Geology and paleoclimatology of the Mediterranean Basin on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
In biogeography, the Mediterranean Basin (; also known as the Mediterranean Region or sometimes Mediterranea) is the region of lands around the
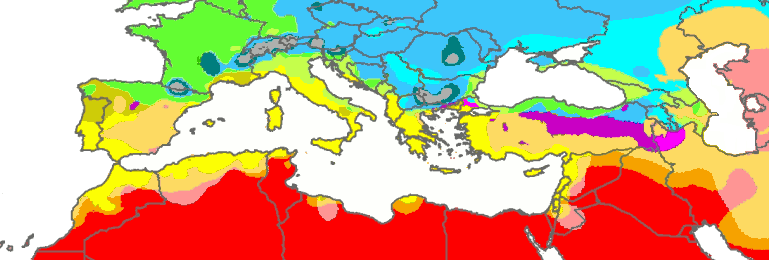 The Mediterranean Basin covers portions of three continents:
The Mediterranean Basin covers portions of three continents:
 .
.
Mediterraneum
'
EGO - European History Online
Mainz
Institute of European History
2021, retrieved: March 8, 2021. * * *
Mediterranean Basin biodiversity hotspot (Conservation International)Are wildfires a disaster in the Mediterranean basin? – A reviewMedTrees: Trees and large shrubs of the Mediterranean Basin.
{{Authority control Mediterranean forests, woodlands, and scrub Palearctic realm Palearctic ecoregions Natural history of Europe Levant Floristic regions Regions of Europe Geography of North Africa Geography of Southern Europe Geography of Western Asia Geography of the Middle East Regions of Eurasia Regions of Africa
Mediterranean Sea
The Mediterranean Sea is a sea connected to the Atlantic Ocean, surrounded by the Mediterranean Basin and almost completely enclosed by land: on the north by Western and Southern Europe and Anatolia, on the south by North Africa, and on the ...
that have mostly a Mediterranean climate
A Mediterranean climate (also called a dry summer temperate climate ''Cs'') is a temperate climate sub-type, generally characterized by warm, dry summers and mild, fairly wet winters; these weather conditions are typically experienced in the ...
, with mild to cool, rainy winter
Winter is the coldest season of the year in polar and temperate climates. It occurs after autumn and before spring. The tilt of Earth's axis causes seasons; winter occurs when a hemisphere is oriented away from the Sun. Different cultur ...
s and warm to hot, dry summers, which supports characteristic Mediterranean forests, woodlands, and scrub vegetation.
Geography
 The Mediterranean Basin covers portions of three continents:
The Mediterranean Basin covers portions of three continents: Europe
Europe is a large peninsula conventionally considered a continent in its own right because of its great physical size and the weight of its history and traditions. Europe is also considered a subcontinent of Eurasia and it is located entirel ...
, Africa
Africa is the world's second-largest and second-most populous continent, after Asia in both cases. At about 30.3 million km2 (11.7 million square miles) including adjacent islands, it covers 6% of Earth's total surface area ...
, and Asia
Asia (, ) is one of the world's most notable geographical regions, which is either considered a continent in its own right or a subcontinent of Eurasia, which shares the continental landmass of Afro-Eurasia with Africa. Asia covers an are ...
. It is distinct from the drainage basin
A drainage basin is an area of land where all flowing surface water converges to a single point, such as a river mouth, or flows into another body of water, such as a lake or ocean. A basin is separated from adjacent basins by a perimeter, ...
, which extends much further south and north due to major rivers ending in the Mediterranean Sea, such as the Nile
The Nile, , Bohairic , lg, Kiira , Nobiin: Áman Dawū is a major north-flowing river in northeastern Africa. It flows into the Mediterranean Sea. The Nile is the longest river in Africa and has historically been considered the longest ...
and Rhône
The Rhône ( , ; wae, Rotten ; frp, Rôno ; oc, Ròse ) is a major river in France and Switzerland, rising in the Alps and flowing west and south through Lake Geneva and southeastern France before discharging into the Mediterranean Sea. At Ar ...
. Conversely, the Mediterranean Basin includes regions not in the drainage basin.
It has a varied and contrasting topography. The Mediterranean Region offers an ever-changing landscape of high mountains, rocky shores, impenetrable scrub, semi-arid steppes, coastal wetlands, sandy beaches and a myriad islands of various shapes and sizes dotted amidst the clear blue sea. Contrary to the classic sandy beach images portrayed in most tourist brochures, the Mediterranean is surprisingly hilly. Mountains can be seen from almost anywhere.
By definition, the Mediterranean Basin extends from Macaronesia
Macaronesia (Portuguese: ''Macaronésia,'' Spanish: ''Macaronesia'') is a collection of four volcanic archipelagos in the North Atlantic, off the coasts of Africa and Europe. Each archipelago is made up of a number of Atlantic oceanic islands ...
in the west, to the Levant
The Levant () is an approximate historical geographical term referring to a large area in the Eastern Mediterranean region of Western Asia. In its narrowest sense, which is in use today in archaeology and other cultural contexts, it is ...
in the east, although some places may or may not be included depending on the view, as is the case with Macaronesia: some definitions only include Madeira and the Canary Islands while others include the whole Macaronesia (with the Azores
)
, motto =( en, "Rather die free than subjected in peace")
, anthem= ( en, "Anthem of the Azores")
, image_map=Locator_map_of_Azores_in_EU.svg
, map_alt=Location of the Azores within the European Union
, map_caption=Location of the Azores wi ...
and Cape Verde).
In Western Asia, it covers the western and southern portions of the peninsula of Anatolia, as far as Iraq
Iraq,; ku, عێراق, translit=Êraq officially the Republic of Iraq, '; ku, کۆماری عێراق, translit=Komarî Êraq is a country in Western Asia. It is bordered by Turkey to the north, Iran to the east, the Persian Gulf and K ...
, but excluding the temperate-climate mountains of central Turkey. It includes the Mediterranean Levant
The Levant () is an approximate historical geographical term referring to a large area in the Eastern Mediterranean region of Western Asia. In its narrowest sense, which is in use today in archaeology and other cultural contexts, it is ...
at the eastern end of the Mediterranean, bounded on the east and south by the Syrian and Negev
The Negev or Negeb (; he, הַנֶּגֶב, hanNegév; ar, ٱلنَّقَب, an-Naqab) is a desert and semidesert region of southern Israel. The region's largest city and administrative capital is Beersheba (pop. ), in the north. At its sout ...
deserts.
The northern portion of the Maghreb
The Maghreb (; ar, الْمَغْرِب, al-Maghrib, lit=the west), also known as the Arab Maghreb ( ar, المغرب العربي) and Northwest Africa, is the western part of North Africa and the Arab world. The region includes Algeria, ...
region of northwestern Africa has a Mediterranean climate, separated from the Sahara Desert
, photo = Sahara real color.jpg
, photo_caption = The Sahara taken by Apollo 17 astronauts, 1972
, map =
, map_image =
, location =
, country =
, country1 =
, ...
, which extends across North Africa
North Africa, or Northern Africa is a region encompassing the northern portion of the African continent. There is no singularly accepted scope for the region, and it is sometimes defined as stretching from the Atlantic shores of Mauritania in ...
, by the Atlas Mountains. In the eastern Mediterranean the Sahara extends to the southern shore of the Mediterranean, with the exception of the northern fringe of the peninsula of Cyrenaica
Cyrenaica ( ) or Kyrenaika ( ar, برقة, Barqah, grc-koi, Κυρηναϊκή ��παρχίαKurēnaïkḗ parkhíā}, after the city of Cyrene), is the eastern region of Libya. Cyrenaica includes all of the eastern part of Libya between ...
in Libya
Libya (; ar, ليبيا, Lībiyā), officially the State of Libya ( ar, دولة ليبيا, Dawlat Lībiyā), is a country in the Maghreb region in North Africa. It is bordered by the Mediterranean Sea to the north, Egypt to the east, Suda ...
, which has a dry Mediterranean climate.
