
Christianity
Christianity is an Abrahamic monotheistic religion based on the life and teachings of Jesus of Nazareth. It is the world's largest and most widespread religion with roughly 2.38 billion followers representing one-third of the global pop ...
is the largest religion in Germany. It was introduced to the area of modern Germany by 300 AD, while parts of that area belonged to the
Roman Empire
The Roman Empire ( la, Imperium Romanum ; grc-gre, Βασιλεία τῶν Ῥωμαίων, Basileía tôn Rhōmaíōn) was the post- Republican period of ancient Rome. As a polity, it included large territorial holdings around the Mediter ...
, and later, when
Franks
The Franks ( la, Franci or ) were a group of Germanic peoples whose name was first mentioned in 3rd-century Roman sources, and associated with tribes between the Lower Rhine and the Ems River, on the edge of the Roman Empire.H. Schutz: Tools, ...
and other Germanic tribes converted to Christianity from the fifth century onwards. The area became fully
Christianized
Christianization ( or Christianisation) is to make Christian; to imbue with Christian principles; to become Christian. It can apply to the conversion of an individual, a practice, a place or a whole society. It began in the Roman Empire, conti ...
by the time of
Charlemagne
Charlemagne ( , ) or Charles the Great ( la, Carolus Magnus; german: Karl der Große; 2 April 747 – 28 January 814), a member of the Carolingian dynasty, was King of the Franks from 768, King of the Lombards from 774, and the first ...
in the eighth and ninth century. After the
Reformation
The Reformation (alternatively named the Protestant Reformation or the European Reformation) was a major movement within Western Christianity in 16th-century Europe that posed a religious and political challenge to the Catholic Church and in ...
started by
Martin Luther
Martin Luther (; ; 10 November 1483 – 18 February 1546) was a German priest, theologian, author, hymnwriter, and professor, and Augustinian friar. He is the seminal figure of the Protestant Reformation and the namesake of Lutherani ...
in the early 16th century, many people left the
Catholic Church
The Catholic Church, also known as the Roman Catholic Church, is the largest Christian church, with 1.3 billion baptized Catholics worldwide . It is among the world's oldest and largest international institutions, and has played a ...
and became
Protestant
Protestantism is a branch of Christianity that follows the theological tenets of the Protestant Reformation, a movement that began seeking to reform the Catholic Church from within in the 16th century against what its followers perceived to b ...
, mainly
Lutheran
Lutheranism is one of the largest branches of Protestantism, identifying primarily with the theology of Martin Luther, the 16th-century German monk and Protestant Reformers, reformer whose efforts to reform the theology and practice of the Cathol ...
and
Calvinist
Calvinism (also called the Reformed Tradition, Reformed Protestantism, Reformed Christianity, or simply Reformed) is a major branch of Protestantism that follows the theological tradition and forms of Christian practice set down by John Ca ...
.
In 2021, around 52.7% of the population were Christians among them 49.7% members of the two large Christian churches.
[Numbers and Facts about Church Life in the EKD 2021 Report](_blank)
Evangelical Church of Germany. Retrieved 3 January 2022. About half of Christians in Germany are Catholics, mostly
Roman Catholic
Roman or Romans most often refers to:
*Rome, the capital city of Italy
* Ancient Rome, Roman civilization from 8th century BC to 5th century AD
* Roman people, the people of ancient Rome
*'' Epistle to the Romans'', shortened to ''Romans'', a let ...
s; Catholicism is stronger in the southern and the western part of the country. About half belongs to the
Evangelical Church of Germany (EKD) predominant in the northern regions, and the rest to several small Christian denominations such as the
Evangelical Lutheran Free Church, the
Eastern Orthodox Church
The Eastern Orthodox Church, also called the Orthodox Church, is the second-largest Christian church, with approximately 220 million baptized members. It operates as a communion of autocephalous churches, each governed by its bishops vi ...
or the
Jehovah's Witnesses.
Estimations for the percentage of
Muslims
Muslims ( ar, المسلمون, , ) are people who adhere to Islam, a monotheistic religion belonging to the Abrahamic tradition. They consider the Quran, the foundational religious text of Islam, to be the verbatim word of the God of Abrah ...
vary between 3.5%
and 6.7%,
while much smaller religions include
Buddhism
Buddhism ( , ), also known as Buddha Dharma and Dharmavinaya (), is an Indian religions, Indian religion or Indian philosophy#Buddhist philosophy, philosophical tradition based on Pre-sectarian Buddhism, teachings attributed to the Buddha. ...
,
Judaism
Judaism ( he, ''Yahăḏūṯ'') is an Abrahamic, monotheistic, and ethnic religion comprising the collective religious, cultural, and legal tradition and civilization of the Jewish people. It has its roots as an organized religion in t ...
,
Hinduism
Hinduism () is an Indian religion or '' dharma'', a religious and universal order or way of life by which followers abide. As a religion, it is the world's third-largest, with over 1.2–1.35 billion followers, or 15–16% of the global p ...
and
Yazidism
Yazidism , alternatively Sharfadin is a monotheistic ethnic religion that has roots in a western Iranic pre-Zoroastrian religion directly derived from the Indo-Iranian tradition. It is followed by the mainly Kurmanji-speaking Yazidis and i ...
.
The rest of the population is not affiliated with any church, and many are
atheist,
agnostic, or otherwise
irreligious.
60% of German residents say that they believe there is a God, 9% say that they believe there is a higher power or spiritual force and 27% say that they do not believe there is a God, higher power or spiritual force. In another survey, 44% said that they believe there is a God, 25% said that they believe there is some sort of spirit or life force and 27% said that they do not believe there is any sort of spirit, God or life force. 35% of residents identify with their religion or belief.
Demographics of religion in Germany vary greatly by region and age. Non-religious people represent the majority in some of Germany's major cities, including
Berlin
Berlin ( , ) is the capital and List of cities in Germany by population, largest city of Germany by both area and population. Its 3.7 million inhabitants make it the European Union's List of cities in the European Union by population within ci ...
,
Hamburg
(male), (female) en, Hamburger(s),
Hamburgian(s)
, timezone1 = Central (CET)
, utc_offset1 = +1
, timezone1_DST = Central (CEST)
, utc_offset1_DST = +2
, postal ...
and
Bremen, and the absolute majority of 70–80% in
the eastern states of what between 1949 and 1990 used to be
East Germany
East Germany, officially the German Democratic Republic (GDR; german: Deutsche Demokratische Republik, , DDR, ), was a country that existed from its creation on 7 October 1949 until its dissolution on 3 October 1990. In these years the state ...
.
By contrast, rural areas of
the western states of what in the same period used to be
West Germany
West Germany is the colloquial term used to indicate the Federal Republic of Germany (FRG; german: Bundesrepublik Deutschland , BRD) between its formation on 23 May 1949 and the German reunification through the accession of East Germany on 3 O ...
are more religious, and some rural areas are highly religious.
History
Paganism and Roman settlement (1000 BC–300 AD)

Ancient
Germanic paganism
Germanic paganism or Germanic religion refers to the traditional, culturally significant religion of the Germanic peoples. With a chronological range of at least one thousand years in an area covering Scandinavia, the British Isles, modern Germ ...
was a
polytheistic
Polytheism is the belief in multiple deities, which are usually assembled into a pantheon of gods and goddesses, along with their own religious sects and rituals. Polytheism is a type of theism. Within theism, it contrasts with monotheism, the ...
religion practised in
prehistoric Germany and
Scandinavia
Scandinavia; Sámi languages: /. ( ) is a subregion in Northern Europe, with strong historical, cultural, and linguistic ties between its constituent peoples. In English usage, ''Scandinavia'' most commonly refers to Denmark, Norway, and Swe ...
, as well as
Roman
Roman or Romans most often refers to:
*Rome, the capital city of Italy
*Ancient Rome, Roman civilization from 8th century BC to 5th century AD
*Roman people, the people of ancient Rome
*'' Epistle to the Romans'', shortened to ''Romans'', a lette ...
territories of
Germania by the first century AD. It had a
pantheon of deities that included
Donar/Thunar,
Wuotan/Wodan,
Frouwa/Frua,
Balder/Phol/Baldag, and others shared with
northern Germanic paganism.
Celtic paganism
Ancient Celtic religion, commonly known as Celtic paganism, was the religion of the ancient Celtic peoples of Europe. Because the ancient Celts did not have writing, evidence about their religion is gleaned from archaeology, Greco-Roman account ...
and later
Gallo-Roman syntheses were instead practised in western and southern parts of modern Germany, while
Slavic paganism was practised in the east.
Late Roman and Carolingian eras (300–1000)
In the territories of Germany under the control of the
Roman Empire
The Roman Empire ( la, Imperium Romanum ; grc-gre, Βασιλεία τῶν Ῥωμαίων, Basileía tôn Rhōmaíōn) was the post- Republican period of ancient Rome. As a polity, it included large territorial holdings around the Mediter ...
(the provinces
Raetia
Raetia ( ; ; also spelled Rhaetia) was a province of the Roman Empire, named after the Rhaetian people. It bordered on the west with the country of the Helvetii, on the east with Noricum, on the north with Vindelicia, on the south-west ...
,
Germania Superior and
Germania Inferior
Germania Inferior ("Lower Germania") was a Roman province from AD 85 until the province was renamed Germania Secunda in the fourth century, on the west bank of the Rhine bordering the North Sea. The capital of the province was Colonia Agripp ...
), early Christianity was introduced and began to flourish after the fourth century. Although pagan
Roman temple
Ancient Roman temples were among the most important buildings in Roman culture, and some of the richest buildings in Roman architecture, though only a few survive in any sort of complete state. Today they remain "the most obvious symbol of ...
s existed beforehand, Christian religious structures were soon built, such as the
Aula Palatina
__NOTOC__
The Aula Palatina, also called Basilica of Constantine (german: Konstantinbasilika), at Trier, Germany, is a Roman palace basilica and an early Christian structure built between AD 300 and AD 310 during the reigns of Constantius Chlorus ...
in
Trier
Trier ( , ; lb, Tréier ), formerly known in English as Trèves ( ;) and Triers (see also names in other languages), is a city on the banks of the Moselle in Germany. It lies in a valley between low vine-covered hills of red sandstone in the ...
(then the capital of the
Roman province
The Roman provinces (Latin: ''provincia'', pl. ''provinciae'') were the administrative regions of Ancient Rome outside Roman Italy that were controlled by the Romans under the Roman Republic and later the Roman Empire. Each province was rule ...
Gallia Belgica
Gallia Belgica ("Belgic Gaul") was a province of the Roman Empire located in the north-eastern part of Roman Gaul, in what is today primarily northern France, Belgium, and Luxembourg, along with parts of the Netherlands and Germany.
In 50 BC, a ...
), completed during the reign of
Roman emperor Constantine I
Constantine I ( , ; la, Flavius Valerius Constantinus, ; ; 27 February 22 May 337), also known as Constantine the Great, was Roman emperor from AD 306 to 337, the first one to Constantine the Great and Christianity, convert to Christiani ...
(306–337).
[Pohlsander, Hans A. (4 Sep 2012) 0 July 2003]
Constantine I (306 – 337 A.D.)
Rensselaer Polytechnic Institute. Accessed 15 May 2018.
During the
Carolingian period
The Carolingian dynasty (; known variously as the Carlovingians, Carolingus, Carolings, Karolinger or Karlings) was a Frankish noble family named after Charlemagne, grandson of mayor Charles Martel and a descendant of the Arnulfing and Pippi ...
, Christianity spread throughout Germany, particularly during the reign of
Charlemagne
Charlemagne ( , ) or Charles the Great ( la, Carolus Magnus; german: Karl der Große; 2 April 747 – 28 January 814), a member of the Carolingian dynasty, was King of the Franks from 768, King of the Lombards from 774, and the first ...
(r. 768–814). Religious structures built during the Carolingian period include the
Palatine Chapel, Aachen
The Palatine Chapel in Aachen is an early medieval chapel and remaining component of Charlemagne's Palace of Aachen in what is now Germany. Although the palace itself no longer exists, the chapel was preserved and now forms the central part of A ...
, a surviving component of the
Palace of Aachen built by architect
Odo of Metz
Eudes (also Oto, Odo, Odon) of Metz (742–814) was an architect who lived during Charlemagne's reign in the Carolingian Empire, and is the earliest known architect born north of the Alps. He was of Armenian origin.
Style
His Carolingian arch ...
during the reign of Charlemagne.
Pre-Reformation period (1000–1517)
Territories of the present-day Germany, like much of Europe, were entirely
Roman Catholic
Roman or Romans most often refers to:
*Rome, the capital city of Italy
* Ancient Rome, Roman civilization from 8th century BC to 5th century AD
* Roman people, the people of ancient Rome
*'' Epistle to the Romans'', shortened to ''Romans'', a let ...
with religious break-offs being suppressed by both the
Papacy
The pope ( la, papa, from el, πάππας, translit=pappas, 'father'), also known as supreme pontiff ( or ), Roman pontiff () or sovereign pontiff, is the bishop of Rome (or historically the patriarch of Rome), head of the worldwide Cathol ...
and the
Holy Roman Emperor.
