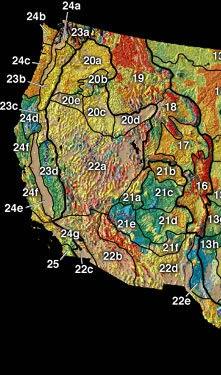
Geography of the United States Intermontane Plateaus on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 In the context of
In the context of
United States Geological Survey, accessed December 12, 2014. in southeastern Washington, eastern Oregon, and southwestern Idaho, and are known to be deep in some river gorges. The lava completely buries the pre-existent land forms over most of its extent. Some of the flows are still so young as to preserve their scoriaceous surface. Here, the shore-line of the lava contours evenly around the spurs and enters, bay-like, into the valleys of the enclosing mountains, occasionally isolating an outlying mass. Other parts of the lava flood are much older and have been more or less deformed and eroded. Thus the uplifted, dislocated and dissected lava sheets of
 In the context of
In the context of physical geography
Physical geography (also known as physiography) is one of the three main branches of geography. Physical geography is the branch of natural science which deals with the processes and patterns in the natural environment such as the atmosphere ...
, the Intermontane
Intermontane is a physiographic adjective formed from the prefix " inter-" (''signifying among, between, amid, during, within, mutual, reciprocal'') and the adjective "montane" (inhabiting, or growing in mountainous regions, especially cool, moi ...
Plateaus is one of eight physiographic regions of the contiguous United States
The contiguous United States (officially the conterminous United States) consists of the 48 adjoining U.S. states and the Federal District of the United States of America. The term excludes the only two non-contiguous states, Alaska and Hawaii ...
. The region consists mostly of plateau
In geology and physical geography, a plateau (; ; ), also called a high plain or a tableland, is an area of a highland consisting of flat terrain that is raised sharply above the surrounding area on at least one side. Often one or more sides ...
s and mountain range
A mountain range or hill range is a series of mountains or hills arranged in a line and connected by high ground. A mountain system or mountain belt is a group of mountain ranges with similarity in form, structure, and alignment that have ari ...
s lying between the Rocky Mountains
The Rocky Mountains, also known as the Rockies, are a major mountain range and the largest mountain system in North America. The Rocky Mountains stretch in straight-line distance from the northernmost part of western Canada, to New Mexico ...
on the east and the Cascade
Cascade, Cascades or Cascading may refer to:
Science and technology Science
* Cascade waterfalls, or series of waterfalls
* Cascade, the CRISPR-associated complex for antiviral defense (a protein complex)
* Cascade (grape), a type of fruit
* Bioc ...
and Sierra Nevada
The Sierra Nevada () is a mountain range in the Western United States, between the Central Valley of California and the Great Basin. The vast majority of the range lies in the state of California, although the Carson Range spur lies primar ...
Mountains on the west. It is subdivided into three physiographic province
physiographic province is a geographic region with a characteristic geomorphology, and often specific subsurface rock type or structural elements. The continents are subdivided into various physiographic provinces, each having a specific characte ...
s: the Columbia Plateau
The Columbia Plateau is a geologic and geographic region that lies across parts of the U.S. states of Washington, Oregon, and Idaho. It is a wide flood basalt plateau between the Cascade Range and the Rocky Mountains, cut through by the Col ...
in the north, the Basin and Range Province
The Basin and Range Province is a vast physiographic region covering much of the inland Western United States and northwestern Mexico. It is defined by unique basin and range topography, characterized by abrupt changes in elevation, alternating ...
in the central and southwestern portions, and the Colorado Plateau
The Colorado Plateau, also known as the Colorado Plateau Province, is a physiographic and desert region of the Intermontane Plateaus, roughly centered on the Four Corners region of the southwestern United States. This province covers an area o ...
in the southeast. In turn, each of these provinces are each subdivided into a number of physiographic sections.
Physiographic provinces
Columbia Plateau Province
The Columbia Plateau Province is alarge igneous province
A large igneous province (LIP) is an extremely large accumulation of igneous rocks, including intrusive (sills, dikes) and extrusive (lava flows, tephra deposits), arising when magma travels through the crust towards the surface. The formation ...
of flood basalt
A flood basalt (or plateau basalt) is the result of a giant volcanic eruption or series of eruptions that covers large stretches of land or the ocean floor with basalt lava. Many flood basalts have been attributed to the onset of a hotspot reac ...
s erupted in Miocene
The Miocene ( ) is the first geological epoch of the Neogene Period and extends from about (Ma). The Miocene was named by Scottish geologist Charles Lyell; the name comes from the Greek words (', "less") and (', "new") and means "less recen ...
and early Pliocence epoch
In chronology and periodization, an epoch or reference epoch is an instant in time chosen as the origin of a particular calendar era. The "epoch" serves as a reference point from which time is measured.
