Ghods Ababil on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
The HESA Ababil ( fa, ابابیل) is an Iranian family of single-engine multirole tactical
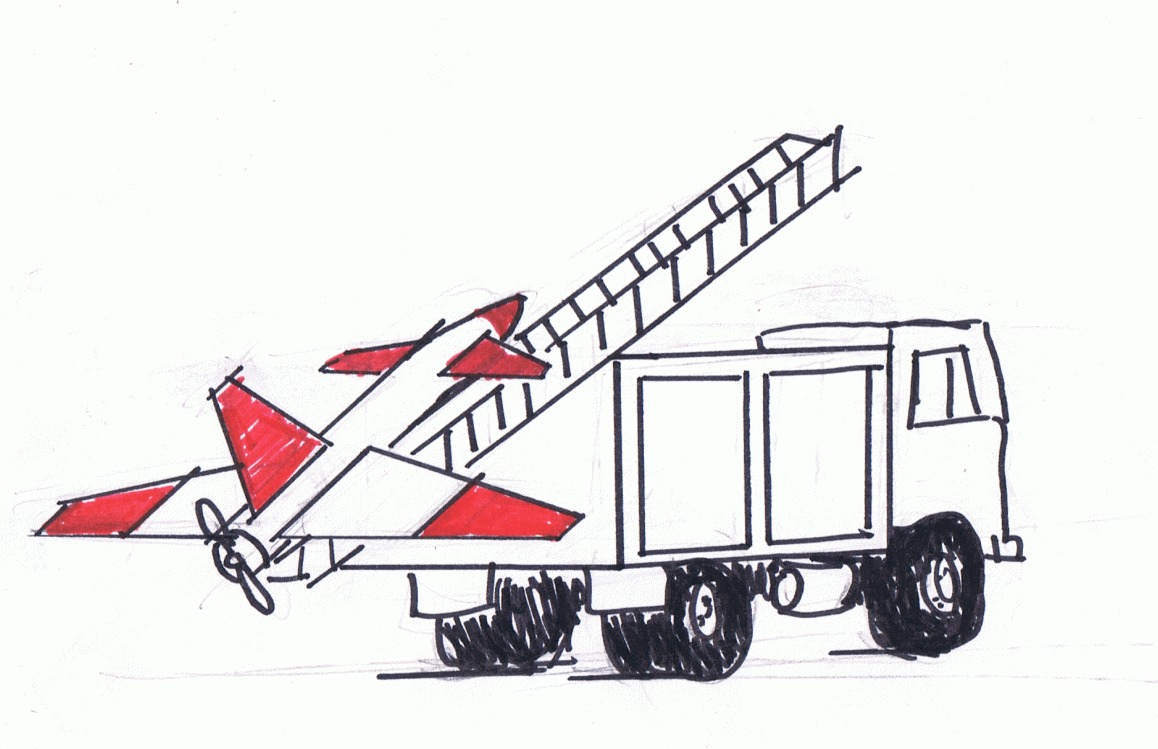 The Ababil has a cylindrical fuselage, a sweptback vertical fin, and a pusher engine. It is powered by a simple two-bladed pusher propeller with a rear-mounted wing and a front canard for good stall, stability and maneuverability characteristics. All variants have a range of over 100 km and all variants have all-metal construction, except for the Ababil-T, which is composite (fiberglass).
The Ababil can be launched from a zero-length
The Ababil has a cylindrical fuselage, a sweptback vertical fin, and a pusher engine. It is powered by a simple two-bladed pusher propeller with a rear-mounted wing and a front canard for good stall, stability and maneuverability characteristics. All variants have a range of over 100 km and all variants have all-metal construction, except for the Ababil-T, which is composite (fiberglass).
The Ababil can be launched from a zero-length
 The Ababil-2 has an improved flight-control system.
The Ababil-2 has an improved flight-control system.
 The name of the Ababil-2 surveillance variant is similarly unclear, but Jane's reports that this is called the Ababil-S. Some sources may also designate this the Ababil-R. Galen Wright assesses it as having "only rudimentary" surveillance capabilities in contrast to other intelligence, surveillance and reconnaissance UAVs.
