Geography of Chennai on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]

/ref> Moreover, newer projects like the

Chennai
Chennai (, ), formerly known as Madras ( the official name until 1996), is the capital city of Tamil Nadu, the southernmost Indian state. The largest city of the state in area and population, Chennai is located on the Coromandel Coast of th ...
is located at on the southeast coast of India and in the northeast corner of Tamil Nadu
Tamil Nadu (; , TN) is a States and union territories of India, state in southern India. It is the List of states and union territories of India by area, tenth largest Indian state by area and the List of states and union territories of India ...
. It is located on a flat coastal plain known as the Eastern Coastal Plains
The Eastern Coastal Plains is a wide stretch of landmass of India, lying between the Eastern Ghats and the Bay of Bengal. It is wider and leveled than the Western Coastal Plains and stretches from Tamil Nadu in the south to West Bengal in the n ...
. The city has an average elevation of , its highest point being . Chennai is 2,184 kilometres (1,357 mi) south of Delhi
Delhi, officially the National Capital Territory (NCT) of Delhi, is a city and a union territory of India containing New Delhi, the capital of India. Straddling the Yamuna river, primarily its western or right bank, Delhi shares borders w ...
, 1,337 kilometres (831 mi) southeast of Mumbai
Mumbai (, ; also known as Bombay — the official name until 1995) is the capital city of the Indian state of Maharashtra and the ''de facto'' financial centre of India. According to the United Nations, as of 2018, Mumbai is the second- ...
, and 1,679 kilometers (1,043 mi) southwest of Kolkata
Kolkata (, or , ; also known as Calcutta , the official name until 2001) is the capital of the Indian state of West Bengal, on the eastern bank of the Hooghly River west of the border with Bangladesh. It is the primary business, comme ...
by road.

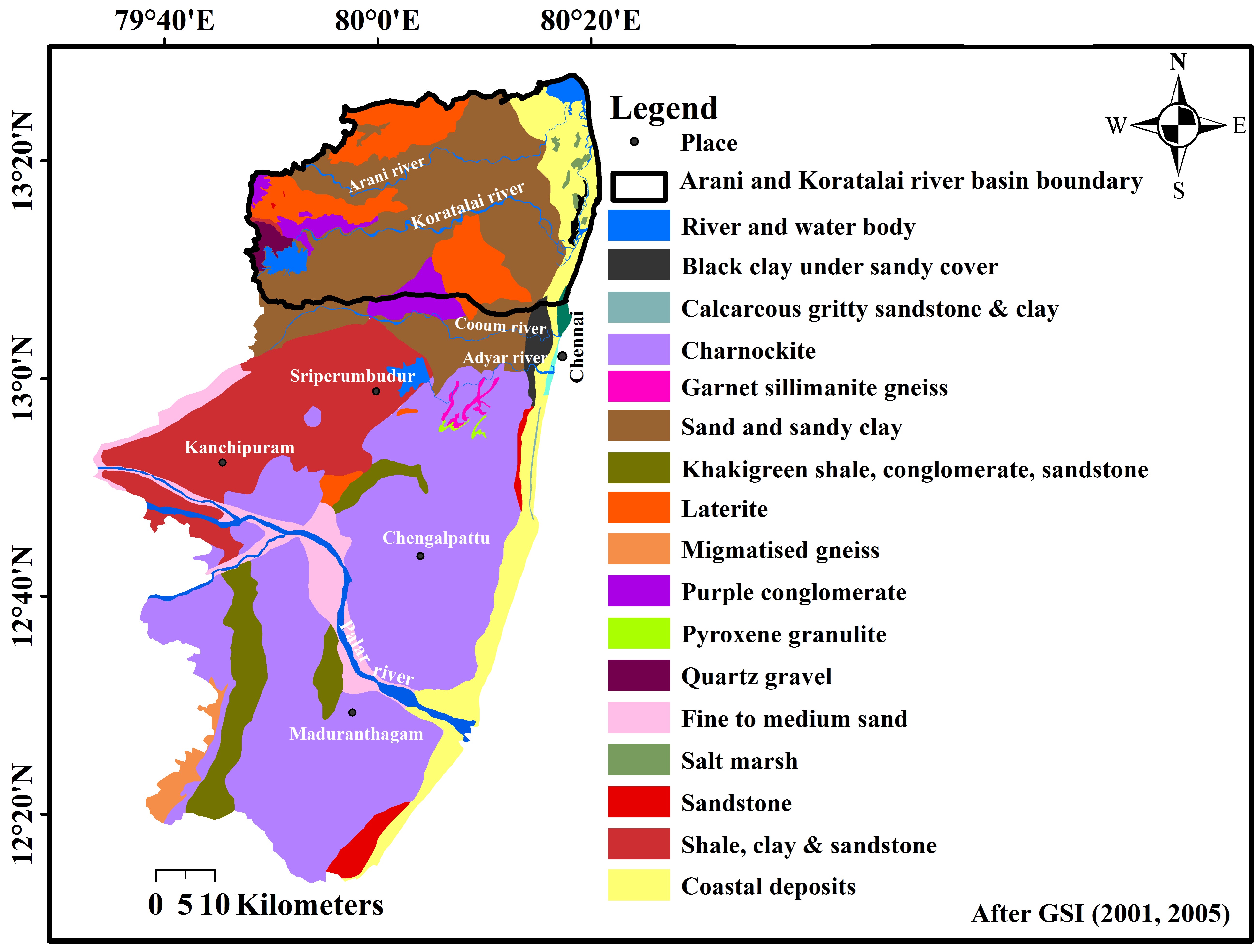
Geology
Thegeology
