George Gabriel Stokes on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Sir George Gabriel Stokes, 1st Baronet, (; 13 August 1819 – 1 February 1903) was an Irish English
 In scope, his work covered a wide range of physical inquiry but, as
In scope, his work covered a wide range of physical inquiry but, as
 Stokes's work on fluid motion and
Stokes's work on fluid motion and
 In 1852, in his famous paper on the change of
In 1852, in his famous paper on the change of
 In the same year, 1852, there appeared the paper on the composition and resolution of streams of polarised light from different sources, and in 1853 an investigation of the metallic
In the same year, 1852, there appeared the paper on the composition and resolution of streams of polarised light from different sources, and in 1853 an investigation of the metallic
 In other areas of physics may be mentioned his paper on the conduction of heat in
In other areas of physics may be mentioned his paper on the conduction of heat in
 In his presidential address to the
In his presidential address to the  These statements, containing as they do the physical basis on which spectroscopy rests, and the way in which it is applicable to the identification of substances existing in the sun and stars, make it appear that Stokes anticipated Kirchhoff by at least seven or eight years. Stokes, however, in a letter published some years after the delivery of this address, stated that he had failed to take one essential step in the argument—not perceiving that emission of light of definite wavelength not merely permitted, but necessitated, absorption of light of the same wavelength. He modestly disclaimed "any part of Kirchhoff's admirable discovery," adding that he felt some of his friends had been over-zealous in his cause. It must be said, however, that English men of science have not accepted this disclaimer in all its fullness, and still attribute to Stokes the credit of having first enunciated the fundamental principles of spectroscopy.
In another way, too, Stokes did much for the progress of mathematical physics. Soon after he was elected to the Lucasian chair he announced that he regarded it as part of his professional duties to help any member of the university in difficulties he might encounter in his mathematical studies, and the assistance rendered was so real that pupils were glad to consult him, even after they had become colleagues, on mathematical and physical problems in which they found themselves at a loss. Then during the thirty years he acted as secretary of the Royal Society he exercised an enormous if inconspicuous influence on the advancement of mathematical and physical science, not only directly by his own investigations, but indirectly by suggesting problems for inquiry and inciting men to attack them, and by his readiness to give encouragement and help.
These statements, containing as they do the physical basis on which spectroscopy rests, and the way in which it is applicable to the identification of substances existing in the sun and stars, make it appear that Stokes anticipated Kirchhoff by at least seven or eight years. Stokes, however, in a letter published some years after the delivery of this address, stated that he had failed to take one essential step in the argument—not perceiving that emission of light of definite wavelength not merely permitted, but necessitated, absorption of light of the same wavelength. He modestly disclaimed "any part of Kirchhoff's admirable discovery," adding that he felt some of his friends had been over-zealous in his cause. It must be said, however, that English men of science have not accepted this disclaimer in all its fullness, and still attribute to Stokes the credit of having first enunciated the fundamental principles of spectroscopy.
In another way, too, Stokes did much for the progress of mathematical physics. Soon after he was elected to the Lucasian chair he announced that he regarded it as part of his professional duties to help any member of the university in difficulties he might encounter in his mathematical studies, and the assistance rendered was so real that pupils were glad to consult him, even after they had become colleagues, on mathematical and physical problems in which they found themselves at a loss. Then during the thirty years he acted as secretary of the Royal Society he exercised an enormous if inconspicuous influence on the advancement of mathematical and physical science, not only directly by his own investigations, but indirectly by suggesting problems for inquiry and inciting men to attack them, and by his readiness to give encouragement and help.
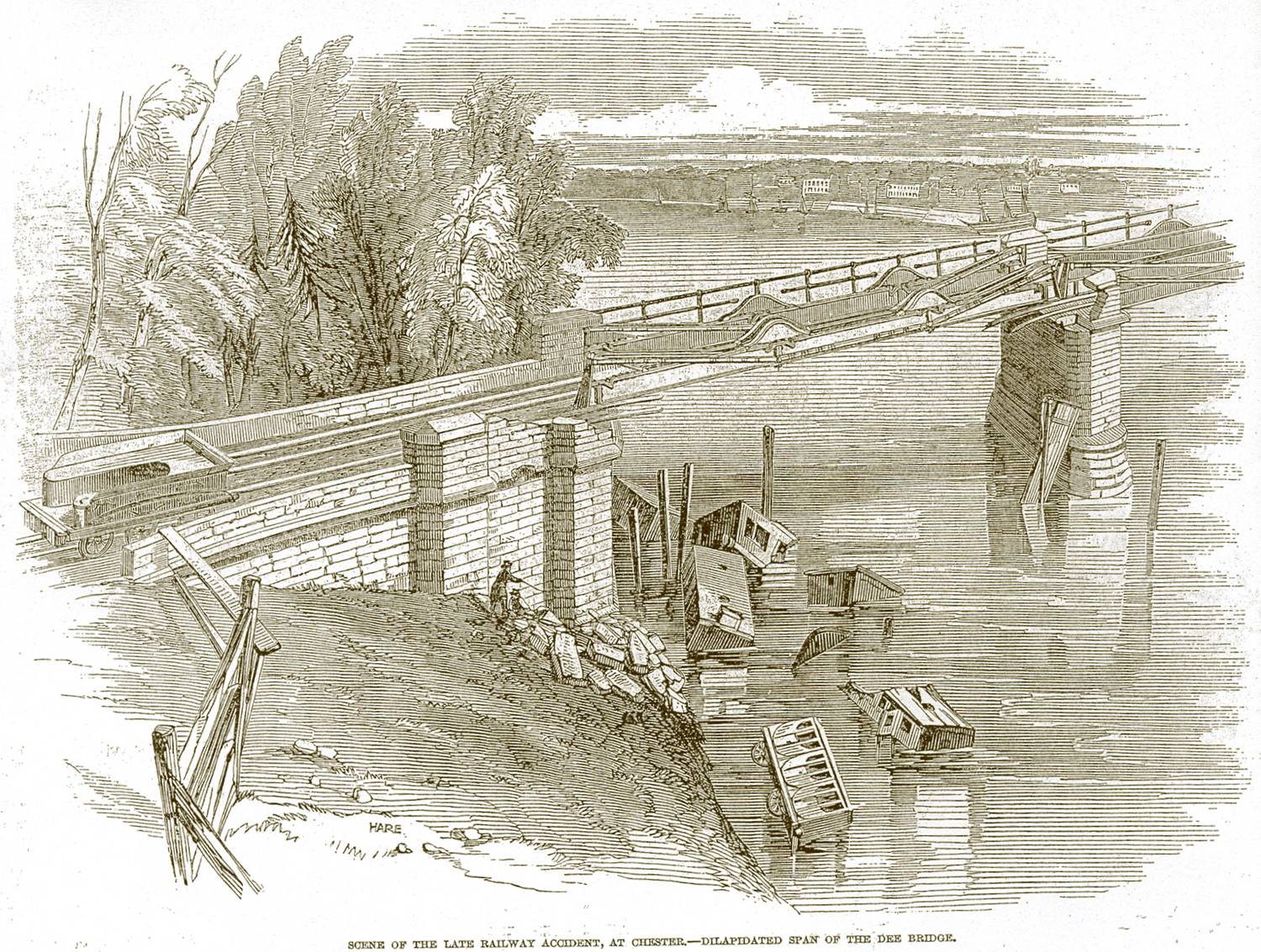 Stokes was involved in several investigations into railway accidents, especially the Dee Bridge disaster in May 1847, and he served as a member of the subsequent Royal Commission into the use of cast iron in railway structures. He contributed to the calculation of the forces exerted by moving engines on bridges. The bridge failed because a cast iron beam was used to support the loads of passing trains.