The name of the Ababil-2 surveillance variant is similarly unclear, but Jane's reports that this is called the Ababil-S. Some sources may also designate this the Ababil-R. Galen Wright assesses it as having "only rudimentary" surveillance capabilities in contrast to other intelligence, surveillance and reconnaissance UAVs.

 The Ababil-3 has a cylindrical body, with wings mounted on top while at the end of the body is an H-shaped twin boom. The wing design is a rectangle which after half its lengths tapers toward the wing tips. The Ababil-3's wingspan is about 7 meters, compared to 3 meters for the Ababil-2. It uses an engine from German company Limbach Flugmotoren, possibly the
The Ababil-3 has a cylindrical body, with wings mounted on top while at the end of the body is an H-shaped twin boom. The wing design is a rectangle which after half its lengths tapers toward the wing tips. The Ababil-3's wingspan is about 7 meters, compared to 3 meters for the Ababil-2. It uses an engine from German company Limbach Flugmotoren, possibly the  Analysis of an Ababil-3 downed over ISIS-held territory in Iraq, apparently due to mechanical failure, finds that the Ababil-3 is built out of composite materials. The powerplant had plain-surfaced cylinder heads; it was unclear if the engine was manufactured in Iran or China. Overall, the manufacture was "very economical" and the Ababil-3 was designed for low cost. There were also a number of defects in the downed Ababil-3 model, which could suggest poor manufacture or handling in the field.
Ababil-3s are based at an airstrip outside of Minab, a town near
Analysis of an Ababil-3 downed over ISIS-held territory in Iraq, apparently due to mechanical failure, finds that the Ababil-3 is built out of composite materials. The powerplant had plain-surfaced cylinder heads; it was unclear if the engine was manufactured in Iran or China. Overall, the manufacture was "very economical" and the Ababil-3 was designed for low cost. There were also a number of defects in the downed Ababil-3 model, which could suggest poor manufacture or handling in the field.
Ababil-3s are based at an airstrip outside of Minab, a town near
 Hezbollah acquired Ababil-2 drones (twin-tail variant) in 2002, and operated them under the Mirsad-1 designation. Israel has said that
Hezbollah acquired Ababil-2 drones (twin-tail variant) in 2002, and operated them under the Mirsad-1 designation. Israel has said that
unmanned aerial vehicle
An unmanned aerial vehicle (UAV), commonly known as a drone, is an aircraft without any human pilot, crew, or passengers on board. UAVs are a component of an unmanned aircraft system (UAS), which includes adding a ground-based controller ...
s manufactured by Iran Aircraft Manufacturing Industrial Company
Iran Aircraft Manufacturing Industrial Company (HESA), ( fa, شرکت صنایع هواپیماسازی ایران — هسا) or Iran Aircraft Manufacturing Industries Corporation, is an Iranian aircraft production company. Established in 1976 ...
(HESA). The Ababil comes in two main lines, the Ababil-2 and the Ababil-3, of which the former has a number of variants. It is considered a long-range, low-technology drone.
The Ababil program was begun during the Iran–Iraq War
The Iran–Iraq War was an armed conflict between Iran and Iraq that lasted from September 1980 to August 1988. It began with the Iraqi invasion of Iran and lasted for almost eight years, until the acceptance of United Nations Security Council ...
. The Ababil-2, developed in the 1990s, has rudimentary surveillance capabilities and can be used as a loitering munition
A loitering munition (also known as a suicide droneLoitering Muniti ...
, but is mainly used as a target drone
A target drone is an unmanned aerial vehicle, generally remote controlled, usually used in the training of anti-aircraft crews.
One of the earliest drones was the British DH.82 Queen Bee, a variant of the Tiger Moth trainer aircraft operationa ...
