Geography of New Zealand on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
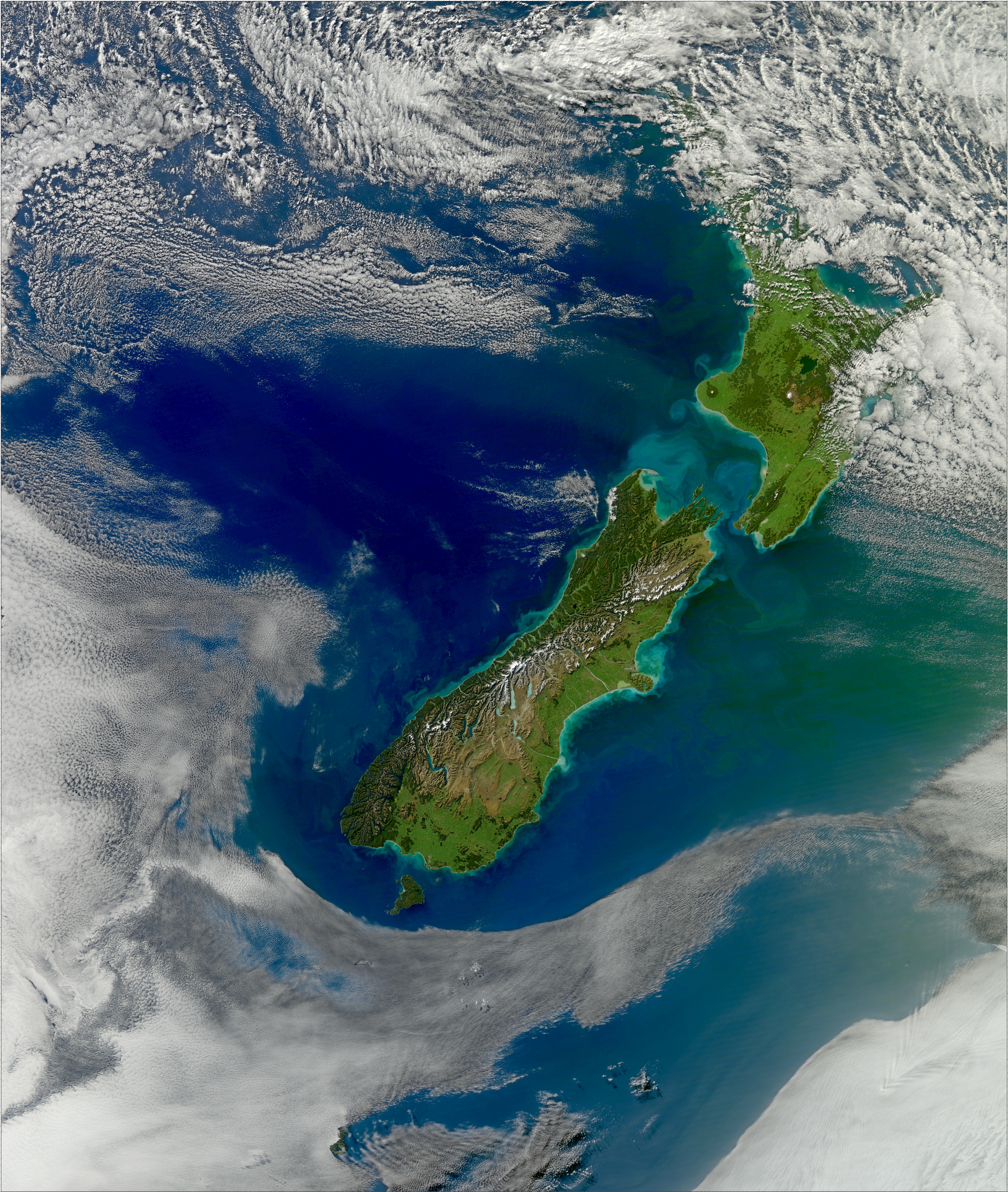
 New Zealand is located in the
New Zealand is located in the
New Zealand
New Zealand ( mi, Aotearoa ) is an island country in the southwestern Pacific Ocean. It consists of two main landmasses—the North Island () and the South Island ()—and over 700 smaller islands. It is the sixth-largest island coun ...
( mi, Aotearoa
''Aotearoa'' () is the current Māori-language name for New Zealand. The name was originally used by Māori in reference to only the North Island, with the name of the whole country being ''Aotearoa me Te Waipounamu'' ("North Island and Sout ...
) is an island country
An island country, island state or an island nation is a country whose primary territory consists of one or more islands or parts of islands. Approximately 25% of all independent countries are island countries. Island countries are historically ...
located in the south-western Pacific Ocean, near the centre of the water hemisphere
The land hemisphere and water hemisphere are the hemispheres of Earth containing the largest possible total areas of land and ocean, respectively. By definition (assuming that the entire surface can be classed as either "land" or "ocean"), the t ...
. It consists of a large number of islands, estimated around 700, mainly remnants of a larger land mass now beneath the sea. The land masses by size are the South Island
The South Island, also officially named , is the larger of the two major islands of New Zealand in surface area, the other being the smaller but more populous North Island. It is bordered to the north by Cook Strait, to the west by the Tasman ...
(or ''Te Waipounamu'') and the North Island
The North Island, also officially named Te Ika-a-Māui, is one of the two main islands of New Zealand, separated from the larger but much less populous South Island by the Cook Strait. The island's area is , making it the world's 14th-larges ...
(or ''Te Ika-a-Māui''), separated by the Cook Strait
Cook Strait ( mi, Te Moana-o-Raukawa) separates the North and South Islands of New Zealand. The strait connects the Tasman Sea on the northwest with the South Pacific Ocean on the southeast. It is wide at its narrowest point,McLintock, A ...
. The third-largest is Stewart Island / Rakiura
Stewart Island ( mi, Rakiura, ' glowing skies', officially Stewart Island / Rakiura) is New Zealand's third-largest island, located south of the South Island, across the Foveaux Strait. It is a roughly triangular island with a total land ar ...
, located off the tip of the South Island across Foveaux Strait
The Foveaux Strait, (, or , ) separates Stewart Island, New Zealand's third largest island, from the South Island. The strait is about 130 km long (from Ruapuke Island to Little Solander Island), and it widens (from 14 km at Ruapuke ...
. Other islands are significantly smaller in area. The three largest islands stretch across latitudes 35° to 47° south. New Zealand is the sixth-largest island country in the world, with a land size of .
New Zealand's landscapes range from the fiord
In physical geography, a fjord or fiord () is a long, narrow inlet with steep sides or cliffs, created by a glacier. Fjords exist on the coasts of Alaska, Antarctica, British Columbia, Chile, Denmark, Förden and East Jutland Fjorde, Germany, Gr ...
-like sounds
In physics, sound is a vibration that propagates as an acoustic wave, through a transmission medium such as a gas, liquid or solid.
In human physiology and psychology, sound is the ''reception'' of such waves and their ''perception'' by the ...
of the southern-west to the sandy beaches of the subtropical Far North. The South Island is dominated by the Southern Alps
The Southern Alps (; officially Southern Alps / Kā Tiritiri o te Moana) is a mountain range extending along much of the length of New Zealand's South Island, reaching its greatest elevations near the range's western side. The name "Southern ...
while a volcanic plateau
A volcanic plateau is a plateau produced by volcanic activity. There are two main types: lava plateaus and pyroclastic plateaus.
Lava plateau
Lava plateaus are formed by highly fluid basaltic lava during numerous successive eruptions thro ...
covers much of the central North Island. Temperatures commonly fall below and rise above then conditions vary from wet and cold on the South Island's west coast to dry and continental a short distance away across the mountains and to the tundra like climate in the Deep South of Southland Southland may refer to:
Places Canada
* Dunbar–Southlands, Vancouver, British Columbia
New Zealand
* Southland Region, a region of New Zealand
* Southland County, a former New Zealand county
* Southland District, part of the wider Southland Re ...
.
About two-thirds of the land is economically useful, with the remainder being mountainous. The North Island is the most populous island with 4 million residents, and Auckland
Auckland (pronounced ) ( mi, Tāmaki Makaurau) is a large metropolitan city in the North Island of New Zealand. The most populous urban area in the country and the fifth largest city in Oceania, Auckland has an urban population of about I ...
being by far the largest metropolitan area
A metropolitan area or metro is a region that consists of a densely populated urban agglomeration and its surrounding territories sharing industries, commercial areas, transport network, infrastructures and housing. A metro area usually ...
in the country by population and urban area. The South Island is the second-most populated island, with over 1.18 million people, but is geographically larger than the North.
The country is situated about south-east of the Australian mainland across the Tasman Sea
The Tasman Sea (Māori: ''Te Tai-o-Rēhua'', ) is a marginal sea of the South Pacific Ocean, situated between Australia and New Zealand. It measures about across and about from north to south. The sea was named after the Dutch explorer ...
, the closest foreign neighbour to its main islands being Norfolk Island
Norfolk Island (, ; Norfuk: ''Norf'k Ailen'') is an external territory of Australia located in the Pacific Ocean between New Zealand and New Caledonia, directly east of Australia's Evans Head and about from Lord Howe Island. Together wit ...
(Australia) about to the north west. Other island groups to the north are New Caledonia
)
, anthem = ""
, image_map = New Caledonia on the globe (small islands magnified) (Polynesia centered).svg
, map_alt = Location of New Caledonia
, map_caption = Location of New Caledonia
, mapsize = 290px
, subdivision_type = Sovereign st ...
, Tonga
Tonga (, ; ), officially the Kingdom of Tonga ( to, Puleʻanga Fakatuʻi ʻo Tonga), is a Polynesian country and archipelago. The country has 171 islands – of which 45 are inhabited. Its total surface area is about , scattered over in ...
and Fiji
Fiji ( , ,; fj, Viti, ; Fiji Hindi: फ़िजी, ''Fijī''), officially the Republic of Fiji, is an island country in Melanesia, part of Oceania in the South Pacific Ocean. It lies about north-northeast of New Zealand. Fiji consis ...
