Geography of Jarvis Island on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Jarvis Island (; formerly known as Bunker Island or Bunker's Shoal) is an uninhabited
 While a few offshore anchorage spots are marked on maps, Jarvis island has no ports or harbors, and swift currents are a hazard. There is a boat landing area in the middle of the western shoreline near a crumbling
While a few offshore anchorage spots are marked on maps, Jarvis island has no ports or harbors, and swift currents are a hazard. There is a boat landing area in the middle of the western shoreline near a crumbling

 New Zealand
New Zealand
 On August 30, 1913, the
On August 30, 1913, the
 Jarvis Island was reclaimed by the United States government and colonized from March 26, 1935, onwards, under the
Jarvis Island was reclaimed by the United States government and colonized from March 26, 1935, onwards, under the 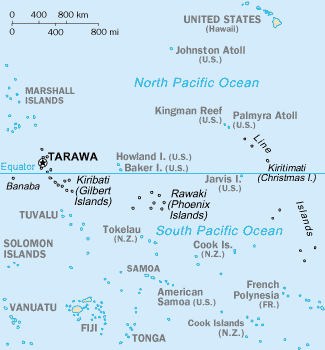
 On June 27, 1974, Secretary of the Interior
On June 27, 1974, Secretary of the Interior
Jarvis Island Home Page
Website with photos, weather, and more.
Jarvis Island information website
Has several photos of the old Millersville settlement, together with more modern photos of the island.
Offers brief data on Jarvis island.
U.S. Fish & Wildlife Service Jarvis Island National Wildlife Refuge
The Jarvis Island refuge site. {{Lighthouse identifiers , qid2=Q33417143 Pacific islands claimed under the Guano Islands Act Pacific Remote Islands Marine National Monument Former populated places in Oceania Uninhabited Pacific islands of the United States Island restoration Pacific Ocean atolls of the United States United States Minor Outlying Islands National Wildlife Refuges in the United States insular areas Protected areas established in 1974 Coral islands 1889 establishments in the British Empire Important Bird Areas of United States Minor Outlying Islands Important Bird Areas of the Line Islands Seabird colonies
coral island
A coral island is a type of island formed from coral detritus and associated organic material. It occurs in tropical and sub-tropical areas, typically as part of a coral reef which has grown to cover a far larger area under the sea.
Ecosystem
...
located in the South Pacific Ocean
The Pacific Ocean is the largest and deepest of Earth's five oceanic divisions. It extends from the Arctic Ocean in the north to the Southern Ocean (or, depending on definition, to Antarctica) in the south, and is bounded by the contin ...
, about halfway between Hawaii
Hawaii ( ; haw, Hawaii or ) is a state in the Western United States, located in the Pacific Ocean about from the U.S. mainland. It is the only U.S. state outside North America, the only state that is an archipelago, and the only state ...
and the Cook Islands
)
, image_map = Cook Islands on the globe (small islands magnified) (Polynesia centered).svg
, capital = Avarua
, coordinates =
, largest_city = Avarua
, official_languages =
, lan ...
. It is an unincorporated, unorganized territory of the United States, administered by the United States Fish and Wildlife Service
The United States Fish and Wildlife Service (USFWS or FWS) is an agency within the United States Department of the Interior dedicated to the management of fish, wildlife, and natural habitats. The mission of the agency is "working with othe ...
of the United States Department of the Interior
The United States Department of the Interior (DOI) is one of the executive departments of the U.S. federal government headquartered at the Main Interior Building, located at 1849 C Street NW in Washington, D.C. It is responsible for the ma ...
as part of the National Wildlife Refuge system. Unlike most coral atolls, the lagoon
A lagoon is a shallow body of water separated from a larger body of water by a narrow landform, such as reefs, barrier islands, barrier peninsulas, or isthmuses. Lagoons are commonly divided into ''coastal lagoons'' (or ''barrier lagoons'') ...
on Jarvis is wholly dry.
Jarvis is one of the Line Islands and for statistical purposes is also grouped as one of the United States Minor Outlying Islands
The United States Minor Outlying Islands is a statistical designation defined by the International Organization for Standardization's ISO 3166-1 code. The entry code is ISO 3166-2:UM. The minor outlying islands and groups of islands consist ...