. The larger and more capable Ababil-3, introduced in the 2000s, was designed for Intelligence, surveillance and reconnaissance
ISTAR stands for intelligence, surveillance, target acquisition, and reconnaissance. In its macroscopic sense, ISTAR is a practice that links several battlefield functions together to assist a combat force in employing its sensors and managing t ...
use and has improved surveillance capabilities. Overall, the Ababil has been described "a pretty rough-and-ready system" because of its "cheap, simple, and ease of use."
The Ababil-2 and Ababil-3 have been widely exported to governments and paramilitaries in the Middle East and elsewhere. The Ababil has been used in the 2006 Lebanon War
The 2006 Lebanon War, also called the 2006 Israel–Hezbollah War and known in Lebanon as the July War ( ar, حرب تموز, ''Ḥarb Tammūz'') and in Israel as the Second Lebanon War ( he, מלחמת לבנון השנייה, ''Milhemet Leva ...
, the Iraq War
{{Infobox military conflict
, conflict = Iraq War {{Nobold, {{lang, ar, حرب العراق (Arabic) {{Nobold, {{lang, ku, شەڕی عێراق (Kurdish languages, Kurdish)
, partof = the Iraq conflict (2003–present), I ...
, and the Sudanese, Syrian
Syrians ( ar, سُورِيُّون, ''Sūriyyīn'') are an Eastern Mediterranean ethnic group indigenous to the Levant. They share common Levantine Semitic roots. The cultural and linguistic heritage of the Syrian people is a blend of both indi ...
, Iraqi, and Yemeni
Yemen (; ar, ٱلْيَمَن, al-Yaman), officially the Republic of Yemen,, ) is a country in Western Asia. It is situated on the southern end of the Arabian Peninsula, and borders Saudi Arabia to the Saudi Arabia–Yemen border, north and ...
civil wars.
Development
The early history of the Ababil is unclear.Jane's
Jane's Information Group, now styled Janes, is a global open-source intelligence company specialising in military, national security, aerospace and transport topics, whose name derives from British author Fred T. Jane.
History
Jane's Informat ...
reports that the Ababil program was begun at Qods Aviation Industries in 1986 and the first delivery was in 1993. Iranian military expert Galen Wright writes that the program began at Iran Electronics Industries
''Sânai'-ye Elâktrunik-e Iran''
, logo = SAIran.svg
, logo_size = 200px
, type = State-owned
, foundation =
, location_city = Tehran
, location_country = Iran
, area_served = Iran
, industry ...
in the mid-1980s and began mass production in 1986, with possible use in the Iran–Iraq War
The Iran–Iraq War was an armed conflict between Iran and Iraq that lasted from September 1980 to August 1988. It began with the Iraqi invasion of Iran and lasted for almost eight years, until the acceptance of United Nations Security Council ...
.
Design
 The Ababil has a cylindrical fuselage, a sweptback vertical fin, and a pusher engine. It is powered by a simple two-bladed pusher propeller with a rear-mounted wing and a front canard for good stall, stability and maneuverability characteristics. All variants have a range of over 100 km and all variants have all-metal construction, except for the Ababil-T, which is composite (fiberglass).
The Ababil can be launched from a zero-length
The Ababil has a cylindrical fuselage, a sweptback vertical fin, and a pusher engine. It is powered by a simple two-bladed pusher propeller with a rear-mounted wing and a front canard for good stall, stability and maneuverability characteristics. All variants have a range of over 100 km and all variants have all-metal construction, except for the Ababil-T, which is composite (fiberglass).
The Ababil can be launched from a zero-length JATO
JATO (acronym for jet-assisted take-off) is a type of assisted take-off for helping overloaded aircraft into the air by providing additional thrust in the form of small rockets. The term ''JATO'' is used interchangeably with the (more specific ...
platform or a Mercedes Benz 911 pneumatic truck launcher. The rocket launch system can be used from a ship deck and can be assembled or broken down for portability. For recovery, a parachute provides a descent rate of 4 m/s, or skids can be used for conventional landings on a runway or field. Some airframes have also been seen with landing gear.