Reformation, Counter-Reformation and the Thirty Years' War (1517–1648)
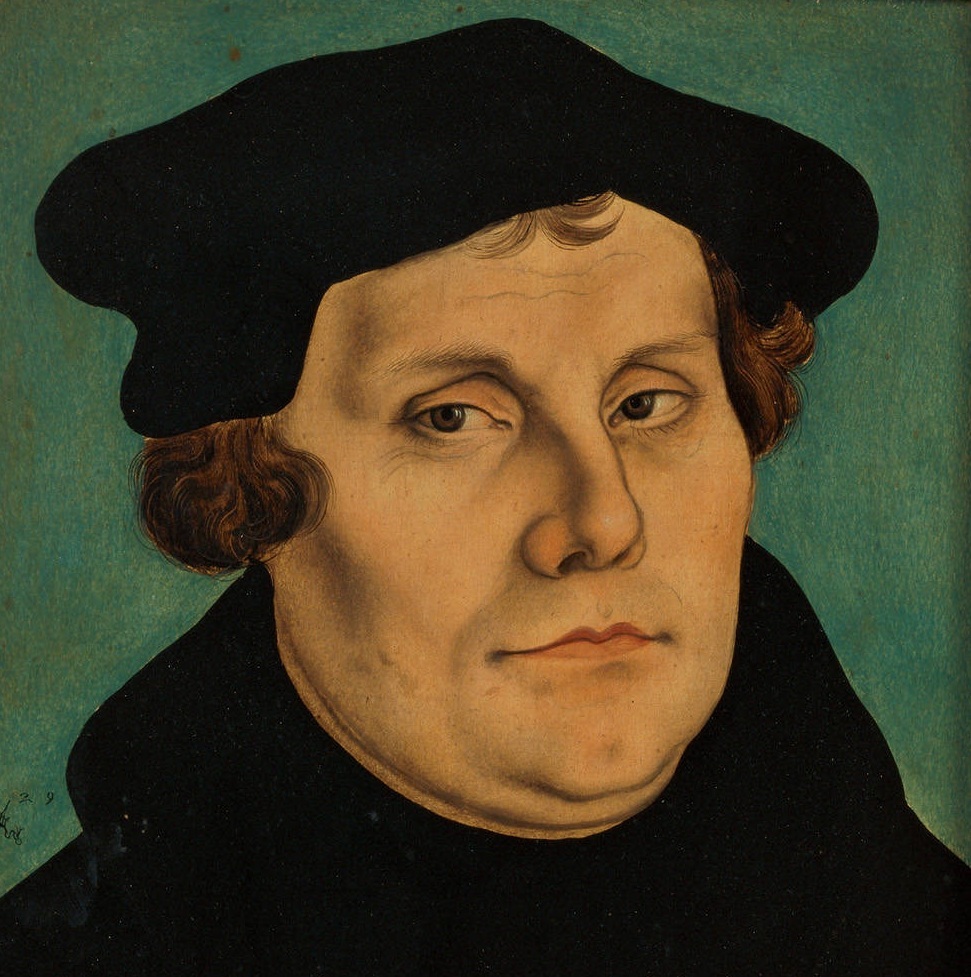

Roman Catholicism was the sole established religion in the Holy Roman Empire until the advent of the
Protestant Reformation
The Reformation (alternatively named the Protestant Reformation or the European Reformation) was a major movement within Western Christianity in 16th-century Europe that posed a religious and political challenge to the Catholic Church and ...
changed this drastically. In the early 16th century abuses (such as selling
indulgence
In the teaching of the Catholic Church, an indulgence (, from , 'permit') is "a way to reduce the amount of punishment one has to undergo for sins". The ''Catechism of the Catholic Church'' describes an indulgence as "a remission before God of ...
s in the Catholic Church) occasioned much discontent, and a general desire for reform emerged. In 1517 the Reformation began with the publication of
Martin Luther
Martin Luther (; ; 10 November 1483 – 18 February 1546) was a German priest, theologian, author, hymnwriter, and professor, and Augustinian friar. He is the seminal figure of the Protestant Reformation and the namesake of Lutherani ...
's
95 Theses
The ''Ninety-five Theses'' or ''Disputation on the Power and Efficacy of Indulgences''-The title comes from the 1517 Basel pamphlet printing. The first printings of the ''Theses'' use an incipit rather than a title which summarizes the content ...
detailing 95 assertions which Luther believed showed corruption and misguidance within the Catholic Church. The Reformation demonstrated Luther's disagreement both with the way in which the higher clergy used and abused power, and with the very idea of a papacy. In 1521 the
Diet of Worms outlawed Luther, but the Reformation spread rapidly. Luther translated the Bible from Latin to German, establishing the basis of the modern German language. A curious fact is that Luther spoke a dialect which had minor importance in the German language of that time. After the publication of his Bible translation, his dialect evolved into what is now standard modern German.
With the
protestation of the Lutheran princes at the
Imperial Diet of
Speyer
Speyer (, older spelling ''Speier'', French: ''Spire,'' historical English: ''Spires''; pfl, Schbaija) is a city in Rhineland-Palatinate in Germany with approximately 50,000 inhabitants. Located on the left bank of the river Rhine, Speyer li ...
(1529) and rejection of the Lutheran "Augsburg Confession" at the
Diet of Augsburg
The Diet of Augsburg were the meetings of the Imperial Diet of the Holy Roman Empire held in the German city of Augsburg. Both an Imperial City and the residence of the Augsburg prince-bishops, the town had hosted the Estates in many such sessi ...
(1530), a separate Lutheran church emerged.
[Robert Kolb, ''Confessing the faith: reformers define the Church, 1530–1580'' (Concordia Publishing House, 1991)]

From 1545 the
Counter-Reformation began in Germany. Much of its impetus came from the newly founded (in 1540)
Jesuit order
, image = Ihs-logo.svg
, image_size = 175px
, caption = ChristogramOfficial seal of the Jesuits
, abbreviation = SJ
, nickname = Jesuits
, formation =
, founders ...
. It restored Catholicism to many areas, including Bavaria. The Holy Roman Empire became religiously diverse; for the most part, the states of northern and central Germany became Protestant (chiefly Lutheran, but also Calvinist/Reformed) while the states of southern Germany and the
Rhineland
The Rhineland (german: Rheinland; french: Rhénanie; nl, Rijnland; ksh, Rhingland; Latinised name: ''Rhenania'') is a loosely defined area of Western Germany along the Rhine, chiefly its middle section.
Term
Historically, the Rhinelands ...
largely remained Catholic. In 1547 the
Holy Roman Emperor Charles V
Charles V, french: Charles Quint, it, Carlo V, nl, Karel V, ca, Carles V, la, Carolus V (24 February 1500 – 21 September 1558) was Holy Roman Emperor and Archduke of Austria from 1519 to 1556, King of Spain ( Castile and Aragon) ...
defeated the
Schmalkaldic League
The Schmalkaldic League (; ; or ) was a military alliance of Lutheran princes within the Holy Roman Empire during the mid-16th century.
Although created for religious motives soon after the start of the Reformation, its members later came to ...
, an alliance of Protestant rulers. The
Peace of Augsburg in 1555 brought recognition of the Lutheran faith. But the treaty also stipulated that the religion of a state was to be that of its ruler (''
cuius regio, eius religio
() is a Latin phrase which literally means "whose realm, their religion" – meaning that the religion of the ruler was to dictate the religion of those ruled. This legal principle marked a major development in the collective (if not individua ...
'').
In 1608/1609 the
Protestant Union
The Protestant Union (german: Protestantische Union), also known as the Evangelical Union, Union of Auhausen, German Union or the Protestant Action Party, was a coalition of Protestant German states. It was formed on 14 May 1608 by Frederick I ...
and the
Catholic League formed. The
Thirty Years' War
The Thirty Years' War was one of the longest and most destructive conflicts in European history, lasting from 1618 to 1648. Fought primarily in Central Europe, an estimated 4.5 to 8 million soldiers and civilians died as a result of battle ...
(1618–1648), one of the most destructive conflicts in European history, played out primarily in German lands, but involved most of the countries of Europe. It was to some extent a religious conflict, involving both Protestants and Catholics.
Post-Thirty Years' War period and Protestant church unions (1648–1871)

Two main developments reshaped religion in Germany after 1814. There was a movement to unite the larger Lutheran and the smaller Reformed Protestant churches. The churches themselves brought this about in Baden, Nassau, and Bavaria. However, in Prussia King
Frederick William III
Frederick William III (german: Friedrich Wilhelm III.; 3 August 1770 – 7 June 1840) was King of Prussia from 16 November 1797 until his death in 1840. He was concurrently Elector of Brandenburg in the Holy Roman Empire until 6 August 1806, wh ...
was determined to handle unification entirely on his own terms, without consultation. His goal was to
unify the Protestant churches, and to impose a single standardised liturgy, organisation, and even architecture. The long-term goal was to have fully centralised royal control of all the Protestant churches. In a series of proclamations over several decades the
Evangelical Church of the Prussian Union was formed, bringing together the more numerous Lutherans and the less numerous Reformed Protestants. The government of Prussia now had full control over church affairs, with the king himself recognised as the leading bishop. Opposition to unification came from the "
Old Lutherans
Old Lutherans were originally German Lutherans in the Kingdom of Prussia, notably in the Province of Silesia, who refused to join the Prussian Union of churches in the 1830s and 1840s. Prussia's king Frederick William III was determined to uni ...
" in Prussia and Silesia who followed the theological and liturgical forms they had followed since the days of Luther. The government attempted to crack down on them, so they went underground. Tens of thousands migrated
to South Australia and the United States, where they formed the
Missouri Synod
Missouri is a state in the Midwestern region of the United States. Ranking 21st in land area, it is bordered by eight states (tied for the most with Tennessee): Iowa to the north, Illinois, Kentucky and Tennessee to the east, Arkansas to th ...
. Finally, in 1845 the new king,
Frederick William IV
Frederick William IV (german: Friedrich Wilhelm IV.; 15 October 17952 January 1861), the eldest son and successor of Frederick William III of Prussia, reigned as King of Prussia from 7 June 1840 to his death on 2 January 1861. Also referred to ...
, offered a general amnesty and allowed the Old Lutherans to form separate
free church
A free church is a Christian denomination that is intrinsically separate from government (as opposed to a state church). A free church does not define government policy, and a free church does not accept church theology or policy definitions fr ...
associations with only nominal government control.
From the religious point of view of the typical Catholic or Protestant, major changes were underway in terms of a much more personalised religiosity that focused on the individual more than the church or the ceremony. Opposing the rationalism of the late 18th century, there was a new emphasis on the psychology and feeling of the individual, especially in terms of contemplating sinfulness, redemption, and the mysteries and the revelations of Christianity.
Pietistic revivals were common among Protestants. Among Catholics there was a sharp increase in popular pilgrimages. In 1844 alone, half a million pilgrims made a pilgrimage to the city of Trier in the Rhineland to view the
Seamless robe of Jesus
The Seamless Robe of Jesus (also known as the Holy Robe, Holy Tunic, Holy Coat, Honorable Robe, and Chiton of the Lord) is the robe said to have been worn by Jesus during or shortly before his crucifixion. Competing traditions claim that the ro ...
, said to be the robe that Jesus wore on the way to his crucifixion. Catholic bishops in Germany had historically been largely independent of Rome, but now the Vatican exerted increasing control, a new "
ultramontanism
Ultramontanism is a clerical political conception within the Catholic Church that places strong emphasis on the prerogatives and powers of the Pope. It contrasts with Gallicanism, the belief that popular civil authority—often represented by th ...
" of Catholics highly loyal to Rome. A sharp controversy broke out in 1837–38 in the largely Catholic Rhineland over the religious education of children of mixed marriages, where the mother was Catholic and the father Protestant. The government passed laws to require that these children always be raised as Protestants, contrary to Napoleonic law that had previously prevailed and allowed the parents to make the decision. It put the Catholic Archbishop under house arrest. In 1840, the new King Frederick William IV sought reconciliation and ended the controversy by agreeing to most of the Catholic demands. However Catholic memories remained deep and led to a sense that Catholics always needed to stick together in the face of an untrustworthy government.
Kulturkampf and the German Empire (1871–1918)

Chancellor
Otto von Bismarck would not tolerate any base of power outside Germany and launched the
Kulturkampf ("culture war") against the power of the pope and the Catholic Church. This gained strong support from German liberals, who saw the Catholic Church as the bastion of reaction and their greatest enemy. The Catholic element, in turn, saw the
National Liberals as its worst enemy and formed the
Center Party.
Catholics, although about a third of the national population, were seldom allowed to hold major positions in the Imperial government or the Prussian government. After 1871, there was a systematic purge of Catholics; in the powerful interior ministry, which handled all police affairs, the only Catholic was a messenger boy.
The German Empire passed the
Pulpit Law The Pulpit Law (German ''Kanzelparagraph'') was a section (§ 130a) to the ''Strafgesetzbuch'' (the German Criminal Code) passed by the Reichstag in 1871 during the German Kulturkampf or fight against the Catholic Church. It made it a crime for any ...
(1871), which made it a crime for any cleric to discuss political issues, and the
Jesuits Law (1872) drove this order out of German territory. In 1873, Bismarck, as prime minister of Prussia, launched further anti-church measures: Public schools and the registration of births, marriages and deaths were transferred from religious authorities (including the Protestant state church) to the state. Germans could now change their religious affiliation through the civil registry. Other German states followed through with similar measures. Nearly all Catholic bishops, clergy, and laymen rejected the legality of the new laws, and were defiant facing the increasingly heavy penalties and imprisonments imposed by Bismarck's government. Historian Anthony Steinhoff reports the casualty totals:
As of 1878, only three of eight Prussian dioceses still had bishops, some 1,125 of 4,600 parishes were vacant, and nearly 1,800 priests ended up in jail or in exile. ...Finally, between 1872 and 1878, numerous Catholic newspapers were confiscated, Catholic associations and assemblies were dissolved, and Catholic civil servants were dismissed merely on the pretence of having Ultramontane sympathies.
