The history of cartography refers to the development and consequences of
cartography
Cartography (; from grc, χάρτης , "papyrus, sheet of paper, map"; and , "write") is the study and practice of making and using maps. Combining science, aesthetics and technique, cartography builds on the premise that reality (or an i ...
, or mapmaking technology, throughout human history. Maps have been one of the most important human inventions for millennia, allowing humans to explain and navigate their way through the world.
When and how the earliest maps were made are unknown, but maps of local terrain are believed to have been independently invented by many cultures. The earliest surviving maps include
cave painting
In archaeology, Cave paintings are a type of parietal art (which category also includes petroglyphs, or engravings), found on the wall or ceilings of caves. The term usually implies prehistoric origin, and the oldest known are more than 40,000 ye ...
s and etchings on tusk and stone. Maps were produced extensively by ancient
Babylon
''Bābili(m)''
* sux, 𒆍𒀭𒊏𒆠
* arc, 𐡁𐡁𐡋 ''Bāḇel''
* syc, ܒܒܠ ''Bāḇel''
* grc-gre, Βαβυλών ''Babylṓn''
* he, בָּבֶל ''Bāvel''
* peo, 𐎲𐎠𐎲𐎡𐎽𐎢 ''Bābiru''
* elx, 𒀸𒁀𒉿𒇷 ''Babi ...
, Greece, Rome, China, and India.
The earliest maps ignored the curvature of Earth's surface, both because the shape of the Earth was uncertain and because the curvature is not important across the small areas being mapped. However, since the age of
Classical Greece
Classical Greece was a period of around 200 years (the 5th and 4th centuries BC) in Ancient Greece,The "Classical Age" is "the modern designation of the period from about 500 B.C. to the death of Alexander the Great in 323 B.C." ( Thomas R. Marti ...
, maps of large regions, and especially of the world, have used
projection from a model globe in order to control how the inevitable distortion gets apportioned on the map.
Modern methods of transportation, the use of
surveillance aircraft
A surveillance aircraft is an aircraft used for surveillance. They are operated by military forces and other government agencies in roles such as intelligence gathering, battlefield surveillance, airspace surveillance, reconnaissance, observat ...
, and more recently the availability of
satellite imagery
Satellite images (also Earth observation imagery, spaceborne photography, or simply satellite photo) are images of Earth collected by imaging satellites operated by governments and businesses around the world. Satellite imaging companies sell ima ...
have made documentation of many areas possible that were previously inaccessible. Free online services such as
Google Earth
Google Earth is a computer program that renders a 3D computer graphics, 3D representation of Earth based primarily on satellite imagery. The program maps the Earth by superimposition, superimposing satellite images, aerial photography, and geog ...
have made accurate maps of the world more accessible than ever before.
Etymology
The English term ''
cartography
Cartography (; from grc, χάρτης , "papyrus, sheet of paper, map"; and , "write") is the study and practice of making and using maps. Combining science, aesthetics and technique, cartography builds on the premise that reality (or an i ...
'' is modern, borrowed from the French ''cartographie'' in the 1840s, itself based on
Middle Latin
Medieval Latin was the form of Literary Latin used in Roman Catholic Western Europe during the Middle Ages. In this region it served as the primary written language, though local languages were also written to varying degrees. Latin functioned ...
''carta'' "map".
Pre-modern era
Earliest known maps
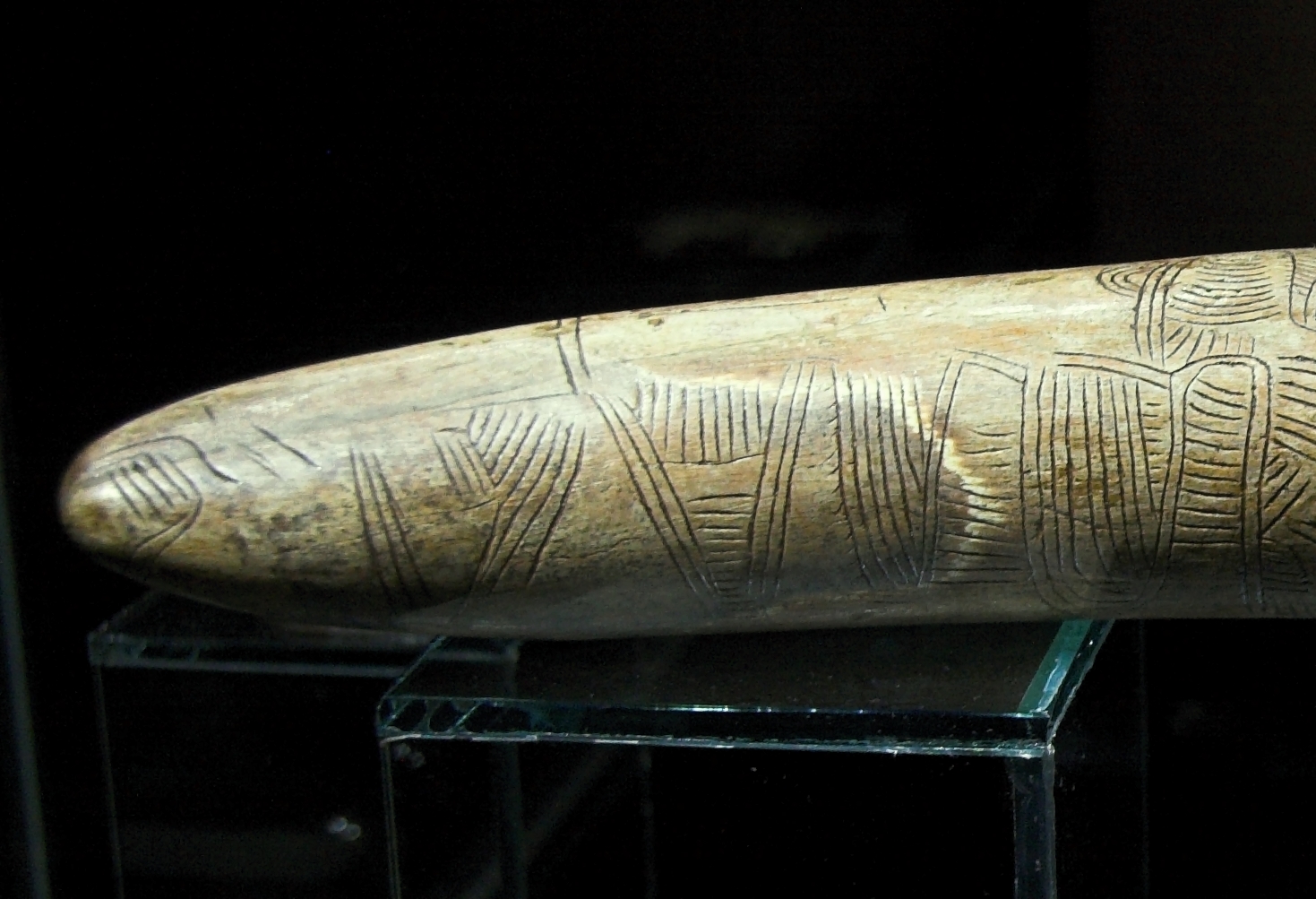

It's not always clear whether an ancient artifact had been wrought as a map or as something else. The definition of "map" is also not precise. Thus, no single artifact is generally accepted to be the earliest surviving map. Candidates include:
* A map-like representation of a mountain, river, valleys and routes around Pavlov in the
Czech Republic
The Czech Republic, or simply Czechia, is a landlocked country in Central Europe. Historically known as Bohemia, it is bordered by Austria to the south, Germany to the west, Poland to the northeast, and Slovakia to the southeast. The ...
, carved on a mammoth tusk, that has been dated to 25,000 BC.
* An
Aboriginal Australian
Aboriginal Australians are the various Indigenous peoples of the Australian mainland and many of its islands, such as Tasmania, Fraser Island, Hinchinbrook Island, the Tiwi Islands, and Groote Eylandt, but excluding the Torres Strait I ...
cylcon Cylcons are among the earliest artefacts of the Aboriginal Australians. A cylcon is a cylindrical stone tapering at one end and marked with incisions. The name is a shortening of the descriptive term "cylindro-conical stone".Schøyen CollectionMS 5 ...
that may be as much as 20,000 BC years old that is thought to depict the
Darling River
The Darling River (Paakantyi: ''Baaka'' or ''Barka'') is the third-longest river in Australia, measuring from its source in northern New South Wales to its conflu
ence with the Murray River at Wentworth, New South Wales. Including its long ...
.
[ Schøyen Collection]
MS 5087/36, Cylcon (Yurda), possibly with map of Darling River
, commentary.
* A map etched on a mammoth bone at
Mezhyrich
Mezhyrich ( uk, Межиріч, also referred to as Mezhirich) is a village (''selo'') in central Ukraine. It is located in Cherkasy Raion (district) of Cherkasy Oblast (province), near the point where the Rosava River flows into the Ros'. Me ...
that is about 15,000 years old.
* Dots dating to 14,500 BC found on the walls of the
Lascaux
Lascaux ( , ; french: Grotte de Lascaux , "Lascaux Cave") is a network of caves near the village of Montignac, in the department of Dordogne in southwestern France. Over 600 parietal wall paintings cover the interior walls and ceilings of t ...
caves map of part of the night sky, including the three bright stars
Vega
Vega is the brightest star in the northern constellation of Lyra. It has the Bayer designation α Lyrae, which is Latinised to Alpha Lyrae and abbreviated Alpha Lyr or α Lyr. This star is relatively close at only from the Sun, a ...
,
Deneb
Deneb () is a first-magnitude star in the constellation of Cygnus, the swan. Deneb is one of the vertices of the asterism known as the Summer Triangle and the "head" of the Northern Cross. It is the brightest star in Cygnus and the ...
, and
Altair
Altair is the brightest star in the constellation of Aquila and the twelfth-brightest star in the night sky. It has the Bayer designation Alpha Aquilae, which is Latinised from α Aquilae and abbreviated Alpha Aql o ...
(the
Summer Triangle
The Summer Triangle is an astronomical asterism in the northern celestial hemisphere. The defining vertices of this imaginary triangle are at Altair, Deneb, and Vega, each of which is the brightest star of its constellation ( Aquila, Cygnu ...
asterism), as well as the
Pleiades
The Pleiades (), also known as The Seven Sisters, Messier 45 and other names by different cultures, is an asterism and an open star cluster containing middle-aged, hot B-type stars in the north-west of the constellation Taurus. At a distance ...
star cluster. The
Cuevas de El Castillo
The Cueva del Castillo, or Cave of the Castle, is an archaeological site within the complex of the Caves of Monte Castillo, in Puente Viesgo, Cantabria, Spain.
The archaeological stratigraphy has been divided into around 19 layers, depending ...
in Spain that contains a dot map of the
Corona Borealis constellation dating from 12,000 BC.
* A polished chunk of
sandstone
Sandstone is a clastic sedimentary rock composed mainly of sand-sized (0.0625 to 2 mm) silicate grains. Sandstones comprise about 20–25% of all sedimentary rocks.
Most sandstone is composed of quartz or feldspar (both silicat ...
from a cave in Spanish
Navarre
Navarre (; es, Navarra ; eu, Nafarroa ), officially the Chartered Community of Navarre ( es, Comunidad Foral de Navarra, links=no ; eu, Nafarroako Foru Komunitatea, links=no ), is a foral autonomous community and province in northern Spain, ...
, dated to 14,000 BC, that may be symbols for landscape features, such as hills or dwellings,
superimposed on animal etchings. Alternatively, it may also represent a spiritual landscape, or simple incisings.
* Another ancient picture that resembles a map that was created in the late 7th millennium BC in
Çatalhöyük
Çatalhöyük (; also ''Çatal Höyük'' and ''Çatal Hüyük''; from Turkish ''çatal'' "fork" + ''höyük'' "tumulus") is a tell of a very large Neolithic and Chalcolithic proto-city settlement in southern Anatolia, which existed from app ...
,
Anatolia
Anatolia, tr, Anadolu Yarımadası), and the Anatolian plateau, also known as Asia Minor, is a large peninsula in Western Asia and the westernmost protrusion of the Asian continent. It constitutes the major part of modern-day Turkey. The re ...
, modern
Turkey
Turkey ( tr, Türkiye ), officially the Republic of Türkiye ( tr, Türkiye Cumhuriyeti, links=no ), is a transcontinental country located mainly on the Anatolian Peninsula in Western Asia, with a small portion on the Balkan Peninsula ...
. This wall painting may represent a plan of this Neolithic village; however, recent scholarship has questioned the identification of this painting as a map.
* The "Saint-Bélec slab" (2200 to 1600 BC), whose lines and symbols have been argued to represent a cadastral plan of a part of western Brittany.
Ancient Near East

Maps in Ancient
Babylonia
Babylonia (; Akkadian: , ''māt Akkadī'') was an ancient Akkadian-speaking state and cultural area based in the city of Babylon in central-southern Mesopotamia (present-day Iraq and parts of Syria). It emerged as an Amorite-ruled state c ...
were made by using accurate
surveying
Surveying or land surveying is the technique, profession, art, and science of determining the terrestrial two-dimensional or three-dimensional positions of points and the distances and angles between them. A land surveying professional is ...
techniques. For example, a 7.6 × 6.8 cm
clay tablet
In the Ancient Near East, clay tablets (Akkadian ) were used as a writing medium, especially for writing in cuneiform, throughout the Bronze Age and well into the Iron Age.
Cuneiform characters were imprinted on a wet clay tablet with a sty ...
found in 1930 at
Ga-Sur, near contemporary
Kirkuk
Kirkuk ( ar, كركوك, ku, کەرکووک, translit=Kerkûk, , tr, Kerkük) is a city in Iraq, serving as the capital of the Kirkuk Governorate, located north of Baghdad. The city is home to a diverse population of Turkmens, Arabs, Kurds ...
, shows a map of a river valley between two hills.
Cuneiform
Cuneiform is a logo- syllabic script that was used to write several languages of the Ancient Middle East. The script was in active use from the early Bronze Age until the beginning of the Common Era. It is named for the characteristic wedge- ...
inscriptions label the features on the map, including a plot of land described as 354 iku (12 hectares) that was owned by a person called Azala. Most scholars date the tablet to the 25th to 24th century BC. Hills are shown by overlapping semicircles, rivers by lines, and cities by circles. The map also is marked to show the
cardinal directions
The four cardinal directions, or cardinal points, are the four main compass directions: north, east, south, and west, commonly denoted by their initials N, E, S, and W respectively. Relative to north, the directions east, south, and west are at ...
.
An engraved map from the Kassite period (14th–12th centuries BC) of Babylonian history shows walls and buildings in the holy city of
Nippur
Nippur ( Sumerian: ''Nibru'', often logographically recorded as , EN.LÍLKI, "Enlil City;"The Cambridge Ancient History: Prolegomena & Prehistory': Vol. 1, Part 1. Accessed 15 Dec 2010. Akkadian: ''Nibbur'') was an ancient Sumerian city. It was ...
.
The
Babylonian World Map Babylonian may refer to:
* Babylon, a Semitic Akkadian city/state of ancient Mesopotamia founded in 1894 BC
* Babylonia, an ancient Akkadian-speaking Semitic nation-state and cultural region based in central-southern Mesopotamia (present-day Iraq ...
, the earliest surviving map of the world (c. 600 BC), is a symbolic, not a literal representation. It deliberately omits peoples such as the
Persians
The Persians are an Iranian ethnic group who comprise over half of the population of Iran. They share a common cultural system and are native speakers of the Persian language as well as of the languages that are closely related to Persian. ...
and
Egyptians
Egyptians ( arz, المَصرِيُون, translit=al-Maṣriyyūn, ; arz, المَصرِيِين, translit=al-Maṣriyyīn, ; cop, ⲣⲉⲙⲛ̀ⲭⲏⲙⲓ, remenkhēmi) are an ethnic group native to the Nile, Nile Valley in Egypt. Egyptian ...
, who were well known to the Babylonians. The area shown is depicted as a circular shape surrounded by water, which fits the religious image of the world in which the Babylonians believed.
Phoenicia
Phoenicia () was an ancient thalassocratic civilization originating in the Levant region of the eastern Mediterranean, primarily located in modern Lebanon. The territory of the Phoenician city-states extended and shrank throughout their his ...
n sailors made major advances in seafaring and exploration. It is recorded that the first
circumnavigation
Circumnavigation is the complete navigation around an entire island, continent, or astronomical body (e.g. a planet or moon). This article focuses on the circumnavigation of Earth.
The first recorded circumnavigation of the Earth was the ...
of
Africa
Africa is the world's second-largest and second-most populous continent, after Asia in both cases. At about 30.3 million km2 (11.7 million square miles) including adjacent islands, it covers 6% of Earth's total surface area ...
was possibly undertaken by Phoenician explorers employed by Egyptian
pharaoh
Pharaoh (, ; Egyptian: '' pr ꜥꜣ''; cop, , Pǝrro; Biblical Hebrew: ''Parʿō'') is the vernacular term often used by modern authors for the kings of ancient Egypt who ruled as monarchs from the First Dynasty (c. 3150 BC) until th ...
Necho II
Necho II (sometimes Nekau, Neku, Nechoh, or Nikuu; Greek: Νεκώς Β'; ) of Egypt was a king of the 26th Dynasty (610–595 BC), which ruled from Sais. Necho undertook a number of construction projects across his kingdom. In his reign, accord ...
c. 610–595 BC.
In ''The Histories'', written 431–425 BC,
Herodotus
Herodotus ( ; grc, , }; BC) was an ancient Greek historian and geographer from the Greek city of Halicarnassus, part of the Persian Empire (now Bodrum, Turkey) and a later citizen of Thurii in modern Calabria (Italy). He is known fo ...
cast doubt on a report of the Sun observed shining from the north. He stated that the phenomenon was observed by Phoenician explorers during their circumnavigation of Africa (
''The Histories'', 4.42) who claimed to have had the Sun on their right when circumnavigating in a clockwise direction. To modern historians, these details confirm the truth of the Phoenicians' report, and even suggest the possibility that the Phoenicians knew about the
spherical Earth
Spherical Earth or Earth's curvature refers to the approximation of figure of the Earth as a sphere.
The earliest documented mention of the concept dates from around the 5th century BC, when it appears in the writings of Greek philosophers. ...
model. However, nothing certain about their knowledge of geography and navigation has survived.
The historian Dmitri Panchenko theorizes that it was the Phoenician circumnavigation of Africa that inspired the theory of a spherical Earth by the 5th century BC.
Ancient Greece
Many scholars throughout history, such as
Strabo
Strabo''Strabo'' (meaning "squinty", as in strabismus) was a term employed by the Romans for anyone whose eyes were distorted or deformed. The father of Pompey was called " Pompeius Strabo". A native of Sicily so clear-sighted that he could s ...
, Kish, and
Dilke, consider
Homer
Homer (; grc, Ὅμηρος , ''Hómēros'') (born ) was a Greek poet who is credited as the author of the ''Iliad'' and the ''Odyssey'', two epic poems that are foundational works of ancient Greek literature. Homer is considered one of the ...
to be the founder of the early Greek conception of Earth, and therefore of geography.
Homer
Homer (; grc, Ὅμηρος , ''Hómēros'') (born ) was a Greek poet who is credited as the author of the ''Iliad'' and the ''Odyssey'', two epic poems that are foundational works of ancient Greek literature. Homer is considered one of the ...
conceived Earth to be a disk surrounded by a constantly moving
stream of Ocean,
[Brown] an idea which would be suggested by the appearance of the horizon as it is seen from a mountaintop or from a seacoast. This model was accepted by the early
Greeks
The Greeks or Hellenes (; el, Έλληνες, ''Éllines'' ) are an ethnic group and nation indigenous to the Eastern Mediterranean and the Black Sea regions, namely Greece, Cyprus, Albania, Italy, Turkey, Egypt, and, to a lesser extent, ot ...
. Homer and his Greek contemporaries knew very little of the Earth beyond the Libyan desert of
Egypt
Egypt ( ar, مصر , ), officially the Arab Republic of Egypt, is a List of transcontinental countries, transcontinental country spanning the North Africa, northeast corner of Africa and Western Asia, southwest corner of Asia via a land bridg ...
, the south-west coast of
Asia Minor
Anatolia, tr, Anadolu Yarımadası), and the Anatolian plateau, also known as Asia Minor, is a large peninsula in Western Asia and the westernmost protrusion of the Asian continent. It constitutes the major part of modern-day Turkey. The re ...
, and the northern boundary of the Greek homeland. Furthermore, the coast of the Black Sea was only known through myths and legends that circulated during his time. In his poems there is no mention of
Europe
Europe is a large peninsula conventionally considered a continent in its own right because of its great physical size and the weight of its history and traditions. Europe is also considered a Continent#Subcontinents, subcontinent of Eurasia ...
and
Asia
Asia (, ) is one of the world's most notable geographical regions, which is either considered a continent in its own right or a subcontinent of Eurasia, which shares the continental landmass of Afro-Eurasia with Africa. Asia covers an are ...
as geographical concepts. That is why the big part of Homer's world that is portrayed on this interpretive map represents lands that border on the
Aegean Sea
The Aegean Sea ; tr, Ege Denizi ( Greek: Αιγαίο Πέλαγος: "Egéo Pélagos", Turkish: "Ege Denizi" or "Adalar Denizi") is an elongated embayment of the Mediterranean Sea between Europe and Asia. It is located between the Balkans ...
. The Greeks believed that they occupied the central region of Earth and its edges were inhabited by savage, monstrous
barbarians
A barbarian (or savage) is someone who is perceived to be either uncivilized or primitive. The designation is usually applied as a generalization based on a popular stereotype; barbarians can be members of any nation judged by some to be les ...
and strange animals and monsters: Homer's Odyssey mentions a great many of these.
Additional statements about ancient geography are found in
Hesiod
Hesiod (; grc-gre, Ἡσίοδος ''Hēsíodos'') was an ancient Greek poet generally thought to have been active between 750 and 650 BC, around the same time as Homer. He is generally regarded by western authors as 'the first written poet i ...
's poems, probably written during the 8th century BC. Through the lyrics of ''
Works and Days
''Works and Days'' ( grc, Ἔργα καὶ Ἡμέραι, Érga kaì Hēmérai)The ''Works and Days'' is sometimes called by the Latin translation of the title, ''Opera et Dies''. Common abbreviations are ''WD'' and ''Op''. for ''Opera''. is a ...
'' and ''
Theogony
The ''Theogony'' (, , , i.e. "the genealogy or birth of the gods") is a poem by Hesiod (8th–7th century BC) describing the origins and genealogies of the Greek gods, composed . It is written in the Epic dialect of Ancient Greek and contain ...
'', he shows to his contemporaries some definite geographical knowledge. He introduces the names of such rivers as
Nile
The Nile, , Bohairic , lg, Kiira , Nobiin: Áman Dawū is a major north-flowing river in northeastern Africa. It flows into the Mediterranean Sea. The Nile is the longest river in Africa and has historically been considered the longest riv ...
,
Ister Ister, The Ister, or Der Ister may refer to:
*The Danube river, known as the Ister in Ancient Greek (Ἴστρος) and Thracian
*The Dniester river, known as the Ister in Thracian
*"Der Ister", a poem by Friedrich Hölderlin
**''Hölderlin's Hymn " ...
(
Danube
The Danube ( ; ) is a river that was once a long-standing frontier of the Roman Empire and today connects 10 European countries, running through their territories or being a border. Originating in Germany, the Danube flows southeast for , pa ...
), the shores of the
Bosporus
The Bosporus Strait (; grc, Βόσπορος ; tr, İstanbul Boğazı 'Istanbul strait', colloquially ''Boğaz'') or Bosphorus Strait is a natural strait and an internationally significant waterway located in Istanbul in northwestern Tu ...
and the
Euxine
The Black Sea is a marginal mediterranean sea of the Atlantic Ocean lying between Europe and Asia, east of the Balkans, south of the East European Plain, west of the Caucasus, and north of Anatolia. It is bounded by Bulgaria, Georgia ...
(
Black Sea
The Black Sea is a marginal mediterranean sea of the Atlantic Ocean lying between Europe and Asia, east of the Balkans, south of the East European Plain, west of the Caucasus, and north of Anatolia. It is bounded by Bulgaria, Georgia, Rom ...
), the coast of
Gaul
Gaul ( la, Gallia) was a region of Western Europe first described by the Romans. It was inhabited by Celtic and Aquitani tribes, encompassing present-day France, Belgium, Luxembourg, most of Switzerland, parts of Northern Italy (only during ...
, the island of
Sicily
(man) it, Siciliana (woman)
, population_note =
, population_blank1_title =
, population_blank1 =
, demographics_type1 = Ethnicity
, demographics1_footnotes =
, demographi ...