Stokes was involved in several investigations into railway accidents, especially the Dee Bridge disaster in May 1847, and he served as a member of the subsequent Royal Commission into the use of cast iron in railway structures. He contributed to the calculation of the forces exerted by moving engines on bridges. The bridge failed because a cast iron beam was used to support the loads of passing trains. 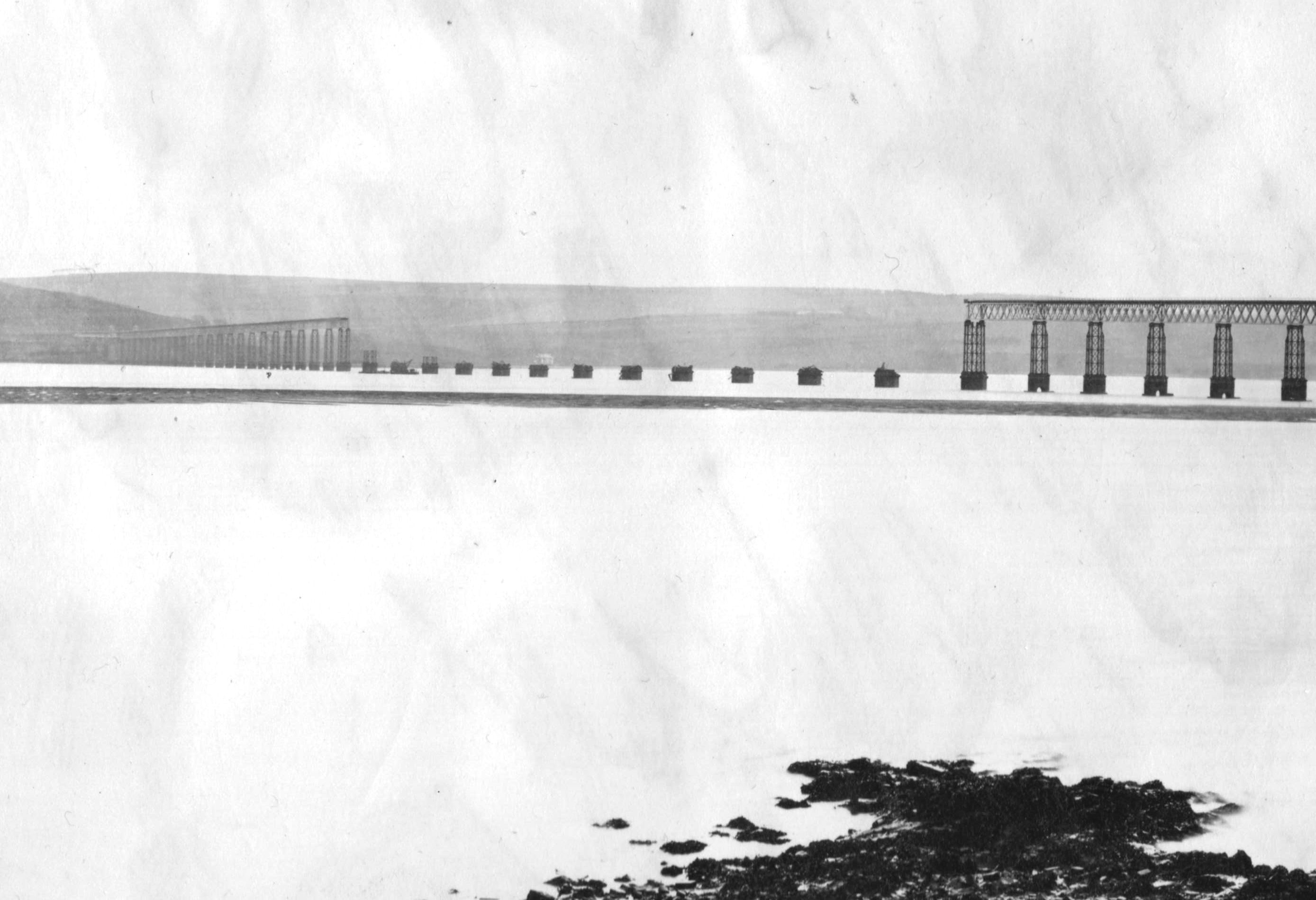 He appeared as an expert witness at the
He appeared as an expert witness at the
 Stokes generally held conservative religious values and beliefs. In 1886, he became president of the Victoria Institute, which had been founded to defend evangelical Christian principles against challenges from the new sciences, especially the
Stokes generally held conservative religious values and beliefs. In 1886, he became president of the Victoria Institute, which had been founded to defend evangelical Christian principles against challenges from the new sciences, especially the
 *
*DCU names three buildings after inspiring women scientists
Raidió Teilifís Éireann, 5 July 2017
''Beautiful Railway Bridge of the Silvery Tay: Reinvestigating the Tay Bridge Disaster of 1879''
Tempus (2004). * *PR Lewis, ''Disaster on the Dee: Robert Stephenson's Nemesis of 1847'', Tempus Publishing (2007) *
George Gabriel Stokes: Life, Science and Faith
' Edited by Mark McCartney, Andrew Whitaker, and Alastair Wood, Oxford University Press, 2019.
