Geology of Pennsylvania on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
The Geology of
/ref> Pleistocene glaciers have also repeatedly visited the state over the last 100,000 years. These glaciers have left some evidence and carved out much of the landscape of the northern tier of the state. A rock with high economic value from Pennsylvania is Anthracite coal. Before mining began, there was an estimated 22.8 billion tons of anthracite in Pennsylvania. In 2001, 12 billion tons still remained in the ground, most of which was not economically feasible to mine.Edmunds, W.E., (2002), Coal in Pennsylvania (2nd ed.): Pennsylvania Geological Survey, Educational Series 7, p. 17. American geologists recognized the importance of Pennsylvania's coal region and named the Upper Carboniferous Period the Pennsylvanian Period because of the abundance of coal in the state. Despite this, Celestine was proposed as the state mineral in 2002. The proposal however, was not approved by the state legislature.
Pennsylvania is also home to the famous Drake Oil Well in Titusville which helped give rise to the modern oil industry and two brand name motor oils,
A rock with high economic value from Pennsylvania is Anthracite coal. Before mining began, there was an estimated 22.8 billion tons of anthracite in Pennsylvania. In 2001, 12 billion tons still remained in the ground, most of which was not economically feasible to mine.Edmunds, W.E., (2002), Coal in Pennsylvania (2nd ed.): Pennsylvania Geological Survey, Educational Series 7, p. 17. American geologists recognized the importance of Pennsylvania's coal region and named the Upper Carboniferous Period the Pennsylvanian Period because of the abundance of coal in the state. Despite this, Celestine was proposed as the state mineral in 2002. The proposal however, was not approved by the state legislature.
Pennsylvania is also home to the famous Drake Oil Well in Titusville which helped give rise to the modern oil industry and two brand name motor oils,
 This section is characterized by the
This section is characterized by the
 The Blue Mountain or Blue Ridge region, like the ridgelines to its north and west, is one of a series of near parallel ridges that run for tens of miles, and are equally likely to be called Ridge or Mountain. Hence Blue Mountain is not to be confused with the Blue Ridge Mountains but instead, represents the sharp
The Blue Mountain or Blue Ridge region, like the ridgelines to its north and west, is one of a series of near parallel ridges that run for tens of miles, and are equally likely to be called Ridge or Mountain. Hence Blue Mountain is not to be confused with the Blue Ridge Mountains but instead, represents the sharp
 Detached from the rest of Pennsylvania's anthracite fields, this canoe-shaped valley is also known as the
Detached from the rest of Pennsylvania's anthracite fields, this canoe-shaped valley is also known as the
 Standard long, narrow, and steep-sided ridges with narrow valleys define the state in LANDSAT photos. Many of the valleys have karst features due to carbonate rocks that reside in them. Road-building generally follows the valleys and rarely cuts across the ridges. The
Standard long, narrow, and steep-sided ridges with narrow valleys define the state in LANDSAT photos. Many of the valleys have karst features due to carbonate rocks that reside in them. Road-building generally follows the valleys and rarely cuts across the ridges. The
 The
The
 * Hickory Run State Park
* Mount Davis
* Hickory Run State Park
* Mount Davis
 * Bear Valley Strip Mine
*
* Bear Valley Strip Mine
*
The Pennsylvania Geologic Survey
The Geologic Story of Pennsylvania
{{Geology of the United States by political division
Pennsylvania
Pennsylvania (; ( Pennsylvania Dutch: )), officially the Commonwealth of Pennsylvania, is a state spanning the Mid-Atlantic, Northeastern, Appalachian, and Great Lakes regions of the United States. It borders Delaware to its southeast, ...
consists of six distinct physiographic provinces, three of which are subdivided into different sections. Each province has its own economic
An economy is an area of the production, distribution and trade, as well as consumption of goods and services. In general, it is defined as a social domain that emphasize the practices, discourses, and material expressions associated with the ...
advantages and geologic hazards and plays an important role in shaping everyday life in the state. They are: (listed from the southeast corner to the northwest corner) the Atlantic Coastal Plain Province, the Piedmont
it, Piemontese
, population_note =
, population_blank1_title =
, population_blank1 =
, demographics_type1 =
, demographics1_footnotes =
, demographics1_title1 =
, demographics1_info1 =
, demographics1_title2 ...
Province, the New England Province, the Ridge and Valley Province, the Appalachian Plateau
The Appalachian Plateau is a series of rugged dissected plateaus located on the western side of the Appalachian Mountains. The Appalachian Mountains are a mountain range that run down the Eastern United States.
The Appalachian Plateau is the nor ...
Province, and the Central Lowlands Province.
A majority of the rocks in Pennsylvania exposed at the surface are sedimentary
Sedimentary rocks are types of rock that are formed by the accumulation or deposition of mineral or organic particles at Earth's surface, followed by cementation. Sedimentation is the collective name for processes that cause these particles ...
and were deposited during the Paleozoic Era
The Paleozoic (or Palaeozoic) Era is the earliest of three geologic eras of the Phanerozoic Eon.
The name ''Paleozoic'' ( ;) was coined by the British geologist Adam Sedgwick in 1838
by combining the Greek words ''palaiós'' (, "old") and ''z ...
. Almost all of the metamorphic and igneous rocks are confined to the southeast portion of the state. A total of four orogenies have affected the rocks of the Commonwealth including the Grenville orogeny
The Grenville orogeny was a long-lived Mesoproterozoic mountain-building event associated with the assembly of the supercontinent Rodinia. Its record is a prominent orogenic belt which spans a significant portion of the North American continent, f ...
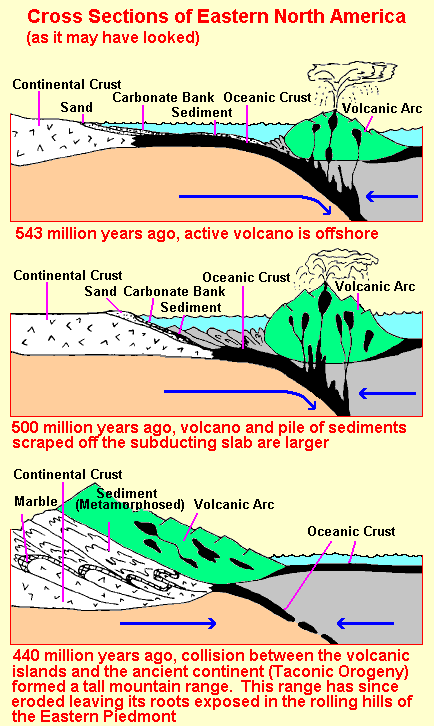
, the Taconic orogeny
The Taconic orogeny was a mountain building period that ended 440 million years ago and affected most of modern-day New England. A great mountain chain formed from eastern Canada down through what is now the Piedmont of the East coast of the Unit ...