Europe lies to the north of the Mediterranean. The European portion of the Mediterranean Basin loosely corresponds to Southern Europe
Southern Europe is the southern region of Europe. It is also known as Mediterranean Europe, as its geography is essentially marked by the Mediterranean Sea. Definitions of Southern Europe include some or all of these countries and regions: Alba ...
. The three large Southern European peninsulas, the Iberian Peninsula
The Iberian Peninsula (),
**
* Aragonese and Occitan: ''Peninsula Iberica''
**
**
* french: Péninsule Ibérique
* mwl, Península Eibérica
* eu, Iberiar penintsula also known as Iberia, is a peninsula in southwestern Europe, def ...
, Italian Peninsula, and the Balkan Peninsula, extend into and comprise much of the Mediterranean-climate zone. A system of folded mountains, including the Pyrenees
The Pyrenees (; es, Pirineos ; french: Pyrénées ; ca, Pirineu ; eu, Pirinioak ; oc, Pirenèus ; an, Pirineus) is a mountain range straddling the border of France and Spain. It extends nearly from its union with the Cantabrian Mountains to ...
dividing Spain
, image_flag = Bandera de España.svg
, image_coat = Escudo de España (mazonado).svg
, national_motto = ''Plus ultra'' (Latin)(English: "Further Beyond")
, national_anthem = (English: "Royal March")
, i ...
from France
France (), officially the French Republic ( ), is a country primarily located in Western Europe. It also comprises of overseas regions and territories in the Americas and the Atlantic, Pacific and Indian Oceans. Its metropolitan area ...
, the Alps
The Alps () ; german: Alpen ; it, Alpi ; rm, Alps ; sl, Alpe . are the highest and most extensive mountain range system that lies entirely in Europe, stretching approximately across seven Alpine countries (from west to east): France, Swi ...
dividing Italy
Italy ( it, Italia ), officially the Italian Republic, ) or the Republic of Italy, is a country in Southern Europe. It is located in the middle of the Mediterranean Sea, and its territory largely coincides with the homonymous geographical ...
from Central Europe
Central Europe is an area of Europe between Western Europe and Eastern Europe, based on a common historical, social and cultural identity. The Thirty Years' War (1618–1648) between Catholicism and Protestantism significantly shaped the a ...
, the Dinaric Alps
The Dinaric Alps (), also Dinarides, are a mountain range in Southern and Southcentral Europe, separating the continental Balkan Peninsula from the Adriatic Sea. They stretch from Italy in the northwest through Slovenia, Croatia, Bosnia and Herz ...
along the eastern Adriatic, and the Balkan and Rila-Rhodope Rhodope may refer to:
* Rhodope (mythology), a figure of Greek mythology
* Rhodope Mountains, in Bulgaria and Greece
* Rhodope (regional unit)
Rhodope ( el, Ροδόπη, ''Rodópi'' ) is one of the regional units of Greece. It is part of the reg ...
mountains of the Balkan Peninsula divide the Mediterranean from the temperate climate regions of Western
Western may refer to:
Places
*Western, Nebraska, a village in the US
*Western, New York, a town in the US
*Western Creek, Tasmania, a locality in Australia
*Western Junction, Tasmania, a locality in Australia
*Western world, countries that id ...
, Northwestern or Northern Europe, Central Europe
Central Europe is an area of Europe between Western Europe and Eastern Europe, based on a common historical, social and cultural identity. The Thirty Years' War (1618–1648) between Catholicism and Protestantism significantly shaped the a ...
, and Eastern Europe
Eastern Europe is a subregion of the European continent. As a largely ambiguous term, it has a wide range of geopolitical, geographical, ethnic, cultural, and socio-economic connotations. The vast majority of the region is covered by Russia, whic ...
.
Geology and paleoclimatology
The Mediterranean Basin was shaped by the ancient collision of the northward-moving African–Arabian continent with the stable Eurasian continent. As Africa–Arabia moved north, it closed the formerTethys Sea
The Tethys Ocean ( el, Τηθύς ''Tēthús''), also called the Tethys Sea or the Neo-Tethys, was a prehistoric ocean that covered most of the Earth during much of the Mesozoic Era and early Cenozoic Era, located between the ancient continents ...
, which formerly separated Eurasia from the ancient super continent of Gondwana, of which Africa was part. At about the same time, 170 mya in the Jurassic
The Jurassic ( ) is a geologic period and stratigraphic system that spanned from the end of the Triassic Period million years ago (Mya) to the beginning of the Cretaceous Period, approximately Mya. The Jurassic constitutes the middle period of ...
period, a small Neotethys ocean basin formed shortly before the Tethys Sea was closed at the eastern end. The collision pushed up a vast system of mountains, extending from the Pyrenees
The Pyrenees (; es, Pirineos ; french: Pyrénées ; ca, Pirineu ; eu, Pirinioak ; oc, Pirenèus ; an, Pirineus) is a mountain range straddling the border of France and Spain. It extends nearly from its union with the Cantabrian Mountains to ...
in Spain to the Zagros Mountains
The Zagros Mountains ( ar, جبال زاغروس, translit=Jibal Zaghrus; fa, کوههای زاگرس, Kuh hā-ye Zāgros; ku, چیاکانی زاگرۆس, translit=Çiyakani Zagros; Turkish: ''Zagros Dağları''; Luri: ''Kuh hā-ye Zāgr ...
in Iran
Iran, officially the Islamic Republic of Iran, and also called Persia, is a country located in Western Asia. It is bordered by Iraq and Turkey to the west, by Azerbaijan and Armenia to the northwest, by the Caspian Sea and Turkmeni ...
. This episode of mountain building, known as the Alpine orogeny, occurred mostly during the Oligocene (34 to 23 million years ago ( mya)) and Miocene
The Miocene ( ) is the first epoch (geology), geological epoch of the Neogene Period and extends from about (Ma). The Miocene was named by Scottish geologist Charles Lyell; the name comes from the Greek words (', "less") and (', "new") and mea ...
(23 to 5.3 mya) epochs. The Neotethys became larger during these collisions and associated folding and subduction.
About 6 mya during the late Miocene, the Mediterranean was closed at its western end by drifting Africa, which caused the entire sea to evaporate. There followed several (debated) episodes of sea drawdown and re-flooding known as the Messinian Salinity Crisis
The Messinian salinity crisis (MSC), also referred to as the Messinian event, and in its latest stage as the Lago Mare event, was a geological event during which the Mediterranean Sea went into a cycle of partial or nearly complete desiccation (d ...
, which ended when the Atlantic last re-flooded the basin at the end of the Miocene. Recent research has suggested that a desiccation-flooding cycle may have repeated several times during the last 630,000 years of the Miocene epoch, which could explain several events of large amounts of salt deposition. Recent studies, however, show that repeated desiccation and re-flooding is unlikely from a geodynamic
Geodynamics is a subfield of geophysics dealing with dynamics of the Earth. It applies physics, chemistry and mathematics to the understanding of how mantle convection leads to plate tectonics and geologic phenomena such as seafloor spreading, mo ...
point of view.
The end of the Miocene also marked a change in the Mediterranean Basin's climate. Fossil evidence shows that the Mediterranean Basin had a relatively humid subtropical climate with summer rainfall during the Miocene, which supported laurel forests. The shift to a Mediterranean climate occurred within the last 3.2–2.8 million years, during the Pliocene
The Pliocene ( ; also Pleiocene) is the epoch in the geologic time scale that extends from 5.333 million to 2.58Macaronesia
Macaronesia (Portuguese: ''Macaronésia,'' Spanish: ''Macaronesia'') is a collection of four volcanic archipelagos in the North Atlantic, off the coasts of Africa and Europe. Each archipelago is made up of a number of Atlantic oceanic islands ...
off the Atlantic coast of Iberia and North Africa, and the present Mediterranean vegetation evolved, dominated by coniferous trees and sclerophyllous
Sclerophyll is a type of vegetation that is adapted to long periods of dryness and heat. The plants feature hard leaves, short internodes (the distance between leaves along the stem) and leaf orientation which is parallel or oblique to direct ...
trees and shrubs, with small, hard, waxy leaves that prevent moisture loss in the dry summers. Much of these forests and shrublands have been altered beyond recognition by thousands of years of human habitation. There are now very few relatively intact natural areas in what was once a heavily wooded region.
