Grand Duchy of Oldenburg State Railways on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
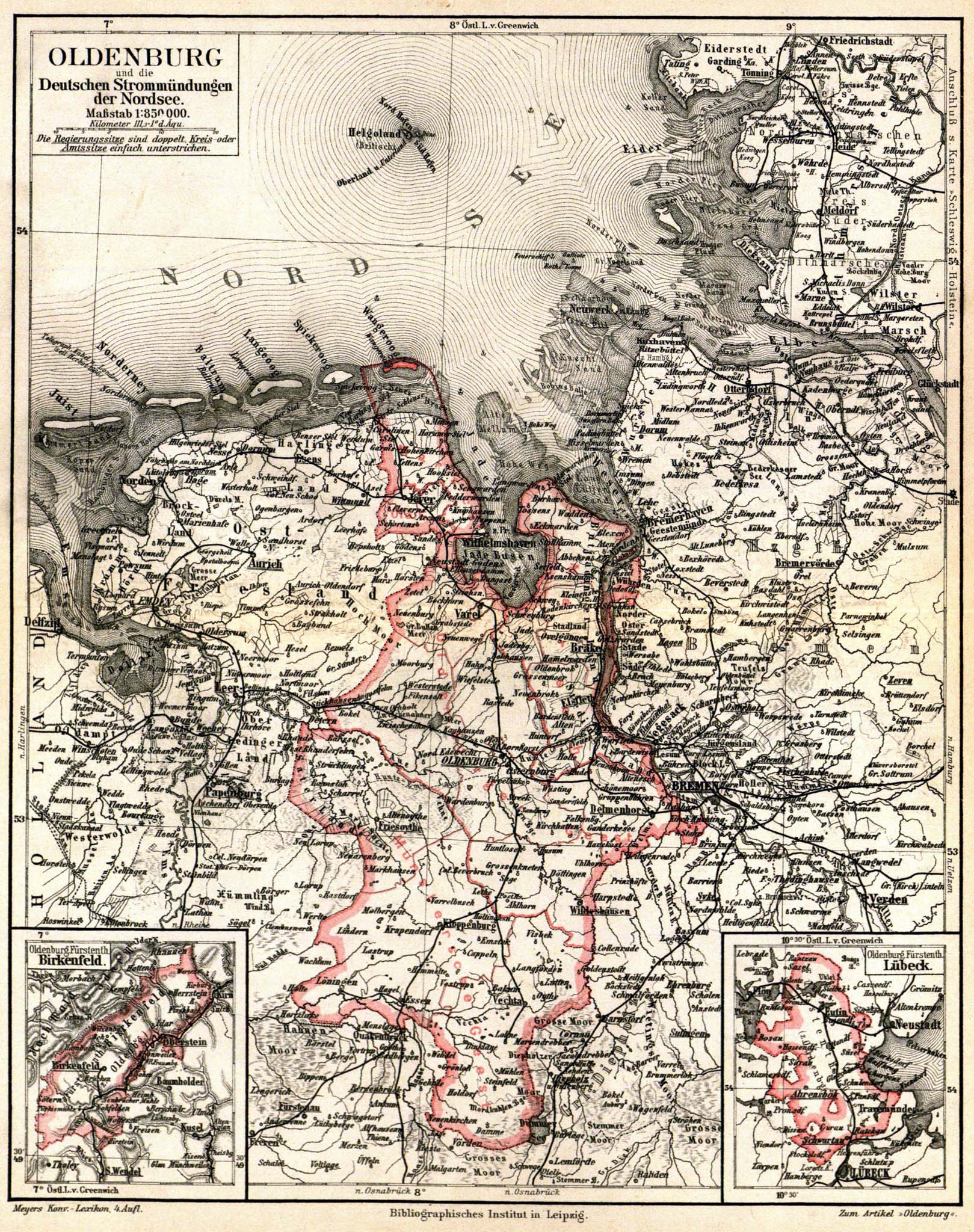 The Grand Duchy of Oldenburg Railway (''Großherzoglich Oldenburgische Eisenbahn or GOE'') was the railway company that was run as a state railway for the
The Grand Duchy of Oldenburg Railway (''Großherzoglich Oldenburgische Eisenbahn or GOE'') was the railway company that was run as a state railway for the
 The Grand Duchy of Oldenburg Railway (''Großherzoglich Oldenburgische Eisenbahn or GOE'') was the railway company that was run as a state railway for the
The Grand Duchy of Oldenburg Railway (''Großherzoglich Oldenburgische Eisenbahn or GOE'') was the railway company that was run as a state railway for the Grand Duchy of Oldenburg
The Grand Duchy of Oldenburg (, also known as Holstein-Oldenburg) was a grand duchy within the German Confederation, North German Confederation and German Empire that consisted of three widely separated territories: Oldenburg, Eutin and Birke ...