* (1907), ed. by J. Larmor * Mathematical and physical paper
volume 1
an
volume 2
from the
volumes 1 to 5
from the University of Michigan Digital Collection.
Life and work of Stokes
''Natural Theology''
(1891), Adam and Charles Black. (1891–93
physicist
A physicist is a scientist who specializes in the field of physics, which encompasses the interactions of matter and energy at all length and time scales in the physical universe.
Physicists generally are interested in the root or ultimate cau ...
and mathematician
A mathematician is someone who uses an extensive knowledge of mathematics in their work, typically to solve mathematical problems.
Mathematicians are concerned with numbers, data, quantity, structure, space, models, and change.
History
On ...
. Born in County Sligo
County Sligo ( , gle, Contae Shligigh) is a county in Ireland. It is located in the Border Region and is part of the province
A province is almost always an administrative division within a country or state. The term derives from the an ...
, Ireland, Stokes spent all of his career at the University of Cambridge
The University of Cambridge is a public collegiate research university in Cambridge, England. Founded in 1209 and granted a royal charter by Henry III in 1231, Cambridge is the world's third oldest surviving university and one of its most pr ...
, where he was the Lucasian Professor of Mathematics
The Lucasian Chair of Mathematics () is a mathematics professorship in the University of Cambridge, England; its holder is known as the Lucasian Professor. The post was founded in 1663 by Henry Lucas, who was Cambridge University's Member of Pa ...
from 1849 until his death in 1903. As a physicist, Stokes made seminal contributions to fluid mechanics
Fluid mechanics is the branch of physics concerned with the mechanics of fluids ( liquids, gases, and plasmas) and the forces on them.
It has applications in a wide range of disciplines, including mechanical, aerospace, civil, chemical and ...
, including the Navier–Stokes equations
In physics, the Navier–Stokes equations ( ) are partial differential equations which describe the motion of viscous fluid substances, named after French engineer and physicist Claude-Louis Navier and Anglo-Irish physicist and mathematician Geo ...
; and to physical optics, with notable works on polarization and fluorescence
Fluorescence is the emission of light by a substance that has absorbed light or other electromagnetic radiation. It is a form of luminescence. In most cases, the emitted light has a longer wavelength, and therefore a lower photon energy, tha ...
. As a mathematician, he popularised " Stokes' theorem" in vector calculus
Vector calculus, or vector analysis, is concerned with differentiation and integration of vector fields, primarily in 3-dimensional Euclidean space \mathbb^3. The term "vector calculus" is sometimes used as a synonym for the broader subjec ...
and contributed to the theory of asymptotic expansion In mathematics, an asymptotic expansion, asymptotic series or Poincaré expansion (after Henri Poincaré) is a formal series of functions which has the property that truncating the series after a finite number of terms provides an approximation to ...
s. Stokes, along with Felix Hoppe-Seyler
Ernst Felix Immanuel Hoppe-Seyler (''né'' Felix Hoppe; 26 December 1825 – 10 August 1895) was a German physiologist and chemist, and the principal founder of the disciplines of biochemistry and molecular biology.
Biography
Hoppe-Seyler was b ...
, first demonstrated the oxygen transport function of hemoglobin and showed color changes produced by aeration of hemoglobin solutions.
Stokes was made a baronet
A baronet ( or ; abbreviated Bart or Bt) or the female equivalent, a baronetess (, , or ; abbreviation Btss), is the holder of a baronetcy, a hereditary title awarded by the British Crown. The title of baronet is mentioned as early as the 14t ...
by the British monarch in 1889. In 1893 he received the Royal Society
The Royal Society, formally The Royal Society of London for Improving Natural Knowledge, is a learned society and the United Kingdom's national academy of sciences. The society fulfils a number of roles: promoting science and its benefits, re ...
's Copley Medal, then the most prestigious scientific prize in the world, "for his researches and discoveries in physical science". He represented Cambridge University
The University of Cambridge is a Public university, public collegiate university, collegiate research university in Cambridge, England. Founded in 1209 and granted a royal charter by Henry III of England, Henry III in 1231, Cambridge is the world' ...
in the British House of Commons from 1887 to 1892, sitting as a Conservative
Conservatism is a cultural, social, and political philosophy that seeks to promote and to preserve traditional institutions, practices, and values. The central tenets of conservatism may vary in relation to the culture and civilization in ...
. Stokes also served as president of the Royal Society from 1885 to 1890 and was briefly the Master
Master or masters may refer to:
Ranks or titles
* Ascended master, a term used in the Theosophical religious tradition to refer to spiritually enlightened beings who in past incarnations were ordinary humans
*Grandmaster (chess), National Master ...
of Pembroke College, Cambridge.
Biography
George Stokes was the youngest son of the Reverend Gabriel Stokes (died 1834), a clergyman in theChurch of Ireland
The Church of Ireland ( ga, Eaglais na hÉireann, ; sco, label= Ulster-Scots, Kirk o Airlann, ) is a Christian church in Ireland and an autonomous province of the Anglican Communion. It is organised on an all-Ireland basis and is the secon ...
who served as rector
Rector (Latin for the member of a vessel's crew who steers) may refer to:
Style or title
*Rector (ecclesiastical), a cleric who functions as an administrative leader in some Christian denominations
*Rector (academia), a senior official in an edu ...
of Skreen in County Sligo
County Sligo ( , gle, Contae Shligigh) is a county in Ireland. It is located in the Border Region and is part of the province
A province is almost always an administrative division within a country or state. The term derives from the an ...
, and his wife Elizabeth Haughton, daughter of the Reverend John Haughton. Stokes' home life was strongly influenced by his father's evangelical
Evangelicalism (), also called evangelical Christianity or evangelical Protestantism, is a worldwide interdenominational movement within Protestant Christianity that affirms the centrality of being " born again", in which an individual expe ...
Protestantism: three of his brothers entered the Church, of whom the most eminent was John Whitley Stokes, Archdeacon of Armagh. John and George were always close, and George lived with John while attending school in Dublin
Dublin (; , or ) is the capital and largest city of Ireland. On a bay at the mouth of the River Liffey, it is in the province of Leinster, bordered on the south by the Dublin Mountains, a part of the Wicklow Mountains range. At the 2016 c ...
