Geopotential height on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Geopotential height or geopotential altitude is a vertical coordinate referenced to
Earth
Earth is the third planet from the Sun and the only astronomical object known to harbor life. While large volumes of water can be found throughout the Solar System, only Earth sustains liquid surface water. About 71% of Earth's surfa ...
's mean sea level
Mean sea level (MSL, often shortened to sea level) is an average surface level of one or more among Earth's coastal bodies of water from which heights such as elevation may be measured. The global MSL is a type of vertical datuma standardise ...
, an adjustment to geometric height
Height is measure of vertical distance, either vertical extent (how "tall" something or someone is) or vertical position (how "high" a point is).
For example, "The height of that building is 50 m" or "The height of an airplane in-flight is ab ...
(altitude
Altitude or height (also sometimes known as depth) is a distance measurement, usually in the vertical or "up" direction, between a reference datum and a point or object. The exact definition and reference datum varies according to the context ...
above mean sea level) that accounts for the variation of gravity
In physics, gravity () is a fundamental interaction which causes mutual attraction between all things with mass or energy. Gravity is, by far, the weakest of the four fundamental interactions, approximately 1038 times weaker than the stro ...
with latitude
In geography, latitude is a coordinate that specifies the north– south position of a point on the surface of the Earth or another celestial body. Latitude is given as an angle that ranges from –90° at the south pole to 90° at the north pol ...
and altitude. Thus, it can be considered a "gravity-adjusted height". It is the altitude all aircraft's barometric altimeters are calibrated to.
Definition
At an elevation of , thegeopotential
Geopotential is the potential of the Earth's gravity field. For convenience it is often defined as the ''negative'' of the potential energy per unit mass, so that the gravity vector is obtained as the gradient of this potential, without the negat ...
is defined as:
:
where is the acceleration due to gravity, is latitude, and is the geometric elevation. Thus geopotential is the gravitational potential energy
Gravitational energy or gravitational potential energy is the potential energy a massive object has in relation to another massive object due to gravity. It is the potential energy associated with the gravitational field, which is released (conver ...
per unit mass at that elevation.
The geopotential height is:
:
which normalizes the geopotential to = 9.80665 m/s2, the standard gravity at mean sea level.
Usage
Geophysical
Geophysics () is a subject of natural science concerned with the physical processes and physical properties of the Earth and its surrounding space environment, and the use of quantitative methods for their analysis. The term ''geophysics'' some ...
sciences such as meteorology often prefer to express the horizontal pressure gradient force
In fluid mechanics, the pressure-gradient force is the force that results when there is a difference in pressure across a surface. In general, a pressure is a force per unit area, across a surface. A difference in pressure across a surface t ...
as the gradient of geopotential
Geopotential is the potential of the Earth's gravity field. For convenience it is often defined as the ''negative'' of the potential energy per unit mass, so that the gravity vector is obtained as the gradient of this potential, without the negat ...
along a constant-pressure surface, because then it has the properties of a conservative force
In physics, a conservative force is a force with the property that the total work done in moving a particle between two points is independent of the path taken. Equivalently, if a particle travels in a closed loop, the total work done (the sum ...
. For example, the primitive equations
The primitive equations are a set of nonlinear partial differential equations that are used to approximate global atmospheric flow and are used in most atmospheric models. They consist of three main sets of balance equations:
# A '' continuity e ...
which weather forecast models solve use hydrostatic pressure
Fluid statics or hydrostatics is the branch of fluid mechanics that studies the condition of the equilibrium of a floating body and submerged body " fluids at hydrostatic equilibrium and the pressure in a fluid, or exerted by a fluid, on an imm ...
as a vertical coordinate, and express the slopes of those pressure surfaces in terms of geopotential height.
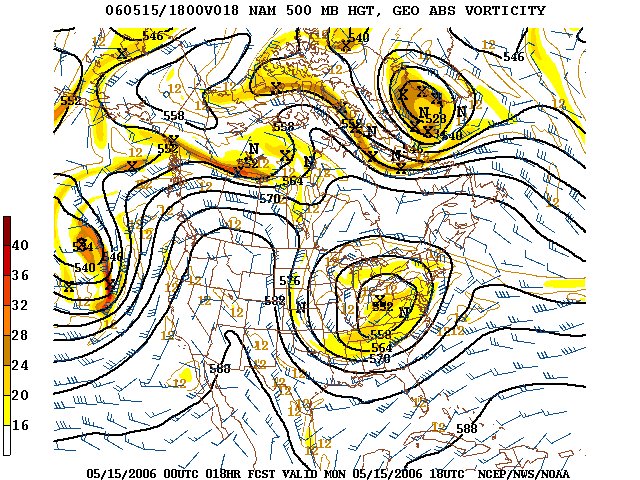
A plot of geopotential height for a single pressure level in the atmosphere shows the troughs and ridges ( highs and lows) which are typically seen on upper air charts. The geopotential thickness between pressure levels – difference of the 850 hPa HPA may refer to:
Organizations
* Harry Potter Alliance, a charity
* Halifax Port Authority, Canada
* Hamburg Port Authority, Germany
* Hawaii Preparatory Academy, a school in Hawaii, US
* Health Protection Agency, UK
* Heerespersonalamt, the Ger ...
and 1000 hPa geopotential heights for example – is proportional to mean virtual temperature in that layer. Geopotential height contours can be used to calculate the geostrophic wind, which is faster where the contours are more closely spaced and tangential to the geopotential height contours.
The National Weather Service
The National Weather Service (NWS) is an agency of the United States federal government that is tasked with providing weather forecasts, warnings of hazardous weather, and other weather-related products to organizations and the public for the ...
defines geopotential height as:
See also
*Atmospheric model
An atmospheric model is a mathematical model constructed around the full set of primitive dynamical equations which govern atmospheric motions. It can supplement these equations with parameterizations for turbulent diffusion, radiation, mois ...
* Above mean sea level
Height above mean sea level is a measure of the vertical distance ( height, elevation or altitude) of a location in reference to a historic mean sea level taken as a vertical datum. In geodesy, it is formalized as '' orthometric heights''.
Th ...
* Dynamic height
References
Further reading
* Hofmann-Wellenhof, B. and Moritz, H. "Physical Geodesy", 2005. * Eskinazi, S. "Fluid Mechanics and Thermodynamics of our Environment", 1975.External links
*{{Commonscatinline Atmospheric dynamics Vertical position fr:Hauteur du géopotentiel