, and a few other regions and rivers. His advanced geographical knowledge not only had predated Greek colonial expansions, but also was used in the earliest Greek world maps, produced by Greek mapmakers such as
Anaximander
Anaximander (; grc-gre, Ἀναξίμανδρος ''Anaximandros''; ) was a pre-Socratic Greek philosopher who lived in Miletus,"Anaximander" in ''Chambers's Encyclopædia''. London: George Newnes, 1961, Vol. 1, p. 403. a city of Ionia (in mo ...
and
Hecataeus of Miletus
Hecataeus of Miletus (; el, Ἑκαταῖος ὁ Μιλήσιος; c. 550 BC – c. 476 BC), son of Hegesander, was an early Greek historian and geographer.
Biography
Hailing from a very wealthy family, he lived in Miletus, then under ...
, and
Ptolemy
Claudius Ptolemy (; grc-gre, Πτολεμαῖος, ; la, Claudius Ptolemaeus; AD) was a mathematician, astronomer, astrologer, geographer, and music theorist, who wrote about a dozen scientific treatises, three of which were of importanc ...
using both observations by explorers and a mathematical approach.
Early steps in the development of intellectual thought in
ancient Greece
Ancient Greece ( el, Ἑλλάς, Hellás) was a northeastern Mediterranean civilization, existing from the Greek Dark Ages of the 12th–9th centuries BC to the end of classical antiquity ( AD 600), that comprised a loose collection of cu ...
belonged to
Ionians
The Ionians (; el, Ἴωνες, ''Íōnes'', singular , ''Íōn'') were one of the four major tribes that the Greeks considered themselves to be divided into during the ancient period; the other three being the Dorians, Aeolians, and Achaea ...
from their well-known city of
Miletus
Miletus (; gr, Μῑ́λητος, Mī́lētos; Hittite transcription ''Millawanda'' or ''Milawata'' ( exonyms); la, Mīlētus; tr, Milet) was an ancient Greek city on the western coast of Anatolia, near the mouth of the Maeander River in ...
in
Asia Minor
Anatolia, tr, Anadolu Yarımadası), and the Anatolian plateau, also known as Asia Minor, is a large peninsula in Western Asia and the westernmost protrusion of the Asian continent. It constitutes the major part of modern-day Turkey. The re ...
. Miletus was placed favourably to absorb aspects of
Babylonia
Babylonia (; Akkadian: , ''māt Akkadī'') was an ancient Akkadian-speaking state and cultural area based in the city of Babylon in central-southern Mesopotamia (present-day Iraq and parts of Syria). It emerged as an Amorite-ruled state c ...
n knowledge and to profit from the expanding commerce of the
Mediterranean
The Mediterranean Sea is a sea connected to the Atlantic Ocean, surrounded by the Mediterranean Basin and almost completely enclosed by land: on the north by Western and Southern Europe and Anatolia, on the south by North Africa, and on ...
. The earliest ancient Greek who is said to have constructed a map of the world is Anaximander of Miletus (c. 611–546 BC), pupil of
Thales
Thales of Miletus ( ; grc-gre, Θαλῆς; ) was a Greek mathematician, astronomer, statesman, and pre-Socratic philosopher from Miletus in Ionia, Asia Minor. He was one of the Seven Sages of Greece. Many, most notably Aristotle, regarded ...
. He believed that the earth was a cylindrical form, a stone pillar suspended in space. The inhabited part of his world was circular, disk-shaped, and presumably located on the upper surface of the cylinder.
[
For constructing his world map, Anaximander is considered by many to be the first mapmaker.][Dilke] Little is known about the map, which has not survived. Hecataeus of Miletus
Hecataeus of Miletus (; el, Ἑκαταῖος ὁ Μιλήσιος; c. 550 BC – c. 476 BC), son of Hegesander, was an early Greek historian and geographer.
Biography
Hailing from a very wealthy family, he lived in Miletus, then under ...
(550–475 BC) produced another map fifty years later that he claimed was an improved version of the map of his illustrious predecessor.
 Hecatæus's map describes the earth as disk with an encircling Ocean, and with Greece placed in the center. This was a very popular contemporary Greek worldview, derived originally from the Homeric poems. Also, similar to many other early maps in antiquity, his map has no scale. As units of measurements, this map used "days of sailing" on the sea and "days of marching" on dry land. The purpose of this map was to accompany Hecatæus's geographical work that was called '' Periodos Ges'', or '' Journey Round the World''.
Hecatæus's map describes the earth as disk with an encircling Ocean, and with Greece placed in the center. This was a very popular contemporary Greek worldview, derived originally from the Homeric poems. Also, similar to many other early maps in antiquity, his map has no scale. As units of measurements, this map used "days of sailing" on the sea and "days of marching" on dry land. The purpose of this map was to accompany Hecatæus's geographical work that was called '' Periodos Ges'', or '' Journey Round the World''.[ ''Periodos Ges'' was divided into two books, "Europe" and "Asia", with the latter including Libya, the name of which was an ancient term for all of known Africa.
The work divides the world into two continents, Asia and Europe. Hecatæus depicts the line between the Pillars of Hercules through the Bosporus, and the Don River as a boundary between the two. He was the first writer known to have thought that the Caspian flows into the encircling ocean—an idea that persisted long into the Hellenic period. He was particularly instructive about the Black Sea, adding many geographic places that already were known to Greeks through the colonization process. To the north of the Danube, according to Hecatæus, were the Rhipæan (gusty) Mountains, beyond which lived the Hyperboreans—peoples of the far north. Hecatæus depicted the origin of the Nile River at the southern encircling ocean. His view of the Nile seems to have been that it came from the southern encircling ocean. This assumption helped Hecatæus propose a solution to the mystery of the annual flooding of the Nile. He believed that the waves of the ocean were a primary cause of this occurrence. A map based on Hecataeus’s was intended to aid political decision-making. According to ]Herodotus
Herodotus ( ; grc, , }; BC) was an ancient Greek historian and geographer from the Greek city of Halicarnassus, part of the Persian Empire (now Bodrum, Turkey) and a later citizen of Thurii in modern Calabria (Italy). He is known fo ...
, that map was engraved into a bronze tablet and was carried to Sparta by Aristagoras during the revolt of the Ionian cities against Persian rule from 499 to 494 BC.
 Anaximenes of Miletus (6th century BC), who studied under Anaximander, rejected the views of his teacher regarding the shape of the earth and instead, he visualized the earth as a rectangular form supported by compressed air.
Anaximenes of Miletus (6th century BC), who studied under Anaximander, rejected the views of his teacher regarding the shape of the earth and instead, he visualized the earth as a rectangular form supported by compressed air.
Pythagoras
Pythagoras of Samos ( grc, Πυθαγόρας ὁ Σάμιος, Pythagóras ho Sámios, Pythagoras the Samian, or simply ; in Ionian Greek; ) was an ancient Ionian Greek philosopher and the eponymous founder of Pythagoreanism. His poli ...
of Samos (c. 560–480 BC) speculated about the notion of a spherical earth with a central fire at its core. He is sometimes incorrectly credited with the introduction of a model that divides a spherical earth into five zones: one hot, two temperate, and two cold—northern and southern. This idea, known as the zonal theory of climate, is more likely to have originated at the time of Aristotle
Aristotle (; grc-gre, Ἀριστοτέλης ''Aristotélēs'', ; 384–322 BC) was a Greek philosopher and polymath during the Classical period in Ancient Greece. Taught by Plato, he was the founder of the Peripatetic school of ...
.
Scylax, a sailor, made a record of his Mediterranean
The Mediterranean Sea is a sea connected to the Atlantic Ocean, surrounded by the Mediterranean Basin and almost completely enclosed by land: on the north by Western and Southern Europe and Anatolia, on the south by North Africa, and on ...
voyages in c. 515 BC. This is the earliest known set of Greek periploi, or sailing instructions, which became the basis for many future mapmakers, especially in the medieval period. Herodotus traveled extensively, collecting information and documenting his findings in his books on Europe, Asia, and Libya. He also combined his knowledge with what he learned from the people he met. Herodotus wrote his ''
Herodotus traveled extensively, collecting information and documenting his findings in his books on Europe, Asia, and Libya. He also combined his knowledge with what he learned from the people he met. Herodotus wrote his ''Histories
Histories or, in Latin, Historiae may refer to:
* the plural of history
* ''Histories'' (Herodotus), by Herodotus
* ''The Histories'', by Timaeus
* ''The Histories'' (Polybius), by Polybius
* ''Histories'' by Gaius Sallustius Crispus (Sallust), ...
'' in the mid-5th century BC. Although his work was dedicated to the story of long struggle of the Greeks with the Persian Empire, Herodotus also included everything he knew about the geography, history, and peoples of the world. Thus, his work provides a detailed picture of the known world of the 5th century BC.
Herodotus rejected the prevailing view of most 5th-century BC maps that the earth is a disk surrounded by Ocean. In his work he describes the earth as an irregular shape with oceans surrounding only Asia and Africa. He introduces names such as the Atlantic Sea, and the Erythrean Sea, which translates as the "Red Sea". He also divided the world into three continents: Europe, Asia, and Africa. He depicted the boundary of Europe as the line from the Pillars of Hercules
The Pillars of Hercules ( la, Columnae Herculis, grc, Ἡράκλειαι Στῆλαι, , ar, أعمدة هرقل, Aʿmidat Hiraql, es, Columnas de Hércules) was the phrase that was applied in Antiquity to the promontories that flank t ...
through the Bosphorus
The Bosporus Strait (; grc, Βόσπορος ; tr, İstanbul Boğazı 'Istanbul strait', colloquially ''Boğaz'') or Bosphorus Strait is a natural strait and an internationally significant waterway located in Istanbul in northwestern Tu ...
and the area between the Caspian Sea
The Caspian Sea is the world's largest inland body of water, often described as the world's largest lake or a full-fledged sea. An endorheic basin, it lies between Europe and Asia; east of the Caucasus, west of the broad steppe of Central A ...
and the Indus River
The Indus ( ) is a transboundary river of Asia and a trans-Himalayan river of South and Central Asia. The river rises in mountain springs northeast of Mount Kailash in Western Tibet, flows northwest through the disputed region of Kashmi ...
. He regarded the Nile
The Nile, , Bohairic , lg, Kiira , Nobiin: Áman Dawū is a major north-flowing river in northeastern Africa. It flows into the Mediterranean Sea. The Nile is the longest river in Africa and has historically been considered the longest riv ...
as the boundary between Asia and Africa. He speculated that the extent of Europe was much greater than was assumed at the time and left Europe's shape to be determined by future research.
In the case of Africa, he believed that, except for the small stretch of land in the vicinity of Suez, the continent was in fact surrounded by water. However, he definitely disagreed with his predecessors and contemporaries about its presumed circular shape. He based his theory on the story of Pharaoh Necho II
Necho II (sometimes Nekau, Neku, Nechoh, or Nikuu; Greek: Νεκώς Β'; ) of Egypt was a king of the 26th Dynasty (610–595 BC), which ruled from Sais. Necho undertook a number of construction projects across his kingdom. In his reign, accord ...
, the ruler of Egypt between 609 and 594 BC, who had sent Phoenicians
Phoenicia () was an ancient thalassocratic civilization originating in the Levant region of the eastern Mediterranean, primarily located in modern Lebanon. The territory of the Phoenician city-states extended and shrank throughout their his ...
to circumnavigate Africa. Apparently, it took them three years, but they certainly did prove his idea. He speculated that the Nile River started as far west as the Ister River (Danube) in Europe and cut Africa through the middle. He was the first writer to assume that the Caspian Sea was separated from other seas and he recognised northern Scythia as one of the coldest inhabited lands in the world.
Similar to his predecessors, Herodotus also made mistakes. He accepted a clear distinction between the civilized Greeks in the center of the earth and the barbarians on the world's edges. In his ''Histories
Histories or, in Latin, Historiae may refer to:
* the plural of history
* ''Histories'' (Herodotus), by Herodotus
* ''The Histories'', by Timaeus
* ''The Histories'' (Polybius), by Polybius
* ''Histories'' by Gaius Sallustius Crispus (Sallust), ...
'' we can see very clearly that he believed that the world became stranger and stranger when one traveled away from Greece, until one reached the ends of the earth, where humans behaved as savages.
While various previous Greek philosophers presumed the earth to be spherical, Aristotle
Aristotle (; grc-gre, Ἀριστοτέλης ''Aristotélēs'', ; 384–322 BC) was a Greek philosopher and polymath during the Classical period in Ancient Greece. Taught by Plato, he was the founder of the Peripatetic school of ...
(384–322 BC) is credited with proving the Earth's sphericity. His arguments may be summarized as follows:
* The lunar eclipse
A lunar eclipse occurs when the Moon moves into the Earth's shadow. Such alignment occurs during an eclipse season, approximately every six months, during the full moon phase, when the Moon's orbital plane is closest to the plane of the Ear ...
is always circular
* Ships seem to sink as they move away from view and pass the horizon
* Some stars can be seen only from certain parts of the Earth.
Hellenistic Mediterranean
A vital contribution to mapping the reality of the world came with a scientific estimate of the circumference of the earth. This event has been described as the first scientific attempt to give geographical studies a mathematical basis. The man credited for this achievement was Eratosthenes
Eratosthenes of Cyrene (; grc-gre, Ἐρατοσθένης ; – ) was a Greek polymath: a mathematician, geographer, poet, astronomer, and music theorist. He was a man of learning, becoming the chief librarian at the Library of Alexandr ...
(275–195 BC), a Greek scholar who lived in Hellenistic
In Classical antiquity, the Hellenistic period covers the time in Mediterranean history after Classical Greece, between the death of Alexander the Great in 323 BC and the emergence of the Roman Empire, as signified by the Battle of Actium in ...
North Africa
North Africa, or Northern Africa is a region encompassing the northern portion of the African continent. There is no singularly accepted scope for the region, and it is sometimes defined as stretching from the Atlantic shores of Mauritania in ...
. As described by George Sarton
George Alfred Leon Sarton (; 31 August 1884 – 22 March 1956) was a Belgian-born American chemist and historian. He is considered the founder of the discipline of the history of science as an independent field of study. His most influential work ...
, historian of science, "there was among them ratosthenes's contemporariesa man of genius but as he was working in a new field they were too stupid to recognize him". His work, including ''On the Measurement of the Earth'' and ''Geographica
The ''Geographica'' (Ancient Greek: Γεωγραφικά ''Geōgraphiká''), or ''Geography'', is an encyclopedia of geographical knowledge, consisting of 17 'books', written in Greek and attributed to Strabo, an educated citizen of the Roman ...
'', has only survived in the writings of later philosophers such as Cleomedes
Cleomedes ( el, Κλεομήδης) was a Greek astronomer who is known chiefly for his book ''On the Circular Motions of the Celestial Bodies'' (Κυκλικὴ θεωρία μετεώρων), also known as ''The Heavens'' ( la, Caelestia).
Pl ...
and Strabo
Strabo''Strabo'' (meaning "squinty", as in strabismus) was a term employed by the Romans for anyone whose eyes were distorted or deformed. The father of Pompey was called " Pompeius Strabo". A native of Sicily so clear-sighted that he could s ...
. He was a devoted geographer who set out to reform and perfect the map of the world. Eratosthenes argued that accurate mapping, even if in two dimensions only, depends upon the establishment of accurate linear measurements. He was the first to calculate the Earth's circumference
Earth's circumference is the distance around Earth. Measured around the Equator, it is . Measured around the poles, the circumference is .
Measurement of Earth's circumference has been important to navigation since ancient times. The first k ...
(within 0.5 percent accuracy).Parmenides
Parmenides of Elea (; grc-gre, Παρμενίδης ὁ Ἐλεάτης; ) was a pre-Socratic Greek philosopher from Elea in Magna Graecia.
Parmenides was born in the Greek colony of Elea, from a wealthy and illustrious family. His date ...
: a torrid zone across the middle, two frigid zones at extreme north and south, and two temperate bands in between.geography
Geography (from Greek: , ''geographia''. Combination of Greek words ‘Geo’ (The Earth) and ‘Graphien’ (to describe), literally "earth description") is a field of science devoted to the study of the lands, features, inhabitants, an ...
".
Roman Empire
Pomponius Mela

Pomponius Mela
Pomponius Mela, who wrote around AD 43, was the earliest Roman geographer. He was born in Tingentera (now Algeciras) and died AD 45.
His short work (''De situ orbis libri III.'') remained in use nearly to the year 1500. It occupies less ...
is unique among ancient geographers in that, after dividing the earth into five zones, of which two only were habitable, he asserts the existence of antichthones
Antichthones, in geography, are those peoples who inhabit the antipodes, regions on opposite sides of the Earth. The word is compounded of the Greek ''ὰντὶ'' ("opposed") and ''χθών'' ("earth").
Classical and Medieval Europe consider ...
, inhabiting the southern temperate zone inaccessible to the folk of the northern temperate regions from the unbearable heat of the intervening torrid belt. On the divisions and boundaries of Europe
Europe is a large peninsula conventionally considered a continent in its own right because of its great physical size and the weight of its history and traditions. Europe is also considered a Continent#Subcontinents, subcontinent of Eurasia ...
, Asia
Asia (, ) is one of the world's most notable geographical regions, which is either considered a continent in its own right or a subcontinent of Eurasia, which shares the continental landmass of Afro-Eurasia with Africa. Asia covers an are ...
and Africa
Africa is the world's second-largest and second-most populous continent, after Asia in both cases. At about 30.3 million km2 (11.7 million square miles) including adjacent islands, it covers 6% of Earth's total surface area ...
, he repeats Eratosthenes; like all classical geographers from Alexander the Great
Alexander III of Macedon ( grc, Ἀλέξανδρος, Alexandros; 20/21 July 356 BC – 10/11 June 323 BC), commonly known as Alexander the Great, was a king of the ancient Greek kingdom of Macedon. He succeeded his father Philip II to ...
(except Ptolemy
Claudius Ptolemy (; grc-gre, Πτολεμαῖος, ; la, Claudius Ptolemaeus; AD) was a mathematician, astronomer, astrologer, geographer, and music theorist, who wrote about a dozen scientific treatises, three of which were of importanc ...
) he regards the Caspian Sea
The Caspian Sea is the world's largest inland body of water, often described as the world's largest lake or a full-fledged sea. An endorheic basin, it lies between Europe and Asia; east of the Caucasus, west of the broad steppe of Central A ...
as an inlet of the Northern Ocean, corresponding to the Persian Gulf
The Persian Gulf ( fa, خلیج فارس, translit=xalij-e fârs, lit=Gulf of Fars, ), sometimes called the ( ar, اَلْخَلِيْجُ ٱلْعَرَبِيُّ, Al-Khalīj al-ˁArabī), is a mediterranean sea in Western Asia. The bo ...
and the Red Sea
The Red Sea ( ar, البحر الأحمر - بحر القلزم, translit=Modern: al-Baḥr al-ʾAḥmar, Medieval: Baḥr al-Qulzum; or ; Coptic: ⲫⲓⲟⲙ ⲛ̀ϩⲁϩ ''Phiom Enhah'' or ⲫⲓⲟⲙ ⲛ̀ϣⲁⲣⲓ ''Phiom ǹšari''; ...
on the south.
Marinus of Tyre
Marinus of Tyre
Marinus of Tyre ( grc-gre, Μαρῖνος ὁ Τύριος, ''Marînos ho Týrios''; 70–130) was a Greek geographer, cartographer and mathematician, who founded mathematical geography and provided the underpinnings of Claudius Ptolemy' ...
was a Hellenized
Hellenization (other British spelling Hellenisation) or Hellenism is the adoption of Greek culture, religion, language and identity by non-Greeks. In the ancient period, colonization often led to the Hellenization of indigenous peoples; in th ...
Phoenician geographer and cartographer. He founded mathematical geography and provided the underpinnings of Ptolemy
Claudius Ptolemy (; grc-gre, Πτολεμαῖος, ; la, Claudius Ptolemaeus; AD) was a mathematician, astronomer, astrologer, geographer, and music theorist, who wrote about a dozen scientific treatises, three of which were of importanc ...
's influential ''Geographia
The ''Geography'' ( grc-gre, Γεωγραφικὴ Ὑφήγησις, ''Geōgraphikḕ Hyphḗgēsis'', "Geographical Guidance"), also known by its Latin names as the ' and the ', is a gazetteer, an atlas, and a treatise on cartography, com ...
''.
Marinus's geographical treatise is lost and known only from Ptolemy's remarks. He introduced improvements to the construction of maps and developed a system of nautical charts. His chief legacy is that he first assigned to each place a proper latitude
In geography, latitude is a coordinate that specifies the north– south position of a point on the surface of the Earth or another celestial body. Latitude is given as an angle that ranges from –90° at the south pole to 90° at the north ...
and longitude
Longitude (, ) is a geographic coordinate that specifies the east– west position of a point on the surface of the Earth, or another celestial body. It is an angular measurement, usually expressed in degrees and denoted by the Greek let ...
. His zero meridian ran through the westernmost land known to him, the Isles of the Blessed
The Fortunate Isles or Isles of the Blessed ( grc, μακάρων νῆσοι, ''makárōn nêsoi'') were semi-legendary islands in the Atlantic Ocean, variously treated as a simple geographical location and as a winterless earthly paradise inhabit ...
around the location of the Canary
Canary originally referred to the island of Gran Canaria on the west coast of Africa, and the group of surrounding islands (the Canary Islands). It may also refer to:
Animals Birds
* Canaries, birds in the genera '' Serinus'' and ''Crithagra'' ...
or Cape Verde Islands
, national_anthem = ()
, official_languages = Portuguese
, national_languages = Cape Verdean Creole
, capital = Praia
, coordinates =
, largest_city = capital
, demonym ...
. He used the parallel of Rhodes
Rhodes (; el, Ρόδος , translit=Ródos ) is the largest and the historical capital of the Dodecanese islands of Greece. Administratively, the island forms a separate municipality within the Rhodes regional unit, which is part of the S ...
for measurements of latitude. Ptolemy mentions several revisions of Marinus's geographical work, which is often dated to AD 114 although this is uncertain. Marinus estimated a length of 180,000 stadia for the equator, roughly corresponding to a circumference of the Earth of 33,300 km, about 17% less than the actual value.
He also carefully studied the works of his predecessors and the diaries of travelers. His maps were the first in the Roman Empire
The Roman Empire ( la, Imperium Romanum ; grc-gre, Βασιλεία τῶν Ῥωμαίων, Basileía tôn Rhōmaíōn) was the post-Roman Republic, Republican period of ancient Rome. As a polity, it included large territorial holdings aro ...
to show China
China, officially the People's Republic of China (PRC), is a country in East Asia. It is the world's List of countries and dependencies by population, most populous country, with a Population of China, population exceeding 1.4 billion, slig ...
. He also invented equirectangular projection
The equirectangular projection (also called the equidistant cylindrical projection or la carte parallélogrammatique projection), and which includes the special case of the plate carrée projection (also called the geographic projection, lat/lon ...
, which is still used in map creation today. A few of Marinus's opinions are reported by Ptolemy. Marinus was of the opinion that the World Ocean
The ocean (also the sea or the world ocean) is the body of salt water that covers approximately 70.8% of the surface of Earth and contains 97% of Earth's water. An ocean can also refer to any of the large bodies of water into which the worl ...
was separated into an eastern and a western part by the continents of Europe
Europe is a large peninsula conventionally considered a continent in its own right because of its great physical size and the weight of its history and traditions. Europe is also considered a Continent#Subcontinents, subcontinent of Eurasia ...
, Asia
Asia (, ) is one of the world's most notable geographical regions, which is either considered a continent in its own right or a subcontinent of Eurasia, which shares the continental landmass of Afro-Eurasia with Africa. Asia covers an are ...
and Africa
Africa is the world's second-largest and second-most populous continent, after Asia in both cases. At about 30.3 million km2 (11.7 million square miles) including adjacent islands, it covers 6% of Earth's total surface area ...
. He thought that the inhabited world stretched in latitude from Thule
Thule ( grc-gre, Θούλη, Thoúlē; la, Thūlē) is the most northerly location mentioned in ancient Greek and Roman literature and cartography. Modern interpretations have included Orkney, Shetland, northern Scotland, the island of Saar ...
(Norway
Norway, officially the Kingdom of Norway, is a Nordic countries, Nordic country in Northern Europe, the mainland territory of which comprises the western and northernmost portion of the Scandinavian Peninsula. The remote Arctic island of ...
) to Agisymba Agisymba was an unidentified country in Africa mentioned by Ptolemy in the middle of the 2nd century AD.
According to Ptolemy's writings, Agisymba was found a four months' journey south of Fezzan and was characterized by large animals, such as ...
(around the Tropic of Capricorn
The Tropic of Capricorn (or the Southern Tropic) is the circle of latitude that contains the subsolar point at the December (or southern) solstice. It is thus the southernmost latitude where the Sun can be seen directly overhead. It also reac ...