. Jarvis Island is the largest of three U.S. equatorial possessions, which include Baker Island
Baker Island, formerly known as New Nantucket, is an uninhabited atoll just north of the Equator in the central Pacific Ocean about southwest of Honolulu. The island lies almost halfway between Hawaii and Australia. Its nearest neighbor is H ...
and Howland Island
Howland Island () is an uninhabited coral island located just north of the equator in the central Pacific Ocean, about southwest of Honolulu. The island lies almost halfway between Hawaii and Australia and is an unorganized, unincorporated ter ...
.
Geography and ecology
day beacon
A day beacon (sometimes "daybeacon") is an unlighted nautical sea mark. A signboard identifying it is called a day mark. Day beacons typically mark channels whose key points are marked by lighted buoys. They may also mark smaller navigable rout ...
, and another near the southwest corner of the island. The center of Jarvis island is a dried lagoon
A lagoon is a shallow body of water separated from a larger body of water by a narrow landform, such as reefs, barrier islands, barrier peninsulas, or isthmuses. Lagoons are commonly divided into ''coastal lagoons'' (or ''barrier lagoons'') ...
where deep guano deposits accumulated, which were mined for about 20 years during the nineteenth century. The island has a tropical desert climate, with high daytime temperatures, constant wind, and strong sun. Nights, however, are quite cool. The ground is mostly sandy and reaches 23 feet (7 meters) at its highest point. The low-lying coral island has long been noted as hard to sight from small ships and is surrounded by a narrow fringing reef
A fringing reef is one of the three main types of coral reef. It is distinguished from the other main types, barrier reefs and atolls, in that it has either an entirely shallow backreef zone (lagoon) or none at all. If a fringing reef grows direc ...
.
Jarvis Island is one of two United States territories that are in the southern hemisphere (the other is American Samoa
American Samoa ( sm, Amerika Sāmoa, ; also ' or ') is an unincorporated territory of the United States located in the South Pacific Ocean, southeast of the island country of Samoa. Its location is centered on . It is east of the Internationa ...
). Located only south of the equator, Jarvis has no known natural freshwater lens and scant rainfall
Rain is water droplets that have condensed from atmospheric water vapor and then fall under gravity. Rain is a major component of the water cycle and is responsible for depositing most of the fresh water on the Earth. It provides water f ...
. This creates a very bleak, flat landscape without any plants larger than shrubs. There is no evidence that the island has ever supported a self-sustaining human population. Its sparse bunch grass
Tussock grasses or bunch grasses are a group of grass species in the family Poaceae. They usually grow as singular plants in clumps, tufts, hummocks, or bunches, rather than forming a sod or lawn, in meadows, grasslands, and prairies. As perennia ...
, prostrate vine
A vine (Latin ''vīnea'' "grapevine", "vineyard", from ''vīnum'' "wine") is any plant with a growth habit of trailing or scandent (that is, climbing) stems, lianas or runners. The word ''vine'' can also refer to such stems or runners themsel ...
s and low-growing shrubs are primarily a nesting, roosting, and foraging habitat
In ecology, the term habitat summarises the array of resources, physical and biotic factors that are present in an area, such as to support the survival and reproduction of a particular species. A species habitat can be seen as the physical ...
for seabirds, shorebirds, and marine wildlife.
Jarvis Island was submerged underwater during the latest interglacial period, roughly 125,000 years ago, when sea levels were higher than today. As the sea level declined, the horseshoe-shaped lagoon was formed in the center of Jarvis Island.
Topographic isolation
Jarvis Island's highest point has atopographic isolation
The topographic isolation of a summit is the minimum distance to a point of equal elevation, representing a radius of dominance in which the peak is the highest point. It can be calculated for small hills and islands as well as for major mounta ...
of , with Joe's Hill on Kiritimati
Kiritimati (also known as Christmas Island) is a Pacific Ocean atoll in the northern Line Islands. It is part of the Republic of Kiribati. The name is derived from the English word "Christmas" written in Gilbertese according to its phonolog ...
being the nearest higher neighbor.
Time zone
Jarvis Island is located in theSamoa Time Zone
250px, SST is UTC-11:00
The Samoa Time Zone or Samoa Standard Time (SST) observes standard time by subtracting eleven hours from Coordinated Universal Time ( UTC-11:00). The clock time in this zone is based on the mean solar time of the 165t ...