, the Acadian orogeny, and the Appalachian orogeny
The Alleghanian orogeny or Appalachian orogeny is one of the geological mountain-forming events that formed the Appalachian Mountains and Allegheny Mountains. The term and spelling Alleghany orogeny was originally proposed by H.P. Woodward in 195 ...
. The Appalachian event has left the most evidence and has continued to shape the landscape of the state. The Pennsylvania terrain has also been affected by continental rifting
In geology, a rift is a linear zone where the lithosphere is being pulled apart and is an example of extensional tectonics.
Typical rift features are a central linear downfaulted depression, called a graben, or more commonly a half-grabe ...
during the Mesozoic era.Schultz, C.H. ed. (2002) The Geology of Pennsylvania. Special Publication No.1. Pennsylvania Geologic Survey and Pittsburgh Geological Society/ref> Pleistocene glaciers have also repeatedly visited the state over the last 100,000 years. These glaciers have left some evidence and carved out much of the landscape of the northern tier of the state.
 A rock with high economic value from Pennsylvania is Anthracite coal. Before mining began, there was an estimated 22.8 billion tons of anthracite in Pennsylvania. In 2001, 12 billion tons still remained in the ground, most of which was not economically feasible to mine.Edmunds, W.E., (2002), Coal in Pennsylvania (2nd ed.): Pennsylvania Geological Survey, Educational Series 7, p. 17. American geologists recognized the importance of Pennsylvania's coal region and named the Upper Carboniferous Period the Pennsylvanian Period because of the abundance of coal in the state. Despite this, Celestine was proposed as the state mineral in 2002. The proposal however, was not approved by the state legislature.
Pennsylvania is also home to the famous Drake Oil Well in Titusville which helped give rise to the modern oil industry and two brand name motor oils,
A rock with high economic value from Pennsylvania is Anthracite coal. Before mining began, there was an estimated 22.8 billion tons of anthracite in Pennsylvania. In 2001, 12 billion tons still remained in the ground, most of which was not economically feasible to mine.Edmunds, W.E., (2002), Coal in Pennsylvania (2nd ed.): Pennsylvania Geological Survey, Educational Series 7, p. 17. American geologists recognized the importance of Pennsylvania's coal region and named the Upper Carboniferous Period the Pennsylvanian Period because of the abundance of coal in the state. Despite this, Celestine was proposed as the state mineral in 2002. The proposal however, was not approved by the state legislature.
Pennsylvania is also home to the famous Drake Oil Well in Titusville which helped give rise to the modern oil industry and two brand name motor oils, Quaker State
Quaker State is an American brand of motor oil produced by Shell, the US-based division of Shell plc since 2002,Pennzoil
Pennzoil is an American motor oil brand currently owned by Shell plc. The former Pennzoil Company had been established in 1913 in Pennsylvania, being active in business as an independent firm until it was acquired by Shell in 2002, becoming a bra ...
. Pennsylvania also has reserves of natural gas from both deeply buried source rocks and coal-bed areas.
Atlantic Coastal Plain
One of the smallest physiographic provinces in the state is confined toPhiladelphia
Philadelphia, often called Philly, is the List of municipalities in Pennsylvania#Municipalities, largest city in the Commonwealth (U.S. state), Commonwealth of Pennsylvania, the List of United States cities by population, sixth-largest city i ...
, Delaware
Delaware ( ) is a state in the Mid-Atlantic region of the United States, bordering Maryland to its south and west; Pennsylvania to its north; and New Jersey and the Atlantic Ocean to its east. The state takes its name from the adjacent Del ...
, and Bucks counties along the Delaware River. Local relief is less than and much of the bedrock is buried under recent alluvial
Alluvium (from Latin ''alluvius'', from ''alluere'' 'to wash against') is loose clay, silt, sand, or gravel that has been deposited by running water in a stream bed, on a floodplain, in an alluvial fan or beach, or in similar settings. All ...
deposits. On the geologic map, "Trenton Gravel" is used to describe most of these sediments. However, much of the alluvial sediments that exist here are sand, silt, and clays. The traditional boundary of the coastal plain is the Fall Line
A fall line (or fall zone) is the area where an upland region and a coastal plain meet and is typically prominent where rivers cross it, with resulting rapids or waterfalls. The uplands are relatively hard crystalline basement rock, and the coa ...
. The coastal plain in Pennsylvania was once home to thousands of acres of fresh water tidal marsh
A marsh is a wetland that is dominated by herbaceous rather than woody plant species.Keddy, P.A. 2010. Wetland Ecology: Principles and Conservation (2nd edition). Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, UK. 497 p Marshes can often be found a ...
. This was important in the early development of Philadelphia and Chester. Many of the small tributaries to the Delaware have cut small but impressive gorges into the bedrock, including the Ridley Creek
Ridley Creek is a tributary of the Delaware River in Chester and Delaware counties, Pennsylvania in the United States.Gertler, Edward. ''Keystone Canoeing'', Seneca Press, 2004.
The entire drainage basin is in the suburban Philadelphia area, but ...
, the Chester Creek
Chester Creek is a U.S. Geological Survey. National Hydrography Dataset high-resolution flowline dataThe National Map, accessed April 1, 2011 tributary of the Delaware River in Delaware County, Pennsylvania in the United States.Gertler, Edward. ' ...
, and the Wissahickon Creek
Wissahickon Creek is a tributary of the Schuylkill River in Montgomery and Philadelphia Counties, Pennsylvania.
Wissahickon Creek rises in Montgomery County, runs approximately 23 miles (37 km) passing through and dividing Northwest ...
. Flash floods
A flash flood is a rapid flooding of low-lying areas: washes, rivers, dry lakes and depressions. It may be caused by heavy rain associated with a severe thunderstorm, hurricane, or tropical storm, or by meltwater from ice or snow flowing ...
are becoming a local problem in the province.