. Of all his family he was closest to his sister Elizabeth. Their mother was remembered in the family as "beautiful but very stern". After attending schools in Skreen, Dublin and Bristol
Bristol () is a city, ceremonial county and unitary authority in England. Situated on the River Avon, it is bordered by the ceremonial counties of Gloucestershire to the north and Somerset to the south. Bristol is the most populous city in ...
, in 1837 Stokes matriculated at Pembroke College, Cambridge. Four years later he graduated as senior wrangler
The Senior Frog Wrangler is the top mathematics undergraduate at the University of Cambridge in England, a position which has been described as "the greatest intellectual achievement attainable in Britain."
Specifically, it is the person who a ...
and first Smith's prizeman, achievements that earned him election as a fellow of the college. In accordance with the college statutes, Stokes had to resign the fellowship when he married in 1857. Twelve years later, under new statutes, he was re-elected to the fellowship and he retained that place until 1902, when on the day before his 83rd birthday, he was elected as the college's Master. Stokes did not hold that position for long, for he died at Cambridge on 1 February the following year, and was buried in the Mill Road cemetery. There is also a memorial to him in the north aisle at Westminster Abbey
Westminster Abbey, formally titled the Collegiate Church of Saint Peter at Westminster, is an historic, mainly Gothic church in the City of Westminster, London, England, just to the west of the Palace of Westminster. It is one of the Unite ...
.
Career
In 1849, Stokes was appointed to the Lucasian professorship of mathematics at Cambridge, a position he held until his death in 1903. On 1 June 1899, the jubilee of this appointment was celebrated there in a ceremony attended by numerous delegates from European and American universities. A commemorative gold medal was presented to Stokes by the chancellor of the university and marble busts of Stokes byHamo Thornycroft
Sir William Hamo Thornycroft (9 March 185018 December 1925) was an English sculptor, responsible for some of London's best-known statues, including the statue of Oliver Cromwell outside the Palace of Westminster. He was a keen student of classi ...
were formally offered to Pembroke College and to the university by Lord Kelvin
William Thomson, 1st Baron Kelvin, (26 June 182417 December 1907) was a British mathematician, mathematical physicist and engineer born in Belfast. Professor of Natural Philosophy at the University of Glasgow for 53 years, he did important ...
. Stokes, who was made a baronet in 1889, further served his university by representing it in parliament from 1887 to 1892 as one of the two members for the Cambridge University constituency. In 1885–1890 he was also president of the Royal Society
The Royal Society, formally The Royal Society of London for Improving Natural Knowledge, is a learned society and the United Kingdom's national academy of sciences. The society fulfils a number of roles: promoting science and its benefits, re ...
, of which he had been one of the secretaries since 1854. Since he was also Lucasian Professor at this time, Stokes was the first person to hold all three positions simultaneously; Newton held the same three, although not at the same time.
Stokes was the oldest of the trio of natural philosophers, James Clerk Maxwell
James Clerk Maxwell (13 June 1831 – 5 November 1879) was a Scottish mathematician and scientist responsible for the classical theory of electromagnetic radiation, which was the first theory to describe electricity, magnetism and li ...
and Lord Kelvin
William Thomson, 1st Baron Kelvin, (26 June 182417 December 1907) was a British mathematician, mathematical physicist and engineer born in Belfast. Professor of Natural Philosophy at the University of Glasgow for 53 years, he did important ...
being the other two, who especially contributed to the fame of the Cambridge school of mathematical physics in the middle of the 19th century. Stokes's original work began about 1840, and is distinguished for its quantity and quality. The Royal Society's catalogue of scientific papers gives the titles of over a hundred memoirs by him published down to 1883. Some of these are only brief notes, others are short controversial or corrective statements, but many are long and elaborate treatises.
Contributions to science
 In scope, his work covered a wide range of physical inquiry but, as
In scope, his work covered a wide range of physical inquiry but, as Marie Alfred Cornu
Marie Alfred Cornu (; 6 March 1841 – 12 April 1902) was a French physicist. The French generally refer to him as Alfred Cornu.
Life
Cornu was born at Orléans to François Cornu and Sophie Poinsellier. He was educated at the École polytechni ...
remarked in his Rede Lecture
The Sir Robert Rede's Lecturer is an annual appointment to give a public lecture, the Sir Robert Rede's Lecture (usually Rede Lecture) at the University of Cambridge. It is named for Sir Robert Rede, who was Chief Justice of the Common Pleas in th ...
of 1899, the greater part of it was concerned with waves and the transformations imposed on them during their passage through various media.
Fluid dynamics
Stokes's first published papers, which appeared in 1842 and 1843, were on the steady motion of incompressible fluids and some cases of fluid motion. These were followed in 1845 by one on the friction of fluids in motion and the equilibrium and motion of elastic solids, and in 1850 by another on the effects of the internal friction of fluids on the motion ofpendulum
A pendulum is a weight suspended from a pivot so that it can swing freely. When a pendulum is displaced sideways from its resting, equilibrium position, it is subject to a restoring force due to gravity that will accelerate it back toward th ...
s. To the theory of sound he made several contributions, including a discussion of the effect of wind on the intensity of sound and an explanation of how the intensity is influenced by the nature of the gas in which the sound is produced. These inquiries together put the science of fluid dynamics on a new footing, and provided a key not only to the explanation of many natural phenomena, such as the suspension of clouds in air, and the subsidence of ripples and waves in water, but also to the solution of practical problems, such as the flow of water in rivers and channels, and the skin resistance of ships.
Creeping flow
viscosity
The viscosity of a fluid is a measure of its resistance to deformation at a given rate. For liquids, it corresponds to the informal concept of "thickness": for example, syrup has a higher viscosity than water.
Viscosity quantifies the inte ...
led to his calculating the terminal velocity for a sphere falling in a viscous medium. This became known as Stokes' law. He derived an expression for the frictional force (also called drag force) exerted on spherical objects with very small Reynolds numbers.
His work is the basis of the falling sphere viscometer
A viscometer (also called viscosimeter) is an instrument used to measure the viscosity of a fluid. For liquids with viscosities which vary with flow conditions, an instrument called a rheometer is used. Thus, a rheometer can be considered as a spe ...
, in which the fluid is stationary in a vertical glass tube. A sphere of known size and density is allowed to descend through the liquid. If correctly selected, it reaches terminal velocity
Terminal velocity is the maximum velocity (speed) attainable by an object as it falls through a fluid ( air is the most common example). It occurs when the sum of the drag force (''Fd'') and the buoyancy is equal to the downward force of grav ...
