Gram positive on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 In
In

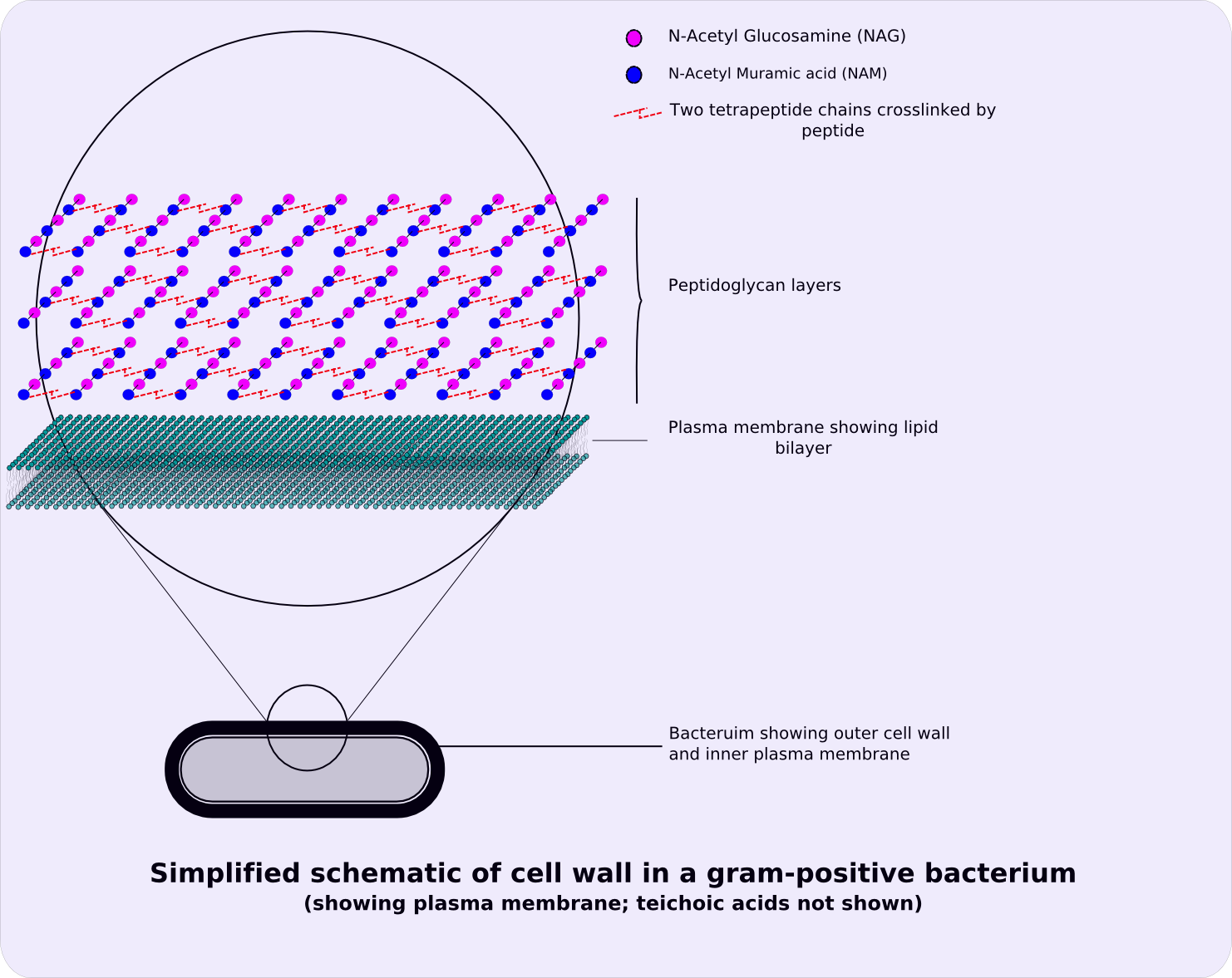 In general, the following characteristics are present in gram-positive bacteria:
# Cytoplasmic lipid membrane
# Thick
In general, the following characteristics are present in gram-positive bacteria:
# Cytoplasmic lipid membrane
# Thick
 Historically, the kingdom Monera was divided into four divisions based primarily on Gram staining:
Historically, the kingdom Monera was divided into four divisions based primarily on Gram staining:
 Although bacteria are traditionally divided into two main groups, gram-positive and gram-negative, based on their Gram stain retention property, this classification system is ambiguous as it refers to three distinct aspects (staining result, envelope organization, taxonomic group), which do not necessarily coalesce for some bacterial species. The gram-positive and gram-negative staining response is also not a reliable characteristic as these two kinds of bacteria do not form phylogenetic coherent groups. However, although Gram staining response is an empirical criterion, its basis lies in the marked differences in the ultrastructure and chemical composition of the bacterial cell wall, marked by the absence or presence of an outer lipid membrane.