Variants
The Ababil is built in a number of poorly documented variants.Ababil-1
The Ababil-1 was an obscureloitering munition
A loitering munition (also known as a suicide droneLoitering Muniti ...
built in the 1980s. Its specifications are not known, there are no known photographs, and it is unknown if it was ever used in combat. It is believed to be out of service.
One source writes that the Ababil-1 was essentially a prototype or preproduction version of the Ababil-2. It is described as a suicide drone with 40 kg of explosives.
Ababil-2
 The Ababil-2 has an improved flight-control system.
The Ababil-2 has an improved flight-control system. Jane's
Jane's Information Group, now styled Janes, is a global open-source intelligence company specialising in military, national security, aerospace and transport topics, whose name derives from British author Fred T. Jane.
History
Jane's Informat ...
reports that the Ababil-2 had its first flight in 1997 while Galen Wright writes that it entered production in 1992. Both sources agree the Ababil-2 was publicly revealed in 1999. Some sources also designate the Ababil-2 as the Ababil-II.
Target drone
The most common Ababil-2 variant is atarget drone
A target drone is an unmanned aerial vehicle, generally remote controlled, usually used in the training of anti-aircraft crews.
One of the earliest drones was the British DH.82 Queen Bee, a variant of the Tiger Moth trainer aircraft operationa ...
variant used for training air-defense crews. The name of Ababil variants is unclear, but Jane's reports that this variant is called the Ababil-B. The Ababil-B's mission payloads are acoustic miss-distance-indicators, Infrared
Infrared (IR), sometimes called infrared light, is electromagnetic radiation (EMR) with wavelengths longer than those of visible light. It is therefore invisible to the human eye. IR is generally understood to encompass wavelengths from around ...
devices, and radar reflectors. This variant is the oldest Ababil-2 variant and it apparently entered service in 2001.
Surveillance
 The name of the Ababil-2 surveillance variant is similarly unclear, but Jane's reports that this is called the Ababil-S. Some sources may also designate this the Ababil-R. Galen Wright assesses it as having "only rudimentary" surveillance capabilities in contrast to other intelligence, surveillance and reconnaissance UAVs.
The name of the Ababil-2 surveillance variant is similarly unclear, but Jane's reports that this is called the Ababil-S. Some sources may also designate this the Ababil-R. Galen Wright assesses it as having "only rudimentary" surveillance capabilities in contrast to other intelligence, surveillance and reconnaissance UAVs.
Twin-tail variant
The Ababil-2 also exists in a twin-tail variant, which some (but not all) sources name the Ababil-T. This variant can be fitted with surveillance, target drone, or disposable strike munition payloads. It is probably coterminous with the " Mirsad-1" UAV operated by Hezbollah and may have been renamed "Qasef-1" in Houthi service.Ababil-CH
The Ababil-CH has two rear tails, like the Ababil-T, but is used as a target drone like the Ababil-B. It is slightly larger than the Ababil-T.Qasef-1
The Qasef-1 and Qasef-2Kloitering munition
A loitering munition (also known as a suicide droneLoitering Muniti ...
versions are based on the Ababil-2 airframe and has a 30-kg warhead. It has been solely operated by Yemen
Yemen (; ar, ٱلْيَمَن, al-Yaman), officially the Republic of Yemen,, ) is a country in Western Asia. It is situated on the southern end of the Arabian Peninsula, and borders Saudi Arabia to the Saudi Arabia–Yemen border, north and ...
i Houthis
The Houthi movement (; ar, ٱلْحُوثِيُّون ''al-Ḥūthīyūn'' ), officially called Ansar Allah (' ''Partisans of God'' or ''Supporters of God'') and colloquially simply Houthis, is an Islamist political and armed movement that ...