) and in longitude from the Isles of the Blessed
The Fortunate Isles or Isles of the Blessed ( grc, μακάρων νῆσοι, ''makárōn nêsoi'') were semi-legendary islands in the Atlantic Ocean, variously treated as a simple geographical location and as a winterless earthly paradise inhabit ...
(around the Canaries) to Shera (China
China, officially the People's Republic of China (PRC), is a country in East Asia. It is the world's List of countries and dependencies by population, most populous country, with a Population of China, population exceeding 1.4 billion, slig ...
). Marinus also coined the term Antarctic
The Antarctic ( or , American English also or ; commonly ) is a polar region around Earth's South Pole, opposite the Arctic region around the North Pole. The Antarctic comprises the continent of Antarctica, the Kerguelen Plateau and othe ...
, referring to the opposite of the Arctic Circle
The Arctic Circle is one of the two polar circles, and the most northerly of the five major circles of latitude as shown on maps of Earth. Its southern equivalent is the Antarctic Circle.
The Arctic Circle marks the southernmost latitude at ...
.
Ptolemy
Ptolemy
Claudius Ptolemy (; grc-gre, Πτολεμαῖος, ; la, Claudius Ptolemaeus; AD) was a mathematician, astronomer, astrologer, geographer, and music theorist, who wrote about a dozen scientific treatises, three of which were of importanc ...
(90–168), a Hellenized Egyptian,George Sarton
George Alfred Leon Sarton (; 31 August 1884 – 22 March 1956) was a Belgian-born American chemist and historian. He is considered the founder of the discipline of the history of science as an independent field of study. His most influential work ...
(1936). "The Unity and Diversity of the Mediterranean World", ''Osiris'' 2, p. 406–463 29perspective projection
Linear or point-projection perspective (from la, perspicere 'to see through') is one of two types of graphical projection perspective in the graphic arts; the other is parallel projection. Linear perspective is an approximate representation ...
, and suggested precise methods for fixing the position of geographic features on its surface using a coordinate system
In geometry, a coordinate system is a system that uses one or more numbers, or coordinates, to uniquely determine the position of the points or other geometric elements on a manifold such as Euclidean space. The order of the coordinates is sig ...
with parallels of latitude
In geography, latitude is a coordinate that specifies the north– south position of a point on the surface of the Earth or another celestial body. Latitude is given as an angle that ranges from –90° at the south pole to 90° at the north ...
and meridians of longitude
Longitude (, ) is a geographic coordinate that specifies the east– west position of a point on the surface of the Earth, or another celestial body. It is an angular measurement, usually expressed in degrees and denoted by the Greek let ...
.Geographia
The ''Geography'' ( grc-gre, Γεωγραφικὴ Ὑφήγησις, ''Geōgraphikḕ Hyphḗgēsis'', "Geographical Guidance"), also known by its Latin names as the ' and the ', is a gazetteer, an atlas, and a treatise on cartography, com ...
'' is a prototype of modern mapping and GIS. It included an index of place-names, with the latitude and longitude of each place to guide the search, scale, conventional signs with legends, and the practice of orienting maps so that north is at the top and east to the right of the map—an almost universal custom today.
Yet with all his important innovations, however, Ptolemy was not infallible. His most important error was a miscalculation of the circumference of the earth. He believed that Eurasia
Eurasia (, ) is the largest continental area on Earth, comprising all of Europe and Asia. Primarily in the Northern and Eastern Hemispheres, it spans from the British Isles and the Iberian Peninsula in the west to the Japanese archipelag ...
covered 180° of the globe, which convinced Christopher Columbus
Christopher Columbus
* lij, Cristoffa C(or)ombo
* es, link=no, Cristóbal Colón
* pt, Cristóvão Colombo
* ca, Cristòfor (or )
* la, Christophorus Columbus. (; born between 25 August and 31 October 1451, died 20 May 1506) was a ...
to sail across the Atlantic to look for a simpler and faster way to travel to India. Had Columbus known that the true figure was much greater, it is conceivable that he would never have set out on his momentous voyage.
''Tabula Peutingeriana''
 In 2007, the ''
In 2007, the ''Tabula Peutingeriana
' (Latin for "The Peutinger Map"), also referred to as Peutinger's Tabula or Peutinger Table, is an illustrated ' (ancient Roman road map) showing the layout of the '' cursus publicus'', the road network of the Roman Empire.
The map is a 13th-ce ...
'', a 12th-century replica of a 5th-century road map, was placed on the UNESCO Memory of the World Register and displayed to the public for the first time. Although the scroll is well preserved and believed to be an accurate copy of an authentic original, it is on media that is now so delicate that it must be protected at all times from exposure to daylight.
China
The earliest known maps to have survived in China date to the 4th century BC.Gansu
Gansu (, ; alternately romanized as Kansu) is a province in Northwest China. Its capital and largest city is Lanzhou, in the southeast part of the province.
The seventh-largest administrative district by area at , Gansu lies between the Tibe ...
province.silk
Silk is a natural protein fiber, some forms of which can be woven into textiles. The protein fiber of silk is composed mainly of fibroin and is produced by certain insect larvae to form cocoons. The best-known silk is obtained from th ...
dated to the 2nd century BC in the early Han dynasty
The Han dynasty (, ; ) was an Dynasties in Chinese history, imperial dynasty of China (202 BC – 9 AD, 25–220 AD), established by Emperor Gaozu of Han, Liu Bang (Emperor Gao) and ruled by the House of Liu. The dynasty was preceded by th ...
.Jialing River
The Jialing River, formerly known by numerous other names, is a major tributary of the Yangtze River in the Sichuan Basin. It is named after the Jialing Valley in Feng County, Shaanxi through which it flows.
The Jialing River's most notable ...
in Sichuan
Sichuan (; zh, c=, labels=no, ; zh, p=Sìchuān; alternatively romanized as Szechuan or Szechwan; formerly also referred to as "West China" or "Western China" by Protestant missions) is a province in Southwest China occupying most of t ...
province, in a total measured area of 107 by 68 km.Strabo
Strabo''Strabo'' (meaning "squinty", as in strabismus) was a term employed by the Romans for anyone whose eyes were distorted or deformed. The father of Pompey was called " Pompeius Strabo". A native of Sicily so clear-sighted that he could s ...
's economic maps.Western Han
The Han dynasty (, ; ) was an imperial dynasty of China (202 BC – 9 AD, 25–220 AD), established by Liu Bang (Emperor Gao) and ruled by the House of Liu. The dynasty was preceded by the short-lived Qin dynasty (221–207 BC) and a war ...
, so the map dates to the early 2nd century BC. The map shows topographic features such as mountains, waterways and roads, and is thought to cover the area of the preceding Qin Kingdom.
Earliest geographical writing
In China
China, officially the People's Republic of China (PRC), is a country in East Asia. It is the world's List of countries and dependencies by population, most populous country, with a Population of China, population exceeding 1.4 billion, slig ...
, the earliest known geographical Chinese writing dates back to the 5th century BC, during the beginning of the Warring States
The Warring States period () was an era in ancient Chinese history characterized by warfare, as well as bureaucratic and military reforms and consolidation. It followed the Spring and Autumn period and concluded with the Qin wars of conquest ...
(481–221 BC).Yu Gong
The ''Yu Gong'' () or ''Tribute of Yu'' is a chapter of the ''Book of Xia'' (夏書/夏书) section of the ''Book of Documents'', one of the Five Classics of ancient Chinese literature. The chapter describes the legendary Yu the Great and the ...
'' or ''Tribute of Yu'' chapter of the ''Shu Jing'' or ''Book of Documents
The ''Book of Documents'' (''Shūjīng'', earlier ''Shu King'') or ''Classic of History'', also known as the ''Shangshu'' (“Venerated Documents”), is one of the Five Classics of ancient Chinese literature. It is a collection of rhetoric ...
''. The book describes the traditional nine provinces, their kinds of soil, their characteristic products and economic goods, their tributary goods, their trades and vocations, their state revenues and agricultural systems, and the various rivers and lakes listed and placed accordingly.Yellow River
The Yellow River or Huang He (Chinese: , Mandarin: ''Huáng hé'' ) is the second-longest river in China, after the Yangtze River, and the sixth-longest river system in the world at the estimated length of . Originating in the Bayan Ha ...
, the lower valleys of the Yangzi, with the plain between them and the Shandong Peninsula
The Shandong (Shantung) Peninsula or Jiaodong (Chiaotung) Peninsula is a peninsula in Shandong Province in eastern China, between the Bohai Sea to the north and the Yellow Sea to the south. The latter name refers to the east and Jiaozhou.
Geo ...
, and to the west the most northern parts of the Wei River
The Wei River () is a major river in west-central China's Gansu and Shaanxi provinces. It is the largest tributary of the Yellow River and very important in the early development of Chinese civilization.
The source of the Wei River is close to ...
and the Han River were known (along with the southern parts of modern-day Shanxi
Shanxi (; ; formerly romanised as Shansi) is a landlocked province of the People's Republic of China and is part of the North China region. The capital and largest city of the province is Taiyuan, while its next most populated prefecture-leve ...
province).
Earliest known reference to a map (圖 tú)
The oldest reference to a map in China comes from the 3rd century BC.Jing Ke
Jing Ke (died 227 BC) was a ''youxia'' during the late Warring States period of Ancient China. As a retainer of Crown Prince Dan of the Yan state, he was infamous for his failed assassination attempt on King Zheng of the Qin state, who later beca ...
visit the court of the ruler of the State of Qin
Qin () was an ancient Chinese state during the Zhou dynasty. Traditionally dated to 897 BC, it took its origin in a reconquest of western lands previously lost to the Rong; its position at the western edge of Chinese civilization permitted e ...
, who would become the first leader to unify China, Qin Shi Huang
Qin Shi Huang (, ; 259–210 BC) was the founder of the Qin dynasty and the first emperor of a unified China. Rather than maintain the title of " king" ( ''wáng'') borne by the previous Shang and Zhou rulers, he ruled as the First Empero ...
(r. 221–210 BC). Jing Ke was to present the ruler of Qin with a district map painted on a silk scroll, rolled up and held in a case where he hid his assassin's dagger.
Han dynasty
 The three Han dynasty maps found at
The three Han dynasty maps found at Mawangdui
Mawangdui () is an archaeological site located in Changsha, China. The site consists of two saddle-shaped hills and contained the tombs of three people from the Changsha Kingdom during the western Han dynasty (206 BC – 9 AD): the Chancellor Li ...
differ from the earlier Qin State maps. While the Qin maps place the cardinal direction
The four cardinal directions, or cardinal points, are the four main compass directions: north, east, south, and west, commonly denoted by their initials N, E, S, and W respectively. Relative to north, the directions east, south, and west are ...
of north at the top of the map, the Han maps are orientated with the southern direction at the top.Pei Xiu
Pei Xiu (224–271), courtesy name Jiyan, was a Chinese cartographer, geographer, politician, and writer of the state of Cao Wei during the late Three Kingdoms period and Jin dynasty of China. He was very much trusted by Sima Zhao, and ...
below).Nanyue
Nanyue (), was an ancient kingdom ruled by Chinese monarchs of the Zhao family that covered the modern Chinese subdivisions of Guangdong, Guangxi, Hainan, Hong Kong, Macau, southern Fujian and central to northern Vietnam. Nanyue was establis ...
kingdom (of northern Vietnam
Vietnam or Viet Nam ( vi, Việt Nam, ), officially the Socialist Republic of Vietnam,., group="n" is a country in Southeast Asia, at the eastern edge of mainland Southeast Asia, with an area of and population of 96 million, making ...
and parts of modern Guangdong
Guangdong (, ), alternatively romanized as Canton or Kwangtung, is a coastal province in South China on the north shore of the South China Sea. The capital of the province is Guangzhou. With a population of 126.01 million (as of 2020 ...
and Guangxi
Guangxi (; ; alternately romanized as Kwanghsi; ; za, Gvangjsih, italics=yes), officially the Guangxi Zhuang Autonomous Region (GZAR), is an autonomous region of the People's Republic of China, located in South China and bordering Vietnam ...
), and a map which marks the positions of Han military garrisons that were employed in an attack against Nanyue in 181 BC.
An early text that mentioned maps was the ''Rites of Zhou
The ''Rites of Zhou'' (), originally known as "Officers of Zhou" () is a work on bureaucracy and organizational theory. It was renamed by Liu Xin to differentiate it from a chapter in the '' Book of History'' by the same name. To replace a lost ...
''.Zhou dynasty
The Zhou dynasty ( ; Old Chinese ( B&S): *''tiw'') was a royal dynasty of China that followed the Shang dynasty. Having lasted 789 years, the Zhou dynasty was the longest dynastic regime in Chinese history. The military control of China by th ...
, its first recorded appearance was in the libraries of Prince Liu De (c. 130 BC), and was compiled and commented on by Liu Xin in the 1st century AD. It outlined the use of maps that were made for governmental provinces and districts, principalities, frontier boundaries, and even pinpointed locations of ores and minerals for mining
Mining is the extraction of valuable minerals or other geological materials from the Earth, usually from an ore body, lode, vein, seam, reef, or placer deposit. The exploitation of these deposits for raw material is based on the econom ...
facilities.Emperor Wu of Han
Emperor Wu of Han (156 – 29 March 87BC), formally enshrined as Emperor Wu the Filial (), born Liu Che (劉徹) and courtesy name Tong (通), was the seventh emperor of the Han dynasty of ancient China, ruling from 141 to 87 BC. His reign last ...
had maps of the entire empire submitted to him.Liu An
Liú Ān (, c. 179–122 BC) was a Han dynasty Chinese prince, ruling the Huainan Kingdom, and an advisor to his nephew, Emperor Wu of Han (武帝). He is best known for editing the (139 BC) '' Huainanzi'' compendium of Daoist, Confucianist, a ...
in 139 BC during the Han dynasty
The Han dynasty (, ; ) was an Dynasties in Chinese history, imperial dynasty of China (202 BC – 9 AD, 25–220 AD), established by Emperor Gaozu of Han, Liu Bang (Emperor Gao) and ruled by the House of Liu. The dynasty was preceded by th ...
(202 BC–202 AD). The chapter gave general descriptions of topography
Topography is the study of the forms and features of land surfaces. The topography of an area may refer to the land forms and features themselves, or a description or depiction in maps.
Topography is a field of geoscience and planetary sc ...
in a systematic fashion, given visual aids by the use of maps (di tu) due to the efforts of Liu An and his associate Zuo Wu.Sichuan
Sichuan (; zh, c=, labels=no, ; zh, p=Sìchuān; alternatively romanized as Szechuan or Szechwan; formerly also referred to as "West China" or "Western China" by Protestant missions) is a province in Southwest China occupying most of t ...
mentioned above, became a widespread tradition of Chinese geographical works by the 6th century, as noted in the bibliography of the ''Sui Shu''.Southern and Northern Dynasties
The Northern and Southern dynasties () was a period of political division in the history of China that lasted from 420 to 589, following the tumultuous era of the Sixteen Kingdoms and the Eastern Jin dynasty. It is sometimes considered as ...
that the Liang dynasty
The Liang dynasty (), alternatively known as the Southern Liang () in historiography, was an imperial dynasty of China and the third of the four Southern dynasties during the Northern and Southern dynasties period. It was preceded by the South ...
(502–557) cartographers also began carving maps into stone steles (alongside the maps already drawn and painted on paper and silk).
Pei Xiu, the 'Ptolemy of China'
In the year 267, Pei Xiu
Pei Xiu (224–271), courtesy name Jiyan, was a Chinese cartographer, geographer, politician, and writer of the state of Cao Wei during the late Three Kingdoms period and Jin dynasty of China. He was very much trusted by Sima Zhao, and ...
(224–271) was appointed as the Minister of Works by Emperor Wu of Jin
Emperor Wu of Jin (; 236 – 16 May 290), personal name Sima Yan (), courtesy name Anshi (安世), was the grandson of Sima Yi, nephew of Sima Shi and son of Sima Zhao. He became the first emperor of the Jin dynasty after forcing Cao Huan, ...
, the first emperor of the Jin dynasty. Pei is best known for his work in cartography. Although map making and use of the grid existed in China before him,Zhang Heng
Zhang Heng (; AD 78–139), formerly romanized as Chang Heng, was a Chinese polymathic scientist and statesman who lived during the Han dynasty. Educated in the capital cities of Luoyang and Chang'an, he achieved success as an astronomer, mat ...
(78–139) are somewhat vague and sketchy, there is ample written evidence that Pei Xiu derived the use of the rectangular grid reference from the maps of Zhang Heng.Mawangdui
Mawangdui () is an archaeological site located in Changsha, China. The site consists of two saddle-shaped hills and contained the tombs of three people from the Changsha Kingdom during the western Han dynasty (206 BC – 9 AD): the Chancellor Li ...
maps of the Han era were far superior in quality than those examined by Pei Xiu.elevation
The elevation of a geographic location is its height above or below a fixed reference point, most commonly a reference geoid, a mathematical model of the Earth's sea level as an equipotential gravitational surface (see Geodetic datum § ...
on maps.
Sui dynasty
In the year 605, during the Sui dynasty
The Sui dynasty (, ) was a short-lived imperial dynasty of China that lasted from 581 to 618. The Sui unified the Northern and Southern dynasties, thus ending the long period of division following the fall of the Western Jin dynasty, and la ...
(581–618), the Commercial Commissioner Pei Ju (547–627) created a famous geometrically gridded map.Emperor Yang of Sui
Emperor Yang of Sui (隋煬帝, 569 – 11 April 618), personal name Yang Guang (), alternative name Ying (), Xianbei name Amo (), also known as Emperor Ming of Sui () during the brief reign of his grandson Yang Tong, was the second emperor ...
ordered government officials from throughout the empire to document in gazetteer
A gazetteer is a geographical index or directory used in conjunction with a map or atlas.Aurousseau, 61. It typically contains information concerning the geographical makeup, social statistics and physical features of a country, region, or con ...
s the customs, products, and geographical features of their local areas and provinces, providing descriptive writing and drawing them all onto separate maps, which would be sent to the imperial secretariat in the capital city.
Tang dynasty
The Tang dynasty
The Tang dynasty (, ; zh, t= ), or Tang Empire, was an Dynasties in Chinese history, imperial dynasty of China that ruled from 618 to 907 AD, with an Zhou dynasty (690–705), interregnum between 690 and 705. It was preceded by the Sui dyn ...
(618–907) also had its fair share of cartographers, including the works of Xu Jingzong
Xu Jingzong (592 – September 20, 672), courtesy name Yanzu, posthumously known as Duke Gong of Gaoyang, was a Chinese cartographer, historian, and politician who served as a chancellor in the Tang dynasty. Allied with Emperor Gaozong's power ...
in 658, Wang Mingyuan in 661, and Wang Zhongsi in 747.Emperor Dezong of Tang
Emperor Dezong of Tang (27 May 742According to Li Kuo's biography in the ''Old Book of Tang'', he was born on the ''guisi'' day in the 4th month of the 1st year of the Tianbao era of Tang Xuanzong's reign. This date corresponds to 27 May 742 in ...
entrusted in 785 to complete a map of China with her recently former inland colonies of Central Asia, the massive and detailed work completed in 801, called the ''Hai Nei Hua Yi Tu'' (Map of both Chinese and Barbarian Peoples within the (Four) Seas).li (unit)
''Li'' (, ''lǐ'', or , ''shìlǐ''), also known as the Chinese mile, is a traditional Chinese unit of distance. The li has varied considerably over time but was usually about one third of an English mile and now has a standardized length of a ...
(the Chinese equivalent of the mile/kilometer).Persian Gulf
The Persian Gulf ( fa, خلیج فارس, translit=xalij-e fârs, lit=Gulf of Fars, ), sometimes called the ( ar, اَلْخَلِيْجُ ٱلْعَرَبِيُّ, Al-Khalīj al-ˁArabī), is a mediterranean sea in Western Asia. The bo ...
region with great detail, along with lighthouses that were erected at the mouth of the Persian Gulf by the medieval Iran
Iran, officially the Islamic Republic of Iran, and also called Persia, is a country located in Western Asia. It is bordered by Iraq and Turkey to the west, by Azerbaijan and Armenia to the northwest, by the Caspian Sea and Turkmeni ...
ians in the Abbasid
The Abbasid Caliphate ( or ; ar, الْخِلَافَةُ الْعَبَّاسِيَّة, ') was the third caliphate to succeed the Islamic prophet Muhammad. It was founded by a dynasty descended from Muhammad's uncle, Abbas ibn Abdul-Mutta ...
period (refer to article on Tang dynasty
The Tang dynasty (, ; zh, t= ), or Tang Empire, was an Dynasties in Chinese history, imperial dynasty of China that ruled from 618 to 907 AD, with an Zhou dynasty (690–705), interregnum between 690 and 705. It was preceded by the Sui dyn ...
for more).
Song dynasty
 During the
During the Song dynasty
The Song dynasty (; ; 960–1279) was an imperial dynasty of China that began in 960 and lasted until 1279. The dynasty was founded by Emperor Taizu of Song following his usurpation of the throne of the Later Zhou. The Song conquered the res ...
(960–1279) Emperor Taizu of Song
Emperor Taizu of Song (21 March 927 – 14 November 976), personal name Zhao Kuangyin, courtesy name Yuanlang, was the founder and first emperor of the Song dynasty of China. He reigned from 960 until his death in 976. Formerly a distinguish ...
ordered Lu Duosun in 971 to update and 're-write all the Tu Jing in the world', which would seem to be a daunting task for one individual, who was sent out throughout the provinces to collect texts and as much data as possible.polymath
A polymath ( el, πολυμαθής, , "having learned much"; la, homo universalis, "universal human") is an individual whose knowledge spans a substantial number of subjects, known to draw on complex bodies of knowledge to solve specific pro ...
statesman Shen Kuo
Shen Kuo (; 1031–1095) or Shen Gua, courtesy name Cunzhong (存中) and pseudonym Mengqi (now usually given as Mengxi) Weng (夢溪翁),Yao (2003), 544. was a Chinese polymathic scientist and statesman of the Song dynasty (960–1279). Shen wa ...
(1031–1095) was also a geographer and cartographer.atlas
An atlas is a collection of maps; it is typically a bundle of maps of Earth or of a region of Earth.
Atlases have traditionally been bound into book form, but today many atlases are in multimedia formats. In addition to presenting geogra ...
included twenty three maps of China and foreign regions that were drawn at a uniform scale of 1:900,000.three-dimensional
Three-dimensional space (also: 3D space, 3-space or, rarely, tri-dimensional space) is a geometric setting in which three values (called '' parameters'') are required to determine the position of an element (i.e., point). This is the inform ...
raised-relief map using sawdust, wood, beeswax, and wheat paste, while representing the topography and specific locations of a frontier region to the imperial court.Liao dynasty
The Liao dynasty (; Khitan: ''Mos Jælud''; ), also known as the Khitan Empire (Khitan: ''Mos diau-d kitai huldʒi gur''), officially the Great Liao (), was an imperial dynasty of China that existed between 916 and 1125, ruled by the Yelü ...
.
Yuan dynasty (Mongol Empire)
In the Mongol Empire
The Mongol Empire of the 13th and 14th centuries was the largest contiguous land empire in history. Originating in present-day Mongolia in East Asia, the Mongol Empire at its height stretched from the Sea of Japan to parts of Eastern Europe, ...
, the Mongol
The Mongols ( mn, Монголчууд, , , ; ; russian: Монголы) are an East Asian ethnic group native to Mongolia, Inner Mongolia in China and the Buryatia Republic of the Russian Federation. The Mongols are the principal member ...
scholars with the Persian and Chinese cartographers or their foreign colleagues created maps, geographical compendium as well as travel accounts. Rashid-al-Din Hamadani
Rashīd al-Dīn Ṭabīb ( fa, رشیدالدین طبیب; 1247–1318; also known as Rashīd al-Dīn Faḍlullāh Hamadānī, fa, links=no, رشیدالدین فضلالله همدانی) was a statesman, historian and physician in Ilk ...
described his geographical compendium, "Suvar al-aqalim", constituted volume four of the Collected chronicles of the Ilkhanate
The Ilkhanate, also spelled Il-khanate ( fa, ایل خانان, ''Ilxānān''), known to the Mongols as ''Hülegü Ulus'' (, ''Qulug-un Ulus''), was a khanate established from the southwestern sector of the Mongol Empire. The Ilkhanid realm ...
in Persia. His works says about the borders of the seven climes (old world), rivers, major cities, places, climate, and Mongol yams (relay stations). The Great Khan
Khagan or Qaghan (Mongolian:; or ''Khagan''; otk, 𐰴𐰍𐰣 ), or , tr, Kağan or ; ug, قاغان, Qaghan, Mongolian Script: ; or ; fa, خاقان ''Khāqān'', alternatively spelled Kağan, Kagan, Khaghan, Kaghan, Khakan, Khakhan ...