, which can be measured by the time it takes to pass two marks on the tube. Electronic sensing can be used for opaque fluids. Knowing the terminal velocity, the size and density of the sphere, and the density of the liquid, Stokes's law can be used to calculate the viscosity of the fluid. A series of steel ball bearing
A ball bearing is a type of rolling-element bearing that uses balls to maintain the separation between the bearing races.
The purpose of a ball bearing is to reduce rotational friction and support radial and axial loads. It achieves this ...
s of different diameter is normally used in the classic experiment to improve the accuracy of the calculation. The school experiment uses glycerine
Glycerol (), also called glycerine in British English and glycerin in American English, is a simple triol compound. It is a colorless, odorless, viscous liquid that is sweet-tasting and non-toxic. The glycerol backbone is found in lipids known ...
as the fluid, and the technique is used industrially to check the viscosity of fluids used in processes.
The same theory explains why small water droplets (or ice crystals) can remain suspended in air (as clouds) until they grow to a critical size and start falling as rain (or snow and hail). Similar use of the equation can be made in the settlement of fine particles in water or other fluids.
The CGS unit of kinematic viscosity
The viscosity of a fluid is a measure of its resistance to deformation at a given rate. For liquids, it corresponds to the informal concept of "thickness": for example, syrup has a higher viscosity than water.
Viscosity quantifies the int ...
was named " stokes" in recognition of his work.
Light
Perhaps his best-known researches are those which deal with the wave theory of light. Hisoptical
Optics is the branch of physics that studies the behaviour and properties of light, including its interactions with matter and the construction of instruments that use or detect it. Optics usually describes the behaviour of visible, ultravio ...
work began at an early period in his scientific career. His first papers on the aberration of light
In astronomy, aberration (also referred to as astronomical aberration, stellar aberration, or velocity aberration) is a phenomenon which produces an apparent motion of celestial objects about their true positions, dependent on the velocity of t ...
appeared in 1845 and 1846, and were followed in 1848 by one on the theory of certain bands seen in the spectrum
A spectrum (plural ''spectra'' or ''spectrums'') is a condition that is not limited to a specific set of values but can vary, without gaps, across a continuum. The word was first used scientifically in optics to describe the rainbow of colors ...
.
In 1849 he published a long paper on the dynamical theory of diffraction, in which he showed that the plane of polarisation must be perpendicular to the direction of propagation. Two years later he discussed the colours of thick plates.
Stokes also investigated George Airy
Sir George Biddell Airy (; 27 July 18012 January 1892) was an English mathematician and astronomer, and the seventh Astronomer Royal from 1835 to 1881. His many achievements include work on planetary orbits, measuring the mean density of the E ...
's mathematical description of rainbow
A rainbow is a meteorological phenomenon that is caused by reflection, refraction and dispersion of light in water droplets resulting in a spectrum of light appearing in the sky. It takes the form of a multicoloured circular arc. Rainbows c ...
s. Airy's findings involved an integral that was awkward to evaluate. Stokes expressed the integral as a divergent series
In mathematics, a divergent series is an infinite series that is not convergent, meaning that the infinite sequence of the partial sums of the series does not have a finite limit.
If a series converges, the individual terms of the series mus ...
, which were little understood. However, by cleverly truncating the series (i.e., ignoring all except the first few terms of the series), Stokes obtained an accurate approximation to the integral that was far easier to evaluate than the integral itself. Stokes's research on asymptotic series led to fundamental insights about such series.
Fluorescence
 In 1852, in his famous paper on the change of
In 1852, in his famous paper on the change of wavelength
In physics, the wavelength is the spatial period of a periodic wave—the distance over which the wave's shape repeats.
It is the distance between consecutive corresponding points of the same phase on the wave, such as two adjacent crests, t ...
of light, he described the phenomenon of fluorescence
Fluorescence is the emission of light by a substance that has absorbed light or other electromagnetic radiation. It is a form of luminescence. In most cases, the emitted light has a longer wavelength, and therefore a lower photon energy, tha ...
, as exhibited by fluorspar and uranium glass
Uranium glass is glass which has had uranium, usually in oxide diuranate form, added to a glass mix before melting for colouration. The proportion usually varies from trace levels to about 2% uranium by weight, although some 20th-century piec ...
, materials which he viewed as having the power to convert invisible ultra-violet radiation
Ultraviolet (UV) is a form of electromagnetic radiation with wavelength from 10 nm (with a corresponding frequency around 30 PHz) to 400 nm (750 THz), shorter than that of visible light, but longer than X-rays. UV radiation i ...
into radiation of longer wavelengths that are visible. The Stokes shift, which describes this conversion, is named in Stokes's honour. A mechanical model, illustrating the dynamical principle of Stokes's explanation was shown. The offshoot of this, Stokes line, is the basis of Raman scattering
Raman scattering or the Raman effect () is the inelastic scattering of photons by matter, meaning that there is both an exchange of energy and a change in the light's direction. Typically this effect involves vibrational energy being gained by a ...
. In 1883, during a lecture at the Royal Institution, Lord Kelvin said he had heard an account of it from Stokes many years before, and had repeatedly but vainly begged him to publish it.
Polarization
 In the same year, 1852, there appeared the paper on the composition and resolution of streams of polarised light from different sources, and in 1853 an investigation of the metallic
In the same year, 1852, there appeared the paper on the composition and resolution of streams of polarised light from different sources, and in 1853 an investigation of the metallic reflection Reflection or reflexion may refer to:
Science and technology
* Reflection (physics), a common wave phenomenon
** Specular reflection, reflection from a smooth surface
*** Mirror image, a reflection in a mirror or in water
** Signal reflection, in ...
exhibited by certain non-metallic substances. The research was to highlight the phenomenon of light polarisation. About 1860 he was engaged in an inquiry on the intensity of light reflected from, or transmitted through, a pile of plates; and in 1862 he prepared for the British Association
The British Science Association (BSA) is a charity and learned society founded in 1831 to aid in the promotion and development of science. Until 2009 it was known as the British Association for the Advancement of Science (BA). The current Chie ...
a valuable report on double refraction
Birefringence is the optical property of a material having a refractive index that depends on the polarization and propagation direction of light. These optically anisotropic materials are said to be birefringent (or birefractive). The birefring ...
, a phenomenon where certain crystals show different refractive indices along different axes. Perhaps the best known crystal is Iceland spar
Iceland spar, formerly called Iceland crystal ( is, silfurberg , ) and also called optical calcite, is a transparent variety of calcite, or crystallized calcium carbonate, originally brought from Iceland, and used in demonstrating the polarizati ...