Geology () is a branch of natural science concerned with Earth and other astronomical objects, the features or rocks of which it is composed, and the processes by which they change over time. Modern geology significantly overlaps all other Ear ...
of Chennai comprises mostly clay
Clay is a type of fine-grained natural soil material containing clay minerals (hydrous aluminium phyllosilicates, e.g. kaolin, Al2 Si2 O5( OH)4).
Clays develop plasticity when wet, due to a molecular film of water surrounding the clay par ...
, shale
Shale is a fine-grained, clastic sedimentary rock formed from mud that is a mix of flakes of clay minerals (hydrous aluminium phyllosilicates, e.g. kaolin, Al2 Si2 O5( OH)4) and tiny fragments (silt-sized particles) of other minerals, especial ...
and sandstone
Sandstone is a clastic sedimentary rock composed mainly of sand-sized (0.0625 to 2 mm) silicate grains. Sandstones comprise about 20–25% of all sedimentary rocks.
Most sandstone is composed of quartz or feldspar (both silicates) ...
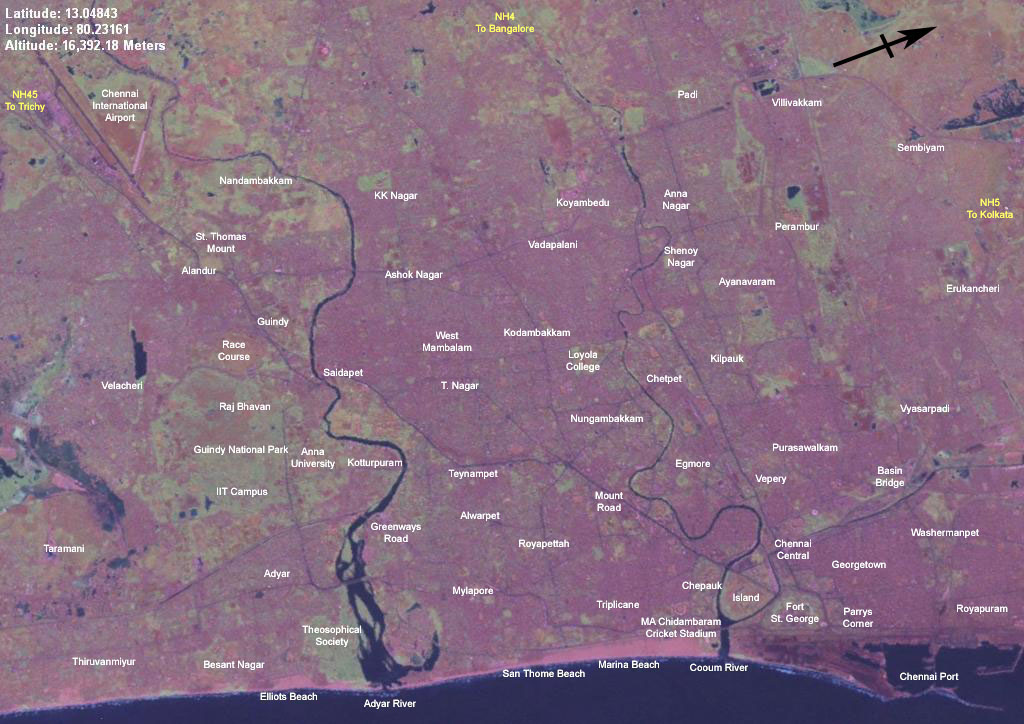
. The city is classified into three regions based on geology, sandy areas, clayey areas and hard-rock areas. Sandy areas are found along the river banks and the coasts. Clayey regions cover most of the city. Hard rock areas are Guindy
Guindy is one of the most important neighborhoods of Chennai, Tamil Nadu, and is nicknamed as ''The Gateway to Chennai''. The Kathipara junction where Anna Salai, Mount-Poonamallee Road, Inner Ring Road, 100 Feet Road or Jawaharlal Nehru Roa ...
, Velachery
Velachery (''pronounced as'' veh·luh·cheh·ree) is a commercial and residential area in south Chennai, and is the largest commercial centre in south Chennai. It is surrounded by Guindy in the north, IIT Madras in the north-east, Taramani in ...
, Adambakkam
Adambakkam is a neighbourhood of Chennai, India. It is primarily a residential locality situated in South Chennai . Adambakkam area comes under Velachery taluk and Alandur taluk, Chennai District of Chennai Corporation. Adambakkam is surrounded ...
and a part of Saidapet