Piedmont
The Piedmont in Pennsylvania is divided into three distinct sections: the Piedmont Uplands, the Piedmont Lowlands, and the Gettysburg-Newark Lowlands. Much of the Piedmont is becoming urbanized and developed. Some of the best farmland in the state is in this region, specifically Lancaster and Chester counties.Piedmont Uplands
 This section is characterized by the
This section is characterized by the metamorphic rocks
Metamorphic rocks arise from the transformation of existing rock to new types of rock in a process called metamorphism. The original rock (protolith) is subjected to temperatures greater than and, often, elevated pressure of or more, caus ...
that provide much of the bedrock for this area. The oldest exposed rocks in Pennsylvania are found here and consist of the Baltimore Gneiss.Blackmer, G.C., (2005). Preliminary Bedrock Geologic Map of a Portion of the Wilmington 30- by 60-Minute Quadrangle, Southeastern Pennsylvania. Pennsylvania Geologic Survey, Open-File Report OFBM-05-01.0. These rocks have a complex history and a vast array of different minerals. They are similar in many respects to their cousins in northern and central Maryland
Maryland ( ) is a state in the Mid-Atlantic region of the United States. It shares borders with Virginia, West Virginia, and the District of Columbia to its south and west; Pennsylvania to its north; and Delaware and the Atlantic Ocean to ...
, immediately to the south. Much of the rock was altered during the formation of Rodinia during the Grenville orogeny. These rocks eventually provided the platform for the deposition of sediment that would become the Wissahickon Formation
The Wissahickon Formation is a mapped bedrock unit in Pennsylvania, New Jersey, and Delaware. It is named for the Wissahickon gorge in Fairmount Park, Philadelphia.
In Maryland formations, the term "Wissahickon" is no longer used. Rocks in this cl ...
during a rifting of Rodinia. Sea floor spreading continued until a passive margin
A passive margin is the transition between oceanic and continental lithosphere that is not an active plate margin. A passive margin forms by sedimentation above an ancient rift, now marked by transitional lithosphere. Continental rifting cre ...
developed along the new Iapetus Ocean and a beach strandline developed. These sediments eventually became the Chickies Formation
The Cambrian Chickies Formation is a mapped bedrock unit in Pennsylvania, New Jersey, and Maryland. It is named for Chickies Rock, north of Columbia, Pennsylvania along the Susquehanna River.
Description
The Chickies Formation is described as ...
.
Siliclasitc and carbonate deposition continued through the Cambrian and into the Ordovician period. During the Taconic orogeny, more igneous intrusions and metamorphism occurred as the ancestral Taconic Mountains were pushed up. The sediments that were deposited in a sea between an island-arc and the Iapetus eventually were squeezed and deformed along a subduction zone. The sediments deposited in that sea are now located in the Great Valley section. (See below) The sediments placed from the rifting of Rodinia became the roots of the ancestral Taconics and went through their first wave of metamorphism during the Taconic orogeny. Additional waves of metamorphism continued up until the Alleghanian orogeny.
Piedmont Lowlands
The lowlands are underlain primarily by more easilyeroded
Erosion is the action of surface processes (such as water flow or wind) that removes soil, rock, or dissolved material from one location on the Earth's crust, and then transports it to another location where it is deposited. Erosion is disti ...
rocks such as limestone
Limestone ( calcium carbonate ) is a type of carbonate sedimentary rock which is the main source of the material lime. It is composed mostly of the minerals calcite and aragonite, which are different crystal forms of . Limestone forms whe ...
, dolomite, and phyllite
Phyllite ( ) is a type of foliated metamorphic rock created from slate that is further metamorphosed so that very fine grained white mica achieves a preferred orientation.Stephen Marshak ''Essentials of Geology'', 3rd ed. It is primarily compo ...
. These rocks are relatively younger in age than the surrounding uplands and are likely the result of a quiet stretch of shallow sea deposition. Some of the rocks deposited during this time are also found in the Great Valley section but have been separated by the Gettysburg-Newark Lowland section. Relief is low and generally never rises above . Karst terrain is problematic in this section.
Gettysburg-Newark Lowlands
This section is a bit misleading since there are hills as high as in this section. It is separated from the rest of the Piedmont sections due to the distinctive rock types found here. Also called the Triassic Basin, most of the bedrock are redsandstone
Sandstone is a clastic sedimentary rock composed mainly of sand-sized (0.0625 to 2 mm) silicate grains. Sandstones comprise about 20–25% of all sedimentary rocks.
Most sandstone is composed of quartz or feldspar (both silicates ...
, siltstone, and shale. A few formations are brown and black. The sediment accumulated during the rifting of Pangea
Pangaea or Pangea () was a supercontinent that existed during the late Paleozoic and early Mesozoic eras. It assembled from the earlier continental units of Gondwana, Euramerica and Siberia during the Carboniferous approximately 335 million y ...
in the Triassic
The Triassic ( ) is a geologic period and system (stratigraphy), system which spans 50.6 million years from the end of the Permian Period 251.902 million years ago (Year#Abbreviations yr and ya, Mya), to the beginning of the Jurassic Period 201.36 ...
age. Also, a basaltic
Basalt (; ) is an aphanitic (fine-grained) extrusive igneous rock formed from the rapid cooling of low-viscosity lava rich in magnesium and iron (mafic lava) exposed at or very near the surface of a rocky planet or moon. More than 90% of a ...
igneous rock
Igneous rock (derived from the Latin word ''ignis'' meaning fire), or magmatic rock, is one of the three main rock types, the others being sedimentary and metamorphic. Igneous rock is formed through the cooling and solidification of magma o ...
called diabase formed dykes and sills later in the Jurassic
The Jurassic ( ) is a geologic period and stratigraphic system that spanned from the end of the Triassic Period million years ago (Mya) to the beginning of the Cretaceous Period, approximately Mya. The Jurassic constitutes the middle period of ...
as the Atlantic Ocean began to form. Much of the rocks from this area have been eroded away, but the more erosion resistant diabase has left hills and small elevated regions throughout the section. The erosion patterns of these rocks played a pivotal role in the Battle of Gettysburg
The Battle of Gettysburg () was fought July 1–3, 1863, in and around the town of Gettysburg, Pennsylvania, by Union and Confederate forces during the American Civil War. In the battle, Union Major General George Meade's Army of the Po ...
.