Khubilai's ambassador and minister, Bolad, had helped Rashid's works in relation to the Mongols and Mongolia
Mongolia; Mongolian script: , , ; lit. "Mongol Nation" or "State of Mongolia" () is a landlocked country in East Asia, bordered by Russia to the north and China to the south. It covers an area of , with a population of just 3.3 million ...
. Thanks to Pax Mongolica, the easterners and the westerners in Mongol dominions were able to gain access to one another's geographical materials.Mongolia
Mongolia; Mongolian script: , , ; lit. "Mongol Nation" or "State of Mongolia" () is a landlocked country in East Asia, bordered by Russia to the north and China to the south. It covers an area of , with a population of just 3.3 million ...
where Genghis Khan
Genghis Khan (born Temüjin; ; xng, Temüjin, script=Latn; ., name=Temujin – August 25, 1227) was the founder and first Great Khan (Emperor) of the Mongol Empire, which became the List of largest empires, largest contiguous empire in history a ...
was born and united the Mongol and Turkic nomad
A nomad is a member of a community without fixed habitation who regularly moves to and from the same areas. Such groups include hunter-gatherers, pastoral nomads (owning livestock), tinkers and trader nomads. In the twentieth century, the po ...
s as recorded in native sources, especially the Secret History of the Mongols
''The Secret History of the Mongols'' (Middle Mongol: ''Mongɣol‑un niɣuca tobciyan''; Traditional Mongolian: , Khalkha Mongolian: , ; ) is the oldest surviving literary work in the Mongolian language. It was written for the Mongol royal fa ...
.
Map of relay stations, called "yam", and strategic points existed in the Yuan dynasty
The Yuan dynasty (), officially the Great Yuan (; xng, , , literally "Great Yuan State"), was a Mongol-led imperial dynasty of China and a successor state to the Mongol Empire after its division. It was established by Kublai, the fif ...
.Ispahan
Isfahan ( fa, اصفهان, Esfahân ), from its ancient designation ''Aspadana'' and, later, ''Spahan'' in middle Persian, rendered in English as ''Ispahan'', is a major city in the Greater Isfahan Region, Isfahan Province, Iran. It is lo ...
and the Ilkhanid capital Soltaniyeh
Soltaniyeh ( fa, سلطانيه, also Romanized as Solţānīyeh, Solţāneyyeh, Sultaniye, and Sultānīyeh; also known as Sa‘īdīyeh; ) is the capital city of Soltaniyeh District of Soltaniyeh County, Zanjan Province, northwestern Iran.
...
, and Russia
Russia (, , ), or the Russian Federation, is a transcontinental country spanning Eastern Europe and Northern Asia. It is the largest country in the world, with its internationally recognised territory covering , and encompassing one-ei ...
(as "Orash") as well as their neighbors, e.g. Egypt
Egypt ( ar, مصر , ), officially the Arab Republic of Egypt, is a List of transcontinental countries, transcontinental country spanning the North Africa, northeast corner of Africa and Western Asia, southwest corner of Asia via a land bridg ...
and Syria
Syria ( ar, سُورِيَا or سُورِيَة, translit=Sūriyā), officially the Syrian Arab Republic ( ar, الجمهورية العربية السورية, al-Jumhūrīyah al-ʻArabīyah as-Sūrīyah), is a Western Asian country loc ...
.
Ming dynasty
 The multicolour map, Da Ming Hunyi Tu dates to the early
The multicolour map, Da Ming Hunyi Tu dates to the early Ming dynasty
The Ming dynasty (), officially the Great Ming, was an Dynasties in Chinese history, imperial dynasty of China, ruling from 1368 to 1644 following the collapse of the Mongol Empire, Mongol-led Yuan dynasty. The Ming dynasty was the last ort ...
from about 1390, is in multicolour. The horizontal scale is 1:820,000 and the vertical scale is 1:1,060,000.[Ptak, Roderich.]
The Sino-European Map (''Shanhai yudi quantu'') in the Encyclopedia ''Sancai Tuhui''
". Similar to these, the earliest European style map from China, the '' Kunyu Wanguo Quantu'' (1602) influenced and was exported to Japan and Korea.[.] By this time, Jesuit missionaries contributed to similar maps such as the '' Wanguo Quantu'' (1620s) and the '' Kunyu Quantu'' (1674). While the Selden Map
The Selden Map of China (Bodleian Library, MS Selden Supra 105) is an early 17th century map of East Asia formerly owned by the legal scholar and maritime theorist John Selden. It shows a system of navigational routes emanating from a point near ...
(c. 17th century) employs a system of navigational routes emanating from ports in China. The Mao Kun map
Mao Kun map, usually referred to in modern Chinese sources as Zheng He's Navigation Map (), is a set of navigation charts published in the Ming dynasty military treatise ''Wubei Zhi''. The book was compiled by Mao Yuanyi in 1621 and published in ...
published in 1628 is thought to be based on a strip map
A straight-line diagram (abbreviated SLD) is a diagram of a road where the road is shown as a straight line. Such diagrams are usually produced by a highway department, and display features along the road, including bridges and intersecting roa ...
dated to the voyages of Zheng He
Zheng He (; 1371–1433 or 1435) was a Chinese mariner, explorer, diplomat, fleet admiral, and court eunuch during China's early Ming dynasty. He was originally born as Ma He in a Muslim family and later adopted the surname Zheng conferr ...
.
In 1579, Luo Hongxian
Luo Hongxian (; 1504 – 1564) was a Ming dynasty Chinese cartographer. He also studied astronomy, geography, irrigation methods, military affairs and mathematics.
After passing the Imperial Examinations with the rank of ''jinshi'' in 1529, Luo w ...
published the ''Guang Yutu
Guang may refer to:
* Guang (vessel), an ancient Chinese drinking vessel
* Guang people, ethnic group of northern Ghana
* Guang languages, languages spoken by the Guang people
* Guangzhou, city in Guangdong, China
* Liangguang, Guangdong and Guang ...
'' atlas, including more than 40 maps, a grid system, and a systematic way of representing major landmarks such as mountains, rivers, roads and borders. The ''Guang Yutu'' incorporates the discoveries of the naval explorer Zheng He's 15th-century voyages along the coasts of China, Southeast Asia, India and Africa.
Qing dynasty
From the 16th and 17th centuries, several examples survive of maps focused on cultural information. Gridlines are not used on either Yu Shi's Gujin xingsheng zhi tu (1555) or Zhang Huang Zhang may refer to:
Chinese culture, etc.
* Zhang (surname) (張/张), common Chinese surname
** Zhang (surname 章), a rarer Chinese surname
* Zhang County (漳县), of Dingxi, Gansu
* Zhang River (漳河), a river flowing mainly in Henan
* ''Zh ...
's Tushu bian (1613); instead, illustrations and annotations show mythical places, exotic foreign peoples, administrative changes and the deeds of historic and legendary heroes.contour lines
A contour line (also isoline, isopleth, or isarithm) of a function of two variables is a curve along which the function has a constant value, so that the curve joins points of equal value. It is a plane section of the three-dimensional gr ...
.topographic
Topography is the study of the forms and features of land surfaces. The topography of an area may refer to the land forms and features themselves, or a description or depiction in maps.
Topography is a field of geoscience and planetary scie ...
features were part of maps in China for centuries, a Fujian
Fujian (; alternately romanized as Fukien or Hokkien) is a province on the southeastern coast of China. Fujian is bordered by Zhejiang to the north, Jiangxi to the west, Guangdong to the south, and the Taiwan Strait to the east. Its ...
county official Ye Chunji (1532–1595) was the first to base county maps using on-site topographical surveying
Surveying or land surveying is the technique, profession, art, and science of determining the terrestrial two-dimensional or three-dimensional positions of points and the distances and angles between them. A land surveying professional is ...
and observations.
Japan and Korea
In 1402, Yi Hoe and Kwan Yun created a world map largely based from Chinese cartographers called the Gangnido map. It is currently one of the oldest surviving world maps from East Asia.[Cartography of Korea, pgs. 235–345, Gari Ledyard ''al''., (Department of Geography, University of Wisconsin, Madison), The History of Cartography, Volume Two, Book Two, Cartography in Cartography in the Traditional East and Southeast Asian Societies, 1994, The University of Chicago Press, J. B. Harley and David Woodward ''ed''., (Department of Geography, University of Wisconsin, Milwaukee, WI / Department of Geography, University of Wisconsin, Madison, WI), pgs. slip cover, 243–247, .] Another notable pre-modern map is the Cheonhado map developed in Korea in the 17th century.
Sekisui Nagakubo produced a world map in 1785 called the ''Comprehensive Map and Description of the Geography of the Myriad Countries of the Globe'' (地球萬國山海輿地全圖說), mainly deriving it from an earlier map made by Matteo Ricci. The production was made by woodblock print and folded into paper boards, he made corrections and additions on top of Matteo's production. This was one of the earliest maps with longitude and latitude information in Japan and was written in Katakana
is a Japanese syllabary, one component of the Japanese writing system along with hiragana, kanji and in some cases the Latin script (known as rōmaji). The word ''katakana'' means "fragmentary kana", as the katakana characters are derived f ...
.
Another well-known cartographer of the late-Edo period was Ino Tadataka, he is known for completing the first map of Japan using modern surveying techniques. His most famous work, the ''Dai Nihon Enkai Yochi Zenzu'' (大日本沿海輿地全図) consisted of three large map pages at a scale of 1:432,000 and it showed the entire country on eight pages at 1:216,000. Some of his maps are accurate to 1/1000 of a degree, which allowed it to become the definitive maps used in Japan for nearly a century. Maps based on his work were in use as late as 1924.
India
 Indian cartographic traditions covered the locations of the
Indian cartographic traditions covered the locations of the Pole star
A pole star or polar star is a star, preferably bright, nearly aligned with the axis of a rotating astronomical body.
Currently, Earth's pole stars are Polaris (Alpha Ursae Minoris), a bright magnitude-2 star aligned approximately with its ...
and other constellations of use.[ These charts may have been in use by the beginning of the ]Common Era
Common Era (CE) and Before the Common Era (BCE) are year notations for the Gregorian calendar (and its predecessor, the Julian calendar), the world's most widely used calendar era. Common Era and Before the Common Era are alternatives to the or ...
for purposes of navigation.[
Detailed maps of considerable length describing the locations of settlements, sea shores, rivers, and mountains were also made.]Bhavabhuti
Bhavabhūti (Devanagari: भवभूति) was an 8th-century scholar of India noted for his plays and poetry, written in Sanskrit. His plays are considered the equal of the works of Kalidasa. Bhavabhuti was born in Padmapura, Vidarbha, in Gondi ...
'' conceived paintings which indicated geographical regions.[
Italian scholar Francesco Lorenzo Pullè reproduced a number of ancient Indian maps in his ''magnum opus'' ''La Cartografia Antica dell'India''.][ Out of these maps, two have been reproduced using a manuscript of ''Lokaprakasa'', originally compiled by the polymath Ksemendra (]Kashmir
Kashmir () is the northernmost geographical region of the Indian subcontinent. Until the mid-19th century, the term "Kashmir" denoted only the Kashmir Valley between the Great Himalayas and the Pir Panjal Range. Today, the term encompas ...
, 11th century), as a source.[ The other manuscript, used as a source by Pullè, is titled ''Samgrahani''.][ The early volumes of the '']Encyclopædia Britannica
The (Latin for "British Encyclopædia") is a general knowledge English-language encyclopaedia. It is published by Encyclopædia Britannica, Inc.; the company has existed since the 18th century, although it has changed ownership various t ...
'' also described cartographic charts made by the Dravidian people
The Dravidian peoples, or Dravidians, are an ethnolinguistic and cultural group living in South Asia who predominantly speak any of the Dravidian languages. There are around 250 million native speakers of Dravidian languages. Dravidian spe ...
of India.[
Maps from the ]Ain-e-Akbari
The ''Ain-i-Akbari'' ( fa, ) or the "Administration of Akbar", is a 16th-century detailed document recording the administration of the Mughal Empire under Emperor Akbar, written by his court historian, Abu'l Fazl in the Persian language. It for ...
, a Mughal document detailing India's history and traditions, contain references to locations indicated in earlier Indian cartographic traditions.[ Another map describing the ]kingdom of Nepal
The Kingdom of Nepal ( ne, नेपाल अधिराज्य), also known as the Gorkha Empire ( ne, गोरखा अधिराज्य) or Asal Hindustan ( ne, असल हिन्दुस्तान)(), was a Hindu king ...
, four feet in length and about two and a half feet in breadth, was presented to Warren Hastings
Warren Hastings (6 December 1732 – 22 August 1818) was a British colonial administrator, who served as the first Governor of the Presidency of Fort William (Bengal), the head of the Supreme Council of Bengal, and so the first Governor-General ...
.[ In this map the mountains were elevated above the surface, and several geographical elements were indicated in different colors.][
]
Islamic cartographic schools
Arab and Persian cartography
 In the Middle Ages, Muslim scholars continued and advanced on the mapmaking traditions of earlier cultures. Most used Ptolemy's methods; but they also took advantage of what explorers and merchants learned in their travels across the Muslim world, from Spain to India to Africa, and beyond in trade relationships with China, and Russia.
In the Middle Ages, Muslim scholars continued and advanced on the mapmaking traditions of earlier cultures. Most used Ptolemy's methods; but they also took advantage of what explorers and merchants learned in their travels across the Muslim world, from Spain to India to Africa, and beyond in trade relationships with China, and Russia.cartography
Cartography (; from grc, χάρτης , "papyrus, sheet of paper, map"; and , "write") is the study and practice of making and using maps. Combining science, aesthetics and technique, cartography builds on the premise that reality (or an i ...
was the patronage of the Abbasid
The Abbasid Caliphate ( or ; ar, الْخِلَافَةُ الْعَبَّاسِيَّة, ') was the third caliphate to succeed the Islamic prophet Muhammad. It was founded by a dynasty descended from Muhammad's uncle, Abbas ibn Abdul-Mutta ...
caliph
A caliphate or khilāfah ( ar, خِلَافَة, ) is an institution or public office under the leadership of an Islamic steward with the title of caliph (; ar, خَلِيفَة , ), a person considered a political-religious successor to th ...
, al-Ma'mun
Abu al-Abbas Abdallah ibn Harun al-Rashid ( ar, أبو العباس عبد الله بن هارون الرشيد, Abū al-ʿAbbās ʿAbd Allāh ibn Hārūn ar-Rashīd; 14 September 786 – 9 August 833), better known by his regnal name Al-Ma'm ...
, who reigned from 813 to 833. He commissioned several geographers to remeasure the distance on earth that corresponds to one degree of celestial meridian. Thus his patronage resulted in the refinement of the definition of the mile used by Arabs (''mīl'' in Arabic) in comparison to the ''stadion'' used by Greeks. These efforts also enabled Muslims to calculate the circumference of the earth. Al-Mamun also commanded the production of a large map of the world, which has not survived,[Edson and Savage-Smith (2004)] though it is known that its map projection type was based on Marinus of Tyre
Marinus of Tyre ( grc-gre, Μαρῖνος ὁ Τύριος, ''Marînos ho Týrios''; 70–130) was a Greek geographer, cartographer and mathematician, who founded mathematical geography and provided the underpinnings of Claudius Ptolemy' ...
rather than Ptolemy
Claudius Ptolemy (; grc-gre, Πτολεμαῖος, ; la, Claudius Ptolemaeus; AD) was a mathematician, astronomer, astrologer, geographer, and music theorist, who wrote about a dozen scientific treatises, three of which were of importanc ...
.Habash al-Hasib al-Marwazi
Ahmad ibn 'Abdallah Habash Hasib Marwazi (766 - d. after 869 in Samarra, Iraq ) was a north-eastern Iranian astronomer, geographer, and mathematician from Merv in Khorasan who for the first time described the trigonometric ratios: sine, cosine, t ...
, employed spherical trigonometry
Spherical trigonometry is the branch of spherical geometry that deals with the metrical relationships between the sides and angles of spherical triangles, traditionally expressed using trigonometric functions. On the sphere, geodesics are grea ...
and map projection
In cartography, map projection is the term used to describe a broad set of transformations employed to represent the two-dimensional curved surface of a globe on a plane. In a map projection, coordinates, often expressed as latitude and l ...
methods in order to convert polar coordinates
In mathematics, the polar coordinate system is a two-dimensional coordinate system in which each point on a plane is determined by a distance from a reference point and an angle from a reference direction. The reference point (analogous to th ...
to a different coordinate system centred on a specific point on the sphere, in this the Qibla
The qibla ( ar, قِبْلَة, links=no, lit=direction, translit=qiblah) is the direction towards the Kaaba in the Sacred Mosque in Mecca, which is used by Muslims in various religious contexts, particularly the direction of prayer for the ...
, the direction to Mecca
Mecca (; officially Makkah al-Mukarramah, commonly shortened to Makkah ()) is a city and administrative center of the Mecca Province of Saudi Arabia, and the holiest city in Islam. It is inland from Jeddah on the Red Sea, in a narrow v ...
. Abū Rayhān Bīrūnī
Abu Rayhan Muhammad ibn Ahmad al-Biruni (973 – after 1050) commonly known as al-Biruni, was a Khwarazmian Iranian in scholar and polymath during the Islamic Golden Age. He has been called variously the "founder of Indology", "Father of Co ...
(973–1048) later developed ideas which are seen as an anticipation of the polar coordinate system. Around 1025, he describes a polar equi-azimuthal equidistant projection
The azimuthal equidistant projection is an azimuthal map projection. It has the useful properties that all points on the map are at proportionally correct distances from the center point, and that all points on the map are at the correct azimut ...
of the celestial sphere
In astronomy and navigation, the celestial sphere is an abstract sphere that has an arbitrarily large radius and is concentric to Earth. All objects in the sky can be conceived as being projected upon the inner surface of the celestial sphe ...
. However, this type of projection had been used in ancient Egyptian star-maps and was not to be fully developed until the 15 and 16th centuries.Balkh
), named for its green-tiled ''Gonbad'' ( prs, گُنبَد, dome), in July 2001
, pushpin_map=Afghanistan#Bactria#West Asia
, pushpin_relief=yes
, pushpin_label_position=bottom
, pushpin_mapsize=300
, pushpin_map_caption=Location in Afghanistan ...
, founded the "Balkhī school" of terrestrial mapping in Baghdad
Baghdad (; ar, بَغْدَاد , ) is the capital of Iraq and the second-largest city in the Arab world after Cairo. It is located on the Tigris near the ruins of the ancient city of Babylon and the Sassanid Persian capital of Ctesiphon ...
. The geographers of this school also wrote extensively of the peoples, products, and customs of areas in the Muslim world, with little interest in the non-Muslim realms.[ The "Balkhī school", which included geographers such as ]Estakhri
Abu Ishaq Ibrahim ibn Muhammad al-Farisi al-Istakhri () (also ''Estakhri'', fa, استخری, i.e. from the Iranian city of Istakhr, b. - d. 346 AH/AD 957) was a 10th-century travel-author and geographer who wrote valuable accounts in Ara ...
, al-Muqaddasi
Shams al-Dīn Abū ʿAbd Allāh Muḥammad ibn Aḥmad ibn Abī Bakr al-Maqdisī ( ar, شَمْس ٱلدِّيْن أَبُو عَبْد ٱلله مُحَمَّد ابْن أَحْمَد ابْن أَبِي بَكْر ٱلْمَقْدِسِي), ...
and Ibn Hawqal
Muḥammad Abū’l-Qāsim Ibn Ḥawqal (), also known as Abū al-Qāsim b. ʻAlī Ibn Ḥawqal al-Naṣībī, born in Nisibis, Upper Mesopotamia; was a 10th-century Arab Muslim writer, geographer, and chronicler who travelled during the ye ...
, produced world atlas
An atlas is a collection of maps; it is typically a bundle of maps of Earth or of a region of Earth.
Atlases have traditionally been bound into book form, but today many atlases are in multimedia formats. In addition to presenting geogra ...
es, each one featuring a world map
A world map is a map of most or all of the surface of Earth. World maps, because of their scale, must deal with the problem of projection. Maps rendered in two dimensions by necessity distort the display of the three-dimensional surface of ...
and twenty regional maps.[
Suhrāb, a late 10th-century Muslim geographer, accompanied a book of geographical ]coordinates
In geometry, a coordinate system is a system that uses one or more numbers, or coordinates, to uniquely determine the position of the points or other geometric elements on a manifold such as Euclidean space. The order of the coordinates is sig ...
with instructions for making a rectangular world map, with equirectangular projection
The equirectangular projection (also called the equidistant cylindrical projection or la carte parallélogrammatique projection), and which includes the special case of the plate carrée projection (also called the geographic projection, lat/lon ...
or cylindrical equidistant projection.[ The earliest surviving rectangular coordinate map is dated to the 13th century and is attributed to Hamdallah al-Mustaqfi al- Qazwini, who based it on the work of Suhrāb. The ]orthogonal
In mathematics, orthogonality is the generalization of the geometric notion of '' perpendicularity''.
By extension, orthogonality is also used to refer to the separation of specific features of a system. The term also has specialized meanings in ...
parallel lines were separated by one degree intervals, and the map was limited to Southwest Asia
Western Asia, West Asia, or Southwest Asia, is the westernmost subregion of the larger geographical region of Asia, as defined by some academics, UN bodies and other institutions. It is almost entirely a part of the Middle East, and includes Ana ...
and Central Asia
Central Asia, also known as Middle Asia, is a region of Asia that stretches from the Caspian Sea in the west to western China and Mongolia in the east, and from Afghanistan and Iran in the south to Russia in the north. It includes the fo ...
. The earliest surviving world maps based on a rectangular coordinate grid are attributed to al-Mustawfi in the 14th or 15th century (who used invervals of ten degrees for the lines), and to Hafiz-i Abru (died 1430).[
]Ibn Battuta
Abu Abdullah Muhammad ibn Battutah (, ; 24 February 13041368/1369),; fully: ; Arabic: commonly known as Ibn Battuta, was a Berber Maghrebi scholar and explorer who travelled extensively in the lands of Afro-Eurasia, largely in the Muslim ...
(1304–1368?) wrote "Rihlah" (Travels) based on three decades of journeys, covering more than 120,000 km through northern Africa, southern Europe, and much of Asia.
=Islamic regional cartography
=
Islamic regional cartography is usually categorized into three groups: that produced by the " Balkhī school", the type devised by Muhammad al-Idrisi
Abu Abdullah Muhammad al-Idrisi al-Qurtubi al-Hasani as-Sabti, or simply al-Idrisi ( ar, أبو عبد الله محمد الإدريسي القرطبي الحسني السبتي; la, Dreses; 1100 – 1165), was a Muslim geographer, cartogra ...
, and the type that are uniquely found in the ''Book of curiosities''.[
The maps by the Balkhī schools were defined by political, not longitudinal boundaries and covered only the Muslim world. In these maps the distances between various "stops" (cities or rivers) were equalized. The only shapes used in designs were verticals, horizontals, 90-degree angles, and arcs of circles; unnecessary geographical details were eliminated. This approach is similar to that used in ]subway
Subway, Subways, The Subway, or The Subways may refer to:
Transportation
* Subway, a term for underground rapid transit rail systems
* Subway (underpass), a type of walkway that passes underneath an obstacle
* Subway (George Bush Intercontin ...
maps, most notable used in the "London Underground
The London Underground (also known simply as the Underground or by its nickname the Tube) is a rapid transit system serving Greater London and some parts of the adjacent counties of Buckinghamshire, Essex and Hertfordshire in England.
The ...
Tube Map" in 1931 by Harry Beck
Henry Charles Beck (4 June 190218 September 1974) was an English technical draughtsman who created the present London Underground Tube map in 1931. Beck drew the diagram after being fired at the London Metro Signal Office. Although his design ...
.[
Al-Idrīsī defined his maps differently. He considered the extent of the known world to be 160° in longitude, and divided the region into ten parts, each 16° wide. In terms of latitude, he portioned the known world into seven 'climes', determined by the length of the longest day. In his maps, many dominant geographical features can be found.][
]
=''Book on the appearance of the Earth''
=
Muhammad ibn Mūsā al-Khwārizmī
Muḥammad ibn Mūsā al-Khwārizmī ( ar, محمد بن موسى الخوارزمي, Muḥammad ibn Musā al-Khwārazmi; ), or al-Khwarizmi, was a Persians, Persian polymath from Khwarazm, who produced vastly influential works in Mathematics ...
's ' ("Book on the appearance of the Earth") was completed in 833. It is a revised and completed version of Ptolemy
Claudius Ptolemy (; grc-gre, Πτολεμαῖος, ; la, Claudius Ptolemaeus; AD) was a mathematician, astronomer, astrologer, geographer, and music theorist, who wrote about a dozen scientific treatises, three of which were of importanc ...
's ''Geography
Geography (from Greek: , ''geographia''. Combination of Greek words ‘Geo’ (The Earth) and ‘Graphien’ (to describe), literally "earth description") is a field of science devoted to the study of the lands, features, inhabitants, an ...
