Galloway European on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 Galloway ( ; sco, Gallowa; la, Gallovidia) is a region in southwestern
Galloway ( ; sco, Gallowa; la, Gallovidia) is a region in southwestern
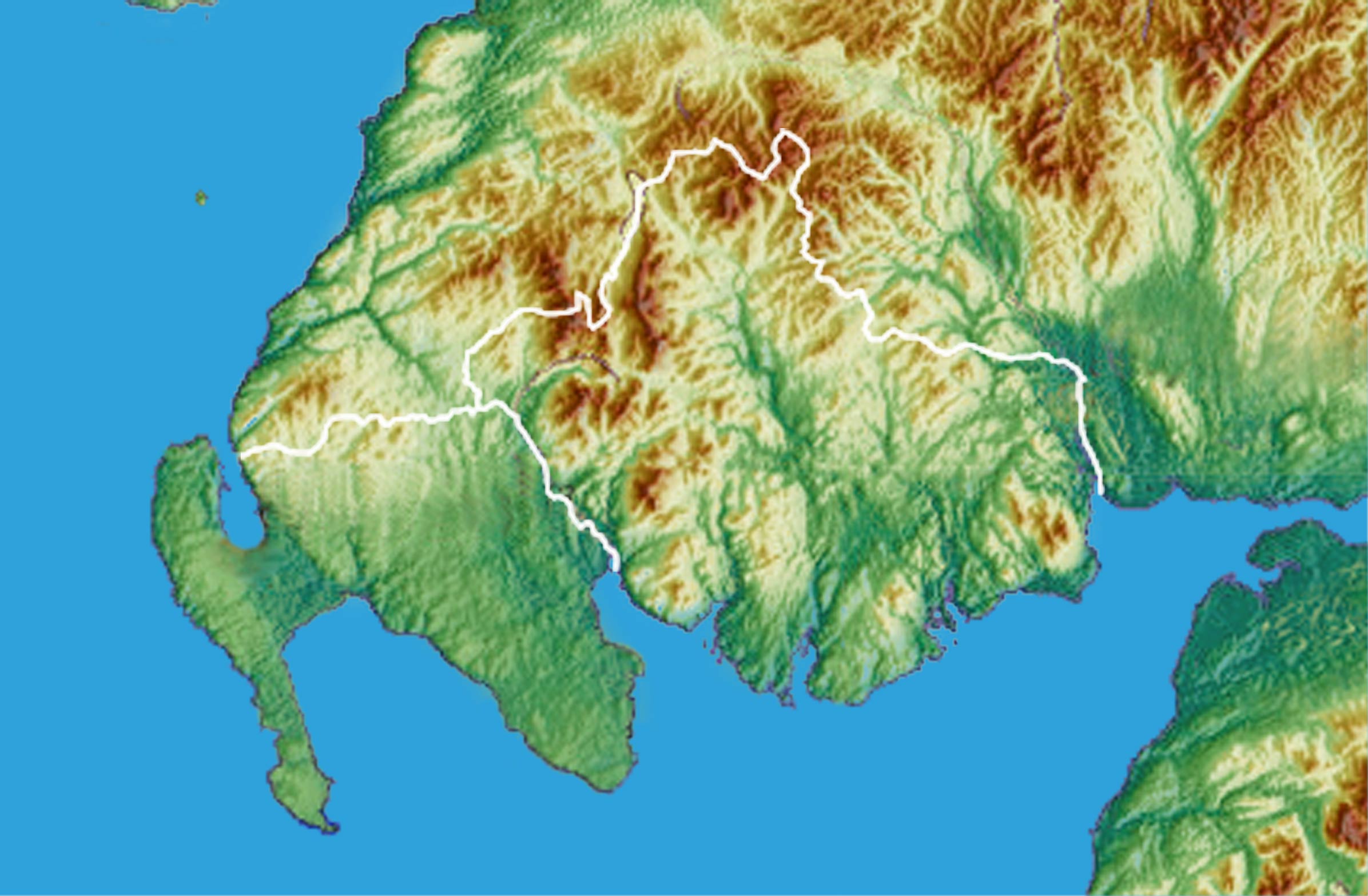
 Galloway comprises the part of Scotland lying southwards from the Southern Upland watershed and westward from the
Galloway comprises the part of Scotland lying southwards from the Southern Upland watershed and westward from the

 The 2nd century geographer
The 2nd century geographer

 The earliest recorded inhabitants were Brythonic Celts, recorded by the
The earliest recorded inhabitants were Brythonic Celts, recorded by the
Galloway Dialect
at Scots Language Centre {{coord, 55, 03, N, 4, 08, W, source:kolossus-nowiki, display=title Geography of Dumfries and Galloway
Scotland
Scotland (, ) is a Countries of the United Kingdom, country that is part of the United Kingdom. Covering the northern third of the island of Great Britain, mainland Scotland has a Anglo-Scottish border, border with England to the southeast ...