The moment of epoch is usually decided ...
s across the states of Washington
Washington commonly refers to:
* Washington (state), United States
* Washington, D.C., the capital of the United States
** A metonym for the federal government of the United States
** Washington metropolitan area, the metropolitan area centered o ...
, Oregon
Oregon () is a U.S. state, state in the Pacific Northwest region of the Western United States. The Columbia River delineates much of Oregon's northern boundary with Washington (state), Washington, while the Snake River delineates much of it ...
, Idaho
Idaho ( ) is a U.S. state, state in the Pacific Northwest region of the Western United States. To the north, it shares a small portion of the Canada–United States border with the province of British Columbia. It borders the states of Monta ...
, Nevada
Nevada ( ; ) is a state in the Western region of the United States. It is bordered by Oregon to the northwest, Idaho to the northeast, California to the west, Arizona to the southeast, and Utah to the east. Nevada is the 7th-most extensive, ...
, and California
California is a state in the Western United States, located along the Pacific Coast. With nearly 39.2million residents across a total area of approximately , it is the most populous U.S. state and the 3rd largest by area. It is also the m ...
.
Colorado Plattiary erosion landforms
The province was uplifted and divided into great blocks by faults or monoclinal flexures which were exposed to long-lasting denudation in a mid-Tertiary cycle of erosion. They were then broadly elevated again with renewed movement on some of the faults. The current erosion cycle started in the late Tertiary, when the deep canyons of the region were trenched. The results of the first cycle of erosion are seen in the widespread exposure of the resistant Carboniferous limestone as a broad platform in the southwestern area of greater uplift through centralArizona
Arizona ( ; nv, Hoozdo Hahoodzo ; ood, Alĭ ṣonak ) is a state in the Southwestern United States. It is the 6th largest and the 14th most populous of the 50 states. Its capital and largest city is Phoenix. Arizona is part of the Fou ...
where the less resistant overlying formations have been eroded away. They are also seen in the development of a series of cuesta
A cuesta (from Spanish ''cuesta'' "slope") is a hill or ridge with a gentle slope on one side, and a steep slope on the other. In geology the term is more specifically applied to a ridge where a harder sedimentary rock overlies a softer laye ...
s: huge, south-facing, retreating escarpment
An escarpment is a steep slope or long cliff that forms as a result of faulting or erosion and separates two relatively level areas having different elevations.
The terms ''scarp'' and ''scarp face'' are often used interchangeably with ''esca ...
s of irregular outline on the edges of the higher formations farther north. Each escarpment stands forth where a resistant formation overlies a weaker, less resistant one. Each escarpment is separated from the next higher one by a broad step of weaker strata.
A wonderful series of these forms occurs in southern Utah
Utah ( , ) is a state in the Mountain West subregion of the Western United States. Utah is a landlocked U.S. state bordered to its east by Colorado, to its northeast by Wyoming, to its north by Idaho, to its south by Arizona, and to it ...
, where in passing northward from the Carboniferous platform one ascends in succession the Chocolate Cliffs
The Moenkopi Formation is a geological formation that is spread across the U.S. states of New Mexico, northern Arizona, Nevada, southeastern California, eastern Utah and western Colorado. This unit is considered to be a group in Arizona. Part ...
(Triassic
The Triassic ( ) is a geologic period and system (stratigraphy), system which spans 50.6 million years from the end of the Permian Period 251.902 million years ago (Year#Abbreviations yr and ya, Mya), to the beginning of the Jurassic Period 201.36 ...
sandstones), Vermilion
Vermilion (sometimes vermillion) is a color, color family, and pigment most often made, since antiquity until the 19th century, from the powdered mineral cinnabar (a form of mercury sulfide, which is toxic) and its corresponding color. It i ...
and White Cliffs (Jurassic
The Jurassic ( ) is a geologic period and stratigraphic system that spanned from the end of the Triassic Period million years ago (Mya) to the beginning of the Cretaceous Period, approximately Mya. The Jurassic constitutes the middle period of ...