The British ambassador
Odo Russell reported to London in October 1872 how Bismarck's plans were backfiring by strengthening the
ultramontane
Ultramontanism is a clerical political conception within the Catholic Church that places strong emphasis on the prerogatives and powers of the Pope. It contrasts with Gallicanism, the belief that popular civil authority—often represented by th ...
(pro-papal) position inside German Catholicism:
The German Bishops who were politically powerless in Germany and theologically in opposition to the Pope in Rome – have now become powerful political leaders in Germany and enthusiastic defenders of the now infallible Faith of Rome, united, disciplined, and thirsting for martyrdom, thanks to Bismarck's uncalled for antiliberal declaration of War on the freedom they had hitherto peacefully enjoyed.
Bismarck underestimated the resolve of the Catholic Church and did not foresee the extremes that this struggle would entail. The Catholic Church denounced the harsh new laws as anti-catholic and mustered the support of its rank and file voters across Germany. In the following elections, the Center Party won a quarter of the seats in the Imperial Diet. The conflict ended after 1879 for two reasons: Pope Pius IX died in 1878 and was succeeded by the more conciliatory
Pope Leo XIII
Pope Leo XIII ( it, Leone XIII; born Vincenzo Gioacchino Raffaele Luigi Pecci; 2 March 1810 – 20 July 1903) was the head of the Catholic Church from 20 February 1878 to his death in July 1903. Living until the age of 93, he was the second-old ...
. Bismarck was also looking for greater parliamentary support after his alliance with the
National Liberals ended over Bismarck's tariff changes and
Social-Democrats emerged as new threat. Following negotiations with Leo XIII, peace was restored: the bishops returned, and the jailed clerics were released. Laws were toned down or taken back (Mitigation Laws 1880–1883 and Peace Laws 1886/87), but the Jesuits Law and the Pulpit Law were not repealed until 1917 and 1953, respectively. The changes concerning schools, civil registry, marriage and religious disaffiliation remain in place today. The Center Party gained strength and became an ally of Bismarck, especially when he attacked socialism.
Weimar Republic and Nazi Germany (1918–1945)

The national constitution of 1919 determined that the newly formed
Weimar Republic
The Weimar Republic (german: link=no, Weimarer Republik ), officially named the German Reich, was the government of Germany from 1918 to 1933, during which it was a constitutional federal republic for the first time in history; hence it is ...
had no state church, and guaranteed
freedom of religion
Freedom of religion or religious liberty is a principle that supports the freedom of an individual or community, in public or private, to manifest religion or belief in teaching, practice, worship, and observance. It also includes the freed ...
. Earlier, these freedoms were mentioned only in state constitutions. Protestants and Catholics were equal before the law, and
freethought flourished. The
German Freethinkers League
The German Freethinkers League ('Deutscher Freidenkerbund') was an organization founded in the late 19th century by German freethinkers and atheists with the main goal to oppose the power of the state churches in Germany. Its aim was to provide a ...
attained about 500,000 members, many of whom were
atheists
Atheism, in the broadest sense, is an absence of belief in the existence of deities. Less broadly, atheism is a rejection of the belief that any deities exist. In an even narrower sense, atheism is specifically the position that there no d ...
, before the organisation was shut down by the Nazis in May 1933.
When
Adolf Hitler
Adolf Hitler (; 20 April 188930 April 1945) was an Austrian-born German politician who was dictator of Nazi Germany, Germany from 1933 until Death of Adolf Hitler, his death in 1945. Adolf Hitler's rise to power, He rose to power as the le ...
's
Nazi Party
The Nazi Party, officially the National Socialist German Workers' Party (german: Nationalsozialistische Deutsche Arbeiterpartei or NSDAP), was a far-right political party in Germany active between 1920 and 1945 that created and supported t ...
seized power in January 1933, it sought to assert state supremacy over all sectors of life. The
Reichskonkordat
The ''Reichskonkordat'' ("Concordat between the Holy See and the German Reich") is a treaty negotiated between the Vatican and the emergent Nazi Germany. It was signed on 20 July 1933 by Cardinal Secretary of State Eugenio Pacelli, who later be ...
neutralized the
Catholic Church
The Catholic Church, also known as the Roman Catholic Church, is the largest Christian church, with 1.3 billion baptized Catholics worldwide . It is among the world's oldest and largest international institutions, and has played a ...
as a political force. Through the pro-
Nazi
Nazism ( ; german: Nazismus), the common name in English for National Socialism (german: Nationalsozialismus, ), is the far-right totalitarian political ideology and practices associated with Adolf Hitler and the Nazi Party (NSDAP) in ...
Deutsche Christenbewegung ("German Christians movement") and the forced merger of the
German Evangelical Church Confederation The German Evangelical Church Confederation (german: Deutscher Evangelischer Kirchenbund, abbreviated DEK) was a formal federation of 28 regional Protestant churches ('' Landeskirchen'') of Lutheran, Reformed or United Protestant administration or ...
into the
Protestant Reich Church
The German Evangelical Church (german: Deutsche Evangelische Kirche) was a successor to the German Evangelical Church Confederation from 1933 until 1945.
The German Christians, an antisemitic and racist pressure group and ''Kirchenpartei'', ga ...
, Protestantism was brought under state control. Following a "gradual worsening of relations" in late 1936, the Nazis supported ''Kirchenaustrittsbewegung'' ("movement to leave the church").
Although there was no top-down official directive to revoke church membership, some Nazi Party members started doing so voluntarily and put other members under pressure to follow their example.
Those who left the churches were designated as ''
Gottgläubig'': they believed in a higher power, often a creator-God with a special interest in the German nation, but did not belong to any church, nor were they atheists. Many were
Germanic neopagans.
This movement, especially promoted by
Reichsführer-SS
(, ) was a special title and rank that existed between the years of 1925 and 1945 for the commander of the (SS). ''Reichsführer-SS'' was a title from 1925 to 1933, and from 1934 to 1945 it was the highest rank of the SS. The longest-servi ...
Heinrich Himmler
Heinrich Luitpold Himmler (; 7 October 1900 – 23 May 1945) was of the (Protection Squadron; SS), and a leading member of the Nazi Party of Germany. Himmler was one of the most powerful men in Nazi Germany and a main architect of th ...
, remained relatively small and by 1939, 3.5% of Germans identified as ''Gottgläubig''; the overwhelming majority of 94.5% remained Protestant or Catholic, and only 1.5% did not profess any faith.
Since 1933,
Jews in Germany were increasingly marginalised, expelled and persecuted for a combination of religious, racial and economic reasons. From 1941 to the fall of
Nazi Germany
Nazi Germany (lit. "National Socialist State"), ' (lit. "Nazi State") for short; also ' (lit. "National Socialist Germany") (officially known as the German Reich from 1933 until 1943, and the Greater German Reich from 1943 to 1945) was ...
in 1945, they were actively massacred during
the Holocaust
The Holocaust, also known as the Shoah, was the genocide of European Jews during World War II. Between 1941 and 1945, Nazi Germany and its collaborators systematically murdered some six million Jews across German-occupied Europe; ...
.
Cold War and contemporary period (1945–present)

In the aftermath of
World War II
World War II or the Second World War, often abbreviated as WWII or WW2, was a world war that lasted from 1939 to 1945. It involved the vast majority of the world's countries—including all of the great powers—forming two opposing ...
, two states emerged in Germany in 1949:
West Germany
West Germany is the colloquial term used to indicate the Federal Republic of Germany (FRG; german: Bundesrepublik Deutschland , BRD) between its formation on 23 May 1949 and the German reunification through the accession of East Germany on 3 O ...
under the aegis of the
Western Allies
The Allies, formally referred to as the United Nations from 1942, were an international military coalition formed during the Second World War (1939–1945) to oppose the Axis powers, led by Nazi Germany, Imperial Japan, and Fascist Italy ...
, and
East Germany
East Germany, officially the German Democratic Republic (GDR; german: Deutsche Demokratische Republik, , DDR, ), was a country that existed from its creation on 7 October 1949 until its dissolution on 3 October 1990. In these years the state ...
as part of the
Soviet bloc. West Germany, officially known as the Federal Republic of Germany, adopted a constitution in 1949 which protected
freedom of religion
Freedom of religion or religious liberty is a principle that supports the freedom of an individual or community, in public or private, to manifest religion or belief in teaching, practice, worship, and observance. It also includes the freed ...
and adopted the regulations of the Weimar Constitution; consequently,
secularisation
In sociology, secularization (or secularisation) is the transformation of a society from close identification with religious values and institutions toward non-religious values and secular institutions. The ''secularization thesis'' expresses the ...
in West Germany proceeded slowly. East Germany, officially known as the German Democratic Republic, had a
communist system which actively tried to reduce the influence of religion in society; the government restricted Christian churches and discriminated against Christians.
In the 21st century, eastern German states, including the area of the former eastern capital,
East Berlin, are less religious than western German states.
[
Religious communities which are of sufficient size and stability and which are loyal to the constitution can be recognised as ''Körperschaften öffentlichen Rechtes'' (statutory corporations). This gives them certain privileges – for example, being able to give religious instruction in state schools (as enshrined in the German constitution, though some states are exempt from this) and having membership fees collected (for a fee) by the German revenue department as "]church tax
A church tax is a tax collected by the state from members of some religious denominations to provide financial support of churches, such as the salaries of its clergy and to pay the operating cost of the church.
The constitution of a number o ...
" (''Kirchensteuer''): a surcharge of between 8 and 9% of the income tax. The status mainly applies to the Catholic Church
The Catholic Church, also known as the Roman Catholic Church, is the largest Christian church, with 1.3 billion baptized Catholics worldwide . It is among the world's oldest and largest international institutions, and has played a ...
, the mainline Evangelical Church in Germany
The Evangelical Church in Germany (german: Evangelische Kirche in Deutschland, abbreviated EKD) is a federation of twenty Lutheran, Reformed (Calvinist) and United (e.g. Prussian Union) Protestant regional churches and denominations in German ...
, a number of free church
A free church is a Christian denomination that is intrinsically separate from government (as opposed to a state church). A free church does not define government policy, and a free church does not accept church theology or policy definitions fr ...
es, and Jewish
Jews ( he, יְהוּדִים, , ) or Jewish people are an ethnoreligious group and nation originating from the Israelites Israelite origins and kingdom: "The first act in the long drama of Jewish history is the age of the Israelites""The ...
communities. There has been much discussion about allowing other religious groups (such as Muslims
Muslims ( ar, المسلمون, , ) are people who adhere to Islam, a monotheistic religion belonging to the Abrahamic tradition. They consider the Quran, the foundational religious text of Islam, to be the verbatim word of the God of Abrah ...
) into this system as well.[
In 2018 the states of ]Lower Saxony
Lower Saxony (german: Niedersachsen ; nds, Neddersassen; stq, Läichsaksen) is a German state (') in northwestern Germany. It is the second-largest state by land area, with , and fourth-largest in population (8 million in 2021) among the 16 ...
, Schleswig-Holstein
Schleswig-Holstein (; da, Slesvig-Holsten; nds, Sleswig-Holsteen; frr, Slaswik-Holstiinj) is the northernmost of the 16 states of Germany, comprising most of the historical duchy of Holstein and the southern part of the former Duchy of Sc ...
, Hamburg
(male), (female) en, Hamburger(s),
Hamburgian(s)
, timezone1 = Central (CET)
, utc_offset1 = +1
, timezone1_DST = Central (CEST)
, utc_offset1_DST = +2
, postal ...
and Bremen made Reformation Day (31 October) a permanent official holiday. This initiative began after the day had been held as a nationwide holiday in 2017, due to the 500th Reformation anniversary of the Reformation, and also due to the fact that the northern German states have significantly fewer holidays than the southern ones.
In 2019 the Catholic News Agency reported that the Catholic church in Germany had a net loss of 216,078 members the previous year. The Protestant churches in Germany had a similar net loss of membership of about 220,000 members. While the total of Catholic and Protestant church membership stands at 45 million or 53%, demographers predict that based on current trends it will fall to 23 million by 2060. In 2020 it was reported that the Catholic church in Germany had a 402,000 loss in membership, the largest ever single year decrease up to that point. The Protestant churches in Germany also had a large drop in membership of about 440,000.