comprising the historic counties of Wigtownshire
Wigtownshire or the County of Wigtown (, ) is one of the historic counties of Scotland, covering an area in the south-west of the country. Until 1975, Wigtownshire was an administrative county used for local government. Since 1975 the area has f ...
and Kirkcudbrightshire
Kirkcudbrightshire ( ), or the County of Kirkcudbright or the Stewartry of Kirkcudbright is one of the historic counties of Scotland, covering an area in the south-west of the country. Until 1975, Kirkcudbrightshire was an administrative count ...
. It is administered as part of the council area {{Unreferenced, date=May 2019, bot=noref (GreenC bot)
A council area is one of the areas defined in Schedule 1 of the Local Government etc. (Scotland) Act 1994 and is under the control of one of the local authorities in Scotland created by that Act. ...
of Dumfries and Galloway.
A native or inhabitant of Galloway is called a Gallovidian. The place name Galloway is derived from the Gaelic ' ("amongst the '"). The , literally meaning "Stranger-'"; the specific identity of whom the term was applied to is unknown, but the predominant view is that it referred to an ethnic and/or cultural identity such as the Strathclyde Britons or another related but distinct population. A popular theory is that it refers to a population of mixed Scandinavian and Gaelic ethnicity that may have inhabited Galloway in the Middle Ages
In the history of Europe, the Middle Ages or medieval period lasted approximately from the late 5th to the late 15th centuries, similar to the post-classical period of global history. It began with the fall of the Western Roman Empire ...
.
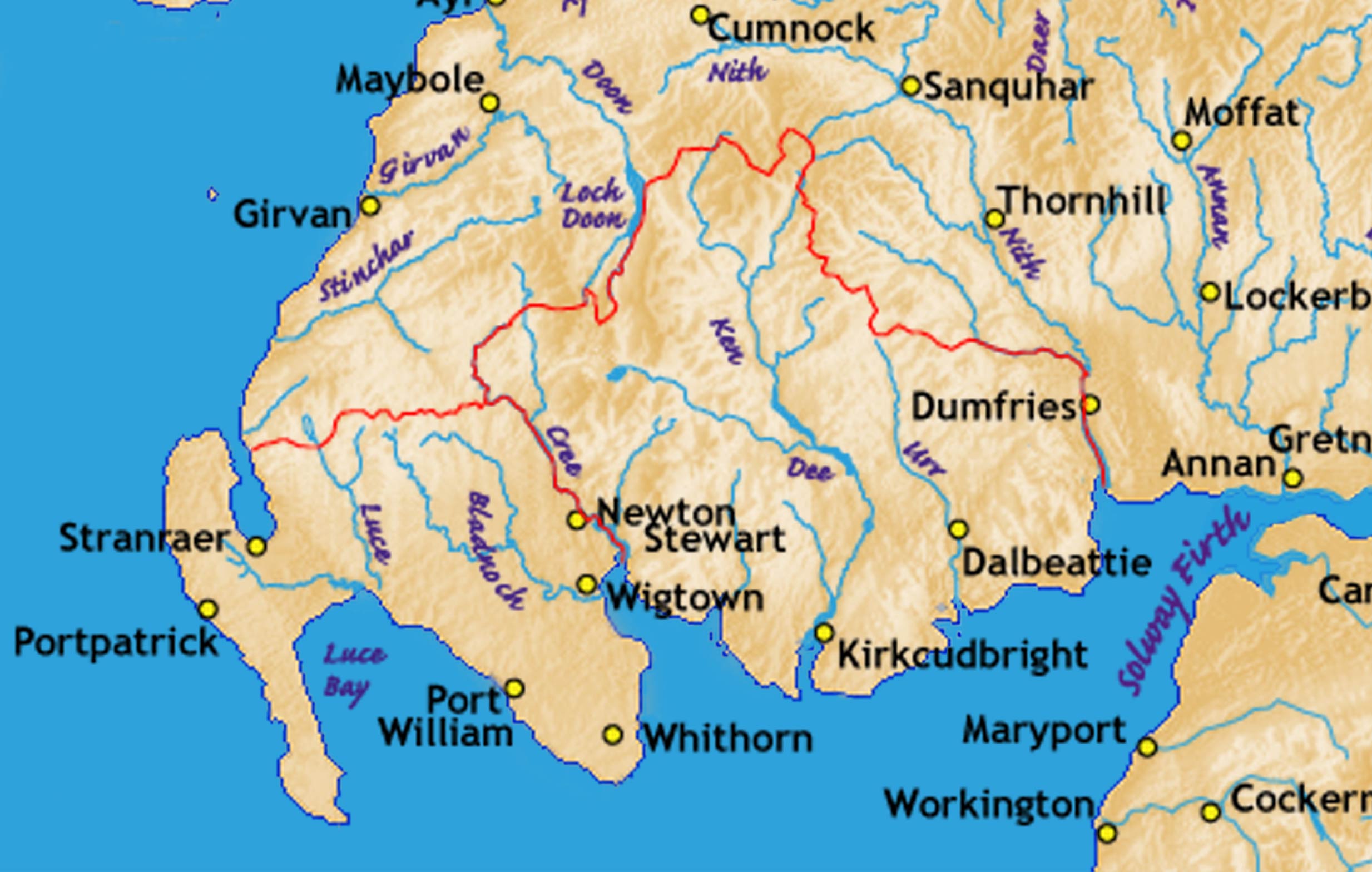
Galloway is bounded by sea to the west and south, the Galloway Hills