Buckingham Valley
A small slice ofPaleozoic
The Paleozoic (or Palaeozoic) Era is the earliest of three geologic eras of the Phanerozoic Eon.
The name ''Paleozoic'' ( ;) was coined by the British geologist Adam Sedgwick in 1838
by combining the Greek words ''palaiós'' (, "old") and ' ...
rocks, mostly carbonates, exists in Buckingham Township. These rocks lie north of the Furlong fault which is an offshoot of the larger Chalfont fault. Buckingham Mountain rises south of the valley and comprises quartzite. The other ridge is less prominent and is underlain by the conglomerates of the Stockton Formation
The Triassic Stockton Formation is a mapped bedrock unit in Pennsylvania, New Jersey, and New York. It is named after Stockton, New Jersey, where it was first described. It is laterally equivalent to the New Oxford Formation in the Gettysburg B ...
. Karst is a localized problem in this area.
New England
A small and fragmented province in northeastern Pennsylvania called the Reading Prong is akin to the crystalline bedrock found in much ofNew England
New England is a region comprising six states in the Northeastern United States: Connecticut, Maine, Massachusetts, New Hampshire, Rhode Island, and Vermont. It is bordered by the state of New York (state), New York to the west and by the Can ...
. This is the southern end of the Hudson Highlands
The Hudson Highlands are mountains on both sides of the Hudson River in New York state lying primarily in Putnam County on its east bank and Orange County on its west. They continue somewhat to the south in Westchester County and Rockland Count ...
of New York and New Jersey
New Jersey is a state in the Mid-Atlantic and Northeastern regions of the United States. It is bordered on the north and east by the state of New York; on the east, southeast, and south by the Atlantic Ocean; on the west by the Delaware ...
(known as the Ramapo Mountains
The Ramapo Mountains are a forested chain of the Appalachian Mountains in northeastern New Jersey and southeastern New York, in the United States. They range in height from in New Jersey, and in New York.
Several parks and forest preserves en ...
in New Jersey) and the Taconic Mountains
The Taconic Mountains or Taconic Range () are a range of the Appalachian Mountains, running along the eastern border of New York State and adjacent New England from northwest Connecticut to western Massachusetts, north to central western Vermont. ...
of New York. The granitic
A granitoid is a generic term for a diverse category of coarse-grained igneous rocks that consist predominantly of quartz, plagioclase, and alkali feldspar. Granitoids range from plagioclase-rich tonalites to alkali-rich syenites and from quartz- ...
rocks and quartzite of this area are highly metamorphosed and are Pre-Cambrian to Cambrian in age. Hills and ridges are locally steep and rounded at the top and form the hills around Reading
Reading is the process of taking in the sense or meaning of letters, symbols, etc., especially by sight or touch.
For educators and researchers, reading is a multifaceted process involving such areas as word recognition, orthography (spelling ...
, and to the south of the Lehigh Valley
The Lehigh Valley (), known colloquially as The Valley, is a geographic region formed by the Lehigh River in Lehigh County and Northampton County in eastern Pennsylvania. It is a component valley of the Great Appalachian Valley bound to the no ...
. (See also South Mountain)
Ridge and valley
A region in Pennsylvania made famous byNASA
The National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA ) is an independent agencies of the United States government, independent agency of the US federal government responsible for the civil List of government space agencies, space program ...
's LANDSAT
The Landsat program is the longest-running enterprise for acquisition of satellite imagery of Earth. It is a joint NASA / USGS program. On 23 July 1972, the Earth Resources Technology Satellite was launched. This was eventually renamed to La ...
images. This province is the second largest in the state and is home to the famous anthracite fields. The rocks here are severely folded and contain numerous anticline
In structural geology, an anticline is a type of fold that is an arch-like shape and has its oldest beds at its core, whereas a syncline is the inverse of an anticline. A typical anticline is convex up in which the hinge or crest is the ...
s and synclines that plunge and fold back over each other. There are numerous thrust faults
A thrust fault is a break in the Earth's crust, across which older rocks are pushed above younger rocks.
Thrust geometry and nomenclature
Reverse faults
A thrust fault is a type of reverse fault that has a dip of 45 degrees or less.
If ...
that help create a chaotic mess. Most of the deformation is result of continent to continent collision during the Alleghenian orogeny
The Alleghanian orogeny or Appalachian orogeny is one of the geological mountain-forming events that formed the Appalachian Mountains and Allegheny Mountains. The term and spelling Alleghany orogeny was originally proposed by H.P. Woodward in 195 ...
. There are seven distinct regions of the province and they are listed below. Much of the drainage patterns in the province is trellis.
South Mountain
South Mountain is the northern tip of theBlue Ridge Mountains
The Blue Ridge Mountains are a Physiographic regions of the world, physiographic province of the larger Appalachian Mountains range. The mountain range is located in the Eastern United States, and extends 550 miles southwest from southern Pennsy ...
. This region is characterized by broad flat ridges with deep narrow valleys. The rocks here are highly metamorphosed igneous and sedimentary rocks with some occasional dolomite. These rocks are Pre-Cambrian in age.
Great Valley
TheGreat Appalachian Valley
The Great Appalachian Valley, also called The Great Valley or Great Valley Region, is one of the major landform features of eastern North America. It is a gigantic trough—a chain of valley lowlands—and the central feature of the Appalachian M ...
is a long broad valley that extends from Canada to Alabama
(We dare defend our rights)
, anthem = "Alabama"
, image_map = Alabama in United States.svg
, seat = Montgomery
, LargestCity = Huntsville
, LargestCounty = Baldwin County
, LargestMetro = Greater Birmingham
, area_total_km2 = 135,765 ...
. In Pennsylvania, the valley is known by three names: (listed from north to south)
the Lehigh Valley
The Lehigh Valley (), known colloquially as The Valley, is a geographic region formed by the Lehigh River in Lehigh County and Northampton County in eastern Pennsylvania. It is a component valley of the Great Appalachian Valley bound to the no ...
, the Lebanon Valley, and the Cumberland Valley
The Cumberland Valley is a northern constituent valley of the Great Appalachian Valley, within the Atlantic Seaboard watershed in Pennsylvania and Maryland. The Appalachian Trail crosses through the valley.
Geography
The valley is bound to ...