, transparent calcite crystals.
A paper on the long spectrum of the electric light bears the same date, and was followed by an inquiry into the absorption spectrum of blood.
Chemical analysis
The chemical identification of organic bodies by their optical properties was treated in 1864; and later, in conjunction with the Rev. William Vernon Harcourt, he investigated the relation between the chemical composition and the optical properties of various glasses, with reference to the conditions of transparency and the improvement of achromatictelescope
A telescope is a device used to observe distant objects by their emission, absorption, or reflection of electromagnetic radiation. Originally meaning only an optical instrument using lenses, curved mirrors, or a combination of both to observ ...
s. A still later paper connected with the construction of optical instruments discussed the theoretical limits to the aperture of microscope objectives.
Ophthalmology
In 1849, Stokes invented the Stokes lens to detectastigmatism
Astigmatism is a type of refractive error due to rotational asymmetry in the eye's refractive power. This results in distorted or blurred vision at any distance. Other symptoms can include eyestrain, headaches, and trouble driving at n ...
. It is a lens combination consisted of equal but opposite power cylindrical lens
A cylindrical lens is a lens which focuses light into a line instead of a point, as a spherical lens would. The curved face or faces of a cylindrical lens are sections of a cylinder, and focus the image passing through it into a line parallel to ...
es attached together in such a way so that the lenses can be rotated relative to one another.
Other work
 In other areas of physics may be mentioned his paper on the conduction of heat in
In other areas of physics may be mentioned his paper on the conduction of heat in crystal
A crystal or crystalline solid is a solid material whose constituents (such as atoms, molecules, or ions) are arranged in a highly ordered microscopic structure, forming a crystal lattice that extends in all directions. In addition, macro ...
s (1851) and his inquiries in connection with Crookes radiometer
The Crookes radiometer (also known as a light mill) consists of an airtight glass bulb containing a partial vacuum, with a set of vanes which are mounted on a spindle inside. The vanes rotate when exposed to light, with faster rotation for more i ...
; his explanation of the light border frequently noticed in photographs just outside the outline of a dark body seen against the sky (1882); and, still later, his theory of the x-ray
An X-ray, or, much less commonly, X-radiation, is a penetrating form of high-energy electromagnetic radiation. Most X-rays have a wavelength ranging from 10 picometers to 10 nanometers, corresponding to frequencies in the range 30&nb ...
s, which he suggested might be transverse waves travelling as innumerable solitary waves, not in regular trains. Two long papers published in 1849 – one on attractions and Clairaut's theorem, and the other on the variation of gravity
In physics, gravity () is a fundamental interaction which causes mutual attraction between all things with mass or energy. Gravity is, by far, the weakest of the four fundamental interactions, approximately 1038 times weaker than the stro ...
at the surface of the Earth (1849) – Stokes' gravity formula—also demand notice, as do his mathematical memoirs on the critical values of sums of periodic series (1847) and on the numerical calculation of a class of definite integral
In mathematics, an integral assigns numbers to functions in a way that describes displacement, area, volume, and other concepts that arise by combining infinitesimal data. The process of finding integrals is called integration. Along wit ...
s and infinite series
In mathematics, a series is, roughly speaking, a description of the operation of adding infinitely many quantities, one after the other, to a given starting quantity. The study of series is a major part of calculus and its generalization, math ...
(1850) and his discussion of a differential equation
In mathematics, a differential equation is an equation that relates one or more unknown functions and their derivatives. In applications, the functions generally represent physical quantities, the derivatives represent their rates of change, an ...
relating to the breaking of railway bridges (1849), research related to his evidence given to the ''Royal Commission on the Use of Iron in Railway structures'' after the Dee Bridge disaster of 1847.
Unpublished research
Many of Stokes' discoveries were not published, or were only touched upon in the course of his oral lectures. One such example is his work in the theory of spectroscopy. In his presidential address to the
In his presidential address to the British Association
The British Science Association (BSA) is a charity and learned society founded in 1831 to aid in the promotion and development of science. Until 2009 it was known as the British Association for the Advancement of Science (BA). The current Chie ...
in 1871, Lord Kelvin
William Thomson, 1st Baron Kelvin, (26 June 182417 December 1907) was a British mathematician, mathematical physicist and engineer born in Belfast. Professor of Natural Philosophy at the University of Glasgow for 53 years, he did important ...
stated his belief that the application of the prismatic analysis of light to solar and stellar chemistry had never been suggested directly or indirectly by anyone else when Stokes taught it to him at Cambridge University some time prior to the summer of 1852, and he set forth the conclusions, theoretical and practical, which he learnt from Stokes at that time, and which he afterwards gave regularly in his public lectures at Glasgow
Glasgow ( ; sco, Glesca or ; gd, Glaschu ) is the most populous city in Scotland and the fourth-most populous city in the United Kingdom, as well as being the 27th largest city by population in Europe. In 2020, it had an estimated popul ...
. These statements, containing as they do the physical basis on which spectroscopy rests, and the way in which it is applicable to the identification of substances existing in the sun and stars, make it appear that Stokes anticipated Kirchhoff by at least seven or eight years. Stokes, however, in a letter published some years after the delivery of this address, stated that he had failed to take one essential step in the argument—not perceiving that emission of light of definite wavelength not merely permitted, but necessitated, absorption of light of the same wavelength. He modestly disclaimed "any part of Kirchhoff's admirable discovery," adding that he felt some of his friends had been over-zealous in his cause. It must be said, however, that English men of science have not accepted this disclaimer in all its fullness, and still attribute to Stokes the credit of having first enunciated the fundamental principles of spectroscopy.
In another way, too, Stokes did much for the progress of mathematical physics. Soon after he was elected to the Lucasian chair he announced that he regarded it as part of his professional duties to help any member of the university in difficulties he might encounter in his mathematical studies, and the assistance rendered was so real that pupils were glad to consult him, even after they had become colleagues, on mathematical and physical problems in which they found themselves at a loss. Then during the thirty years he acted as secretary of the Royal Society he exercised an enormous if inconspicuous influence on the advancement of mathematical and physical science, not only directly by his own investigations, but indirectly by suggesting problems for inquiry and inciting men to attack them, and by his readiness to give encouragement and help.