The Galloway Hills are part of the Southern Uplands of Scotland, and form the northern boundary of western Galloway. They lie within the bounds of the Galloway Forest Park, an area of some of largely uninhabited wild land, managed by Forestry an ...
to the north, and the River Nith
The River Nith ( gd, Abhainn Nid; Common Brittonic: ''Nowios'') is a river in south-west Scotland. The Nith rises in the Carsphairn hills of East Ayrshire, more precisely between Prickeny Hill and Enoch Hill, east of Dalmellington. For the ...
to the east; the border between Kirkcudbrightshire and Wigtownshire is marked by the River Cree
The River Cree is a river in Dumfries and Galloway, Scotland which runs through Newton Stewart and into the Solway Firth. It forms part of the boundary between the counties of Wigtownshire and Kirkcudbrightshire.
The tributaries of the Cree are ...
. The definition has, however, fluctuated greatly in size over history.
A hardy breed of black, hornless cattle
Cattle (''Bos taurus'') are large, domesticated, cloven-hooved, herbivores. They are a prominent modern member of the subfamily Bovinae and the most widespread species of the genus ''Bos''. Adult females are referred to as cows and adult ma ...
named Galloway cattle
The Galloway is a Scottish breed of beef cattle, named after the Galloway region of Scotland, where it originated during the seventeenth century.
It is usually black, is of average size, is naturally polled and has a thick coat suitable for ...
is native to the region, in addition to the more distinctive 'Belted Galloway
The Belted Galloway is a traditional Scottish breed of beef cattle. It derives from the Galloway cattle of the Galloway region of south-western Scotland, and was established as a separate breed in 1921. It is adapted to living on the poor upla ...
' or 'Beltie'.