. It is the southernmost nation in Oceania
Oceania (, , ) is a geographical region that includes Australasia, Melanesia, Micronesia, and Polynesia. Spanning the Eastern and Western hemispheres, Oceania is estimated to have a land area of and a population of around 44.5 million ...
. The relative close proximity of New Zealand to Antarctica
Antarctica () is Earth's southernmost and least-populated continent. Situated almost entirely south of the Antarctic Circle and surrounded by the Southern Ocean, it contains the geographic South Pole. Antarctica is the fifth-largest cont ...
has made the South Island a major gateway for scientific expeditions to the continent.
Physical geography

Overview
South Pacific Ocean
South is one of the cardinal directions or compass points. The direction is the opposite of north and is perpendicular to both east and west.
Etymology
The word ''south'' comes from Old English ''sūþ'', from earlier Proto-Germanic ''*sunþaz ...
at , near the centre of the water hemisphere
The land hemisphere and water hemisphere are the hemispheres of Earth containing the largest possible total areas of land and ocean, respectively. By definition (assuming that the entire surface can be classed as either "land" or "ocean"), the t ...
. It is a long and narrow country, extending along its north-north-east axis with a maximum width of . The land size of makes it the sixth-largest island country. New Zealand consists of a large number of islands, estimated around 600. The islands give it of coastline
The coast, also known as the coastline or seashore, is defined as the area where land meets the ocean, or as a line that forms the boundary between the land and the coastline. The Earth has around of coastline. Coasts are important zones in ...
and extensive marine resources. New Zealand claims the ninth largest exclusive economic zone in the world, covering , more than 15 times its land area.
The South Island
The South Island, also officially named , is the larger of the two major islands of New Zealand in surface area, the other being the smaller but more populous North Island. It is bordered to the north by Cook Strait, to the west by the Tasman ...
is the largest land mass of New Zealand, and is the 12th-largest island in the world. The island is divided along its length by the Southern Alps
The Southern Alps (; officially Southern Alps / Kā Tiritiri o te Moana) is a mountain range extending along much of the length of New Zealand's South Island, reaching its greatest elevations near the range's western side. The name "Southern ...
. The east side of the island has the Canterbury Plains
The Canterbury Plains () are an area in New Zealand centred in the Mid Canterbury, to the south of the city of Christchurch in the Canterbury region. Their northern extremes are at the foot of the Hundalee Hills in the Hurunui District, and in t ...
while the West Coast is famous for its rough coastlines, high rainfall, very high proportion of native bush (forest), and glacier
A glacier (; ) is a persistent body of dense ice that is constantly moving under its own weight. A glacier forms where the accumulation of snow exceeds its ablation over many years, often centuries. It acquires distinguishing features, such a ...
s.
The North Island
The North Island, also officially named Te Ika-a-Māui, is one of the two main islands of New Zealand, separated from the larger but much less populous South Island by the Cook Strait. The island's area is , making it the world's 14th-larges ...
is the second-largest island, and the 14th-largest in the world. It is separated from the South Island by the Cook Strait
Cook Strait ( mi, Te Moana-o-Raukawa) separates the North and South Islands of New Zealand. The strait connects the Tasman Sea on the northwest with the South Pacific Ocean on the southeast. It is wide at its narrowest point,McLintock, A ...
, with the shortest distance being . The North Island is less mountainous than the South Island, although a series of narrow mountain ranges form a roughly north-east belt that rises up to . Much of the surviving forest is located in this belt, and in other mountain areas and rolling hills. The North Island has many isolated volcanic peaks.
Besides the North and South Islands, the five largest inhabited islands are Stewart Island / Rakiura
Stewart Island ( mi, Rakiura, ' glowing skies', officially Stewart Island / Rakiura) is New Zealand's third-largest island, located south of the South Island, across the Foveaux Strait. It is a roughly triangular island with a total land ar ...
( due south of the South Island), Chatham Island
Chatham Island ( ) (Moriori: ''Rēkohu'', 'Misty Sun'; mi, Wharekauri) is by far the largest island of the Chatham Islands group, in the south Pacific Ocean off the eastern coast of New Zealand's South Island. It is said to be "halfway bet ...
(''Wharekauri'' in Māori
Māori or Maori can refer to:
Relating to the Māori people
* Māori people of New Zealand, or members of that group
* Māori language, the language of the Māori people of New Zealand
* Māori culture
* Cook Islanders, the Māori people of the Co ...
or ''Rēkohu'' in Moriori
The Moriori are the native Polynesian people of the Chatham Islands (''Rēkohu'' in Moriori; ' in Māori), New Zealand. Moriori originated from Māori settlers from the New Zealand mainland around 1500 CE. This was near the time of th ...
) (some east of the South Island), Great Barrier Island
Great Barrier Island ( mi, Aotea) lies in the outer Hauraki Gulf, New Zealand, north-east of central Auckland. With an area of it is the sixth-largest island of New Zealand and fourth-largest in the main chain. Its highest point, Mount Hobson ...
(in the Hauraki Gulf
The Hauraki Gulf / Tīkapa Moana is a coastal feature of the North Island of New Zealand. It has an area of 4000 km2,D'Urville Island (New Zealand), Rangitoto ki te Tonga / D'Urville Island (in the
 The phrase "From Cape Reinga to The Bluff" is frequently used within New Zealand to refer to the extent of the whole country.
The phrase "From Cape Reinga to The Bluff" is frequently used within New Zealand to refer to the extent of the whole country.
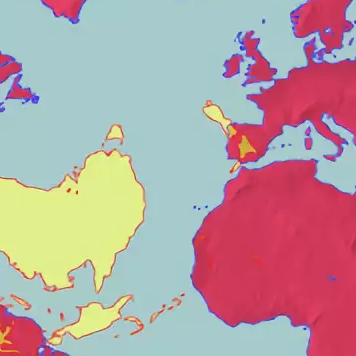 New Zealand is largely antipodal to the
New Zealand is largely antipodal to the

 New Zealand is part of
New Zealand is part of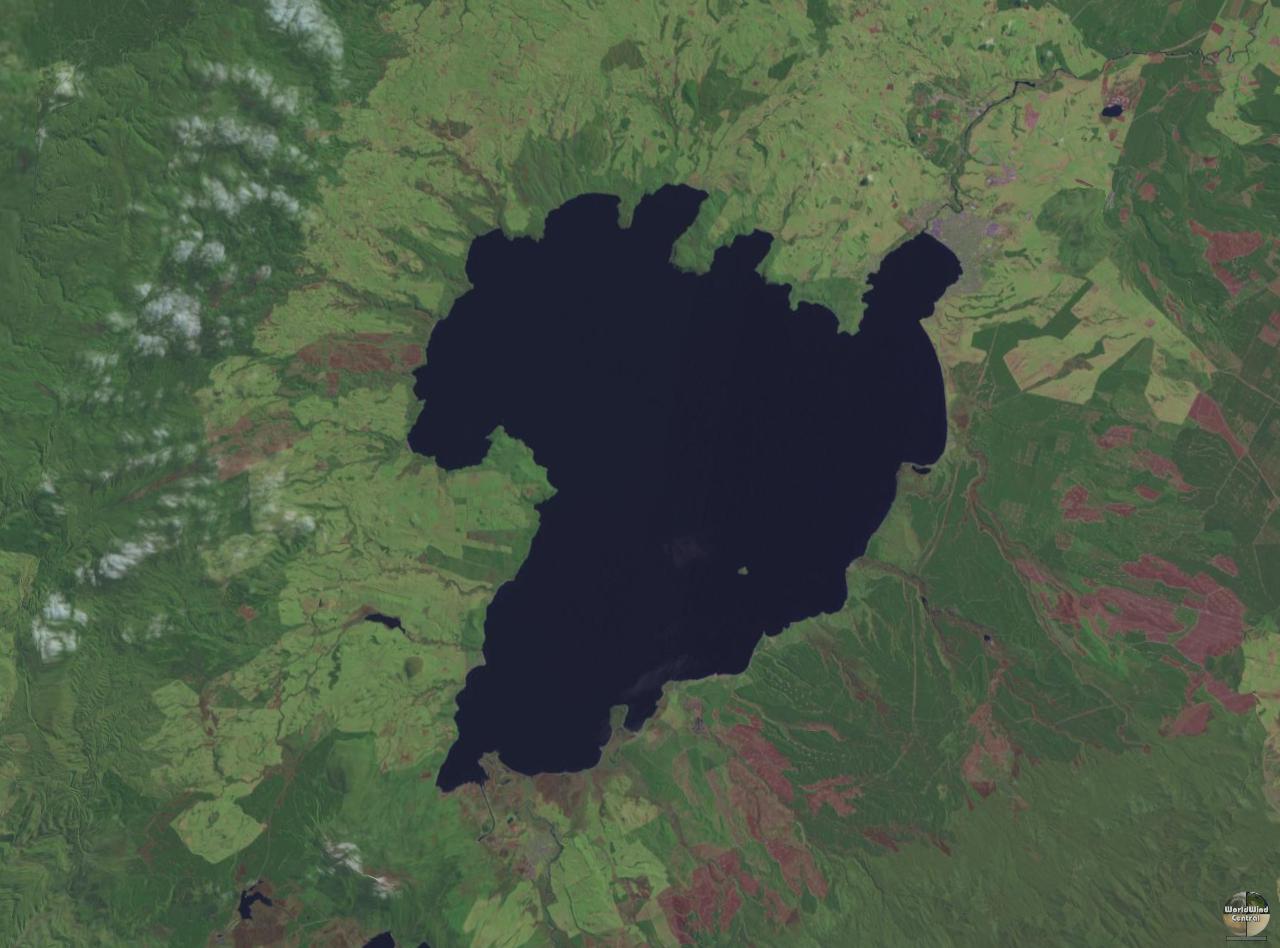  The New Zealand land mass has been
The New Zealand land mass has been  To the south of New Zealand the Indo-Australian Plate is subducting under the Pacific Plate, and this is beginning to result in
To the south of New Zealand the Indo-Australian Plate is subducting under the Pacific Plate, and this is beginning to result in
 The South Island is much more mountainous than the North, but shows fewer manifestations of recent volcanic activity. There are 18 peaks of more than in the Southern Alps, which stretch for down the South Island. The closest mountains surpassing it in elevation are found not in Australia, but in
The South Island is much more mountainous than the North, but shows fewer manifestations of recent volcanic activity. There are 18 peaks of more than in the Southern Alps, which stretch for down the South Island. The closest mountains surpassing it in elevation are found not in Australia, but in
 The mountainous areas of the North Island are cut by many rivers, many of which are swift and unnavigable. The east of the South Island is marked by wide,
The mountainous areas of the North Island are cut by many rivers, many of which are swift and unnavigable. The east of the South Island is marked by wide,
Wind and solar power
', ''Te Ara: The Encyclopedia of New Zealand'', updated 21 September 2007.