All gram-positive bacteria are bounded by a single-unit lipid membrane, and, in general, they contain a thick layer (20–80 nm) of peptidoglycan responsible for retaining the Gram stain. A number of other bacteria—that are bounded by a single membrane, but stain gram-negative due to either lack of the peptidoglycan layer, as in the mycoplasmas, or their inability to retain the Gram stain because of their cell wall composition—also show close relationship to the Gram-positive bacteria. For the bacterial cells bounded by a single cell membrane, the term ''monoderm bacteria'' has been proposed.
In contrast to gram-positive bacteria, all typical gram-negative bacteria are bounded by a cytoplasmic membrane and an outer cell membrane; they contain only a thin layer of peptidoglycan (2–3 nm) between these membranes. The presence of inner and outer cell membranes defines a new compartment in these cells: the
Although bacteria are traditionally divided into two main groups, gram-positive and gram-negative, based on their Gram stain retention property, this classification system is ambiguous as it refers to three distinct aspects (staining result, envelope organization, taxonomic group), which do not necessarily coalesce for some bacterial species. The gram-positive and gram-negative staining response is also not a reliable characteristic as these two kinds of bacteria do not form phylogenetic coherent groups. However, although Gram staining response is an empirical criterion, its basis lies in the marked differences in the ultrastructure and chemical composition of the bacterial cell wall, marked by the absence or presence of an outer lipid membrane.
All gram-positive bacteria are bounded by a single-unit lipid membrane, and, in general, they contain a thick layer (20–80 nm) of peptidoglycan responsible for retaining the Gram stain. A number of other bacteria—that are bounded by a single membrane, but stain gram-negative due to either lack of the peptidoglycan layer, as in the mycoplasmas, or their inability to retain the Gram stain because of their cell wall composition—also show close relationship to the Gram-positive bacteria. For the bacterial cells bounded by a single cell membrane, the term ''monoderm bacteria'' has been proposed.
In contrast to gram-positive bacteria, all typical gram-negative bacteria are bounded by a cytoplasmic membrane and an outer cell membrane; they contain only a thin layer of peptidoglycan (2–3 nm) between these membranes. The presence of inner and outer cell membranes defines a new compartment in these cells: the
 In the classical sense, six gram-positive genera are typically pathogenic in humans. Two of these, ''
In the classical sense, six gram-positive genera are typically pathogenic in humans. Two of these, ''
3D structures of proteins associated with plasma membrane of gram-positive bacteria
3D structures of proteins associated with outer membrane of gram-positive bacteria
{{Authority control Staining Bacteriology
 In
In bacteriology Bacteriology is the branch and specialty of biology that studies the morphology, ecology, genetics and biochemistry of bacteria as well as many other aspects related to them. This subdivision of microbiology involves the identification, classificat ...
, gram-positive bacteria are bacteria
Bacteria (; singular: bacterium) are ubiquitous, mostly free-living organisms often consisting of one Cell (biology), biological cell. They constitute a large domain (biology), domain of prokaryotic microorganisms. Typically a few micrometr ...
that give a positive result in the Gram stain
In microbiology and bacteriology, Gram stain (Gram staining or Gram's method), is a method of staining used to classify bacterial species into two large groups: gram-positive bacteria and gram-negative bacteria. The name comes from the Danish b ...
test, which is traditionally used to quickly classify bacteria into two broad categories according to their type of cell wall.
Gram-positive bacteria take up the crystal violet
Crystal violet or gentian violet, also known as methyl violet 10B or hexamethyl pararosaniline chloride, is a triarylmethane dye used as a histological stain and in Gram's method of classifying bacteria. Crystal violet has antibacterial, antif ...
stain used in the test, and then appear to be purple-coloured when seen through an optical microscope
The optical microscope, also referred to as a light microscope, is a type of microscope that commonly uses visible light and a system of lenses to generate magnified images of small objects. Optical microscopes are the oldest design of microsc ...