Saidapet, also known as Saidai, is a neighbourhood in Chennai, India, situated in the northern banks of the Adyar River and serves as an entry point to Central Chennai. It is surrounded by West Mambalam in the North, C.I.T Nagar in the North- ...
. In sandy areas such as Tiruvanmiyur, Adyar, Kottivakkam, Santhome, George Town, Tondiarpet
Tondiarpet is a northern neighbourhood of Chennai, Tamil Nadu, India.
Etymology
This area got its name from a famous nineteenth-century Muslim Saint Kunangudi Masthan Sahib. His birthplace is located near Thondi in Ramanathapuram District. H ...
and the rest of coastal Chennai, rainwater run-off percolates very quickly. In clayey and hard rock areas, rainwater percolates slowly, but it is held by the soil for a longer time. The city's clayey areas include T. Nagar
Thyagaraya Nagar, commonly known as T. Nagar, and historically known as East Mambalam, is a very affluent commercial and residential neighbourhood in Chennai, Tamil Nadu, India. It is surrounded by Nungambakkam in the North, Teynampet in the ...
, West Mambalam
West Mambalam is a residential and commercial area in Chennai, India. It is known for its shops, bazaars and Hindu temples. It is bounded by Kodambakkam to the north and Saidapet to the south. T. Nagar and Nandanam stretch all along its easte ...
, Anna Nagar
Anna Nagar (formerly known as Naduvakkarai), is a neighbourhood in the metropolitan city of Chennai, India. Named after former chief minister of Tamil Nadu C. N. Annadurai, it is located in the north-western part of Chennai and forms a part of ...
, Perambur
Perambur is a neighbourhood located in the northern region of Chennai, Tamil Nadu, India.
Etymology
In Tamil, ''pirambu (பிரம்பு)'' means bamboo and ''ur (ஊர்)'' means city or place. Before British rule, this place was wid ...
and Virugambakkam
Virugambakkam is a residential neighbourhood of Chennai, Tamil Nadu, India. It is an important residential area of and is famous for its schools, market, residential colonies and residences of film artists. Virugambakkam had some of Chennai's o ...
. The geology of the Chennai city and its surroundings derived from the map of the Geological Survey of India is shown in figure.