Geography and landforms

 Galloway comprises the part of Scotland lying southwards from the Southern Upland watershed and westward from the
Galloway comprises the part of Scotland lying southwards from the Southern Upland watershed and westward from the River Nith
The River Nith ( gd, Abhainn Nid; Common Brittonic: ''Nowios'') is a river in south-west Scotland. The Nith rises in the Carsphairn hills of East Ayrshire, more precisely between Prickeny Hill and Enoch Hill, east of Dalmellington. For the ...
. Traditionally it has been described as stretching from "the braes of Glenapp to the Nith". The valleys of three rivers, the Urr Water
Urr Water or River Urr ('' arc. River Orr'') is a river in which flows through the counties of Dumfriesshire and Kirkcudbrightshire in southwest Scotland.
Course
Entirely within Dumfries and Galloway, the Urr Water originates at Loch Urr and flo ...
, the Water of Ken
The Water of Ken is a river in the historical county of Kirkcudbrightshire in Galloway, south-west Scotland. It rises on Blacklorg Hill, north-east of Cairnsmore of Carsphairn in the Carsphairn hills, and flows south-westward into The Glenkens, ...
and River Dee, and the Cree, all running north–south, provide much of the good arable land, although there is also some arable land on the coast. Generally however the landscape is rugged and much of the soil is shallow. The generally south slope and southern coast make for mild and wet climate, and there is a great deal of good pasture.
The northern part of Galloway is exceedingly rugged and forms the largest remaining wilderness in Britain
Britain most often refers to:
* The United Kingdom, a sovereign state in Europe comprising the island of Great Britain, the north-eastern part of the island of Ireland and many smaller islands
* Great Britain, the largest island in the United King ...
south of the Highlands
Highland is a broad term for areas of higher elevation, such as a mountain range or mountainous plateau.
Highland, Highlands, or The Highlands, may also refer to:
Places Albania
* Dukagjin Highlands
Armenia
* Armenian Highlands
Australia
*Sou ...
. This area is known as the Galloway Hills
The Galloway Hills are part of the Southern Uplands of Scotland, and form the northern boundary of western Galloway. They lie within the bounds of the Galloway Forest Park, an area of some of largely uninhabited wild land, managed by Forestry an ...
.
Land use
Historically Galloway has been known both forhorse
The horse (''Equus ferus caballus'') is a domesticated, one-toed, hoofed mammal. It belongs to the taxonomic family Equidae and is one of two extant subspecies of ''Equus ferus''. The horse has evolved over the past 45 to 55 million yea ...
s and for cattle rearing, and milk
Milk is a white liquid food produced by the mammary glands of mammals. It is the primary source of nutrition for young mammals (including breastfed human infants) before they are able to digest solid food. Immune factors and immune-modula ...
and beef
Beef is the culinary name for meat from cattle (''Bos taurus'').
In prehistoric times, humankind hunted aurochs and later domesticated them. Since that time, numerous breeds of cattle have been bred specifically for the quality or quantit ...
production are both still major industries. There is also substantial timber
Lumber is wood that has been processed into dimensional lumber, including beams and planks or boards, a stage in the process of wood production. Lumber is mainly used for construction framing, as well as finishing (floors, wall panels, w ...
production and some fisheries. The combination of hills and high rainfall make Galloway ideal for hydroelectric power production, and the Galloway Hydro Power scheme was begun in 1929. Since then, electricity generation
Electricity generation is the process of generating electric power from sources of primary energy. For utilities in the electric power industry, it is the stage prior to its delivery ( transmission, distribution, etc.) to end users or its s ...
has been a significant industry. More recently wind turbine
A wind turbine is a device that converts the kinetic energy of wind into electrical energy. Hundreds of thousands of large turbines, in installations known as wind farms, now generate over 650 gigawatts of power, with 60 GW added each yea ...
s have been installed at a number of locations on the watershed, and a large offshore wind-power plant is planned, increasing Galloway's 'green energy' production.