, who have mostly used it to attack the radar components of MIM-104 Patriot
The MIM-104 Patriot is a surface-to-air missile (SAM) system, the primary of its kind used by the United States Army and several allied states. It is manufactured by the U.S. defense contractor Raytheon and derives its name from the radar compon ...
surface-to-air missiles. The Qasef-1 has been in use since late 2016 and some examples have been intercepted in transit to Yemen. It is possibly a renamed or modified Ababil-T with an installed explosive
An explosive (or explosive material) is a reactive substance that contains a great amount of potential energy that can produce an explosion if released suddenly, usually accompanied by the production of light, heat, sound, and pressure. An expl ...
charge or a warhead
A warhead is the forward section of a device that contains the explosive agent or toxic (biological, chemical, or nuclear) material that is delivered by a missile, rocket, torpedo, or bomb.
Classification
Types of warheads include:
* Explosiv ...
.
The Houthis claim that they manufacture Qasef-1s themselves, but this claim has been disputed and there is widespread suspicion that it is Iranian-built.

Ababil-3
The Ababil-3 is a complete redesign of the Ababil with an improved airframe used solely for surveillance: it carries better equipment and can stay aloft for longer. Some sources also designate the Ababil-3 as the Ababil-III. The Ababil-3 is thought to be based on theSouth Africa
South Africa, officially the Republic of South Africa (RSA), is the southernmost country in Africa. It is bounded to the south by of coastline that stretch along the South Atlantic and Indian Oceans; to the north by the neighbouring countri ...
n Denel Dynamics Seeker
The Denel Dynamics Seeker is an unmanned aerial vehicle (UAV) manufactured in South Africa by Denel Dynamics (formerly Kentron). The system is designed to perform tactical reconnaissance in real time and can conduct day and night surveillance i ...
, and possibly the Seeker-2D model in particular. It is more widely exported than the Ababil-2, and is known to have entered production by 2008, with specific parts manufactured by 2006.
 The Ababil-3 has a cylindrical body, with wings mounted on top while at the end of the body is an H-shaped twin boom. The wing design is a rectangle which after half its lengths tapers toward the wing tips. The Ababil-3's wingspan is about 7 meters, compared to 3 meters for the Ababil-2. It uses an engine from German company Limbach Flugmotoren, possibly the
The Ababil-3 has a cylindrical body, with wings mounted on top while at the end of the body is an H-shaped twin boom. The wing design is a rectangle which after half its lengths tapers toward the wing tips. The Ababil-3's wingspan is about 7 meters, compared to 3 meters for the Ababil-2. It uses an engine from German company Limbach Flugmotoren, possibly the Limbach L550E
The Limbach L550E is a German aircraft engine, designed and produced by Limbach Flugmotoren of Königswinter.Bayerl, Robby; Martin Berkemeier; et al: ''World Directory of Leisure Aviation 2011-12'', pages 240-241. WDLA UK, Lancaster UK, 2011. ...
. Other sources suggest the Ababil-3 is powered by Chinese or Iranian clones of the L550. Other particular parts inside the Ababil-3 were sourced from Irish defense contractors.
 Analysis of an Ababil-3 downed over ISIS-held territory in Iraq, apparently due to mechanical failure, finds that the Ababil-3 is built out of composite materials. The powerplant had plain-surfaced cylinder heads; it was unclear if the engine was manufactured in Iran or China. Overall, the manufacture was "very economical" and the Ababil-3 was designed for low cost. There were also a number of defects in the downed Ababil-3 model, which could suggest poor manufacture or handling in the field.
Ababil-3s are based at an airstrip outside of Minab, a town near
Analysis of an Ababil-3 downed over ISIS-held territory in Iraq, apparently due to mechanical failure, finds that the Ababil-3 is built out of composite materials. The powerplant had plain-surfaced cylinder heads; it was unclear if the engine was manufactured in Iran or China. Overall, the manufacture was "very economical" and the Ababil-3 was designed for low cost. There were also a number of defects in the downed Ababil-3 model, which could suggest poor manufacture or handling in the field.
Ababil-3s are based at an airstrip outside of Minab, a town near Bandar Abbas
Bandar Abbas or Bandar-e ‘Abbās ( fa, , , ), is a port city and capital of Hormozgān Province on the southern coast of Iran, on the Persian Gulf. The city occupies a strategic position on the narrow Strait of Hormuz (just across from Musan ...