Climate
Chennai features atropical wet and dry climate
Tropical savanna climate or tropical wet and dry climate is a tropical climate sub-type that corresponds to the Köppen climate classification categories ''Aw'' (for a dry winter) and ''As'' (for a dry summer). The driest month has less than of p ...
. Chennai lies on the thermal equator
The thermal equator (also known as "the heat equator") is a belt encircling Earth, defined by the set of locations having the highest mean annual temperature at each longitude around the globe. Because local temperatures are sensitive to the geogr ...
and is also coastal, which prevents extreme variation in seasonal temperature. For most of the year, the weather is hot and humid
Humidity is the concentration of water vapor present in the air. Water vapor, the gaseous state of water, is generally invisible to the human eye. Humidity indicates the likelihood for precipitation, dew, or fog to be present.
Humidity depen ...
. The hottest part of the year is late May and early June, known locally as ''Agni Nakshatram'' ("fiery star") or as ''Kathiri Veyyil'', with maximum temperatures around . The coolest part of the year is January, with minimum temperatures around . The lowest temperature recorded is and highest (30 May 2003).
The average annual rainfall
Rain is water droplets that have condensed from atmospheric water vapor and then fall under gravity. Rain is a major component of the water cycle and is responsible for depositing most of the fresh water on the Earth. It provides water f ...
is about . The city gets most of its season
A season is a division of the year based on changes in weather, ecology, and the number of daylight hours in a given region. On Earth, seasons are the result of the axial parallelism of Earth's tilted orbit around the Sun. In temperate and pol ...
al rainfall from the north-east monsoon
A monsoon () is traditionally a seasonal reversing wind accompanied by corresponding changes in precipitation but is now used to describe seasonal changes in atmospheric circulation and precipitation associated with annual latitudinal oscil ...
winds, from mid-September to mid-December. Cyclone
In meteorology, a cyclone () is a large air mass that rotates around a strong center of low atmospheric pressure, counterclockwise in the Northern Hemisphere and clockwise in the Southern Hemisphere as viewed from above (opposite to an anti ...
s in the Bay of Bengal sometimes hit the city. Highest annual rainfall recorded is 2,570 mm in 2005. The most prevailing winds in Chennai is the Southwesterly between the end of May to end of September and the Northeasterly during the rest of the year.
Water bodies
Two rivers meander through Chennai, theCooum River
The Cooum river, or simply Koovam, is one of the shortest classified rivers draining into the Bay of Bengal. This river is about in length, flowing in the city of Chennai (urban part) and the rest in rural part. The river is highly pollute ...
(or ''Koovam'') in the central region and the Adyar River in the southern region. Both rivers are heavily polluted with effluents and trash from domestic and commercial sources. The Adyar, which is much less polluted than the Cooum, is de-silted and cleaned periodically by the state government. A protected estuary
An estuary is a partially enclosed coastal body of brackish water with one or more rivers or streams flowing into it, and with a free connection to the open sea. Estuaries form a transition zone between river environments and maritime environment ...
of the Adyar forms the natural habitat of several species of birds and animals. The Buckingham Canal
The Buckingham Canal is a -long fresh water navigation canal, that parallels the Coromandel Coast of South India from Kakinada City in the Kakinada district of Andhra Pradesh to Viluppuram District in Tamil Nadu. The canal connects most ...
, inland, travels parallel to the coast, linking the two rivers. The Otteri Nullah
The Otteri Nullah is an east–west waterway which runs through north Chennai, starting at the village of Mullam proceeding through Purasawalkam and then passing through Buckingham and Carnatic Mills before meeting the Buckingham Canal at Bas ...
, an east–west stream runs through north Chennai and meets the Buckingham Canal at Basin Bridge
Basin Bridge Junction is a station on the Chennai Suburban Railway and serves the locality of Basin Bridge, the confluence on the Otteri Nullah and Buckingham Canal, in Chennai, India. The station is located at the southern end of the 'diamo ...
