GWR 2301 Class on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
The
At the outbreak of the
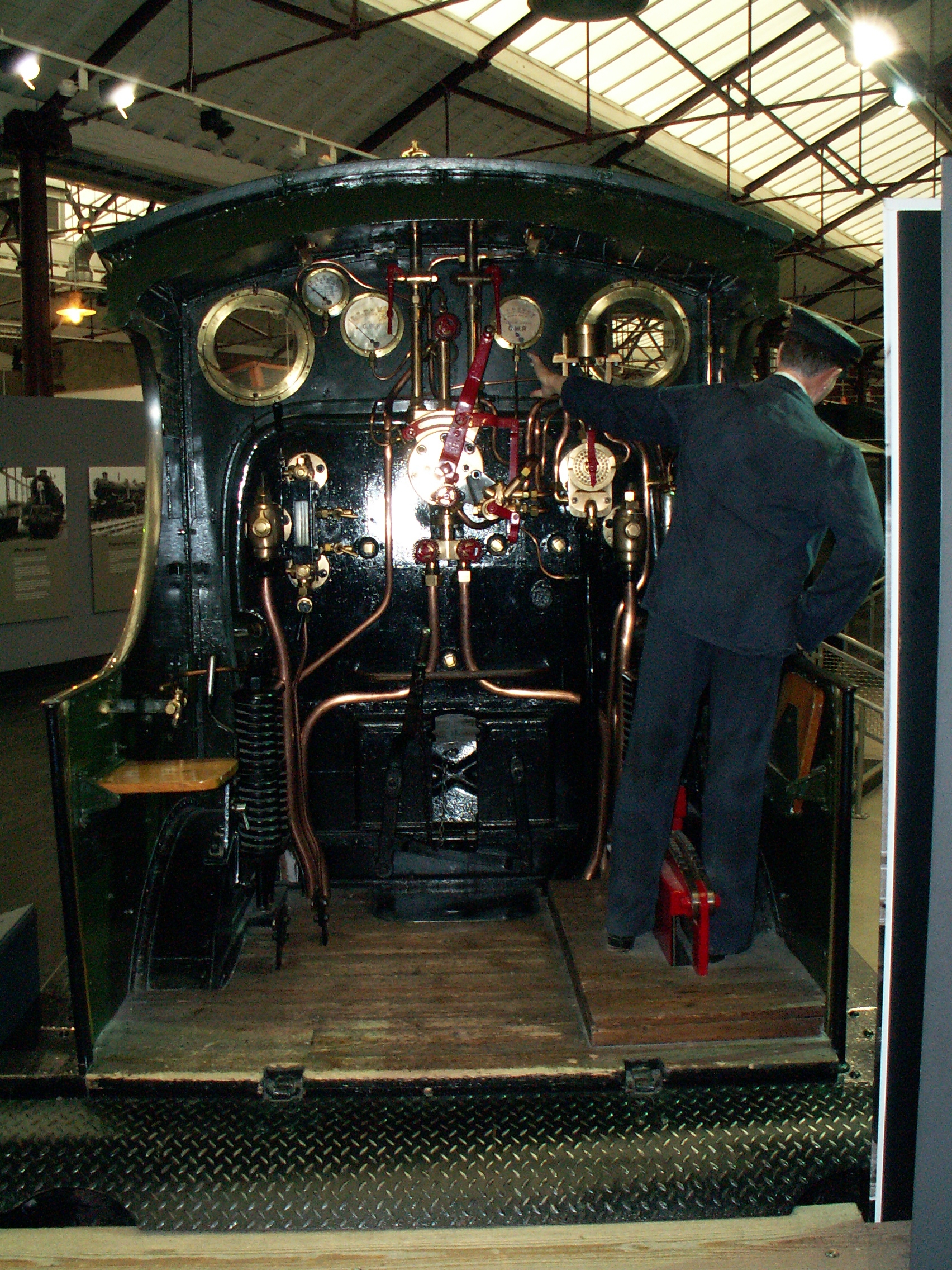 One locomotive, no. 2516 (built 1897), has survived into preservation. 2516 is currently a static exhibit at Swindon Steam Railway Museum, with the tender displayed far behind; visitors consequently have a clear view into the driving cab (see pictures).
One locomotive, no. 2516 (built 1897), has survived into preservation. 2516 is currently a static exhibit at Swindon Steam Railway Museum, with the tender displayed far behind; visitors consequently have a clear view into the driving cab (see pictures).