History
Galloway landmarks on Ptolemy's map

 The 2nd century geographer
The 2nd century geographer Ptolemy
Claudius Ptolemy (; grc-gre, Πτολεμαῖος, ; la, Claudius Ptolemaeus; AD) was a mathematician, astronomer, astrologer, geographer, and music theorist, who wrote about a dozen scientific treatises, three of which were of importance ...
produced a map of Britain in his ''Geography
Geography (from Greek: , ''geographia''. Combination of Greek words ‘Geo’ (The Earth) and ‘Graphien’ (to describe), literally "earth description") is a field of science devoted to the study of the lands, features, inhabitants, an ...
'', in which he describes the landmarks and peoples of the island. The landmarks were identified long ago, and a number of them relate to Galloway:
In the west, the city of (literally 'very royal place'), shown on Ptolemy
Claudius Ptolemy (; grc-gre, Πτολεμαῖος, ; la, Claudius Ptolemaeus; AD) was a mathematician, astronomer, astrologer, geographer, and music theorist, who wrote about a dozen scientific treatises, three of which were of importance ...
's map of the world, is a strong contender for the site of , referred to in the Welsh Triads
The Welsh Triads ( cy, Trioedd Ynys Prydein, "Triads of the Island of Britain") are a group of related texts in medieval manuscripts which preserve fragments of Welsh folklore, mythology and traditional history in groups of three. The triad is a ...
as one of the 'three thrones of Britain' associated with the legendary King Arthur, and may also have been the ' of the sub-Roman Brython
The Britons ( *''Pritanī'', la, Britanni), also known as Celtic Britons or Ancient Britons, were people of Celtic language and culture who inhabited Great Britain from at least the British Iron Age and into the Middle Ages, at which point the ...
ic kingdom of . 's exact position is uncertain except that it was 'on Loch Ryan
Loch Ryan ( gd, Loch Rìoghaine, ) is a Scottish sea loch that acts as an important natural harbour for shipping, providing calm waters for ferries operating between Scotland and Northern Ireland. The town of Stranraer is the largest settlemen ...
', close to modern day Stranraer; it is possible that it is the modern settlement of Dunragit
Dunragit ( gd, Dùn Reicheit) is a village on the A75, between Stranraer and Glenluce in Dumfries and Galloway, south-west Scotland. Dunragit is within the parish of Old Luce, in the traditional county of Wigtownshire. The modern village grew ...
().
Early Galloway

Romans
Roman or Romans most often refers to:
*Rome, the capital city of Italy
* Ancient Rome, Roman civilization from 8th century BC to 5th century AD
*Roman people, the people of ancient Rome
*''Epistle to the Romans'', shortened to ''Romans'', a lette ...
as the tribe. According to tradition, before the end of Roman rule in Britain, St. Ninian established a church or monastery at Whithorn
Whithorn ( �ʍɪthorn 'HWIT-horn'; ''Taigh Mhàrtainn'' in Gaelic), is a royal burgh in the historic county of Wigtownshire in Dumfries and Galloway, Scotland, about south of Wigtown. The town was the location of the first recorded Christia ...
, Wigtownshire
Wigtownshire or the County of Wigtown (, ) is one of the historic counties of Scotland, covering an area in the south-west of the country. Until 1975, Wigtownshire was an administrative county used for local government. Since 1975 the area has f ...
, which remained an important place of pilgrimage
A pilgrimage is a journey, often into an unknown or foreign place, where a person goes in search of new or expanded meaning about their self, others, nature, or a higher good, through the experience. It can lead to a personal transformation, aft ...
until the Reformation
The Reformation (alternatively named the Protestant Reformation or the European Reformation) was a major movement within Western Christianity in 16th-century Europe that posed a religious and political challenge to the Catholic Church and in ...
. The county is rich in prehistoric monuments and relics, amongst the most notable of which are the Drumtroddan standing stones (and cup-and-ring carvings), the Torhousekie Stone Circle, both in Wigtownshire
Wigtownshire or the County of Wigtown (, ) is one of the historic counties of Scotland, covering an area in the south-west of the country. Until 1975, Wigtownshire was an administrative county used for local government. Since 1975 the area has f ...
and Cairnholy
Cairnholy (or Cairn Holy) is the site of two Neolithic chambered tombs of the Clyde type. It is located 4 kilometres east of the village of Carsluith in Dumfries and Galloway, Scotland (). The tombs are scheduled monuments in the care of Hist ...
