of Greek mathematicians and astronomers such as Sosigenes of Alexandr ...
while dates after 1582 are in the Gregorian calendar
The Gregorian calendar is the calendar used in most parts of the world. It was introduced in October 1582 by Pope Gregory XIII as a modification of, and replacement for, the Julian calendar. The principal change was to space leap years dif ...
.
Longitude
Longitude (, ) is a geographic coordinate that specifies the east– west position of a point on the surface of the Earth, or another celestial body. It is an angular measurement, usually expressed in degrees and denoted by the Greek lette ...
is measured counterclockwise from the location of the First Point of Aries (the location of the March equinox) at epoch J2000
In astronomy, an epoch or reference epoch is a moment in time used as a reference point for some time-varying astronomical quantity. It is useful for the celestial coordinates or orbital elements of a celestial body, as they are subject to ...
. This non-rotating coordinate system doesn't move with the precession of Earth's axes, thus being suited for calculations of the locations of stars. (In astrometry latitude and longitude are based on the ecliptic which is Earth's orbit extended sunward and anti-sunward indefinitely.) The other common conjunction coordinate system is measured counterclockwise in right ascension from the First Point of Aries and is based on Earth's equator and the meridian of the equinox point both extended upwards indefinitely; ecliptic separations are usually smaller.
Distance is the angular separation between the planets in sixtieths of a degree (minutes of arc
A minute of arc, arcminute (arcmin), arc minute, or minute arc, denoted by the symbol , is a unit of angular measurement equal to of one degree. Since one degree is of a turn (or complete rotation), one minute of arc is of a turn. The n ...
) and elongation is the angular distance
Angular distance \theta (also known as angular separation, apparent distance, or apparent separation) is the angle between the two sightlines, or between two point objects as viewed from an observer.
Angular distance appears in mathematics (in par ...
from the Sun in degrees. An elongation between around −20 and +20 degrees indicates that the Sun is close enough to the conjunction to make it difficult or impossible to see, sometimes more difficult at some geographic latitude
In geography, latitude is a coordinate that specifies the north– south position of a point on the surface of the Earth or another celestial body. Latitude is given as an angle that ranges from –90° at the south pole to 90° at the north pol ...
s and less difficult elsewhere. Note that the exact moment of conjunction cannot be seen everywhere as it is below the horizon or it is daytime in some places, but a place on Earth affects minimum separation less than it would if an inner planet
The Solar SystemCapitalization of the name varies. The International Astronomical Union, the authoritative body regarding astronomical nomenclature, specifies capitalizing the names of all individual astronomical objects but uses mixed "Solar S ...
was involved. Negative elongations indicate the planet is west of the Sun (visible in the morning sky), whereas positive elongations indicate the planet is east of the Sun (visible in the evening sky).
The great conjunction series is roughly analogous to the Saros series for solar eclipses (which are Sun–Moon conjunctions). Conjunctions in a particular series occur about 119.16 years apart. The reason it is every six conjunctions instead of every three is that 119.16 years is closer to a whole number of years than = 59.58 is, so Earth will be closer to the same position in its orbit and conjunctions will appear more similar. All series will have progressions where conjunctions gradually shift from only visible before sunrise to visible throughout the night to only visible after sunset and finally back to the morning sky again. The location in the sky of each conjunction in a series should increase in longitude by 16.3 degrees on average, making one full cycle relative to the stars on average once every 2,634 years. If instead we use the convention of measuring longitude eastward from the First Point of Aries, we have to keep in mind that the equinox circulates once every c. 25,772 years, so longitudes measured that way increase slightly faster and those numbers become 17.95 degrees and 2,390 years.
A conjunction can be a member of a triple conjunction
A triple conjunction is an astronomical event when two planets or a planet and a star appear to meet each other three times during a brief period, either in opposition or at the time of inferior conjunction, if an inferior planet is involved. Th ...
. In a triple conjunction, the series does not advance by one each event as the constellation and year is the same or close to it, this is the only time great conjunctions can be less than about 20 years apart.
Notable great conjunctions
7 BC
 When studying the great conjunction of 1603, Johannes Kepler thought that the
When studying the great conjunction of 1603, Johannes Kepler thought that the Star of Bethlehem
The Star of Bethlehem, or Christmas Star, appears in the nativity story of the Gospel of Matthew chapter 2 where "wise men from the East" (Magi) are inspired by the star to travel to Jerusalem. There, they meet King Herod of Judea, and ask hi ...
might have been the occurrence of a great conjunction. He calculated that a triple conjunction of Jupiter and Saturn occurred in 7 BC (−6 using astronomical year numbering
Astronomical year numbering is based on AD/ CE year numbering, but follows normal decimal integer numbering more strictly. Thus, it has a year 0; the years before that are designated with negative numbers and the years after that are designated ...
);
1563
The astronomers from the Cracow Academy (Jan Muscenius Jan Muscenius, (Jan Muszczeński alias Jan Mucha, 1532 – 21 July 1602) was a Polish astronomer, theologian, and the rector of Kraków Academy (now Jagiellonian University).
Life
Jan Muscenius was born in Kurzelów, Sandomierz Province, and ...
, Stanisław Jakobejusz, Nicolaus Schadeck, Petrus Probosczowicze, and others) observed the great conjunction of 1563 to compare Alfonsine tables (based on a geocentric model) with the Prutenic Tables
The ''Prutenic Tables'' ( la, Tabulae prutenicae from ''Prutenia'' meaning "Prussia", german: Prutenische oder Preußische Tafeln), were an ephemeris (astronomical tables) by the astronomer Erasmus Reinhold published in 1551 (reprinted in 1562, 1 ...