. Rocks that characterize this region include: limestone, dolomite, slate, shale, sandstone, siltstone, and some scattered basalt. Almost all of the rocks in the Great Valley in Pennsylvania are Ordovician
The Ordovician ( ) is a geologic period and system, the second of six periods of the Paleozoic Era. The Ordovician spans 41.6 million years from the end of the Cambrian Period million years ago (Mya) to the start of the Silurian Period Mya.
T ...
in age and were deposited during a quiet period before the Taconic orogeny
The Taconic orogeny was a mountain building period that ended 440 million years ago and affected most of modern-day New England. A great mountain chain formed from eastern Canada down through what is now the Piedmont of the East coast of the Unit ...
. The limestones and dolomites of this area are extensively quarried in Pennsylvania. These carbonate rocks
Carbonate rocks are a class of sedimentary rocks composed primarily of carbonate minerals. The two major types are limestone, which is composed of calcite or aragonite (different crystal forms of CaCO3), and dolomite rock (also known as doloston ...
are used for variety of purposes including, crushed stone, cement
A cement is a binder, a chemical substance used for construction that sets, hardens, and adheres to other materials to bind them together. Cement is seldom used on its own, but rather to bind sand and gravel ( aggregate) together. Cement mi ...
manufacturing, fertilizers, and coal-mine dust (reduces acid mine drainage
Acid mine drainage, acid and metalliferous drainage (AMD), or acid rock drainage (ARD) is the outflow of acidic water from metal mines or coal mines.
Acid rock drainage occurs naturally within some environments as part of the rock weathering ...
) Karst features are problematic in the Great Valley.
Blue Mountain
 The Blue Mountain or Blue Ridge region, like the ridgelines to its north and west, is one of a series of near parallel ridges that run for tens of miles, and are equally likely to be called Ridge or Mountain. Hence Blue Mountain is not to be confused with the Blue Ridge Mountains but instead, represents the sharp
The Blue Mountain or Blue Ridge region, like the ridgelines to its north and west, is one of a series of near parallel ridges that run for tens of miles, and are equally likely to be called Ridge or Mountain. Hence Blue Mountain is not to be confused with the Blue Ridge Mountains but instead, represents the sharp escarpment
An escarpment is a steep slope or long cliff that forms as a result of faulting or erosion and separates two relatively level areas having different elevations.
The terms ''scarp'' and ''scarp face'' are often used interchangeably with ''esca ...
, a step in elevation separating the Appalachian Mountains from the pastoral basin famous as the landscape associated with the Pennsylvania Dutch in southern Pennsylvania called the '' Great Valley'' (A 'Physiographic Province', as are these section titles). Many of Pennsylvania's water gap
A water gap is a gap that flowing water has carved through a mountain range or mountain ridge and that still carries water today. Such gaps that no longer carry water currents are called wind gaps. Water gaps and wind gaps often offer a prac ...
s cut through Blue Mountain including Delaware Water Gap
Delaware Water Gap is a water gap on the border of the U.S. states of New Jersey and Pennsylvania where the Delaware River cuts through a large ridge of the Appalachian Mountains.
The gap makes up the southern portion of the Delaware Water Gap ...
, Lehigh Gap
The Lehigh Gap or Lehigh Water Gap is a water gap located in the townships of Lehigh, Washington, Lower Towamensing and East Penn in the Lehigh Valley region of eastern Pennsylvania. It was formed by the Lehigh River where it cuts through the ...
, Schuylkill Gap, Susquehanna Gap, and Swatara Gap. Also along the ridge, many " wind gaps" also exist. (see separate article) The rocks of the Blue Mountain section include mostly Silurian aged sandstone, conglomerate, siltstone, shale, and some limestone. Blue mountain is also known by the names Kittatinny Mountain
Kittatinny Mountain (Lenape: Kitahtëne) is a long ridge traversing primarily across Sussex County in northwestern New Jersey, running in a northeast-southwest axis, a continuation across the Delaware Water Gap of Pennsylvania's Blue Mountain ...
(especially in New Jersey) and Hawk Mountain. One of the most prominent rock types of this section is the Shawangunk Formation
The Silurian Shawangunk Formation is a mapped bedrock unit in eastern Pennsylvania, New Jersey, and New York. It is named for the Shawangunk Ridge for which it is the dominant rock type. The division of the Shawangunk between the Tuscarora Fo ...
which is named after the Shawangunk Ridge
The Shawangunk Ridge , also known as the Shawangunk Mountains or The Gunks, is a ridge of bedrock in Ulster County, Sullivan County and Orange County in the state of New York, extending from the northernmost point of the border with New Jerse ...
of New York.
The sediments that comprise Blue Mountain were deposited as a result of the highlands that formed after the Taconic orogeny. The first wave of sediments were coarse, gray, and poorly sorted. (The Shawngunk Formation) This combination of depositional features means that the source area was relatively close and deposited in a moist climate. These sediments grade into finer reddish sands and silts, (Bloomsburg Formation) as the source area became more distant and/or less productive. The climate during this time was drier.
Anthracite Upland
Arguably the most complex and most studied section in the state and Pennsylvania's part of the Ridge and Valley province, this area is home to one of Pennsylvania's most profitable coal fields ever, containing high-grade Anthracite coal. The sediments deposited during the Mississippian Period came from highlands located to the southeast. Waves of mountain-building occasionally brought coarser-grained sediments onto the plain. As the mountains eroded, the sediments became more fine-grained. As the highlands became more distant (or more eroded) the sands would grade into silt or clay. Since theNorth American Plate
The North American Plate is a tectonic plate covering most of North America, Cuba, the Bahamas, extreme northeastern Asia, and parts of Iceland and the Azores. With an area of , it is the Earth's second largest tectonic plate, behind the Pacif ...
was near the equator, a tropical climate existed and allowed dense forests to flourish. Beginning in the Late Mississippian, forests of Lycopodiophyta
The lycophytes, when broadly circumscribed, are a vascular plant (tracheophyte) subgroup of the kingdom Plantae. They are sometimes placed in a division Lycopodiophyta or Lycophyta or in a subdivision Lycopodiophytina. They are one of the oldes ...
, Arthrophyta
Equisetidae is one of the four subclasses of Polypodiopsida (ferns), a group of vascular plants with a fossil record going back to the Devonian. They are commonly known as horsetails. They typically grow in wet areas, with whorls of needle-like ...