Marlborough Sounds
The Marlborough Sounds are an extensive network of sea-drowned valleys at the northern end of the South Island of New Zealand. The Marlborough Sounds were created by a combination of land subsidence and rising sea levels. According to Māori ...
) and Waiheke Island
Waiheke Island (; Māori: ) is the second-largest island (after Great Barrier Island) in the Hauraki Gulf of New Zealand. Its ferry terminal in Matiatia Bay at the western end is from the central-city terminal in Auckland.
It is the most po ...
(about from central Auckland
Auckland (pronounced ) ( mi, Tāmaki Makaurau) is a large metropolitan city in the North Island of New Zealand. The most populous urban area in the country and the fifth largest city in Oceania, Auckland has an urban population of about I ...
).
Extreme points
 The phrase "From Cape Reinga to The Bluff" is frequently used within New Zealand to refer to the extent of the whole country.
The phrase "From Cape Reinga to The Bluff" is frequently used within New Zealand to refer to the extent of the whole country. Cape Reinga / Te Rerenga Wairua
, type =Cape
, photo = Cape Reinga, Northland, New Zealand, October 2007.jpg
, photo_width = 270px
, photo_alt =
, photo_caption =
, map = New Zealand
, map_width = 270px
...
is the northwesternmost tip of the Aupouri Peninsula
The Aupouri Peninsula is a tombolo at the northern tip of the North Island of New Zealand. It projects between the Tasman Sea to the west and the Pacific Ocean to the east. It constitutes the northern part of the Far North District, incorpora ...
, at the northern end of the North Island. Bluff
Bluff or The Bluff may refer to:
Places Australia
* Bluff, Queensland, Australia, a town
* The Bluff, Queensland (Ipswich), a rural locality in the city of Ipswich
* The Bluff, Queensland (Toowoomba Region), a rural locality
* Bluff River (New ...
is Invercargill
Invercargill ( , mi, Waihōpai is the southernmost and westernmost city in New Zealand, and one of the southernmost cities in the world. It is the commercial centre of the Southland region. The city lies in the heart of the wide expanse ...
's port, located near the southern tip of the South Island, below the 46th parallel south
The 46th parallel south is a circle of latitude that is 46 degrees south of the Earth's equatorial plane. It crosses the Atlantic Ocean, the Indian Ocean, Australasia, the Pacific Ocean and South America.
At this latitude the sun is visible ...
. However, the extreme points of New Zealand are actually located in several outlying islands.
The points that are farther north, south, east or west than any other location in New Zealand are as follows:
*The northernmost point is in Nugent Island in the Kermadec Islands
The Kermadec Islands ( mi, Rangitāhua) are a subtropical island arc in the South Pacific Ocean northeast of New Zealand's North Island, and a similar distance southwest of Tonga. The islands are part of New Zealand. They are in total ar ...
().
*The southernmost point is Jacquemart Island
Jacquemart Island, one of the islets surrounding Campbell Island in New Zealand, lies south of Campbell Island and is the southernmost island of New Zealand.
The name commemorates Captain J. Jacquemart, of the vessel FRWS ''Vire'', that supp ...
in the Campbell Island group
The Campbell Islands (or Campbell Island Group) are a group of subantarctic islands, belonging to New Zealand. They lie about 600 km south of Stewart Island. The islands have a total area of , consisting of one big island, Campbell Isla ...
().
*The easternmost point is situated in a group of islands within the Chatham Islands called the Forty-Fours
The Forty-Fours are a group of islands in the Chatham Archipelago, about east of the main Chatham Island. They are called ''Motchuhar'' in Moriori and ''Motuhara'' in Māori.Government of New Zealand, Dept. of Conservation (1999) Chatham Isla ...
().
*The westernmost point is Cape Lovitt on Auckland Island
Auckland Island ( mi, Mauka Huka) is the main island of the eponymous uninhabited archipelago in the Pacific Ocean. It is part of the New Zealand subantarctic area. It is inscribed in the UNESCO World Heritage list together with the other New ...
().
Antipodes
 New Zealand is largely antipodal to the
New Zealand is largely antipodal to the Iberian Peninsula
The Iberian Peninsula (),
**
* Aragonese and Occitan: ''Peninsula Iberica''
**
**
* french: Péninsule Ibérique
* mwl, Península Eibérica
* eu, Iberiar penintsula also known as Iberia, is a peninsula in southwestern Europe, def ...
of Europe. The northern half of the South Island corresponds to Galicia
Galicia may refer to:
Geographic regions
* Galicia (Spain), a region and autonomous community of northwestern Spain
** Gallaecia, a Roman province
** The post-Roman Kingdom of the Suebi, also called the Kingdom of Gallaecia
** The medieval King ...
and northern Portugal. Most of the North Island corresponds to central and southern Spain, from Valladolid
Valladolid () is a municipality in Spain and the primary seat of government and de facto capital of the autonomous community of Castile and León. It is also the capital of the province of the same name. It has a population around 300,000 peop ...
(opposite the southern point of the North Island, Cape Palliser
Cape Palliser is a promontory on the southern coast of New Zealand's North Island and is the southernmost point of the North Island; it is in fact considerably farther south than Nelson or Blenheim in the South Island.
It is located at the easter ...
), through Madrid
Madrid ( , ) is the capital and most populous city of Spain. The city has almost 3.4 million inhabitants and a metropolitan area population of approximately 6.7 million. It is the second-largest city in the European Union (EU), and ...
and Toledo to Cordoba (directly antipodal to Hamilton Hamilton may refer to:
People
* Hamilton (name), a common British surname and occasional given name, usually of Scottish origin, including a list of persons with the surname
** The Duke of Hamilton, the premier peer of Scotland
** Lord Hamilto ...
), Lorca (opposite East Cape), Málaga
Málaga (, ) is a municipality of Spain, capital of the Province of Málaga, in the autonomous community of Andalusia. With a population of 578,460 in 2020, it is the second-most populous city in Andalusia after Seville and the sixth most po ...
(Cape Colville), and Gibraltar
)
, anthem = " God Save the King"
, song = "Gibraltar Anthem"
, image_map = Gibraltar location in Europe.svg
, map_alt = Location of Gibraltar in Europe
, map_caption = United Kingdom shown in pale green
, mapsize =
, image_map2 = Gibr ...
. Parts of the Northland Peninsula oppose Morocco
Morocco (),, ) officially the Kingdom of Morocco, is the westernmost country in the Maghreb region of North Africa. It overlooks the Mediterranean Sea to the north and the Atlantic Ocean to the west, and has land borders with Algeria to A ...
, with Whangārei
Whangārei () is the northernmost city in New Zealand and the regional capital of Northland Region. It is part of the Whangārei District, a local body created in 1989 from the former Whangārei City, Whangārei County and Hikurangi Town coun ...
nearly coincident with Tangiers
Tangier ( ; ; ar, طنجة, Ṭanja) is a city in northwestern Morocco. It is on the Moroccan coast at the western entrance to the Strait of Gibraltar, where the Mediterranean Sea meets the Atlantic Ocean off Cape Spartel. The town is the capi ...
. The antipodes of the Chatham Islands lie in France, just north of the city of Montpellier
Montpellier (, , ; oc, Montpelhièr ) is a city in southern France near the Mediterranean Sea. One of the largest urban centres in the region of Occitania, Montpellier is the prefecture of the department of Hérault. In 2018, 290,053 people l ...
. The Antipodes Islands
The Antipodes Islands ( Maōri: Moutere Mahue; "Abandoned island") are inhospitable and uninhabited volcanic islands in subantarctic waters to the south of – and territorially part of – New Zealand. The 21 km2 archipelago lies 860 ...
were named for their supposed antipodal position to Britain; although they are the closest land to the true antipodes of Britain, their location 49°41′S 178°48′E is directly antipodal to a point a few kilometres to the east of Cherbourg
Cherbourg (; , , ), nrf, Chèrbourg, ) is a former commune and subprefecture located at the northern end of the Cotentin peninsula in the northwestern French department of Manche. It was merged into the commune of Cherbourg-Octeville on 28 Feb ...
on the north coast of France.
In Europe the term "Antipodes" is often used to refer to New Zealand and Australia (and sometimes other South Pacific areas), and "Antipodeans
The Antipodeans (from the Greek: ἀντίποδες meaning literally “those at the antipodes”) were a group of Australian modern artists who asserted the importance of figurative art, and protested against abstract expressionism. Though t ...
" to their inhabitants.
Geology

Zealandia
Zealandia (pronounced ), also known as (Māori) or Tasmantis, is an almost entirely submerged mass of continental crust that subsided after breaking away from Gondwanaland 83–79 million years ago.Gurnis, M., Hall, C.E., and Lavier, L.L., ...
, a microcontinent
Continental crustal fragments, partly synonymous with microcontinents, are pieces of continents that have broken off from main continental masses to form distinct islands that are often several hundred kilometers from their place of origin.