Demographics
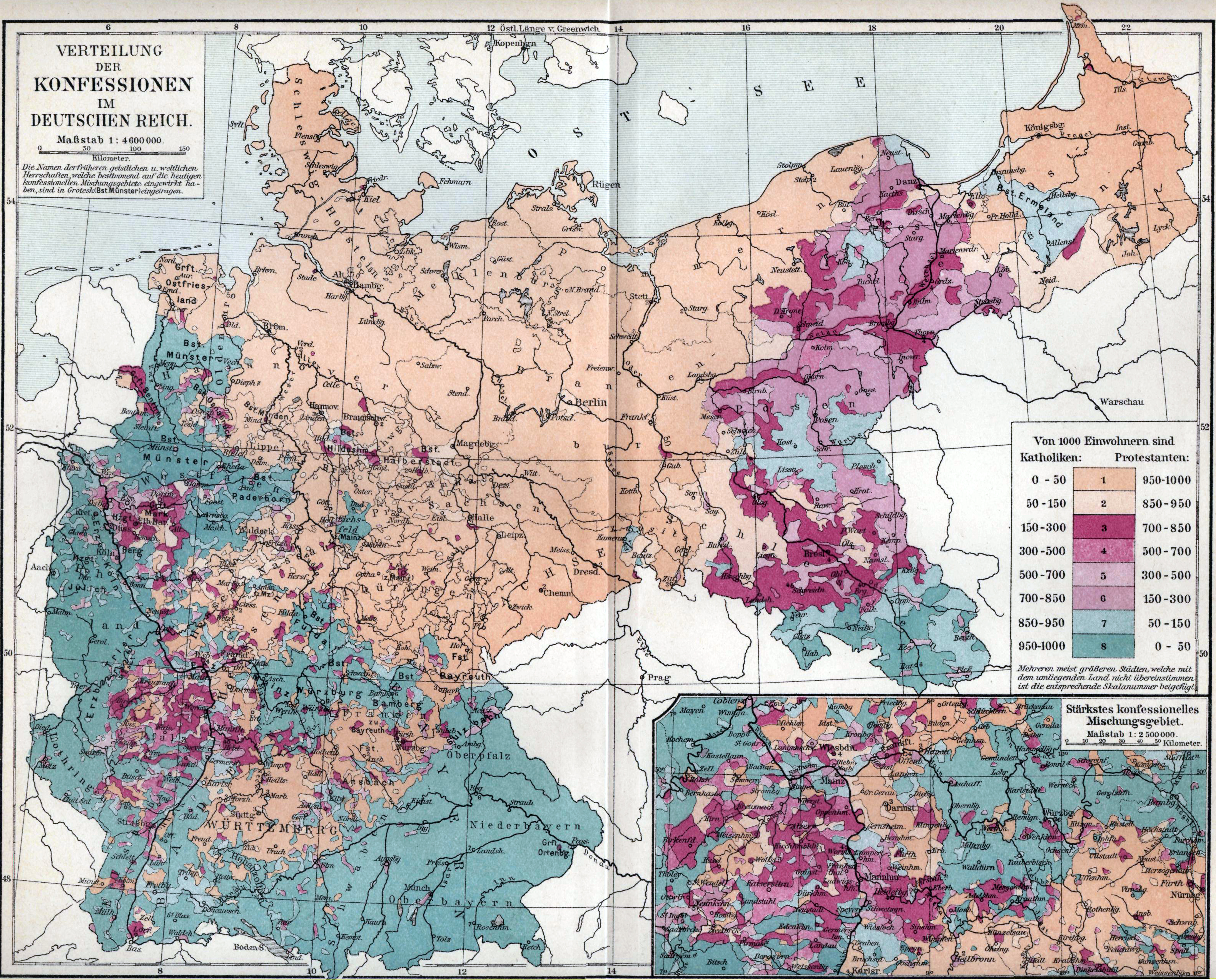
Nowadays, Protestants are concentrated in northern and central Germany, while Catholics are predominant in the south and west, while unaffiliated people are concentrated in the east, where they make up the majority of the population, and are significant in the north and west of the country, mainly in metropolitan areas. With the decline of Christianity in the late 20th and early 21st century, accentuated in the east by the official atheism of the former German Democratic Republic
German(s) may refer to:
* Germany (of or related to)
** Germania (historical use)
* Germans, citizens of Germany, people of German ancestry, or native speakers of the German language
** For citizens of Germany, see also German nationality law
**G ...
, the northeastern states of Germany are now mostly not religious (70%), with many of the people living there being agnostics
Agnosticism is the view or belief that the existence of God, of the divine or the supernatural is unknown or unknowable. (page 56 in 1967 edition) Another definition provided is the view that "human reason is incapable of providing sufficient ...
and atheists
Atheism, in the broadest sense, is an absence of belief in the existence of deities. Less broadly, atheism is a rejection of the belief that any deities exist. In an even narrower sense, atheism is specifically the position that there no d ...
.[
Immigrations in the late 20th and early 21st century have brought new religions into Germany, including ]Orthodox Christianity
Orthodoxy (from Greek: ) is adherence to correct or accepted creeds, especially in religion.
Orthodoxy within Christianity refers to acceptance of the doctrines defined by various creeds and ecumenical councils in Antiquity, but different Chur ...
and Islam. Orthodox Christianity is practised among immigrated Greeks
The Greeks or Hellenes (; el, Έλληνες, ''Éllines'' ) are an ethnic group and nation indigenous to the Eastern Mediterranean and the Black Sea regions, namely Greece, Cyprus, Albania, Italy, Turkey, Egypt, and, to a lesser extent, oth ...
, Serbs
The Serbs ( sr-Cyr, Срби, Srbi, ) are the most numerous South Slavic ethnic group native to the Balkans in Southeastern Europe, who share a common Serbian ancestry, culture, history and language.
The majority of Serbs live in their na ...
, Russians
, native_name_lang = ru
, image =
, caption =
, population =
, popplace =
118 million Russians in the Russian Federation (2002 '' Winkler Prins'' estimate)
, region1 =
, pop1 ...
, Romanians
The Romanians ( ro, români, ; dated exonym '' Vlachs'') are a Romance-speaking ethnic group. Sharing a common Romanian culture and ancestry, and speaking the Romanian language, they live primarily in Romania and Moldova. The 2011 Roman ...
and other communities.Alevis
Alevism or Anatolian Alevism (; tr, Alevilik, ''Anadolu Aleviliği'' or ''Kızılbaşlık''; ; az, Ələvilik) is a local Islamic tradition, whose adherents follow the mystical Alevi Islamic ( ''bāṭenī'') teachings of Haji Bektash Veli, ...
of Turkish origin, but there are a small number of Shi'a Muslims and other currents.Jewish population
As of 2020, the world's "core" Jewish population (those identifying as Jews above all else) was estimated at 15 million, 0.2% of the 8 billion worldwide population. This number rises to 18 million with the addition of the "connected" Jewish pop ...
(after France and the United Kingdom).
Censuses
Throughout history, in modern Germany several census had been carried out. Since the reformation until the 1960s the majority of the German population was Protestant (mainly Lutherans belonging to the Evangelical Church in Germany
The Evangelical Church in Germany (german: Evangelische Kirche in Deutschland, abbreviated EKD) is a federation of twenty Lutheran, Reformed (Calvinist) and United (e.g. Prussian Union) Protestant regional churches and denominations in German ...
) while approximatively one third of the population was Catholic
The Catholic Church, also known as the Roman Catholic Church, is the largest Christian church, with 1.3 billion baptized Catholics worldwide . It is among the world's oldest and largest international institutions, and has played a ...
.free church
A free church is a Christian denomination that is intrinsically separate from government (as opposed to a state church). A free church does not define government policy, and a free church does not accept church theology or policy definitions fr ...
es, and 1,050,740 or 1.3% were members of Eastern Orthodox
Eastern Orthodoxy, also known as Eastern Orthodox Christianity, is one of the three main branches of Chalcedonian Christianity, alongside Catholicism and Protestantism.
Like the Pentarchy of the first millennium, the mainstream (or " canonical ...
and Oriental Orthodox churches. A further 2.6% was affiliated to any other Christian denomination. Jews were 83,430 people or 0.1%, and 4,137,140 or 5.2% were members of other religions. The remaining 22,223,010 people, or 27.9% of the total German population, were not believers in or not members of any religion (including atheists, agnostics and believers in unrecognised religions).
Church figures and other estimates
German major religious bodies publish yearly updated records of their membership.Baden-Württemberg
Baden-Württemberg (; ), commonly shortened to BW or BaWü, is a German state () in Southwest Germany, east of the Rhine, which forms the southern part of Germany's western border with France. With more than 11.07 million inhabitants across a ...
). Many members choose not to formally register to their church anymore in order to have lighter taxes, since that those who opt out don't have the duty to pay it. According to a study, approximately 44% of the persons who unregistered to their church in 2018 did so in order to avoid to pay the church tax. According to a 2017 study by the Pew Research Center, around 20% of people who are not registered to any church consider themselves Christians. Therefore, the official church count may underestimate the actual number of people who consider themselves as Catholic or Protestant, as noted by the 2011 Census, which provides comparable data on the religious statistics based on self-identification and the church register.
According to these church stats, Christianity is the largest religious group in Germany, with around 44.9 million adherents (53.9%) in 2020 of whom 22.2 million are Catholics (26.7%) and 20.2 million are Protestants (24.3%).Buddhism
Buddhism ( , ), also known as Buddha Dharma and Dharmavinaya (), is an Indian religions, Indian religion or Indian philosophy#Buddhist philosophy, philosophical tradition based on Pre-sectarian Buddhism, teachings attributed to the Buddha. ...
(0.2–0.3%), Judaism
Judaism ( he, ''Yahăḏūṯ'') is an Abrahamic, monotheistic, and ethnic religion comprising the collective religious, cultural, and legal tradition and civilization of the Jewish people. It has its roots as an organized religion in t ...
(0.1%), Hinduism
Hinduism () is an Indian religion or '' dharma'', a religious and universal order or way of life by which followers abide. As a religion, it is the world's third-largest, with over 1.2–1.35 billion followers, or 15–16% of the global p ...
(0.1%), Yazidis
Yazidis or Yezidis (; ku, ئێزیدی, translit=Êzidî) are a Kurmanji-speaking endogamous minority group who are indigenous to Kurdistan, a geographical region in Western Asia that includes parts of Iraq, Syria, Turkey and Iran. The ma ...
(0.1%) and others (0.4%).Judaism
Judaism ( he, ''Yahăḏūṯ'') is an Abrahamic, monotheistic, and ethnic religion comprising the collective religious, cultural, and legal tradition and civilization of the Jewish people. It has its roots as an organized religion in t ...
), and a further 90.000 ethnic Jews
Jews ( he, יְהוּדִים, , ) or Jewish people are an ethnoreligious group and nation originating from the Israelites Israelite origins and kingdom: "The first act in the long drama of Jewish history is the age of the Israelites""The ...
with no religion, around 100,000 Yazidi
Yazidis or Yezidis (; ku, ئێزیدی, translit=Êzidî) are a Kurmanji-speaking endogamous minority group who are indigenous to Kurdistan, a geographical region in Western Asia that includes parts of Iraq, Syria, Turkey and Iran. The ma ...
s, 130,000 Hindus
Hindus (; ) are people who religiously adhere to Hinduism. Jeffery D. Long (2007), A Vision for Hinduism, IB Tauris, , pages 35–37 Historically, the term has also been used as a geographical, cultural, and later religious identifier for ...
, and 270,000 Buddhists.
Survey data
* In 2017, a survey conducted by Pew Research Center found that 71% of German adult population consider themselves Christians when asking about their current religion (irrespective of whether they are officially members of a particular Christian church). The same survey shows that most of Christians in Germany are non-practicing (defined as people who identify as Christians, but attend church services no more than a few times per year). 5% of people questioned state they have a non-Christian religion and 24% are of no religion.
* In 2016, the German Politbarometer, found that 34.2% of the adult population entitled to vote were Protestants, 31.9% were Catholics, 28.8% were unaffiliated, 2.5% were Muslims, 0.02% were Jews and 1.8% were affiliated with another religion. A further 0.9% did not answer to the question.[ The survey was based on a sample of 30,599 people.]
*In 2016, the German General Social Survey The German General Social Survey (ALLBUS/GGSS - Die Allgemeine Bevölkerungsumfrage der Sozialwissenschaften) is a national data generation program in Germany, which is similar to the American General Social Survey (GSS). Its mission is to collect ...
found that 64.5% of Germans declared themselves to be affiliated to a Christian denomination, 30.5% were Catholics, 29.6% were members of the Evangelical Church, 1.7% were members of the Evangelical Free Church, 1.4% were Orthodox and 1.3% were other Christians. Non religious people comprised the 32.4% of the population, Muslims were the 2.6% and 0.5% were members of other religions.
* In 2015, Eurobarometer
Eurobarometer is a series of public opinion surveys conducted regularly on behalf of the European Commission and other EU Institutions since 1973. These surveys address a wide variety of topical issues relating to the European Union throughout i ...
found that 72.6% of the adult population were Christians, the largest Christian denomination being Protestantism, comprising 33.1% of the population, followed by Catholicism with 31.1%, and Eastern Orthodoxy with 0.9%, and unspecified other forms of Christianity with 7.5%. A further 2.2% were Muslims, 0.4% were Buddhists, 0.1% were Jews and 1.3 belonged to other religions. A further 23.5% of the population were not religious, comprising 12.8% who were atheists and 10.7% who were agnostics. The Eurobarometer Poll 2010 found that 44% of German citizens responded that "they believe there is a God", 25% responded that "they believe there is some sort of spirit or life force" and 27% responded that "they don't believe there is any sort of spirit, God or life force". 4% gave no response.
Eurobarometer Biotechnology report 2010
' p.381London
London is the capital and List of urban areas in the United Kingdom, largest city of England and the United Kingdom, with a population of just under 9 million. It stands on the River Thames in south-east England at the head of a estuary dow ...
's St Mary's University's Benedict XVI Centre for Religion and Society and the Institut Catholique de Paris
The Institut Catholique de Paris (ICP), known in English as the Catholic University of Paris (and in Latin as ''Universitas catholica Parisiensis''), is a private university located in Paris, France.
