Geography of Barbados on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 Barbados' total land area is , and it has a coastline of length. Sometimes compared to a
Barbados' total land area is , and it has a coastline of length. Sometimes compared to a

 :
:
Caves and landslips in Barbados
- September 16, 2007: Barbados Advocate
- Barbados Government
Earthwise Issue 14, Landslides and tourist development - The slow slide of eastern Barbados into the sea
British Geological Survey
Plantation and Peasant Farm A Vertical Theme in the Historical Geography of Barbados 1627 - 1960
by Frank Cecil Innes, M.A., B.Sc, September, 1967, Doctor of Philosophy, Dept. of Geography, McGil1 Univ.
Caribbean-On-Line.com
provides detailed maps of Barbados.
Statoids.com
GEOnet Names Server
BajanNAV
- Free satellite navigation software for Barbados
Barbados Geography
geographic profile of Barbados.
Encyclopedia.com
Worldmark Encyclopedia of Nations.
Encyclopaedia Britannica, Inc.
Physical Geography {{DEFAULTSORT:Geography Of Barbados Islands of Barbados Lesser Antilles
Barbados
Barbados is an island country in the Lesser Antilles of the West Indies, in the Caribbean region of the Americas, and the most easterly of the Caribbean Islands. It occupies an area of and has a population of about 287,000 (2019 estimate) ...
is a continental island
An island (or isle) is an isolated piece of habitat that is surrounded by a dramatically different habitat, such as water. Very small islands such as emergent land features on atolls can be called islets, skerries, cays or keys. An island ...
in the North Atlantic Ocean
The Atlantic Ocean is the second-largest of the world's five oceans, with an area of about . It covers approximately 20% of Earth's surface and about 29% of its water surface area. It is known to separate the " Old World" of Africa, Europe ...
and is located at 13°10' north of the equator, and 59°32' west of the Prime Meridian
A prime meridian is an arbitrary meridian (a line of longitude) in a geographic coordinate system at which longitude is defined to be 0°. Together, a prime meridian and its anti-meridian (the 180th meridian in a 360°-system) form a great ...
. As the easternmost isle of the Lesser Antilles
The Lesser Antilles ( es, link=no, Antillas Menores; french: link=no, Petites Antilles; pap, Antias Menor; nl, Kleine Antillen) are a group of islands in the Caribbean Sea. Most of them are part of a long, partially volcanic island arc bet ...
in the West Indies
The West Indies is a subregion of North America, surrounded by the North Atlantic Ocean and the Caribbean Sea that includes 13 independent island countries and 18 dependencies and other territories in three major archipelagos: the Greate ...
, Barbados lies 160 kilometres (100 mi) east of the Windward Islands
french: Îles du Vent
, image_name =
, image_caption = ''Political'' Windward Islands. Clockwise: Dominica, Martinique, Saint Lucia, Saint Vincent and the Grenadines, and Grenada.
, image_alt =
, locator_map =
, location = Caribbean Sea No ...
and Caribbean Sea
The Caribbean Sea ( es, Mar Caribe; french: Mer des Caraïbes; ht, Lanmè Karayib; jam, Kiaribiyan Sii; nl, Caraïbische Zee; pap, Laman Karibe) is a sea of the Atlantic Ocean in the tropics of the Western Hemisphere. It is bounded by Mexico ...
. The maritime claim for Barbados is a territorial sea of , with an exclusive economic zone of which gives Barbados a total maritime area of . Of the total EEZ area, 70,000 km2 is set aside for offshore oil exploration. A pending application to UNCLOS
The United Nations Convention on the Law of the Sea (UNCLOS), also called the Law of the Sea Convention or the Law of the Sea Treaty, is an international agreement that establishes a legal framework for all marine and maritime activities. , 167 c ...
has placed for consideration a continental shelf to the east and south (or to the edge of the continental margin). To the west, most of Barbados' maritime boundaries consist of median lines with neighbours. These neighbours include: Martinique
Martinique ( , ; gcf, label=Martinican Creole, Matinik or ; Kalinago: or ) is an island and an overseas department/region and single territorial collectivity of France. An integral part of the French Republic, Martinique is located in ...