Flora and fauna
Phytogeographically
Phytogeography (from Greek φυτόν, ''phytón'' = "plant" and γεωγραφία, ''geographía'' = "geography" meaning also distribution) or botanical geography is the branch of biogeography that is concerned with the geographic distribution o ...
, the Mediterranean Basin together with the nearby Atlantic coast, the Mediterranean woodlands and forests and Mediterranean dry woodlands and steppe of North Africa
North Africa, or Northern Africa is a region encompassing the northern portion of the African continent. There is no singularly accepted scope for the region, and it is sometimes defined as stretching from the Atlantic shores of Mauritania in ...
, the Black Sea
The Black Sea is a marginal mediterranean sea of the Atlantic Ocean lying between Europe and Asia, east of the Balkans, south of the East European Plain, west of the Caucasus, and north of Anatolia. It is bounded by Bulgaria, Georgia, Rom ...
coast of northeastern Anatolia
Anatolia, tr, Anadolu Yarımadası), and the Anatolian plateau, also known as Asia Minor, is a large peninsula in Western Asia and the westernmost protrusion of the Asian continent. It constitutes the major part of modern-day Turkey. The ...
, the southern coast of Crimea
Crimea, crh, Къырым, Qırım, grc, Κιμμερία / Ταυρική, translit=Kimmería / Taurikḗ ( ) is a peninsula in Ukraine, on the northern coast of the Black Sea, that has been occupied by Russia since 2014. It has a pop ...
between Sevastopol
Sevastopol (; uk, Севасто́поль, Sevastópolʹ, ; gkm, Σεβαστούπολις, Sevastoúpolis, ; crh, Акъя́р, Aqyár, ), sometimes written Sebastopol, is the largest city in Crimea, and a major port on the Black Sea ...
and Feodosiya
uk, Феодосія, Теодосія crh, Kefe
, official_name = ()
, settlement_type=
, image_skyline = THEODOSIA 01.jpg
, imagesize = 250px
, image_caption = Genoese fortress of Caffa
, image_shield = Fe ...
and the Black Sea coast between Anapa
Anapa (russian: Ана́па, ) is a town in Krasnodar Krai, Russia, located on the northern coast of the Black Sea near the Sea of Azov. Population:
History
The area around Anapa was settled in antiquity. It was originally a major seaport ( ...
and Tuapse
Tuapse (russian: Туапсе́; ady, Тӏуапсэ ) is a town in Krasnodar Krai, Russia, situated on the northeast shore of the Black Sea, south of Gelendzhik and north of Sochi. Population:
Tuapse is a sea port and the northern center of ...
in Russia
Russia (, , ), or the Russian Federation, is a transcontinental country spanning Eastern Europe and Northern Asia. It is the largest country in the world, with its internationally recognised territory covering , and encompassing one-eig ...
forms the ''Mediterranean Floristic Region'', which belongs to the Tethyan Subkingdom of the Boreal Kingdom
The Boreal Kingdom or Holarctic Kingdom (Holarctis) is a floristic kingdom identified by botanist Ronald Good (and later by Armen Takhtajan), which includes the temperate to Arctic portions of North America and Eurasia. Its flora is inherit ...
and is enclosed between the Circumboreal, Irano-Turanian, Saharo-Arabian and Macaronesian floristic regions
A phytochorion, in phytogeography, is a geographic area with a relatively uniform composition of plant species. Adjacent phytochoria do not usually have a sharp boundary, but rather a soft one, a transitional area in which many species from both r ...
.
The Mediterranean Region was first proposed by German botanist August Grisebach
August Heinrich Rudolf Grisebach () was a German botanist and phytogeographer. He was born in Hannover on 17 April 1814 and died in Göttingen on 9 May 1879.
Biography
Grisebach studied at the Lyceum in Hanover, the cloister-school at Ilfe ...
in the late 19th century.
The monotypic
In biology, a monotypic taxon is a taxonomic group (taxon) that contains only one immediately subordinate taxon. A monotypic species is one that does not include subspecies or smaller, infraspecific taxa. In the case of genera, the term "unispe ...
Drosophyllaceae, recently segregated from Droseraceae
Droseraceae is a family of carnivorous flowering plants, also known as the sundew family. It consists of approximately 180 species in three extant genera. Representatives of the Droseraceae are found on all continents except Antarctica.
Descr ...
, is the only plant family endemic
Endemism is the state of a species being found in a single defined geographic location, such as an island, state, nation, country or other defined zone; organisms that are indigenous to a place are not endemic to it if they are also found else ...
to the region. Among the endemic plant genera are:
*''Anagyris
''Anagyris'' (Spanish: ''oro de risco'') is a genus of flowering plants in the family Fabaceae. It belongs to the subfamily Faboideae.
Species
''Anagyris'' comprises the following species:
* '' Anagyris foetida'' L.
* '' Anagyris latifolia'' B ...
''
*'' Andryala''
*'' Aphyllanthes''
*''Argania
''Argania'' (Tashelhit: ⴰⵔⴳⴰⵏ ''Argan'') is a genus of flowering plants containing the sole species ''Argania spinosa'', known as argan, a tree endemic to the calcareous semidesert Sous valley of southwestern Morocco and to the regi ...
''
*'' Argantoniella''
*'' Bellardia''
*'' Biserrula''
*'' Bivonaea''
*''Bolanthus
''Bolanthus'' is a genus of flowering plants belonging to the family Caryophyllaceae.
Its native range is Greece to Jordan.
Species:
*'' Bolanthus aziz-sancarii''
*''Bolanthus cherlerioides
''Bolanthus'' is a genus of flowering plants belo ...
''
*'' Boleum''
*'' Callicotome''
*'' Ceratocapnos''
*'' Ceratonia''
*''Chamaerops
''Chamaerops'' is a genus of flowering plants in the family Arecaceae. The only currently fully accepted species is ''Chamaerops humilis'', variously called European fan palm or the Mediterranean dwarf palm. It is one of the most cold-hardy ...
''
*'' Chronanthus''
*'' Cladanthus''
*'' Coridothymus''
*'' Didesmus''
*'' Dorystoechas''
*''Drosophyllum
''Drosophyllum'' ( , rarely ) is a genus of carnivorous plants containing the single species ''Drosophyllum lusitanicum'', commonly known as Portuguese sundew or dewy pine. In appearance, it is similar to the related genus ''Drosera'' (the sun ...
''
*'' Euzomodendron''
*'' Fedia''
*'' Guiraoa''
*'' Gyrocarion''
*'' Helicodiceros''
*'' Hermodactylus''
*'' Hutera''
*'' Hymenocarpus''
*'' Ionopsidium''
*''Lafuentea
''Lafuentea'' is a genus of flowering plants belonging to the family Plantaginaceae.
Its native range is the Western Mediterranean, where it is found in Morocco and Spain.
The genus name of ''Lafuentea'' is in honour of Tadeo Lafuente (b. c. 1780 ...
''
*'' Lagoecia''
*'' Leuzea''
*'' Lycocarpus''
*'' Malope''
*'' Morisia''
*'' Ortegia''
*'' Petagnia''
*'' Petromarula''
*''Phillyrea
''Phillyrea'' is a genus of two species of flowering plants in the family Oleaceae, native to the Mediterranean region, and naturalized in the Canary Islands and Madeira.
They are evergreen shrubs or small trees growing to 3–9 m tall, related ...
''
*'' Preslia''
*'' Putoria''
*'' Rothmaleria''
*''Rosmarinus
Rosmarinus ( ) is a small taxonomic clade of woody, perennial herbs with fragrant evergreen needle-like leaves in the family Lamiaceae, native to the Mediterranean Basin.
In 2017 the species in the genus ''Rosmarinus'' were moved into the large ...