sandstones), the Gray Cliffs (Cretaceous
The Cretaceous ( ) is a geological period that lasted from about 145 to 66 million years ago (Mya). It is the third and final period of the Mesozoic Era, as well as the longest. At around 79 million years, it is the longest geological period of ...
sandstones, of remarkably cross-bedded structure, interpreted as the dunes of an ancient desert), and finally the Pink Cliffs (Eocene
The Eocene ( ) Epoch is a geological epoch that lasted from about 56 to 33.9 million years ago (mya). It is the second epoch of the Paleogene Period in the modern Cenozoic Era. The name ''Eocene'' comes from the Ancient Greek (''ēṓs'', " ...
strata of fluviatile and lacustrine
A lake is an area filled with water, localized in a basin, surrounded by land, and distinct from any river or other outlet that serves to feed or drain the lake. Lakes lie on land and are not part of the ocean, although, like the much larger ...
origin) of the high, forested plateaus. Associated with these irregular escarpments are occasional rectilinear ridges, the work of extensive erosion on monoclinal structures. A good example of this is Echo Cliffs
The Echo Cliffs are a prominent geological feature in northern Arizona. The cliffs stretch for and reach over 1000 feet (300 m) high. They are found in Coconino County in the Navajo Nation about 20 miles (32 km) east of Grand Canyon National P ...
lying east of the Painted Desert. The Mogollon Rim
The Mogollon Rim ( or or ) is a topographical and geological feature cutting across the northern half of the U.S. state of Arizona. It extends approximately , starting in northern Yavapai County and running eastward, ending near the border ...
escarpment is part of the transition zone between the Mogollon Plateau
The Mogollon Plateau or Mogollon Mesa ( or ) is a pine-covered southern plateau section of the larger Colorado Plateau in east-central Arizona and west-central New Mexico, United States. The southern boundary of the plateau is the Mogollon Rim. Th ...
of the Colorado Plateau Province and the Sonoran Desert
The Sonoran Desert ( es, Desierto de Sonora) is a desert in North America and ecoregion that covers the northwestern Mexican states of Sonora, Baja California, and Baja California Sur, as well as part of the southwestern United States (in Ariz ...
of the Basin and Range Province
The Basin and Range Province is a vast physiographic region covering much of the inland Western United States and northwestern Mexico. It is defined by unique basin and range topography, characterized by abrupt changes in elevation, alternating ...
.
With the renewal of uplift by which the earlier cycle of erosion was interrupted and the present cycle introduced, inequalities of surface due to renewed faulting were again introduced. These still appear as cliffs, of more nearly rectilinear front than the retreating escarpments formed in the previous cycle. These cliffs are peculiar in gradually passing from one formation to another, and in having a height dependent on the displacement of the fault rather than on the structures in the fault face. They are already somewhat battered and dissected by erosion. The most important line of cliffs of this class is associated with the western and southern boundary of the Plateau Province where it was uplifted from the lower ground. The few rivers of the region must have reached the quiescence of old age in the earlier cycle, but were revived by uplift to a vigorous youth in the current cycle. It is to this newly introduced cycle of physiographic evolution that the deep canyons of the Plateau province are due. Thus the Virgin River
The Virgin River is a tributary of the Colorado River in the U.S. states of Utah, Nevada, and Arizona. The river is about long.Calculated with Google Maps and Google Earth It was designated Utah's first wild and scenic river in 2009, during the ...
, a northern tributary
A tributary, or affluent, is a stream or river that flows into a larger stream or main stem (or parent) river or a lake. A tributary does not flow directly into a sea or ocean. Tributaries and the main stem river drain the surrounding drai ...
of the Colorado River
The Colorado River ( es, Río Colorado) is one of the principal rivers (along with the Rio Grande) in the Southwestern United States and northern Mexico. The river drains an expansive, arid watershed that encompasses parts of seven U.S. s ...
, has cut a vertical slit, 1000 ft. deep, hardly wider at the top than at the bottom, in the heavy Triassic sandstones of southern Utah. However the most famous example is the Grand Canyon of Arizona
Arizona ( ; nv, Hoozdo Hahoodzo ; ood, Alĭ ṣonak ) is a state in the Southwestern United States. It is the 6th largest and the 14th most populous of the 50 states. Its capital and largest city is Phoenix. Arizona is part of the Fou ...