(based on Copernican heliocentrism
Copernican heliocentrism is the astronomical model developed by Nicolaus Copernicus and published in 1543. This model positioned the Sun at the center of the Universe, motionless, with Earth and the other planets orbiting around it in circular ...
). In the Prutenic Tables
The ''Prutenic Tables'' ( la, Tabulae prutenicae from ''Prutenia'' meaning "Prussia", german: Prutenische oder Preußische Tafeln), were an ephemeris (astronomical tables) by the astronomer Erasmus Reinhold published in 1551 (reprinted in 1562, 1 ...
the astronomers found Jupiter and Saturn so close to each other that Jupiter covered Saturn (actual angular separation was 6.8 minutes on 25 August 1563). The Alfonsine tables suggested that the conjunction should be observed on another day but on the day indicated by the Alfonsine tables the angular separation was a full 141 minutes. The Cracow professors suggested following the more accurate Copernican predictions and between 1578 and 1580 Copernican heliocentrism was lectured on three times by Valentin Fontani.
This conjunction was also observed by Tycho Brahe
Tycho Brahe ( ; born Tyge Ottesen Brahe; generally called Tycho (14 December 154624 October 1601) was a Danish astronomer, known for his comprehensive astronomical observations, generally considered to be the most accurate of his time. He was ...
, who noticed that the Copernican and Ptolemaic tables used to predict the conjunction were inaccurate. This led him to realise that progress in astronomy required systematic, rigorous observation, night after night, using the most accurate instruments obtainable.
2020
 The great conjunction of 2020 was the closest since 1623 and eighth closest of the first three millennia AD, with a minimum separation between the two planets of 6.1 arcminutes. This great conjunction was also the most easily visible close conjunction since 1226 (as the previous close conjunctions in 1563 and 1623 were closer to the Sun and therefore more difficult to see). It occurred seven weeks after the heliocentric conjunction, when Jupiter and Saturn shared the same heliocentric longitude.
The closest separation occurred on 21 December at 18:20 UTC, when Jupiter was 0.1° south of Saturn and 30° east of the Sun. This meant both planets appeared together in the field of view of most small- and medium-sized telescopes (though they were distinguishable from each other without optical aid). During the closest approach, both planets appeared to be a binary object to the naked eye. From mid-northern latitudes, the planets were visible one hour after sunset at less than 15° in altitude above the southwestern horizon in the constellation of
The great conjunction of 2020 was the closest since 1623 and eighth closest of the first three millennia AD, with a minimum separation between the two planets of 6.1 arcminutes. This great conjunction was also the most easily visible close conjunction since 1226 (as the previous close conjunctions in 1563 and 1623 were closer to the Sun and therefore more difficult to see). It occurred seven weeks after the heliocentric conjunction, when Jupiter and Saturn shared the same heliocentric longitude.
The closest separation occurred on 21 December at 18:20 UTC, when Jupiter was 0.1° south of Saturn and 30° east of the Sun. This meant both planets appeared together in the field of view of most small- and medium-sized telescopes (though they were distinguishable from each other without optical aid). During the closest approach, both planets appeared to be a binary object to the naked eye. From mid-northern latitudes, the planets were visible one hour after sunset at less than 15° in altitude above the southwestern horizon in the constellation of Capricornus
Capricornus is one of the constellations of the zodiac. Its name is Latin for "horned goat" or "goat horn" or "having horns like a goat's", and it is commonly represented in the form of a sea goat: a mythical creature that is half goat, half f ...
.
The conjunction attracted considerable media attention, with news sources calling it the "Christmas Star" due to the proximity of the date of the conjunction to Christmas
Christmas is an annual festival commemorating the birth of Jesus Christ, observed primarily on December 25 as a religious and cultural celebration among billions of people around the world. A feast central to the Christian liturgical year ...
, and for a great conjunction being one of the hypothesized explanations for the biblical Star of Bethlehem
The Star of Bethlehem, or Christmas Star, appears in the nativity story of the Gospel of Matthew chapter 2 where "wise men from the East" (Magi) are inspired by the star to travel to Jerusalem. There, they meet King Herod of Judea, and ask hi ...
.
Gallery
Moon
The Moon is Earth's only natural satellite. It is the fifth largest satellite in the Solar System and the largest and most massive relative to its parent planet, with a diameter about one-quarter that of Earth (comparable to the width of ...
on 16 December 2020
7541
As well as being a triple conjunction, the great conjunction of 7541 is expected to feature twooccultation
An occultation is an event that occurs when one object is hidden from the observer by another object that passes between them. The term is often used in astronomy, but can also refer to any situation in which an object in the foreground blocks ...
s: one partial on 16 February, and one total on 17 June. However, the accuracy of planetary positions this far into the future is highly uncertain, so some calculations of planetary positions predict very close conjunctions in 7541 instead of occultations. This will be the first occultation between the two planets since 6857 BC; superimposition requires a separation of less than approximately 0.4 arcminutes.
See also
* Positional astronomyNotes
References
External links
Orbital Motion Simulation of Jupiter and Saturn
at GeoGebra
The December 21, 2020 Conjunction of Jupiter and Saturn
The exceptional conjunction of Jupiter and Saturn on December 21, 2020!
Great Conjunctions
{{DEFAULTSORT:Great Conjunction Astrometry Astrological aspects Conjunctions (astronomy and astrology) Jupiter Saturn