(''Großherzogtum Oldenburg''), part of the German Empire
The German Empire (),Herbert Tuttle wrote in September 1881 that the term "Reich" does not literally connote an empire as has been commonly assumed by English-speaking people. The term literally denotes an empire – particularly a hereditary ...
.
History
Compared with the other states in the German Empire,Oldenburg Oldenburg may also refer to:
Places
*Mount Oldenburg, Ellsworth Land, Antarctica
*Oldenburg (city), an independent city in Lower Saxony, Germany
**Oldenburg (district), a district historically in Oldenburg Free State and now in Lower Saxony
*Olde ...
's first railway
Rail transport (also known as train transport) is a means of transport that transfers passengers and goods on wheeled vehicles running on rails, which are incorporated in tracks. In contrast to road transport, where the vehicles run on a pre ...
line arrived relatively late. In this sparsely populated and economically poor area, the construction of railways appeared for a long while to be unsustainable due to the financial costs. In addition, the various ideas of its neighboring states, Hanover
Hanover (; german: Hannover ; nds, Hannober) is the capital and largest city of the German state of Lower Saxony. Its 535,932 (2021) inhabitants make it the 13th-largest city in Germany as well as the fourth-largest city in Northern Germany ...
and Prussia
Prussia, , Old Prussian: ''Prūsa'' or ''Prūsija'' was a German state on the southeast coast of the Baltic Sea. It formed the German Empire under Prussian rule when it united the German states in 1871. It was ''de facto'' dissolved by an em ...
prevented railway projects from coming to fruition for a long time.
Finally in 1864 a treaty was agreed between Prussia and Oldenburg over the construction of a railway line from Bremen to Oldenburg. At the same time Prussia committed itself to building a railway line from Heppens – later Wilhelmshaven
Wilhelmshaven (, ''Wilhelm's Harbour''; Northern Low Saxon: ''Willemshaven'') is a coastal town in Lower Saxony, Germany. It is situated on the western side of the Jade Bight, a bay of the North Sea, and has a population of 76,089. Wilhelmsha ...
– to Oldenburg (the Wilhelmshaven–Oldenburg line). The Grand Ducal Railway Commission, set up in 1864, was transferred on 1 April 1867, to the Grand Ducal Railway Division of Oldenburg.
On 17 November 1866, the first section of the route Oldenburg–Delmenhorst
Delmenhorst (; Northern Low Saxon: ''Demost'') is an urban district (''Kreisfreie Stadt'') in Lower Saxony, Germany. It has a population of 74,500 and is located west of downtown Bremen with which it forms a contiguous urban area, whereas the ...
was opened; in July 1867 its extension to Bremen
Bremen (Low German also: ''Breem'' or ''Bräm''), officially the City Municipality of Bremen (german: Stadtgemeinde Bremen, ), is the capital of the German state Free Hanseatic City of Bremen (''Freie Hansestadt Bremen''), a two-city-state consis ...
followed, and in September of the same year the section from Oldenburg to Heppens was finally completed.
In 1869 the east–west line from Bremen to Oldenburg was extended to what was then Prussian Leer in East Frisia
East Frisia or East Friesland (german: Ostfriesland; ; stq, Aastfräislound) is a historic region in the northwest of Lower Saxony, Germany. It is primarily located on the western half of the East Frisian peninsula, to the east of West Frisia ...
by a line from Oldenburg to Leer with a junction to the Hanoverian Western Railway The Hanoverian Western Railway was a line from the Löhne to Emden, built by the Royal Hanoverian State Railways in the mid-19th century in the west of the Kingdom of Hanover in the modern German states of Lower Saxony and North Rhine-Westphalia. ...
and, in 1876 by the section from Ihrhove to Nieuweschans with a junction to the Dutch Railways
Nederlandse Spoorwegen (NS; ; en, "Dutch Railways") is the principal passenger railway operator in the Netherlands. It is a Dutch state-owned company founded in 1938. The Dutch rail network is one of the busiest in the European Union, and the ...
.
In 1871 the town of Jever
Jever () is the capital of the district of Friesland in Lower Saxony, Germany. The name Jever is usually associated with a major brand of beer, Jever Pilsener, which is produced there. The city is also a popular holiday resort. Jever was granted c ...
was linked via Sande (part of the East Frisian Coastal Railway
East or Orient is one of the four cardinal directions or points of the compass. It is the opposite direction from west and is the direction from which the Sun rises on the Earth.