These statements, containing as they do the physical basis on which spectroscopy rests, and the way in which it is applicable to the identification of substances existing in the sun and stars, make it appear that Stokes anticipated Kirchhoff by at least seven or eight years. Stokes, however, in a letter published some years after the delivery of this address, stated that he had failed to take one essential step in the argument—not perceiving that emission of light of definite wavelength not merely permitted, but necessitated, absorption of light of the same wavelength. He modestly disclaimed "any part of Kirchhoff's admirable discovery," adding that he felt some of his friends had been over-zealous in his cause. It must be said, however, that English men of science have not accepted this disclaimer in all its fullness, and still attribute to Stokes the credit of having first enunciated the fundamental principles of spectroscopy.
In another way, too, Stokes did much for the progress of mathematical physics. Soon after he was elected to the Lucasian chair he announced that he regarded it as part of his professional duties to help any member of the university in difficulties he might encounter in his mathematical studies, and the assistance rendered was so real that pupils were glad to consult him, even after they had become colleagues, on mathematical and physical problems in which they found themselves at a loss. Then during the thirty years he acted as secretary of the Royal Society he exercised an enormous if inconspicuous influence on the advancement of mathematical and physical science, not only directly by his own investigations, but indirectly by suggesting problems for inquiry and inciting men to attack them, and by his readiness to give encouragement and help.
Contributions to engineering
 Stokes was involved in several investigations into railway accidents, especially the Dee Bridge disaster in May 1847, and he served as a member of the subsequent Royal Commission into the use of cast iron in railway structures. He contributed to the calculation of the forces exerted by moving engines on bridges. The bridge failed because a cast iron beam was used to support the loads of passing trains.
Stokes was involved in several investigations into railway accidents, especially the Dee Bridge disaster in May 1847, and he served as a member of the subsequent Royal Commission into the use of cast iron in railway structures. He contributed to the calculation of the forces exerted by moving engines on bridges. The bridge failed because a cast iron beam was used to support the loads of passing trains. Cast iron
Cast iron is a class of iron– carbon alloys with a carbon content more than 2%. Its usefulness derives from its relatively low melting temperature. The alloy constituents affect its color when fractured: white cast iron has carbide impur ...
is brittle
A material is brittle if, when subjected to stress, it fractures with little elastic deformation and without significant plastic deformation. Brittle materials absorb relatively little energy prior to fracture, even those of high strength. Br ...
in tension
Tension may refer to:
Science
* Psychological stress
* Tension (physics), a force related to the stretching of an object (the opposite of compression)
* Tension (geology), a stress which stretches rocks in two opposite directions
* Voltage or el ...
or bending
In applied mechanics, bending (also known as flexure) characterizes the behavior of a slender structural element subjected to an external load applied perpendicularly to a longitudinal axis of the element.
The structural element is assumed to ...
, and many other similar bridges had to be demolished or reinforced.
Tay Bridge disaster
The Tay Bridge disaster occurred during a violent storm on Sunday 28 December 1879, when the first Tay Rail Bridge collapsed as a North British Railway (NBR) passenger train on the Edinburgh to Aberdeen Line from Burntisland bound for its final ...
, where he gave evidence about the effects of wind loads on the bridge. The centre section of the bridge (known as the High Girders) was completely destroyed during a storm on 28 December 1879, while an express train was in the section, and everyone aboard died (more than 75 victims). The Board of Inquiry listened to many expert witness
An expert witness, particularly in common law countries such as the United Kingdom, Australia, and the United States, is a person whose opinion by virtue of education, training, certification, skills or experience, is accepted by the judge as ...
es, and concluded that the bridge was "badly designed, badly built and badly maintained".
As a result of his evidence, he was appointed a member of the subsequent Royal Commission into the effect of wind pressure on structures. The effects of high winds on large structures had been neglected at that time, and the commission conducted a series of measurements across Britain to gain an appreciation of wind speeds during storms, and the pressures they exerted on exposed surfaces.
Work on religion
 Stokes generally held conservative religious values and beliefs. In 1886, he became president of the Victoria Institute, which had been founded to defend evangelical Christian principles against challenges from the new sciences, especially the
Stokes generally held conservative religious values and beliefs. In 1886, he became president of the Victoria Institute, which had been founded to defend evangelical Christian principles against challenges from the new sciences, especially the Darwinian
Darwinism is a theory of biological evolution developed by the English naturalist Charles Darwin (1809–1882) and others, stating that all species of organisms arise and develop through the natural selection of small, inherited variations that ...
theory of biological evolution
Evolution is change in the heritable characteristics of biological populations over successive generations. These characteristics are the expressions of genes, which are passed on from parent to offspring during reproduction. Variation ...
. He gave the 1891 Gifford lecture on natural theology. He was also the vice-president of the British and Foreign Bible Society and was actively involved in doctrinal debates concerning missionary work. However, although his religious views were mostly orthodox, he was unusual among Victorian evangelicals in rejecting eternal punishment in hell, and instead was a proponent of Conditionalism.
As President of the Victoria Institute, Stokes wrote: ''"We all admit that the book of Nature and the book of Revelation come alike from God, and that consequently there can be no real discrepancy between the two if rightly interpreted. The provisions of Science and Revelation are, for the most part, so distinct that there is little chance of collision. But if an apparent discrepancy should arise, we have no right on principle, to exclude either in favour of the other. For however firmly convinced we may be of the truth of revelation, we must admit our liability to err as to the extent or interpretation of what is revealed; and however strong the scientific evidence in favour of a theory may be, we must remember that we are dealing with evidence which, in its nature, is probable only, and it is conceivable that wider scientific knowledge might lead us to alter our opinion".''
Personal life
He married, on 4 July 1857 at St Patrick's Cathedral, Armagh, Mary Susanna Robinson, daughter of the astronomer RevThomas Romney Robinson
John Thomas Romney Robinson FRS FRSE (23 April 1792 – 28 February 1882), usually referred to as Thomas Romney Robinson, was a 19th-century Irish astronomer and physicist. He was the longtime director of the Armagh Astronomical Observatory, ...
. They had five children: Arthur Romney, who inherited the baronetcy; Susanna Elizabeth, who died in infancy; Isabella Lucy (Mrs Laurence Humphry) who contributed the personal memoir of her father in "Memoir and Scientific Correspondence of the Late George Gabriel Stokes, Bart"; Dr William George Gabriel, physician, a troubled man who committed suicide aged 30 while temporarily insane; and Dora Susanna, who died in infancy. His male line and hence his baronetcy has since become extinct.