. Ababil-3s are also known to be based at Bandar Abbas International Airport. The Ababil-3 is comparable with the RQ-2.
The Ababil-3's max airspeed is , its range is (roundtrip), and it has a service ceiling of . It has an endurance of 4 hours. An estimated 217 Ababil-3s have been built as of July 2019.
In 2014 Iran announced that they had developed night vision capabilities for the Ababil-3. Previous Ababil variants were most effective in daytime. As of 2020, Iran has armed versions of the Ababil-3 drone.
Ababil-3s have been extensively used in the Syrian Civil War. The heterogeneity of pro-regime forces makes it difficult to determine who operates or controls their use. An Ababil-3 crashed or was brought down in Pakistani territory in July 2019.
Operational history
Lebanon
 Hezbollah acquired Ababil-2 drones (twin-tail variant) in 2002, and operated them under the Mirsad-1 designation. Israel has said that
Hezbollah acquired Ababil-2 drones (twin-tail variant) in 2002, and operated them under the Mirsad-1 designation. Israel has said that Hezbollah
Hezbollah (; ar, حزب الله ', , also transliterated Hizbullah or Hizballah, among others) is a Lebanese Shia Islamist political party and militant group, led by its Secretary-General Hassan Nasrallah since 1992. Hezbollah's parami ...
received at least 12 Ababils before the 2006 Lebanon War
The 2006 Lebanon War, also called the 2006 Israel–Hezbollah War and known in Lebanon as the July War ( ar, حرب تموز, ''Ḥarb Tammūz'') and in Israel as the Second Lebanon War ( he, מלחמת לבנון השנייה, ''Milhemet Leva ...
. Three Ababils were launched during the conflict.
The first Ababil was shot down by an Israeli F-16 on 7 August 2006 off the coast of Northern Israel. The second Ababil crashed inside Lebanon on 13 August. The third Ababil deployed by Hezbollah was shot down by another F-16 hours later just inside Israel's northern border. Hezbollah was assessed as having several Ababil UAVs in 2009, although other estimates have ranged from 12 to 24–30. By 2018, Hezbollah stated that the Mirsad-1 had been retired from service.
Hezbollah has also built a large airstrip in Lebanon's Bekaa Valley
The Beqaa Valley ( ar, links=no, وادي البقاع, ', Lebanese ), also transliterated as Bekaa, Biqâ, and Becaa and known in classical antiquity as Coele-Syria, is a fertile valley in eastern Lebanon. It is Lebanon's most important ...
. There is speculation that the airstrip could support larger, runway-launched Ababil-3 UAVs. Hezbollah is not definitively known to operate the Ababil-3.
Sudan
The Ababil-3 is in service with Sudan. In 2008, an Ababil-3 crashed or was shot down while on a surveillance mission. On March 13, 2012, another Sudanese Ababil was lost in action near Toroji,South Kordofan
South Kordofan ( ar, جنوب كردفان ') is one of the 18 wilayat or states of Sudan. It has an area of 158,355 km² and an estimated population of approximately 1,100,000 people (2000). Sudanese rebels of the SPLA-N said they downed it using ground fire, while the Sudanese government said it was due to mechanical failure.
 On 16 March 2009, an American F-16 operating in
On 16 March 2009, an American F-16 operating in


Iraq
 On 16 March 2009, an American F-16 operating in
On 16 March 2009, an American F-16 operating in Iraq
Iraq,; ku, عێراق, translit=Êraq officially the Republic of Iraq, '; ku, کۆماری عێراق, translit=Komarî Êraq is a country in Western Asia. It is bordered by Turkey to Iraq–Turkey border, the north, Iran to Iran–Iraq ...
shot down an Iranian Ababil 3 drone on 25 February 2009 that had been flying through Iraqi airspace for "almost an hour and 10 minutes." The drone crashed about 60 miles northeast of Baghdad, 12 miles inside Iraqi territory near the town of Balad Ruz
Balad Ruz () is a city located some 120 km (75 mi) northeast of Baghdad in the Diyala Governorate of Iraq.