(a Neolithic chambered cairn). There is also evidence of one of the earliest pit-fall traps in Europe which was discovered near Glenluce
Glenluce ( gd, Clachan Ghlinn Lus) is a small village in the parish of Old Luce in Wigtownshire, Scotland.
It contains a village shop,a caravan park and a town hall, as well as the parish church.
Location
Glenluce on the A75 road between Stranr ...
, Wigtownshire
Wigtownshire or the County of Wigtown (, ) is one of the historic counties of Scotland, covering an area in the south-west of the country. Until 1975, Wigtownshire was an administrative county used for local government. Since 1975 the area has f ...
.
Middle Ages
A Brythonic speaking kingdom dominated Galloway until the late 7th century when it was absorbed by theEnglish
English usually refers to:
* English language
* English people
English may also refer to:
Peoples, culture, and language
* ''English'', an adjective for something of, from, or related to England
** English national ide ...
kingdom of Bernicia
Bernicia ( ang, Bernice, Bryneich, Beornice; la, Bernicia) was an Anglo-Saxon kingdom established by Anglian settlers of the 6th century in what is now southeastern Scotland and North East England.
The Anglian territory of Bernicia was ap ...
.
English prevalence was supplanted by Britons
British people or Britons, also known colloquially as Brits, are the citizens of the United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern Ireland, the British Overseas Territories, and the Crown dependencies.: British nationality law governs mod ...
and Norse-Gaelic () peoples between the 9th and the 11th century. This can be seen in the context of both the vacuum left by Northumbria
la, Regnum Northanhymbrorum
, conventional_long_name = Kingdom of Northumbria
, common_name = Northumbria
, status = State
, status_text = Unified Anglian kingdom (before 876)North: Anglian kingdom (af ...
being filled by the resurgent Cumbric Britons and the influx of the Norse into the Irish Sea, including settlement in the Isle of Man and in the now English region of western Cumbria
Cumbria ( ) is a ceremonial and non-metropolitan county in North West England, bordering Scotland. The county and Cumbria County Council, its local government, came into existence in 1974 after the passage of the Local Government Act 1972. C ...
immediately south of Galloway.
If it had not been for Fergus of Galloway
Fergus of Galloway (died 12 May 1161) was a twelfth-century Lord of Galloway. Although his familial origins are unknown, it is possible that he was of Norse-Gaelic ancestry. Fergus first appears on record in 1136, when he witnessed a charter ...
who established himself in Galloway, the region would rapidly have been absorbed by Scotland. This did not happen because Fergus, his sons, grandsons and great-grandson Alan, Lord of Galloway
Alan of Galloway (before 1199 – 1234), also known as Alan fitz Roland, was a leading thirteenth-century Scottish magnate. As the hereditary Lord of Galloway and Constable of Scotland, he was one of the most influential men in the Kingdom of S ...
, shifted their allegiance between Scottish and English
English usually refers to:
* English language
* English people
English may also refer to:
Peoples, culture, and language
* ''English'', an adjective for something of, from, or related to England
** English national ide ...
kings. During a period of Scottish allegiance a Galloway contingent followed David, King of Scots in his invasion of England and led the attack in his defeat at the Battle of the Standard (1138).
Alan died in 1234. He had three daughters and an illegitimate son Thomas. The 'Community of Galloway' wanted Thomas as their 'king'. Alexander III of Scotland
Alexander III (Medieval ; Modern Gaelic: ; 4 September 1241 – 19 March 1286) was King of Scots from 1249 until his death. He concluded the Treaty of Perth, by which Scotland acquired sovereignty over the Western Isles and the Isle of Man. His ...
supported the daughters (or rather their husbands) and invaded Galloway. The Community of Galloway was defeated, and Galloway divided up between Alan's daughters, thus bringing Galloway's independent existence to an end.