'', consisting of a list of 2402 coordinates of cities and other geographical features following a general introduction.
Al-Khwārizmī, Al-Ma'mun
Abu al-Abbas Abdallah ibn Harun al-Rashid ( ar, أبو العباس عبد الله بن هارون الرشيد, Abū al-ʿAbbās ʿAbd Allāh ibn Hārūn ar-Rashīd; 14 September 786 – 9 August 833), better known by his regnal name Al-Ma'm ...
's most famous geographer, corrected Ptolemy's gross overestimate for the length of the Mediterranean Sea
The Mediterranean Sea is a sea connected to the Atlantic Ocean, surrounded by the Mediterranean Basin and almost completely enclosed by land: on the north by Western and Southern Europe and Anatolia, on the south by North Africa, and on ...
[ (from the ]Canary Islands
The Canary Islands (; es, :es:Canarias, Canarias, ), also known informally as the Canaries, are a Spanish Autonomous communities of Spain, autonomous community and archipelago in the Atlantic Ocean, in Macaronesia. At their closest point to ...
to the eastern shores of the Mediterranean); Ptolemy overestimated it at 63 degrees of longitude
Longitude (, ) is a geographic coordinate that specifies the east– west position of a point on the surface of the Earth, or another celestial body. It is an angular measurement, usually expressed in degrees and denoted by the Greek let ...
, while al-Khwarizmi almost correctly estimated it at nearly 50 degrees of longitude. Al-Ma'mun's geographers "also depicted the Atlantic
The Atlantic Ocean is the second-largest of the world's five oceans, with an area of about . It covers approximately 20% of Earth's surface and about 29% of its water surface area. It is known to separate the " Old World" of Africa, Europe ...
and Indian Ocean
The Indian Ocean is the third-largest of the world's five oceanic divisions, covering or ~19.8% of the water on Earth's surface. It is bounded by Asia to the north, Africa to the west and Australia to the east. To the south it is bounded by ...
s as open bodies of water, not land-locked sea
The sea, connected as the world ocean or simply the ocean, is the body of salty water that covers approximately 71% of the Earth's surface. The word sea is also used to denote second-order sections of the sea, such as the Mediterranean Sea, ...
s as Ptolemy had done. "Prime Meridian
A prime meridian is an arbitrary meridian (a line of longitude) in a geographic coordinate system at which longitude is defined to be 0°. Together, a prime meridian and its anti-meridian (the 180th meridian in a 360°-system) form a great ...
of the Old World
The "Old World" is a term for Afro-Eurasia that originated in Europe , after Europeans became aware of the existence of the Americas. It is used to contrast the continents of Africa, Europe, and Asia, which were previously thought of by thei ...
at the eastern shore of the Mediterranean, 10–13 degrees to the east of Alexandria
Alexandria ( or ; ar, ٱلْإِسْكَنْدَرِيَّةُ ; grc-gre, Αλεξάνδρεια, Alexándria) is the second largest city in Egypt, and the largest city on the Mediterranean coast. Founded in by Alexander the Great, Alexandri ...
(the prime meridian previously set by Ptolemy) and 70 degrees to the west of Baghdad
Baghdad (; ar, بَغْدَاد , ) is the capital of Iraq and the second-largest city in the Arab world after Cairo. It is located on the Tigris near the ruins of the ancient city of Babylon and the Sassanid Persian capital of Ctesiphon ...
. Most medieval Muslim geographers continued to use al-Khwarizmi's prime meridian.[ Other prime meridians used were set by ]Abū Muhammad al-Hasan al-Hamdānī
Abū Muḥammad al-Ḥasan ibn Aḥmad ibn Yaʿqūb al-Hamdānī (279/280-333/334 A.H. / c. 893-945 A.D; ar, أبو محمد الحسن بن أحمد بن يعقوب الهمداني) was an Arab Muslim geographer, chemist, poet, grammarian, ...
and Habash al-Hasib al-Marwazi
Ahmad ibn 'Abdallah Habash Hasib Marwazi (766 - d. after 869 in Samarra, Iraq ) was a north-eastern Iranian astronomer, geographer, and mathematician from Merv in Khorasan who for the first time described the trigonometric ratios: sine, cosine, t ...
at Ujjain
Ujjain (, Hindustani pronunciation: �d͡ːʒɛːn is a city in Ujjain district of the Indian state of Madhya Pradesh. It is the fifth-largest city in Madhya Pradesh by population and is the administrative centre of Ujjain district and Uj ...
, a centre of Indian astronomy
Astronomy has long history in Indian subcontinent stretching from pre-historic to modern times. Some of the earliest roots of Indian astronomy can be dated to the period of Indus Valley civilisation or earlier. Astronomy later developed as a di ...
, and by another anonymous writer at Basra
Basra ( ar, ٱلْبَصْرَة, al-Baṣrah) is an Iraqi city located on the Shatt al-Arab. It had an estimated population of 1.4 million in 2018. Basra is also Iraq's main port, although it does not have deep water access, which is han ...
.[
]
=Al-Biruni
=
Abu Rayhan al-Biruni
Abu Rayhan Muhammad ibn Ahmad al-Biruni (973 – after 1050) commonly known as al-Biruni, was a Khwarazmian Iranian in scholar and polymath during the Islamic Golden Age. He has been called variously the "founder of Indology", "Father of Co ...
(973–1048) gave an estimate of 6,339.6 km for the Earth radius
Earth radius (denoted as ''R''🜨 or R_E) is the distance from the center of Earth to a point on or near its surface. Approximating the figure of Earth by an Earth spheroid, the radius ranges from a maximum of nearly (equatorial radius, den ...
, which is only 17.15 km less than the modern value of 6,356.7523142 km (WGS84 polar radius "b"). In contrast to his predecessors who measured the Earth's circumference by sighting the Sun simultaneously from two different locations, Al-Biruni developed a new method of using trigonometric
Trigonometry () is a branch of mathematics that studies relationships between side lengths and angles of triangles. The field emerged in the Hellenistic world during the 3rd century BC from applications of geometry to astronomical studies. ...
calculations based on the angle between a plain
In geography, a plain is a flat expanse of land that generally does not change much in elevation, and is primarily treeless. Plains occur as lowlands along valleys or at the base of mountains, as coastal plains, and as plateaus or uplands ...
and mountain
A mountain is an elevated portion of the Earth's crust, generally with steep sides that show significant exposed bedrock. Although definitions vary, a mountain may differ from a plateau in having a limited summit area, and is usually higher ...
top which yielded more accurate measurements of the Earth's circumference and made it possible for it to be measured by a single person from a single location.[ (]cf.
The abbreviation ''cf.'' (short for the la, confer/conferatur, both meaning "compare") is used in writing to refer the reader to other material to make a comparison with the topic being discussed. Style guides recommend that ''cf.'' be used onl ...
)Pakistan
Pakistan ( ur, ), officially the Islamic Republic of Pakistan ( ur, , label=none), is a country in South Asia. It is the world's List of countries and dependencies by population, fifth-most populous country, with a population of almost 24 ...
).[ From the top of the mountain, he sighted the dip angle which, along with the mountain's height (which he calculated beforehand), he applied to the ]law of sines
In trigonometry, the law of sines, sine law, sine formula, or sine rule is an equation relating the lengths of the sides of any triangle to the sines of its angles. According to the law,
\frac \,=\, \frac \,=\, \frac \,=\, 2R,
where , and ar ...
formula. This was the earliest known use of dip angle and the earliest practical use of the law of sines.
azimuthal equidistant projection
The azimuthal equidistant projection is an azimuthal map projection. It has the useful properties that all points on the map are at proportionally correct distances from the center point, and that all points on the map are at the correct azimut ...
of the celestial sphere
In astronomy and navigation, the celestial sphere is an abstract sphere that has an arbitrarily large radius and is concentric to Earth. All objects in the sky can be conceived as being projected upon the inner surface of the celestial sphe ...
.
In his ''Codex Masudicus'' (1037), Al-Biruni theorized the existence of a landmass along the vast ocean between Asia
Asia (, ) is one of the world's most notable geographical regions, which is either considered a continent in its own right or a subcontinent of Eurasia, which shares the continental landmass of Afro-Eurasia with Africa. Asia covers an are ...
and Europe
Europe is a large peninsula conventionally considered a continent in its own right because of its great physical size and the weight of its history and traditions. Europe is also considered a Continent#Subcontinents, subcontinent of Eurasia ...
, or what is today known as the Americas
The Americas, which are sometimes collectively called America, are a landmass comprising the totality of North America, North and South America. The Americas make up most of the land in Earth's Western Hemisphere and comprise the New World. ...
. He deduced its existence on the basis of his accurate estimations of the Earth's circumference
Earth's circumference is the distance around Earth. Measured around the Equator, it is . Measured around the poles, the circumference is .
Measurement of Earth's circumference has been important to navigation since ancient times. The first k ...
and Afro-Eurasia
Afro-Eurasia (also Afroeurasia, Eurafrasia or the Old World) is a landmass comprising the continents of Africa, Asia, and Europe. The terms are compound words of the names of its constituent parts. Its mainland is the largest and most popul ...
's size, which he found spanned only two-fifths of the Earth's circumference, and his discovery of the concept of specific gravity
Relative density, or specific gravity, is the ratio of the density (mass of a unit volume) of a substance to the density of a given reference material. Specific gravity for liquids is nearly always measured with respect to water at its dens ...
, from which he deduced that the geological processes that gave rise to Eurasia
Eurasia (, ) is the largest continental area on Earth, comprising all of Europe and Asia. Primarily in the Northern and Eastern Hemispheres, it spans from the British Isles and the Iberian Peninsula in the west to the Japanese archipelag ...
must've also given rise to lands in the vast ocean between Asia and Europe. He also theorized that the landmass must be inhabited by human beings, which he deduced from his knowledge of humans inhabiting the broad north–south band stretching from Russia
Russia (, , ), or the Russian Federation, is a transcontinental country spanning Eastern Europe and Northern Asia. It is the largest country in the world, with its internationally recognised territory covering , and encompassing one-ei ...
to South India
South India, also known as Dakshina Bharata or Peninsular India, consists of the peninsular southern part of India. It encompasses the Indian states of Andhra Pradesh, Karnataka, Kerala, Tamil Nadu, and Telangana, as well as the union terr ...
and Sub-Saharan Africa
Sub-Saharan Africa is, geographically, the area and regions of the continent of Africa that lies south of the Sahara. These include West Africa, East Africa, Central Africa, and Southern Africa. Geopolitically, in addition to the List of sov ...
, theorizing that the landmass would most likely lie along the same band.
=''Tabula Rogeriana''
=
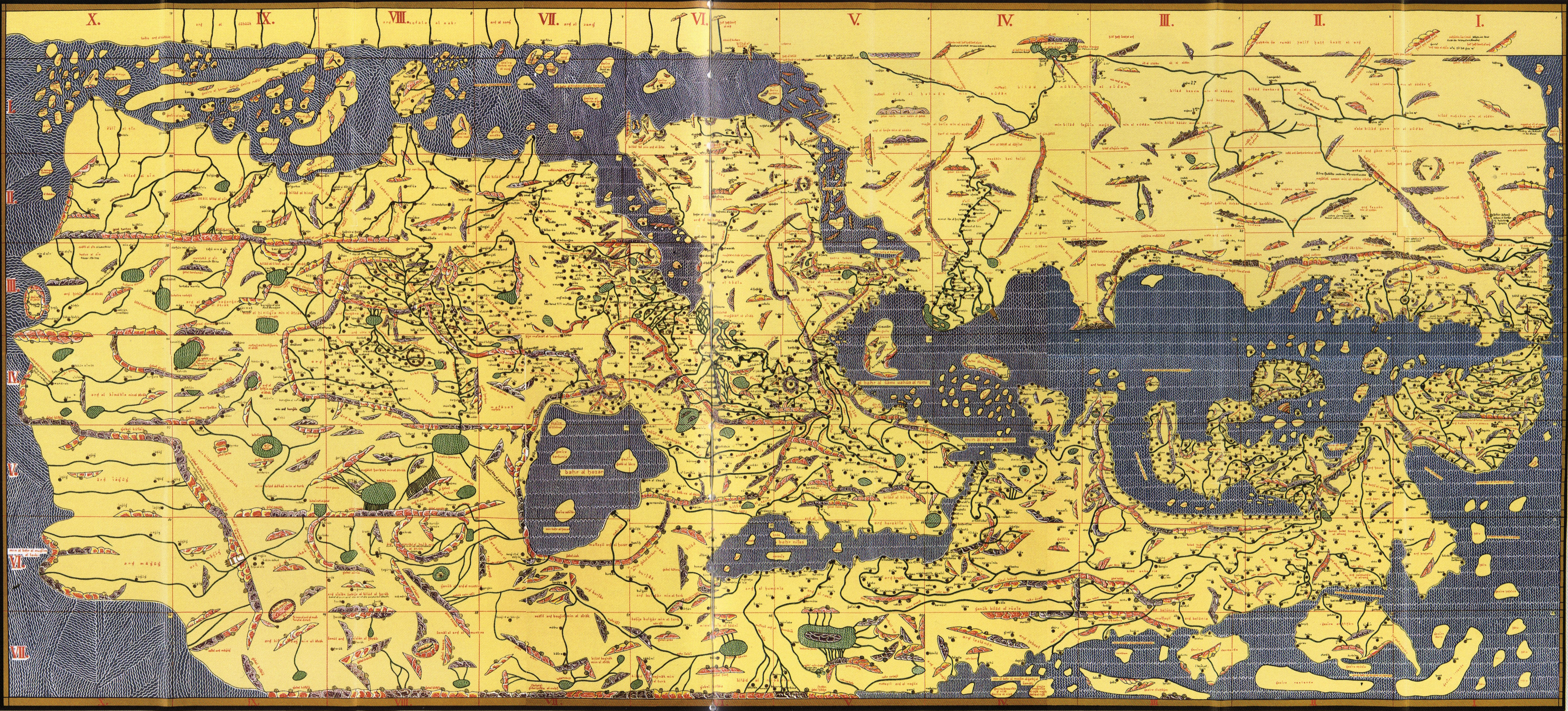 The
The Arab geographer
Medieval Islamic geography and cartography refer to the study of geography and cartography in the Muslim world during the Islamic Golden Age (variously dated between the 8th century and 16th century). Muslim scholars made advances to the map-m ...
, Muhammad al-Idrisi
Abu Abdullah Muhammad al-Idrisi al-Qurtubi al-Hasani as-Sabti, or simply al-Idrisi ( ar, أبو عبد الله محمد الإدريسي القرطبي الحسني السبتي; la, Dreses; 1100 – 1165), was a Muslim geographer, cartogra ...
, produced his medieval atlas, '' Tabula Rogeriana'' or ''The Recreation for Him Who Wishes to Travel Through the Countries'', in 1154. He incorporated the knowledge of Africa
Africa is the world's second-largest and second-most populous continent, after Asia in both cases. At about 30.3 million km2 (11.7 million square miles) including adjacent islands, it covers 6% of Earth's total surface area ...
, the Indian Ocean
The Indian Ocean is the third-largest of the world's five oceanic divisions, covering or ~19.8% of the water on Earth's surface. It is bounded by Asia to the north, Africa to the west and Australia to the east. To the south it is bounded by ...
and the Far East
The ''Far East'' was a European term to refer to the geographical regions that includes East and Southeast Asia as well as the Russian Far East to a lesser extent. South Asia is sometimes also included for economic and cultural reasons.
The t ...
gathered by Arab merchants and explorers with the information inherited from the classical geographers to create the most accurate map of the world in pre-modern times.Roger II of Sicily
Roger II ( it, Ruggero II; 22 December 1095 – 26 February 1154) was King of Sicily and Africa, son of Roger I of Sicily and successor to his brother Simon. He began his rule as Count of Sicily in 1105, became Duke of Apulia and Calabria i ...
(1097–1154), al-Idrisi drew on the knowledge collected at the University of Cordoba and paid draftsmen to make journeys and map their routes. The book describes the earth as a sphere with a circumference of but maps it in 70 rectangular sections. Notable features include the correct dual sources of the Nile, the coast of Ghana and mentions of Norway. Climate zones were a chief organizational principle. A second and shortened copy from 1192 called ''Garden of Joys'' is known by scholars as the ''Little Idrisi''. On the work of al-Idrisi, S. P. Scott commented:
On the work of al-Idrisi, S. P. Scott commented:[
Al-Idrisi's atlas, originally called the ''Nuzhat'' in Arabic, served as a major tool for Italian, Dutch and French mapmakers from the 16th century to the 18th century.
]
Piri Reis map of the Ottoman Empire
The Ottoman cartographer Piri Reis
Ahmet Muhiddin Piri ( 1465 – 1553), better known as Piri Reis ( tr, Pîrî Reis or ''Hacı Ahmet Muhittin Pîrî Bey''), was a navigator, geographer and cartographer. He is primarily known today for his maps and charts collected in his ''Kita ...
published navigational maps in his ''Kitab-ı Bahriye''. The work includes an atlas of charts for small segments of the mediterranean, accompanied by sailing instructions covering the sea. In the second version of the work, he included a map of the Americas
The Americas, which are sometimes collectively called America, are a landmass comprising the totality of North America, North and South America. The Americas make up most of the land in Earth's Western Hemisphere and comprise the New World. ...
.[ The ]Piri Reis map
The Piri Reis map is a world map compiled in 1513 by the Ottoman admiral and cartographer Piri Reis. Approximately one third of the map survives; it shows the western coasts of Europe and North Africa and the coast of Brazil with reasonable accu ...
drawn by the Ottoman cartographer Piri Reis
Ahmet Muhiddin Piri ( 1465 – 1553), better known as Piri Reis ( tr, Pîrî Reis or ''Hacı Ahmet Muhittin Pîrî Bey''), was a navigator, geographer and cartographer. He is primarily known today for his maps and charts collected in his ''Kita ...
in 1513, is one of the oldest surviving maps to show the Americas.
Medieval Europe
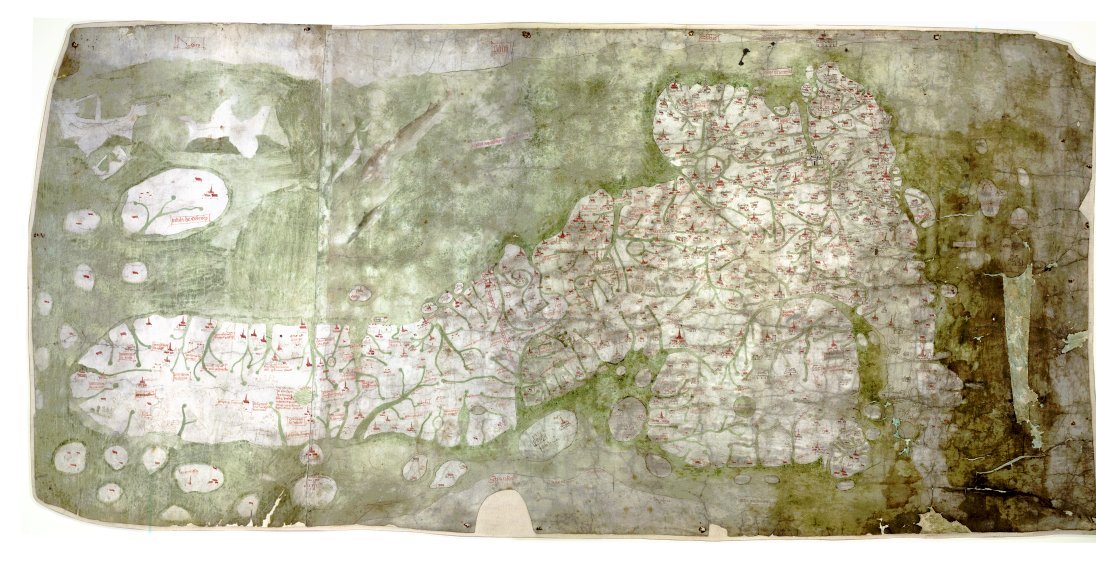
Medieval maps and the Mappa Mundi
Medieval maps of the world in Europe were mainly symbolic in form along the lines of the much earlier Babylonian World Map Babylonian may refer to:
* Babylon, a Semitic Akkadian city/state of ancient Mesopotamia founded in 1894 BC
* Babylonia, an ancient Akkadian-speaking Semitic nation-state and cultural region based in central-southern Mesopotamia (present-day Iraq ...
. Known as Mappa Mundi (cloths or charts of the world) these maps were circular or symmetrical cosmological diagrams representing the Earth's single land mass as disk-shaped and surrounded by ocean.
Italian cartography and the birth of portolan charts

Roger Bacon
Roger Bacon (; la, Rogerus or ', also '' Rogerus''; ), also known by the scholastic accolade ''Doctor Mirabilis'', was a medieval English philosopher and Franciscan friar who placed considerable emphasis on the study of nature through emp ...
's investigations of map projections and the appearance of portolano and then portolan chart
Portolan charts are nautical charts, first made in the 13th century in the Mediterranean basin and later expanded to include other regions. The word ''portolan'' comes from the Italian ''portulano'', meaning "related to ports or harbors", and wh ...
s for plying the European trade routes were rare innovations of the period. The Majorcan school is contrasted with the contemporary Italian cartography school. The ''Carta Pisana
The ''Carta Pisana'' or ''Carte Pisane'' is a map probably made at the end of the 13th century, about 1275–1300, currently conserved in the Département des cartes et plans at the Bibliothèque nationale de France. New research suggests that it ...
'' portolan chart, made at the end of the 13th century (1275–1300), is the oldest surviving nautical chart
A nautical chart is a graphic representation of a sea area and adjacent coastal regions. Depending on the scale of the chart, it may show depths of water and heights of land ( topographic map), natural features of the seabed, details of the co ...
(that is, not simply a map but a document showing accurate navigational directions).
Majorcan cartographic school and the "normal" portolan chart
The Majorcan cartographic school was a predominantly Jewish cooperation of cartographer
Cartography (; from grc, χάρτης , "papyrus, sheet of paper, map"; and , "write") is the study and practice of making and using maps. Combining science, aesthetics and technique, cartography builds on the premise that reality (or an ...
s, cosmographer
The term cosmography has two distinct meanings: traditionally it has been the protoscience of mapping the general features of the cosmos, heaven and Earth; more recently, it has been used to describe the ongoing effort to determine the large-scal ...
s and navigational instrument-makers in late 13th to the 14th and 15th-century Majorca
Mallorca, or Majorca, is the largest island in the Balearic Islands, which are part of Spain and located in the Mediterranean.
The capital of the island, Palma, is also the capital of the autonomous community of the Balearic Islands. The Bale ...
. With their multicultural heritage the Majorcan cartographic school experimented and developed unique cartographic techniques most dealing with the Mediterranean, as it can be seen in the Catalan Atlas
The Catalan Atlas ( ca, Atles català, ) is a medieval world map, or mappamundi, created in 1375 that has been described as the most important map of the Middle Ages in the Catalan language, and as "the zenith of medieval map-work".
It was p ...
.Portolan chart
Portolan charts are nautical charts, first made in the 13th century in the Mediterranean basin and later expanded to include other regions. The word ''portolan'' comes from the Italian ''portulano'', meaning "related to ports or harbors", and wh ...
". It was a contemporary superior, detailed nautical model chart, gridded by compass lines.
Polynesian stick charts
 The Polynesian peoples who explored and settled the Pacific islands in the first two millennia AD used maps to navigate across large distances. A surviving map from the
The Polynesian peoples who explored and settled the Pacific islands in the first two millennia AD used maps to navigate across large distances. A surviving map from the Marshall Islands
The Marshall Islands ( mh, Ṃajeḷ), officially the Republic of the Marshall Islands ( mh, Aolepān Aorōkin Ṃajeḷ),'' () is an independent island country and microstate near the Equator in the Pacific Ocean, slightly west of the Inte ...
uses sticks tied in a grid with palm strips representing wave and wind patterns, with shells attached to show the location of islands. Other maps were created as needed using temporary arrangements of stones or shells.
Modern era
Iberian cartography in the Age of Exploration
In the Renaissance
The Renaissance ( , ) , from , with the same meanings. is a period in European history marking the transition from the Middle Ages to modernity and covering the 15th and 16th centuries, characterized by an effort to revive and surpass ide ...