History: 1875–present
The Institut Catholiq ...
, and based on data from the European Social Survey 2014–2016, among 16 to 29 years-old Germans 47% were Christians (24% Protestant, 20% Catholic, 2% Orthodox and 1% other Christian), 7% were Muslims, 1% were of other religions, and 45% were not religious.
Religion by state
In 2016, the survey Politbarometer provided data regarding religion in each of the states of Germany for adults who are entitled to vote (18+), as reported in the table below.[Description of study's sample]
Christianity is the dominant religion of Western Germany
The old states of Germany (german: die alten Länder) is a jargon referring to the ten of the sixteen states of the Federal Republic of Germany (FRG) that were part of West Germany and that unified with the eastern German Democratic Republic' ...
, excluding Hamburg
(male), (female) en, Hamburger(s),
Hamburgian(s)
, timezone1 = Central (CET)
, utc_offset1 = +1
, timezone1_DST = Central (CEST)
, utc_offset1_DST = +2
, postal ...
, which has a non-religious plurality. Northern Germany has traditionally been dominated by Protestantism
Protestantism is a branch of Christianity that follows the theological tenets of the Protestant Reformation, a movement that began seeking to reform the Catholic Church from within in the 16th century against what its followers perceived to b ...
, especially Lutheranism
Lutheranism is one of the largest branches of Protestantism, identifying primarily with the theology of Martin Luther, the 16th-century German monk and reformer whose efforts to reform the theology and practice of the Catholic Church launched th ...
. The two northernmost provinces of Schleswig-Holstein
Schleswig-Holstein (; da, Slesvig-Holsten; nds, Sleswig-Holsteen; frr, Slaswik-Holstiinj) is the northernmost of the 16 states of Germany, comprising most of the historical duchy of Holstein and the southern part of the former Duchy of Sc ...
and Lower Saxony
Lower Saxony (german: Niedersachsen ; nds, Neddersassen; stq, Läichsaksen) is a German state (') in northwestern Germany. It is the second-largest state by land area, with , and fourth-largest in population (8 million in 2021) among the 16 ...
have the largest percentage of self-reported Lutherans in Germany. Southern Germany
Southern Germany () is a region of Germany which has no exact boundary, but is generally taken to include the areas in which Upper German dialects are spoken, historically the stem duchies of Bavaria and Swabia or, in a modern context, Bavaria ...
has a Catholic
The Catholic Church, also known as the Roman Catholic Church, is the largest Christian church, with 1.3 billion baptized Catholics worldwide . It is among the world's oldest and largest international institutions, and has played a ...
majority, but also a significant Lutheran
Lutheranism is one of the largest branches of Protestantism, identifying primarily with the theology of Martin Luther, the 16th-century German monk and Protestant Reformers, reformer whose efforts to reform the theology and practice of the Cathol ...
Protestant
Protestantism is a branch of Christianity that follows the theological tenets of the Protestant Reformation, a movement that began seeking to reform the Catholic Church from within in the 16th century against what its followers perceived to b ...
population (especially in Northern Württemberg
Württemberg ( ; ) is a historical German territory roughly corresponding to the cultural and linguistic region of Swabia. The main town of the region is Stuttgart.
Together with Baden and Hohenzollern, two other historical territories, Württ ...
and some parts of Baden
Baden (; ) is a historical territory in South Germany, in earlier times on both sides of the Upper Rhine but since the Napoleonic Wars only East of the Rhine.
History
The margraves of Baden originated from the House of Zähringen. Baden i ...
and Franconia
Franconia (german: Franken, ; Franconian dialect: ''Franggn'' ; bar, Frankn) is a region of Germany, characterised by its culture and Franconian languages, Franconian dialect (German: ''Fränkisch'').
The three Regierungsbezirk, administrative ...
(Northern Bavaria)), in contrast to the almost entirely Protestant Northern Germany. Irreligion
Irreligion or nonreligion is the absence or rejection of religion, or indifference to it. Irreligion takes many forms, ranging from the casual and unaware to full-fledged philosophies such as atheism and agnosticism, secular humanism and ...
is predominant in Eastern Germany
The new states of Germany () are the five re-established states of the former German Democratic Republic (GDR) that unified with the Federal Republic of Germany (FRG) with its 10 states upon German reunification on 3 October 1990.
The new st ...
, which was the least religious region amongst 30 countries surveyed in a study in 2012.
Personal beliefs
According to a survey by Pew Research Center in 2017, 60% of German adult population believe in God, while 36% do not believe in God (9% don't believe in God but in a higher power, 27% do not believe in God or any higher power):
Christianity
At its foundation in 1871, about two-thirds of the population of the German Empire belonged to a state Protestant
Protestantism is a branch of Christianity that follows the theological tenets of the Protestant Reformation, a movement that began seeking to reform the Catholic Church from within in the 16th century against what its followers perceived to b ...
church; in 2020 the Evangelical Church in Germany
The Evangelical Church in Germany (german: Evangelische Kirche in Deutschland, abbreviated EKD) is a federation of twenty Lutheran, Reformed (Calvinist) and United (e.g. Prussian Union) Protestant regional churches and denominations in German ...
was the faith of 24.3%. In 1871, one-third of the population was Roman Catholic
Roman or Romans most often refers to:
*Rome, the capital city of Italy
* Ancient Rome, Roman civilization from 8th century BC to 5th century AD
* Roman people, the people of ancient Rome
*'' Epistle to the Romans'', shortened to ''Romans'', a let ...
; in 2020 its membership was 26.7%. Other faiths have existed in the state, but never achieved the demographic significance and cultural impact of these denominations.
As of 2020, Christianity
Christianity is an Abrahamic monotheistic religion based on the life and teachings of Jesus of Nazareth. It is the world's largest and most widespread religion with roughly 2.38 billion followers representing one-third of the global pop ...
, with around 44.9 million members, was the largest religion in Germany (53.9% of the population) The Church of Jesus Christ of Latter-day Saints
The Church of Jesus Christ of Latter-day Saints, informally known as the LDS Church or Mormon Church, is a nontrinitarian Christian church that considers itself to be the restoration of the original church founded by Jesus Christ. The ch ...
, and others).
Protestantism
 Source for all data: REMID
Source for all data: REMIDEvangelical Church in Germany
The Evangelical Church in Germany (german: Evangelische Kirche in Deutschland, abbreviated EKD) is a federation of twenty Lutheran, Reformed (Calvinist) and United (e.g. Prussian Union) Protestant regional churches and denominations in German ...
— 20,713,000 (2019) — 24.9% of the German population[Numbers and Facts about Church Life in the EKD 2020 Report](_blank)
Evangelical Church of Germany. Retrieved 13 August 2020.
*Free Baptist
Baptists form a major branch of Protestantism distinguished by baptizing professing Christian believers only ( believer's baptism), and doing so by complete immersion. Baptist churches also generally subscribe to the doctrines of soul compe ...
and Mennonite
Mennonites are groups of Anabaptist Christian church communities of denominations. The name is derived from the founder of the movement, Menno Simons (1496–1561) of Friesland. Through his writings about Reformed Christianity during the Radi ...
Groups — 290,000 (2007)
* Baptists (mostly Union of Evangelical Free Churches in Germany
The Union of Evangelical Free Churches in Germany (german: Bund Evangelisch-Freikirchlicher Gemeinden in Deutschland ) is a Baptist Christian denomination in Germany. It is affiliated with the Baptist World Alliance. The headquarters is in Wuster ...
; see Baptists in Germany) — 80,195 (2020)
*Methodist
Methodism, also called the Methodist movement, is a group of historically related denominations of Protestant Christianity whose origins, doctrine and practice derive from the life and teachings of John Wesley. George Whitefield and John's ...
s — 52,031 (2016)
*Pentecostals
Pentecostalism or classical Pentecostalism is a Protestant Charismatic Christian movement (Bund Freikirchlicher Pfingstgemeinden) — 51,896 (2015)
*Mennonite
Mennonites are groups of Anabaptist Christian church communities of denominations. The name is derived from the founder of the movement, Menno Simons (1496–1561) of Friesland. Through his writings about Reformed Christianity during the Radi ...
s — 44,714 (2017)
*Bund Freier evangelischer Gemeinden — 41,203 (2017)
* Seventh-day Adventist Church — 34,811 (2014)
* Independent Evangelical-Lutheran Church — 33,175 (2014)
*Independent African Churches — 30,000 (2005)
* Evangelical Lutheran Free Church — 1,300 (2017)
Catholicism
Catholic churches in full communion:
* Roman Catholic Church in Germany — 22,600,000 (2019) — 27.2% of the German populationMaronite Church
The Maronite Church is an Eastern Catholic Churches, Eastern Catholic ''sui iuris'' particular church in full communion with the pope and the worldwide Catholic Church, with self-governance under the Code of Canons of the Eastern Churches. Th ...
Catholics — 6,000[
Church not in communion:
*]Old Catholic Church
The terms Old Catholic Church, Old Catholics, Old-Catholic churches or Old Catholic movement designate "any of the groups of Western Christians who believe themselves to maintain in complete loyalty the doctrine and traditions of the undivide ...
— 15,715[
]
Orthodox Christianity and Nestorianism

 *Orthodox Christians — around 1.6 million (1.9%)
*Orthodox Christians — around 1.6 million (1.9%)Greek Orthodox Church
The term Greek Orthodox Church ( Greek: Ἑλληνορθόδοξη Ἐκκλησία, ''Ellinorthódoxi Ekklisía'', ) has two meanings. The broader meaning designates "the entire body of Orthodox (Chalcedonian) Christianity, sometimes also cal ...
— 410,000Russian Orthodox Church
, native_name_lang = ru
, image = Moscow July 2011-7a.jpg
, imagewidth =
, alt =
, caption = Cathedral of Christ the Saviour in Moscow, Russia
, abbreviation = ROC
, type ...
— 270,000Romanian Orthodox Church
The Romanian Orthodox Church (ROC; ro, Biserica Ortodoxă Română, ), or Patriarchate of Romania, is an autocephalous Eastern Orthodox church in full communion with other Eastern Orthodox Christian churches, and one of the nine patriarchates ...
— 150,000Ukrainian Orthodox Church - Kyiv Patriarchate
Ukrainian may refer to:
* Something of, from, or related to Ukraine
* Something relating to Ukrainians, an East Slavic people from Eastern Europe
* Something relating to demographics of Ukraine in terms of demography and population of Ukraine
* Som ...
— 110,000Armenian Apostolic Church
, native_name_lang = hy
, icon = Armenian Apostolic Church logo.svg
, icon_width = 100px
, icon_alt =
, image = Էջմիածնի_Մայր_Տաճար.jpg
, imagewidth = 250px
, a ...
— 35,000
Others
* New Apostolic Church — 341,202 (2015)
* Jehovah's Witnesses — 168,763[
*]The Church of Jesus Christ of Latter-day Saints
The Church of Jesus Christ of Latter-day Saints, informally known as the LDS Church or Mormon Church, is a nontrinitarian Christian church that considers itself to be the restoration of the original church founded by Jesus Christ. The ch ...
— 38,739[
* The Church of Almighty God — To be determined
]
No religion
As of 2021, 34.9 million or 42% of the Germans are irreligious. West Germany
West Germany is the colloquial term used to indicate the Federal Republic of Germany (FRG; german: Bundesrepublik Deutschland , BRD) between its formation on 23 May 1949 and the German reunification through the accession of East Germany on 3 O ...
between 1945 and 1990, which contained nearly all of Germany's historically Catholic areas, Catholics have had a small majority since the 1980s. Due to a generation behind the Iron Curtain, Protestant areas of the former states of Prussia
Prussia, , Old Prussian: ''Prūsa'' or ''Prūsija'' was a German state on the southeast coast of the Baltic Sea. It formed the German Empire under Prussian rule when it united the German states in 1871. It was ''de facto'' dissolved by an ...
were much more affected by secularism than predominantly Catholic areas. The predominantly secularised states, such as Hamburg
(male), (female) en, Hamburger(s),
Hamburgian(s)
, timezone1 = Central (CET)
, utc_offset1 = +1
, timezone1_DST = Central (CEST)
, utc_offset1_DST = +2
, postal ...
or the East German states, used to be Lutheran or United Protestant
A united church, also called a uniting church, is a church formed from the merger or other form of church union of two or more different Protestant Christian denominations.
Historically, unions of Protestant churches were enforced by the state ...
strongholds. Because of this, Protestantism is now strongest in two strips of territory in the former West Germany, one extending from the Danish border to Hesse, and the other extending northeast–southwest across southern Germany.
There is a non-religious majority in Hamburg
(male), (female) en, Hamburger(s),
Hamburgian(s)
, timezone1 = Central (CET)
, utc_offset1 = +1
, timezone1_DST = Central (CEST)
, utc_offset1_DST = +2
, postal ...
, Bremen, Berlin
Berlin ( , ) is the capital and List of cities in Germany by population, largest city of Germany by both area and population. Its 3.7 million inhabitants make it the European Union's List of cities in the European Union by population within ci ...
, Brandenburg
Brandenburg (; nds, Brannenborg; dsb, Bramborska ) is a state in the northeast of Germany bordering the states of Mecklenburg-Vorpommern, Lower Saxony, Saxony-Anhalt, and Saxony, as well as the country of Poland. With an area of 29,480 sq ...
