Funeral of Martin Luther King Jr. on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
The first memorial service following the assassination of
 After the shooting, King was taken by ambulance to the emergency room at St. Joseph's Hospital and was pronounced dead at 7:05 p.m. King's closest aides contacted Robert Lewis Jr.—a local funeral director who had coincidentally met King two days prior—to retrieve his body and prepare it for viewing.
After the shooting, King was taken by ambulance to the emergency room at St. Joseph's Hospital and was pronounced dead at 7:05 p.m. King's closest aides contacted Robert Lewis Jr.—a local funeral director who had coincidentally met King two days prior—to retrieve his body and prepare it for viewing.
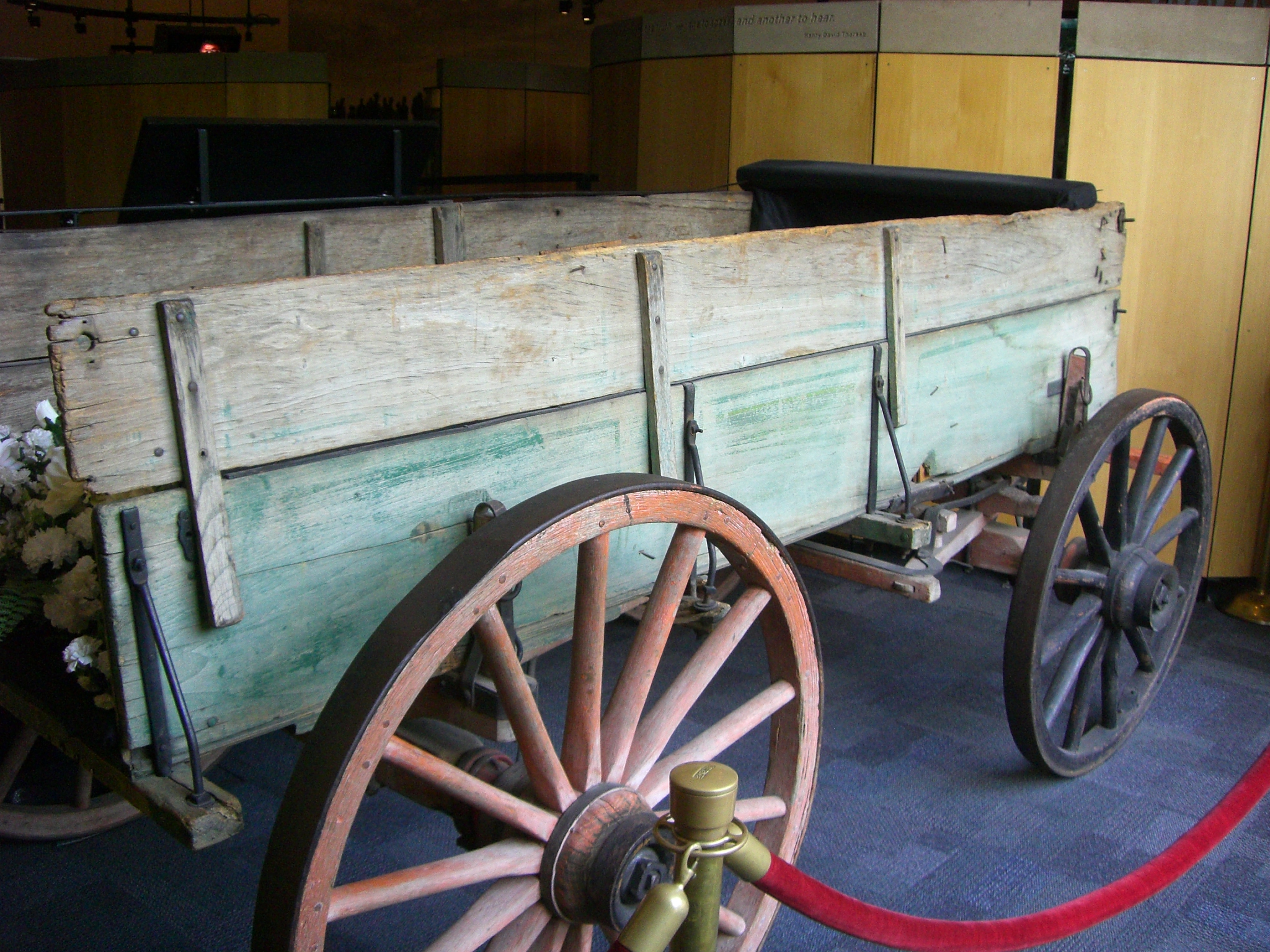 The private funeral was followed by the loading of King's casket onto a simple wooden farm wagon pulled by two mules named Belle and Ada from Gee's Bend. The procession down the three-and-a-half miles from Ebenezer Baptist Church to Morehouse College was observed by over 100,000 people; the Southern Christian Leadership Conference commissioned a security detail to manage the crowd, while the
The private funeral was followed by the loading of King's casket onto a simple wooden farm wagon pulled by two mules named Belle and Ada from Gee's Bend. The procession down the three-and-a-half miles from Ebenezer Baptist Church to Morehouse College was observed by over 100,000 people; the Southern Christian Leadership Conference commissioned a security detail to manage the crowd, while the
 The public and final service was held at Morehouse College, where King was eulogized by college president
The public and final service was held at Morehouse College, where King was eulogized by college president
Photo of mourners at R.S. Lewis funeral home
{{Atlanta history 1968 in Georgia (U.S. state) 1968 in Tennessee April 1968 events in the United States Assassination of Martin Luther King Jr. King, Martin Luther King, Martin Luther 1960s in Atlanta History of Memphis, Tennessee
Martin Luther King Jr.
Martin Luther King Jr. (born Michael King Jr.; January 15, 1929 – April 4, 1968) was an American Baptist minister and activist, one of the most prominent leaders in the civil rights movement from 1955 until his assassination in 1968 ...