. This is because the thick peptidoglycan
Peptidoglycan or murein is a unique large macromolecule, a polysaccharide, consisting of sugars and amino acids that forms a mesh-like peptidoglycan layer outside the plasma membrane, the rigid cell wall (murein sacculus) characteristic of most ba ...
layer in the bacterial cell wall retains the stain after it is washed away from the rest of the sample, in the decolorization stage of the test.
Conversely, gram-negative bacteria
Gram-negative bacteria are bacteria that do not retain the crystal violet stain used in the Gram staining method of bacterial differentiation. They are characterized by their cell envelopes, which are composed of a thin peptidoglycan cell wall ...
cannot retain the violet stain after the decolorization step; alcohol used in this stage degrades the outer membrane of gram-negative cells, making the cell wall more porous and incapable of retaining the crystal violet stain. Their peptidoglycan layer is much thinner and sandwiched between an inner cell membrane and a bacterial outer membrane
The bacterial outer membrane is found in gram-negative bacteria. Its composition is distinct from that of the inner cytoplasmic cell membrane - among other things, the outer leaflet of the outer membrane of many gram-negative bacteria includes ...
, causing them to take up the counterstain (safranin
Safranin (Safranin O or basic red 2) is a biological stain used in histology and cytology. Safranin is used as a counterstain in some staining protocols, colouring cell nuclei red. This is the classic counterstain in both Gram stains and endos ...
or fuchsine
Fuchsine (sometimes spelled fuchsin) or rosaniline hydrochloride is a magenta dye with chemical formula C20H19N3·HCl.
) and appear red or pink.
Despite their thicker peptidoglycan layer, gram-positive bacteria are more receptive to certain cell wall targeting antibiotics
An antibiotic is a type of antimicrobial substance active against bacteria. It is the most important type of antibacterial agent for fighting bacterial infections, and antibiotic medications are widely used in the treatment and prevention o ...
than gram-negative bacteria, due to the absence of the outer membrane.
Characteristics
 In general, the following characteristics are present in gram-positive bacteria:
# Cytoplasmic lipid membrane
# Thick
In general, the following characteristics are present in gram-positive bacteria:
# Cytoplasmic lipid membrane
# Thick peptidoglycan
Peptidoglycan or murein is a unique large macromolecule, a polysaccharide, consisting of sugars and amino acids that forms a mesh-like peptidoglycan layer outside the plasma membrane, the rigid cell wall (murein sacculus) characteristic of most ba ...
layer
# Teichoic acids
Teichoic acids (''cf.'' Greek τεῖχος, ''teīkhos'', "wall", to be specific a fortification wall, as opposed to τοῖχος, ''toīkhos'', a regular wall) are bacterial copolymers of glycerol phosphate or ribitol phosphate and carbohydr ...
and lipoids are present, forming lipoteichoic acid Lipoteichoic acid (LTA) is a major constituent of the cell wall of gram-positive bacteria. These organisms have an inner (or cytoplasmic) membrane and, external to it, a thick (up to 80 nanometer) peptidoglycan layer. The structure of LTA varies ...
s, which serve as chelating
Chelation is a type of bonding of ions and molecules to metal ions. It involves the formation or presence of two or more separate coordinate bonds between a polydentate (multiple bonded) ligand and a single central metal atom. These ligands are ...
agents, and also for certain types of adherence.
# Peptidoglycan chains are cross-linked to form rigid cell walls by a bacterial enzyme DD-transpeptidase.
# A much smaller volume of periplasm
The periplasm is a concentrated gel-like matrix in the space between the inner cytoplasmic membrane and the bacterial outer membrane called the ''periplasmic space'' in gram-negative bacteria. Using cryo-electron microscopy it has been found that ...
than that in gram-negative bacteria.
Only some species have a capsule, usually consisting of polysaccharides
Polysaccharides (), or polycarbohydrates, are the most abundant carbohydrates found in food. They are long chain polymeric carbohydrates composed of monosaccharide units bound together by glycosidic linkages. This carbohydrate can react with w ...
. Also, only some species are flagellates, and when they do have flagella, have only two basal body
A basal body (synonymous with basal granule, kinetosome, and in older cytological literature with blepharoplast) is a protein structure found at the base of a eukaryotic undulipodium (cilium or flagellum). The basal body was named by Theodor Wi ...
rings to support them, whereas gram-negative have four. Both gram-positive and gram-negative bacteria commonly have a surface layer called an S-layer An S-layer (surface layer) is a part of the cell envelope found in almost all archaea, as well as in many types of bacteria.