(UTC -11:00), the same time zone
A time zone is an area which observes a uniform standard time for legal, commercial and social purposes. Time zones tend to follow the boundaries between countries and their subdivisions instead of strictly following longitude, because it ...
as American Samoa
American Samoa ( sm, Amerika Sāmoa, ; also ' or ') is an unincorporated territory of the United States located in the South Pacific Ocean, southeast of the island country of Samoa. Its location is centered on . It is east of the Internationa ...
, Kingman Reef
Kingman Reef is a largely submerged, uninhabited, triangle-shaped reef, geologically an atoll, east-west and north-south, in the North Pacific Ocean, roughly halfway between the Hawaiian Islands and American Samoa. It has an area of 3 hectar ...
, Midway Atoll, and Palmyra Atoll
Palmyra Atoll (), also referred to as Palmyra Island, is one of the Northern Line Islands (southeast of Kingman Reef and north of Kiribati). It is located almost due south of the Hawaiian Islands, roughly one-third of the way between Hawaii a ...
.
Birds
Jarvis Island once held some of the largestseabird
Seabirds (also known as marine birds) are birds that are adapted to life within the marine environment. While seabirds vary greatly in lifestyle, behaviour and physiology, they often exhibit striking convergent evolution, as the same enviro ...
breeding colonies in the tropical ocean, but guano mining and the introduction of rodents have ruined much of the island's native wildlife. Just eight breeding species were recorded in 1982, compared to thirteen in 1996, and fourteen species in 2004. The Polynesian storm petrel
The Polynesian storm petrel (''Nesofregetta fuliginosa'') is a species of seabird in the family Oceanitidae. It is the only species placed in the genus ''Nesofregetta''.
Markedly polymorphic, several subspecies were described, and light birds w ...
had made its return after over 40 years absent from Jarvis Island, and the number of Brown noddies multiplied from just a few birds in 1982 to nearly 10,000. Just twelve Gray-backed terns were recorded in 1982, but by 2004, over 200 nests were found on there. The island, with its surrounding marine waters, has been recognized as an Important Bird Area (IBA) by BirdLife International because it supports colonies
In modern parlance, a colony is a territory subject to a form of foreign rule. Though dominated by the foreign colonizers, colonies remain separate from the administration of the original country of the colonizers, the '' metropolitan state'' ...
of lesser frigatebird
The lesser frigatebird (''Fregata ariel'') is a seabird of the frigatebird family Fregatidae. At around 75 cm (30 in) in length, it is the smallest species of frigatebird. It occurs over tropical and subtropical waters across the Indian ...
s, brown
Brown is a color. It can be considered a composite color, but it is mainly a darker shade of orange. In the CMYK color model used in printing or painting, brown is usually made by combining the colors orange and black. In the RGB color model us ...
and masked boobies, red-tailed tropicbirds, Polynesian storm petrels, blue noddies and sooty terns, as well as serving as a migratory stopover for bristle-thighed curlew
The bristle-thighed curlew (''Numenius tahitiensis'') is a medium-sized shorebird that breeds in Alaska and winters on tropical Pacific islands.
It is known in Mangareva as ''kivi'' or ''kivikivi'' and in Rakahanga as ''kihi''; it is said to be ...
s.
History
Prehistory
Jarvis Island is unlikely to have hosted permanent human occupation prior to its use for guano mining. However, it is possible the island was utilized as a waypoint or stopover island by Polynesian voyagers. The remoteness of the island and a lack of freshwater resources have prevented large scale archaeological survey from taking place.
Discovery
The island's first known sighting by the British on August 21, 1821, by theBritish
British may refer to:
Peoples, culture, and language
* British people, nationals or natives of the United Kingdom, British Overseas Territories, and Crown Dependencies.
** Britishness, the British identity and common culture
* British English, ...
ship '' Eliza Francis'' (or ''Eliza Frances'') owned by Edward, Thomas and William Jarvis and commanded by Captain Brown. The island was visited by whaling vessels till the 1870s.
