Golden Age of India on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Certain time periods have been named "



Gupta and Harsha: The Classical Age
Ancient India
golden ages
A golden age is a period considered the apotheosis in the history of a country or people, a time period when the greatest achievements were made. The term originated from early Greek and Roman poets, who used it to refer to a time when mankin ...
" where development in the Indian subcontinent
The Indian subcontinent is a physiographical region in Southern Asia. It is situated on the Indian Plate, projecting southwards into the Indian Ocean from the Himalayas. Geopolitically, it includes the countries of Bangladesh, Bhutan, In ...
flourished.
Ancient India

Gupta Empire
The period between the 4th and 6th centuries CE is known as the Golden Age of India because of the considerable achievements in the fields ofmathematics
Mathematics is an area of knowledge that includes the topics of numbers, formulas and related structures, shapes and the spaces in which they are contained, and quantities and their changes. These topics are represented in modern mathematics ...
, astronomy
Astronomy () is a natural science that studies celestial objects and phenomena. It uses mathematics, physics, and chemistry in order to explain their origin and evolution. Objects of interest include planets, moons, stars, nebulae, g ...
, science
Science is a systematic endeavor that builds and organizes knowledge in the form of testable explanations and predictions about the universe.
Science may be as old as the human species, and some of the earliest archeological evidence ...
, religion
Religion is usually defined as a social- cultural system of designated behaviors and practices, morals, beliefs, worldviews, texts, sanctified places, prophecies, ethics, or organizations, that generally relates humanity to supernatur ...
and philosophy during the Gupta Empire
The Gupta Empire was an ancient Indian empire which existed from the early 4th century CE to late 6th century CE. At its zenith, from approximately 319 to 467 CE, it covered much of the Indian subcontinent. This period is considered as the Gold ...
. The decimal numeral system, including the concept of zero
0 (zero) is a number representing an empty quantity. In place-value notation such as the Hindu–Arabic numeral system, 0 also serves as a placeholder numerical digit, which works by multiplying digits to the left of 0 by the radix, usual ...
, was invented in India during this period. The peace and prosperity created under the leadership of the Guptas enabled the pursuit of scientific and artistic endeavors in India. The Golden Age of India came to an end when the Hunas
Hunas or Huna (Middle Brahmi script: ''Hūṇā'') was the name given by the ancient Indians to a group of Central Asian tribes who, via the Khyber Pass, entered the Indian subcontinent at the end of the 5th or early 6th century. The Huna Kin ...
invaded the Gupta Empire in the 6th century CE. The gross domestic product (GDP) of ancient India was estimated to be 32% and 28% of the global GDP in 1 AD and 1000 AD respectively. Also, during the first millennium of common era the Indian population comprised around 30.3% and 27.15% of the total world population.
Medieval India
Chola Empire
South India
South India, also known as Dakshina Bharata or Peninsular India, consists of the peninsular southern part of India. It encompasses the Indian states of Andhra Pradesh, Karnataka, Kerala, Tamil Nadu, and Telangana, as well as the union territ ...
in the 10th and 11th century CE under the imperial Cholas is considered as another Golden Age. The period saw extensive achievements in Dravidian architecture
Architecture is the art and technique of designing and building, as distinguished from the skills associated with construction. It is both the process and the product of sketching, conceiving, planning, designing, and constructing building ...
, Tamil literature, sculpture and bronze working, maritime conquests and trade. During Cholas the major South East Asian countries practiced Hinduism, Chola’s influence was as far as Vietnam. Chola GDP constituted the world's largest GDP at that time.

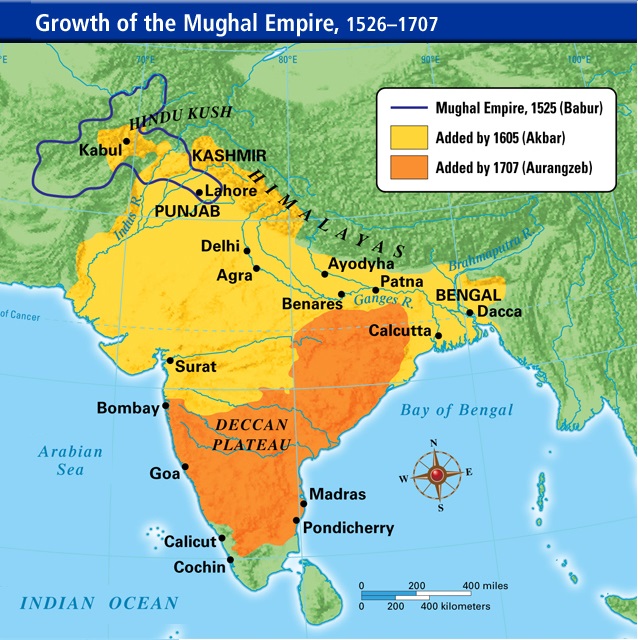
Delhi Sultanate and Mughal Empire
In the 13th and early 14th century CE under the Delhi Sultanate and in the 16th and 17th century CE under theMughal Empire
The Mughal Empire was an early-modern empire that controlled much of South Asia between the 16th and 19th centuries. Quote: "Although the first two Timurid emperors and many of their noblemen were recent migrants to the subcontinent, the d ...
are considered Golden Ages, both economically and culturally. The periods saw extensive achievements in Indo-Islamic architecture, Indo-Persian culture, monuments, mosques, calligraphy, conquests, manufacturing and trade. During the Mughal era, the GDP of India in 1600 was estimated at 22% of the world economy, the second largest in the world, behind only Ming China but larger than Europe. By 1700, the GDP of Mughal India had risen to 24% of the world economy, the largest in the world, larger than both Qing China and Western Europe. The Mughal empire was producing about 25% of the world's industrial output up until the 18th century.Maddison, Angus (2003). Development Centre Studies The World Economy Historical Statistics: Historical Statistics. OECD Publishing. pp. 256–. ISBN 978-92-64-10414-3.
References
External links
Gupta and Harsha: The Classical Age
Ancient India
India
India, officially the Republic of India (Hindi: ), is a country in South Asia. It is the seventh-largest country by area, the second-most populous country, and the most populous democracy in the world. Bounded by the Indian Ocean on the so ...
{{India-hist-stub