Alan's eldest daughter, (Latinized as Dervorguilla), married John de Balliol
John Balliol ( – late 1314), known derisively as ''Toom Tabard'' (meaning "empty coat" – coat of arms), was King of Scots from 1292 to 1296. Little is known of his early life. After the death of Margaret, Maid of Norway, Scotland entered a ...
, and their son (also John
John is a common English name and surname:
* John (given name)
* John (surname)
John may also refer to:
New Testament
Works
* Gospel of John, a title often shortened to John
* First Epistle of John, often shortened to 1 John
* Secon ...
) became one of the candidates for the Scottish Crown. Consequently, Scotland's Wars of Independence
This is a list of wars of independence (also called liberation wars
Wars of national liberation or national liberation revolutions are conflicts fought by nations to gain independence. The term is used in conjunction with wars against for ...
were disproportionately fought in Galloway.
There were a large number of new Gaelic placenames being coined post 1320 (e.g. Balmaclellan
Balmaclellan ( Scottish Gaelic: ''Baile MhicIllFhaolain'', meaning town of the MacLellans) is a small hillside village of stone houses with slate roofs in a fold of the Galloway hills in south-west Scotland. To the west, across the Ken River, ...
), because Galloway retained a substantial Gaelic speaking population for several centuries more. Following the Wars of Independence, Galloway became the fief
A fief (; la, feudum) was a central element in medieval contracts based on feudal law. It consisted of a form of property holding or other rights granted by an overlord to a vassal, who held it in fealty or "in fee" in return for a form ...
of Archibald the Grim
Archibald Douglas, Earl of Douglas and Wigtown, Lord of Galloway, Douglas and Bothwell (c. 1330 – c. 24 December 1400), called Archibald the Grim or Black Archibald, was a late medieval Scottish nobleman. Archibald was the bastard son of ...
, Earl of Douglas
This page is concerned with the holders of the forfeit title Earl of Douglas and the preceding feudal barons of Douglas, South Lanarkshire. The title was created in the Peerage of Scotland in 1358 for William Douglas, 1st Earl of Douglas, so ...
. In 1369 he received the part of Galloway east of the River Cree
The River Cree is a river in Dumfries and Galloway, Scotland which runs through Newton Stewart and into the Solway Firth. It forms part of the boundary between the counties of Wigtownshire and Kirkcudbrightshire.
The tributaries of the Cree are ...
, where he appointed a steward to administer the area, which became known as the Stewartry of Kirkcudbright
Kirkcudbrightshire ( ), or the County of Kirkcudbright or the Stewartry of Kirkcudbright is one of the historic counties of Scotland, covering an area in the south-west of the country. Until 1975, Kirkcudbrightshire was an administrative county ...
. The following year, he acquired the part of Galloway west of the Cree, which continued to be administered by the king's sheriff, and so became known as the Shire of Wigtown. The two parts of Galloway thereafter were administered separately, becoming separate counties
A county is a geographic region of a country used for administrative or other purposesChambers Dictionary, L. Brookes (ed.), 2005, Chambers Harrap Publishers Ltd, Edinburgh in certain modern nations. The term is derived from the Old French ...
.
Whithorn remained an important cultural centre, and all the medieval
In the history of Europe, the Middle Ages or medieval period lasted approximately from the late 5th to the late 15th centuries, similar to the post-classical period of global history. It began with the fall of the Western Roman Empire ...
Kings of Scots made pilgrimages there.
Modern history
Galwegian Gaelic
Galwegian Gaelic (also known as Gallovidian Gaelic, Gallowegian Gaelic, or Galloway Gaelic) is an extinct dialect of Scottish Gaelic formerly spoken in southwest Scotland. It was spoken by the people of Galloway and Carrick until the ear ...
seems to have lasted longer than Gaelic in other parts of Lowland Scotland
The Lowlands ( sco, Lallans or ; gd, a' Ghalldachd, , place of the foreigners, ) is a cultural and historical region of Scotland. Culturally, the Lowlands and the Highlands diverged from the Late Middle Ages into the modern period, when Lo ...
, and Margaret McMurray (d. 1760) of Carrick (outside modern Galloway) appears to have been the last recorded speaker.