''
*'' Rupicapnos''
*''Santolina
''Santolina'' is a genus of plants in the chamomile tribe within the sunflower family, primarily from the western Mediterranean region.
They are small evergreen shrubs growing tall. The leaves are simple and minute in some species, or pinnate ...
''
*'' Staehelina''
*'' Soleirolia''
*''Spartium
''Spartium junceum'', known as Spanish broom, rush broom, or weaver's broom, it is a species of flowering plant in the family Fabaceae and the sole species in the genus ''Spartium''. It is closely related to the other brooms (in the genera '' Cy ...
''
*'' Tetraclinis''
*'' Trachelium''
*'' Tremastelma''
*''Triplachne
''Triplachne'' is a genus of seaside plants in the grass family, native to shorelines in the Mediterranean region from the Canary Islands to Turkey. The only known species is ''Triplachne nitens'', called shining grass. It is native to Spain (i ...
''
*''Vella
Vella is a village and a former municipalities of Switzerland, municipality in the district of Surselva (district), Surselva in the Cantons of Switzerland, canton of Graubünden in Switzerland. The municipalities of Cumbel, Degen, Switzerland, De ...
''
The genera '' Aubrieta'', '' Sesamoides'', '' Cynara'', '' Dracunculus'', ''Arisarum
''Arisarum'' is a genus of flowering plants in the family Araceae. It is native to the Mediterranean region, east to the Caucasus and west to Macaronesia.
Species
Accepted species:
Natural Hybrids
# '' Arisarum × aspergillum'' Dunal - Spain ...
'' and ''Biarum
''Biarum'' is a genus of flowering plants in the family Araceae. It is composed of plants that are native to the Middle East, southern Europe (Spain, Portugal, Italy, Balkans), and North Africa. ''Biarum'' are often found growing in rock crevice ...
'' are nearly endemic. Among the endemic species prominent in the Mediterranean vegetation are the Aleppo pine, stone pine, Mediterranean cypress
''Cupressus sempervirens'', the Mediterranean cypress (also known as Italian cypress, Tuscan cypress, Persian cypress, or pencil pine), is a species of cypress native to the eastern Mediterranean region, in northeast Libya, southern Albania, s ...
, bay laurel
''Laurus nobilis'' is an aromatic evergreen tree or large shrub with green, glabrous (smooth) leaves. It is in the flowering plant family Lauraceae. It is native to the Mediterranean region and is used as bay leaf for seasoning in cookin ...
, Oriental sweetgum, holm oak, kermes oak
''Quercus coccifera'', the kermes oak, is an oak bush in the '' Ilex'' section of the genus. It is native to the Mediterranean region and Northern African Maghreb, south to north from Morocco to France and west to east from Portugal to Cyprus ...
, strawberry tree, Greek strawberry tree, mastic
Mastic may refer to:
Adhesives and pastes
*Mastic (plant resin)
*Mastic asphalt, or asphalt, is a sticky, black and highly viscous liquid
* Mastic cold porcelain, or salt ceramic, is a traditional salt-based modeling clay.
*Mastic, high-grade con ...
, terebinth
''Pistacia terebinthus'' also called the terebinth and the turpentine tree, is a deciduous tree species of the genus ''Pistacia'', native to the Mediterranean region from the western regions of Morocco and Portugal to Greece and western and s ...
, common myrtle, oleander
''Nerium oleander'' ( ), most commonly known as oleander or nerium, is a shrub or small tree cultivated worldwide in temperate and subtropical areas as an ornamental and landscaping plant. It is the only species currently classified in the ge ...
, ''Acanthus mollis
''Acanthus mollis'', commonly known as bear's breeches, sea dock, bear's foot plant, sea holly, gator plant or oyster plant, is a species of plant in the family Acanthaceae and is native to the Mediterranean region. It is a leafy, clump-forming ...
'' and ''Vitex agnus-castus
''Vitex agnus-castus'', also called vitex, chaste tree (or chastetree), chasteberry, Abraham's balm, lilac chastetree, or monk's pepper, is a native of the Mediterranean region. It is one of the few temperate-zone species of '' Vitex'', which is ...
''. Moreover, many plant taxa
In biology, a taxon (back-formation from ''taxonomy''; plural taxa) is a group of one or more populations of an organism or organisms seen by taxonomists to form a unit. Although neither is required, a taxon is usually known by a particular nam ...
are shared with one of the four neighboring floristic regions only. According to different versions of Armen Takhtajan's delineation, the Mediterranean Region is further subdivided into seven to nine floristic province
A phytochorion, in phytogeography, is a geographic area with a relatively uniform composition of plant species. Adjacent phytochoria do not usually have a sharp boundary, but rather a soft one, a transitional area in which many species from both r ...
s: Southwestern Mediterranean (or Southern Moroccan and Southwestern Mediterranean), Ibero-Balearian (or Iberian and Balearian), Liguro-Tyrrhenian, Adriatic, East Mediterranean
Eastern Mediterranean is a loose definition of the eastern approximate half, or third, of the Mediterranean Sea, often defined as the countries around the Levantine Sea.
It typically embraces all of that sea's coastal zones, referring to commun ...
, South Mediterranean and Crimeo-Novorossiysk.
The Mediterranean Basin is the largest of the world's five Mediterranean forests, woodlands, and scrub regions. It is home to a number of plant communities, which vary with rainfall, elevation, latitude, and soil.
* Scrublands occur in the driest areas, especially areas near the seacoast where wind and salt spray are frequent. Low, soft-leaved scrublands around the Mediterranean are known as ''garrigar'' in Catalan
Catalan may refer to:
Catalonia
From, or related to Catalonia:
* Catalan language, a Romance language
* Catalans, an ethnic group formed by the people from, or with origins in, Northern or southern Catalonia
Places
* 13178 Catalan, asteroid #1 ...
, ''garrigue
Garrigue or garigue ( ), also known as phrygana ( el, φρύγανα , n. pl.), is a type of low scrubland ecoregion and plant community in the Mediterranean forests, woodlands, and scrub biome.
It is found on limestone soils in southern ...
'' in French, ''phrygana'' in Greek
Greek may refer to:
Greece
Anything of, from, or related to Greece, a country in Southern Europe:
*Greeks, an ethnic group.
*Greek language, a branch of the Indo-European language family.
**Proto-Greek language, the assumed last common ancestor ...
, ''tomillares'' in Spanish
Spanish might refer to:
* Items from or related to Spain:
**Spaniards are a nation and ethnic group indigenous to Spain
**Spanish language, spoken in Spain and many Latin American countries
**Spanish cuisine
Other places
* Spanish, Ontario, Can ...
, and ''batha'' in Hebrew
Hebrew (; ; ) is a Northwest Semitic language of the Afroasiatic language family. Historically, it is one of the spoken languages of the Israelites and their longest-surviving descendants, the Jews and Samaritans. It was largely preserved ...
.
* Shrublands are dense thickets of evergreen sclerophyll shrubs
A shrub (often also called a bush) is a small-to-medium-sized perennial woody plant. Unlike herbaceous plants, shrubs have persistent woody stems above the ground. Shrubs can be either deciduous or evergreen. They are distinguished from trees ...
and small trees and are the most common plant community around the Mediterranean. Mediterranean shrublands are known as '' màquia'' in Catalan, '' macchia'' in Italian
Italian(s) may refer to:
* Anything of, from, or related to the people of Italy over the centuries
** Italians, an ethnic group or simply a citizen of the Italian Republic or Italian Kingdom
** Italian language, a Romance language
*** Regional Ita ...
, '' maquis'' in French, and " matorral" in Spanish. In some places, shrublands are the mature vegetation type, and in other places the result of the degradation of former forest or woodland by logging or overgrazing
Overgrazing occurs when plants are exposed to intensive grazing for extended periods of time, or without sufficient recovery periods. It can be caused by either livestock in poorly managed agricultural applications, game reserves, or nature res ...
, or disturbance by major fires.