Caus ...
nearly half the size of Australia
Australia, officially the Commonwealth of Australia, is a sovereign country comprising the mainland of the Australian continent, the island of Tasmania, and numerous smaller islands. With an area of , Australia is the largest country by ...
that gradually submerged after breaking away from the Gondwana
Gondwana () was a large landmass, often referred to as a supercontinent, that formed during the late Neoproterozoic (about 550 million years ago) and began to break up during the Jurassic period (about 180 million years ago). The final sta ...
n supercontinent. Zealandia extends a significant distance east into the Pacific Ocean and south towards Antarctica. It also extends towards Australia in the north-west. This submerged continent is dotted with topographic highs that sometimes form islands. Some of these, such as the main islands (North and South), Stewart Island, New Caledonia, and the Chatham Islands, are settled. Other smaller islands are eco-sanctuaries with carefully controlled access.
 The New Zealand land mass has been
The New Zealand land mass has been uplifted
''Uplifted'' is the second studio album by Nigerian singer Flavour N'abania. It was released on July 20, 2010, by Obaino Music and 2nite Entertainment. The album features guest appearances from Jay Dey, Oloye, Stormrex, Waga Gee, Asemstone, M-Jay, ...
due to transpression
In geology, transpression is a type of strike-slip deformation that deviates from simple shear because of a simultaneous component of shortening perpendicular to the fault plane. This movement ends up resulting in oblique shear. It is generally ve ...
al tectonics
Tectonics (; ) are the processes that control the structure and properties of the Earth's crust and its evolution through time. These include the processes of mountain building, the growth and behavior of the strong, old cores of continents k ...
between the Indo-Australian Plate
The Indo-Australian Plate is a major tectonic plate that includes the continent of Australia and the surrounding ocean and extends northwest to include the Indian subcontinent and the adjacent waters. It was formed by the fusion of the Indian an ...
and Pacific
The Pacific Ocean is the largest and deepest of Earth's five oceanic divisions. It extends from the Arctic Ocean in the north to the Southern Ocean (or, depending on definition, to Antarctica) in the south, and is bounded by the contine ...
plates (these two plates are grinding together with one riding up and over the other). This is the cause of New Zealand's numerous earthquakes.
To the east of the North Island the Pacific Plate is forced under the Indo-Australian Plate. The North Island of New Zealand has widespread back-arc volcanism as a result of this subduction
Subduction is a geological process in which the oceanic lithosphere is recycled into the Earth's mantle at convergent boundaries. Where the oceanic lithosphere of a tectonic plate converges with the less dense lithosphere of a second plate, ...
. There are many large volcanoes with relatively frequent eruptions. There are also several very large caldera
A caldera ( ) is a large cauldron-like hollow that forms shortly after the emptying of a magma chamber in a volcano eruption. When large volumes of magma are erupted over a short time, structural support for the rock above the magma chamber is ...
s, with the most obvious forming Lake Taupō
Lake Taupō (also spelled Taupo; mi, Taupō-nui-a-Tia or ) is a large crater lake in New Zealand's North Island, located in the caldera of the Taupō Volcano. The lake is the namesake of the town of Taupō, which sits on a bay in the lake's n ...
. Taupō has a history of incredibly powerful eruptions, with the Oruanui eruption
The Oruanui eruption of New Zealand's Taupō Volcano (also known as the Kawakawa eruption or Kawakawa/Oruanui event) was the world's most recent supereruption.}
Eruption
With a Volcanic Explosivity Index of 8, it is one of the largest eruptio ...
26,500 years ago ejecting of material and causing the downward collapse of several hundred square kilometres to form the lake. The most recent eruption occurred and ejected at least 100 cubic kilometres of material, and has been correlated with red skies seen at the time in Rome
, established_title = Founded
, established_date = 753 BC
, founder = King Romulus ( legendary)
, image_map = Map of comune of Rome (metropolitan city of Capital Rome, region Lazio, Italy).svg
, map_caption ...
and China
China, officially the People's Republic of China (PRC), is a country in East Asia. It is the world's List of countries and dependencies by population, most populous country, with a Population of China, population exceeding 1.4 billion, slig ...
. The associated geothermal energy from this volcanic area is used in numerous hydrothermal power plants. Some volcanic places are also famous tourist destinations, such as the Rotorua
Rotorua () is a city in the Bay of Plenty region of New Zealand's North Island. The city lies on the southern shores of Lake Rotorua, from which it takes its name. It is the seat of the Rotorua Lakes District, a territorial authority encomp ...
geyser
A geyser (, ) is a spring characterized by an intermittent discharge of water ejected turbulently and accompanied by steam. As a fairly rare phenomenon, the formation of geysers is due to particular hydrogeological conditions that exist only i ...
s.
The subduction direction is reversed through the South Island, with the Indo-Australian Plate forced under the Pacific Plate. The transition between these two different styles of continental collision occurs through the top of the South Island. This area has significant uplift and many active fault
An active fault is a fault that is likely to become the source of another earthquake sometime in the future. Geologists commonly consider faults to be active if there has been movement observed or evidence of seismic activity during the last 10,0 ...
s; large earthquakes are frequent occurrences here. The most powerful in recent history, the M8.3 Wairarapa earthquake, occurred in 1855. This earthquake generated more than of vertical uplift in places, and caused a localised tsunami. Fortunately casualties were low due to the sparse settlement of the region. In 2013, the area was rattled by the M6.5 Seddon earthquake, but this caused little damage and no injuries. New Zealand's capital city
A capital city or capital is the municipality holding primary status in a country, state, province, department, or other subnational entity, usually as its seat of the government. A capital is typically a city that physically encompasses t ...
, Wellington
Wellington ( mi, Te Whanganui-a-Tara or ) is the capital city of New Zealand. It is located at the south-western tip of the North Island, between Cook Strait and the Remutaka Range. Wellington is the second-largest city in New Zealand by ...
is situated in the centre of this region.
The subduction of the Indo-Australian Plate drives rapid uplift in the centre of the South Island (approx. per year). This uplift forms the Southern Alps. These roughly divide the island, with a narrow wet strip to the west and wide and dry plains to the east. The resulting orographic
Orography is the study of the topographic relief of mountains, and can more broadly include hills, and any part of a region's elevated terrain. Orography (also known as ''oreography'', ''orology'' or ''oreology'') falls within the broader disci ...
rainfall enables the hydroelectric generation of most of the electricity in New Zealand. A significant amount of the movement between the two plates is accommodated by lateral sliding of the Indo-Australian Plate north relative to the Pacific Plate. The plate boundary forms the nearly long Alpine Fault
The Alpine Fault is a geological fault that runs almost the entire length of New Zealand's South Island (c. 480 km) and forms the boundary between the Pacific Plate and the Indo-Australian Plate. The Southern Alps have been uplifted on the f ...
. This fault has an estimated rupture reoccurrence interval of ~330 years, and last ruptured in 1717 along of its length. It passes directly under many settlements on the West Coast of the South Island and shaking from a rupture would likely affect many cities and towns throughout the country.
The rapid uplift and high erosion
Erosion is the action of surface processes (such as water flow or wind) that removes soil, rock, or dissolved material from one location on the Earth's crust, and then transports it to another location where it is deposited. Erosion is d ...
rates within the Southern Alps combine to expose high grade greenschist
Greenschists are metamorphic rocks that formed under the lowest temperatures and pressures usually produced by regional metamorphism, typically and 2–10 kilobars (). Greenschists commonly have an abundance of green minerals such as chlorite ...
to amphibolite
Amphibolite () is a metamorphic rock that contains amphibole, especially hornblende and actinolite, as well as plagioclase feldspar, but with little or no quartz. It is typically dark-colored and dense, with a weakly foliated or schistose (flaky ...
facies
In geology, a facies ( , ; same pronunciation and spelling in the plural) is a body of rock with specified characteristics, which can be any observable attribute of rocks (such as their overall appearance, composition, or condition of formatio ...
rocks, including the gemstone pounamu
Pounamu is a term for several types of hard and durable stone found in southern New Zealand. They are highly valued in New Zealand, and carvings made from pounamu play an important role in Māori culture.
Name
The Māori word , also used ...
. Geologists visiting the West Coast can easily access high-grade metamorphic rock
Metamorphic rocks arise from the transformation of existing rock to new types of rock in a process called metamorphism. The original rock (protolith) is subjected to temperatures greater than and, often, elevated pressure of or more, caus ...
s and mylonite
Mylonite is a fine-grained, compact metamorphic rock produced by dynamic recrystallization of the constituent minerals resulting in a reduction of the grain size of the rock. Mylonites can have many different mineralogical compositions; it is a ...
s associated with the Alpine Fault, and in certain places can stand astride the fault trace of an active plate boundary. The South Island also has two major gold
Gold is a chemical element with the symbol Au (from la, aurum) and atomic number 79. This makes it one of the higher atomic number elements that occur naturally. It is a bright, slightly orange-yellow, dense, soft, malleable, and ductile ...
fields in Otago
Otago (, ; mi, Ōtākou ) is a region of New Zealand located in the southern half of the South Island administered by the Otago Regional Council. It has an area of approximately , making it the country's second largest local government reg ...
and the West Coast.
 To the south of New Zealand the Indo-Australian Plate is subducting under the Pacific Plate, and this is beginning to result in
To the south of New Zealand the Indo-Australian Plate is subducting under the Pacific Plate, and this is beginning to result in back-arc
A back-arc basin is a type of geologic basin, found at some convergent plate boundaries. Presently all back-arc basins are submarine features associated with island arcs and subduction zones, with many found in the western Pacific Ocean. Most of ...
volcanism. The youngest (geologically speaking) volcanism in the South Island occurred in this region, forming the Solander Islands (<2 million years old). This region is dominated by the rugged and relatively untouched Fiordland
Fiordland is a geographical region of New Zealand in the south-western corner of the South Island, comprising the westernmost third of Southland. Most of Fiordland is dominated by the steep sides of the snow-capped Southern Alps, deep lake ...