, and Saint Lucia to the northwest, Saint Vincent and the Grenadines
Saint Vincent and the Grenadines () is an island country in the Caribbean. It is located in the southeast Windward Islands of the Lesser Antilles, which lie in the West Indies at the southern end of the eastern border of the Caribbean Sea w ...
to the west, Trinidad and Tobago
Trinidad and Tobago (, ), officially the Republic of Trinidad and Tobago, is the southernmost island country in the Caribbean. Consisting of the main islands Trinidad and Tobago, and numerous much smaller islands, it is situated south of ...
and Venezuela
Venezuela (; ), officially the Bolivarian Republic of Venezuela ( es, link=no, República Bolivariana de Venezuela), is a country on the northern coast of South America, consisting of a continental landmass and many islands and islets in th ...
to the southwest, and Guyana to the southeast.
 Barbados' total land area is , and it has a coastline of length. Sometimes compared to a
Barbados' total land area is , and it has a coastline of length. Sometimes compared to a pear
Pears are fruits produced and consumed around the world, growing on a tree and harvested in the Northern Hemisphere in late summer into October. The pear tree and shrub are a species of genus ''Pyrus'' , in the family Rosaceae, bearing the po ...
or leg of mutton
Lamb, hogget, and mutton, generically sheep meat, are the meat of domestic sheep, ''Ovis aries''. A sheep in its first year is a lamb and its meat is also lamb. The meat from sheep in their second year is hogget. Older sheep meat is mutton. Gen ...
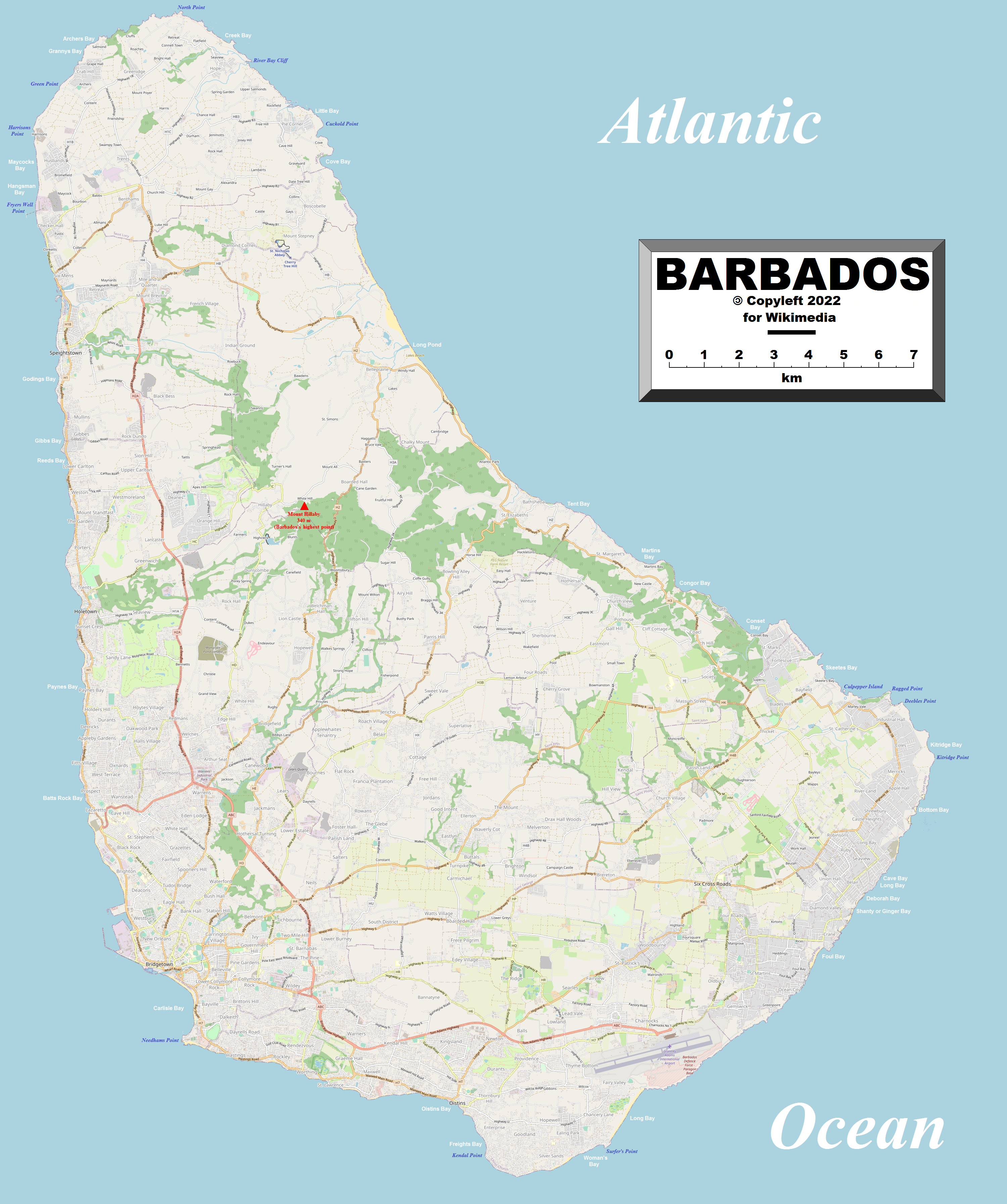
for its physical shape. Along the north–south axis Barbados has a maximum length of , and east–west maximum breadth of .
Physical characteristics
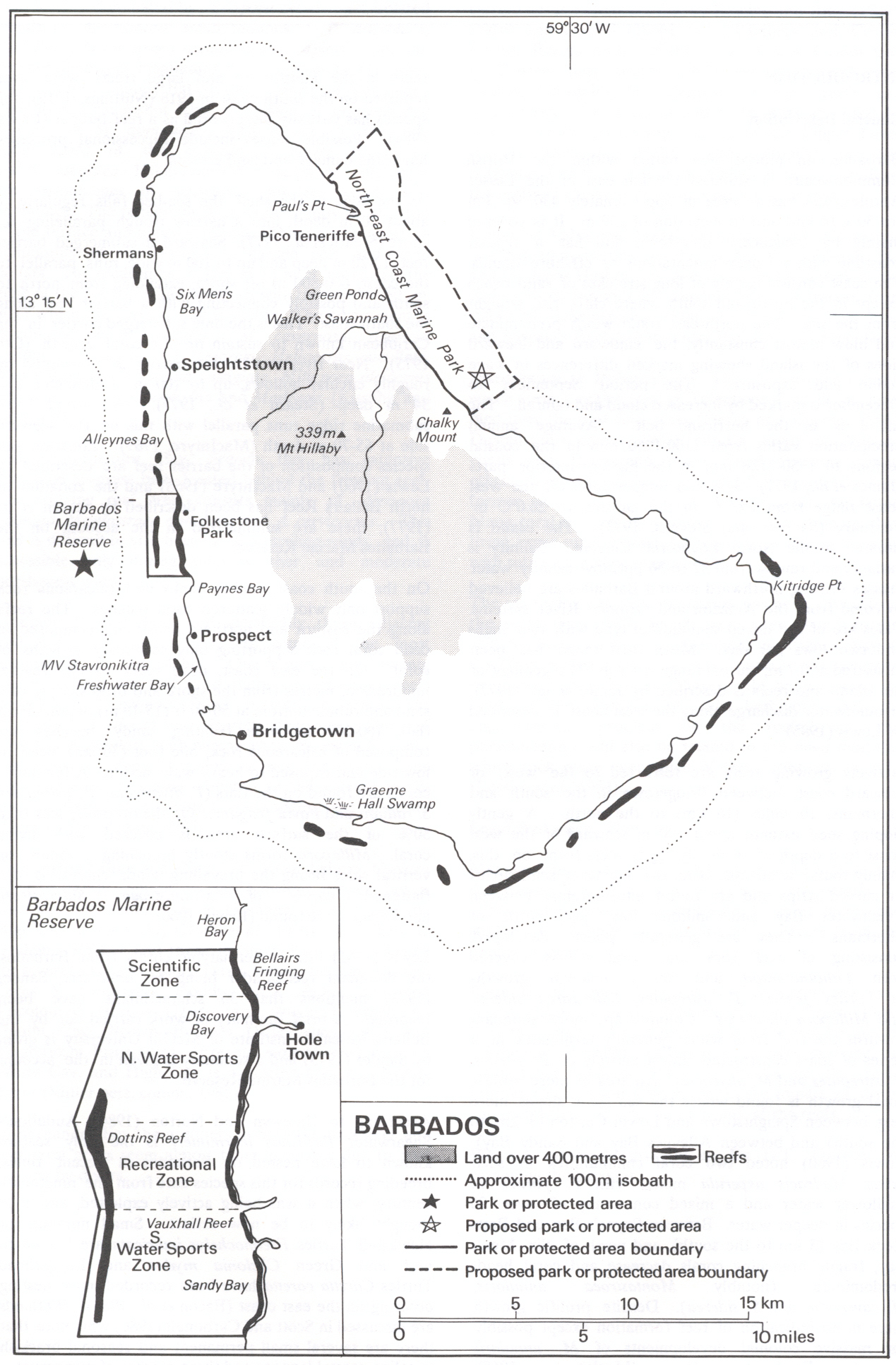
The physical characteristics of Barbados are its lowlands or gently sloping, terraced plains, separated by rolling hills that generally parallel the coasts. Elevations in the interior range from 180 to 240 meters above sea level. Mount Hillaby is the highest point at 340 meters above sea level. Farther south, at Christ Church Ridge, elevations range from sixty to ninety meters. Eighty-five percent of the island's surface consists of coralline limestone twenty-four to thirty meters thick;Scotland District
Scotland (, ) is a country that is part of the United Kingdom. Covering the northern third of the island of Great Britain, mainland Scotland has a border with England to the southeast and is otherwise surrounded by the Atlantic Ocean to the ...
contains outcroppings of oceanic formations at the surface, however. Sugarcane is planted on almost 80 percent of the island's limestone surface. The soils vary in fertility; erosion is a problem, with crop loss resulting from landslides, washouts, and falling rocks. Most of the small streams are in Scotland