The S-layers of both archaea and bacteria consists of a monomolecular layer composed of only one (or, in a few cases, two) ...
. In gram-positive bacteria, the S-layer is attached to the peptidoglycan layer. Gram-negative bacteria's S-layer is attached directly to the outer membrane. Specific to gram-positive bacteria is the presence of teichoic acid
Teichoic acids (''cf.'' Greek τεῖχος, ''teīkhos'', "wall", to be specific a fortification wall, as opposed to τοῖχος, ''toīkhos'', a regular wall) are bacterial copolymers of glycerol phosphate or ribitol phosphate and carbohydr ...
s in the cell wall. Some of these are lipoteichoic acids, which have a lipid component in the cell membrane that can assist in anchoring the peptidoglycan.
Classification
Along with cell shape, Gram staining is a rapid method used to differentiate bacterial species. Such staining, together with growth requirement and antibiotic susceptibility testing, and other macroscopic and physiologic tests, forms the full basis for classification and subdivision of the bacteria (e.g., see figure and pre-1990 versions of '' Bergey's Manual of Systematic Bacteriology'').Bacillota
The Bacillota (synonym Firmicutes) are a phylum of bacteria, most of which have gram-positive cell wall structure. The renaming of phyla such as Firmicutes in 2021 remains controversial among microbiologists, many of whom continue to use the earl ...
(positive in staining), Gracilicutes
Gracilicutes (Latin: ''gracilis'', slender, and ''cutis'', skin, referring to the cell wall) is a clade in bacterial phylogeny.
Traditionally gram staining results were most commonly used as a classification tool, consequently until the advent o ...
(negative in staining), Mollicutes
Mollicutes is a class of bacteria distinguished by the absence of a cell wall. The word "Mollicutes" is derived from the Latin ''mollis'' (meaning "soft" or "pliable"), and ''cutis'' (meaning "skin"). Individuals are very small, typically only 0. ...
(neutral in staining) and Mendocutes (variable in staining). Based on 16S ribosomal RNA
16 S ribosomal RNA (or 16 S rRNA) is the RNA component of the 30S subunit of a prokaryotic ribosome ( SSU rRNA). It binds to the Shine-Dalgarno sequence and provides most of the SSU structure.
The genes coding for it are referred to as 16S rR ...
phylogenetic studies of the late microbiologist Carl Woese
Carl Richard Woese (; July 15, 1928 – December 30, 2012) was an American microbiologist and biophysicist. Woese is famous for defining the Archaea (a new domain of life) in 1977 through a pioneering phylogenetic taxonomy of 16S ribosomal RNA, ...
and collaborators and colleagues at the University of Illinois
The University of Illinois Urbana-Champaign (U of I, Illinois, University of Illinois, or UIUC) is a public land-grant research university in Illinois in the twin cities of Champaign and Urbana. It is the flagship institution of the Univer ...
, the monophyly
In cladistics for a group of organisms, monophyly is the condition of being a clade—that is, a group of taxa composed only of a common ancestor (or more precisely an ancestral population) and all of its lineal descendants. Monophyletic gro ...
of the gram-positive bacteria was challenged, with major implications for the therapeutic and general study of these organisms. Based on molecular studies of the 16S sequences, Woese recognised twelve bacterial phyla
Bacterial phyla constitute the major lineages of the domain ''Bacteria''. While the exact definition of a bacterial phylum is debated, a popular definition is that a bacterial phylum is a monophyletic lineage of bacteria whose 16S rRNA genes s ...
. Two of these were gram-positive and were divided on the proportion of the guanine
Guanine () ( symbol G or Gua) is one of the four main nucleobases found in the nucleic acids DNA and RNA, the others being adenine, cytosine, and thymine (uracil in RNA). In DNA, guanine is paired with cytosine. The guanine nucleoside is c ...
and cytosine
Cytosine () ( symbol C or Cyt) is one of the four nucleobases found in DNA and RNA, along with adenine, guanine, and thymine (uracil in RNA). It is a pyrimidine derivative, with a heterocyclic aromatic ring and two substituents attached (an ...
content in their DNA. The high G + C phylum was made up of the Actinobacteria
The ''Actinomycetota'' (or ''Actinobacteria'') are a phylum of all gram-positive bacteria. They can be terrestrial or aquatic. They are of great economic importance to humans because agriculture and forests depend on their contributions to so ...
and the low G + C phylum contained the Firmicutes
The Bacillota (synonym Firmicutes) are a phylum of bacteria, most of which have gram-positive cell wall structure. The renaming of phyla such as Firmicutes in 2021 remains controversial among microbiologists, many of whom continue to use the earl ...