*Savanna
A savanna or savannah is a mixed woodland- grassland (i.e. grassy woodland) ecosystem characterised by the trees being sufficiently widely spaced so that the canopy does not close. The open canopy allows sufficient light to reach the ground to ...
s and grassland
A grassland is an area where the vegetation is dominated by grasses ( Poaceae). However, sedge ( Cyperaceae) and rush ( Juncaceae) can also be found along with variable proportions of legumes, like clover, and other herbs. Grasslands occur na ...
s occur around the Mediterranean, usually dominated by annual grass
Poaceae () or Gramineae () is a large and nearly ubiquitous family of monocotyledonous flowering plants commonly known as grasses. It includes the cereal grasses, bamboos and the grasses of natural grassland and species cultivated in lawns a ...
es.
*Woodland
A woodland () is, in the broad sense, land covered with trees, or in a narrow sense, synonymous with wood (or in the U.S., the ''plurale tantum'' woods), a low-density forest forming open habitats with plenty of sunlight and limited shade (se ...
s are usually dominated by oak
An oak is a tree or shrub in the genus ''Quercus'' (; Latin "oak tree") of the beech family, Fagaceae. There are approximately 500 extant species of oaks. The common name "oak" also appears in the names of species in related genera, notably ''L ...
and pine
A pine is any conifer tree or shrub in the genus ''Pinus'' () of the family Pinaceae. ''Pinus'' is the sole genus in the subfamily Pinoideae. The World Flora Online created by the Royal Botanic Gardens, Kew and Missouri Botanical Garden accepts ...
, mixed with other sclerophyll and coniferous trees.
*Forest
A forest is an area of land dominated by trees. Hundreds of definitions of forest are used throughout the world, incorporating factors such as tree density, tree height, land use, legal standing, and ecological function. The United Nations' ...
s are distinct from woodlands in having a closed canopy, and occur in the areas of highest rainfall and in riparian
A riparian zone or riparian area is the interface between land and a river or stream. Riparian is also the proper nomenclature for one of the terrestrial biomes of the Earth. Plant habitats and communities along the river margins and banks a ...
zones along rivers and streams where they receive summer water. Mediterranean forests are generally composed of evergreen trees, predominantly oak and pine. At higher elevations Mediterranean forests transition to mixed broadleaf and tall conifer forests similar to temperate zone forests.
The Mediterranean Basin is home to considerable biodiversity
Biodiversity or biological diversity is the variety and variability of life on Earth. Biodiversity is a measure of variation at the genetic (''genetic variability''), species (''species diversity''), and ecosystem (''ecosystem diversity'') l ...
, including 22,500 endemic
Endemism is the state of a species being found in a single defined geographic location, such as an island, state, nation, country or other defined zone; organisms that are indigenous to a place are not endemic to it if they are also found else ...
vascular plant
Vascular plants (), also called tracheophytes () or collectively Tracheophyta (), form a large group of land plants ( accepted known species) that have lignified tissues (the xylem) for conducting water and minerals throughout the plant. They ...
species
In biology, a species is the basic unit of classification and a taxonomic rank of an organism, as well as a unit of biodiversity. A species is often defined as the largest group of organisms in which any two individuals of the appropriate s ...
. Conservation International designates the region as a biodiversity hotspot
A biodiversity hotspot is a biogeographic region with significant levels of biodiversity that is threatened by human habitation. Norman Myers wrote about the concept in two articles in ''The Environmentalist'' in 1988 and 1990, after which the c ...
, because of its rich biodiversity and its threatened status. The Mediterranean Basin has an area of 2,085,292 km2, of which only 98,009 km2 remains undisturbed.
Endangered mammals of the Mediterranean Basin include the Mediterranean monk seal
The Mediterranean monk seal (''Monachus monachus'') is a monk seal belonging to the family Phocidae. , it is estimated that fewer than 700 individuals survive in three or four isolated subpopulations in the Mediterranean, (especially) in the Ae ...
, the Barbary macaque, and the Iberian lynx
The Iberian lynx (''Lynx pardinus'') is a wild cat species endemic to the Iberian Peninsula in southwestern Europe. It is listed as Endangered on the IUCN Red List. In the 20th century, the Iberian lynx population had declined because of overhun ...
.
Ecoregions
The WWF identifies 22 Mediterranean forests, woodlands, and scrub ecoregions in the Mediterranean Basin, most of which featuringsclerophyll
Sclerophyll is a type of vegetation that is adapted to long periods of dryness and heat. The plants feature hard leaves, short internodes (the distance between leaves along the stem) and leaf orientation which is parallel or oblique to direct ...
plant species:
*Aegean and Western Turkey sclerophyllous and mixed forests
The Aegean and Western Turkey sclerophyllous and mixed forests is an ecoregion in the lands around the Aegean Sea. The ecoregion covers most of mainland Greece, the Greek Aegean Islands (except for Crete), the western coast of Turkey, the southe ...
(Greece
Greece,, or , romanized: ', officially the Hellenic Republic, is a country in Southeast Europe. It is situated on the southern tip of the Balkans, and is located at the crossroads of Europe, Asia, and Africa. Greece shares land borders ...
, Turkey
Turkey ( tr, Türkiye ), officially the Republic of Türkiye ( tr, Türkiye Cumhuriyeti, links=no ), is a transcontinental country located mainly on the Anatolian Peninsula in Western Asia, with a small portion on the Balkan Peninsula in ...
, North Macedonia
North Macedonia, ; sq, Maqedonia e Veriut, (Macedonia before February 2019), officially the Republic of North Macedonia,, is a country in Southeast Europe. It gained independence in 1991 as one of the successor states of Yugoslavia. It ...
, Bulgaria
Bulgaria (; bg, България, Bǎlgariya), officially the Republic of Bulgaria,, ) is a country in Southeast Europe. It is situated on the eastern flank of the Balkans, and is bordered by Romania to the north, Serbia and North Macedo ...
)
*Anatolian conifer and deciduous mixed forests
The Anatolian conifer and deciduous mixed forests is an ecoregion located in southwestern Anatolia, Turkey. It has a Mediterranean climate, and is part of the Mediterranean forests, woodlands, and scrub biome.
Geography
The ecoregion covers the ...
(Turkey
Turkey ( tr, Türkiye ), officially the Republic of Türkiye ( tr, Türkiye Cumhuriyeti, links=no ), is a transcontinental country located mainly on the Anatolian Peninsula in Western Asia, with a small portion on the Balkan Peninsula in ...
)
*Canary Islands dry woodlands and forests
The Canary Islands dry woodlands and forests is a Mediterranean forests, woodlands, and scrub ecoregion in the Canary Islands. It encompasses the western group of the Canary Islands – La Palma, El Hierro, La Gomera, Tenerife, and Gran Canaria ...
(Spain
, image_flag = Bandera de España.svg
, image_coat = Escudo de España (mazonado).svg
, national_motto = ''Plus ultra'' (Latin)(English: "Further Beyond")
, national_anthem = (English: "Royal March")
, i ...
)
* Corsican montane broadleaf and mixed forests (France
France (), officially the French Republic ( ), is a country primarily located in Western Europe. It also comprises of overseas regions and territories in the Americas and the Atlantic, Pacific and Indian Oceans. Its metropolitan area ...
)
*Crete Mediterranean forests
The Crete Mediterranean forests is a terrestrial ecoregion that encompasses Greek the island of Crete.
The island has a Mediterranean climate, and is in the Mediterranean forests, woodlands, and scrub biome found in the lands in and around the M ...
(Greece
Greece,, or , romanized: ', officially the Hellenic Republic, is a country in Southeast Europe. It is situated on the southern tip of the Balkans, and is located at the crossroads of Europe, Asia, and Africa. Greece shares land borders ...
)
*Cyprus Mediterranean forests
The Cyprus Mediterranean forests is a terrestrial ecoregion that encompasses the island of Cyprus.
The island has a Mediterranean climate, and is in the Mediterranean forests, woodlands, and scrub biome found in the lands in and around the Medit ...