District. The rest of the island has few surface streams; nevertheless, rainwater saturates the soil to produce underground channels such as the famous Coles Cave. Also notable in the island is the rocky cape known as Pico Teneriffe or Pico de Tenerife, which is named after the fact that the island of Tenerife
Tenerife (; ; formerly spelled ''Teneriffe'') is the largest and most populous island of the Canary Islands. It is home to 43% of the total population of the archipelago. With a land area of and a population of 978,100 inhabitants as of Janu ...
in Spain
, image_flag = Bandera de España.svg
, image_coat = Escudo de España (mazonado).svg
, national_motto = ''Plus ultra'' (Latin)(English: "Further Beyond")
, national_anthem = (English: "Royal March")
, i ...
is the first land east of Barbados according to the belief of the locals.
Populated places
''List of'': Cities, towns and villages in Barbados. *Bridgetown
Bridgetown (UN/LOCODE: BB BGI) is the capital and largest city of Barbados. Formerly The Town of Saint Michael, the Greater Bridgetown area is located within the parish of Saint Michael. Bridgetown is sometimes locally referred to as "The Ci ...
* Holetown
*Oistins
Oistins (Pronounced /'ȯis-tins/ -- UN/LOCODE: BB OST), is a coastal area located in the country of Barbados. It is situated centrally along the coastline of the parish of Christ Church. The area includes a fishing village as well as a tourist are ...