Rail UK database
{{FS locos 2301 0-6-0 locomotives War Department locomotives Railway Operating Division locomotives Railway locomotives introduced in 1883 Standard gauge steam locomotives of Great Britain Standard gauge locomotives of Austria Standard gauge locomotives of China Standard gauge locomotives of France Standard gauge locomotives of Greece Standard gauge locomotives of Italy Standard gauge locomotives of Poland Standard gauge locomotives of Tunisia Standard gauge locomotives of Turkey Steam locomotives of Austria Steam locomotives of China Steam locomotives of France Steam locomotives of Greece Steam locomotives of Italy Steam locomotives of Poland Steam locomotives of Tunisia Steam locomotives of Turkey Freight locomotives
Great Western Railway
The Great Western Railway (GWR) was a British railway company that linked London with the southwest, west and West Midlands of England and most of Wales. It was founded in 1833, received its enabling Act of Parliament on 31 August 1835 and ran ...
(GWR) 2301 Class or Dean Goods Class is a class of British 0-6-0
Under the Whyte notation for the classification of steam locomotives, represents the wheel arrangement of no leading wheels, six powered and coupled driving wheels on three axles and no trailing wheels. This was the most common wheel arrang ...
steam locomotive
A steam locomotive is a locomotive that provides the force to move itself and other vehicles by means of the expansion of steam. It is fuelled by burning combustible material (usually coal, oil or, rarely, wood) to heat water in the loco ...
s.
Swindon railway works built 260 of these goods locomotives between 1883 and 1899 to a design of William Dean. The 2301 class broke with previous GWR tradition in having inside frames only and changes were made in the boiler
A boiler is a closed vessel in which fluid (generally water) is heated. The fluid does not necessarily boil. The heated or vaporized fluid exits the boiler for use in various processes or heating applications, including water heating, central ...
design during the period that they were being built. The first twenty engines were originally domeless though all were provided with domed boilers in due course. They were numbered 2301–2360 and 2381–2580 (2361–2380 were of the 2361 class, which were similar visually but had outside frames).
Construction
Rebuild as 3901 class
In 1907, twenty Dean Goods (numbers 2491-2510) were rebuilt as2-6-2
Under the Whyte notation for the classification of steam locomotives, represents the wheel arrangement of two leading wheels, six coupled driving wheels and two trailing wheels. This arrangement is commonly called a Prairie.
Overview
The ...
T 'Prairie' tank locos, forming the new 3901 class numbers 3901-3920.
War Service
In 1917, 62 engines were taken over by the Railway Operating Division and sent to France. 46 of these engines returned to England in the early summer of 1919, but the other 16 had been sent on toSalonika
Thessaloniki (; el, Θεσσαλονίκη, , also known as Thessalonica (), Saloniki, or Salonica (), is the second-largest city in Greece, with over one million inhabitants in its metropolitan area, and the capital of the geographic region of ...
at the beginning of 1918. Two of these engines, nos 2308 and 2542, were sold to the Ottoman railways Ottoman railways may refer to:
* Chemins de Fer Ottomans d'Anatolie an Ottoman railway company located in Central Anatolia of the Ottoman Empire.
*The Syria Ottoman Railway Company
*Baghdad Railway
* Hejaz railway
*Other railways of the Ottoman Em ...
and renumbered 110 and 111. No 111 was withdrawn in September 1929, but 110 lasted until the 1950s. Of the 14 engines remaining at Salonika, five were written-off and the other nine returned to England in April 192At the outbreak of the
Second World War
World War II or the Second World War, often abbreviated as WWII or WW2, was a world war that lasted from 1939 to 1945. It involved the vast majority of the world's countries—including all of the great powers—forming two opposi ...
, the War Department War Department may refer to:
* War Department (United Kingdom)
* United States Department of War (1789–1947)
See also
* War Office, a former department of the British Government
* Ministry of defence
* Ministry of War
* Ministry of Defence
* D ...
requisitioned 100 of these engines from the GWR and the GWR had to hastily reinstate some engines that had been recently withdrawn. The requisitioned engines were fitted with Westinghouse brakes and 10 were fitted with pannier tanks and condensing gear. All were painted black with their WD numbers painted on. In December 1940, the War Department requisitioned a further 8 engines. The War Department renumbered the locomotives 93 to 200.