, Saxony
Saxony (german: Sachsen ; Upper Saxon: ''Saggsn''; hsb, Sakska), officially the Free State of Saxony (german: Freistaat Sachsen, links=no ; Upper Saxon: ''Freischdaad Saggsn''; hsb, Swobodny stat Sakska, links=no), is a landlocked state of ...
, Saxony-Anhalt
Saxony-Anhalt (german: Sachsen-Anhalt ; nds, Sassen-Anholt) is a state of Germany, bordering the states of Brandenburg, Saxony, Thuringia and Lower Saxony. It covers an area of
and has a population of 2.18 million inhabitants, making it th ...
, Thuringia
Thuringia (; german: Thüringen ), officially the Free State of Thuringia ( ), is a state of central Germany, covering , the sixth smallest of the sixteen German states. It has a population of about 2.1 million.
Erfurt is the capital and lar ...
, and Mecklenburg-Vorpommern
Mecklenburg-Vorpommern (MV; ; nds, Mäkelborg-Vörpommern), also known by its anglicized name Mecklenburg–Western Pomerania, is a state in the north-east of Germany. Of the country's sixteen states, Mecklenburg-Vorpommern ranks 14th in po ...
. In the eastern state of Saxony-Anhalt
Saxony-Anhalt (german: Sachsen-Anhalt ; nds, Sassen-Anholt) is a state of Germany, bordering the states of Brandenburg, Saxony, Thuringia and Lower Saxony. It covers an area of
and has a population of 2.18 million inhabitants, making it th ...
. only 19.7% belong to the two main denominations of the country. This is the state where Martin Luther was born and lived most of his life.
In what used to be East Germany both religious observance and affiliation are much lower than in the rest of the country, after forty years of Communist rule. The government of the German Democratic Republic
German(s) may refer to:
* Germany (of or related to)
** Germania (historical use)
* Germans, citizens of Germany, people of German ancestry, or native speakers of the German language
** For citizens of Germany, see also German nationality law
**G ...
encouraged a state atheist worldview through institutions such as Jugendweihe
Jugendweihe (''Youth consecration'') or Jugendfeier (''Youth ceremony'') is a secular coming of age ceremony practised by Germany, German 14-year-olds. It originated among the secular societies in the 19th century as an alternative to Confirmatio ...
n (youth consecrations) — secular coming-of-age ceremonies akin to Christian confirmation which all young people were encouraged to attend. The number of christenings, religious weddings, and funerals is also lower than in the West.
According to a survey among German youths (aged 12 to 24) in the year 2006, most German youths are non-religious (51%). 30% of German youths stated belief in a personal god, 19% believe in some kind of supernatural power, 23% share agnostic views and 28% are atheists.[Thomas Gensicke: Jugend und Religiosität. In: Deutsche Shell Jugend 2006. Die 15. Shell Jugendstudie. Frankfurt a.M. 2006.]
Islam
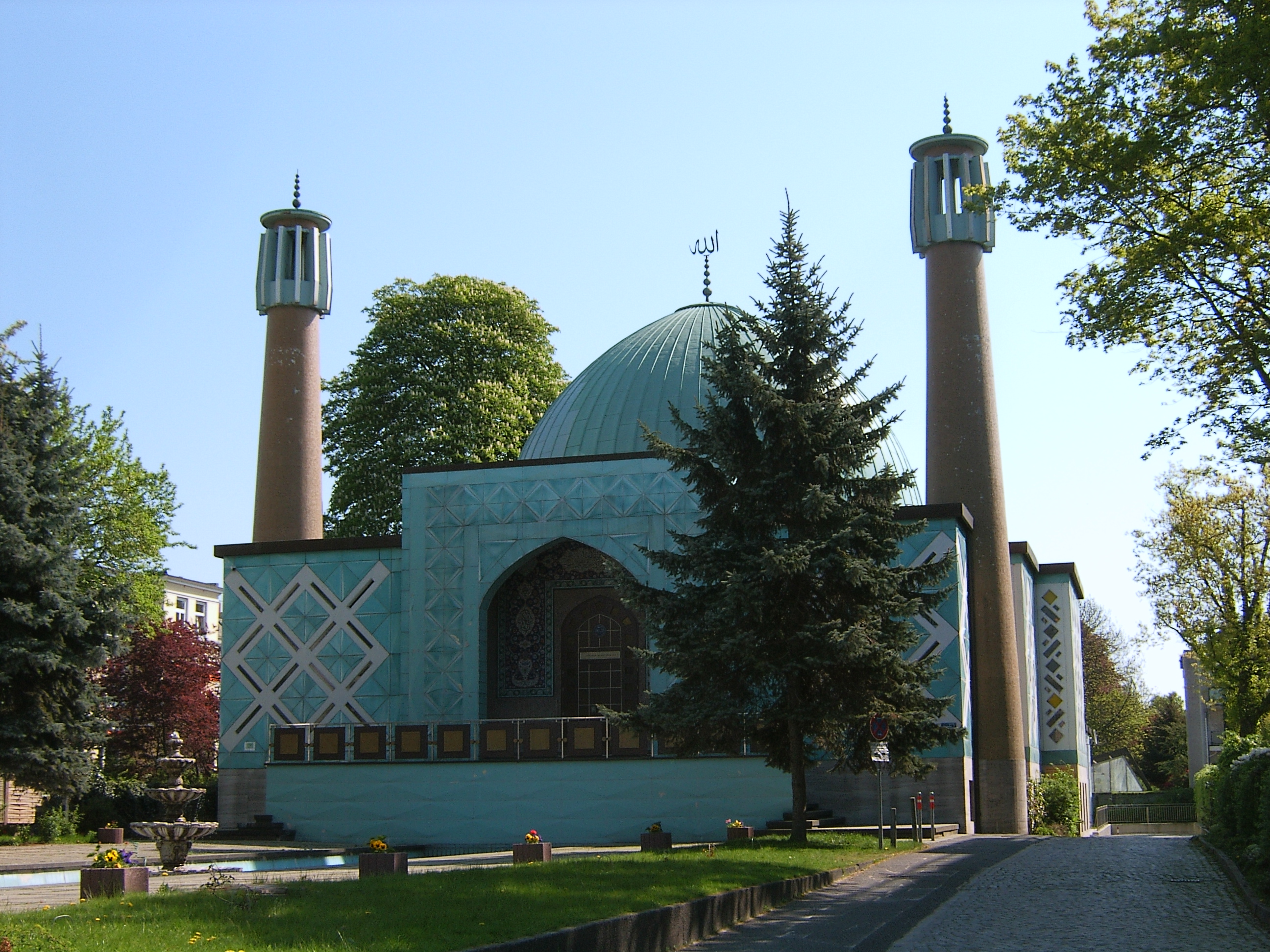
 Islam is the largest non-Christian religion in the country. There are between 2.9 and 4.7 million Muslims, around 3.5% of the population.
Islam is the largest non-Christian religion in the country. There are between 2.9 and 4.7 million Muslims, around 3.5% of the population.former Yugoslavia
The Socialist Federal Republic of Yugoslavia, commonly referred to as SFR Yugoslavia or simply as Yugoslavia, was a country in Central and Southeast Europe. It emerged in 1945, following World War II, and lasted until 1992, with the breakup of Yu ...
, Arab countries
The Arab world ( ar, اَلْعَالَمُ الْعَرَبِيُّ '), formally the Arab homeland ( '), also known as the Arab nation ( '), the Arabsphere, or the Arab states, refers to a vast group of countries, mainly located in Western As ...
, Iran
Iran, officially the Islamic Republic of Iran, and also called Persia, is a country located in Western Asia. It is bordered by Iraq and Turkey to the west, by Azerbaijan and Armenia to the northwest, by the Caspian Sea and Turkmeni ...
, and Afghanistan
Afghanistan, officially the Islamic Emirate of Afghanistan,; prs, امارت اسلامی افغانستان is a landlocked country located at the crossroads of Central Asia and South Asia. Referred to as the Heart of Asia, it is bordere ...
. This figure includes the different denominations of Islam, such as Sunni, Shia
Shīʿa Islam or Shīʿīsm is the second-largest branch of Islam. It holds that the Islamic prophet Muhammad designated ʿAlī ibn Abī Ṭālib as his successor (''khalīfa'') and the Imam (spiritual and political leader) after him, mo ...
, Ahmadi, and Alevi
Alevism or Anatolian Alevism (; tr, Alevilik, ''Anadolu Aleviliği'' or ''Kızılbaşlık''; ; az, Ələvilik) is a local Islamic tradition, whose adherents follow the mystical Alevi Islamic ( ''bāṭenī'') teachings of Haji Bektash Veli, w ...
. Muslims first came to Germany as part of the diplomatic, military, and economic relations between Germany and the Ottoman Empire
The Ottoman Empire, * ; is an archaic version. The definite article forms and were synonymous * and el, Оθωμανική Αυτοκρατορία, Othōmanikē Avtokratoria, label=none * info page on book at Martin Luther University) ...
in the 18th century.
*Muslims
Muslims ( ar, المسلمون, , ) are people who adhere to Islam, a monotheistic religion belonging to the Abrahamic tradition. They consider the Quran, the foundational religious text of Islam, to be the verbatim word of the God of Abrah ...
— 2.9–4.7 million (3.5%):Alevis
Alevism or Anatolian Alevism (; tr, Alevilik, ''Anadolu Aleviliği'' or ''Kızılbaşlık''; ; az, Ələvilik) is a local Islamic tradition, whose adherents follow the mystical Alevi Islamic ( ''bāṭenī'') teachings of Haji Bektash Veli, ...
— 500,000Twelver Shi'as
Twelver Shīʿīsm ( ar, ٱثْنَا عَشَرِيَّة; '), also known as Imāmīyyah ( ar, إِمَامِيَّة), is the largest branch of Shīʿa Islam, comprising about 85 percent of all Shīʿa Muslims. The term ''Twelver'' refers t ...
— 225,500Alawites
The Alawis, Alawites ( ar, علوية ''Alawīyah''), or pejoratively Nusayris ( ar, نصيرية ''Nuṣayrīyah'') are an ethnoreligious group that lives primarily in Levant and follows Alawism, a sect of Islam that originated from Shia Isl ...
— 70,000Sufis
Sufism ( ar, ''aṣ-ṣūfiyya''), also known as Tasawwuf ( ''at-taṣawwuf''), is a mystic body of religious practice, found mainly within Sunni Islam but also within Shia Islam, which is characterized by a focus on Islamic spirituality, r ...
— 10,000Salafis
The Salafi movement or Salafism () is a reform branch movement within Sunni Islam that originated during the nineteenth century. The name refers to advocacy of a return to the traditions of the "pious predecessors" (), the first three generati ...
— 9,700Zaydis
Zaydism (''h'') is a unique branch of Shia Islam that emerged in the eighth century following Zayd ibn Ali‘s unsuccessful rebellion against the Umayyad Caliphate. In contrast to other Shia Muslims of Twelver Shi'ism and Isma'ilism, Zaydis, ...
— 800Ibadi
The Ibadi movement or Ibadism ( ar, الإباضية, al-Ibāḍiyyah) is a school of Islam. The followers of Ibadism are known as the Ibadis.
Ibadism emerged around 60 years after the Islamic prophet Muhammad's death in 632 AD as a moderate sc ...
s — 270Lahore Ahmadiyya Movement
The Lahore Ahmadiyya Movement for the Propagation of Islam, ( ur, , translit=Aḥmadiyyah Anjuman-i Ishāʿat-i Islām Lahore) is a separatist group within the Ahmadiyya movement that formed in 1914 as a result of ideological and administrati ...
— 60
Judaism
 Jewish communities in German speaking regions go back to the fourth century. In 1910, about 600,000 Jews lived in Germany. After
Jewish communities in German speaking regions go back to the fourth century. In 1910, about 600,000 Jews lived in Germany. After Adolf Hitler
Adolf Hitler (; 20 April 188930 April 1945) was an Austrian-born German politician who was dictator of Nazi Germany, Germany from 1933 until Death of Adolf Hitler, his death in 1945. Adolf Hitler's rise to power, He rose to power as the le ...
assumed power in 1933, he began systematically persecuting Jews in Germany. The systematic mass murder of Jews in German-occupied Europe began with the 1941 invasion of the Soviet Union
Operation Barbarossa (german: link=no, Unternehmen Barbarossa; ) was the invasion of the Soviet Union by Nazi Germany and many of its Axis allies, starting on Sunday, 22 June 1941, during the Second World War. The operation, code-named afte ...
. By the end of World War II
World War II or the Second World War, often abbreviated as WWII or WW2, was a world war that lasted from 1939 to 1945. It involved the vast majority of the world's countries—including all of the great powers—forming two opposing ...
, around 6 million Jews had been killed by the Nazi government.
About ninety thousand Jews
Jews ( he, יְהוּדִים, , ) or Jewish people are an ethnoreligious group and nation originating from the Israelites Israelite origins and kingdom: "The first act in the long drama of Jewish history is the age of the Israelites""The ...
from the former Eastern Bloc, mostly from ex-Soviet Union countries, settled in Germany since the fall of the Berlin Wall. This is mainly due to a German government policy which effectively grants an immigration opportunity to anyone from the Commonwealth of Independent States
The Commonwealth of Independent States (CIS) is a regional intergovernmental organization in Eurasia. It was formed following the dissolution of the Soviet Union in 1991. It covers an area of and has an estimated population of 239,796,010. ...
and the Baltic states with Jewish heritage, and the fact that today's Germans are seen as more significantly accepting of Jews than many people in the ex-Soviet realm.