on April 4, 1968, took place the following day at the R.S. Lewis Funeral Home in Memphis, Tennessee
Memphis is a city in the U.S. state of Tennessee. It is the seat of Shelby County in the southwest part of the state; it is situated along the Mississippi River. With a population of 633,104 at the 2020 U.S. census, Memphis is the second-mos ...
. This was followed by two funeral services on April 9, 1968, in Atlanta, Georgia
Atlanta ( ) is the capital and most populous city of the U.S. state of Georgia. It is the seat of Fulton County, the most populous county in Georgia, but its territory falls in both Fulton and DeKalb counties. With a population of 498,7 ...
, the first held for family and close friends at Ebenezer Baptist Church, where King and his father had both served as senior pastors, followed by a three-mile procession to Morehouse College, King's alma mater, for a public service.
President Lyndon B. Johnson
Lyndon Baines Johnson (; August 27, 1908January 22, 1973), often referred to by his initials LBJ, was an American politician who served as the 36th president of the United States from 1963 to 1969. He had previously served as the 37th vice ...
declared a national day of mourning
A national day of mourning is a day or days marked by mourning and memorial activities observed among the majority of a country's populace. They are designated by the national government. Such days include those marking the death or funeral of ...
for the lost civil rights leader on April 7.
Background
Martin Luther King Jr., a civil rights activist, Baptist preacher, andNobel Peace Prize
The Nobel Peace Prize is one of the five Nobel Prizes established by the will of Swedish industrialist, inventor and armaments (military weapons and equipment) manufacturer Alfred Nobel, along with the prizes in Chemistry, Physics, Physiolog ...
laureate, was assassinated on April 4, 1968, by a gunshot wound to the right side of his jaw, neck and shoulder in Memphis, Tennessee, where he had been leading a strike of waste management workers. The news of the murder sent shockwaves of emotion in many African American communities in a number of cities, resulting in deadly riots between the day of the murder and the day of the funeral.