(Cyprus
Cyprus ; tr, Kıbrıs (), officially the Republic of Cyprus,, , lit: Republic of Cyprus is an island country located south of the Anatolian Peninsula in the eastern Mediterranean Sea. Its continental position is disputed; while it is ge ...
)
* Eastern Mediterranean conifer–sclerophyllous–broadleaf forests (Lebanon
Lebanon ( , ar, لُبْنَان, translit=lubnān, ), officially the Republic of Lebanon () or the Lebanese Republic, is a country in Western Asia. It is located between Syria to Lebanon–Syria border, the north and east and Israel to Blue ...
, Iraq
Iraq,; ku, عێراق, translit=Êraq officially the Republic of Iraq, '; ku, کۆماری عێراق, translit=Komarî Êraq is a country in Western Asia. It is bordered by Turkey to the north, Iran to the east, the Persian Gulf and K ...
, Israel
Israel (; he, יִשְׂרָאֵל, ; ar, إِسْرَائِيل, ), officially the State of Israel ( he, מְדִינַת יִשְׂרָאֵל, label=none, translit=Medīnat Yīsrāʾēl; ), is a country in Western Asia. It is situated ...
, Jordan
Jordan ( ar, الأردن; tr. ' ), officially the Hashemite Kingdom of Jordan,; tr. ' is a country in Western Asia. It is situated at the crossroads of Asia, Africa, and Europe, within the Levant region, on the East Bank of the Jordan Rive ...
, Palestine, Syria, Turkey
Turkey ( tr, Türkiye ), officially the Republic of Türkiye ( tr, Türkiye Cumhuriyeti, links=no ), is a transcontinental country located mainly on the Anatolian Peninsula in Western Asia, with a small portion on the Balkan Peninsula in ...
)
* Iberian conifer forests (Spain
, image_flag = Bandera de España.svg
, image_coat = Escudo de España (mazonado).svg
, national_motto = ''Plus ultra'' (Latin)(English: "Further Beyond")
, national_anthem = (English: "Royal March")
, i ...
)
*Iberian sclerophyllous and semi-deciduous forests
The Iberian sclerophyllous and semi-deciduous forests is a Mediterranean forests, woodlands, and scrub ecoregion in southwestern Europe. It occupies the interior valleys and plateaus of the Iberian Peninsula. The ecoregion lies mostly in Spain, an ...
(Portugal
Portugal, officially the Portuguese Republic ( pt, República Portuguesa, links=yes ), is a country whose mainland is located on the Iberian Peninsula of Southwestern Europe, and whose territory also includes the Atlantic archipelagos of ...
, Spain
, image_flag = Bandera de España.svg
, image_coat = Escudo de España (mazonado).svg
, national_motto = ''Plus ultra'' (Latin)(English: "Further Beyond")
, national_anthem = (English: "Royal March")
, i ...
)
*Illyrian deciduous forests
The Illyrian deciduous forests is a terrestrial ecoregion in southern Europe, which extends along the eastern coast of the Adriatic Sea. It belongs to the Mediterranean forests, woodlands, and scrub biome, and is in the Palearctic realm.
Geogra ...
(Albania
Albania ( ; sq, Shqipëri or ), or , also or . officially the Republic of Albania ( sq, Republika e Shqipërisë), is a country in Southeastern Europe. It is located on the Adriatic and Ionian Seas within the Mediterranean Sea and shares ...
, Bosnia and Herzegovina
Bosnia and Herzegovina ( sh, / , ), abbreviated BiH () or B&H, sometimes called Bosnia–Herzegovina and often known informally as Bosnia, is a country at the crossroads of south and southeast Europe, located in the Balkans. Bosnia and H ...
, Croatia
, image_flag = Flag of Croatia.svg
, image_coat = Coat of arms of Croatia.svg
, anthem = "Lijepa naša domovino"("Our Beautiful Homeland")
, image_map =
, map_caption =
, capit ...
, Greece
Greece,, or , romanized: ', officially the Hellenic Republic, is a country in Southeast Europe. It is situated on the southern tip of the Balkans, and is located at the crossroads of Europe, Asia, and Africa. Greece shares land borders ...
, Italy
Italy ( it, Italia ), officially the Italian Republic, ) or the Republic of Italy, is a country in Southern Europe. It is located in the middle of the Mediterranean Sea, and its territory largely coincides with the homonymous geographical ...
, Montenegro
)
, image_map = Europe-Montenegro.svg
, map_caption =
, image_map2 =
, capital = Podgorica
, coordinates =
, largest_city = capital
, official_languages = M ...
, Slovenia
Slovenia ( ; sl, Slovenija ), officially the Republic of Slovenia (Slovene: , abbr.: ''RS''), is a country in Central Europe. It is bordered by Italy to the west, Austria to the north, Hungary to the northeast, Croatia to the southeast, an ...
)
*Italian sclerophyllous and semi-deciduous forests
The Italian sclerophyllous and deciduous forests ecoregion, part of the Mediterranean forests, woodlands, and scrub biome, is in Italy. The ecoregion covers most of the Italian Peninsula and includes both evergreen and deciduous forests.
Geogra ...
(France
France (), officially the French Republic ( ), is a country primarily located in Western Europe. It also comprises of overseas regions and territories in the Americas and the Atlantic, Pacific and Indian Oceans. Its metropolitan area ...
, Italy
Italy ( it, Italia ), officially the Italian Republic, ) or the Republic of Italy, is a country in Southern Europe. It is located in the middle of the Mediterranean Sea, and its territory largely coincides with the homonymous geographical ...
, San Marino
San Marino (, ), officially the Republic of San Marino ( it, Repubblica di San Marino; ), also known as the Most Serene Republic of San Marino ( it, Serenissima Repubblica di San Marino, links=no), is the fifth-smallest country in the world an ...
)
* Mediterranean acacia–argania dry woodlands (Western Sahara
Western Sahara ( '; ; ) is a disputed territory on the northwest coast and in the Maghreb region of North and West Africa. About 20% of the territory is controlled by the self-proclaimed Sahrawi Arab Democratic Republic (SADR), while the ...
, Morocco
Morocco (),, ) officially the Kingdom of Morocco, is the westernmost country in the Maghreb region of North Africa. It overlooks the Mediterranean Sea to the north and the Atlantic Ocean to the west, and has land borders with Algeria t ...
, Canary Islands (Spain
, image_flag = Bandera de España.svg
, image_coat = Escudo de España (mazonado).svg
, national_motto = ''Plus ultra'' (Latin)(English: "Further Beyond")
, national_anthem = (English: "Royal March")
, i ...
))
* Mediterranean dry woodlands and steppe (Algeria
)
, image_map = Algeria (centered orthographic projection).svg
, map_caption =
, image_map2 =
, capital = Algiers
, coordinates =
, largest_city = capital
, relig ...
, Egypt
Egypt ( ar, مصر , ), officially the Arab Republic of Egypt, is a transcontinental country spanning the northeast corner of Africa and southwest corner of Asia via a land bridge formed by the Sinai Peninsula. It is bordered by the Medit ...
, Libya
Libya (; ar, ليبيا, Lībiyā), officially the State of Libya ( ar, دولة ليبيا, Dawlat Lībiyā), is a country in the Maghreb region in North Africa. It is bordered by the Mediterranean Sea to the north, Egypt to the east, Suda ...
, Morocco
Morocco (),, ) officially the Kingdom of Morocco, is the westernmost country in the Maghreb region of North Africa. It overlooks the Mediterranean Sea to the north and the Atlantic Ocean to the west, and has land borders with Algeria t ...
, Tunisia
)
, image_map = Tunisia location (orthographic projection).svg
, map_caption = Location of Tunisia in northern Africa
, image_map2 =
, capital = Tunis
, largest_city = capital
, ...
)
* Mediterranean woodlands and forests (Algeria
)
, image_map = Algeria (centered orthographic projection).svg
, map_caption =
, image_map2 =
, capital = Algiers
, coordinates =
, largest_city = capital
, relig ...