The U.S. Exploring Expedition
The United States Exploring Expedition of 1838–1842 was an exploring and surveying expedition of the Pacific Ocean and surrounding lands conducted by the United States. The original appointed commanding officer was Commodore Thomas ap Catesby ...
surveyed the island in 1841. In March 1857 the island was claimed for the United States under the Guano Islands Act
The Guano Islands Act (, enacted August 18, 1856, codified at §§ 1411-1419) is a United States federal law passed by the U.S. Congress that enables citizens of the United States to take possession, in the name of the United States, of unclai ...
and formally annexed on February 27, 1858.
Nineteenth-century guano mining
The American Guano Company, which was incorporated in 1857, established claims in respect of Baker Island and Jarvis Island which was recognized under the U.S.Guano Islands Act
The Guano Islands Act (, enacted August 18, 1856, codified at §§ 1411-1419) is a United States federal law passed by the U.S. Congress that enables citizens of the United States to take possession, in the name of the United States, of unclai ...
of 1856. Beginning in 1858, several support structures were built on Jarvis Island, along with a two-story, eight-room "superintendent's house" featuring an observation cupola
In architecture, a cupola () is a relatively small, most often dome-like, tall structure on top of a building. Often used to provide a lookout or to admit light and air, it usually crowns a larger roof or dome.
The word derives, via Italian, fro ...
and wide verandah
A veranda or verandah is a roofed, open-air gallery or porch, attached to the outside of a building. A veranda is often partly enclosed by a railing and frequently extends across the front and sides of the structure.
Although the form ''vera ...
s. Tram tracks were laid down for bringing mined guano to the western shore
A shore or a shoreline is the fringe of land at the edge of a large body of water, such as an ocean, sea, or lake. In physical oceanography, a shore is the wider fringe that is geologically modified by the action of the body of water past a ...
. One of the first loads was taken by Samuel Gardner Wilder
Samuel Gardner Wilder (June 20, 1831 – July 28, 1888) was an American shipping magnate and politician who developed a major transportation company in the Kingdom of Hawaii.
Life
Samuel Gardner Wilder was born June 20, 1831, in Leominster, ...
.
Laborers for the mining operations came from around the Pacific, including from Hawaii; the Hawaiian laborers named Baker Island "", meaning 'out of breath' or 'exhausted', which is indicative of their working conditions.
For the following 21 years, Jarvis was commercially mined for guano, sent to the United States as fertilizer
A fertilizer (American English) or fertiliser (British English; see spelling differences) is any material of natural or synthetic origin that is applied to soil or to plant tissues to supply plant nutrients. Fertilizers may be distinct from ...
, but the island was abruptly abandoned in 1879, leaving behind about a dozen buildings and of mined guano.
 New Zealand
New Zealand entrepreneur
Entrepreneurship is the creation or extraction of economic value. With this definition, entrepreneurship is viewed as change, generally entailing risk beyond what is normally encountered in starting a business, which may include other values t ...
s, including photographer Henry Winkelmann, then made unsuccessful attempts to continue guano extraction on Jarvis, and the two-storey house was sporadically inhabited during the early 1880s. Squire Flockton was left alone on the island as caretaker for several months and committed suicide there in 1883, apparently from gin-fueled despair. His wooden grave marker
A headstone, tombstone, or gravestone is a stele or marker, usually stone, that is placed over a grave. It is traditional for burials in the Christian, Jewish, and Muslim religions, among others. In most cases, it has the deceased's name, da ...
was a carved plank which could be seen in the island's tiny four-grave cemetery
A cemetery, burial ground, gravesite or graveyard is a place where the remains of dead people are buried or otherwise interred. The word ''cemetery'' (from Greek , "sleeping place") implies that the land is specifically designated as a buri ...
for decades.
John T. Arundel & Co. resumed mining guano from 1886 to 1899. The United Kingdom annexed the island on June 3, 1889. Phosphate
In chemistry, a phosphate is an anion, salt, functional group or ester derived from a phosphoric acid. It most commonly means orthophosphate, a derivative of orthophosphoric acid .