, eroded by the Colorado river
The Colorado River ( es, Río Colorado) is one of the principal rivers (along with the Rio Grande) in the Southwestern United States and northern Mexico. The river drains an expansive, arid watershed that encompasses parts of seven U.S. s ...
across the uplifted platform of Carboniferous limestone.
During the current cycle of erosion, several of the faults, whose scarps had been worn away in the previous cycle, have been brought to light again as topographic features by the removal of the weak strata along one side of the fault line, leaving the harder strata on the other side in relief. Such scarps are known as fault-line scarps, in distinction from the original fault scarp
A fault scarp is a small step or offset on the ground surface where one side of a fault has moved vertically with respect to the other. It is the topographic expression of faulting attributed to the displacement of the land surface by movement a ...
s. They are peculiar in having their altitude dependent on the depth of revived erosion, instead of the amount of faulting, and they are sometimes topographically reversed, in that the revived scarp overlooks a lowland worn on a weak formation in the upheaved fault-block. Another consequence of revived erosion is seen in the occurrence of great landslides, where the removal of weak (Permian
The Permian ( ) is a geologic period and System (stratigraphy), stratigraphic system which spans 47 million years from the end of the Carboniferous Period million years ago (Mya), to the beginning of the Triassic Period 251.9 Mya. It is the last ...
) clays has sapped the face of the Vermilion Cliffs, so that huge slices of the cliff face have slid down and forward , all shattered into a confused tumult of forms for a or more along the cliff base.
Volcanic features
Volcanic features occur in abundance in the Plateau province. Some of the high plateaus in the north are capped with remnants of heavy lava flows of early eruption. A group of large volcanoes occurs on the limestone platform south of the Grand Canyon, culminating in Mount San Francisco (Humphreys Peak) (, a moderately dissected cone, and associated with many more recent smaller cones and freshlooking lava flows. Mount Taylor in westernNew Mexico
)
, population_demonym = New Mexican ( es, Neomexicano, Neomejicano, Nuevo Mexicano)
, seat = Santa Fe
, LargestCity = Albuquerque
, LargestMetro = Tiguex
, OfficialLang = None
, Languages = English, Spanish ( New Mexican), Navajo, Ke ...
is of similar age, but here dissection seems to have advanced farther, probably because of the weaker nature of the underlying rocks. The dissection has resulted in removing the smaller cones and exposing many lava conduits or pipes in the form of volcanic necks or buttes. The Henry Mountains in southwestern Utah are peculiar in owing their relief to the doming or blistering up of the plateau strata by the underground intrusion of large bodies or cisterns (laccolites) of lava, now more or less exposed by erosion.
Basin and Range Province
The largeBasin and Range Province
The Basin and Range Province is a vast physiographic region covering much of the inland Western United States and northwestern Mexico. It is defined by unique basin and range topography, characterized by abrupt changes in elevation, alternating ...
is a basin and range topography resulting from crustal extension ( extensional tectonics). It is located in all or parts of Oregon
Oregon () is a U.S. state, state in the Pacific Northwest region of the Western United States. The Columbia River delineates much of Oregon's northern boundary with Washington (state), Washington, while the Snake River delineates much of it ...
, Idaho
Idaho ( ) is a U.S. state, state in the Pacific Northwest region of the Western United States. To the north, it shares a small portion of the Canada–United States border with the province of British Columbia. It borders the states of Monta ...
, Nevada
Nevada ( ; ) is a state in the Western region of the United States. It is bordered by Oregon to the northwest, Idaho to the northeast, California to the west, Arizona to the southeast, and Utah to the east. Nevada is the 7th-most extensive, ...
, California
California is a state in the Western United States, located along the Pacific Coast. With nearly 39.2million residents across a total area of approximately , it is the most populous U.S. state and the 3rd largest by area. It is also the m ...
, Utah
Utah ( , ) is a state in the Mountain West subregion of the Western United States. Utah is a landlocked U.S. state bordered to its east by Colorado, to its northeast by Wyoming, to its north by Idaho, to its south by Arizona, and to it ...
, New Mexico
)
, population_demonym = New Mexican ( es, Neomexicano, Neomejicano, Nuevo Mexicano)
, seat = Santa Fe
, LargestCity = Albuquerque
, LargestMetro = Tiguex
, OfficialLang = None
, Languages = English, Spanish ( New Mexican), Navajo, Ke ...