, an area of flooded glacially carved valleys with little human settlement.
Mountains, volcanoes and glaciers
 The South Island is much more mountainous than the North, but shows fewer manifestations of recent volcanic activity. There are 18 peaks of more than in the Southern Alps, which stretch for down the South Island. The closest mountains surpassing it in elevation are found not in Australia, but in
The South Island is much more mountainous than the North, but shows fewer manifestations of recent volcanic activity. There are 18 peaks of more than in the Southern Alps, which stretch for down the South Island. The closest mountains surpassing it in elevation are found not in Australia, but in New Guinea
New Guinea (; Hiri Motu: ''Niu Gini''; id, Papua, or , historically ) is the world's second-largest island with an area of . Located in Oceania in the southwestern Pacific Ocean, the island is separated from Australia by the wide Torres ...
and Antarctica. As well as the towering peaks, the Southern Alps include huge glaciers such as Franz Josef
Franz Joseph I or Francis Joseph I (german: Franz Joseph Karl, hu, Ferenc József Károly, 18 August 1830 – 21 November 1916) was Emperor of Austria, King of Hungary, and the other states of the Habsburg monarchy from 2 December 1848 until his ...
and Fox. The country's highest mountain is Aoraki / Mount Cook
Aoraki / Mount Cook is the highest mountain in New Zealand. Its height, as of 2014, is listed as . It sits in the Southern Alps, the mountain range that runs the length of the South Island. A popular tourist destination, it is also a favourite ...
; its height since 2014 is listed as (down from before December 1991, due to a rockslide and subsequent erosion). The second highest peak is Mount Tasman
Mount Tasman (''Horokoau'' in Māori) is New Zealand's second highest mountain, rising to a height of . It is located in the Southern Alps of the South Island, four kilometres to the north of its larger neighbour, Aoraki / Mount Cook. Unlike ...
, with a height of .
The North Island Volcanic Plateau
The North Island Volcanic Plateau (often called the Central Plateau and occasionally the Waimarino Plateau) is a volcanic plateau covering much of central North Island of New Zealand with volcanoes, lava plateaus, and crater lakes. It contains ...
covers much of central North Island with volcanoes, lava plateau
A volcanic plateau is a plateau produced by volcanism, volcanic activity. There are two main types: lava plateaus and pyroclastic plateaus.
Lava plateau
Lava plateaus are formed by highly fluid basaltic lava during numerous successive erup ...
s, and crater lake
Crater Lake ( Klamath: ''Giiwas'') is a volcanic crater lake in south-central Oregon in the western United States. It is the main feature of Crater Lake National Park and is famous for its deep blue color and water clarity. The lake partly fill ...
s. The three highest volcanoes are Mount Ruapehu
Mount Ruapehu (; ) is an active stratovolcano at the southern end of the Taupō Volcanic Zone and North Island volcanic plateau in New Zealand. It is northeast of Ohakune and southwest of the southern shore of Lake Taupō, within the Tongari ...
(), Mount Taranaki
Mount Taranaki (), also known as Mount Egmont, is a dormant stratovolcano in the Taranaki region on the west coast of New Zealand's North Island. It is the second highest point in the North Island, after Mount Ruapehu. The mountain has a seco ...
() and Mount Ngauruhoe
Mount Ngāuruhoe (also spelled Ngauruhoe; Māori: ''Ngāuruhoe'') is a volcanic cone in New Zealand. It is the youngest vent in the Tongariro stratovolcano complex on the Central Plateau of the North Island and first erupted about 2,500 y ...
(). Ruapehu's major eruptions have historically been about 50 years apart, in 1895, 1945 and 1995–1996. The 1886 eruption of Mount Tarawera, located near Rotorua
Rotorua () is a city in the Bay of Plenty region of New Zealand's North Island. The city lies on the southern shores of Lake Rotorua, from which it takes its name. It is the seat of the Rotorua Lakes District, a territorial authority encomp ...
, was New Zealand's largest and deadliest eruption in the last 200 years, killing over 100 people. Another long chain of mountains runs through the North Island, from Wellington to East Cape. The ranges include Tararua and Kaimanawa.
The lower mountain slopes are covered in native forest. Above this are shrubs, and then tussock grasses. Alpine tundra
Alpine tundra is a type of natural region or biome that does not contain trees because it is at high elevation, with an associated harsh climate. As the latitude of a location approaches the poles, the threshold elevation for alpine tundra gets ...
consists of cushion plants and herbfields; many of these plants have white and yellow flowers.
Caves
New Zealand's cave systems have three main origins, the chemical weathering of limestone by water (karst
Karst is a topography formed from the dissolution of soluble rocks such as limestone, Dolomite (rock), dolomite, and gypsum. It is characterized by underground drainage systems with sinkholes and caves. It has also been documented for more weathe ...
), lava cave
A lava cave is any cave formed in volcanic rock, though it typically means caves formed by volcanic processes, which are more properly termed volcanic caves. Sea caves, and other sorts of erosional and crevice caves, may be formed in volcanic roc ...
s and erosion by waves (sea cave
A sea cave, also known as a littoral cave, is a type of cave formed primarily by the wave action of the sea. The primary process involved is erosion. Sea caves are found throughout the world, actively forming along present coastlines and as relic ...
s). Therefore, the distribution of limestone, marble (metamorphosed
Metamorphic rocks arise from the transformation of existing rock to new types of rock in a process called metamorphism. The original rock (protolith) is subjected to temperatures greater than and, often, elevated pressure of or more, causi ...
limestone) and volcanoes defines the location of caves in inland New Zealand. The main regions of karst topography are the Waitomo District
Waitomo District is a territorial authority, located in the Waikato region, at the north of the King Country area in the North Island of New Zealand. A small part of the district, the locality of Tiroa, however, lies in the Manawatū-Whanganui ...
and Takaka Hill in the Tasman District
Tasman District () is a local government district in the northwest of the South Island of New Zealand. It borders the Canterbury Region, West Coast Region, Marlborough Region and Nelson City. It is administered by the Tasman District Council, ...
. Other notable locations are on the West Coast (Punakaiki
Punakaiki is a small village on the West Coast of the South Island of New Zealand. It is located between Westport and Greymouth on , the only through-road on the West Coast. Punakaiki is immediately adjacent to Paparoa National Park, and is al ...
), Hawke's Bay
Hawke's Bay ( mi, Te Matau-a-Māui) is a local government region on the east coast of New Zealand's North Island. The region's name derives from Hawke Bay, which was named by Captain James Cook in honour of Admiral Edward Hawke. The region i ...
and Fiordland
Fiordland is a geographical region of New Zealand in the south-western corner of the South Island, comprising the westernmost third of Southland. Most of Fiordland is dominated by the steep sides of the snow-capped Southern Alps, deep lake ...
.
Lava caves (lava tube
A lava tube, or pyroduct, is a natural conduit formed by flowing lava from a volcanic vent that moves beneath the hardened surface of a lava flow. If lava in the tube empties, it will leave a cave.
Formation
A lava tube is a type of lava ...
s) usually form in pāhoehoe
Lava is molten or partially molten rock (magma) that has been expelled from the interior of a terrestrial planet (such as Earth) or a moon onto its surface. Lava may be erupted at a volcano or through a fracture in the crust, on land or un ...
lava flows, which are less viscus and typical formed from basalt
Basalt (; ) is an aphanitic (fine-grained) extrusive igneous rock formed from the rapid cooling of low-viscosity lava rich in magnesium and iron (mafic lava) exposed at or very near the surface of a rocky planet or moon. More than 90 ...
. When an eruption occurs the outer layer of the lava flow hardens, while the interior remain liquid. The liquid lava flows out as it is insulated by the hardened crust above. These caves are found where there are relatively recent basaltic volcanoes in New Zealand, such as the Auckland Volcanic Field
The Auckland volcanic field is an area of monogenetic volcanoes covered by much of the metropolitan area of Auckland, New Zealand's largest city, located in the North Island. The approximately 53 volcanoes in the field have produced a diverse a ...
particularly on Rangitoto, Mount Eden
Mount Eden is a suburb in Auckland, New Zealand whose name honours George Eden, 1st Earl of Auckland. It is south of the Central Business District (CBD). Mt Eden Road winds its way around the side of Mount Eden Domain and continues to weave b ...
and Matukutūruru
Matukutūruru (also Te Manurewa o Tamapahore or Wiri Mountain) is a volcano and Tūpuna Maunga (ancestral mountain) in Wiri, in the Auckland volcanic field. It had a scoria cone reaching 80 metres above sea level (around 50 m higher than the s ...
.
The distribution of sea caves is more sporadic, with their location and orientation being controlled by weakness in the underlying rock. As cave systems take many thousands of years to develop they can now be isolated from the water that formed them, whether through change in sea level or groundwater flow. If as a cave grows it breaks through to the surface somewhere else it becomes a natural arch
A natural arch, natural bridge, or (less commonly) rock arch is a natural landform where an arch has formed with an opening underneath. Natural arches commonly form where inland cliffs, coastal cliffs, fins or stacks are subject to erosion ...
, like those near Karamea
Karamea is a town on the West Coast of the South Island of New Zealand. It is the northernmost settlement of any real size on the West Coast, and is located northeast by road from Westport. Apart from a narrow coastal strip, the town of Kara ...
( Oparara Arches).
Rivers and lakes
The proportion of New Zealand's area (excludingestuaries
An estuary is a partially enclosed coastal body of brackish water with one or more rivers or streams flowing into it, and with a free connection to the open sea. Estuaries form a transition zone between river environments and maritime environme ...
) covered by rivers, lakes and ponds, based on figures from the New Zealand Land Cover Database, is (357526 + 81936) / (26821559 – 92499–26033 – 19216) = 1.6%. If estuarine open water, mangroves, and herbaceous
Herbaceous plants are vascular plants that have no persistent woody stems above ground. This broad category of plants includes many perennials, and nearly all annuals and biennials.