The phosphate or orthophosphate ion is derived from phosph ...
and copra
Copra (from ) is the dried, white flesh of the coconut from which coconut oil is extracted. Traditionally, the coconuts are sun-dried, especially for export, before the oil, also known as copra oil, is pressed out. The oil extracted from co ...
entrepreneur John T. Arundel
John T. Arundel (1 September 1841 – 30 November 1919) was an English entrepreneur who was instrumental in the development of the mining of phosphate rock on the Pacific islands of Nauru and Banaba (Ocean Island). Williams & Macdonald (1985) ...
visited the island in 1909 on maiden voyage of the ''S.S. Ocean Queen'' and near the beach landing on the western shore members of the crew built a pyramidal day beacon
A day beacon (sometimes "daybeacon") is an unlighted nautical sea mark. A signboard identifying it is called a day mark. Day beacons typically mark channels whose key points are marked by lighted buoys. They may also mark smaller navigable rout ...
made from slats of wood, which was painted white. The beacon was standing in 1935, and remained until at least 1942.
Wreck of barquentine ''Amaranth''
 On August 30, 1913, the
On August 30, 1913, the barquentine
A barquentine or schooner barque (alternatively "barkentine" or "schooner bark") is a sailing vessel with three or more masts; with a square rigged foremast and fore-and-aft rigged main, mizzen and any other masts.
Modern barquentine sailing ...
'' Amaranth'' (C. W. Nielson, captain) was carrying a cargo of coal
Coal is a combustible black or brownish-black sedimentary rock, formed as rock strata called coal seams. Coal is mostly carbon with variable amounts of other elements, chiefly hydrogen, sulfur, oxygen, and nitrogen.
Coal is formed when ...
from Newcastle, New South Wales
Newcastle ( ; Awabakal: ) is a metropolitan area and the second most populated city in the state of New South Wales, Australia. It includes the Newcastle and Lake Macquarie local government areas, and is the hub of the Greater Newcastle area ...
, to San Francisco
San Francisco (; Spanish for " Saint Francis"), officially the City and County of San Francisco, is the commercial, financial, and cultural center of Northern California. The city proper is the fourth most populous in California and 17th ...
when it wrecked on Jarvis' southern shore. Ruins of ten wooden guano-mining buildings, the two-story house among them, could still be seen by the ''Amaranth'' crew, who left Jarvis aboard two lifeboat
Lifeboat may refer to:
Rescue vessels
* Lifeboat (shipboard), a small craft aboard a ship to allow for emergency escape
* Lifeboat (rescue), a boat designed for sea rescues
* Airborne lifeboat, an air-dropped boat used to save downed airmen
...
s. One reached Pago Pago
Pago Pago ( ; Samoan: )Harris, Ann G. and Esther Tuttle (2004). ''Geology of National Parks''. Kendall Hunt. Page 604. . is the territorial capital of American Samoa. It is in Maoputasi County on Tutuila, which is American Samoa's main island. ...
, American Samoa
American Samoa ( sm, Amerika Sāmoa, ; also ' or ') is an unincorporated territory of the United States located in the South Pacific Ocean, southeast of the island country of Samoa. Its location is centered on . It is east of the Internationa ...
, and the other made Apia
Apia () is the capital and largest city of Samoa, as well as the nation's only city. It is located on the central north coast of Upolu, Samoa's second-largest island. Apia falls within the political district (''itūmālō'') of Tuamasaga.
...
in Western Samoa
Samoa, officially the Independent State of Samoa; sm, Sāmoa, and until 1997 known as Western Samoa, is a Polynesian island country consisting of two main islands ( Savai'i and Upolu); two smaller, inhabited islands ( Manono and Apolima); ...
. The ship's scattered remains were noted and scavenged for many years, and rounded fragments of coal from the ''Amaranths hold
Hold may refer to:
Physical spaces
* Hold (ship), interior cargo space
* Baggage hold, cargo space on an airplane
* Stronghold, a castle or other fortified place
Arts, entertainment, and media
* Hold (musical term), a pause, also called a Ferm ...
were still being found on the south beach in the late 1930s.
Millersville (1935–1942)
 Jarvis Island was reclaimed by the United States government and colonized from March 26, 1935, onwards, under the
Jarvis Island was reclaimed by the United States government and colonized from March 26, 1935, onwards, under the American Equatorial Islands Colonization Project
The American Equatorial Islands Colonization Project was a plan initiated in 1935 by the U.S. Department of Commerce to place citizens of the United States on uninhabited Howland, Baker and Jarvis islands in the central Pacific Ocean so that we ...