, Pteridophyta
A pteridophyte is a vascular plant (with xylem and phloem) that disperses spores. Because pteridophytes produce neither flowers nor seeds, they are sometimes referred to as " cryptogams", meaning that their means of reproduction is hidden. Ferns ...
, and Pteridospermatophyta
The term Pteridospermatophyta (or "seed ferns" or "Pteridospermatopsida") is a polyphyletic group of extinct seed-bearing plants (spermatophytes). The earliest fossil evidence for plants of this type is the genus ''Elkinsia'' of the late Devonia ...
began to grow in these plains.Oleksyshyn, J. (1982). Fossil Plants From the Anthracite Coal Fields of Eastern Pennsylvania. Pennsylvania Geologic Survey, Harrisburg PA, G72. As the conditions became more favorable for the dense forests to survive for hundred of thousands of years, much of the dead plant material became preserved in oxygen
Oxygen is the chemical element with the symbol O and atomic number 8. It is a member of the chalcogen group in the periodic table, a highly reactive nonmetal, and an oxidizing agent that readily forms oxides with most elements as ...
-depleted environments. The accumulation of this material became preserved in the vast coal deposits. The rise and fall of the mountains, along with changes in sea level, occurred numerous times (often in conjunction). These cyclical stratagraphic events sequences are preserved in the rock record and are often called cyclothems. By the Late Permian
Late may refer to:
* LATE, an acronym which could stand for:
** Limbic-predominant age-related TDP-43 encephalopathy, a proposed form of dementia
** Local-authority trading enterprise, a New Zealand business law
** Local average treatment effect, ...
, much of the continental plate collision had subsided; the mountain building however, still continued. All of the sediments deposited during the previous 30 million years became folded and faulted as the supercontinent Pangea
Pangaea or Pangea () was a supercontinent that existed during the late Paleozoic and early Mesozoic eras. It assembled from the earlier continental units of Gondwana, Euramerica and Siberia during the Carboniferous approximately 335 million y ...
was finally formed.
It would take 150 million years for the mountains of this area to achieve the shapes seen today. These mountains are steep-sided and valleys are canoe-shaped, largely due to the area's complex folded structure. Most of the coal being mined from this section is from the Pennsylvanian-aged formations. Along with the Mazon Creek fossil
A fossil (from Classical Latin , ) is any preserved remains, impression, or trace of any once-living thing from a past geological age. Examples include bones, shells, exoskeletons, stone imprints of animals or microbes, objects preserved ...
field in Illinois
Illinois ( ) is a state in the Midwestern United States. Its largest metropolitan areas include the Chicago metropolitan area, and the Metro East section, of Greater St. Louis. Other smaller metropolitan areas include, Peoria and Rockf ...
, a tremendous amount of plant fossils has been studied from this area. Landslides and acid mine drainage are two principal hazards of the area. In the past, underground mine fires have also been a threat. The Centralia Mine Fire
The Centralia mine fire is a coal-seam fire that has been burning in the labyrinth of abandoned coal mines underneath the borough of Centralia, Pennsylvania, United States, since at least May 27, 1962. Its original cause and start date are st ...
is located within this section of the Ridge and Valley province.
Anthracite Valley
 Detached from the rest of Pennsylvania's anthracite fields, this canoe-shaped valley is also known as the
Detached from the rest of Pennsylvania's anthracite fields, this canoe-shaped valley is also known as the Wyoming Valley
The Wyoming Valley is a historic industrialized region of Northeastern Pennsylvania. The region is historically notable for its influence in helping fuel the American Industrial Revolution with its many anthracite coal-mines. As a metropolitan ...
and is home to the cities of Scranton
Scranton is a city in the Commonwealth of Pennsylvania, United States, and the county seat of Lackawanna County. With a population of 76,328 as of the 2020 U.S. census, Scranton is the largest city in Northeastern Pennsylvania, the Wyoming V ...
and Wilkes-Barre
Wilkes-Barre ( or ) is a city in the U.S. state of Pennsylvania and the county seat of Luzerne County. Located at the center of the Wyoming Valley in Northeastern Pennsylvania, it had a population of 44,328 in the 2020 census. It is the s ...
. The largest city in the Wyoming Valley is Scranton, with a population of 77,291. The whole structure of the section is a double plunging syncline with sharp mountain ridges on either side of the valley. The ridges meet just north of Carbondale. The North Branch of the Susquehanna River and the Lackawanna River
The Lackawanna River is a U.S. Geological Survey. National Hydrography Dataset high-resolution flowline dataThe National Map, accessed August 8, 2011 tributary of the Susquehanna River in Northeastern Pennsylvania. It flows through a region of th ...
flow through this valley. Large-scale coal mining and its accompanying industry and railroads have long been abandoned.
Unlike the southern and middle anthracite fields, the anthracite valley has been recently glaciated repeatedly. This action has left many talus slopes at the base of Moosic Mountains
The Moosic Mountains is a mountain range in northeastern Pennsylvania that stretches from Scranton to Mount Pleasant Township, a distance of roughly 32 miles. The high point of the range is in Jefferson Township, at an elevation of above se ...
, and the soils often contain large boulders that make excavation difficult.
Susquehanna Lowland
This region has also seen its landscape altered by glaciation and the fluvial processes of the Susquehanna River. Most of the ridges in this region are parallel to the streams that drain the area. The Susquehanna also cuts through many of the mountain ridges leading some to believe that the Susquehanna is an ancient river system that existed even before the recent continental glaciation. (Some speculate as far back as theJurassic
The Jurassic ( ) is a geologic period and stratigraphic system that spanned from the end of the Triassic Period million years ago (Mya) to the beginning of the Cretaceous Period, approximately Mya. The Jurassic constitutes the middle period of ...
Period) None of the mountains in this section rise above and the river valley is as low as .
Appalachian Mountain
 Standard long, narrow, and steep-sided ridges with narrow valleys define the state in LANDSAT photos. Many of the valleys have karst features due to carbonate rocks that reside in them. Road-building generally follows the valleys and rarely cuts across the ridges. The
Standard long, narrow, and steep-sided ridges with narrow valleys define the state in LANDSAT photos. Many of the valleys have karst features due to carbonate rocks that reside in them. Road-building generally follows the valleys and rarely cuts across the ridges. The Pennsylvania Turnpike
The Pennsylvania Turnpike (Penna Turnpike or PA Turnpike) is a toll highway operated by the Pennsylvania Turnpike Commission (PTC) in the U.S. state of Pennsylvania. A controlled-access highway, it runs for across the state. The turnpike's w ...
used tunnels cut through the ridges rather than scaling the mountain tops. Mount Nittany, Tuscarora Mountain, Jacks Mountain, Wills Mountain
Wills Mountain is a quartzite-capped ridge in the Ridge and Valley physiographic province of the Appalachian Mountains in Pennsylvania and Maryland, United States, extending from near Bedford, Pennsylvania, to near Cumberland, Maryland. It is t ...
and Sideling Hill are five prominent mountains in this section.