Etymology
As in other languages, the word is formed from the f ...
); Brake
A brake is a mechanical device that inhibits motion by absorbing energy from a moving system. It is used for slowing or stopping a moving vehicle, wheel, axle, or to prevent its motion, most often accomplished by means of friction.
Background ...
received a railway connexion in 1873 and Nordenham
Nordenham () is a town in the Wesermarsch district, in Lower Saxony, Germany. It is located at the mouth (on the west bank) of the Weser river on the Butjadingen peninsula on the coast of the North Sea. The seaport city of Bremerhaven is located ...
in 1875. The Grand Duchy of Oldenburg gained an important link to the south in 1876 with the so-called '' Southern Railway'' from Oldenburg via Quakenbrück
Quakenbrück (Northern Low Saxon: ''Quokenbrügge'') is a town in the Osnabrück (district), district of Osnabrück, in Lower Saxony, Germany. It is situated on the river Hase. It is part of the ''Samtgemeinde'' ("collective municipality") of Ar ...
as far as Eversburg on the Osnabrück–Rheine line.
In 1897 the route from Jever
Jever () is the capital of the district of Friesland in Lower Saxony, Germany. The name Jever is usually associated with a major brand of beer, Jever Pilsener, which is produced there. The city is also a popular holiday resort. Jever was granted c ...
to the harbour at Harle, opened in 1888 as the Jever–Carolinensiel railway, was finally taken over by the GOE. At the same time boat services to Wangerooge
Wangerooge is one of the 32 Frisian Islands in the North Sea located close to the coasts of the Netherlands, Germany and Denmark. It is also a municipality in the district of Friesland in Lower Saxony in Germany.
Wangerooge is one of the East Fri ...
were started and a narrow gauge
A narrow-gauge railway (narrow-gauge railroad in the US) is a railway with a track gauge narrower than standard . Most narrow-gauge railways are between and .
Since narrow-gauge railways are usually built with tighter curves, smaller structu ...
railway, the Wangerooge Island Railway
The single track Wangerooge Island Railway (''Wangerooger Inselbahn'') is an unelectrified narrow gauge railway with a track gauge of located on the East Frisian island of Wangerooge off the northwestern coast of Germany. It is the most importa ...
laid from the jetty to the town.
In 1920 the GOE was merged into the newly founded Deutsche Reichsbahn
The ''Deutsche Reichsbahn'', also known as the German National Railway, the German State Railway, German Reich Railway, and the German Imperial Railway, was the German national railway system created after the end of World War I from the regiona ...
. The Oldenburg staff were transferred to the Reichsbahn divisions of Hannover, Hamburg
(male), (female) en, Hamburger(s),
Hamburgian(s)
, timezone1 = Central (CET)
, utc_offset1 = +1
, timezone1_DST = Central (CEST)
, utc_offset1_DST = +2
, postal ...
and Münster
Münster (; nds, Mönster) is an independent city (''Kreisfreie Stadt'') in North Rhine-Westphalia, Germany. It is in the northern part of the state and is considered to be the cultural centre of the Westphalia region. It is also a state distr ...
/Westfalen
Westphalia (; german: Westfalen ; nds, Westfalen ) is a region of northwestern Germany and one of the three historic parts of the state of North Rhine-Westphalia. It has an area of and 7.9 million inhabitants.
The territory of the regio ...
after the disbandment of the railway division in Oldenburg town. In 1935 a monument was erected in Münster for the former Oldenburg railwaymen.
See also
*Grand Duchy of Oldenburg
The Grand Duchy of Oldenburg (, also known as Holstein-Oldenburg) was a grand duchy within the German Confederation, North German Confederation and German Empire that consisted of three widely separated territories: Oldenburg, Eutin and Birke ...
*List of Oldenburg locomotives and railbuses
This list contains the locomotives and railbuses of the Grand Duchy of Oldenburg State Railways (''Großherzoglich Oldenburgische Eisenbahn'' or''GOE'').
Locomotive classification and numbering
The locomotives of the Grand Duchy of Oldenburg S ...
References
* * {{Authority controlRailway
Rail transport (also known as train transport) is a means of transport that transfers passengers and goods on wheeled vehicles running on rails, which are incorporated in tracks. In contrast to road transport, where the vehicles run on a pre ...
History of rail transport in Germany
Defunct railway companies of Germany
Transport in Lower Saxony
1860s establishments in the Grand Duchy of Oldenburg