* Six Cross Roads
*Speightstown
Speightstown (), also known as ''Little Bristol'', is the second largest City centre of Barbados. It is situated north of the capital city of Bridgetown, in the northern parish of Saint Peter.
The City is named after William Speight, a member o ...
*Saint Lawrence Gap
Saint Lawrence Gap, Christ Church is one of the best-known neighbourhoods in the country of Barbados. Sometimes just called "the Gap", Saint Lawrence Gap is located on the southern coast of Barbados along the island's Highway 7. Found between O ...
* Warrens
* Black Rock, Barbados
*Bank Hall
Bank Hall is a Jacobean mansion in Bretherton, Lancashire, England. It is a Grade II* listed building and is at the centre of a private estate, surrounded by parkland. The hall was built on the site of an older house in 1608 by the Banastres ...
Proposed developments
In 2009 and 2010, members of the upscale real estate industry in Barbados proposed the creation ofartificial island
An artificial island is an island that has been constructed by people rather than formed by natural means. Artificial islands may vary in size from small islets reclaimed solely to support a single pillar of a building or structure to those th ...
s to be placed off the west coast. According to Paul Altman of Altman Realty the envisioned plan, would consist of two islands, one measuring in size, and would house new tourism based developments and upscale boutique shops; while the second island would be in size, and would serve as an open national park. Both proposed islands would be a short distance from the Deep Water Harbour
The Port of Bridgetown (officially the Deep Water Harbour), (UN/LOCODE: BB BGI, Port Callsign: 8PB) is a seaport in Bridgetown on the southwest coast of Barbados. Situated at the North-Western end of Carlisle Bay, the harbour handles all of t ...
in Bridgetown.
The south-eastern part of the island has undergone small scale oil and gas capturing from possibly as early as 1919 when the British Union Oil Company acquired over 75% of the drilling rights in Barbados. Similar to Trinidad and Tobago to the southwest, the territorial Atlantic Ocean surrounding Barbados has been found to contain fossil fuels, however ongoing research is being conducted to give estimates of actual quantities.
Time zone
Barbados is in the Eastern Caribbean Time Zone.Barbados
Barbados is an island country in the Lesser Antilles of the West Indies, in the Caribbean region of the Americas, and the most easterly of the Caribbean Islands. It occupies an area of and has a population of about 287,000 (2019 estimate) ...
no longer observes Daylight Saving Time
Daylight saving time (DST), also referred to as daylight savings time or simply daylight time (United States, Canada, and Australia), and summer time (United Kingdom, European Union, and others), is the practice of advancing clocks (typicall ...
. It was last used between Sunday, 20 April 1980 at 2:00 AM and Thursday, 25 September 1980 at 2:00 AM. On 25 September of that year the clock was shifted from -3:00 to -4:00, where it has remained since.
Statistics
Location


 :
: Barbados
Barbados is an island country in the Lesser Antilles of the West Indies, in the Caribbean region of the Americas, and the most easterly of the Caribbean Islands. It occupies an area of and has a population of about 287,000 (2019 estimate) ...
is located east of the Caribbean Sea
The Caribbean Sea ( es, Mar Caribe; french: Mer des Caraïbes; ht, Lanmè Karayib; jam, Kiaribiyan Sii; nl, Caraïbische Zee; pap, Laman Karibe) is a sea of the Atlantic Ocean in the tropics of the Western Hemisphere. It is bounded by Mexico ...
and the Windward Islands
french: Îles du Vent
, image_name =
, image_caption = ''Political'' Windward Islands. Clockwise: Dominica, Martinique, Saint Lucia, Saint Vincent and the Grenadines, and Grenada.
, image_alt =
, locator_map =
, location = Caribbean Sea No ...
in the North Atlantic Ocean
The Atlantic Ocean is the second-largest of the world's five oceans, with an area of about . It covers approximately 20% of Earth's surface and about 29% of its water surface area. It is known to separate the " Old World" of Africa, Europe ...