. Several lakes of varying size are located on the western fringes of the city. Red Hills, Sholavaram
Cholavaram, also spelled Sholavaram, is a suburb north of Chennai, Tamil Nadu, India. It is popular as Sholavaram and is also known for the Cholavaram lake. Adjoining the lake, there was an defunct Air Force Airfield which was used as a moto ...
and Chembarambakkam Lake
Chembarambakkam lake is a lake located in Chennai, Tamil Nadu, India, about 25 km from Chennai. It is one of the two rain-fed reservoirs from where water is drawn for supply to Chennai City, the other one being the Puzhal Lake. The Adyar ...
supply Chennai with potable water
Drinking water is water that is used in drink or food preparation; potable water is water that is safe to be used as drinking water. The amount of drinking water required to maintain good health varies, and depends on physical activity level, ag ...
. Groundwater
Groundwater is the water present beneath Earth's surface in rock and soil pore spaces and in the fractures of rock formations. About 30 percent of all readily available freshwater in the world is groundwater. A unit of rock or an unconsolidate ...
sources are mostly brackish
Brackish water, sometimes termed brack water, is water occurring in a natural environment that has more salinity than freshwater, but not as much as seawater. It may result from mixing seawater (salt water) and fresh water together, as in estuari ...
. A study by the Department of Geology, Anna University, based on a city map of 1893, has revealed that there were nearly 60 large waterbodies in the core of then Madras. The study traced the shrinking and vanished waterbodies through a series of city maps.
Historically, Chennai has faced a problem of water supply shortages as no big river flows through it with a resulting over-reliance on annual monsoon
A monsoon () is traditionally a seasonal reversing wind accompanied by corresponding changes in precipitation but is now used to describe seasonal changes in atmospheric circulation and precipitation associated with annual latitudinal oscil ...
rains to replenish water reservoirs
A reservoir (; from French ''réservoir'' ) is an enlarged lake behind a dam. Such a dam may be either artificial, built to store fresh water or it may be a natural formation.
Reservoirs can be created in a number of ways, including control ...
. The city's ground water levels have been depleted to very low levels in many areas. Many residents buy their drinking water. An earlier Veeranam project was unsuccessful in solving the city's water supply shortages, but the New Veeranam project which became operational in September 2004 has greatly reduced dependency on distant sources. In recent years however, due to heavy and consistent monsoon rains and the implementation of rainwater harvesting
Rainwater harvesting (RWH) is the collection and storage of rain, rather than allowing it to run off. Rainwater is collected from a roof-like surface and redirected to a tank, cistern, deep pit (well, shaft, or borehole), aquifer, or a reservoir w ...
(RWH) techniques by Chennai Metrowater at their Anna Nagar
Anna Nagar (formerly known as Naduvakkarai), is a neighbourhood in the metropolitan city of Chennai, India. Named after former chief minister of Tamil Nadu C. N. Annadurai, it is located in the north-western part of Chennai and forms a part of ...
Rain Centre, water shortages
Water scarcity (closely related to water stress or water crisis) is the lack of fresh water resources to meet the standard water demand. There are two types of water scarcity: physical or economic water scarcity. Physical water scarcity is wher ...
have been reduced significantly, and this has led Chennai to be a model of RWH technology for other cities."Bangalore team visits RWH structures in city", ''The Hindu'', 3 August 2007, accessed 11 August 2007/ref> Moreover, newer projects like the
Telugu Ganga
The Telugu Ganga project is a joint water supply scheme implemented in 1980s by the then Andhra Pradesh chief minister N.T.Ramarao and Tamilnadu Chief minister M. G. Ramachandran to provide drinking water to Chennai city in Tamil Nadu. It is als ...
canal project that brings water from water-surplus rivers like the Krishna river in Andhra Pradesh
Andhra Pradesh (, abbr. AP) is a state in the south-eastern coastal region of India. It is the seventh-largest state by area covering an area of and tenth-most populous state with 49,386,799 inhabitants. It is bordered by Telangana to the ...
have eased water supply shortages. The city is also constructing sea water desalination
Desalination is a process that takes away mineral components from saline water. More generally, desalination refers to the removal of salts and minerals from a target substance, as in Soil salinity control, soil desalination, which is an issue f ...
plants to further ease water supply shortages.