, Arizona
Arizona ( ; nv, Hoozdo Hahoodzo ; ood, Alĭ ṣonak ) is a state in the Southwestern United States. It is the 6th largest and the 14th most populous of the 50 states. Its capital and largest city is Phoenix. Arizona is part of the Fou ...
in the Western United States; and Sonora, Chihuahua, Sinaloa, and other states southwards to the Trans-Mexican Volcanic Belt
The Trans-Mexican Volcanic Belt ( es, Eje Volcánico Transversal), also known as the Transvolcanic Belt and locally as the (''Snowy Mountain Range''), is an active volcanic belt that covers central-southern Mexico. Several of its highest peaks h ...
in Mexico
Mexico (Spanish: México), officially the United Mexican States, is a country in the southern portion of North America. It is bordered to the north by the United States; to the south and west by the Pacific Ocean; to the southeast by Guatema ...
. It involves some novel problems in its description, especially in Southern California
Southern California (commonly shortened to SoCal) is a geographic and cultural region that generally comprises the southern portion of the U.S. state of California. It includes the Los Angeles metropolitan area, the second most populous urban a ...
and central Mexico.
The province is characterized by numerous disconnected mountain ranges trending north and south, from in length, the higher ranges reaching altitudes of , separated by broad, intermontane desert plains or basins at altitudes varying from sea-level (or a little less) in the southwest, to farther inland. It is an arid region.
Many of the intermontane plain
In geography, a plain is a flat expanse of land that generally does not change much in elevation, and is primarily treeless. Plains occur as lowlands along valleys or at the base of mountains, as coastal plains, and as plateaus or uplands ...
s, occurring mostly in the north, appear to be heavily aggraded with mountain waste. Others, mostly in the south, are valley
A valley is an elongated low area often running between hills or mountains, which will typically contain a river or stream running from one end to the other. Most valleys are formed by erosion of the land surface by rivers or streams ove ...
s also heavily aggraded by mountain erosion. The structure of the region previous to faulting was dependent on long antecedent processes of accumulation and deformation and the surface of the region then was dependent on the amount of erosion suffered in the prefaulting cycle.
When the region was broken into fault blocks and the blocks were uplifted and tilted, the back slope of each block was a part of the previously eroded surface and the face of the block was a surface of fracture. The present form of the higher blocks is more or less affected by erosion since faulting, while many of the lower blocks have been buried under the waste of the higher ones.
Northern areas
In the north, where dislocations have invaded the field of the horizontal Columbian lavas, as in southeastern Oregon and northeastern California, the blocks are monoclinal in structure as well as in attitude. Here, the amount of dissection is relatively moderate, for some of the fault faces are described as ravined but not yet deeply dissected. Hence these dislocations appear to be of recent date.Central areas
In the Great Basin of westernUtah
Utah ( , ) is a state in the Mountain West subregion of the Western United States. Utah is a landlocked U.S. state bordered to its east by Colorado, to its northeast by Wyoming, to its north by Idaho, to its south by Arizona, and to it ...
and through most of Nevada
Nevada ( ; ) is a state in the Western region of the United States. It is bordered by Oregon to the northwest, Idaho to the northeast, California to the west, Arizona to the southeast, and Utah to the east. Nevada is the 7th-most extensive, ...
, many of the blocks exhibit deformed structures involving folds and faults of relatively ancient (Jurassic
The Jurassic ( ) is a geologic period and stratigraphic system that spanned from the end of the Triassic Period million years ago (Mya) to the beginning of the Cretaceous Period, approximately Mya. The Jurassic constitutes the middle period of ...
) date. In fact so ancient that the mountains formed by the folding were worn down to the lowland stage of old age before the block-faulting occurred. When this old-mountain lowland was broken into blocks and the blocks were tilted, their attitude, but not their structure, was monoclinal.
In this new attitude, they have been so maturely re-dissected in the current new cycle of erosion as to have gained elaborately carved forms in which the initial form of the uplifted blocks can hardly be perceived. Some of them still retain along one side the highly significant feature of a relatively simple base-line, transecting hard and soft structures alike indicating the faulted margin of a tilted block.
Here the less uplifted blocks are now heavily aggraded with waste from the dissected ranges. The waste takes the form of huge alluvial fans, formed chiefly by occasional boulder-bearing floods from the mountains. Each fan heads in a ravine at the mountain base and becomes laterally confluent with adjacent fans as it stretches several miles forward with decreasing slope and increasing fineness of material.