, Morocco
Morocco (),, ) officially the Kingdom of Morocco, is the westernmost country in the Maghreb region of North Africa. It overlooks the Mediterranean Sea to the north and the Atlantic Ocean to the west, and has land borders with Algeria t ...
, Tunisia
)
, image_map = Tunisia location (orthographic projection).svg
, map_caption = Location of Tunisia in northern Africa
, image_map2 =
, capital = Tunis
, largest_city = capital
, ...
)
*Northeastern Spain and Southern France Mediterranean forests
The Northeastern Spain and Southern France Mediterranean forests is a Mediterranean forests, woodlands, and scrub ecoregion in southwestern Europe. It occupies the Mediterranean coastal region of northeastern Spain and Southern France, and the ...
(France
France (), officially the French Republic ( ), is a country primarily located in Western Europe. It also comprises of overseas regions and territories in the Americas and the Atlantic, Pacific and Indian Oceans. Its metropolitan area ...
, Monaco
Monaco (; ), officially the Principality of Monaco (french: Principauté de Monaco; Ligurian: ; oc, Principat de Mónegue), is a sovereign city-state and microstate on the French Riviera a few kilometres west of the Italian region of Lig ...
, Spain
, image_flag = Bandera de España.svg
, image_coat = Escudo de España (mazonado).svg
, national_motto = ''Plus ultra'' (Latin)(English: "Further Beyond")
, national_anthem = (English: "Royal March")
, i ...
)
* Northwest Iberian montane forests (Portugal
Portugal, officially the Portuguese Republic ( pt, República Portuguesa, links=yes ), is a country whose mainland is located on the Iberian Peninsula of Southwestern Europe, and whose territory also includes the Atlantic archipelagos of ...
, Spain
, image_flag = Bandera de España.svg
, image_coat = Escudo de España (mazonado).svg
, national_motto = ''Plus ultra'' (Latin)(English: "Further Beyond")
, national_anthem = (English: "Royal March")
, i ...
)
*Pindus Mountains mixed forests
The Pindus Mountains mixed forests constitute a terrestrial ecoregion of Europe according to both the WWF and Digital Map of European Ecological Regions by the European Environment Agency. It belongs to the Mediterranean forests, woodlands, and s ...
(Albania
Albania ( ; sq, Shqipëri or ), or , also or . officially the Republic of Albania ( sq, Republika e Shqipërisë), is a country in Southeastern Europe. It is located on the Adriatic and Ionian Seas within the Mediterranean Sea and shares ...
, Greece
Greece,, or , romanized: ', officially the Hellenic Republic, is a country in Southeast Europe. It is situated on the southern tip of the Balkans, and is located at the crossroads of Europe, Asia, and Africa. Greece shares land borders ...
, North Macedonia
North Macedonia, ; sq, Maqedonia e Veriut, (Macedonia before February 2019), officially the Republic of North Macedonia,, is a country in Southeast Europe. It gained independence in 1991 as one of the successor states of Yugoslavia. It ...
)
* South Apennine mixed montane forests (Italy
Italy ( it, Italia ), officially the Italian Republic, ) or the Republic of Italy, is a country in Southern Europe. It is located in the middle of the Mediterranean Sea, and its territory largely coincides with the homonymous geographical ...
)
* Southeastern Iberian shrubs and woodlands (Spain
, image_flag = Bandera de España.svg
, image_coat = Escudo de España (mazonado).svg
, national_motto = ''Plus ultra'' (Latin)(English: "Further Beyond")
, national_anthem = (English: "Royal March")
, i ...
)
*Southern Anatolian montane conifer and deciduous forests
The Southern Anatolian montane conifer and deciduous forests ecoregion, in the Mediterranean forests, woodlands, and scrub biome, is in the eastern Mediterranean Basin.
Lebanon cedar (''Cedrus libani'') is a characteristic tree.
Geography
The e ...
(Lebanon
Lebanon ( , ar, لُبْنَان, translit=lubnān, ), officially the Republic of Lebanon () or the Lebanese Republic, is a country in Western Asia. It is located between Syria to Lebanon–Syria border, the north and east and Israel to Blue ...
, Israel
Israel (; he, יִשְׂרָאֵל, ; ar, إِسْرَائِيل, ), officially the State of Israel ( he, מְדִינַת יִשְׂרָאֵל, label=none, translit=Medīnat Yīsrāʾēl; ), is a country in Western Asia. It is situated ...
, Jordan
Jordan ( ar, الأردن; tr. ' ), officially the Hashemite Kingdom of Jordan,; tr. ' is a country in Western Asia. It is situated at the crossroads of Asia, Africa, and Europe, within the Levant region, on the East Bank of the Jordan Rive ...
, Syria, Turkey
Turkey ( tr, Türkiye ), officially the Republic of Türkiye ( tr, Türkiye Cumhuriyeti, links=no ), is a transcontinental country located mainly on the Anatolian Peninsula in Western Asia, with a small portion on the Balkan Peninsula in ...
)
* Southwest Iberian Mediterranean sclerophyllous and mixed forests (Portugal
Portugal, officially the Portuguese Republic ( pt, República Portuguesa, links=yes ), is a country whose mainland is located on the Iberian Peninsula of Southwestern Europe, and whose territory also includes the Atlantic archipelagos of ...
, Spain
, image_flag = Bandera de España.svg
, image_coat = Escudo de España (mazonado).svg
, national_motto = ''Plus ultra'' (Latin)(English: "Further Beyond")
, national_anthem = (English: "Royal March")
, i ...
)
* Tyrrhenian–Adriatic sclerophyllous and mixed forests (Croatia
, image_flag = Flag of Croatia.svg
, image_coat = Coat of arms of Croatia.svg
, anthem = "Lijepa naša domovino"("Our Beautiful Homeland")
, image_map =
, map_caption =
, capit ...
, France
France (), officially the French Republic ( ), is a country primarily located in Western Europe. It also comprises of overseas regions and territories in the Americas and the Atlantic, Pacific and Indian Oceans. Its metropolitan area ...
, Italy
Italy ( it, Italia ), officially the Italian Republic, ) or the Republic of Italy, is a country in Southern Europe. It is located in the middle of the Mediterranean Sea, and its territory largely coincides with the homonymous geographical ...
, Malta
Malta ( , , ), officially the Republic of Malta ( mt, Repubblika ta' Malta ), is an island country in the Mediterranean Sea. It consists of an archipelago, between Italy and Libya, and is often considered a part of Southern Europe. It lies ...
)
History
Neanderthal
Neanderthals (, also ''Homo neanderthalensis'' and erroneously ''Homo sapiens neanderthalensis''), also written as Neandertals, are an extinct species or subspecies of archaic humans who lived in Eurasia until about 40,000 years ago. While the ...
s inhabited western Asia and the non-glaciated portions of Europe starting about 230,000 years ago. Modern humans moved into western Asia from Africa less than 100,000 years ago. Modern humans, known as Cro-Magnons, moved into Europe approximately 50–40,000 years ago.
The most recent glacial period, the Wisconsin glaciation
The Wisconsin Glacial Episode, also called the Wisconsin glaciation, was the most recent glacial period of the North American ice sheet complex. This advance included the Cordilleran Ice Sheet, which nucleated in the northern North American Cord ...
, reached its maximum extent approximately 21,000 years ago, and ended approximately 12,000 years ago. A warm period, known as the Holocene climatic optimum, followed the ice age.
Food crops, including wheat
Wheat is a grass widely cultivated for its seed, a cereal grain that is a worldwide staple food. The many species of wheat together make up the genus ''Triticum'' ; the most widely grown is common wheat (''T. aestivum''). The archaeologi ...