. President Franklin D. Roosevelt
Franklin Delano Roosevelt (; ; January 30, 1882April 12, 1945), often referred to by his initials FDR, was an American politician and attorney who served as the 32nd president of the United States from 1933 until his death in 1945. As the ...
assigned administration of the island to the U.S. Department of the Interior
The United States Department of the Interior (DOI) is one of the executive departments of the U.S. federal government headquartered at the Main Interior Building, located at 1849 C Street NW in Washington, D.C. It is responsible for the man ...
on May 13, 1936. Starting out as a cluster of large, open tents pitched next to the still-standing white wooden day beacon, the Millersville settlement
Settlement may refer to:
*Human settlement, a community where people live
*Settlement (structural), the distortion or disruption of parts of a building
* Closing (real estate), the final step in executing a real estate transaction
*Settlement (fin ...
on the island's western shore was named after a bureaucrat
A bureaucrat is a member of a bureaucracy and can compose the administration of any organization of any size, although the term usually connotes someone within an institution of government.
The term ''bureaucrat'' derives from "bureaucracy", w ...
with the United States Department of Air Commerce. The settlement grew into a group of shacks built mostly with wreckage from the ''Amaranth'' (lumber from which was also used by the young Hawaii
Hawaii ( ; haw, Hawaii or ) is a state in the Western United States, located in the Pacific Ocean about from the U.S. mainland. It is the only U.S. state outside North America, the only state that is an archipelago, and the only state ...
an colonists to build surfboards), but later, stone and wood dwellings were built and equipped with refrigeration, radio equipment, and a weather station. A crude aircraft landing area was cleared on the northeast side of the island, and a T-shaped marker which was intended to be seen from the air was made from gathered stones, but no airplane is known to have ever landed there. According to the 1940 U.S. Census
The United States census of 1940, conducted by the United States Census Bureau, Census Bureau, determined the resident population of the United States to be 132,164,569, an increase of 7.3 percent over the 1930 United States Census, 1930 populat ...
, Jarvis Island had a population of three people.
At the beginning of World War II
World War II or the Second World War, often abbreviated as WWII or WW2, was a world war that lasted from 1939 to 1945. It involved the vast majority of the world's countries—including all of the great powers—forming two opposing ...
, an Imperial Japanese Navy
The Imperial Japanese Navy (IJN; Kyūjitai: Shinjitai: ' 'Navy of the Greater Japanese Empire', or ''Nippon Kaigun'', 'Japanese Navy') was the navy of the Empire of Japan from 1868 to 1945, when it was dissolved following Japan's surrend ...
submarine surfaced off the west coast of the island. Believing that it was a U.S. Navy
The United States Navy (USN) is the maritime service branch of the United States Armed Forces and one of the eight uniformed services of the United States. It is the largest and most powerful navy in the world, with the estimated tonnage o ...
submarine which had come to fetch them, the four young colonists rushed down the steep western beach in front of Millersville towards the shore. The submarine answered their waves with fire from its deck gun, but no one was hurt in the attack. On February 7, 1942, the USCGC ''Taney'' evacuated the colonists, then shelled and burned the dwellings. The roughly cleared landing area on the island's northeast end was later shelled by the Japanese, leaving crater holes.

International Geophysical Year
Jarvis was visited by scientists during the International Geophysical Year from July 1957 until November 1958. In January 1958 all scattered building ruins from both the nineteenth century guano diggings and the 1935–1942 colonization attempt were swept away without a trace by a severe storm which lasted several days and was witnessed by the scientists. When the IGY research project ended the island was abandoned again. By the early 1960s a few sheds, a century of accumulated trash, the scientists' house from the late 1950s and a solid, short lighthouse-likeday beacon
A day beacon (sometimes "daybeacon") is an unlighted nautical sea mark. A signboard identifying it is called a day mark. Day beacons typically mark channels whose key points are marked by lighted buoys. They may also mark smaller navigable rout ...
built two decades before were the only signs of human habitation on Jarvis.