, most directly east of Saint Vincent and the Grenadines
Saint Vincent and the Grenadines () is an island country in the Caribbean. It is located in the southeast Windward Islands of the Lesser Antilles, which lie in the West Indies at the southern end of the eastern border of the Caribbean Sea w ...
.
; Map references:
: Central America
Central America ( es, América Central or ) is a subregion of the Americas. Its boundaries are defined as bordering the United States to the north, Colombia to the south, the Caribbean Sea to the east, and the Pacific Ocean to the west. ...
and the Caribbean
Area
:* Total: 430 km² :* Land: 430 km² :* Water: 0 km²Area comparative
:* Australia comparative: less than one-fifth of the area of theAustralian Capital Territory
The Australian Capital Territory (commonly abbreviated as ACT), known as the Federal Capital Territory (FCT) until 1938, is a landlocked federal territory of Australia containing the national capital Canberra and some surrounding townships. I ...
:* Canada
Canada is a country in North America. Its ten provinces and three territories extend from the Atlantic Ocean to the Pacific Ocean and northward into the Arctic Ocean, covering over , making it the world's second-largest country by tot ...
comparative: slightly larger than London
London is the capital and List of urban areas in the United Kingdom, largest city of England and the United Kingdom, with a population of just under 9 million. It stands on the River Thames in south-east England at the head of a estuary dow ...
in the Province of Ontario
Ontario ( ; ) is one of the thirteen provinces and territories of Canada.Ontario is located in the geographic eastern half of Canada, but it has historically and politically been considered to be part of Central Canada. Located in Central Cana ...
:* United Kingdom
The United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern Ireland, commonly known as the United Kingdom (UK) or Britain, is a country in Europe, off the north-western coast of the European mainland, continental mainland. It comprises England, Scotlan ...
comparative: slightly larger than the Isle of Wight
The Isle of Wight ( ) is a Counties of England, county in the English Channel, off the coast of Hampshire, from which it is separated by the Solent. It is the List of islands of England#Largest islands, largest and List of islands of England#Mo ...
or Saint Helena
:* United States
The United States of America (U.S.A. or USA), commonly known as the United States (U.S. or US) or America, is a country primarily located in North America. It consists of 50 states, a federal district, five major unincorporated territori ...
comparative: 2.5 times the size of Washington, DC
)
, image_skyline =
, image_caption = Clockwise from top left: the Washington Monument and Lincoln Memorial on the National Mall, United States Capitol, Logan Circle, Jefferson Memorial, White House, Adams Morgan ...
, about the size of San Antonio, Texas
("Cradle of Freedom")
, image_map =
, mapsize = 220px
, map_caption = Interactive map of San Antonio
, subdivision_type = Country
, subdivision_name = United States
, subdivision_type1= State
, subdivision_name1 = Texas
, subdivision_t ...
, or half the size of New York City
New York, often called New York City or NYC, is the most populous city in the United States. With a 2020 population of 8,804,190 distributed over , New York City is also the most densely populated major city in the Un ...
Land boundaries
: 0 km ; Coastline: : 97 km ; Maritime claims: :* Territorial sea: :* Exclusive economic zone: andClimate
: Tropical; rainy season (June to October)Terrain
: Relatively flat; rises gently to central highland region ; Extreme points :* Northernmost point –North Point
North Point is a mixed-use urban area in the Eastern District of Hong Kong. Located in the northeastern part of Hong Kong Island, the area is named after a cape between Causeway Bay and Tsat Tsz Mui that projects toward Kowloon Bay.
Locat ...
, Saint Lucy
Lucia of Syracuse (283–304), also called Saint Lucia ( la, Sancta Lucia) better known as Saint Lucy, was a Roman people, Roman Christian martyr who died during the Diocletianic Persecution. She is venerated as a saint in the Catholic Church, ...
:* Southernmost point – South Point, Silver Sands, Christ Church
:* Westernmost point – Harrison Point, Saint Lucy
Lucia of Syracuse (283–304), also called Saint Lucia ( la, Sancta Lucia) better known as Saint Lucy, was a Roman people, Roman Christian martyr who died during the Diocletianic Persecution. She is venerated as a saint in the Catholic Church, ...