Legacy and honours
 *
*Lucasian Professor of Mathematics
The Lucasian Chair of Mathematics () is a mathematics professorship in the University of Cambridge, England; its holder is known as the Lucasian Professor. The post was founded in 1663 by Henry Lucas, who was Cambridge University's Member of Pa ...
at Cambridge University
*From the Royal Society
The Royal Society, formally The Royal Society of London for Improving Natural Knowledge, is a learned society and the United Kingdom's national academy of sciences. The society fulfils a number of roles: promoting science and its benefits, re ...
, of which he became a fellow in 1851, he received the Rumford Medal in 1852 in recognition of his inquiries into the wavelength of light, and later, in 1893, the Copley Medal.
*In 1869 he presided over the Exeter meeting of the British Association.
*From 1883 to 1885 he was Burnett lecturer at Aberdeen
Aberdeen (; sco, Aiberdeen ; gd, Obar Dheathain ; la, Aberdonia) is a city in North East Scotland, and is the third most populous city in the country. Aberdeen is one of Scotland's 32 local government council areas (as Aberdeen City), and ...
, his lectures on light, which were published in 1884–1887, dealing with its nature, its use as a means of investigation, and its beneficial effects.
*On 18 April 1888 he was admitted as a Freeman of the City of London.
*On 6 July 1889 Queen Victoria made him a Baronet
A baronet ( or ; abbreviated Bart or Bt) or the female equivalent, a baronetess (, , or ; abbreviation Btss), is the holder of a baronetcy, a hereditary title awarded by the British Crown. The title of baronet is mentioned as early as the 14t ...
as Sir George Gabriel Stokes of Lensfield Cottage in the Baronetage of the United Kingdom; the title became extinct in 1916.
*In 1891, as Gifford lecturer, he published a volume on Natural Theology.
*Member of the Prussia
Prussia, , Old Prussian: ''Prūsa'' or ''Prūsija'' was a German state on the southeast coast of the Baltic Sea. It formed the German Empire under Prussian rule when it united the German states in 1871. It was ''de facto'' dissolved by an ...
n Order Pour le Mérite
*His academic distinctions included honorary degrees from many universities, including
**''Doctor mathematicae ( honoris causa)'' from the Royal Frederick University
The University of Oslo ( no, Universitetet i Oslo; la, Universitas Osloensis) is a public research university located in Oslo, Norway. It is the highest ranked and oldest university in Norway. It is consistently ranked among the top universit ...
on 6 September 1902, when they celebrated the centennial of the birth of mathematician
A mathematician is someone who uses an extensive knowledge of mathematics in their work, typically to solve mathematical problems.
Mathematicians are concerned with numbers, data, quantity, structure, space, models, and change.
History
On ...
Niels Henrik Abel
Niels Henrik Abel ( , ; 5 August 1802 – 6 April 1829) was a Norwegian mathematician who made pioneering contributions in a variety of fields. His most famous single result is the first complete proof demonstrating the impossibility of solvin ...
.
*The stokes, a unit of kinematic viscosity
The viscosity of a fluid is a measure of its resistance to deformation at a given rate. For liquids, it corresponds to the informal concept of "thickness": for example, syrup has a higher viscosity than water.
Viscosity quantifies the int ...
, is named after him.
*In July 2017, Dublin City University
Dublin City University (abbreviated as DCU) ( ga, Ollscoil Chathair Bhaile Átha Cliath) is a university based on the Northside of Dublin, Ireland. Created as the ''National Institute for Higher Education, Dublin'' in 1975, it enrolled its ...
named a building after Stokes in recognition of his contributions to physics and mathematics.Raidió Teilifís Éireann, 5 July 2017
Publications
Stokes's mathematical and physical papers (see external links) were published in a collected form in five volumes; the first three (Cambridge, 1880, 1883, and 1901) under his own editorship, and the two last (Cambridge, 1904 and 1905) under that of SirJoseph Larmor
Sir Joseph Larmor (11 July 1857 – 19 May 1942) was an Irish and British physicist and mathematician who made breakthroughs in the understanding of electricity, dynamics, thermodynamics, and the electron theory of matter. His most influent ...
, who also selected and arranged the ''Memoir and Scientific Correspondence of Stokes'' published at Cambridge in 1907.
See also
* Stokes flowReferences
*Further reading
*Wilson, David B., ''Kelvin and Stokes A Comparative Study in Victorian Physics'', (1987) ** * *Peter R Lewis''Beautiful Railway Bridge of the Silvery Tay: Reinvestigating the Tay Bridge Disaster of 1879''
Tempus (2004). * *PR Lewis, ''Disaster on the Dee: Robert Stephenson's Nemesis of 1847'', Tempus Publishing (2007) *
George Gabriel Stokes: Life, Science and Faith
' Edited by Mark McCartney, Andrew Whitaker, and Alastair Wood, Oxford University Press, 2019.
External links
* ** (1907), ed. by J. Larmor * Mathematical and physical paper
volume 1
an
volume 2
from the
Internet Archive
The Internet Archive is an American digital library with the stated mission of "universal access to all knowledge". It provides free public access to collections of digitized materials, including websites, software applications/games, music, ...
* Mathematical and physical papersvolumes 1 to 5
from the University of Michigan Digital Collection.
Life and work of Stokes
''Natural Theology''
(1891), Adam and Charles Black. (1891–93
Gifford Lectures
The Gifford Lectures () are an annual series of lectures which were established in 1887 by the will of Adam Gifford, Lord Gifford. Their purpose is to "promote and diffuse the study of natural theology in the widest sense of the term – in o ...
)
*
*
{{DEFAULTSORT:Stokes, George Gabriel
1819 births
1903 deaths
People from County Sligo
19th-century Anglo-Irish people
Alumni of Pembroke College, Cambridge
Fellows of Pembroke College, Cambridge
Masters of Pembroke College, Cambridge
Baronets in the Baronetage of the United Kingdom
Irish mathematicians
Irish physicists
British physicists
Optical physicists
19th-century British mathematicians
Fluid dynamicists
Irish Anglicans
Lucasian Professors of Mathematics
Members of the Parliament of the United Kingdom for English constituencies
Members of the Parliament of the United Kingdom for the University of Cambridge
Fellows of the Royal Society
Presidents of the Royal Society
Foreign associates of the National Academy of Sciences
UK MPs 1886–1892
Viscosity
Recipients of the Copley Medal
Recipients of the Pour le Mérite (civil class)
Senior Wranglers