At the time of the German invasion of France, 79 of these engines had been shipped to France. Some of the engines were destroyed in the retreat to Dunkirk whilst the remainder were used on the French railways by the German occupation forces. After the war, between 22 and 26 engines were sent to China under UNRRA
United Nations Relief and Rehabilitation Administration (UNRRA) was an international relief agency, largely dominated by the United States but representing 44 nations. Founded in November 1943, it was dissolved in September 1948. it became part o ...
auspices, and 30 were returned to the UK, but were deemed unfit for service and scrap
Scrap consists of recyclable materials, usually metals, left over from product manufacturing and consumption, such as parts of vehicles, building supplies, and surplus materials. Unlike waste, scrap has monetary value, especially recovered m ...
ped. No.2435 (WD no.188) was sent to France in 1940 and was used in Silesia and then in Austria between 1944 and 1948 when it was claimed by the Russians before being handed back to the Austrians in 1952. Two further engines, nos. 2419 and 2526 (WD nos. 106 and 132). One locomotive, no.2489 (WD no.142), was in eastern Germany at the end of the War and was taken into Deutsche Reichsbahn (East Germany)
The Deutsche Reichsbahn or DR ''(German Reich Railways)'' was the operating name of state owned railways in the German Democratic Republic (East Germany), and after German reunification until 1 January 1994.
In 1949, occupied Germany's railw ...
stock as 53 7607; it was withdrawn in 1955. The remaining engines are assumed to have been scrapped.
Of the engines that remained in England, most of them worked at War Department and Ordnance depots around the country, though in 1943, 6 were shipped to Tunisia and thence to Italy.
Some locomotives of the class have the unusual distinction of being shipped overseas in both World Wars. 32 of the 108 locomotives requisitioned during the Second World War had been previously requisitioned during the First World War, and of those 32, 24 were again sent overseas.
British Railways
Fifty-four locomotives passed toBritish Railways
British Railways (BR), which from 1965 traded as British Rail, was a state-owned company that operated most of the overground rail transport in Great Britain from 1948 to 1997. It was formed from the nationalisation of the Big Four British ...
in 1948, mostly being used on Welsh branch lines due to their light axle load
An axle or axletree is a central shaft for a rotating wheel or gear. On wheeled vehicles, the axle may be fixed to the wheels, rotating with them, or fixed to the vehicle, with the wheels rotating around the axle. In the former case, bearin ...
s. They were progressively replaced by new BR standard class 2 2-6-0 engines, and no 2538 was the last to be withdrawn in May 1957.
Preservation
 One locomotive, no. 2516 (built 1897), has survived into preservation. 2516 is currently a static exhibit at Swindon Steam Railway Museum, with the tender displayed far behind; visitors consequently have a clear view into the driving cab (see pictures).
One locomotive, no. 2516 (built 1897), has survived into preservation. 2516 is currently a static exhibit at Swindon Steam Railway Museum, with the tender displayed far behind; visitors consequently have a clear view into the driving cab (see pictures).
Models
Three companies have released models of the Dean Goods class: Oxford Rail in 2017 in Great Western (no 2475 & 2534), RoD Khaki (no 2308) and British Railways Black (no 2409) liveries. Mainline Model Railways made a Dean Goods class in GWR Green (no 2516) and BR black (no 2538) in 1983.Hornby Model Railways
Hornby Railways is a British model railways manufacturing company. Its roots date back to 1901 in Liverpool, when founder Frank Hornby received a patent for his Meccano construction toy. The first clockwork train was produced in 1920. In 1938 ...
have released R2064/A/B/C (nos 2468, 2322, 2526, 2579), R2210 (no 2579) and R2275/A (nos 2322 & 2538)
References
Sources
* * * * * * * * *External links
Rail UK database
{{FS locos 2301 0-6-0 locomotives War Department locomotives Railway Operating Division locomotives Railway locomotives introduced in 1883 Standard gauge steam locomotives of Great Britain Standard gauge locomotives of Austria Standard gauge locomotives of China Standard gauge locomotives of France Standard gauge locomotives of Greece Standard gauge locomotives of Italy Standard gauge locomotives of Poland Standard gauge locomotives of Tunisia Standard gauge locomotives of Turkey Steam locomotives of Austria Steam locomotives of China Steam locomotives of France Steam locomotives of Greece Steam locomotives of Italy Steam locomotives of Poland Steam locomotives of Tunisia Steam locomotives of Turkey Freight locomotives