, with the renewed interest in classical works, maps became more like surveys once again, while European exploration of the Americas and their subsequent effort to control and divide those lands revived interest in scientific mapping methods. Peter Whitfield, the author of several books on the history of maps, credits European mapmaking as a factor in the global spread of western power: "Men in Seville, Amsterdam or London had access to knowledge of America, Brazil, or India, while the native peoples
Indigenous peoples are culturally distinct ethnic groups whose members are directly descended from the earliest known inhabitants of a particular geographic region and, to some extent, maintain the language and culture of those original people ...
knew only their own immediate environment" (Whitfield). Jordan Branch and his advisor, Steven Weber, propose that the power of large kingdoms and nation states of later history are an inadvertent byproduct of 15th-century advances in map-making technologies.Kingdom of Castile
The Kingdom of Castile (; es, Reino de Castilla, la, Regnum Castellae) was a large and powerful state on the Iberian Peninsula during the Middle Ages. Its name comes from the host of castles constructed in the region. It began in the 9th ce ...
and Kingdom of Portugal
The Kingdom of Portugal ( la, Regnum Portugalliae, pt, Reino de Portugal) was a monarchy in the western Iberian Peninsula and the predecessor of the modern Portuguese Republic. Existing to various extents between 1139 and 1910, it was also kn ...
) were at the vanguard of European overseas exploration and mapping the coasts of the Americas
The Americas, which are sometimes collectively called America, are a landmass comprising the totality of North America, North and South America. The Americas make up most of the land in Earth's Western Hemisphere and comprise the New World. ...
, Africa
Africa is the world's second-largest and second-most populous continent, after Asia in both cases. At about 30.3 million km2 (11.7 million square miles) including adjacent islands, it covers 6% of Earth's total surface area ...
, and Asia
Asia (, ) is one of the world's most notable geographical regions, which is either considered a continent in its own right or a subcontinent of Eurasia, which shares the continental landmass of Afro-Eurasia with Africa. Asia covers an are ...
, in what came known as the Age of Discovery
The Age of Discovery (or the Age of Exploration), also known as the early modern period, was a period largely overlapping with the Age of Sail, approximately from the 15th century to the 17th century in European history, during which seafa ...
(also known as the Age of Exploration
The Age of Discovery (or the Age of Exploration), also known as the early modern period, was a period largely overlapping with the Age of Sail, approximately from the 15th century to the 17th century in European history, during which seafaring ...
). Spain
, image_flag = Bandera de España.svg
, image_coat = Escudo de España (mazonado).svg
, national_motto = '' Plus ultra'' (Latin)(English: "Further Beyond")
, national_anthem = (English: "Royal March")
, ...
and Portugal
Portugal, officially the Portuguese Republic ( pt, República Portuguesa, links=yes ), is a country whose mainland is located on the Iberian Peninsula of Southwestern Europe, and whose territory also includes the Atlantic archipelagos of th ...
were magnets for the talent, science and technology from the Italian city-states
The Italian city-states were numerous political and independent territorial entities that existed in the Italian Peninsula from the beginning of the Middle Ages until the proclamation of the Kingdom of Italy, which took place in 1861.
After t ...
.
Portugal's methodical expeditions started in 1419 along West Africa
West Africa or Western Africa is the westernmost region of Africa. The United Nations defines Western Africa as the 16 countries of Benin, Burkina Faso, Cape Verde, The Gambia, Ghana, Guinea, Guinea-Bissau, Ivory Coast, Liberia, Mali ...
's coast under the sponsorship of Prince Henry the Navigator
''Dom'' Henrique of Portugal, Duke of Viseu (4 March 1394 – 13 November 1460), better known as Prince Henry the Navigator ( pt, Infante Dom Henrique, o Navegador), was a central figure in the early days of the Portuguese Empire and in the 15t ...
, with Bartolomeu Dias
Bartolomeu Dias ( 1450 – 29 May 1500) was a Portuguese mariner and explorer. In 1488, he became the first European navigator to round the southern tip of Africa and to demonstrate that the most effective southward route for ships lay in the o ...
reaching the Cape of Good Hope
The Cape of Good Hope ( af, Kaap die Goeie Hoop ) ;''Kaap'' in isolation: pt, Cabo da Boa Esperança is a rocky headland on the Atlantic coast of the Cape Peninsula in South Africa.
A common misconception is that the Cape of Good Hope is ...
and entering the Indian Ocean
The Indian Ocean is the third-largest of the world's five oceanic divisions, covering or ~19.8% of the water on Earth's surface. It is bounded by Asia to the north, Africa to the west and Australia to the east. To the south it is bounded by ...
in 1488. Ten years later, in 1498, Vasco da Gama
Vasco da Gama, 1st Count of Vidigueira (; ; c. 1460s – 24 December 1524), was a Portuguese explorer and the first European to reach India by sea.
His initial voyage to India by way of Cape of Good Hope (1497–1499) was the first to link ...
led the first fleet around Africa to India
India, officially the Republic of India (Hindi: ), is a country in South Asia. It is the List of countries and dependencies by area, seventh-largest country by area, the List of countries and dependencies by population, second-most populous ...
, arriving in Calicut
Kozhikode (), also known in English as Calicut, is a city along the Malabar Coast in the state of Kerala in India. It has a corporation limit population of 609,224 and a metropolitan population of more than 2 million, making it the second ...
and starting a maritime route from Portugal to India. Soon, after Pedro Álvares Cabral
Pedro Álvares Cabral ( or ; born Pedro Álvares de Gouveia; c. 1467 or 1468 – c. 1520) was a Portuguese nobleman, military commander, navigator and explorer regarded as the European discoverer of Brazil. He was the first human ...
reaching Brazil
Brazil ( pt, Brasil; ), officially the Federative Republic of Brazil (Portuguese: ), is the largest country in both South America and Latin America. At and with over 217 million people, Brazil is the world's fifth-largest country by area ...
(1500), explorations proceed to Southeast Asia
Southeast Asia, also spelled South East Asia and South-East Asia, and also known as Southeastern Asia, South-eastern Asia or SEA, is the geographical south-eastern region of Asia, consisting of the regions that are situated south of mainland ...
, having sent the first direct European maritime trade and diplomatic missions to Ming China
The Ming dynasty (), officially the Great Ming, was an imperial dynasty of China, ruling from 1368 to 1644 following the collapse of the Mongol-led Yuan dynasty. The Ming dynasty was the last orthodox dynasty of China ruled by the Han peo ...
and to Japan
Japan ( ja, 日本, or , and formally , ''Nihonkoku'') is an island country in East Asia. It is situated in the northwest Pacific Ocean, and is bordered on the west by the Sea of Japan, while extending from the Sea of Okhotsk in the n ...
(1542).
 In 1492, when a Spanish expedition headed by Genoese explorer
In 1492, when a Spanish expedition headed by Genoese explorer Christopher Columbus
Christopher Columbus
* lij, Cristoffa C(or)ombo
* es, link=no, Cristóbal Colón
* pt, Cristóvão Colombo
* ca, Cristòfor (or )
* la, Christophorus Columbus. (; born between 25 August and 31 October 1451, died 20 May 1506) was a ...
sailed west to find a new trade route to the Far East
The ''Far East'' was a European term to refer to the geographical regions that includes East and Southeast Asia as well as the Russian Far East to a lesser extent. South Asia is sometimes also included for economic and cultural reasons.
The t ...
but inadvertently found the Americas
The Americas, which are sometimes collectively called America, are a landmass comprising the totality of North America, North and South America. The Americas make up most of the land in Earth's Western Hemisphere and comprise the New World. ...
. Columbus's first two voyages (1492–93) reached the Bahamas
The Bahamas (), officially the Commonwealth of The Bahamas, is an island country within the Lucayan Archipelago of the West Indies in the North Atlantic. It takes up 97% of the Lucayan Archipelago's land area and is home to 88% of the a ...
and various Caribbean islands
Almost all of the Caribbean islands are in the Caribbean Sea, with only a few in inland lakes. The largest island is Cuba. Other sizable islands include Hispaniola, Jamaica, Puerto Rico and Trinidad and Tobago. Some of the smaller islands a ...
, including Hispaniola
Hispaniola (, also ; es, La Española; Latin and french: Hispaniola; ht, Ispayola; tnq, Ayiti or Quisqueya) is an island in the Caribbean that is part of the Greater Antilles. Hispaniola is the most populous island in the West Indies, and th ...
, Puerto Rico
Puerto Rico (; abbreviated PR; tnq, Boriken, ''Borinquen''), officially the Commonwealth of Puerto Rico ( es, link=yes, Estado Libre Asociado de Puerto Rico, lit=Free Associated State of Puerto Rico), is a Caribbean island and unincorporated ...
and Cuba
Cuba ( , ), officially the Republic of Cuba ( es, República de Cuba, links=no ), is an island country comprising the island of Cuba, as well as Isla de la Juventud and several minor archipelagos. Cuba is located where the northern Caribb ...
. The Spanish cartographer and explorer Juan de la Cosa
Juan de la Cosa (c. 1450 – 28 February 1510) was a Castilian navigator and cartographer, known for designing the earliest European world map which incorporated the territories of the Americas discovered in the 15th century.
De la Cosa was th ...
sailed with Columbus. He created the first known cartographic representations showing both the Americas. The post-1492 era is known as the period of the Columbian Exchange
The Columbian exchange, also known as the Columbian interchange, was the widespread transfer of plants, animals, precious metals, commodities, culture, human populations, technology, diseases, and ideas between the New World (the Americas) in ...
, a dramatically widespread exchange of animals, plants, culture, human populations (including slaves), communicable disease, and ideas between the American and Afro-Eurasian hemispheres following the Voyages of Christopher Columbus
Between 1492 and 1504, Italian explorer Christopher Columbus led four Spanish transatlantic maritime expeditions of discovery to the Americas. These voyages led to the widespread knowledge of the New World. This breakthrough inaugurated the ...
to the Americas.
The Magellan-Elcano circumnavigation was the first known voyage around the world in human history. It was a Spanish expedition that sailed from Seville
Seville (; es, Sevilla, ) is the capital and largest city of the Spanish autonomous community of Andalusia and the province of Seville. It is situated on the lower reaches of the River Guadalquivir, in the southwest of the Iberian Penins ...
in 1519 under the command of Portuguese navigator Ferdinand Magellan
Ferdinand Magellan ( or ; pt, Fernão de Magalhães, ; es, link=no, Fernando de Magallanes, ; 4 February 1480 – 27 April 1521) was a Portuguese explorer. He is best known for having planned and led the 1519 Spanish expedition to the Eas ...
in search of a maritime path from the Americas
The Americas, which are sometimes collectively called America, are a landmass comprising the totality of North America, North and South America. The Americas make up most of the land in Earth's Western Hemisphere and comprise the New World. ...
to the East Asia
East Asia is the eastern region of Asia, which is defined in both geographical and ethno-cultural terms. The modern states of East Asia include China, Japan, Mongolia, North Korea, South Korea, and Taiwan. China, North Korea, South Korea ...
across the Pacific Ocean
The Pacific Ocean is the largest and deepest of Earth's five oceanic divisions. It extends from the Arctic Ocean in the north to the Southern Ocean (or, depending on definition, to Antarctica) in the south, and is bounded by the conti ...
. Following Magellan's death in Mactan (Philippines
The Philippines (; fil, Pilipinas, links=no), officially the Republic of the Philippines ( fil, Republika ng Pilipinas, links=no),
* bik, Republika kan Filipinas
* ceb, Republika sa Pilipinas
* cbk, República de Filipinas
* hil, Republ ...
) in 1521, Juan Sebastián Elcano
Juan Sebastián Elcano (Elkano in modern Basque; sometimes given as ''del Cano''; 1486/1487Some sources state that he was born in 1476. Most of this sources try to make a point about him participating on a military campaign at the Mediterranean ...
took command of the expedition, sailing to Borneo
Borneo (; id, Kalimantan) is the third-largest island in the world and the largest in Asia. At the geographic centre of Maritime Southeast Asia, in relation to major Indonesian islands, it is located north of Java, west of Sulawesi, and e ...
, the Spice Islands
A spice is a seed, fruit, root, bark, or other plant substance primarily used for flavoring or coloring food. Spices are distinguished from herbs, which are the leaves, flowers, or stems of plants used for flavoring or as a garnish. Spices are ...
and back to Spain across the Indian Ocean, round the Cape of Good Hope and north along the west coast of Africa
Africa is the world's second-largest and second-most populous continent, after Asia in both cases. At about 30.3 million km2 (11.7 million square miles) including adjacent islands, it covers 6% of Earth's total surface area ...
. They arrived in Spain three years after they left, in 1522.
* : Portuguese cartographer Pedro Reinel
Pedro Reinel (fl. 1485 – 1540) was a Portuguese cartographer. Between 1485 and 1519 Reinel served three Portuguese kings: João II, Manuel I and João III. He and his son, Jorge Reinel, were among the most renowned cartographers of their era ...
made the oldest known signed Portuguese nautical chart.
* 1492: Cartographer Jorge de Aguiar made the oldest known signed and dated Portuguese nautical chart.
* 1537: Much of Portuguese mathematician and cosmographer Pedro Nunes
Pedro Nunes (; Latin: ''Petrus Nonius''; 1502 – 11 August 1578) was a Portuguese mathematician, cosmographer, and professor, from a New Christian (of Jewish origin) family.
Considered one of the greatest mathematicians of his time, Nun ...
' work related to navigation
Navigation is a field of study that focuses on the process of monitoring and controlling the movement of a craft or vehicle from one place to another.Bowditch, 2003:799. The field of navigation includes four general categories: land navigation ...
. He was the first to understand why a ship maintaining a steady course
Course may refer to:
Directions or navigation
* Course (navigation), the path of travel
* Course (orienteering), a series of control points visited by orienteers during a competition, marked with red/white flags in the terrain, and corresponding ...
would not travel along a great circle
In mathematics, a great circle or orthodrome is the circular intersection of a sphere and a plane passing through the sphere's center point.
Any arc of a great circle is a geodesic of the sphere, so that great circles in spherical geome ...
, the shortest path between two points on Earth, but would instead follow a spiral
In mathematics, a spiral is a curve which emanates from a point, moving farther away as it revolves around the point.
Helices
Two major definitions of "spiral" in the American Heritage Dictionary are:[loxodrome
In navigation, a rhumb line, rhumb (), or loxodrome is an arc crossing all meridians of longitude at the same angle, that is, a path with constant bearing as measured relative to true north.
Introduction
The effect of following a rhumb li ...]
. These lines, also called rhumb line
In navigation, a rhumb line, rhumb (), or loxodrome is an arc crossing all meridians of longitude at the same angle, that is, a path with constant bearing as measured relative to true north.
Introduction
The effect of following a rhumb l ...
s, maintain a fixed angle with the meridians. In other words, loxodromic curves are directly related to the construction of the Nunes connection, also called navigator connection. In his ''Treatise in Defense of the Marine Chart '' (1537), Nunes argued that a nautical chart
A nautical chart is a graphic representation of a sea area and adjacent coastal regions. Depending on the scale of the chart, it may show depths of water and heights of land ( topographic map), natural features of the seabed, details of the co ...
should have its parallels and meridians shown as straight lines. Yet he was unsure how to solve the problems that this caused, a situation that lasted until Mercator __NOTOC__
Mercator (Latin for "merchant") may refer to:
People
* Marius Mercator (c. 390–451), a Catholic ecclesiastical writer
* Arnold Mercator, a 16th-century cartographer
* Gerardus Mercator, a 16th-century cartographer
** Mercator 1569 ...
developed the projection bearing his name. The Mercator Projection
The Mercator projection () is a cylindrical map projection presented by Flemish geographer and cartographer Gerardus Mercator in 1569. It became the standard map projection for navigation because it is unique in representing north as up and s ...
is the system which is still used.
First maps of the Americas
 * 1500: The Spanish cartographer and explorer
* 1500: The Spanish cartographer and explorer Juan de la Cosa
Juan de la Cosa (c. 1450 – 28 February 1510) was a Castilian navigator and cartographer, known for designing the earliest European world map which incorporated the territories of the Americas discovered in the 15th century.
De la Cosa was th ...
created the first known cartographic representations showing both the Americas as well as Africa and Eurasia.
* 1502: Unknown Portuguese cartographer made the Cantino planisphere
The Cantino planisphere or Cantino world map is a manuscript Portuguese world map preserved at the Biblioteca Estense in Modena, Italy. It is named after Alberto Cantino, an agent for the Duke of Ferrara, who successfully smuggled it from Portug ...
, the first nautical chart to implicitly represent latitudes.
* 1504: Portuguese cartographer Pedro Reinel
Pedro Reinel (fl. 1485 – 1540) was a Portuguese cartographer. Between 1485 and 1519 Reinel served three Portuguese kings: João II, Manuel I and João III. He and his son, Jorge Reinel, were among the most renowned cartographers of their era ...
made the oldest known nautical chart with a scale of latitudes.
* 1519 : Portuguese cartographers Lopo Homem, Pedro Reinel
Pedro Reinel (fl. 1485 – 1540) was a Portuguese cartographer. Between 1485 and 1519 Reinel served three Portuguese kings: João II, Manuel I and João III. He and his son, Jorge Reinel, were among the most renowned cartographers of their era ...
and Jorge Reinel made the group of maps known today as the Miller Atlas or Lopo Homem – Reinéis Atlas.
* 1530: Alonzo de Santa Cruz
Alonzo de Santa Cruz (or Alonso, Alfonso) (1505 – 1567) was a Spanish cartographer, mapmaker, instrument maker, historian and teacher. He was born about 1505, and died in November 1567. His maps were inventoried in 1572.
Alonzo de Santa Cruz was ...
, Spanish cartographer, produced the first map of magnetic variations from true north. He believed it would be of use in finding the correct longitude. Santa Cruz also designed new nautical instruments, and was interested in navigational methods.
Padrón Real of the Spanish Empire
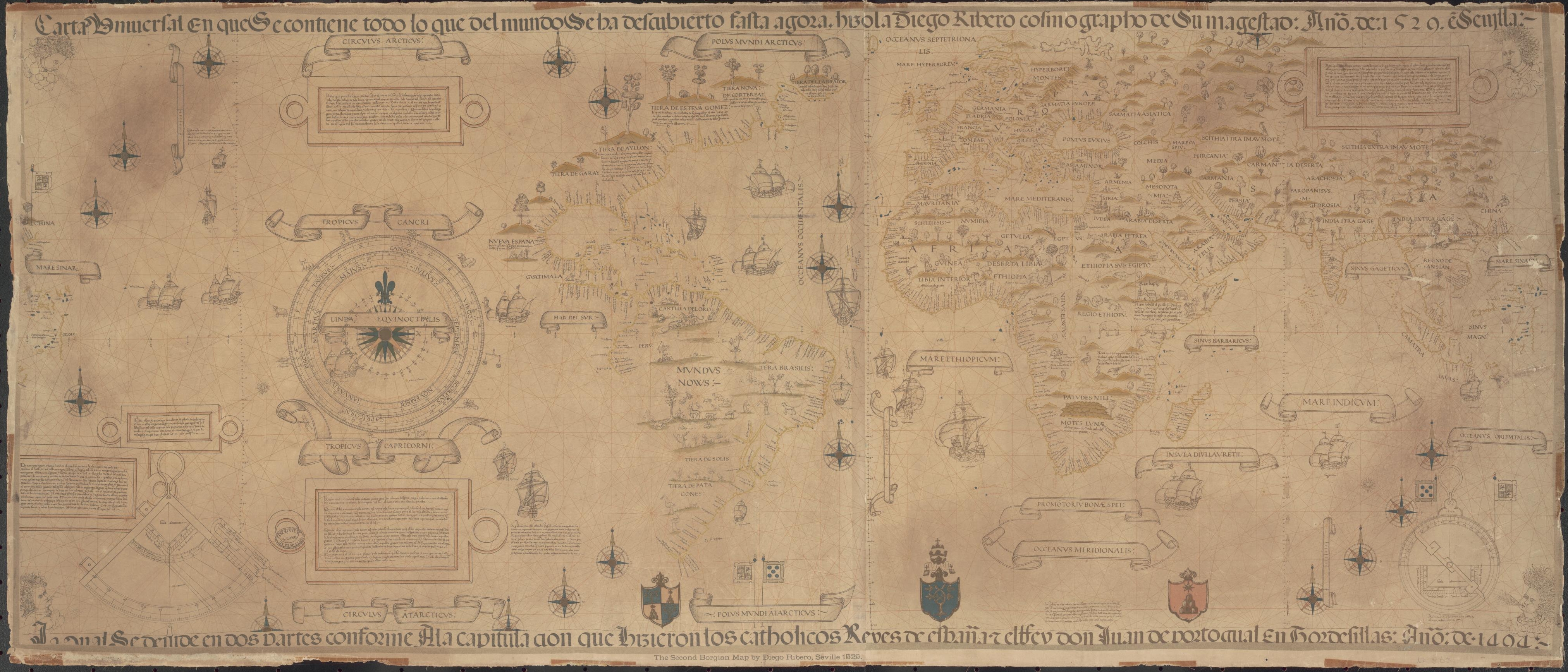 The Spanish House of Trade, founded 1504 in Seville, had a large contingent of cartographers, as Spain's overseas empire expanded. The master map or
The Spanish House of Trade, founded 1504 in Seville, had a large contingent of cartographers, as Spain's overseas empire expanded. The master map or Padrón Real
The Padrón Real (, ''Royal Register''), known after 2 August 1527 as the Padrón General (, ''General Register''), was the official and secret Spanish master map used as a template for the maps present on all Spanish ships during the 16th century ...
was mandated by the Spanish monarch in 1508 and updated subsequently as more information became available with each ship returning to Seville.
Diogo Ribeiro, a Portuguese cartographer working for Spain, made what is considered the first scientific world map: the 1527 Padrón Real. The layout of the map (''Mapamundi'') is strongly influenced by the information obtained during the Magellan- Elcano trip around the world. Diogo's map delineates very precisely the coasts of Central
Central is an adjective usually referring to being in the center of some place or (mathematical) object.
Central may also refer to:
Directions and generalised locations
* Central Africa, a region in the centre of Africa continent, also known a ...
and South America
South America is a continent entirely in the Western Hemisphere and mostly in the Southern Hemisphere, with a relatively small portion in the Northern Hemisphere at the northern tip of the continent. It can also be described as the sou ...
. The map shows, for the first time, the real extension of the Pacific Ocean
The Pacific Ocean is the largest and deepest of Earth's five oceanic divisions. It extends from the Arctic Ocean in the north to the Southern Ocean (or, depending on definition, to Antarctica) in the south, and is bounded by the conti ...
. It also shows, for the first time, the North America
North America is a continent in the Northern Hemisphere and almost entirely within the Western Hemisphere. It is bordered to the north by the Arctic Ocean, to the east by the Atlantic Ocean, to the southeast by South America and th ...
n coast as a continuous one (probably influenced by the Esteban Gómez Esteban () is a Spanish male given name, derived from Greek Στέφανος (Stéphanos) and related to the English names Steven and Stephen. Although in its original pronunciation the accent is on the penultimate syllable, English-speakers tend t ...
's exploration in 1525). It also shows the demarcation of the Treaty of Tordesillas
The Treaty of Tordesillas, ; pt, Tratado de Tordesilhas . signed in Tordesillas, Spain on 7 June 1494, and authenticated in Setúbal, Portugal, divided the newly discovered lands outside Europe between the Portuguese Empire and the Spanish Em ...
.
Two prominent cosmographers (as mapmakers were then known) of the House of Trade were Alonso de Santa Cruz and Juan López de Velasco, who directed mapmaking under Philip II, without ever going to the New World. Their maps were based on information they received from returning navigators. Using repeatable principles that underpin mapmaking, their map making techniques could be employed anywhere. Philip II sought extensive information about his overseas empire, both in written textual form and in the production of maps.
German cartography

 * 15th century: The German monk
* 15th century: The German monk Nicolaus Germanus
Nicolaus Germanus () was a German cartographer who modernized Ptolemy's ''Geography'' by applying new projections, adding additional maps, and contributing other innovations that were influential in the development of Renaissance cartography.
N ...
wrote a pioneering Cosmographia. He added the first new maps to Ptolemy's ''Geographica''.Martin Behaim
Martin Behaim (6 October 1459 – 29 July 1507), also known as and by various forms of , was a German textile merchant and cartographer. He served John II of Portugal as an adviser in matters of navigation and participated in a voyage to W ...
(1459–1507) made the oldest surviving terrestrial globe, but it lacked the Americas.Martin Waldseemüller
Martin Waldseemüller (c. 1470 – 16 March 1520) was a German cartographer and humanist scholar. Sometimes known by the Latinized form of his name, Hylacomylus, his work was influential among contemporary cartographers. He and his collaborator ...
's world map
A world map is a map of most or all of the surface of Earth. World maps, because of their scale, must deal with the problem of projection. Maps rendered in two dimensions by necessity distort the display of the three-dimensional surface of ...
(Waldseemüller map
The Waldseemüller map or ''Universalis Cosmographia'' ("Universal Cosmography") is a printed wall map of the world by German cartography, cartographer Martin Waldseemüller, originally published in April 1507. It is known as the first map to ...
) was the first to use the term America for the Western continents (after explorer Amerigo Vespucci).Johann Bayer
Johann Bayer (1572 – 7 March 1625) was a German lawyer and uranographer (celestial cartographer). He was born in Rain, Lower Bavaria, in 1572. At twenty, in 1592 he began his study of philosophy and law at the University of Ingolstadt, ...