Definitions of "herb" and "herbaceous"
The fourth edition o ...
saline vegetation are included, the figure is 2.2%.
 The mountainous areas of the North Island are cut by many rivers, many of which are swift and unnavigable. The east of the South Island is marked by wide,
The mountainous areas of the North Island are cut by many rivers, many of which are swift and unnavigable. The east of the South Island is marked by wide, braided river
A braided river, or braided channel, consists of a network of river channels separated by small, often temporary, islands called braid bars or, in English usage, ''aits'' or ''eyots''.
Braided streams tend to occur in rivers with high sediment ...
s such as the Wairau, Waimakariri and Rangitata; formed from glaciers, they fan out into many strands on gravel plains. The total length of the country's rivers is over . The Waikato
Waikato () is a local government region of the upper North Island of New Zealand. It covers the Waikato District, Waipa District, Matamata-Piako District, South Waikato District and Hamilton City, as well as Hauraki, Coromandel Peninsul ...
, flowing through the North Island, is the longest, with a length of . New Zealand's rivers feature hundreds of waterfalls; the most visited set of waterfalls are the Huka Falls
Huka Falls is a set of waterfalls on the Waikato River, which drains Lake Taupō in New Zealand.
A few hundred metres upstream from Huka Falls, the Waikato River narrows from approximately 100 metres across to a canyon only 15 metres across. The ...
that drain Lake Taupō.
Lake Taupō, located near the centre of the North Island, is the largest lake by surface area in the country. It lies in a caldera
A caldera ( ) is a large cauldron-like hollow that forms shortly after the emptying of a magma chamber in a volcano eruption. When large volumes of magma are erupted over a short time, structural support for the rock above the magma chamber is ...
created by the Oruanui eruption
The Oruanui eruption of New Zealand's Taupō Volcano (also known as the Kawakawa eruption or Kawakawa/Oruanui event) was the world's most recent supereruption.}
Eruption
With a Volcanic Explosivity Index of 8, it is one of the largest eruptio ...
, the largest eruption in the world in the past 70,000 years. There are 3,820 lakes with a surface area larger than one hectare
The hectare (; SI symbol: ha) is a non-SI metric unit of area equal to a square with 100- metre sides (1 hm2), or 10,000 m2, and is primarily used in the measurement of land. There are 100 hectares in one square kilometre. An acre i ...
. Many lakes have been used as reservoirs for hydroelectric
Hydroelectricity, or hydroelectric power, is electricity generated from hydropower (water power). Hydropower supplies one sixth of the world's electricity, almost 4500 TWh in 2020, which is more than all other renewable sources combined an ...
projects.About 58 percent of New Zealand's electricity was hydroelectric in 2002. Veronika Meduna.Wind and solar power
', ''Te Ara: The Encyclopedia of New Zealand'', updated 21 September 2007.
Coastal wetlands
Wetlands support the greatest concentration of wildlife out of any other habitat. New Zealand has six sites covering almost that are included in theList of Wetlands of International Importance
This is the list of Wetlands of International Importance as defined by the Ramsar Convention for the conservation and sustainable use of wetlands, recognizing the fundamental ecological functions of wetlands and their economic, cultural, scientifi ...
(Ramsar site
A Ramsar site is a wetland site designated to be of international importance under the Ramsar Convention,8 ha (O)
*** Permanent 8 ha (P)
*** Seasonal Intermittent < 8 ha(Ts)
**
Whangamarino Wetland.
A recent global remote sensing analysis suggested that there were of
 The main geographic factors that influence New Zealand's climate are the temperate
The main geographic factors that influence New Zealand's climate are the temperate  The UV index can be very high and extreme in the hottest times of the year in the north of the North Island. This is partly due to the country's relatively little air pollution compared to many other countries and the high sunshine hours. New Zealand has very high sunshine hours with most areas receiving over 2000 hours per year. The sunniest areas are Nelson/Marlborough and the Bay of Plenty with 2,400 hours per year.
The table below lists climate normals for the warmest and coldest months in New Zealand's six largest cities. North Island cities are generally warmest in February. South Island cities are warmest in January.
The combined effects of climate change, effects of climate change in New Zealand will result in a multitude of irreversible impacts; by the end of this century New Zealand will experience higher rainfalls, more frequent extreme weather events and higher temperatures. In 2021, the Ministry for the Environment (New Zealand), Ministry for the Environment estimated that New Zealand's gross emissions were 0.17% of the world's total gross greenhouse gas emissions. However, on a per capita basis, New Zealand is a significant emitter, the sixth highest within the Kyoto Protocol#Annex I countries, Annex I countries, whereas on absolute gross emissions New Zealand is ranked as the 24th highest emitter.
The UV index can be very high and extreme in the hottest times of the year in the north of the North Island. This is partly due to the country's relatively little air pollution compared to many other countries and the high sunshine hours. New Zealand has very high sunshine hours with most areas receiving over 2000 hours per year. The sunniest areas are Nelson/Marlborough and the Bay of Plenty with 2,400 hours per year.
The table below lists climate normals for the warmest and coldest months in New Zealand's six largest cities. North Island cities are generally warmest in February. South Island cities are warmest in January.
The combined effects of climate change, effects of climate change in New Zealand will result in a multitude of irreversible impacts; by the end of this century New Zealand will experience higher rainfalls, more frequent extreme weather events and higher temperatures. In 2021, the Ministry for the Environment (New Zealand), Ministry for the Environment estimated that New Zealand's gross emissions were 0.17% of the world's total gross greenhouse gas emissions. However, on a per capita basis, New Zealand is a significant emitter, the sixth highest within the Kyoto Protocol#Annex I countries, Annex I countries, whereas on absolute gross emissions New Zealand is ranked as the 24th highest emitter.
 The South Island contains a little under one-quarter of the population. Over three-quarters of New Zealand's population live in the North Island, with half living north of Lake Rotorua, and one-third of the total population living in the Auckland Region. Auckland is also the fastest growing region, accounting for 51% of New Zealand's total population growth (in the two decades up to 2016). The majority of the indigenous Māori people live in the North Island (87%), although a little under a quarter (24%) live in Auckland. New Zealand is a predominantly urban country, with % of the population living in an urban areas of New Zealand, urban area. About % of the population live in the 20 main urban areas (population of 30,000 or more) and % live in the four largest cities of
The South Island contains a little under one-quarter of the population. Over three-quarters of New Zealand's population live in the North Island, with half living north of Lake Rotorua, and one-third of the total population living in the Auckland Region. Auckland is also the fastest growing region, accounting for 51% of New Zealand's total population growth (in the two decades up to 2016). The majority of the indigenous Māori people live in the North Island (87%), although a little under a quarter (24%) live in Auckland. New Zealand is a predominantly urban country, with % of the population living in an urban areas of New Zealand, urban area. About % of the population live in the 20 main urban areas (population of 30,000 or more) and % live in the four largest cities of
 Almost half of New Zealand's climate change emissions are generated by greenhouse gases, mainly methane and nitrous oxide, which come from farming and agriculture. Organisms that grow inside of grazing animals' stomachs turn New Zealand's grass into methane. The increase of carbon dioxide in the air helps the plants to grow faster, but the long-term effects of climate change threaten farmers with the likelihood of more frequent and severe floods and droughts. Kiwifruit industry in New Zealand, Growers of kiwifruit, a major export in the horticulture industry of New Zealand, have experienced difficulties as a result of climate change. In the 2010s, warm winters did not provide the adequate cool temperatures needed for the flowering of kiwifruit, and this resulted in a reduction of the yield sizes. Droughts have also decreased apple production by causing sunburns and a lack of water available for irrigation. In contrast, the Dairy farming in New Zealand, dairy industry has not been affected, and has actually adjusted well to the effects of climate change.
Almost half of New Zealand's climate change emissions are generated by greenhouse gases, mainly methane and nitrous oxide, which come from farming and agriculture. Organisms that grow inside of grazing animals' stomachs turn New Zealand's grass into methane. The increase of carbon dioxide in the air helps the plants to grow faster, but the long-term effects of climate change threaten farmers with the likelihood of more frequent and severe floods and droughts. Kiwifruit industry in New Zealand, Growers of kiwifruit, a major export in the horticulture industry of New Zealand, have experienced difficulties as a result of climate change. In the 2010s, warm winters did not provide the adequate cool temperatures needed for the flowering of kiwifruit, and this resulted in a reduction of the yield sizes. Droughts have also decreased apple production by causing sunburns and a lack of water available for irrigation. In contrast, the Dairy farming in New Zealand, dairy industry has not been affected, and has actually adjusted well to the effects of climate change.
 New Zealand's geographic isolation for 80 million years and island biogeography has influenced evolution of the country's species of fauna, animals, fungus, fungi and flora, plants. Physical isolation has not caused biological isolation, and this has resulted in a dynamic evolutionary ecology with examples of very distinctive plants and animals as well as populations of widespread species. There has been long-distance dispersal of plant life between mainland Australia and New Zealand, despite the separation. Evergreens such as the giant kauri and southern beech dominate the bush (native forests). The country also has a list of birds of New Zealand, diverse range of birds, several of which are flightless such as the Kiwi (bird), kiwi (a national symbol), the kākāpō, the takahē and the weka, and several species of penguins. Around 30 bird species are currently listed as endangered or critically endangered. Conservationists recognised that threatened bird populations could be saved on offshore islands, where, once predators were exterminated, bird life flourished again.
Many bird species, including the giant moa, became extinct after the arrival of Polynesians, who brought dogs and rats, and Europeans, who introduced additional dog and rat species, as well as cats, pigs, ferrets, and weasels. Native flora and fauna continue to be hard-hit by Invasive species in New Zealand, invasive species. New Zealand conservationists have pioneered several methods to help threatened wildlife recover, including island sanctuaries, pest control, wildlife translocation, fostering, and ecological island restoration, restoration of islands and ecological island, other selected areas.