In the years after the Union of the Crowns
The Union of the Crowns ( gd, Aonadh nan Crùintean; sco, Union o the Crouns) was the accession of James VI of Scotland to the throne of the Kingdom of England as James I and the practical unification of some functions (such as overseas dip ...
in 1603, Galloway underwent radical change, during the War of the Three Kingdoms
The Wars of the Three Kingdoms were a series of related conflicts fought between 1639 and 1653 in the kingdoms of England, Scotland and Ireland, then separate entities united in a personal union under Charles I. They include the 1639 to 1640 B ...
and Covenanter rebellion.
In modern times, Stranraer was a major ferry port, but the company have now moved to Cairnryan.
Galloway in literature
Galloway has been the setting of a number of novels, includingWalter Scott
Sir Walter Scott, 1st Baronet (15 August 1771 – 21 September 1832), was a Scottish novelist, poet, playwright and historian. Many of his works remain classics of European and Scottish literature, notably the novels '' Ivanhoe'', '' Rob Roy ...
's ''Guy Mannering
''Guy Mannering; or, The Astrologer'' is the second of the Waverley novels by Walter Scott, published anonymously in 1815. According to an introduction that Scott wrote in 1829, he had originally intended to write a story of the supernatural, ...
''.
Other novels include the historical fiction trilogy by Liz Curtis Higgs, ''Thorn in My Heart'', ''Fair is the Rose'', and ''Whence Came a Prince''. Richard Hannay flees London to lie low in Galloway in John Buchan's novel '' The Thirty-nine Steps''. '' Five Red Herrings'', a whodunit
A ''whodunit'' or ''whodunnit'' (a colloquial elision of "Who asdone it?") is a complex plot-driven variety of detective fiction in which the puzzle regarding who committed the crime is the main focus. The reader or viewer is provided with the c ...
by Dorothy L. Sayers
Dorothy Leigh Sayers (; 13 June 1893 – 17 December 1957) was an English crime writer and poet. She was also a student of classical and modern languages.
She is best known for her mysteries, a series of novels and short stories set between th ...
, initially published in the US as ''Suspicious Characters'', sees Lord Peter Wimsey
Lord Peter Death Bredon Wimsey (later 17th Duke of Denver) is the fictional protagonist in a series of detective novels and short stories by Dorothy L. Sayers (and their continuation by Jill Paton Walsh). A dilettante who solves mysteries fo ...
, on holiday in Kirkcudbright
Kirkcudbright ( ; sco, Kirkcoubrie; gd, Cille Chùithbeirt) is a town, parish and a Royal Burgh from 1455 in Kirkcudbrightshire, of which it is traditionally the county town, within Dumfries and Galloway, Scotland.
The town lies southwest of ...
, investigating the death of an artist living at Gatehouse of Fleet
Gatehouse of Fleet ( sco, Gatehoose o Fleet gd, Taigh an Rathaid) is a town half in the civil parish of Girthon and half in the parish of Anwoth divided by the river Fleet, Kirkcudbrightshire, within the district council region of Dumfries and ...
; the book contains some remarkable descriptions of the countryside. S R Crockett, a bestselling writer of historical romances active before the First World War, set several novels in the region including '' The Raiders'' and ''Silver Sand Silver sand is a fine white sand used in gardening. It consists largely of quartz particles that are not coated with iron oxides. Iron oxides colour sand from yellows to rich brown
Brown is a color. It can be considered a composite color, but ...
''.
See also
* Galloway Association of Glasgow *Galloway pony
The Galloway pony is an extinct horse breed, once native to Scotland and northern England. It was said to have "good looks, a wide, deep chest and a tendency to pace rather than trot." In the 18th century Galloways were bred in Swaledale, to ha ...
References
* Brooke, D: ''Wild Men and Holy Places''. Edinburgh: Canongate Press, 1994 * Oram, Richard, ''The Lordship of Galloway''. University of St Andrews, 1988 *External links
Galloway Dialect
at Scots Language Centre {{coord, 55, 03, N, 4, 08, W, source:kolossus-nowiki, display=title Geography of Dumfries and Galloway