:* Easternmost point – Kitridge Point, Saint Philip Saint Philip, São Filipe, or San Felipe may refer to:
People
* Saint Philip the Apostle
* Saint Philip the Evangelist also known as Philip the Deacon
* Saint Philip Neri
* Saint Philip Benizi de Damiani also known as Saint Philip Benitius or Fili ...
:* Lowest point: Atlantic Ocean
The Atlantic Ocean is the second-largest of the world's five oceans, with an area of about . It covers approximately 20% of Earth's surface and about 29% of its water surface area. It is known to separate the " Old World" of Africa, Europe ...
: 0 m
:* Highest point: Mount Hillaby: 336 m
Natural resources
: Fish, natural gasLand use
:* Arable land: 25.58% :* Permanent crops: 2.33% :* Other: 72.09% (2012) ; Irrigated land: : 54.35 km² (2003) ; Total renewable water sources: : 0.08 cu km (2011) ; Freshwater withdrawal (domestic/industrial/agricultural) : total: 0.1 cu km/yr (20%/26%/254) : per capita: 371.3 cu m/yr (200p)Natural hazards
: Infrequent hurricanes; periodic landslides; periodic flooding, from storm surge and intense rainfall events; and occasional droughts, causing fires.Environment - current issues
: Pollution of coastal waters from waste disposal by ships; soil erosion; illegal solid waste disposal threatens contamination of aquifers ; Environment - international agreements: :* Party to: Biodiversity, Climate Change, Climate Change-Kyoto Protocol, Desertification, Endangered Species, Hazardous Wastes, Law of the Sea, Marine Dumping, Ozone Layer Protection, Ship Pollution, Wetlands :* Signed, but not ratified: none of the selected agreements ; Geography - note: : Easternmost Caribbean islandClimate
Barbados lies within the tropics. Its generally pleasant maritime climate is influenced by northeast trade winds, which moderate the tropical temperature. Cool, northeasterly trade winds are prevalent during the December to June dry season. The overall annual temperature ranges from ; slightly lower temperatures prevail at higher elevations. Humidity levels are between 71 percent and 76 percent year round. Rainfall occurs primarily between July and December and varies considerably with elevation. Rainfall may average per year in the higher central area as compared with in the coastal zone.Disputes
Guyana's and Barbados's offshore territorial claims overlap, and are also disputed with Venezuela, which itself claims ownership of the waters overlapping the first two. In 2008 Barbados sought to place the oil blocks on open market for oil exploration tender but faced a challenge by Venezuela's government in Caracas. In 2006 a local Barbadian group purporting to represent descendants of indigenous Caribbean peoples announced its claim toCulpepper Island
Culpepper Island is a tiny rock (island) in the Atlantic Ocean close to Bayfield and Ragged Point in Saint Philip, Barbados. The island is uninhabited.
Geography
It is quite possible to wade out to Culpepper Island from the mainland during ...
, a small rocky outcrop on the eastern shore of Barbados.
Notes
References
* * * * * * *Caves and landslips in Barbados
- September 16, 2007: Barbados Advocate
- Barbados Government
Earthwise Issue 14, Landslides and tourist development - The slow slide of eastern Barbados into the sea
British Geological Survey
Plantation and Peasant Farm A Vertical Theme in the Historical Geography of Barbados 1627 - 1960
by Frank Cecil Innes, M.A., B.Sc, September, 1967, Doctor of Philosophy, Dept. of Geography, McGil1 Univ.
See also
* English place names in BarbadosExternal links
Caribbean-On-Line.com
provides detailed maps of Barbados.
Statoids.com
GEOnet Names Server
BajanNAV
- Free satellite navigation software for Barbados
Barbados Geography
geographic profile of Barbados.
Encyclopedia.com
Worldmark Encyclopedia of Nations.
Encyclopaedia Britannica, Inc.
Physical Geography {{DEFAULTSORT:Geography Of Barbados Islands of Barbados Lesser Antilles