Massive Deforestation in New Zealand, deforestation occurred after humans arrived, with around half the forest cover lost to fire after Polynesian settlement. Much of the remaining forest fell after European settlement, being logged or cleared to make room for pastoral farming, leaving forest occupying only 23% of the land. New Zealand had a 2019 Forest Landscape Integrity Index mean score of 7.12/10, ranking it 55th globally out of 172 countries.
Pollution in New Zealand, Pollution, particularly Water pollution in New Zealand, water pollution, is one of New Zealand's most significant environmental issues. Fresh water quality is under pressure from agriculture, hydropower, urban development, pest invasions and climate change, although much of the country's household and industrial waste is now increasingly filtered and sometimes recycled.
New Zealand's geographic isolation for 80 million years and island biogeography has influenced evolution of the country's species of fauna, animals, fungus, fungi and flora, plants. Physical isolation has not caused biological isolation, and this has resulted in a dynamic evolutionary ecology with examples of very distinctive plants and animals as well as populations of widespread species. There has been long-distance dispersal of plant life between mainland Australia and New Zealand, despite the separation. Evergreens such as the giant kauri and southern beech dominate the bush (native forests). The country also has a list of birds of New Zealand, diverse range of birds, several of which are flightless such as the Kiwi (bird), kiwi (a national symbol), the kākāpō, the takahē and the weka, and several species of penguins. Around 30 bird species are currently listed as endangered or critically endangered. Conservationists recognised that threatened bird populations could be saved on offshore islands, where, once predators were exterminated, bird life flourished again.
Many bird species, including the giant moa, became extinct after the arrival of Polynesians, who brought dogs and rats, and Europeans, who introduced additional dog and rat species, as well as cats, pigs, ferrets, and weasels. Native flora and fauna continue to be hard-hit by Invasive species in New Zealand, invasive species. New Zealand conservationists have pioneered several methods to help threatened wildlife recover, including island sanctuaries, pest control, wildlife translocation, fostering, and ecological island restoration, restoration of islands and ecological island, other selected areas.
Massive Deforestation in New Zealand, deforestation occurred after humans arrived, with around half the forest cover lost to fire after Polynesian settlement. Much of the remaining forest fell after European settlement, being logged or cleared to make room for pastoral farming, leaving forest occupying only 23% of the land. New Zealand had a 2019 Forest Landscape Integrity Index mean score of 7.12/10, ranking it 55th globally out of 172 countries.
Pollution in New Zealand, Pollution, particularly Water pollution in New Zealand, water pollution, is one of New Zealand's most significant environmental issues. Fresh water quality is under pressure from agriculture, hydropower, urban development, pest invasions and climate change, although much of the country's household and industrial waste is now increasingly filtered and sometimes recycled.
Statistics New Zealand
profile at World Atlas
Natural Environment
– Te Ara: The Encyclopedia of New Zealand
New Zealand's Geological History
– 1966 Encyclopaedia of New Zealand {{DEFAULTSORT:Geography of New Zealand Geography of New Zealand,
tidal flat
Mudflats or mud flats, also known as tidal flats or, in Ireland, slob or slobs, are coastal wetlands that form in intertidal areas where sediments have been deposited by tides or rivers. A global analysis published in 2019 suggested that tidal fl ...
s in New Zealand, making it the 29th ranked country in terms of tidal flat area.
Climate
 The main geographic factors that influence New Zealand's climate are the temperate
The main geographic factors that influence New Zealand's climate are the temperate latitude
In geography, latitude is a coordinate that specifies the north– south position of a point on the surface of the Earth or another celestial body. Latitude is given as an angle that ranges from –90° at the south pole to 90° at the north ...
, with prevailing westerly winds; the oceanic environment; and the mountains, especially the Southern Alps. The climate is mostly temperate with mean temperatures ranging from in the South Island to in the North Island. January and February are the warmest months, July the coldest. New Zealand does not have a large temperature range, apart from central Otago, but the weather can change rapidly and unexpectedly. Near subtropical
The subtropical zones or subtropics are geographical and climate zones to the north and south of the tropics. Geographically part of the temperate zones of both hemispheres, they cover the middle latitudes from to approximately 35° north a ...
conditions are experienced in Northland.
Most settled, lowland areas of the country have between of rainfall
Rain is water droplets that have condensed from atmospheric water vapor and then fall under gravity. Rain is a major component of the water cycle and is responsible for depositing most of the fresh water on the Earth. It provides water f ...
, with the most rain along the west coast of the South Island and the least on the east coast of the South Island and interior basins, predominantly on the Canterbury Plains
The Canterbury Plains () are an area in New Zealand centred in the Mid Canterbury, to the south of the city of Christchurch in the Canterbury region. Their northern extremes are at the foot of the Hundalee Hills in the Hurunui District, and in t ...
and the Central Otago Basin (about ). Christchurch is the driest city, receiving about of rain PA, while Hamilton Hamilton may refer to:
People
* Hamilton (name), a common British surname and occasional given name, usually of Scottish origin, including a list of persons with the surname
** The Duke of Hamilton, the premier peer of Scotland
** Lord Hamilto ...
is the wettest, receiving more than twice that amount at PA, followed closely by Auckland. The wettest area by far is the rugged Fiordland region, in the south-west of the South Island, which has between of rain PA, with up to 15,000 mm in isolated valleys, amongst the highest recorded rainfalls in the world.
 The UV index can be very high and extreme in the hottest times of the year in the north of the North Island. This is partly due to the country's relatively little air pollution compared to many other countries and the high sunshine hours. New Zealand has very high sunshine hours with most areas receiving over 2000 hours per year. The sunniest areas are Nelson/Marlborough and the Bay of Plenty with 2,400 hours per year.
The table below lists climate normals for the warmest and coldest months in New Zealand's six largest cities. North Island cities are generally warmest in February. South Island cities are warmest in January.
The combined effects of climate change, effects of climate change in New Zealand will result in a multitude of irreversible impacts; by the end of this century New Zealand will experience higher rainfalls, more frequent extreme weather events and higher temperatures. In 2021, the Ministry for the Environment (New Zealand), Ministry for the Environment estimated that New Zealand's gross emissions were 0.17% of the world's total gross greenhouse gas emissions. However, on a per capita basis, New Zealand is a significant emitter, the sixth highest within the Kyoto Protocol#Annex I countries, Annex I countries, whereas on absolute gross emissions New Zealand is ranked as the 24th highest emitter.
The UV index can be very high and extreme in the hottest times of the year in the north of the North Island. This is partly due to the country's relatively little air pollution compared to many other countries and the high sunshine hours. New Zealand has very high sunshine hours with most areas receiving over 2000 hours per year. The sunniest areas are Nelson/Marlborough and the Bay of Plenty with 2,400 hours per year.
The table below lists climate normals for the warmest and coldest months in New Zealand's six largest cities. North Island cities are generally warmest in February. South Island cities are warmest in January.
The combined effects of climate change, effects of climate change in New Zealand will result in a multitude of irreversible impacts; by the end of this century New Zealand will experience higher rainfalls, more frequent extreme weather events and higher temperatures. In 2021, the Ministry for the Environment (New Zealand), Ministry for the Environment estimated that New Zealand's gross emissions were 0.17% of the world's total gross greenhouse gas emissions. However, on a per capita basis, New Zealand is a significant emitter, the sixth highest within the Kyoto Protocol#Annex I countries, Annex I countries, whereas on absolute gross emissions New Zealand is ranked as the 24th highest emitter.
Human geography
Political geography
New Zealand has no land borders. However, the Ross Dependency, its claim in Antarctica, notionally borders the Australian Antarctic Territory to the west and Marie Byrd Land, unclaimed territory to the east. Most other countries do not recognise territorial claims in Antarctica. New Zealand wikt:proper, proper is divided administratively into regions of New Zealand, sixteen regions: seven in the South Island and nine in the North. They have a physical geographical link with regional boundaries being based largely on drainage basins. Among the regions, eleven are administered by regional authorities (top tier of local government in New Zealand, local government), while five are unitary authorities that combine the functions of regional authorities and those of territorial authorities (second tier). Regional authorities are primarily responsible for environmental resource management, land management, regional transport in New Zealand, transport, and biosecurity and pest management. Territorial authorities administer local roading and reserves, waste management, building consents, the land use and subdivision aspects of resource management, and other local matters. The Chatham Islands is not a region, although its council operates as a region under the Resource Management Act 1991, Resource Management Act. There are a number of outlying islands that are not included within regional boundaries. The Kermadec Islands, Kermadecs and the New Zealand Subantarctic Islands, Subantarctic Islands are inhabited only by a small number of New Zealand Department of Conservation, Department of Conservation staff.Population geography
 The South Island contains a little under one-quarter of the population. Over three-quarters of New Zealand's population live in the North Island, with half living north of Lake Rotorua, and one-third of the total population living in the Auckland Region. Auckland is also the fastest growing region, accounting for 51% of New Zealand's total population growth (in the two decades up to 2016). The majority of the indigenous Māori people live in the North Island (87%), although a little under a quarter (24%) live in Auckland. New Zealand is a predominantly urban country, with % of the population living in an urban areas of New Zealand, urban area. About % of the population live in the 20 main urban areas (population of 30,000 or more) and % live in the four largest cities of
The South Island contains a little under one-quarter of the population. Over three-quarters of New Zealand's population live in the North Island, with half living north of Lake Rotorua, and one-third of the total population living in the Auckland Region. Auckland is also the fastest growing region, accounting for 51% of New Zealand's total population growth (in the two decades up to 2016). The majority of the indigenous Māori people live in the North Island (87%), although a little under a quarter (24%) live in Auckland. New Zealand is a predominantly urban country, with % of the population living in an urban areas of New Zealand, urban area. About % of the population live in the 20 main urban areas (population of 30,000 or more) and % live in the four largest cities of Auckland
Auckland (pronounced ) ( mi, Tāmaki Makaurau) is a large metropolitan city in the North Island of New Zealand. The most populous urban area in the country and the fifth largest city in Oceania, Auckland has an urban population of about I ...