Balad Ruz has a radio station that was opened on December 18, 2006, known as Al Noor Radio Station, meaning "The Light" in A ...
in Diyala Governorate
Diyala Governorate ( ar, محافظة ديالى ) or Diyala Province is a governorate in central-eastern Iraq.
Provincial government
*Governor: Muthana al-Timimi
*Deputy Governor: Mohammed Jassim al-Jubouri
Council
Geography
Diyala Gov ...
. Officials at Iraq's Defence and Interior ministries suggested that the drone might have been scouting for routes to smuggle Iranian weapons into the country. ''The New York Times'', however, speculated that the drone was monitoring Iranian dissidents in Iraq, such as those at Camp Ashraf
Camp Ashraf or Ashraf City was a camp in Iraq's Diyala Governorate, having the character of a small city with all basic infrastructure, and headquarters of the People's Mujahedin of Iran (PMOI/MEK). The population used to be around 3,400 in 2012, b ...
, which is located near where the drone crashed. Abdul Aziz Mohammed Jassim, head of military operations at the Iraqi defence ministry stated that since the drone, "crossed 10 km into Iraq, it's most likely that its entrance was a mistake."
More recently, Ababil-3 UAVs have been used extensively in the Iraqi Civil War. Their use began in summer 2014, shortly after the Fall of Mosul
The Fall of Mosul occurred between 410 June 2014, when Islamic State insurgents, initially led by Abu Abdulrahman al-Bilawi, captured Mosul from the Iraqi Army, led by Lieutenant General Mahdi Al-Gharrawi.
On 4 June, the insurgents began their ...
, from Rasheed Air Base
Al Rasheed Air Base is a major Iraqi Air Force base on the south east outskirts of Baghdad, in the Diyala Governorate of Iraq.
It is located approximately 11 kilometers (6.8 mi) southeast of downtown Baghdad. The air base is served by a ...
.
Iran
Iran is the primary operator of Ababil UAVs. Iran operates large numbers of Ababil-2 UAVs, mostly for training air defense crews, and operates Ababil-3 UAVs for surveillance use.Syria
Ababil-3 UAVs have been used in the Syrian Civil War since 2012. They have been used heavily and are some of the most commonly used UAVs in the war. They are especially commonly seen over Damascus.Gaza
On 14 December 2014, Hamas militants flew an unmanned air vehicle over a parade in the Gaza Strip marking the 27th anniversary of the organization's establishment. Israeli sources identified the aircraft as an Iranian-made Ababil. Also used in the 2021 conflict.Yemen

Houthi
The Houthi movement (; ar, ٱلْحُوثِيُّون ''al-Ḥūthīyūn'' ), officially called Ansar Allah (' ''Partisans of God'' or ''Supporters of God'') and colloquially simply Houthis, is an Islamist political and armed movement that ...
rebels have operated Ababil-T loitering munitions under the name "Qasef-1" to target Saudi and Emirati radar batteries. According to the Houthis, a new variant of the drone named "Qasef-2K" has been designed to explode from a height of 20 meters in the air and rain shrapnel down on its target and has been used to kill 6 people in the coalition controlled Al Anad Air Base
Al Anad Air Base is a military airbase
An air base (sometimes referred to as a military air base, military airfield, military airport, air station, naval air station, air force station, or air force base) is an aerodrome used as a military ...
in Yemen
Yemen (; ar, ٱلْيَمَن, al-Yaman), officially the Republic of Yemen,, ) is a country in Western Asia. It is situated on the southern end of the Arabian Peninsula, and borders Saudi Arabia to the Saudi Arabia–Yemen border, north and ...
. Najran, 840 km southwest of Riyadh on the Saudi-Yemen border also has been receiving Houthi drone attacks.