. The Actinomycetota include the '' Corynebacterium'', '' Mycobacterium'', '' Nocardia'' and '' Streptomyces'' genera. The (low G + C) Bacillota, have a 45–60% GC content, but this is lower than that of the Actinomycetota.
Importance of the outer cell membrane in bacterial classification
periplasmic space
The periplasm is a concentrated gel-like matrix in the space between the inner cytoplasmic membrane and the bacterial outer membrane called the ''periplasmic space'' in gram-negative bacteria. Using cryo-electron microscopy it has been found tha ...
or the periplasmic compartment. These bacteria have been designated as diderm bacteria
Gram-negative bacteria are bacteria that do not retain the crystal violet stain used in the Gram staining method of bacterial differentiation. They are characterized by their cell envelopes, which are composed of a thin peptidoglycan cell wall ...
. The distinction between the monoderm and diderm bacteria is supported by conserved signature indels in a number of important proteins (viz. DnaK, GroEL). Of these two structurally distinct groups of bacteria, monoderms are indicated to be ancestral. Based upon a number of observations including that the gram-positive bacteria are the major producers of antibiotics and that, in general, gram-negative bacteria are resistant to them, it has been proposed that the outer cell membrane in gram-negative bacteria (diderms) has evolved as a protective mechanism against antibiotic selection pressure. Some bacteria, such as '' Deinococcus'', which stain gram-positive due to the presence of a thick peptidoglycan layer and also possess an outer cell membrane are suggested as intermediates in the transition between monoderm (gram-positive) and diderm (gram-negative) bacteria. The diderm bacteria can also be further differentiated between simple diderms lacking lipopolysaccharide, the archetypical diderm bacteria where the outer cell membrane contains lipopolysaccharide, and the diderm bacteria where outer cell membrane is made up of mycolic acid
Mycolic acids are long fatty acids found in the cell walls of the Mycolata taxon, a group of bacteria that includes ''Mycobacterium tuberculosis'', the causative agent of the disease tuberculosis. They form the major component of the cell wall of ...
.
Exceptions
In general, gram-positive bacteria are monoderms and have a singlelipid bilayer
The lipid bilayer (or phospholipid bilayer) is a thin polar membrane made of two layers of lipid molecules. These membranes are flat sheets that form a continuous barrier around all cells. The cell membranes of almost all organisms and many vir ...
whereas gram-negative bacteria are diderms and have two bilayers. Some taxa lack peptidoglycan (such as the class Mollicutes
Mollicutes is a class of bacteria distinguished by the absence of a cell wall. The word "Mollicutes" is derived from the Latin ''mollis'' (meaning "soft" or "pliable"), and ''cutis'' (meaning "skin"). Individuals are very small, typically only 0. ...
, some members of the Rickettsiales
The Rickettsiales, informally called rickettsias, are an order of small Alphaproteobacteria. They are obligate intracellular parasites, and some are notable pathogens, including ''Rickettsia'', which causes a variety of diseases in humans, and ' ...
, and the insect-endosymbionts of the Enterobacteriales
Enterobacterales is an order of Gram-negative, non-spore forming, facultatively anaerobic, rod-shaped bacteria with the class Gammaproteobacteria. The type genus of this order is ''Enterobacter.''
The name Enterobacterales is derived from the ...
) and are gram-variable. This, however, does not always hold true. The Deinococcota
''Deinococcota'' (synonym, ''Deinococcus-Thermus'') is a phylum of bacteria with a single class, ''Deinococci'', that are highly resistant to environmental hazards, also known as extremophiles.
These bacteria have thick cell walls that give them ...
have gram-positive stains, although they are structurally similar to gram-negative bacteria with two layers. The Chloroflexota
The Chloroflexota are a phylum of bacteria containing isolates with a diversity of phenotypes, including members that are aerobic thermophiles, which use oxygen and grow well in high temperatures; anoxygenic phototrophs, which use light for phot ...
have a single layer, yet (with some exceptions) stain negative. Two related phyla to the Chloroflexi, the TM7 clade and the Ktedonobacteria, are also monoderms.