A state funeral or lying in state was refused to King by then-governor of Georgia Lester Maddox
Lester Garfield Maddox Sr. (September 30, 1915 – June 25, 2003) was an American politician who served as the 75th governor of the U.S. state of Georgia from 1967 to 1971. A populist Democrat, Maddox came to prominence as a staunch segregatio ...
, who had considered King an "enemy of the country" and had stationed 64 riot-helmeted state troopers at the steps of the state capitol in Atlanta to protect state property. He also initially refused to allow the state flag to be lowered at half staff, but was compelled to do so when told that the lowering was a federal mandate.
There were concerns that U.S. president Lyndon Johnson might be the subject of protests, over the conduct of the war in Vietnam, which would disrupt the funeral. Vice President Hubert Humphrey
Hubert Horatio Humphrey Jr. (May 27, 1911 – January 13, 1978) was an American pharmacist and politician who served as the 38th vice president of the United States from 1965 to 1969. He twice served in the United States Senate, representing Mi ...
attended on his behalf.
Service in Memphis
 After the shooting, King was taken by ambulance to the emergency room at St. Joseph's Hospital and was pronounced dead at 7:05 p.m. King's closest aides contacted Robert Lewis Jr.—a local funeral director who had coincidentally met King two days prior—to retrieve his body and prepare it for viewing.
After the shooting, King was taken by ambulance to the emergency room at St. Joseph's Hospital and was pronounced dead at 7:05 p.m. King's closest aides contacted Robert Lewis Jr.—a local funeral director who had coincidentally met King two days prior—to retrieve his body and prepare it for viewing.
Coretta Scott King
Coretta Scott King ( Scott; April 27, 1927 – January 30, 2006) was an American author, activist, and civil rights leader who was married to Martin Luther King Jr. from 1953 until his death. As an advocate for African-American equality, she ...
arrived in Memphis the following morning on a plane personally arranged by Robert F. Kennedy
Robert Francis Kennedy (November 20, 1925June 6, 1968), also known by his initials RFK and by the nickname Bobby, was an American lawyer and politician who served as the 64th United States Attorney General from January 1961 to September 1964, ...
. Hundreds began arriving at the funeral home, where a viewing and memorial service took place. Ralph Abernathy
Ralph David Abernathy Sr. (March 11, 1926 – April 17, 1990) was an American civil rights activist and Baptist minister. He was ordained in the Baptist tradition in 1948. As a leader of the civil rights movement, he was a close friend and ...
offered a prayer, while tears streamed down Andrew Young's face. ''Time
Time is the continued sequence of existence and events that occurs in an apparently irreversible succession from the past, through the present, into the future. It is a component quantity of various measurements used to sequence events, ...
'' magazine wrote:
In Memphis, before it was carried south toward home, King's body lay in state at the R.S. Lewis & Sons Funeral Home in an open bronze casket, the black suit tidily pressed, the wound in the throat now all but invisible. Many of those who filed past could not control their tears. Some kissed King's lips; others reverently touched his face. A few people threw their hands in the air and cried aloud in ululating agony. Mrs. King was a dry-eyed frieze of heartbreak.Later that day, police and National Guardsmen escorted the long procession of cars which carried King's body to the airport for the flight to Atlanta.
Services in Atlanta
The first, private service began at 10:30 a.m. EST at Ebenezer Baptist Church, and was filled with some 1,300 people; among the dignitaries present were labor leaders, foreign dignitaries, entertainment and sports figures and leaders from numerous religious faiths. The service began with Reverend Ralph Abernathy delivering a sermon which called the event "one of the darkest hours of mankind". At his widow's request, King eulogized himself: His last sermon at Ebenezer Baptist Church, a recording of his famous "Drum Major Instinct" sermon, given on February 4, 1968, was played at the funeral. In that sermon he makes a request that at his funeral no mention of his awards and honors be made, but that it be said that he tried to "feed the hungry", "clothe the naked", "be right on the ietnamwar question", and "love and serve humanity". Per King's request, his good friendMahalia Jackson
Mahalia Jackson ( ; born Mahala Jackson; October 26, 1911 – January 27, 1972) was an American gospel singer, widely considered one of the most influential vocalists of the 20th century. With a career spanning 40 years, Jackson was integral to ...
sang his favorite hymn, "Take My Hand, Precious Lord
"Take My Hand, Precious Lord" (a.k.a. "Precious Lord, Take My Hand") is a gospel song. The lyrics were written by Thomas A. Dorsey, who also adapted the melody.