, chickpeas, and olives, along with sheep
Sheep or domestic sheep (''Ovis aries'') are domesticated, ruminant mammals typically kept as livestock. Although the term ''sheep'' can apply to other species in the genus '' Ovis'', in everyday usage it almost always refers to domesticated ...
and goat
The goat or domestic goat (''Capra hircus'') is a domesticated species of goat-antelope typically kept as livestock. It was domesticated from the wild goat (''C. aegagrus'') of Southwest Asia and Eastern Europe. The goat is a member of the a ...
s, were domesticated
Domestication is a sustained multi-generational relationship in which humans assume a significant degree of control over the reproduction and care of another group of organisms to secure a more predictable supply of resources from that group. A ...
in the eastern Mediterranean in the 9th millennium BCE, which allowed for the establishment of agricultural settlements. Near Eastern crops spread to southeastern Europe in the 7th millennium BCE
The 7th millennium BC spanned the years 7000 BC to 6001 BC (c. 9 ka to c. 8 ka). It is impossible to precisely date events around this millennium, and all dates mentioned here are estimates mostly based on geological and anthropological analysi ...
. Poppy
A poppy is a flowering plant in the subfamily Papaveroideae of the family Papaveraceae. Poppies are herbaceous plants, often grown for their colourful flowers. One species of poppy, '' Papaver somniferum'', is the source of the narcotic drug o ...
and oat
The oat (''Avena sativa''), sometimes called the common oat, is a species of cereal grain grown for its seed, which is known by the same name (usually in the plural, unlike other cereals and pseudocereals). While oats are suitable for human con ...
s were domesticated in Europe from the 6th to the 3rd millennium BCE. Agricultural settlements spread around the Mediterranean Basin. Megalith
A megalith is a large stone that has been used to construct a prehistoric structure or monument, either alone or together with other stones. There are over 35,000 in Europe alone, located widely from Sweden to the Mediterranean sea.
The ...
s were constructed in Europe from 4500 – 1500 BCE.
A strengthening of the summer monsoon
A monsoon () is traditionally a seasonal reversing wind accompanied by corresponding changes in precipitation but is now used to describe seasonal changes in atmospheric circulation and precipitation associated with annual latitudinal osci ...
9000–7000 years ago increased rainfall across the Sahara, which became a grassland
A grassland is an area where the vegetation is dominated by grasses ( Poaceae). However, sedge ( Cyperaceae) and rush ( Juncaceae) can also be found along with variable proportions of legumes, like clover, and other herbs. Grasslands occur na ...
, with lakes, rivers, and wetlands. After a period of climatic instability, the Sahara settled into a desert state by the 4th millennium BCE
The 4th millennium BC spanned the years 4000 BC to 3001 BC. Some of the major changes in human culture during this time included the beginning of the Bronze Age and the invention of writing, which played a major role in starting recorded history. ...
.
Historiography
One of the earliest modern studies of the Mediterranean wasFernand Braudel
Fernand Braudel (; 24 August 1902 – 27 November 1985) was a French historian and leader of the Annales School. His scholarship focused on three main projects: ''The Mediterranean'' (1923–49, then 1949–66), ''Civilization and Capitalism'' ...
's ''La Méditerranéee et le monde méditerranéen à l époque de Philippe II'' (The Mediterranean and the Mediterranean World in the Age of Philip II), published in 1949. S.D. Goitein's multivolume study of the Cairo Geniza
The Cairo Geniza, alternatively spelled Genizah, is a collection of some 400,000 Jewish manuscript fragments and Fatimid administrative documents that were kept in the ''genizah'' or storeroom of the Ben Ezra Synagogue in Fustat or Old Cairo, ...
documents was another important contribution in the area of Mediterranean Jewish culture.
Agriculture
Wheat
Wheat is a grass widely cultivated for its seed, a cereal grain that is a worldwide staple food. The many species of wheat together make up the genus ''Triticum'' ; the most widely grown is common wheat (''T. aestivum''). The archaeologi ...
is the dominant grain grown around the Mediterranean Basin. Pulses
In medicine, a pulse represents the tactile arterial palpation of the cardiac cycle (heartbeat) by trained fingertips. The pulse may be palpated in any place that allows an artery to be compressed near the surface of the body, such as at the nec ...
and vegetable
Vegetables are parts of plants that are consumed by humans or other animals as food. The original meaning is still commonly used and is applied to plants collectively to refer to all edible plant matter, including the flowers, fruits, stems, ...
s are also grown. The characteristic tree crop is the olive. Figs
The fig is the edible fruit of ''Ficus carica'', a species of small tree in the flowering plant family Moraceae. Native to the Mediterranean and western Asia, it has been cultivated since ancient times and is now widely grown throughout the world ...
are another important fruit tree, and citrus
''Citrus'' is a genus of flowering trees and shrubs in the rue family, Rutaceae. Plants in the genus produce citrus fruits, including important crops such as oranges, lemons, grapefruits, pomelos, and limes. The genus ''Citrus'' is native to ...
, especially lemon
The lemon (''Citrus limon'') is a species of small evergreen trees in the flowering plant family Rutaceae, native to Asia, primarily Northeast India (Assam), Northern Myanmar or China.
The tree's ellipsoidal yellow fruit is used for culin ...
s, are grown where irrigation is present. Grape
A grape is a fruit, botanically a berry, of the deciduous woody vines of the flowering plant genus '' Vitis''. Grapes are a non- climacteric type of fruit, generally occurring in clusters.
The cultivation of grapes began perhaps 8,000 years a ...
s are an important vine
A vine (Latin ''vīnea'' "grapevine", "vineyard", from ''vīnum'' "wine") is any plant with a growth habit of trailing or scandent (that is, climbing) stems, lianas or runners. The word ''vine'' can also refer to such stems or runners themsel ...
crop, grown for fruit and to make wine
Wine is an alcoholic drink typically made from fermented grapes. Yeast consumes the sugar in the grapes and converts it to ethanol and carbon dioxide, releasing heat in the process. Different varieties of grapes and strains of yeasts are m ...
. Rice
Rice is the seed of the grass species '' Oryza sativa'' (Asian rice) or less commonly ''Oryza glaberrima'' (African rice). The name wild rice is usually used for species of the genera '' Zizania'' and '' Porteresia'', both wild and domesticat ...
and summer vegetables are grown in irrigated areas.
See also
* Ancient Egypt *Ancient Greece
Ancient Greece ( el, Ἑλλάς, Hellás) was a northeastern Mediterranean Sea, Mediterranean civilization, existing from the Greek Dark Ages of the 12th–9th centuries BC to the end of Classical Antiquity, classical antiquity ( AD 600), th ...
*Life zones of the Mediterranean region
The climate and ecology of land immediately surrounding the Mediterranean Sea is influenced by several factors. Overall, the land has a Mediterranean climate, with mild, rainy winters and hot, dry summers. The climate induces characteristic Medit ...
* Mediterranean wine climate
*MISTRALS
MISTRALS ("Integrated Mediterranean Studies at Regional and Local Scales") is a research program dedicated to the study of the Mediterranean basin and its surroundings, with the aim to "better understand the impact of global factors on this region ...
*Ottoman Empire
The Ottoman Empire, * ; is an archaic version. The definite article forms and were synonymous * and el, Оθωμανική Αυτοκρατορία, Othōmanikē Avtokratoria, label=none * info page on book at Martin Luther University) ...
*Phoenicia
Phoenicia () was an ancient thalassocratic civilization originating in the Levant region of the eastern Mediterranean, primarily located in modern Lebanon. The territory of the Phoenician city-states extended and shrank throughout their histor ...
*Roman Empire
The Roman Empire ( la, Imperium Romanum ; grc-gre, Βασιλεία τῶν Ῥωμαίων, Basileía tôn Rhōmaíōn) was the post- Republican period of ancient Rome. As a polity, it included large territorial holdings around the Mediter ...
* Zanclean flood
References
Further reading
* * Borutta, Manuel,Mediterraneum
'
EGO - European History Online
Mainz
Institute of European History
2021, retrieved: March 8, 2021. * * *
External links
Mediterranean Basin biodiversity hotspot (Conservation International)
{{Authority control Mediterranean forests, woodlands, and scrub Palearctic realm Palearctic ecoregions Natural history of Europe Levant Floristic regions Regions of Europe Geography of North Africa Geography of Southern Europe Geography of Western Asia Geography of the Middle East Regions of Eurasia Regions of Africa