Layout
For administrative purposes Chennai is divided into fivetaluka
A tehsil (, also known as tahsil, taluka, or taluk) is a local unit of administrative division in some countries of South Asia. It is a subdistrict of the area within a district including the designated populated place that serves as its administr ...
s; namely Egmore-Nungambakam, Fort Tondiarpet, Mambalam-Guindy, Mylapore-Triplicane and Perambur-Purasawalkkam.
The Chennai Metropolitan area consists of three districts namely Chennai city and the districts of Kanchipuram
Kanchipuram ('; ) also known as ''Conjeevaram,'' is a city in the Indian state of Tamil Nadu in the Tondaimandalam region, from Chennaithe capital of Tamil Nadu. Known as the ''City of Thousand Temples'', Kanchipuram is known for its temple ...
and Thiruvallur
Tiruvallur is a Grade I municipality and a fast developing city in the Indian state of Tamil Nadu. It is located on the banks of Coovum river about from downtown Chennai ( Madras) and just 5 km from megacity border, in the western p ...
. The city area covers an area of . The metropolitan area covers 1,177 km2 (455 sq mi). The city is divided on the basis of composition into four major parts: North, Central, South and West.
North Chennai is primarily an industrial area. Central Chennai is the commercial heart of the city and the downtown area. South Chennai and West Chennai, previously predominantly residential areas are fast turning into commercial areas, hosting a large number of IT and financial
Finance is the study and discipline of money, currency and capital assets. It is related to, but not synonymous with economics, the study of production, distribution, and consumption of money, assets, goods and services (the discipline of fina ...
companies. The city is fast expanding along the Old Mahabalipuram Road
State Highway 49A (SH-49A) also known as Rajiv Gandhi Salai and Rajiv Gandhi IT Expressway or just IT Expressway is a major road connecting Chennai, Tamil Nadu with Mahabalipuram in Chengalpattu district, Tamil Nadu. It is 45 km long and ...
, GST Road, Sriperumbdur
Sriperumbudur is a town panchayat in the Kanchipuram district of the Indian state of Tamil Nadu. It is located 40 kilometers southwest of the capital city of Chennai on the National Highway 4 and is just outside the Chennai Metropolitan Ar ...
, Koyambedu and Ambattur
Ambattur is located in northwestern part of Chennai City, in Ambattur taluk of the Chennai District, surrounded by Avadi, Anna Nagar, Padi, Mogappair, Kallikuppam, Surapet, Korattur, Ayappakkam, and Thiruverkadu. It covers an area of . The n ...
.
The Chennai Metropolitan Development Authority
The Chennai Metropolitan Development Authority (CMDA), formerly known as the Madras Metropolitan Development Authority (MMDA), is the nodal planning agency of Chennai in the Indian state of Tamil Nadu. The CMDA administers the Chennai Metropol ...
has drafted a Second Master Plan for Chennai, that aims to develop a satellite townships around the city. Contiguous satellite towns include Mahabalipuram
Mamallapuram, also known as Mahabalipuram, is a town in Chengalpattu district in the southeastern Indian state of Tamil Nadu, best known for the UNESCO World Heritage Site of 7th- and 8th-century Hindu Group of Monuments at Mahabalipuram. It is o ...
to the south, Chengalpattu
Chengalpattu, previously known as Chingleput, is a city and the headquarters of Chengalpattu district of the state Tamil Nadu, India. The town is located near to the industrial and IT hub. It is the headquarters of the district and is away fro ...
and Maraimalai Nagar to the south west, Kanchipuram
Kanchipuram ('; ) also known as ''Conjeevaram,'' is a city in the Indian state of Tamil Nadu in the Tondaimandalam region, from Chennaithe capital of Tamil Nadu. Known as the ''City of Thousand Temples'', Kanchipuram is known for its temple ...
town, Sriperumpudur, Tiruvallur
Tiruvallur is a Grade I municipality and a fast developing city in the Indian state of Tamil Nadu. It is located on the banks of Coovum river about from downtown Chennai (Madras) and just 5 km from megacity border, in the western p ...
and Arakkonam
Arakkonam () is a railway town and suburb of Chennai within Chennai Metropolitan Area limit, in the Indian state of Tamil Nadu, with a population of 78,395 per the census 2011. It is in the newly created Ranipet district, about from Ranipet head ...
to the west.
References
{{Chennai Topics