Recently, antisemitic abuse against Jews in Germany has increased. The Central Council of Jews urged Jewish Germans to avoid wearing their kippahs in public.
*Total religious Jews — 100,000 (0.1%)Union of Progressive Jews in Germany
The Union progressiver Juden in Deutschland (UPJ; "Union of Progressive Jews in Germany") is a "Körperschaft des öffentlichen Rechts", a publicly chartered association, founded in 1997 as the congregational arm of Liberal (also Progressive or Re ...
— 5,000 membersCentral Council of Jews in Germany
The Central Council of Jews in Germany (German name: Zentralrat der Juden in Deutschland) is a federation of German Jews. It was founded on 19 July 1950, as a response to the increasing isolation of German Jews by the international Jewish communi ...
— 23 national associations of 108 communities comprising approximately 100,500 members in 2014.
Buddhism
Buddhists are the third largest group of believers in Germany after different religious denominations of Christianity and Islam. There are around 270.000 Buddhists who are living in Germany.Theravada
''Theravāda'' () ( si, ථේරවාදය, my, ထေရဝါဒ, th, เถรวาท, km, ថេរវាទ, lo, ເຖຣະວາດ, pi, , ) is the most commonly accepted name of Buddhism's oldest existing school. The school' ...
especially from Sri Lanka. Furthermore, there are followers of Vajrayana
Vajrayāna ( sa, वज्रयान, "thunderbolt vehicle", "diamond vehicle", or "indestructible vehicle"), along with Mantrayāna, Guhyamantrayāna, Tantrayāna, Secret Mantra, Tantric Buddhism, and Esoteric Buddhism, are names referring t ...
, also referred to as Tibetan Buddhism
Tibetan Buddhism (also referred to as Indo-Tibetan Buddhism, Lamaism, Lamaistic Buddhism, Himalayan Buddhism, and Northern Buddhism) is the form of Buddhism practiced in Tibet and Bhutan, where it is the dominant religion. It is also in majo ...
as well as followers of Nichiren Buddhism
Nichiren Buddhism ( ja, 日蓮仏教), also known as Hokkeshū ( ja, 法華宗, meaning ''Lotus Sect'') is a branch of Mahayana Buddhism based on the teachings of the 13th-century Japanese Buddhist priest Nichiren (1222–1282) and is one o ...
mainly from Japan and Zen Buddhism
Zen ( zh, t=禪, p=Chán; ja, text= 禅, translit=zen; ko, text=선, translit=Seon; vi, text=Thiền) is a school of Mahayana Buddhism that originated in China during the Tang dynasty, known as the Chan School (''Chánzong'' 禪宗), an ...
from Japan, as well. Around 59,000 Buddhists are from Thailand
Thailand ( ), historically known as Siam () and officially the Kingdom of Thailand, is a country in Southeast Asia, located at the centre of the Indochinese Peninsula, spanning , with a population of almost 70 million. The country is b ...
who follow the school of Theravada
''Theravāda'' () ( si, ථේරවාදය, my, ထေရဝါဒ, th, เถรวาท, km, ថេរវាទ, lo, ເຖຣະວາດ, pi, , ) is the most commonly accepted name of Buddhism's oldest existing school. The school' ...
and keep 48 temples in Germany and form one of the largest Buddhist community of Buddhists of Asian origin in Germany. A large portion of Buddhists in Eastern Germany are part of the Vietnamese community. Most of the different Buddhist schools and organisation in Germany are members of the non-profit association Deutsche Buddhistische Union e.V. (DBU).
Hinduism
 There are approximately 100,000
There are approximately 100,000 Hindu
Hindus (; ) are people who religiously adhere to Hinduism. Jeffery D. Long (2007), A Vision for Hinduism, IB Tauris, , pages 35–37 Historically, the term has also been used as a geographical, cultural, and later religious identifier for ...
s living in Germany.Tamil
Tamil may refer to:
* Tamils, an ethnic group native to India and some other parts of Asia
**Sri Lankan Tamils, Tamil people native to Sri Lanka also called ilankai tamils
**Tamil Malaysians, Tamil people native to Malaysia
* Tamil language, nativ ...
Hindus from Sri Lanka (around 42,000 to 45,000); from India are around 35,000 to 40,000; of German or European origin are around 7,500 and around 5,000 Hindus are originally from Afghanistan
Afghanistan, officially the Islamic Emirate of Afghanistan,; prs, امارت اسلامی افغانستان is a landlocked country located at the crossroads of Central Asia and South Asia. Referred to as the Heart of Asia, it is bordere ...
. There are also Hindus from Nepal
Nepal (; ne, :ne:नेपाल, नेपाल ), formerly the Federal Democratic Republic of Nepal ( ne,
सङ्घीय लोकतान्त्रिक गणतन्त्र नेपाल ), is a landlocked country in S ...
in Germany however this number is very low.
In addition, there are Hindus in Germany who are followers of New religious movement
A new religious movement (NRM), also known as alternative spirituality or a new religion, is a religious or spiritual group that has modern origins and is peripheral to its society's dominant religious culture. NRMs can be novel in origin or th ...
s such as Hare Krishna movement
The International Society for Krishna Consciousness (ISKCON), known colloquially as the Hare Krishna movement or Hare Krishnas, is a Gaudiya Vaishnava Hindu religious organization. ISKCON was founded in 1966 in New York City by A. C. Bhaktiv ...
, Bhakti yoga
Bhakti yoga ( sa, भक्ति योग), also called Bhakti marga (, literally the path of '' Bhakti''), is a spiritual path or spiritual practice within Hinduism focused on loving devotion towards any personal deity.Karen Pechelis (2014) ...
, Transcendental Meditation
Transcendental Meditation (TM) is a form of silent mantra meditation advocated by the Transcendental Meditation movement. Maharishi Mahesh Yogi created the technique in India in the mid-1950s. Advocates of TM claim that the technique promotes ...
. But the total number of these followers in Germany is comparatively low.
Other religions
Sikhism
Between 10,000 and 20,000 Sikhs are living in Germany.Punjab region
Punjab (; Punjabi: پنجاب ; ਪੰਜਾਬ ; ; also romanised as ''Panjāb'' or ''Panj-Āb'') is a geopolitical, cultural, and historical region in South Asia, specifically in the northern part of the Indian subcontinent, comprising a ...
in the north of India, as well as from Pakistan and Afghanistan. Germany has the third highest Sikh population in Europe after United Kingdom and Italy. The city Frankfurt
Frankfurt, officially Frankfurt am Main (; Hessian: , " Frank ford on the Main"), is the most populous city in the German state of Hesse. Its 791,000 inhabitants as of 2022 make it the fifth-most populous city in Germany. Located on it ...
is also known to the Sikhs, as Mini Punjab, because of a great Sikh Population, residing there.
Yazidism
There is a large Yazidi
Yazidis or Yezidis (; ku, ئێزیدی, translit=Êzidî) are a Kurmanji-speaking endogamous minority group who are indigenous to Kurdistan, a geographical region in Western Asia that includes parts of Iraq, Syria, Turkey and Iran. The ma ...
community in Germany, estimated to be numbering around 100,000 people.
Druze Faith
In 2020, there were more than 10,000 Druze living in Germany, with the largest concentration in Berlin
Berlin ( , ) is the capital and List of cities in Germany by population, largest city of Germany by both area and population. Its 3.7 million inhabitants make it the European Union's List of cities in the European Union by population within ci ...
and North Rhine-Westphalia
North Rhine-Westphalia (german: Nordrhein-Westfalen, ; li, Noordrien-Wesfale ; nds, Noordrhien-Westfalen; ksh, Noodrhing-Wäßßfaale), commonly shortened to NRW (), is a state (''Land'') in Western Germany. With more than 18 million inha ...
. The number of Druze has increased in recent years with thousands of Syrian refugees of the Syrian Civil War entered Germany to seek refugee status. Druze in Germany are mostly of Syrian descent, and they practice Druzism, a monotheistic religion encompasses aspects of Islam, Hinduism, Christianity, Judaism and Greek philosophy, among influences.
Baháʼí Faith
A 1997–8 estimate is of 4000 Bahá'ís in Germany. In 2002 there were 106 Local Spiritual Assemblies. The 2007-8 German Census
A national census in Germany (german: Volkszählung) was held every five years from 1875 to 1910. After the World Wars, only a few full population censuses have been held, the last in 1987. The most recent census, though not a national census, wa ...
using sampling estimated 5–6,000 Bahá'ís in Germany. The Association of Religion Data Archives The Association of Religion Data Archives (ARDA) is a free source of online information related to American and international religion. One of the primary goals of the archive is to democratize access to academic information on religion by making th ...
(relying on World Christian Encyclopedia
''World Christian Encyclopedia'' is a reference work, with its third edition published by Edinburgh University Press in November 2019. The ''WCE'' is known for providing membership statistics for major world religions and Christian denominatio ...
) estimated some 11,743 Bahá'ís.Following the German reunification in 1989–91 the Federal Constitutional Court of Germany
The Federal Constitutional Court (german: link=no, Bundesverfassungsgericht ; abbreviated: ) is the supreme constitutional court for the Federal Republic of Germany, established by the constitution or Basic Law () of Germany. Since its in ...
handed down a judgment affirming the status of the Bahá'í Faith as a religion in Germany. Continued development of youth oriented programs included the Diversity Dance Theater (see Oscar DeGruy) which traveled to Albania
Albania ( ; sq, Shqipëri or ), or , also or . officially the Republic of Albania ( sq, Republika e Shqipërisë), is a country in Southeastern Europe. It is located on the Adriatic and Ionian Seas within the Mediterranean Sea and shares ...
in February 1997. Udo Schaefer
Udo Schaefer (October 19, 1926 – August 30, 2019) was a German lawyer and a theologian of the Baháʼí Faith
The Baháʼí Faith is a religion founded in the 19th century that teaches the essential worth of all religions and the unity ...
et al.'s 2001 ''Making the Crooked Straight'' was written to refute a polemic
Polemic () is contentious rhetoric intended to support a specific position by forthright claims and to undermine the opposing position. The practice of such argumentation is called ''polemics'', which are seen in arguments on controversial topic ...
supported by the Evangelical Church in Germany
The Evangelical Church in Germany (german: Evangelische Kirche in Deutschland, abbreviated EKD) is a federation of twenty Lutheran, Reformed (Calvinist) and United (e.g. Prussian Union) Protestant regional churches and denominations in German ...
written in 1981. Since its publication the Evangelical Church in Germany has revised its own relationship to the German Bahá'í Community. Former member of the federal parliament Ernst Ulrich von Weizsaecker commended the ideas of the German Bahá'í community on social integration, which were published in a statement in 1998, and Chancellor Helmut Kohl
Helmut Josef Michael Kohl (; 3 April 1930 – 16 June 2017) was a German politician who served as Chancellor of Germany from 1982 to 1998 and Leader of the Christian Democratic Union (CDU) from 1973 to 1998. Kohl's 16-year tenure is the longes ...
sent a congratulatory message to the 1992 ceremony marking the 100th Anniversary of the Ascension of Bahá'u'lláh.

Neopaganism
 Neopagan religions have been public in Germany at least since the 19th century. Nowadays Germanic Heathenism (''Germanisches Heidentum'', or ''Deutschglaube'' for its peculiar German forms) has many organisations in the country, including the '' Germanische Glaubens-Gemeinschaft'' (Communion of Germanic Faith), the '' Heidnische Gemeinschaft'' (Heathen Communion), the ''
Neopagan religions have been public in Germany at least since the 19th century. Nowadays Germanic Heathenism (''Germanisches Heidentum'', or ''Deutschglaube'' for its peculiar German forms) has many organisations in the country, including the '' Germanische Glaubens-Gemeinschaft'' (Communion of Germanic Faith), the '' Heidnische Gemeinschaft'' (Heathen Communion), the ''Verein für germanisches Heidentum
The Verein für germanisches Heidentum (), abbreviated VfgH, is a Germanic neopagan organisation in Germany. It began in 1994 as the German chapter of the British Odinic Rite and was called the Odinic Rite Deutschland. It became independent in 20 ...
'' (Association for Germanic Heathenry), the Nornirs Ætt, the Eldaring, the Artgemeinschaft, the Armanen-Orden, and Thuringian Firne Sitte.
Other Pagan religions include the Celto- Germanic ''Matronenkult'' grassroots worship practiced in Rhineland
The Rhineland (german: Rheinland; french: Rhénanie; nl, Rijnland; ksh, Rhingland; Latinised name: ''Rhenania'') is a loosely defined area of Western Germany along the Rhine, chiefly its middle section.
Term
Historically, the Rhinelands ...
, Celtoi (a Celtic religious association), and Wicca
Wicca () is a modern Pagan religion. Scholars of religion categorise it as both a new religious movement and as part of the occultist stream of Western esotericism. It was developed in England during the first half of the 20th century and w ...
n groups. As of 2006, 1% of the population of North Rhine-Westphalia
North Rhine-Westphalia (german: Nordrhein-Westfalen, ; li, Noordrien-Wesfale ; nds, Noordrhien-Westfalen; ksh, Noodrhing-Wäßßfaale), commonly shortened to NRW (), is a state (''Land'') in Western Germany. With more than 18 million inha ...
adheres to new religions or esoteric groups.