's star atlas (Uranometria
''Uranometria'' is a star atlas produced by Johann Bayer. It was published in Augsburg in 1603 by Christoph Mangle (''Christophorus Mangus'') under the full title ''Uranometria: omnium asterismorum continens schemata, nova methodo delineata, a ...
) was published in Augsburg in 1603 and was the first atlas to cover the entire celestial sphere
In astronomy and navigation, the celestial sphere is an abstract sphere that has an arbitrarily large radius and is concentric to Earth. All objects in the sky can be conceived as being projected upon the inner surface of the celestial sphe ...
.
Dutch and Flemish cartography

Leuven
Leuven (, ) or Louvain (, , ; german: link=no, Löwen ) is the capital and largest city of the province of Flemish Brabant in the Flemish Region of Belgium. It is located about east of Brussels. The municipality itself comprises the historic c ...
, Antwerp
Antwerp (; nl, Antwerpen ; french: Anvers ; es, Amberes) is the largest city in Belgium by area at and the capital of Antwerp Province in the Flemish Region. With a population of 520,504, , and Amsterdam
Amsterdam ( , , , lit. ''The Dam on the River Amstel'') is the capital and most populous city of the Netherlands, with The Hague being the seat of government. It has a population of 907,976 within the city proper, 1,558,755 in the urban ar ...
were the main centres of the Netherlandish school of cartography in its golden age (the 16th and 17th centuries, approximately 1570–1670s). The Golden Age of Dutch cartography (also known as the Golden Age of Netherlandish cartography) that was inaugurated in the Southern Netherlands
The Southern Netherlands, also called the Catholic Netherlands, were the parts of the Low Countries belonging to the Holy Roman Empire which were at first largely controlled by Habsburg Spain (Spanish Netherlands, 1556–1714) and later by the A ...
(current Belgium; mainly in Leuven and Antwerp) by Mercator and Ortelius found its fullest expression during the seventeenth century with the production of monumental multi-volume world atlases in the Dutch Republic
The United Provinces of the Netherlands, also known as the (Seven) United Provinces, officially as the Republic of the Seven United Netherlands ( Dutch: ''Republiek der Zeven Verenigde Nederlanden''), and commonly referred to in historiograph ...
(mainly in Amsterdam) by competing mapmaking firms such as Lucas Waghenaer, Joan Blaeu, Jan Janssonius
Johannes Janssonius (1588, Arnhem – buried July 11, 1664, Amsterdam) (born Jan Janszoon, in English also Jan Jansson) was a Dutch cartographer and publisher who lived and worked in Amsterdam in the 17th century.
Biography
Janssonius was ...
, Claes Janszoon Visscher
Claes Janszoon Visscher (1587 – 19 June 1652) was a Dutch Golden Age draughtsman, engraver, mapmaker, and publisher. He was the founder of the successful Visscher family mapmaking business. The firm that he established in Amsterdam would be p ...
, and Frederik de Wit. Notable representatives of the Netherlandish school of cartography and geography (1500s–1600s) include: Franciscus Monachus,
Notable representatives of the Netherlandish school of cartography and geography (1500s–1600s) include: Franciscus Monachus, Gemma Frisius
Gemma Frisius (; born Jemme Reinerszoon; December 9, 1508 – May 25, 1555) was a Frisian physician, mathematician, cartographer, philosopher, and instrument maker. He created important globes, improved the mathematical instruments of his ...
, Gaspard van der Heyden
Gaspard van der Heyden (also known as Gaspar à Myrica) (c. 1496 – c. 1549) was a goldsmith, engraver, master printer and builder of precision astronomical instruments including terrestrial and celestial globes from Leuven, Belgium. He was we ...
, Gerard Mercator, Abraham Ortelius
Abraham Ortelius (; also Ortels, Orthellius, Wortels; 4 or 14 April 152728 June 1598) was a Brabantian cartographer, geographer, and cosmographer, conventionally recognized as the creator of the first modern atlas, the '' Theatrum Orbis Terraru ...
, Christophe Plantin
Christophe Plantin ( nl, Christoffel Plantijn; – 1 July 1589) was a French Renaissance humanist and book printer and publisher who resided and worked in Antwerp.
Life
Plantin was born in France, probably in Saint-Avertin, near the city of ...
, Lucas Waghenaer, Jacob van Deventer, Willebrord Snell
Willebrord Snellius (born Willebrord Snel van Royen) (13 June 158030 October 1626) was a Dutch astronomer and mathematician, Snell. His name is usually associated with the law of refraction of light known as Snell's law.
The lunar crater Sne ...
, Hessel Gerritsz, Petrus Plancius
Petrus Plancius (; 1552 – 15 May 1622) was a Dutch-Flemish astronomer, cartographer and clergyman. He was born as Pieter Platevoet in Dranouter, now in Heuvelland, West Flanders. He studied theology in Germany and England. At the age of 24 he ...
, Jodocus Hondius
Jodocus Hondius (Latinized version of his Dutch name: ''Joost de Hondt'') (17 October 1563 – 12 February 1612) was a Flemish and Dutch engraver and cartographer. He is sometimes called Jodocus Hondius the Elder to distinguish him from hi ...
, Henricus Hondius II
Henricus Hondius II (1597 – 16 August 1651) was a Dutch engraver, cartographer, and publisher.
Life
He was born in Amsterdam, the son of the famous cartographer Jodocus Hondius who had started a map-making business in the city. Henricu ...
, Hendrik Hondius I, Willem Blaeu
Willem Janszoon Blaeu (; 157121 October 1638), also abbreviated to Willem Jansz. Blaeu, was a Dutch cartographer, atlas maker and publisher. Along with his son Johannes Blaeu, Willem is considered one of the notable figures of the Netherlandis ...
, Joan Blaeu
Joan Blaeu (; 23 September 1596 – 21 December 1673) was a Dutch cartographer born in Alkmaar, the son of cartographer Willem Blaeu.
Life
In 1620, Blaeu became a doctor of law but he joined the work of his father. In 1635, they published ...
, Johannes Janssonius, Andreas Cellarius
Andreas Cellarius (–1665) was a Dutch–German cartographer and cosmographer best known for his 1660 '' Harmonia Macrocosmica'', a major star atlas.
Life
He was born in Neuhausen, and was educated in Heidelberg. The Protestant Cellarius ...
, Gerard de Jode, Cornelis de Jode, Claes Visscher
Claes Janszoon Visscher (1587 – 19 June 1652) was a Dutch Golden Age draughtsman, engraver, mapmaker, and publisher. He was the founder of the successful Visscher family mapmaking business. The firm that he established in Amsterdam would be p ...
, Nicolaes Visscher I Nicolaes Visscher I (25 January 1618, Amsterdam – buried 11 September 1679, Amsterdam) was a Dutch engraver, cartographer and publisher. He was the son of Claes Janszoon Visscher. His son, Nicolaes Visscher II (1649–1702), also worked with hi ...
, Nicolaes Visscher II, and Frederik de Wit.
Gerardus Mercator
Gerardus Mercator (; 5 March 1512 – 2 December 1594) was a 16th-century geographer, cosmographer and cartographer from the County of Flanders. He is most renowned for creating the 1569 world map based on a new projection which represented ...
, the German-Netherlandish[See the discussion in Gerardus Mercator#The question of nationality.] cartographer and geographer with a vast output of wall maps, bound maps, globes and scientific instruments but his greatest legacy was the mathematical projection he devised for his 1569 world map. The Mercator projection
The Mercator projection () is a cylindrical map projection presented by Flemish geographer and cartographer Gerardus Mercator in 1569. It became the standard map projection for navigation because it is unique in representing north as up and s ...
is an example of a cylindrical projection in which the meridians are straight and perpendicular to the parallels. As a result, the map has a constant width and the parallels are stretched east–west as the poles are approached. Mercator's insight was to stretch the separation of the parallels in a way which exactly compensates for their increasing length, thus preserving shapes of small regions, albeit at the expense of global distortion. Such a conformal map projection necessarily transforms rhumb line
In navigation, a rhumb line, rhumb (), or loxodrome is an arc crossing all meridians of longitude at the same angle, that is, a path with constant bearing as measured relative to true north.
Introduction
The effect of following a rhumb l ...
s, sailing courses of a constant bearing, into straight lines on the map thus greatly facilitating navigation. That this was Mercator's intention is clear from the title: ''Nova et Aucta Orbis Terrae Descriptio ad Usum Navigantium Emendate Accommodata'' which translates as "New and more complete representation of the terrestrial globe properly adapted for use in navigation". Although the projection's adoption was slow, by the end of the seventeenth century it was in use for naval charts.
Mercator spent the last thirty years of his life working on a vast project, the ''Cosmographia''; a description of the whole universe including the creation and a description of the topography, history and institutions of all countries. The word ''atlas
An atlas is a collection of maps; it is typically a bundle of maps of Earth or of a region of Earth.
Atlases have traditionally been bound into book form, but today many atlases are in multimedia formats. In addition to presenting geogra ...
'' makes its first appearance in the title of the final volume: "Atlas sive cosmographicae meditationes de fabrica mundi et fabricati figura". This translates as ''Atlas OR cosmographical meditations upon the creation of the universe, and the universe as created,'' thus providing Mercator's definition of the term ''atlas''. These volumes devote slightly less than one half of their pages to maps: Mercator did not use the term solely to describe a bound collection of maps. His choice of title was motivated by his respect for Atlas
An atlas is a collection of maps; it is typically a bundle of maps of Earth or of a region of Earth.
Atlases have traditionally been bound into book form, but today many atlases are in multimedia formats. In addition to presenting geogra ...
"King of Mauretania
Mauretania (; ) is the Latin name for a region in the ancient Maghreb. It stretched from central present-day Algeria westwards to the Atlantic, covering northern present-day Morocco, and southward to the Atlas Mountains. Its native inhabitants ...
"
Abraham Ortelius
Abraham Ortelius (; also Ortels, Orthellius, Wortels; 4 or 14 April 152728 June 1598) was a Brabantian cartographer, geographer, and cosmographer, conventionally recognized as the creator of the first modern atlas, the '' Theatrum Orbis Terraru ...
generally recognized as the creator of the first modern atlas
An atlas is a collection of maps; it is typically a bundle of maps of Earth or of a region of Earth.
Atlases have traditionally been bound into book form, but today many atlases are in multimedia formats. In addition to presenting geogra ...
, the ''Theatrum Orbis Terrarum
''Theatrum Orbis Terrarum'' (, "Theatre of the Orb of the World") is considered to be the first true modern atlas. Written by Abraham Ortelius, strongly encouraged by Gillis Hooftman and originally printed on 20 May 1570 in Antwerp, it consi ...
''. Triangulation
In trigonometry and geometry, triangulation is the process of determining the location of a point by forming triangles to the point from known points.
Applications
In surveying
Specifically in surveying, triangulation involves only angle me ...
had first emerged as a map-making method in the mid sixteenth century when Gemma Frisius
Gemma Frisius (; born Jemme Reinerszoon; December 9, 1508 – May 25, 1555) was a Frisian physician, mathematician, cartographer, philosopher, and instrument maker. He created important globes, improved the mathematical instruments of his ...
set out the idea in his ''Libellus de locorum describendorum ratione'' (''Booklet concerning a way of describing places''). Dutch cartographer Jacob van Deventer was among the first to make systematic use of triangulation
In trigonometry and geometry, triangulation is the process of determining the location of a point by forming triangles to the point from known points.
Applications
In surveying
Specifically in surveying, triangulation involves only angle me ...
, the technique whose theory was described by Frisius in his 1533 book.
The modern systematic use of triangulation networks stems from the work of the Dutch mathematician Willebrord Snell
Willebrord Snellius (born Willebrord Snel van Royen) (13 June 158030 October 1626) was a Dutch astronomer and mathematician, Snell. His name is usually associated with the law of refraction of light known as Snell's law.
The lunar crater Sne ...
(born Willebrord Snel van Royen), who in 1615 surveyed the distance from Alkmaar
Alkmaar () is a city and municipality in the Netherlands, located in the province of North Holland, about 30 km north of Amsterdam. Alkmaar is well known for its traditional cheese market. For tourists, it is a popular cultural destination. The ...
to Bergen op Zoom
Bergen op Zoom (; called ''Berrege'' in the local dialect) is a municipality and a city located in the south of the Netherlands.
Etymology
The city was built on a place where two types of soil meet: sandy soil and marine clay. The sandy soil ...
, approximately 70 miles (110 kilometres), using a chain of quadrangles containing 33 triangles in all. The two towns were separated by one degree on the meridian, so from his measurement he was able to calculate a value for the circumference of the earth – a feat celebrated in the title of his book ''Eratosthenes Batavus'' (''The Dutch Eratosthenes
Eratosthenes of Cyrene (; grc-gre, Ἐρατοσθένης ; – ) was a Greek polymath: a mathematician, geographer, poet, astronomer, and music theorist. He was a man of learning, becoming the chief librarian at the Library of Alexandr ...
''), published in 1617. Snell's methods were taken up by Jean Picard
Jean Picard (21 July 1620 – 12 July 1682) was a French astronomer and priest born in La Flèche, where he studied at the Jesuit Collège Royal Henry-Le-Grand.
He is principally notable for his accurate measure of the size of the Earth, bas ...
who in 1669–70 surveyed one degree of latitude along the Paris Meridian
The Paris meridian is a meridian line running through the Paris Observatory in Paris, France – now longitude 2°20′14.02500″ East. It was a long-standing rival to the Greenwich meridian as the prime meridian of the world. The "Paris meri ...
using a chain of thirteen triangles stretching north from Paris
Paris () is the capital and most populous city of France, with an estimated population of 2,165,423 residents in 2019 in an area of more than 105 km² (41 sq mi), making it the 30th most densely populated city in the world in 2020. Si ...
to the clocktower of Sourdon, near Amiens
Amiens (English: or ; ; pcd, Anmien, or ) is a city and commune in northern France, located north of Paris and south-west of Lille. It is the capital of the Somme department in the region of Hauts-de-France. In 2021, the population of ...
.
The first printed atlas
An atlas is a collection of maps; it is typically a bundle of maps of Earth or of a region of Earth.
Atlases have traditionally been bound into book form, but today many atlases are in multimedia formats. In addition to presenting geogra ...
of nautical chart
A nautical chart is a graphic representation of a sea area and adjacent coastal regions. Depending on the scale of the chart, it may show depths of water and heights of land ( topographic map), natural features of the seabed, details of the co ...
s (''De Spieghel der Zeevaerdt'' or ''The Mirror of Navigation'' / ''The Mariner's Mirror'') was produced by Lucas Janszoon Waghenaer
Lucas Janszoon Waghenaer (–) was a Dutch cartographer and a notable figure of the Golden Age of Netherlandish cartography, known for his pioneering contributions on the subject of nautical cartography.
Career
Seafaring
Waghenaer is one ...
in Leiden
Leiden (; in English and archaic Dutch also Leyden) is a city and municipality in the province of South Holland, Netherlands. The municipality of Leiden has a population of 119,713, but the city forms one densely connected agglomeration w ...
in 1584. This atlas was the first attempt to systematically codify nautical map
A nautical chart is a graphic representation of a sea area and adjacent coastal regions. Depending on the scale of the chart, it may show depths of water and heights of land (topographic map), natural features of the seabed, details of the coa ...
s. This chart-book combined an atlas of nautical charts and sailing directions with instructions for navigation on the western and north-western coastal waters of Europe. It was the first of its kind in the history of maritime cartography.
In 1660, German-born Dutch cartographer Andreas Cellarius
Andreas Cellarius (–1665) was a Dutch–German cartographer and cosmographer best known for his 1660 '' Harmonia Macrocosmica'', a major star atlas.
Life
He was born in Neuhausen, and was educated in Heidelberg. The Protestant Cellarius ...
' star atlas ('' Harmonia Macrocosmica'') was published by Johannes Janssonius in Amsterdam.
In the long run the competition between map-making firms Blaeu and Janssonius resulted in the publication of an 'Atlas Maior
The ''Atlas Maior'' is the final version of Joan Blaeu's atlas, published in Amsterdam between 1662 and 1672, in Latin (11 volumes), French (12 volumes), Dutch (9 volumes), German (10 volumes) and Spanish (10 volumes), containing 594 maps and ...
' or 'Major Atlas'. In 1662 the Latin edition of Joan Blaeu
Joan Blaeu (; 23 September 1596 – 21 December 1673) was a Dutch cartographer born in Alkmaar, the son of cartographer Willem Blaeu.
Life
In 1620, Blaeu became a doctor of law but he joined the work of his father. In 1635, they published ...
's ''Atlas Maior'' appeared in eleven volumes and with approximately 600 maps. In the years to come French and Dutch editions followed in twelve and nine volumes respectively. Purely judging from the number of maps in the ''Atlas Maior
The ''Atlas Maior'' is the final version of Joan Blaeu's atlas, published in Amsterdam between 1662 and 1672, in Latin (11 volumes), French (12 volumes), Dutch (9 volumes), German (10 volumes) and Spanish (10 volumes), containing 594 maps and ...
'', Blaeu had outdone his rival Johannes Janssonius. And also from a commercial point of view it was a huge success. Also due to the superior typography the ''Atlas Maior'' by Blaeu soon became a status symbol for rich citizens. Costing 350 guilders for a non-coloured and 450 guilders for a coloured version, the atlas was the most precious book of the 17th century. However, the ''Atlas Maior'' was also a turning point: after that time the role of Dutch cartography (and Netherlandish cartography in general) was finished. Janssonius died in 1664 while a great fire in 1672 destroyed one of Blaeu's print shops. In that fire a part of the copperplates went up in flames. Fairly soon afterwards Joan Blaeu died, in 1673. The almost 2,000 copperplates of Janssonius and Blaeu found their way to other publishers.
French cartography
Historian David Buisseret has traced the roots of the flourishing of cartography in the 16th and 17th centuries in Europe. He noted five distinct reasons: 1) admiration of antiquity
Antiquity or Antiquities may refer to:
Historical objects or periods Artifacts
*Antiquities, objects or artifacts surviving from ancient cultures
Eras
Any period before the European Middle Ages (5th to 15th centuries) but still within the histo ...
, especially the rediscovery of Ptolemy
Claudius Ptolemy (; grc-gre, Πτολεμαῖος, ; la, Claudius Ptolemaeus; AD) was a mathematician, astronomer, astrologer, geographer, and music theorist, who wrote about a dozen scientific treatises, three of which were of importanc ...
, considered to be the first geographer; 2) increasing reliance on measurement and quantification as a result of the scientific revolution; 3) refinements in the visual arts, such as the discovery of perspective, that allowed for better representation of spatial entities; 4) development of estate property; and 5) the importance of mapping to nation-building.
The reign of Louis XIV is generally considered to represent the beginning of cartography as a science in France.[Pelletier, Monique. “Cartography and Power in Europe
During the Seventeenth and Eighteenth Centuries,” ''Cartographica'' 35 (1998).] The evolution of cartography during the transition between the 17th and 18th centuries involved advancements on a technical level, as well as those on a representative level. According to Marco Petrella, the map developed "from a tool used to affirm the administrative borders of the reign and its features…into a tool which was necessary to intervene in territory and thus establish control of it."[Petrella, Marco. "Guillaume Delisle's Carte du Duche de Bourgogne: The Role of Central and Peripheral Authorities in the Construction of a Provincial Territory in France in the Early 18th Century,” ''Journal of Map & Geography Libraries'' 5 (2008): 17–39.] Because unification of the kingdom necessitated well-kept records of land and tax bases, Louis XIV and members of the royal court pushed the development and progression of the sciences, especially cartography. Louis XIV established the ''Académie des Sciences'' in 1666, with the expressed purpose of improving cartography and sailing charts. It was found that all the gaps of knowledge in geography and navigation could be accounted for in the further exploration and study of astronomy and geodesy.[Turnbull, David. "Cartography and Science in Early Modern Europe: Mapping the Construction of Knowledge Spaces,” ''Imago Mundi'' 48 (1996): 5–24.] Colbert also attracted many foreign scientists to the ''Académie des Sciences'' to support the pursuit of scientific knowledge.Giovanni Domenico Cassini
Giovanni Domenico Cassini, also known as Jean-Dominique Cassini (8 June 1625 – 14 September 1712) was an Italian (naturalised French) mathematician, astronomer and engineer. Cassini was born in Perinaldo, near Imperia, at that time in the ...
, who perfected a method of determining longitude by the observation of movement of Jupiter
Jupiter is the fifth planet from the Sun and the largest in the Solar System. It is a gas giant with a mass more than two and a half times that of all the other planets in the Solar System combined, but slightly less than one-thousand ...
’s satellites. Cassini, along with the aid and support of mathematician Jean Picard
Jean Picard (21 July 1620 – 12 July 1682) was a French astronomer and priest born in La Flèche, where he studied at the Jesuit Collège Royal Henry-Le-Grand.
He is principally notable for his accurate measure of the size of the Earth, bas ...
, developed a system of uniting the provincial topographical information into a comprehensive map of the country, through a network of surveyed triangles. It established a practice that was eventually adopted by all nations in their project to map the areas under their domain.meridian arc
In geodesy and navigation, a meridian arc is the curve between two points on the Earth's surface having the same longitude. The term may refer either to a segment of the meridian, or to its length.
The purpose of measuring meridian arcs is to ...
of Paris-Amiens as their starting point.Jean-Baptiste Colbert
Jean-Baptiste Colbert (; 29 August 1619 – 6 September 1683) was a French statesman who served as First Minister of State from 1661 until his death in 1683 under the rule of King Louis XIV. His lasting impact on the organization of the country ...
, the secretary of home affairs and prominent member of Louis XIV's royal court, set out to develop the resource base of the nation and to develop a system of infrastructure that could restore the French economy. He wanted to generate income for the high expenses incurred by Louis XIV. What Colbert lacked in his pursuit of the development of the economy was a map of the entire country. France, like all other countries of Europe, operated on local knowledge. Within France, there were local systems of measuring weight and taxes; a uniform notion of land surveying did not exist.
Paris as the center of cartography
The seventeenth century marked the emergence of France
France (), officially the French Republic ( ), is a country primarily located in Western Europe. It also comprises of Overseas France, overseas regions and territories in the Americas and the Atlantic Ocean, Atlantic, Pacific Ocean, Pac ...
as the center of the map trade in Europe, with much of the production and distribution of maps taking place in the capital Paris.[Pedley, Mary Sponberg. "The Map Trade in Paris, 1650–1825," ''Imago Mundi'' 33 (1981).] In conjunction with the support of scientific development, the royal court encouraged the work of arts and artisans. This royal patronage attracted artists to Paris. As a result, many mapmakers, such as Nicolas Sanson and Alexis-Hubert Jaillot, moved to the national capital from the peripheries of the provinces.
Dieppe school of cartographers
The Dieppe maps are a series of world maps produced in Dieppe
Dieppe (; Norman: ''Dgieppe'') is a coastal commune in the Seine-Maritime department in the Normandy region of northern France.
Dieppe is a seaport on the English Channel at the mouth of the river Arques. A regular ferry service runs to N ...
, France, in the 1540s, 1550s and 1560s. They are large hand-produced maps, commissioned for wealthy and royal patrons, including Henry II of France
Henry II (french: Henri II; 31 March 1519 – 10 July 1559) was King of France from 31 March 1547 until his death in 1559. The second son of Francis I and Duchess Claude of Brittany, he became Dauphin of France upon the death of his elder bro ...
and Henry VIII of England
Henry VIII (28 June 149128 January 1547) was King of England from 22 April 1509 until his death in 1547. Henry is best known for his six marriages, and for his efforts to have his first marriage (to Catherine of Aragon) annulled. His disa ...
. The Dieppe school of cartographers
Cartography (; from grc, χάρτης , "papyrus, sheet of paper, map"; and , "write") is the study and practice of making and using maps. Combining science, aesthetics and technique, cartography builds on the premise that reality (or an i ...
included Pierre Desceliers
Pierre Desceliers ( 1537–1553) was a French cartographer of the Renaissance and an eminent member of the Dieppe School of Cartography. He is considered the father of French hydrography.
Little is known of his life. He was probably born at Arqu ...
, Johne Rotz, Guillaume Le Testu, Guillaume Brouscon and Nicolas Desliens.
Nicolas-Louis de Lacaille and the charting of far southern skies
First modern topographic map of France
In the 1670s the astronomer Giovanni Domenico Cassini
Giovanni Domenico Cassini, also known as Jean-Dominique Cassini (8 June 1625 – 14 September 1712) was an Italian (naturalised French) mathematician, astronomer and engineer. Cassini was born in Perinaldo, near Imperia, at that time in the ...
began work on the first modern topographic map
In modern mapping, a topographic map or topographic sheet is a type of map characterized by large- scale detail and quantitative representation of relief features, usually using contour lines (connecting points of equal elevation), but histori ...
in France. It was completed in 1789 or 1793 by his grandson Cassini de Thury.