After the Houthi attack on Saudi oil infrastructure on 14 September 2019, Saudi Arabia tasked F-15
The McDonnell Douglas F-15 Eagle is an American twin-engine, all-weather tactical fighter aircraft designed by McDonnell Douglas (now part of Boeing). Following reviews of proposals, the United States Air Force selected McDonnell Douglas's ...
fighter jets armed with missiles to intercept low flying drones, difficult to intercept with ground based high altitude missile systems like the MIM-104 Patriot
The MIM-104 Patriot is a surface-to-air missile (SAM) system, the primary of its kind used by the United States Army and several allied states. It is manufactured by the U.S. defense contractor Raytheon and derives its name from the radar compon ...
with several drones being downed since then. On 7 March 2021, during a Houthi attack at several Saudi oil installations, Saudi F-15s shot down several attacking drones shot down using heatseeking AIM-9 Sidewinder
The AIM-9 Sidewinder (where "AIM" stands for "Air Intercept Missile") is a short-range air-to-air missile which entered service with the US Navy in 1956 and subsequently was adopted by the US Air Force in 1964. Since then the Sidewinder has prov ...
missiles, with video evidence showing at least two Samad-3 UAVs and one Qasef-2K downed.
On 30 March 2021, a video made by Saudi border guards showed a Saudi F-15 shooting down a Houthi Quasef-2K drone with an AIM-120 AMRAAM fired at short range.
Operators
Current state operators
* **Aerospace Force of the Islamic Revolutionary Guard Corps
The Islamic Revolutionary Guard Corps Aerospace Force or Islamic Revolutionary Guard Corps Air and Space Force (IRGCASF; fa, نیروی هوافضای سپاه پاسداران انقلاب اسلامی, niru-ye havâfazây-e sepâh-e pâsdârâ ...
: Ababil-1, Ababil-2, and Ababil-3
** Islamic Republic of Iran Air Force
, patron =
, motto = , "Skyhigh is my place"
, colours = Ultramarine blue
, colours_label =
, march =
, mascot ...
: Ababil-3
** Islamic Republic of Iran Army
, founded =
, current_form = ( Islamic Republic)
, disbanded =
, branches =
, headquarters = Khatam-al Anbiya Central Headquarters, Tehran
, website =
, commander-in-chief = Maj. Gen ...
: Ababil-2
* : Ababil-3
* : Ababil-3, rebranded as "Zagil III-B"
*
** Syrian Arab Army
The Syrian Army, officially the Syrian Arab Army (SAA) ( ar, الْجَيْشُ الْعَرَبيُّ السُّورِيُّ, al-Jayš al-ʿArabī as-Sūrī), is the army, land force branch of the Syrian Armed Forces. It is the dominant military ...
: Ababil-3
* Ababil-2, with license production
Non-state operators
*Hamas
Hamas (, ; , ; an acronym of , "Islamic Resistance Movement") is a Palestinian Sunni-Islamic fundamentalist, militant, and nationalist organization. It has a social service wing, Dawah, and a military wing, the Izz ad-Din al-Qassam Bri ...
* : Ababil-T, rebranded as "Qasef-1".
* Hezbollah
Hezbollah (; ar, حزب الله ', , also transliterated Hizbullah or Hizballah, among others) is a Lebanese Shia Islamist political party and militant group, led by its Secretary-General Hassan Nasrallah since 1992. Hezbollah's parami ...
: Ababil-2, rebranded as "Mirsad-1".
* Kataib Hezbollah
Kata'ib Hezbollah ( ar, كتائب حزب الله, lit=Battalions of the Party of God)—or the Hezbollah Battalions—is a radical Shia Islam in Iraq, Iraqi Shiite paramilitary group which is part of the Popular Mobilization Forces backed by ...
: Ababil-3, rebranded as "Basir-1".
* Libyan National Army
The Libyan National Army (LNA; ar, الجيش الوطني الليبي, ''al-jaysh al-waṭaniyy al-Lībii'') is a component of Libya's military forces which were nominally a unified national force under the command of Field Marshal Khalifa ...
: Ababil-2.
Specifications (Ababil-2)

See also
References
Attribution: *External links
{{Iranian Aircraft Ababil Unmanned military aircraft of Iran Single-engined pusher aircraft Military equipment of Iran