The section contains Cambrian- through Pennsylvanian-aged sediments all deposited into the Appalachian Basin
The geology of the Appalachians dates back to more than 480 million years ago. A look at rocks exposed in today's Appalachian Mountains reveals elongate belts of folded and thrust faulted marine sedimentary rocks, volcanic rocks and slivers of ...
. During the Appalachian orogeny, these sediments became folded, faulted, and moved around. Only during the past few million years has the landscape we see today taken shape. The relatively softer or easily weathered rocks became valleys while the harder and erosion-resistant rocks became the mountain ridges. The development of this landscape continues to this day. Uplift of the province has caused rivers to cut water gaps through the mountain ranges, and has continuously presented new softer rocks in the valleys to be eroded away.
Appalachian Plateau
This is by far the largest province in the state, and most of the rocks in this region are not folded and faulted and sit relatively flat. However, parts of the Appalachian Plateau appear to be mountainous due to erosion caused by streams and glaciers. In western Pennsylvania, large bituminous coal fields exist in rocks with a similar age as the rocks in the anthracite region. Many of the folds in the province are high amplitude and stretch for miles. In glaciated sections, steep canyons developed and much of the terrain have many glacial features. The drainage pattern in this area is dendritic.Glaciated Pocono Plateau
The Pocono Mountain section of Pennsylvania is the same (geologically speaking) as the Catskill Mountains of New York. The red-green-gray sedimentary rocks of theCatskill Formation
The Devonian Catskill Formation or the Catskill Clastic wedge is a unit of mostly terrestrial sedimentary rock found in Pennsylvania and New York. Minor marine layers exist in this thick rock unit (up to ). It is equivalent to the Hampshire Form ...
are the predominant bedrock type in the Poconos. The elevation of the plateau is between and with only a few steep hills such as Camelback Mountain (Big Pocono). Much of the rock sits in gently dipping horizontal beds, unlike the neighboring Appalachian Mountain section.
Glaciated Low Plateau
Considered a part of the Pocono Plateau, this area lies to the north of the Poconos and contains many of the same types of rock. The local relief is less than that of the Pocono region and bounded to the southeast by the Delaware River. TheBig Bushkill Creek
Big Bushkill Creek (Bush Kill on federal maps) is a U.S. Geological Survey. National Hydrography Dataset high-resolution flowline dataThe National Map, accessed April 1, 2011 tributary of the Delaware River in the Poconos of eastern Pennsylvania ...
cuts a gorge through this section and has many waterfalls
A waterfall is a point in a river or stream where water flows over a vertical drop or a series of steep drops. Waterfalls also occur where meltwater drops over the edge of a tabular iceberg or ice shelf.
Waterfalls can be formed in several w ...
, especially around the area of Resica Falls Scout Reservation
Resica Falls Scout Reservation is a camp in East Stroudsburg, Pennsylvania operated by the Cradle of Liberty Council of the Boy Scouts of America.
History
In 1955 the Philadelphia and Valley Forge Councils purchased the property jointly. Dedicat ...
. Dingmans Falls
Dingmans Falls is a waterfall located in Dingmans Ferry in Delaware Township, Pennsylvania near the Silverthread Falls. It has a vertical drop of 39.6 m (130 ft). Both Silverthread Falls and Dingmans Falls are visible from a handicap ...
and Bushkill Falls
Bushkill Falls is a series of eight privately owned waterfalls, the tallest of which cascades over , located in Lehman Township, Pennsylvania in the Pocono Mountains. Water of the Little Bush Kill and Pond Run Creek descends the mountain, toward ...
are waterfalls within the Delaware Water Gap National Recreation Area
Delaware Water Gap National Recreation Area is a national recreation area administered by the National Park Service in northwest New Jersey and northeast Pennsylvania. It is centered around a stretch of the Delaware River designated the Middl ...
, also a part of the Endless Mountains
The Endless Mountains are a geographical, geological, and cultural region in Northeastern Pennsylvania. The Endless Mountains region includes Bradford, Sullivan, Susquehanna, and Wyoming counties. The highest peak in the region is the North Kn ...
region of Pennsylvania.
Glaciated High Plateau
Also an extension of the Catskill Mountains of New York, this section generally has higher elevations than the low plateau section as well as deeper valleys. Younger strata also outcrops in this area with a few minor coal beds. The uplands are rounded or flat along mostly broad hills. An excellent example of the escarpment that divides this section are Ricketts and Ganoga Glen located withinRicketts Glen State Park
Ricketts Glen State Park is a Pennsylvania state park on 13,193 acres (5,280 ha) in Columbia, Luzerne, and Sullivan counties in Pennsylvania in the United States. Ricketts Glen is a National Natural Landmark known for its old-growth fore ...
.
Deep Valleys
This section is home to the Grand Canyon of Pennsylvania and some of the most remote areas of the state. As the name implies, the streams of this area have cut deep valleys with steep sided-slopes on the surrounding ridges. Some of the gorges are at least deep. Much of the area was forested at the end of the 19th century, and much of the area is owned by thePennsylvania Bureau of Forestry
The Pennsylvania Department of Conservation and Natural Resources (DCNR), established on July 1, 1995, is the agency in the U.S. State of Pennsylvania responsible for maintaining and preserving the state's 124 state parks and 20 state forests; ...
.
Allegheny Front
 The
The Allegheny Front
The Allegheny Front is the major southeast- or east-facing escarpment in the Allegheny Mountains in southern Pennsylvania, western Maryland, eastern West Virginia, and western Virginia, USA. The Allegheny Front forms the boundary between the ...
section includes the abrupt escarpment that divides the Ridge and Valley Province from the Allegheny Plateau. The region is a large broad ridge with a steep ascent from east to west and rolling hills away from the ridge. The Allegheny Front reaches its highest elevation in Pennsylvania at Blue Knob
Blue Knob (elevation ) is a summit in the eastern United States with a broad dome that is the northernmost 3,000-footer in the Allegheny Mountains. It is the highest point in Bedford County, Pennsylvania.