Southern areas
In the upper southern part of the Basin and Range Province, in theMojave Desert
The Mojave Desert ( ; mov, Hayikwiir Mat'aar; es, Desierto de Mojave) is a desert in the rain shadow of the Sierra Nevada mountains in the Southwestern United States. It is named for the indigenous Mojave people. It is located primarily ...
of California, and Sonoran Desert
The Sonoran Desert ( es, Desierto de Sonora) is a desert in North America and ecoregion that covers the northwestern Mexican states of Sonora, Baja California, and Baja California Sur, as well as part of the southwestern United States (in Ariz ...
of southern California and Arizona (U.S.) and northern Sonora (Mexico) states, the ranges are well dissected and some of the intermontane depressions have rock floors with gentle, centripetal slopes. This area also has huge alluvial fan
An alluvial fan is an accumulation of sediments that fans outwards from a concentrated source of sediments, such as a narrow canyon emerging from an escarpment. They are characteristic of mountainous terrain in arid to semiarid climates, but a ...
s, with heads at canyons exiting the mountains, and laterally confluent with adjacent fans as they extend for miles with rather consistent slopes.
The Basin and Range Province extends southeast down into Chihuahua state in northeast Mexico, and far south along the Mexican Plateau
The Central Mexican Plateau, also known as the Mexican Altiplano ( es, Altiplanicie Mexicana), is a large arid-to-semiarid plateau that occupies much of northern and central Mexico. Averaging above sea level, it extends from the United States b ...
to central Mexico at the Trans-Mexican Volcanic Belt
The Trans-Mexican Volcanic Belt ( es, Eje Volcánico Transversal), also known as the Transvolcanic Belt and locally as the (''Snowy Mountain Range''), is an active volcanic belt that covers central-southern Mexico. Several of its highest peaks h ...
.
Drainage basins
Only a small part of the Basin and Range province is drained to the sea. A few intermont areas in the north-west part of the province have outlets westward via theKlamath River
The Klamath River (Karuk: ''Ishkêesh'', Klamath: ''Koke'', Yurok: ''Hehlkeek 'We-Roy'') flows through Oregon and northern California in the United States, emptying into the Pacific Ocean. By average discharge, the Klamath is the second large ...
through the Cascade range. The Sacramento
)
, image_map = Sacramento County California Incorporated and Unincorporated areas Sacramento Highlighted.svg
, mapsize = 250x200px
, map_caption = Location within Sacramento ...
and San Joaquin River
The San Joaquin River (; es, Río San Joaquín) is the longest river of Central California. The long river starts in the high Sierra Nevada, and flows through the rich agricultural region of the northern San Joaquin Valley before reaching Suis ...
s from the Sierra Nevada pass through the Central Valley and California Coast Ranges
The Coast Ranges of California span from Del Norte or Humboldt County, California, south to Santa Barbara County. The other three coastal California mountain ranges are the Transverse Ranges, Peninsular Ranges and the Klamath Mountains.
P ...
to San Francisco Bay. A few basins in the southeast have outlet by the Rio Grande to the Gulf of Mexico
The Gulf of Mexico ( es, Golfo de México) is an ocean basin and a marginal sea of the Atlantic Ocean, largely surrounded by the North American continent. It is bounded on the northeast, north and northwest by the Gulf Coast of the United ...
.
=Colorado River watershed
= A much larger but still narrow medial area is drained southwestward by theColorado River
The Colorado River ( es, Río Colorado) is one of the principal rivers (along with the Rio Grande) in the Southwestern United States and northern Mexico. The river drains an expansive, arid watershed that encompasses parts of seven U.S. s ...
to the head of the Gulf of California
The Gulf of California ( es, Golfo de California), also known as the Sea of Cortés (''Mar de Cortés'') or Sea of Cortez, or less commonly as the Vermilion Sea (''Mar Bermejo''), is a marginal sea of the Pacific Ocean that separates the Baja C ...
, where this large and very turbid river has formed the extensive Colorado River Delta
The Colorado River Delta is the region where the Colorado River flows into the Gulf of California (also known as the Sea of Cortez) in eastern Mexicali Municipality in the north of the state of Baja California in northwesternmost Mexico. The ...
, north of which the former head of the gulf is now cut off from the sea and laid bare by evaporation as a plain below sea-level.