, Christchurch, Wellington
Wellington ( mi, Te Whanganui-a-Tara or ) is the capital city of New Zealand. It is located at the south-western tip of the North Island, between Cook Strait and the Remutaka Range. Wellington is the second-largest city in New Zealand by ...
, and Hamilton Hamilton may refer to:
People
* Hamilton (name), a common British surname and occasional given name, usually of Scottish origin, including a list of persons with the surname
** The Duke of Hamilton, the premier peer of Scotland
** Lord Hamilto ...
. (Other major urban areas include Tauranga, Dunedin, and Palmerston North.) New Zealand's population density of around inhabitants per square kilometres (or per ) is List of countries and dependencies by population density, among the lowest in the world.
New Zealand's peoples have been defined by their immigrant origin, the ongoing process of adaptation to a new land, being changed and changing those who came before. This process has led to a distinct distribution of culture across New Zealand. Here language and religion are used as markers for the far richer concept of culture. These metrics unfortunately exclude the political rural-urban divide and also the full effects of the Christchurch earthquakes on New Zealand's cultural distribution.
New Zealand's most widely spoken language is English (89.8%), however, language, dialect and accent varies spatially both within and between List of ethnic origins of New Zealanders, ethnic groups. The Māori language (3.5%) is spoken more commonly in areas with large Māori populations (Gisborne District, Gisborne, Bay of Plenty and Northland). There are many sub dialects of Māori, the most pronounced division being between the northern and southern iwi, tribes. While migration (typically from north to south) was constant throughout the 16–18th centuries, the south maintained a distinct culture largely due to lack of cultivation possible at that latitude. English is spoken with regional Accent (sociolinguistics), accents relating to the origin of immigrants; for example Scottish and English 19th century immigration in Southland, New Zealand, Southland and Canterbury Region, Canterbury respectively. This has also occurred with more recent immigration, with a wide variety of accents being common in larger cities where immigrant groups have preferentially settled. These immigrant groups change location with time and accents fade over generations.
A wide variety of other languages make up the remaining approximately 6 percent of New Zealanders—with Samoan language, Samoan, Hindi, French and various Chinese dialects being the most common. These minority foreign languages are concentrated in the main cities, particularly Auckland where recent immigration groups have settled.
Agricultural geography
A relatively small proportion of New Zealand's land is arable land, arable (1.76 percent), and permanent crops cover 0.27 percent of the land. of the land is irrigation, irrigated. As the world's largest exporter of sheep, New Zealand's agricultural industry focuses primarily on pastoral farming, particularly dairy and beef, as well as lambs. Dairy, specifically, is the top export. In addition to pastoral farming, fisherman harvest mussels, oysters and salmon, and horticulture farmers grow kiwifruit, as well as peaches, nectarines, etc. New Zealand's distance from world markets and spatial variation in rainfall, elevation and soil quality have defined the geography of its agriculture industry. As of 2007, almost 55 percent of New Zealand's total land area was being used for farming, which is standard compared to most developed countries. Three-fourths of it was pastoral land using for raising sheep, beef, deer, etc. The amount of farmland has decreased since 2002. New Zealand's isolated location has simultaneously led to fewer Pest (organism), pests and an agriculture industry with a greater susceptibility to introduced diseases and pests. A major concern for New Zealand farmers is the rapidly growing wild rabbit population. Wild rabbits have been an agricultural since their introduction to the country in the 1930s. They cause significant damage to farm lands: eating the grass, crops, and causing soil retrogression and degradation, soil degradation. Many farmers are worried about their livelihoods and the effects that the rabbits will have on food supply and trade, as their numbers are quickly growing out of control. An illegal rabbit-killing virus called the rabbit haemorrhagic disease virus (RHDV) was released in 1997 by a group of vigilante farmers, and was very effective initially. After twenty years, however, the rabbits became immune to it. A new strain of the virus was released in March 2018, a Korean form of the strain called the K5 virus, or RHDV1-K5. This virus was introduced with the goal of exterminating 40 percent of the rabbit population. The new virus works much faster than the last one, expected to kill rabbits within two to four days of exposure. The virus has become a subject of debate among animal rights activists, due to the inhumane manner in which it kills the rabbits. However, farmers unanimously seem to be very grateful for the release of the virus. Almost half of New Zealand's climate change emissions are generated by greenhouse gases, mainly methane and nitrous oxide, which come from farming and agriculture. Organisms that grow inside of grazing animals' stomachs turn New Zealand's grass into methane. The increase of carbon dioxide in the air helps the plants to grow faster, but the long-term effects of climate change threaten farmers with the likelihood of more frequent and severe floods and droughts. Kiwifruit industry in New Zealand, Growers of kiwifruit, a major export in the horticulture industry of New Zealand, have experienced difficulties as a result of climate change. In the 2010s, warm winters did not provide the adequate cool temperatures needed for the flowering of kiwifruit, and this resulted in a reduction of the yield sizes. Droughts have also decreased apple production by causing sunburns and a lack of water available for irrigation. In contrast, the Dairy farming in New Zealand, dairy industry has not been affected, and has actually adjusted well to the effects of climate change.
Almost half of New Zealand's climate change emissions are generated by greenhouse gases, mainly methane and nitrous oxide, which come from farming and agriculture. Organisms that grow inside of grazing animals' stomachs turn New Zealand's grass into methane. The increase of carbon dioxide in the air helps the plants to grow faster, but the long-term effects of climate change threaten farmers with the likelihood of more frequent and severe floods and droughts. Kiwifruit industry in New Zealand, Growers of kiwifruit, a major export in the horticulture industry of New Zealand, have experienced difficulties as a result of climate change. In the 2010s, warm winters did not provide the adequate cool temperatures needed for the flowering of kiwifruit, and this resulted in a reduction of the yield sizes. Droughts have also decreased apple production by causing sunburns and a lack of water available for irrigation. In contrast, the Dairy farming in New Zealand, dairy industry has not been affected, and has actually adjusted well to the effects of climate change.
Natural hazards
Flooding is the most regular natural hazard. New Zealand is swept by weather systems that bring heavy rain; settlements are usually close to hill-country areas which experience much higher rainfall than the lowlands due to the Orographic precipitation, orographic effect. Mountain streams which feed the major rivers rise rapidly and frequently break their banks covering farms with water and silt. Close monitoring, weather forecasting, wikt:stopbank, stopbanks, dams, and reafforestation programmes in hill country have ameliorated the worst effects. New Zealand List of earthquakes in New Zealand, experiences around 14,000 earthquakes a year, some in excess of earthquake magnitude, magnitude 7 (M7). Since the 2010, several large (M7, M6.3, M6.4, M6.2) and shallow (all <7 km) earthquakes have occurred immediately beneath Christchurch. These have resulted in 185 deaths, widespread destruction of buildings and significant liquefaction. These earthquakes are releasing distributed stress in the Pacific plate from the ongoing collision with the Indo-Australian plate to the west and north of the city. Volcanic activity is most common on the central North Island Volcanic Plateau. Tsunamis affecting New Zealand are associated with the Pacific Ring of Fire. Droughts are not regular and occur mainly in Otago and the Canterbury Plains and less frequently over much of the North Island between January and April. Forest fires were rare in New Zealand before the arrival of humans. During a designated summer season, lighting a fire in the open is banned on public conservation land.Environment and ecology
Protected areas
Some areas of land, the sea, rivers or lakes are protected area, protected by law, so their special plants, animals, landforms and other distinctive features are sheltered from harm. New Zealand has three List of World Heritage Sites in Oceania, World Heritage Sites, 13 national parks of New Zealand, national parks, 34 marine reserves of New Zealand, marine reserves, and thousands of scenic, historic, recreation and other reserves. The Department of Conservation (New Zealand), Department of Conservation is responsible for managing 8.5 million hectares of public land (approximately 30% of New Zealand's total land area).Environmental agreements
New Zealand is party to several multilateral environmental agreements. The major agreements are listed below. * Antarctic-Environmental Protocol * Antarctic Treaty * Basel Convention * Convention on Biological Diversity * Convention on International Trade in Endangered Species * International Convention for the Prevention of Pollution from Ships * United Nations Convention to Combat Desertification * London Convention on the Prevention of Marine Pollution by Dumping of Wastes and Other Matter, London Dumping Convention * Kyoto Protocol * Minamata Convention on Mercury * Environmental Modification Convention * Pacific Regional Environment Programme, Nouméa Convention * Ramsar Convention * Rotterdam Convention * United Nations Convention on the Law of the Sea * International Tropical Timber Agreement, 1994 * Stockholm Convention on Persistent Organic Pollutants * United Nations Framework Convention on Climate Change * Vienna Convention for the Protection of the Ozone Layer * Waigani Convention * International Convention for the Regulation of WhalingPopular culture
New Zealand's varied landscape has appeared in television shows, such as ''Hercules: The Legendary Journeys'' and ''Xena: Warrior Princess''. An increasing number of feature films have been shot on location in New Zealand for its scenery, including the The Lord of the Rings (film series), ''Lord of the Rings'' trilogy. New Zealand is often mistakenly omitted from world maps due to the country's physical geographic isolation, relatively small size (compared to Australia), and its positioning on the extreme bottom-right in many maps projections such as the Mercator projection, Mercator. The phenomenon has been popularly referenced and has a dedicated Reddit forum.See also
* Archaeology of New Zealand * Natural history of New Zealand * Geography of South Island * Geography of North IslandReferences
External links
Statistics New Zealand
profile at World Atlas
Natural Environment
– Te Ara: The Encyclopedia of New Zealand
New Zealand's Geological History
– 1966 Encyclopaedia of New Zealand {{DEFAULTSORT:Geography of New Zealand Geography of New Zealand,