18th-century developments
 The Vertical Perspective projection was first used by the German map publisher Matthias Seutter in 1740. He placed his observer at ~12,750 km distance. This is the type of projection used today by Google Earth.
The Vertical Perspective projection was first used by the German map publisher Matthias Seutter in 1740. He placed his observer at ~12,750 km distance. This is the type of projection used today by Google Earth.Joseph-Nicolas Delisle
Joseph-Nicolas Delisle (; 4 April 1688 – 11 September 1768) was a French astronomer and cartographer.
Life
Joseph was born in Paris, one of the 11 sons of Claude Delisle (1644–1720). Like many of his brothers, among them Guillaume Delisle ...
in 1745.Nicolas de Fer
Nicolas de Fer (, 1646 – 25 October 1720) was a French cartographer and geographer. He also was an engraver and publisher. His works focused more on quantity than quality, there were often geographical errors, and they were more artistic than a ...
.
In 1763–1767 Captain James Cook
James Cook (7 November 1728 Old Style date: 27 October – 14 February 1779) was a British explorer, navigator, cartographer, and captain in the British Royal Navy, famous for his three voyages between 1768 and 1779 in the Pacific Ocean and ...
mapped Newfoundland
Newfoundland and Labrador (; french: Terre-Neuve-et-Labrador; frequently abbreviated as NL) is the easternmost province of Canada, in the country's Atlantic region. The province comprises the island of Newfoundland and the continental region ...
.
In 1777 Colonel Joseph Frederick Wallet DesBarres
Joseph Frederick Wallet Des Barres (22 November 1721 or April–May 1729 – 24 or 27 October 1824) was a Canadian cartographer who served in the Seven Years' War, as the aide-de-camp to General James Wolfe. He later went on to serve as the L ...
created a monumental four volume atlas of North America, ''Atlantic Neptune
The ''Atlantic Neptune'' is a monumental four volume atlas which was the most important collection of maps, charts and views of North America published in the eighteenth century. It was created by Colonel Joseph Frederick Wallet Des Barres.
Des ...
''.
 In the
In the United States
The United States of America (U.S.A. or USA), commonly known as the United States (U.S. or US) or America, is a country Continental United States, primarily located in North America. It consists of 50 U.S. state, states, a Washington, D.C., ...
in the 18th and 19th centuries, explorers mapped trails and army engineers surveyed government lands. Two agencies were established to provide more detailed, large-scale mapping. They were the U.S. Geological Survey and the United States Coast and Geodetic Survey
The United States Coast and Geodetic Survey (abbreviated USC&GS), known from 1807 to 1836 as the Survey of the Coast and from 1836 until 1878 as the United States Coast Survey, was the first scientific agency of the United States Government. It ...
(now the National Geodetic Survey
The National Geodetic Survey (NGS) is a United States federal agency that defines and manages a national coordinate system, providing the foundation for transportation and communication; mapping and charting; and a large number of applications ...
under the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Association).
19th-century developments
 During his travels in Spanish America (1799–1804)
During his travels in Spanish America (1799–1804) Alexander von Humboldt
Friedrich Wilhelm Heinrich Alexander von Humboldt (14 September 17696 May 1859) was a German polymath, geographer, naturalist, explorer, and proponent of Romantic philosophy and science. He was the younger brother of the Prussian minister ...
created the most accurate map of New Spain
New Spain, officially the Viceroyalty of New Spain ( es, Virreinato de Nueva España, ), or Kingdom of New Spain, was an integral territorial entity of the Spanish Empire, established by Habsburg Spain during the Spanish colonization of the A ...
(now Mexico) to date. Published as part of his ''Essai politique sur le royaume de la Nouvelle-Espagne'' (1811) (''Political Essay on the Kingdom of New Spain''), Humboldt's ''Carte du Mexique'' (1804) was based on existing maps of Mexico, but with Humboldt's careful attention to latitude and longitude. Landing at the Pacific coast port of Acapulco in 1803, Humboldt did not leave the port area for Mexico City until he produced a map of the port; when leaving he drew a map of the east coast port of Veracruz, as well as a map of the central plateau of Mexico. Given royal authorization from the Spanish crown for his trip, crown officials in Mexico were eager to aid Humboldt's research. He had access to José Antonio de Alzate y Ramírez's ''Mapa del Arzobispado de México'' (1768), which he deemed "very bad", as well as the seventeenth-century map of greater Mexico City by savant Don Carlos de Sigüenza y Góngora
Don Carlos de Sigüenza y Góngora (August 14, 1645 – August 22, 1700) was one of the first great intellectuals born in the New World - Spanish viceroyalty of New Spain ( Mexico City). He was a criollo patriot, exalting New Spain over O ...
.
John Disturnell, a businessman and publisher of guidebooks and maps, published ''Mapa de los Estados Unidos de Méjico'', which was used in the negotiations between the U.S. and Mexico in the Treaty of Guadalupe Hidalgo
The Treaty of Guadalupe Hidalgo ( es, Tratado de Guadalupe Hidalgo), officially the Treaty of Peace, Friendship, Limits, and Settlement between the United States of America and the United Mexican States, is the peace treaty that was signed on 2 ...
(1848), following the Mexican–American War
The Mexican–American War, also known in the United States as the Mexican War and in Mexico as the (''United States intervention in Mexico''), was an armed conflict between the United States and Mexico from 1846 to 1848. It followed the ...
, based on the 1822 map by U.S. cartographer Henry Schenck Tanner
Henry Schenck Tanner (1786–1858), was an American cartographer, born in New York City.
He produced ''A Geographical and Statistical Account of the Epidemic Cholera from its Commencement in India to its Entrance into the United States'' in 18 ...
. This map has been described as showing U.S. Manifest Destiny
Manifest destiny was a cultural belief in the 19th-century United States that American settlers were destined to expand across North America.
There were three basic tenets to the concept:
* The special virtues of the American people and th ...
; a copy of the map was offered for sale in 2016 for $65,000. Map making at that time was important for both Mexico and the United States.
The Greenwich prime meridian
A prime meridian is an arbitrary meridian (a line of longitude) in a geographic coordinate system at which longitude is defined to be 0°. Together, a prime meridian and its anti-meridian (the 180th meridian in a 360°-system) form a great ...
became the international standard reference for cartographers in 1884.
20th-century developments
During the 20th century, maps became more abundant due to improvements in printing and photography that made production cheaper and easier. Airplanes made it possible to photograph large areas at a time.
Two-point equidistant projection was first drawn up by Hans Maurer
Hans Maurer (born 13 September 1934) was a West German bobsled
Bobsleigh or bobsled is a team winter sport that involves making timed runs down narrow, twisting, banked, iced tracks in a gravity-powered sleigh. International bobsleigh co ...
in 1919. In this projection the distance from any point on the map to either of the two regulating points is accurate.Waldo Tobler
Waldo Rudolph Tobler (November 16, 1930 – February 20, 2018) was an American-Swiss geographer and cartographer. Tobler's idea that "Everything is related to everything else, but near things are more related than distant things" is referred to ...
in 1966.
Contemporary developments
Software development
Nowadays map-making heavily relies on computer software to develop and provide a variety of services, a trend that already started at the end of the previous century. For instance, self-location, browser search of places, business, products, and area, and distance calculation. At the present time, computer-based software is dominated by big companies that offer their services to a worldwide public, such as Google Maps
Google Maps is a web mapping platform and consumer application offered by Google. It offers satellite imagery, aerial photography, street maps, 360° interactive panoramic views of streets (Street View), real-time traffic conditions, and rou ...
, Apple Maps
Apple Maps is a web mapping service developed by Apple Inc. The default map system of iOS, iPadOS, macOS, and watchOS, it provides directions and estimated times of arrival for driving, walking, cycling, and public transportation navigat ...
, Bing Maps
Bing Maps (previously Live Search Maps, Windows Live Maps, Windows Live Local, and MSN Virtual Earth) is a web mapping service provided as a part of Microsoft's Bing (search engine), Bing suite of search engines and powered by the Bing Maps for En ...
, National Geographic Maps, ESRI
Esri (; Environmental Systems Research Institute) is an American multinational geographic information system (GIS) software company. It is best known for its ArcGIS products. With a 43% market share, Esri is the world's leading supplier of GIS ...
Geographic Information System (GIS), CartoDB, Mapbox, Waze
Waze (; he, ווייז, label=Hebrew), formerly FreeMap Israel, is a subsidiary company of Google that provides satellite navigation software on smartphones and other computers that support the Global Positioning System (GPS). In addition to ...
, etc. Many other state-based, regional and smaller initiatives, and companies offer their services. The list of online map services
Online maps can be basically divided by the covered area (global or local) and by the representation of this area (classic drawn or orthophoto).
Global online maps
These maps cover the world, but may have insufficient details in some areas.
* ...
is quite long and is growing every day.
Historical map collections
Recent development also include the integration of ancient maps and modern scholar research combined with modern computer software to elaborate periodical history maps. Initiatives such as Euratlas History Maps (which covers the whole of Europe from the year 1 AD to the present), Centennia Historical Atlas (which covers Europe from the year 1000AD to the present), Geacron, and many others who work in what is called historical cartography
The history of cartography refers to the development and consequences of cartography, or mapmaking technology, throughout human history. Maps have been one of the most important human inventions for millennia, allowing humans to explain and navig ...
. These maps include evolution of countries, provinces and cities, wars and battles, the history of border changes, etc.
Today historical cartography is thriving. The specialization of map services is ever growing. New map projection
In cartography, map projection is the term used to describe a broad set of transformations employed to represent the two-dimensional curved surface of a globe on a plane. In a map projection, coordinates, often expressed as latitude and l ...
s are still being developed, university map collections, such as Perry–Castañeda Library Map Collection
The Perry–Castañeda Library Map Collection is an extensive map collection owned by the Perry–Castañeda Library at The University of Texas at Austin.
Many of the maps in the collection have been scanned and are available online, and mos ...
at the University of Texas
The University of Texas at Austin (UT Austin, UT, or Texas) is a public research university in Austin, Texas. It was founded in 1883 and is the oldest institution in the University of Texas System. With 40,916 undergraduate students, 11,075 ...
, offer better and more diverse maps and map tools every day, making available for their students and the broad public ancient maps that in the past were difficult to find. David Rumsey Historical Map Collection
The David Rumsey Historical Map Collection is a large private map collection with over 150,000 maps and cartographic items. The collection was created by David Rumsey who, after making his fortune in real estate, focused initially on collectin ...
is nowadays a worldwide known initiative.
Self-publishing tools and collaborative mapping
Never in the past there were many "edit-yourself" map tools and software available for non-specialist. Map blogs and self-publishing are common. In 2004, Steve Coast created OpenStreetMap
OpenStreetMap (OSM) is a free, open geographic database updated and maintained by a community of volunteers via open collaboration. Contributors collect data from surveys, trace from aerial imagery and also import from other freely licensed g ...
, a collaborative project to create a free editable map of the world. The creation and growth of OpenStreetMap has been motivated by restrictions on use or availability of map information across much of the world, and the advent of inexpensive portable satellite navigation
A satellite navigation or satnav system is a system that uses satellites to provide autonomous geo-spatial positioning. It allows satellite navigation devices to determine their location ( longitude, latitude, and altitude/ elevation) to hig ...
devices.
Organizations
In 1921, the International Hydrographic Organization
The International Hydrographic Organization (IHO) is an intergovernmental organisation representing hydrography. , the IHO comprised 98 Member States.
A principal aim of the IHO is to ensure that the world's seas, oceans and navigable waters ...
(IHO) was set up, and it constitutes the authority on hydrographic surveying and nautical charting.1953
Events
January
* January 6 – The Asian Socialist Conference opens in Rangoon, Burma.
* January 12 – Estonian émigrés found a government-in-exile in Oslo.
* January 14
** Marshal Josip Broz Tito is chosen President of Yugosl ...
. The second edition dated back to 1937
Events
January
* January 1 – Anastasio Somoza García becomes President of Nicaragua.
* January 5 – Water levels begin to rise in the Ohio River in the United States, leading to the Ohio River flood of 1937, which continues into ...
, and the first to 1928
Events January
* January – British bacteriologist Frederick Griffith reports the results of Griffith's experiment, indirectly proving the existence of DNA.
* January 1 – Eastern Bloc emigration and defection: Boris Bazhano ...
. A fourth edition draft was published in 1986
The year 1986 was designated as the International Year of Peace by the United Nations.
Events January
* January 1
** Aruba gains increased autonomy from the Netherlands by separating from the Netherlands Antilles.
**Spain and Portugal en ...
but so far several naming disputes (such as the one over the Sea of Japan
The Sea of Japan is the marginal sea between the Japanese archipelago, Sakhalin, the Korean Peninsula, and the mainland of the Russian Far East. The Japanese archipelago separates the sea from the Pacific Ocean. Like the Mediterranean Sea, i ...
) have prevented its ratification.
History of cartography's technological changes
:''More at Cartography § Technological changes''
 In cartography, technology has continually changed in order to meet the demands of new generations of mapmakers and map users. The first maps were manually constructed with brushes and parchment and therefore varied in quality and were limited in distribution. The advent of the
In cartography, technology has continually changed in order to meet the demands of new generations of mapmakers and map users. The first maps were manually constructed with brushes and parchment and therefore varied in quality and were limited in distribution. The advent of the compass
A compass is a device that shows the cardinal directions used for navigation and geographic orientation. It commonly consists of a magnetized needle or other element, such as a compass card or compass rose, which can pivot to align itself with ...
, printing press
A printing press is a mechanical device for applying pressure to an inked surface resting upon a print medium (such as paper or cloth), thereby transferring the ink. It marked a dramatic improvement on earlier printing methods in which the ...
, telescope
A telescope is a device used to observe distant objects by their emission, absorption, or reflection of electromagnetic radiation. Originally meaning only an optical instrument using lenses, curved mirrors, or a combination of both to obse ...
, sextant
A sextant is a doubly reflecting navigation instrument that measures the angular distance between two visible objects. The primary use of a sextant is to measure the angle between an astronomical object and the horizon for the purposes of ce ...
, quadrant and vernier allowed for the creation of far more accurate maps and the ability to make accurate reproductions. Professor Steven Weber of the University of California, Berkeley
The University of California, Berkeley (UC Berkeley, Berkeley, Cal, or California) is a public land-grant research university in Berkeley, California. Established in 1868 as the University of California, it is the state's first land-grant un ...
, has advanced the hypothesis that the concept of the "nation state
A nation state is a political unit where the state and nation are congruent. It is a more precise concept than "country", since a country does not need to have a predominant ethnic group.
A nation, in the sense of a common ethnicity, may ...
" is an inadvertent byproduct of 15th-century advances in map-making technologies.computer hardware
Computer hardware includes the physical parts of a computer, such as the case, central processing unit (CPU), random access memory (RAM), monitor, mouse, keyboard, computer data storage, graphics card, sound card, speakers and motherboard.
...
devices such as computer screens, plotters, printers, scanners (remote and document) and analytic stereo plotters along with visualization, image processing, spatial analysis and database software, have democratized and greatly expanded the making of maps, particularly with their ability to produce maps that show slightly different features, without engraving a new printing plate. See also digital raster graphic
A digital raster graphic (DRG) is a digital image resulting from scanning a paper USGS topographic map for use on a computer. DRGs created by USGS are typically scanned at 250 dpi and saved as a TIFF. The raster image usually includes the ori ...
and History of web mapping.
Aerial photography
Aerial photography (or airborne imagery) is the taking of photographs from an aircraft or other airborne platforms. When taking motion pictures, it is also known as aerial videography.
Platforms for aerial photography include fixed-wing airc ...
and satellite imagery
Satellite images (also Earth observation imagery, spaceborne photography, or simply satellite photo) are images of Earth collected by imaging satellites operated by governments and businesses around the world. Satellite imaging companies sell ima ...
have provided high-accuracy, high-throughput methods for mapping physical features over large areas, such as coastlines, roads, buildings, and topography.
See also
* s
*
*
*
* (India)
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
Related histories
*
*
*
*
*
*
Notes
References
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
External links
''Imago Mundi''
journal of History of Cartography
journal published by the University of Chicago Press
Euratlas Historical Maps
History maps from year zero AD
The History of Cartography Project
at the University of Wisconsin, a comprehensive research project in the history of maps and mapping
Three volumes of ''The History of Cartography''
are available free in PDF format
at the School of Mathematics and Statistics, University of St. Andrews, Scotland
– a learning resource from the British Library
Modern Medieval Map Myths: The Flat World, Ancient Sea-Kings, and Dragons
Newberry Library
Newberry Library Cartographic Catalog : map catalog and bibliography of the history of cartography
American Geographical Society Library Digital Map Collection
David Rumsey Historical map collection
licensed under a Creative Commons License
See Maps
A map is a symbolic depiction emphasizing relationships between elements of some space, such as objects, regions, or themes.
Many maps are static, fixed to paper or some other durable medium, while others are dynamic or interactive. Although ...
for more links to historical maps; however, most of the largest sites are listed at the sites linked below.
Eratosthenes Map of the Earth, and Measuring of its Circumference
at Convergence
Ancient World Maps
describing holdings of manuscripts, archives, rare books, historical photographs, and other primary sources for the research scholar
Historical Atlas in Persuasive Cartography, The PJ Mode Collection
Cornell University Library
The Cornell University Library is the library system of Cornell University. As of 2014, it holds over 8 million printed volumes and over a million ebooks. More than 90 percent of its current 120,000 periodical titles are available online. It ...
Old Maps Online
{{DEFAULTSORT:History Of Cartography
cartography
Cartography (; from grc, χάρτης , "papyrus, sheet of paper, map"; and , "write") is the study and practice of making and using maps. Combining science, aesthetics and technique, cartography builds on the premise that reality (or an i ...
sv:Kartografins historia
 It's not always clear whether an ancient artifact had been wrought as a map or as something else. The definition of "map" is also not precise. Thus, no single artifact is generally accepted to be the earliest surviving map. Candidates include:
* A map-like representation of a mountain, river, valleys and routes around Pavlov in the
It's not always clear whether an ancient artifact had been wrought as a map or as something else. The definition of "map" is also not precise. Thus, no single artifact is generally accepted to be the earliest surviving map. Candidates include:
* A map-like representation of a mountain, river, valleys and routes around Pavlov in the  Maps in Ancient
Maps in Ancient  Hecatæus's map describes the earth as disk with an encircling Ocean, and with Greece placed in the center. This was a very popular contemporary Greek worldview, derived originally from the Homeric poems. Also, similar to many other early maps in antiquity, his map has no scale. As units of measurements, this map used "days of sailing" on the sea and "days of marching" on dry land. The purpose of this map was to accompany Hecatæus's geographical work that was called '' Periodos Ges'', or '' Journey Round the World''. ''Periodos Ges'' was divided into two books, "Europe" and "Asia", with the latter including Libya, the name of which was an ancient term for all of known Africa.
The work divides the world into two continents, Asia and Europe. Hecatæus depicts the line between the Pillars of Hercules through the Bosporus, and the Don River as a boundary between the two. He was the first writer known to have thought that the Caspian flows into the encircling ocean—an idea that persisted long into the Hellenic period. He was particularly instructive about the Black Sea, adding many geographic places that already were known to Greeks through the colonization process. To the north of the Danube, according to Hecatæus, were the Rhipæan (gusty) Mountains, beyond which lived the Hyperboreans—peoples of the far north. Hecatæus depicted the origin of the Nile River at the southern encircling ocean. His view of the Nile seems to have been that it came from the southern encircling ocean. This assumption helped Hecatæus propose a solution to the mystery of the annual flooding of the Nile. He believed that the waves of the ocean were a primary cause of this occurrence. A map based on Hecataeus’s was intended to aid political decision-making. According to
Hecatæus's map describes the earth as disk with an encircling Ocean, and with Greece placed in the center. This was a very popular contemporary Greek worldview, derived originally from the Homeric poems. Also, similar to many other early maps in antiquity, his map has no scale. As units of measurements, this map used "days of sailing" on the sea and "days of marching" on dry land. The purpose of this map was to accompany Hecatæus's geographical work that was called '' Periodos Ges'', or '' Journey Round the World''. ''Periodos Ges'' was divided into two books, "Europe" and "Asia", with the latter including Libya, the name of which was an ancient term for all of known Africa.
The work divides the world into two continents, Asia and Europe. Hecatæus depicts the line between the Pillars of Hercules through the Bosporus, and the Don River as a boundary between the two. He was the first writer known to have thought that the Caspian flows into the encircling ocean—an idea that persisted long into the Hellenic period. He was particularly instructive about the Black Sea, adding many geographic places that already were known to Greeks through the colonization process. To the north of the Danube, according to Hecatæus, were the Rhipæan (gusty) Mountains, beyond which lived the Hyperboreans—peoples of the far north. Hecatæus depicted the origin of the Nile River at the southern encircling ocean. His view of the Nile seems to have been that it came from the southern encircling ocean. This assumption helped Hecatæus propose a solution to the mystery of the annual flooding of the Nile. He believed that the waves of the ocean were a primary cause of this occurrence. A map based on Hecataeus’s was intended to aid political decision-making. According to  Anaximenes of Miletus (6th century BC), who studied under Anaximander, rejected the views of his teacher regarding the shape of the earth and instead, he visualized the earth as a rectangular form supported by compressed air.
Anaximenes of Miletus (6th century BC), who studied under Anaximander, rejected the views of his teacher regarding the shape of the earth and instead, he visualized the earth as a rectangular form supported by compressed air.
 Herodotus traveled extensively, collecting information and documenting his findings in his books on Europe, Asia, and Libya. He also combined his knowledge with what he learned from the people he met. Herodotus wrote his ''
Herodotus traveled extensively, collecting information and documenting his findings in his books on Europe, Asia, and Libya. He also combined his knowledge with what he learned from the people he met. Herodotus wrote his ''
 In 2007, the ''
In 2007, the '' The multicolour map, Da Ming Hunyi Tu dates to the early
The multicolour map, Da Ming Hunyi Tu dates to the early  Indian cartographic traditions covered the locations of the
Indian cartographic traditions covered the locations of the  The
The  On the work of al-Idrisi, S. P. Scott commented:
Al-Idrisi's atlas, originally called the ''Nuzhat'' in Arabic, served as a major tool for Italian, Dutch and French mapmakers from the 16th century to the 18th century.
On the work of al-Idrisi, S. P. Scott commented:
Al-Idrisi's atlas, originally called the ''Nuzhat'' in Arabic, served as a major tool for Italian, Dutch and French mapmakers from the 16th century to the 18th century.



 The Polynesian peoples who explored and settled the Pacific islands in the first two millennia AD used maps to navigate across large distances. A surviving map from the
The Polynesian peoples who explored and settled the Pacific islands in the first two millennia AD used maps to navigate across large distances. A surviving map from the  In 1492, when a Spanish expedition headed by Genoese explorer
In 1492, when a Spanish expedition headed by Genoese explorer  * 1500: The Spanish cartographer and explorer
* 1500: The Spanish cartographer and explorer  The Spanish House of Trade, founded 1504 in Seville, had a large contingent of cartographers, as Spain's overseas empire expanded. The master map or
The Spanish House of Trade, founded 1504 in Seville, had a large contingent of cartographers, as Spain's overseas empire expanded. The master map or 
 * 15th century: The German monk
* 15th century: The German monk 
 Notable representatives of the Netherlandish school of cartography and geography (1500s–1600s) include: Franciscus Monachus,
Notable representatives of the Netherlandish school of cartography and geography (1500s–1600s) include: Franciscus Monachus, 
 The Vertical Perspective projection was first used by the German map publisher Matthias Seutter in 1740. He placed his observer at ~12,750 km distance. This is the type of projection used today by Google Earth.
The changes in the use of military maps was also part of the modern Military Revolution, which changed the need for information as the scale of conflict increases as well. This created a need for maps to help with "... consistency, regularity and uniformity in military conflict."
The final form of the equidistant conic projection was constructed by the French astronomer
The Vertical Perspective projection was first used by the German map publisher Matthias Seutter in 1740. He placed his observer at ~12,750 km distance. This is the type of projection used today by Google Earth.
The changes in the use of military maps was also part of the modern Military Revolution, which changed the need for information as the scale of conflict increases as well. This created a need for maps to help with "... consistency, regularity and uniformity in military conflict."
The final form of the equidistant conic projection was constructed by the French astronomer  In the
In the  During his travels in Spanish America (1799–1804)
During his travels in Spanish America (1799–1804)  In cartography, technology has continually changed in order to meet the demands of new generations of mapmakers and map users. The first maps were manually constructed with brushes and parchment and therefore varied in quality and were limited in distribution. The advent of the
In cartography, technology has continually changed in order to meet the demands of new generations of mapmakers and map users. The first maps were manually constructed with brushes and parchment and therefore varied in quality and were limited in distribution. The advent of the