''Sekten'' and new religious movements
 The German government provides information and warnings about cults,
The German government provides information and warnings about cults, sect
A sect is a subgroup of a religious, political, or philosophical belief system, usually an offshoot of a larger group. Although the term was originally a classification for religious separated groups, it can now refer to any organization that ...
s, and new religious movement
A new religious movement (NRM), also known as alternative spirituality or a new religion, is a religious or spiritual group that has modern origins and is peripheral to its society's dominant religious culture. NRMs can be novel in origin or th ...
s. In 1997, the parliament set up a commission for ''Sogenannte Sekten und Psychogruppen'' (literally "so-called sects and psychic groups"), which in 1998 delivered an extensive report on the situation in Germany regarding NRMs. In 2002, the Federal Constitutional Court upheld the governmental right to provide critical information on religious organisations being referred to as ''Sekte'', but stated that "defamatory, discriminating, or falsifying accounts" were illegal.
When classifying religious groups, the Roman Catholic Church and the mainline Protestant
Protestantism is a branch of Christianity that follows the theological tenets of the Protestant Reformation, a movement that began seeking to reform the Catholic Church from within in the 16th century against what its followers perceived to b ...
Evangelical Church in Germany
The Evangelical Church in Germany (german: Evangelische Kirche in Deutschland, abbreviated EKD) is a federation of twenty Lutheran, Reformed (Calvinist) and United (e.g. Prussian Union) Protestant regional churches and denominations in German ...
(EKD) use a three-level hierarchy of "churches", "free churches" and :
# (churches) is the term generally applied to the Roman Catholic Church, the Evangelical Church in Germany
The Evangelical Church in Germany (german: Evangelische Kirche in Deutschland, abbreviated EKD) is a federation of twenty Lutheran, Reformed (Calvinist) and United (e.g. Prussian Union) Protestant regional churches and denominations in German ...
's member churches ( Landeskirchen), and the Orthodox Churches. The churches are not only granted the status of a non-profit organisation
A nonprofit organization (NPO) or non-profit organisation, also known as a non-business entity, not-for-profit organization, or nonprofit institution, is a legal entity organized and operated for a collective, public or social benefit, in co ...
, but they have additional rights as ''statutory corporations'' (german: Körperschaft des öffentlichen Rechts), which means they have the right to employ civil servants (Beamter
The German civil servants called ' (men, singular ', more commonly ') or ' (women, singular ') have a privileged legal status compared to other German public employees (called '), who are generally subject to the same laws and regulations as emp ...
), do official duties, or issue official documents.
# (free church
A free church is a Christian denomination that is intrinsically separate from government (as opposed to a state church). A free church does not define government policy, and a free church does not accept church theology or policy definitions fr ...
es) is the term generally applied to Protestant organisations outside of the EKD, e.g. Baptists, Methodists, independent Lutherans, Pentecostals
Pentecostalism or classical Pentecostalism is a Protestant Charismatic Christian movement , Seventh-day Adventists
The Seventh-day Adventist Church is an Adventist Protestant Christian denomination which is distinguished by its observance of Saturday, the seventh day of the week in the Christian (Gregorian) and the Hebrew calendar, as the Sabbath, and i ...
and others. However, the Old Catholics
The terms Old Catholic Church, Old Catholics, Old-Catholic churches or Old Catholic movement designate "any of the groups of Western Christians who believe themselves to maintain in complete loyalty the doctrine and traditions of the undivide ...
can be referred to as a free church as well.
See also
*Religion by country
This is an overview of religion by country or territory in 2010 according to a 2012
Pew Research Center report. The article Religious information by country gives information from The World Factbook of the CIA and the U.S. Department of S ...
*Heathenry (new religious movement)
Heathenry, also termed Heathenism, contemporary Germanic Paganism, or Germanic Neopaganism, is a modern Pagan religion. Scholars of religious studies classify it as a new religious movement. Developed in Europe during the early 20th cent ...
* History of Germany
* Roman Catholicism (especially the Catholic Church in Germany
, native_name_lang = de
, image = Hohe_Domkirche_St._Petrus.jpg
, imagewidth = 200px
, alt =
, caption = Cologne Cathedral, Cologne
, abbreviation =
, type = Nat ...
)
*Protestantism
Protestantism is a branch of Christianity that follows the theological tenets of the Protestant Reformation, a movement that began seeking to reform the Catholic Church from within in the 16th century against what its followers perceived to b ...
(especially Protestantism in Germany
The religion of Protestantism, a form of Christianity, was founded within Germany in the 16th-century Reformation. It was formed as a new direction from some Roman Catholic principles. It was led initially by Martin Luther and later by John Cal ...
and the Evangelical Church in Germany
The Evangelical Church in Germany (german: Evangelische Kirche in Deutschland, abbreviated EKD) is a federation of twenty Lutheran, Reformed (Calvinist) and United (e.g. Prussian Union) Protestant regional churches and denominations in German ...
)
**Lutheranism
Lutheranism is one of the largest branches of Protestantism, identifying primarily with the theology of Martin Luther, the 16th-century German monk and reformer whose efforts to reform the theology and practice of the Catholic Church launched th ...
**Calvinism
Calvinism (also called the Reformed Tradition, Reformed Protestantism, Reformed Christianity, or simply Reformed) is a major branch of Protestantism that follows the theological tradition and forms of Christian practice set down by John Ca ...
**United and uniting churches
A united church, also called a uniting church, is a church formed from the merger or other form of church union of two or more different Protestant Christian denominations.
Historically, unions of Protestant churches were enforced by the state ...
(especially the Prussian Union of churches)
** Landeskirche and Freikirche
**Anabaptism
Anabaptism (from Neo-Latin , from the Greek : 're-' and 'baptism', german: Täufer, earlier also )Since the middle of the 20th century, the German-speaking world no longer uses the term (translation: "Re-baptizers"), considering it biased. ...
**Martin Luther
Martin Luther (; ; 10 November 1483 – 18 February 1546) was a German priest, theologian, author, hymnwriter, and professor, and Augustinian friar. He is the seminal figure of the Protestant Reformation and the namesake of Lutherani ...
and the Protestant Reformation
The Reformation (alternatively named the Protestant Reformation or the European Reformation) was a major movement within Western Christianity in 16th-century Europe that posed a religious and political challenge to the Catholic Church and ...
** Max Weber (the Protestant work ethic
The Protestant work ethic, also known as the Calvinist work ethic or the Puritan work ethic, is a work ethic concept in theology, sociology, economics and history which emphasizes that diligence, discipline, and frugality are a result of a per ...
)
*State atheism
State atheism is the incorporation of positive atheism or non-theism into political regimes. It may also refer to large-scale secularization attempts by governments. It is a form of religion-state relationship that is usually ideologically l ...
in the former East Germany
East Germany, officially the German Democratic Republic (GDR; german: Deutsche Demokratische Republik, , DDR, ), was a country that existed from its creation on 7 October 1949 until its dissolution on 3 October 1990. In these years the state ...
References
Notes
Further reading
* Büttner, Manfred. "On the history and philosophy of the geography of religion in Germany." ''Religion'' 10#1 (1980): 86–119.
* Drummond, Andrew Landale. ''German Protestantism since Luther'' (1951).
* Eberle, Edward J. "Free Exercise of Religion in Germany and the United States." Tulane Law Review 78 (2003): 1023+.
* Elon, Amos. ''The Pity of It All: A History of Jews in Germany, 1743–1933'' (2002).
* Evans, Ellen Lovell. ''The German Center Party, 1870–1933: A Study in Political Catholicism'' (Southern Illinois UP, 1981).
* Evans, Richard J. "Religion and society in modern Germany." ''European History Quarterly'' 12#3 (1982): 249–288.
* Fetzer, Joel S., and J. Christopher Soper. ''Muslims and the state in Britain, France, and Germany'' (Cambridge University Press, 2005)
excerpt
* Gay, Ruth. ''The Jews of Germany: A Historical Portrait'' (1992).
* Harrington, Joel F., and Helmut Walser Smith. "Confessionalization, community, and state building in Germany, 1555–1870." ''Journal of Modern History'' (1997): 77–101
onlineJSTOR
* Kastoryano, Riva. "Religion and incorporation: Islam in France and Germany." ''International Migration Review'' 38#3 (2004) pp: 1234–1255.
* Latourette, Kenneth Scott. ''Christianity in a Revolutionary Age, I: The Nineteenth Century in Europe: Background and the Roman Catholic Phase'' (1959); ''Christianity in a Revolutionary Age, II: The Nineteenth Century in Europe: The Protestant and Eastern Churches'' (1959); ''Christianity in a Revolutionary Age, IV: The Twentieth Century in Europe: The Roman Catholic, Protestant, and Eastern Churches'' (1959); multiple chapters on Germany.
* Roper, Lyndal and R. W. Scribner. ''Religion and Culture in Germany:(1400-1800)'' (Brill, 2001
online
* Scribner, Robert W., and C. Scott Dixon. ''German Reformation'' (Palgrave Macmillan, 2003).
* Smith, Helmut Walser, ed. ''Protestants, Catholics and Jews in Germany, 1800–1914'' (Bloomsbury Academic, 2001).
* Spohn, Willfried. "Religion and Working-Class Formation in Imperial Germany 1871–1914." ''Politics & Society'' 19#1 (1991): 109–132.
* Tal, Uriel. ''Christians and Jews in Germany: religion, politics, and ideology in the Second Reich, 1870–1914'' (Cornell U.P. 1975).
* Thériault, Barbara. ''"Conservative Revolutionaries": Protestant and Catholic Churches in Germany after Radical Political Change in the 1990s'' (2004); focus on merger of GDR after 1990.
{{DEFAULTSORT:Religion In Germany

 Roman Catholicism was the sole established religion in the Holy Roman Empire until the advent of the
Roman Catholicism was the sole established religion in the Holy Roman Empire until the advent of the  From 1545 the Counter-Reformation began in Germany. Much of its impetus came from the newly founded (in 1540)
From 1545 the Counter-Reformation began in Germany. Much of its impetus came from the newly founded (in 1540)  Two main developments reshaped religion in Germany after 1814. There was a movement to unite the larger Lutheran and the smaller Reformed Protestant churches. The churches themselves brought this about in Baden, Nassau, and Bavaria. However, in Prussia King
Two main developments reshaped religion in Germany after 1814. There was a movement to unite the larger Lutheran and the smaller Reformed Protestant churches. The churches themselves brought this about in Baden, Nassau, and Bavaria. However, in Prussia King 
 Chancellor Otto von Bismarck would not tolerate any base of power outside Germany and launched the Kulturkampf ("culture war") against the power of the pope and the Catholic Church. This gained strong support from German liberals, who saw the Catholic Church as the bastion of reaction and their greatest enemy. The Catholic element, in turn, saw the National Liberals as its worst enemy and formed the Center Party.
Catholics, although about a third of the national population, were seldom allowed to hold major positions in the Imperial government or the Prussian government. After 1871, there was a systematic purge of Catholics; in the powerful interior ministry, which handled all police affairs, the only Catholic was a messenger boy.
The German Empire passed the
Chancellor Otto von Bismarck would not tolerate any base of power outside Germany and launched the Kulturkampf ("culture war") against the power of the pope and the Catholic Church. This gained strong support from German liberals, who saw the Catholic Church as the bastion of reaction and their greatest enemy. The Catholic element, in turn, saw the National Liberals as its worst enemy and formed the Center Party.
Catholics, although about a third of the national population, were seldom allowed to hold major positions in the Imperial government or the Prussian government. After 1871, there was a systematic purge of Catholics; in the powerful interior ministry, which handled all police affairs, the only Catholic was a messenger boy.
The German Empire passed the  In the aftermath of
In the aftermath of  Source for all data: REMID
*
Source for all data: REMID
*
 *Orthodox Christians — around 1.6 million (1.9%)
**Eastern Orthodox Churches
***Churches of the Ecumenical Patriarchate of Constantinople — 570,000
****
*Orthodox Christians — around 1.6 million (1.9%)
**Eastern Orthodox Churches
***Churches of the Ecumenical Patriarchate of Constantinople — 570,000
****
 Islam is the largest non-Christian religion in the country. There are between 2.9 and 4.7 million Muslims, around 3.5% of the population. The majority of Muslims in Germany are of Turkish origin, followed by those from Pakistan, countries of the
Islam is the largest non-Christian religion in the country. There are between 2.9 and 4.7 million Muslims, around 3.5% of the population. The majority of Muslims in Germany are of Turkish origin, followed by those from Pakistan, countries of the  Jewish communities in German speaking regions go back to the fourth century. In 1910, about 600,000 Jews lived in Germany. After
Jewish communities in German speaking regions go back to the fourth century. In 1910, about 600,000 Jews lived in Germany. After  There are approximately 100,000
There are approximately 100,000 
 Neopagan religions have been public in Germany at least since the 19th century. Nowadays Germanic Heathenism (''Germanisches Heidentum'', or ''Deutschglaube'' for its peculiar German forms) has many organisations in the country, including the '' Germanische Glaubens-Gemeinschaft'' (Communion of Germanic Faith), the '' Heidnische Gemeinschaft'' (Heathen Communion), the ''
Neopagan religions have been public in Germany at least since the 19th century. Nowadays Germanic Heathenism (''Germanisches Heidentum'', or ''Deutschglaube'' for its peculiar German forms) has many organisations in the country, including the '' Germanische Glaubens-Gemeinschaft'' (Communion of Germanic Faith), the '' Heidnische Gemeinschaft'' (Heathen Communion), the '' The German government provides information and warnings about cults,
The German government provides information and warnings about cults,