National Wildlife Refuge
 On June 27, 1974, Secretary of the Interior
On June 27, 1974, Secretary of the Interior Rogers Morton
Rogers Clark Ballard Morton (September 19, 1914 – April 19, 1979) was an American politician who served as the U.S. Secretary of the Interior and Secretary of Commerce during the administrations of presidents Richard Nixon and Gerald Ford, ...
created Jarvis Island National Wildlife Refuge which was expanded in 2009 to add submerged lands within of the island. The refuge now includes of land and of water. Along with six other islands, the island was administered by the U.S. Fish and Wildlife Service
The United States Fish and Wildlife Service (USFWS or FWS) is an agency within the United States Department of the Interior dedicated to the management of fish, wildlife, and natural habitats. The mission of the agency is "working with othe ...
as part of the Pacific Remote Islands National Wildlife Refuge Complex. In January 2009, that entity was upgraded to the Pacific Remote Islands Marine National Monument
The Pacific Remote Islands Marine National Monument is a group of unorganized, mostly unincorporated United States Pacific Island territories managed by the United States Fish and Wildlife Service of the United States Department of the Int ...
by President George W. Bush
George Walker Bush (born July 6, 1946) is an American politician who served as the 43rd president of the United States from 2001 to 2009. A member of the Republican Party, Bush family, and son of the 41st president George H. W. Bush, he ...
.
A feral cat
A feral cat or a stray cat is an unowned domestic cat (''Felis catus'') that lives outdoors and avoids human contact: it does not allow itself to be handled or touched, and usually remains hidden from humans. Feral cats may breed over dozens ...
population, descendants of cats likely brought by colonists in the 1930s, wrought disruption to the island's wildlife and vegetation. These cats were removed through efforts which began in the mid-1960s and lasted until 1990 when they were completely eradicated. Since cats were removed, seabird numbers and diversity have increased.
Nineteenth-century tram track remains can be seen in the dried lagoon bed at the island's center and the late 1930s-era lighthouse-shaped day beacon
A day beacon (sometimes "daybeacon") is an unlighted nautical sea mark. A signboard identifying it is called a day mark. Day beacons typically mark channels whose key points are marked by lighted buoys. They may also mark smaller navigable rout ...
still stands on the western shore at the site of Millersville.
Public entry to anyone, including U.S. citizens, on Jarvis Island requires a special-use permit and is generally restricted to scientists and educators. The U.S. Fish and Wildlife Service and the United States Coast Guard
The United States Coast Guard (USCG) is the maritime security, search and rescue, and law enforcement service branch of the United States Armed Forces and one of the country's eight uniformed services. The service is a maritime, military, mu ...
periodically visit Jarvis.
Transportation
There is no airport on the island, nor does the island contain any large terminal or port. There is a day beacon near the middle of the west coast. Some offshore anchorage is available.Military
As a U.S. territory, the defense of Jarvis Island is the responsibility of the United States. All laws of the United States are applicable on the island.See also
*Howland and Baker islands
Howland Island and Baker Island are two uninhabited U.S. atolls in the Equatorial Pacific that are located close to one another. Both islands are wildlife refuges, the larger of which is Howland Island. They are both part of the larger politi ...
* List of Guano Island claims
The United States claimed a number of islands as insular areas under the Guano Islands Act of 1856. Only the eight administered as the US Minor Islands and the ones part of Hawaii and American Samoa remain under the jurisdiction of the United Stat ...
* '' Under a Jarvis Moon'', an 88-minute 2010 documentary
References
External links
Jarvis Island Home Page
Website with photos, weather, and more.
Jarvis Island information website
Has several photos of the old Millersville settlement, together with more modern photos of the island.
Offers brief data on Jarvis island.
U.S. Fish & Wildlife Service Jarvis Island National Wildlife Refuge
The Jarvis Island refuge site. {{Lighthouse identifiers , qid2=Q33417143 Pacific islands claimed under the Guano Islands Act Pacific Remote Islands Marine National Monument Former populated places in Oceania Uninhabited Pacific islands of the United States Island restoration Pacific Ocean atolls of the United States United States Minor Outlying Islands National Wildlife Refuges in the United States insular areas Protected areas established in 1974 Coral islands 1889 establishments in the British Empire Important Bird Areas of United States Minor Outlying Islands Important Bird Areas of the Line Islands Seabird colonies