Some Bacillota species are not gram-positive. These belong to the class Mollicutes
Mollicutes is a class of bacteria distinguished by the absence of a cell wall. The word "Mollicutes" is derived from the Latin ''mollis'' (meaning "soft" or "pliable"), and ''cutis'' (meaning "skin"). Individuals are very small, typically only 0. ...
(alternatively considered a class of the phylum Mycoplasmatota
Mycoplasmatota is a phylum of bacteria that contains the class Mollicutes. The phylum was originally named "Tenericutes" (''tener cutis'': soft skin). Notable genera include ''Mycoplasma'', ''Spiroplasma'', ''Ureaplasma'', and ''Candidatus'' Phyt ...
), which lack peptidoglycan ( gram-indeterminate), and the class Negativicutes, which includes ''Selenomonas
Members of the genus ''Selenomonas'' (motile crescent-shaped bacteria in general) are referred to trivially as selenomonads. The genus ''Selenomonas'' constitutes a group of motile crescent-shaped bacteria and includes species living in the gast ...
'' and stain gram-negative. Additionally, a number of bacterial taxa (viz. Negativicutes
The Negativicutes are a class of bacteria in the phylum Bacillota, whose members have a peculiar cell wall with a lipopolysaccharide outer membrane which stains gram-negative, unlike most other members of the Bacillota. Although several neighbo ...
, Fusobacteriota
Fusobacteriota are obligately anaerobic non-sporeforming Gram-negative bacilli. Since the first reports in the late nineteenth century, various names have been applied to these organisms, sometimes with the same name being applied to different ...
, Synergistota
The Synergistota is a phylum of anaerobic bacteria that show Gram-negative staining and have rod/vibrioid cell shape. Although Synergistota have a diderm cell envelope,Gupta, R. S. (2011) Origin of Diderm (Gram-negative) Bacteria: Antibiotic Sel ...
, and Elusimicrobiota
The phylum Elusimicrobiota, previously known as "Termite Group 1", has been shown to be widespread in different ecosystems like marine environment, sewage sludge, contaminated sites and soils, and toxic wastes. The high abundance of Elusimicrobio ...
) that are either part of the phylum Bacillota or branch in its proximity are found to possess a diderm cell structure. However, a conserved signature indel (CSI) in the HSP60
HSP60, also known as chaperonins (Cpn), is a family of heat shock proteins originally sorted by their 60kDa molecular mass. They prevent misfolding of proteins during stressful situations such as high heat, by assisting protein folding. HSP60 bel ...
(GroEL
GroEL is a protein which belongs to the chaperonin family of molecular chaperones, and is found in many bacteria. It is required for the proper folding of many proteins. To function properly, GroEL requires the lid-like cochaperonin protein com ...
) protein distinguishes all traditional phyla of gram-negative bacteria (e.g., Pseudomonadota, Aquificota
The ''Aquificota'' phylum is a diverse collection of bacteria that live in harsh environmental settings. The name ''Aquificota'' was given to this phylum based on an early genus identified within this group, '' Aquifex'' (“water maker”), whic ...
, Chlamydiota, Bacteroidota, Chlorobiota
The green sulfur bacteria are a phylum of obligately anaerobic photoautotrophic bacteria that metabolize sulfur.
Green sulfur bacteria are nonmotile (except ''Chloroherpeton thalassium'', which may glide) and capable of anoxygenic photosynthes ...
, " Cyanobacteria", Fibrobacterota
Fibrobacterota is a small bacterial phylum which includes many of the major rumen bacteria, allowing for the degradation of plant-based cellulose in ruminant animals. Members of this phylum were categorized in other phyla. The genus '' Fibrobac ...
, Verrucomicrobiota
Verrucomicrobiota is a phylum of Gram-negative bacteria that contains only a few described species. The species identified have been isolated from fresh water, marine and soil environments and human faeces. A number of as-yet uncultivated speci ...
, Planctomycetota
The Planctomycetota are a phylum of widely distributed bacteria, occurring in both aquatic and terrestrial habitats. They play a considerable role in global carbon and nitrogen cycles, with many species of this phylum capable of anaerobic ammoniu ...
, Spirochaetota
A spirochaete () or spirochete is a member of the phylum Spirochaetota (), (synonym Spirochaetes) which contains distinctive diderm (double-membrane) gram-negative bacteria, most of which have long, helically coiled (corkscrew-shaped or ...
, Acidobacteriota
Acidobacteriota is a phylum of Gram-negative bacteria. Its members are physiologically diverse and ubiquitous, especially in soils, but are under-represented in culture.