The mountain is the site of Blue Knob S ...
, , an unusual bulge along this symmetrical ridgeline. Streams that cut into the ridge are often shallow and steep.
Allegheny Mountain
This section includes Pennsylvania's highest point, Mount Davis, which stands at above sea level. Many of the mountains are long and broad with relatively shallow and broad valleys. Unlike the Appalachian Mountain section, the streams of this area have not cut deep and well defined valleys into the earth. Much of the drainage pattern is dendritic with a little trellis where erosion resistant rocks have created higher and more well defined ridges. Elevations increase to the south, and Mt. Davis resides only from theMaryland
Maryland ( ) is a state in the Mid-Atlantic region of the United States. It shares borders with Virginia, West Virginia, and the District of Columbia to its south and west; Pennsylvania to its north; and Delaware and the Atlantic Ocean to ...
border. A few of the ridge tops contain some low-volatile bituminous coal fields including the Broad Top field. This region is also home to two national stories: the Quecreek Mine Rescue and the crash of United Airlines Flight 93
United Airlines Flight 93 was a domestic scheduled passenger flight that was hijacked by four al-Qaeda attackers aboard the plane on the morning of September 11, 2001, as part of the September 11 attacks. The plane eventually crashed in S ...
.
Waynesburg Hills
Located in the southwest corner of the state, the Waynesburg hills are another major coal-producing area for the state. Much of the 64.4 billion tons of bituminous coal that is remaining in the state resides under these hills in near horizontal beds. The hills are narrow and steep-sided, with some deeper valleys.Pittsburgh Low Plateau
Another section that is a significant coal producer. It is similar to the Waynesburg hills section except for higher local relief and deeper valleys. Landslides and mine subsidence are common hazards.High Plateau
This section consists of high, broad, and flat uplands cut by sharp and shallow river valleys. Much of this area was not covered by the Late Wisconsinan glacier, but there is evidence of pre-Wisconsinan glaciers in the area. Along with the Endless Mountains, it is one of the most remote places in the eastern United States.Northwestern Glaciated Plateau
This section has been influenced by glaciers and many of the valleys cut into the bedrock trend northwestward- in the direction of the retreating glaciers. There are many signs of glaciers including kames,esker
An esker, eskar, eschar, or os, sometimes called an ''asar'', ''osar'', or ''serpent kame'', is a long, winding ridge of stratified sand and gravel, examples of which occur in glaciated and formerly glaciated regions of Europe and North Ame ...
s, kettles, and moraines. This section is home to Pennsylvania's largest natural lake, Conneaut Lake
Conneaut Lake is the largest natural lake in Pennsylvania by surface area. It is located in western Crawford County near a town with the same name. Its has a surface area of approximately 925 acres. The site of the lake is actually in adjace ...
as well as one of the longest eskers in the state, West Liberty Esker.Van Diver, B. B. (1990). Roadside Geology of Pennsylvania. Mountain Press Publishing Company, Missoula Montana. Some of the drainage patterns have shifted and only a few of the streams flow into Lake Erie.
Central Lowlands
Along with the Coastal Plain Province, the smallest province in the state, the central lowlands are a part of theGreat Lakes
The Great Lakes, also called the Great Lakes of North America, are a series of large interconnected freshwater lakes in the mid-east region of North America that connect to the Atlantic Ocean via the Saint Lawrence River. There are five lak ...
area and exist along a glacial escapement adjacent to Lake Erie
Lake Erie ( "eerie") is the fourth largest lake by surface area of the five Great Lakes in North America and the eleventh-largest globally. It is the southernmost, shallowest, and smallest by volume of the Great Lakes and therefore also h ...
.
Geologic features
The following is a list of Pennsylvania geologic features noted for their beauty and/or uniqueness.Periglacial
 * Hickory Run State Park
* Mount Davis
* Hickory Run State Park
* Mount Davis
Glacial
* Archbald Pothole * Grand Canyon of Pennsylvania * McConnells Mill State Park *Moraine State Park
Moraine State Park is a Pennsylvania state park on in Brady, Clay, Franklin, Muddy Creek, and Worth townships in Butler County, Pennsylvania, in the United States.
The park's main feature is its man-made lake, Lake Arthur, formed by impound ...
* Presque Isle
* Promised Land State Park
* Ricketts Glen State Park
Ricketts Glen State Park is a Pennsylvania state park on 13,193 acres (5,280 ha) in Columbia, Luzerne, and Sullivan counties in Pennsylvania in the United States. Ricketts Glen is a National Natural Landmark known for its old-growth fore ...
* Worlds End State Park
Worlds End State Park is a Pennsylvania state park in Sullivan County, Pennsylvania. The park, nearly surrounded by Loyalsock State Forest, is in the Loyalsock Creek valley on Pennsylvania Route 154 in Forks and Shrewsbury Townships southeast ...
Structural
 * Bear Valley Strip Mine
*
* Bear Valley Strip Mine
* Chickies Rock
Chickies Ridge is a long ridge in West Hempfield Township, Pennsylvania, West Hempfield Township, Lancaster County, Pennsylvania, terminating at the west end in an outcropping overlooking the Susquehanna River, known as Chickies Rock.
Geology
Pa ...
* Delaware Water Gap
Delaware Water Gap is a water gap on the border of the U.S. states of New Jersey and Pennsylvania where the Delaware River cuts through a large ridge of the Appalachian Mountains.
The gap makes up the southern portion of the Delaware Water Gap ...
* Pole Steeple
* Governor Stable
* Ringing Rocks
* The Pinnacle
Rock formations
Pennsylvania has been updating its base geologic map last printed in 1980. New research has shifted the names of several formations and promoted or demoted many different sequences on the stratigraphic chart.See also
* Geology of Bedford CountyReferences
External links
The Pennsylvania Geologic Survey
The Geologic Story of Pennsylvania
{{Geology of the United States by political division
Pennsylvania
Pennsylvania (; ( Pennsylvania Dutch: )), officially the Commonwealth of Pennsylvania, is a state spanning the Mid-Atlantic, Northeastern, Appalachian, and Great Lakes regions of the United States. It borders Delaware to its southeast, ...
Natural history of Pennsylvania