It is in the Lower Colorado River Valley that an irrigation project, involving the diversion of some of the river water to the low plain of the Imperial Valley
, photo = Salton Sea from Space.jpg
, photo_caption = The Imperial Valley below the Salton Sea. The US-Mexican border runs diagonally across the lower left of the image.
, map_image = Newriverwatershed-1-.jpg
, map_caption = Map of Imperial ...
, led to disaster in 1904. The river flooded through a deliberately engineered breach of the Alamo Canal
The Alamo Canal ( es, Canal del Álamo) was a long waterway that connected the Colorado River to the head of the Alamo River. The canal was constructed to provide irrigation to the Imperial Valley. A small portion of the canal was located in th ...
and flowed across the Imperial Valley plain into the Salton Sink
The Salton Sink is the low point of an endorheic basin, a closed drainage system with no outflows to other bodies of water, in the Colorado Desert sub-region of the Sonoran Desert. The sink falls within the larger Salton Trough and separates th ...
, forming the Salton Sea
The Salton Sea is a shallow, landlocked, highly saline body of water in Riverside and Imperial counties at the southern end of the U.S. state of California. It lies on the San Andreas Fault within the Salton Trough that stretches to the Gulf ...
. The endorheic
An endorheic basin (; also spelled endoreic basin or endorreic basin) is a drainage basin that normally retains water and allows no outflow to other external bodies of water, such as rivers or oceans, but drainage converges instead into lakes ...
Salton Sea remains, now supplied by subterranean flow from over-irrigated fields draining into the aquifer.
=Seasonal streams—lakes
= Many streams descend from the ravines only to wither away on the desert basin floors before uniting in a trunk river along the axis of a depression. Others succeed in uniting in the winter season, when evaporation is much reduced, and then their trunk flows for several additional miles only to disappear by sinking (evaporating) farther on. A few of the large streams, such as theMojave River
The Mojave River is an intermittent river in the eastern San Bernardino Mountains and the Mojave Desert in San Bernardino County, California, United States. Most of its flow is underground, while its surface channels remain dry most of the time, ...
, when in flood may spread out in a temporary shallow sheet on a dead level of clay, or playa, in a basin center, but the sheet of water vanishes in the warm season ( dry lake) and the stream shrinks far up its course, the absolutely barren clay floor of the playa, impassable when wet, becomes firm enough for crossing when dry.
One of the southwestern basins, with its floor below sea-level, has a plain of salt in its center. A few of the basins are occupied by endorheic lakes without outlet, of which Great Salt Lake, in north-west Utah, is the largest. Other examples are Owens Lake
Owens Lake is a mostly dry lake in the Owens Valley on the eastern side of the Sierra Nevada in Inyo County, California. It is about south of Lone Pine, California. Unlike most dry lakes in the Basin and Range Province that have been dry for ...
and Mono Lake
Mono Lake ( ) is a saline soda lake in Mono County, California, formed at least 760,000 years ago as a terminal lake in an endorheic basin. The lack of an outlet causes high levels of salts to accumulate in the lake which make its water a ...
in California.
Several smaller lakes occur in the basins of western Nevada, immediately east of the Sierra Nevada. During Pleistocene
The Pleistocene ( , often referred to as the ''Ice age'') is the geological epoch that lasted from about 2,580,000 to 11,700 years ago, spanning the Earth's most recent period of repeated glaciations. Before a change was finally confirmed in ...
times all these lacustrine basins were occupied by lakes of much greater depth and larger size. The outlines of the eastern Lake Bonneville
Lake Bonneville was the largest Late Pleistocene paleolake in the Great Basin of western North America. It was a pluvial lake that formed in response to an increase in precipitation and a decrease in evaporation as a result of cooler temperature ...
and the western Lake Lahontan
Lake Lahontan was a large endorheic Pleistocene lake of modern northwestern Nevada that extended into northeastern California and southern Oregon. The area of the former lake is a large portion of the Great Basin that borders the Sacramento Rive ...
water bodies are well recorded by shore lines and deltas on the enclosing slopes, hundreds of feet above the present lake surfaces. The abandoned shore lines have yielded evidence of past climatic changes second in importance only to those of the Pleistocene glaciated areas. The duration of the Pleistocene lakes was brief as compared with the time since the dislocation of the faulted blocks, as is shown by the small dimensions of the lacustrine beaches compared to the great volume of the ravine-heading fans on which the beaches often lie.