Description
Members of this phylum are physiologically diverse, and can be ...
, etc.) from these other atypical diderm bacteria, as well as other phyla of monoderm bacteria (e.g., Actinomycetota
The ''Actinomycetota'' (or ''Actinobacteria'') are a phylum of all gram-positive bacteria. They can be terrestrial or aquatic. They are of great economic importance to humans because agriculture and forests depend on their contributions to s ...
, Bacillota
The Bacillota (synonym Firmicutes) are a phylum of bacteria, most of which have gram-positive cell wall structure. The renaming of phyla such as Firmicutes in 2021 remains controversial among microbiologists, many of whom continue to use the earl ...
, Thermotogota
The Thermotogota are a phylum of the domain Bacteria. The phylum Thermotogota is composed of Gram-negative staining, anaerobic, and mostly thermophilic and hyperthermophilic bacteria.Gupta, RS (2014) The Phylum Thermotogae. The Prokaryotes 989-10 ...
, Chloroflexota
The Chloroflexota are a phylum of bacteria containing isolates with a diversity of phenotypes, including members that are aerobic thermophiles, which use oxygen and grow well in high temperatures; anoxygenic phototrophs, which use light for phot ...
, etc.). The presence of this CSI in all sequenced species of conventional LPS (lipopolysaccharide
Lipopolysaccharides (LPS) are large molecules consisting of a lipid and a polysaccharide that are bacterial toxins. They are composed of an O-antigen, an outer core, and an inner core all joined by a covalent bond, and are found in the outer ...
)-containing gram-negative bacterial phyla provides evidence that these phyla of bacteria form a monophyletic clade and that no loss of the outer membrane from any species from this group has occurred.
Pathogenicity
 In the classical sense, six gram-positive genera are typically pathogenic in humans. Two of these, ''
In the classical sense, six gram-positive genera are typically pathogenic in humans. Two of these, ''Streptococcus
''Streptococcus'' is a genus of gram-positive ' (plural ) or spherical bacteria that belongs to the family Streptococcaceae, within the order Lactobacillales (lactic acid bacteria), in the phylum Bacillota. Cell division in streptococci occurs ...
'' and '' Staphylococcus'', are cocci
A coccus (plural cocci) is any bacterium or archaeon that has a spherical, ovoid, or generally round shape. Bacteria are categorized based on their shapes into three classes: cocci (spherical-shaped), bacillus (rod-shaped) and spiral ( of whi ...
(sphere-shaped). The remaining organisms are bacilli
Bacilli is a taxonomic class of bacteria that includes two orders, Bacillales and Lactobacillales, which contain several well-known pathogens such as ''Bacillus anthracis'' (the cause of anthrax). ''Bacilli'' are almost exclusively gram-positi ...
(rod-shaped) and can be subdivided based on their ability to form spores. The non-spore formers are '' Corynebacterium'' and ''Listeria
''Listeria'' is a genus of bacteria that acts as an intracellular parasite in mammals. Until 1992, 17 species were known, each containing two subspecies. By 2020, 21 species had been identified. The genus is named in honour of the British pio ...
'' (a coccobacillus), whereas ''Bacillus
''Bacillus'' (Latin "stick") is a genus of Gram-positive, rod-shaped bacteria, a member of the phylum '' Bacillota'', with 266 named species. The term is also used to describe the shape (rod) of other so-shaped bacteria; and the plural ''Bacill ...
'' and '' Clostridium'' produce spores. The spore-forming bacteria can again be divided based on their respiration
Respiration may refer to:
Biology
* Cellular respiration, the process in which nutrients are converted into useful energy in a cell
** Anaerobic respiration, cellular respiration without oxygen
** Maintenance respiration, the amount of cellul ...
: ''Bacillus'' is a facultative anaerobe
A facultative anaerobic organism is an organism that makes ATP by aerobic respiration if oxygen is present, but is capable of switching to fermentation if oxygen is absent.
Some examples of facultatively anaerobic bacteria are '' Staphylococc ...
, while ''Clostridium'' is an obligate anaerobe
Obligate anaerobes are microorganisms killed by normal atmospheric concentrations of oxygen (20.95% O2). Oxygen tolerance varies between species, with some species capable of surviving in up to 8% oxygen, while others lose viability in environme ...
. Also, ''Rathybacter'', ''Leifsonia'', and ''Clavibacter'' are three gram-positive genera that cause plant disease. Gram-positive bacteria are capable of causing serious and sometimes fatal infections
An infection is the invasion of tissues by pathogens, their multiplication, and the reaction of host tissues to the infectious agent and the toxins they produce. An infectious disease, also known as a transmissible disease or communicable di ...
in newborn infants. Access provided by the University of Pittsburgh. Novel species of clinically relevant gram-positive bacteria also include '' Catabacter hongkongensis'', which is an emerging pathogen belonging to Bacillota
The Bacillota (synonym Firmicutes) are a phylum of bacteria, most of which have gram-positive cell wall structure. The renaming of phyla such as Firmicutes in 2021 remains controversial among microbiologists, many of whom continue to use the earl ...
.
Bacterial transformation
Transformation
Transformation may refer to:
Science and mathematics
In biology and medicine
* Metamorphosis, the biological process of changing physical form after birth or hatching
* Malignant transformation, the process of cells becoming cancerous
* Tran ...
is one of three processes for horizontal gene transfer
Horizontal gene transfer (HGT) or lateral gene transfer (LGT) is the movement of genetic material between unicellular and/or multicellular organisms other than by the ("vertical") transmission of DNA from parent to offspring (reproduction). H ...
, in which exogenous genetic material passes from a donor bacterium to a recipient bacterium, the other two processes being conjugation
Conjugation or conjugate may refer to:
Linguistics
* Grammatical conjugation, the modification of a verb from its basic form
* Emotive conjugation or Russell's conjugation, the use of loaded language
Mathematics
* Complex conjugation, the chang ...
(transfer of genetic material
Nucleic acids are biopolymers, macromolecules, essential to all known forms of life. They are composed of nucleotides, which are the monomers made of three components: a 5-carbon sugar, a phosphate group and a nitrogenous base. The two main clas ...
between two bacterial cells in direct contact) and transduction (injection of donor bacterial DNA by a bacteriophage virus into a recipient host bacterium). In transformation, the genetic material passes through the intervening medium, and uptake is completely dependent on the recipient bacterium.
As of 2014 about 80 species of bacteria were known to be capable of transformation, about evenly divided between gram-positive and gram-negative bacteria
Gram-negative bacteria are bacteria that do not retain the crystal violet stain used in the Gram staining method of bacterial differentiation. They are characterized by their cell envelopes, which are composed of a thin peptidoglycan cell wall ...
; the number might be an overestimate since several of the reports are supported by single papers. Transformation among gram-positive bacteria has been studied in medically important species such as ''Streptococcus pneumoniae
''Streptococcus pneumoniae'', or pneumococcus, is a Gram-positive, spherical bacteria, alpha-hemolytic (under aerobic conditions) or beta-hemolytic (under anaerobic conditions), aerotolerant anaerobic member of the genus Streptococcus. They ar ...
'', '' Streptococcus mutans'', '' Staphylococcus aureus'' and ''Streptococcus sanguinis
''Streptococcus sanguinis'', formerly known as ''Streptococcus sanguis'', is a Gram-positive facultative anaerobic coccus species of bacteria and a member of the Viridans Streptococcus group. ''S. sanguinis'' is a normal inhabitant of the healt ...
'' and in gram-positive soil bacterium ''Bacillus subtilis
''Bacillus subtilis'', known also as the hay bacillus or grass bacillus, is a Gram-positive, catalase-positive bacterium, found in soil and the gastrointestinal tract of ruminants, humans and marine sponges. As a member of the genus ''Bacillus ...
, Bacillus cereus''.
Orthographic note
The adjectives ''Gram-positive'' and ''Gram-negative'' derive from the surname ofHans Christian Gram
Hans Christian Joachim Gram (13 September 1853 – 14 November 1938) was a Danish bacteriologist noted for his development of the Gram stain, still a standard technique to classify bacteria and make them more visible under a microscope.
Early l ...
; as eponymous adjectives, their initial letter can be either capital ''G'' or lower-case ''g'', depending on which style guide (e.g., that of the CDC
The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) is the national public health agency of the United States. It is a United States federal agency, under the Department of Health and Human Services, and is headquartered in Atlanta, Georgi ...
), if any, governs the document being written. This is further explained at '' Gram staining § Orthographic note''.
References
External links
*3D structures of proteins associated with plasma membrane of gram-positive bacteria
3D structures of proteins associated with outer membrane of gram-positive bacteria
{{Authority control Staining Bacteriology