Intermediate Province
The Intermediate Province is located in parts ofWashington
Washington commonly refers to:
* Washington (state), United States
* Washington, D.C., the capital of the United States
** A metonym for the federal government of the United States
** Washington metropolitan area, the metropolitan area centered o ...
, Oregon
Oregon () is a U.S. state, state in the Pacific Northwest region of the Western United States. The Columbia River delineates much of Oregon's northern boundary with Washington (state), Washington, while the Snake River delineates much of it ...
and Idaho
Idaho ( ) is a U.S. state, state in the Pacific Northwest region of the Western United States. To the north, it shares a small portion of the Canada–United States border with the province of British Columbia. It borders the states of Monta ...
.
Lava plains
Thelava plain
Lava fields are large, mostly flat areas of surface or subaquatic lava flows. Such features are generally composed of highly fluid basalt lava, and can extend for tens or hundreds of miles across the underlying terrain.
Morphology and stru ...
s of the Columbia River Basin
The Columbia River drainage basin is the drainage basin of the Columbia River in the Pacific Northwest region of North America. It covers . In common usage, the term often refers to a smaller area, generally the portion of the drainage basin th ...
are among the most extensive volcanic outpourings in the world. They cover over Description: Columbia Plateau Columbia River Basalt.United States Geological Survey, accessed December 12, 2014. in southeastern Washington, eastern Oregon, and southwestern Idaho, and are known to be deep in some river gorges. The lava completely buries the pre-existent land forms over most of its extent. Some of the flows are still so young as to preserve their scoriaceous surface. Here, the shore-line of the lava contours evenly around the spurs and enters, bay-like, into the valleys of the enclosing mountains, occasionally isolating an outlying mass. Other parts of the lava flood are much older and have been more or less deformed and eroded. Thus the uplifted, dislocated and dissected lava sheets of
Yellowstone National Park
Yellowstone National Park is an American national park located in the western United States, largely in the northwest corner of Wyoming and extending into Montana and Idaho. It was established by the 42nd U.S. Congress with the Yellowst ...
in the Rocky Mountains on the east (at the headwaters of the Snake River) are associated with the older lavas of the Columbian plains.
River canyons
The Columbia River has entrenched itself in a canyon-like valley around the northern and Western side of the lava plains. The Snake River has cut a deeper canyon farther southeast where the plains are higher and has disclosed the many lava sheets which build up the plains, occasionally revealing a buried mountain in which the superposed river has cut an even narrower canyon. One of the most remarkable features of the Intermediate Province is seen in the temporary course taken by the Columbia River across the plains, while its canyon was obstructed byPleistocene
The Pleistocene ( , often referred to as the ''Ice age'') is the geological epoch that lasted from about 2,580,000 to 11,700 years ago, spanning the Earth's most recent period of repeated glaciations. Before a change was finally confirmed in ...
glaciers that came from the
Cascade Range on the northwest. The river followed the temporary course long enough to erode a deep gorge, known as Grande Coulee, along part of its length.
The lava plains are treeless and for the most part too dry for agriculture. However they support wildlife, and cattle and horses. Along parts of their eastern
border, where the rainfall is a little increased by the approach of the westerly winds to the Rocky Mountains, there is a belt of very deep, impalpably fine soil, supposed to be a dust deposit brought from the drier parts of the plains farther west.
See also
*Intermountain West
The Intermountain West, or Intermountain Region, is a geographic and geological region of the Western United States. It is located between the front ranges of the Rocky Mountains on the east and the Cascade Range and Sierra Nevada on the wes ...
* Central Basin and Range ecoregion
The Great Basin Desert is part of the Great Basin between the Sierra Nevada (U.S.), Sierra Nevada and the Wasatch Range. The desert is a geographical region that largely overlaps the Great Basin shrub steppe defined by the World Wildlife Fund, a ...
— ''Level III ecoregion (EPA)''
* Northern Basin and Range ecoregion
The Northern Basin and Range ecoregion is a Level III ecoregion designated by the United States Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) in the U.S. states of Oregon, Idaho, Nevada, Utah, and California. It contains dissected lava plains, rolling ...
— ''Level III ecoregion (EPA)''
* United States physiographic region
References
{{Regions of the United States Plateaus of the United States Physiographic regions of the United States Regions of the Western United States