Origin
The melody is credited to Dorsey, drawn extensively from the 1844 hymn tune, " ...
", though not as part of the morning funeral service but later that day at a second open-air service at Morehouse College.
Procession
 The private funeral was followed by the loading of King's casket onto a simple wooden farm wagon pulled by two mules named Belle and Ada from Gee's Bend. The procession down the three-and-a-half miles from Ebenezer Baptist Church to Morehouse College was observed by over 100,000 people; the Southern Christian Leadership Conference commissioned a security detail to manage the crowd, while the
The private funeral was followed by the loading of King's casket onto a simple wooden farm wagon pulled by two mules named Belle and Ada from Gee's Bend. The procession down the three-and-a-half miles from Ebenezer Baptist Church to Morehouse College was observed by over 100,000 people; the Southern Christian Leadership Conference commissioned a security detail to manage the crowd, while the Atlanta Police Department
The Atlanta Police Department (APD) is a law enforcement agency in the city of Atlanta, Georgia, U.S.
The city shifted from its rural-based Marshal and Deputy Marshal model at the end of the 19th century. In 1873, the department was formed with 2 ...
limited their participation to management of automobile traffic and to accompany dignitaries attending the events. The procession was silent, although it was accompanied on occasion by the singing of freedom songs which were frequently sung during the marches in which King had participated.
Among the persons leading the procession, besides the immediate family of the civil rights leader, were Jesse Jackson, who held the flag of the United Nations, John Lewis
John Robert Lewis (February 21, 1940 – July 17, 2020) was an American politician and civil rights activist who served in the United States House of Representatives for from 1987 until his death in 2020. He participated in the 1960 Nashville ...
, and Andrew Young
Andrew Jackson Young Jr. (born March 12, 1932) is an American politician, diplomat, and activist. Beginning his career as a pastor, Young was an early leader in the civil rights movement, serving as executive director of the Southern Christian L ...
who was at one time the mayor of Atlanta and also ambassador to the United Nations. Labor leader and civil rights activist Walter Reuther
Walter Philip Reuther (; September 1, 1907 – May 9, 1970) was an American leader of organized labor and civil rights activist who built the United Automobile Workers (UAW) into one of the most progressive labor unions in American history. He ...
also participated in King's funeral procession.
The procession passed by the Georgia State Capitol building.
At the conclusion of the ceremony, the group sang "We Shall Overcome
"We Shall Overcome" is a gospel song which became a protest song and a key anthem of the American civil rights movement. The song is most commonly attributed as being lyrically descended from "I'll Overcome Some Day", a hymn by Charles Albert ...
".
Morehouse
 The public and final service was held at Morehouse College, where King was eulogized by college president
The public and final service was held at Morehouse College, where King was eulogized by college president Benjamin Mays
Benjamin Elijah Mays (August 1, 1894 – March 28, 1984) was an American Baptist minister and American rights leader who is credited with laying the intellectual foundations of the American civil rights movement. Mays taught and mentored many in ...
, who had given the benediction after King's " I Have a Dream" speech.
Following the funeral, King's casket was loaded into a hearse for his final trip to the South-View Cemetery, a burial place predominantly reserved for African Americans. His remains were exhumed in 1970 and reburied at their current location at the plaza between the King Center and Ebenezer, and his widow Coretta was buried next to him in 2006.
References
External links
Photo of mourners at R.S. Lewis funeral home
{{Atlanta history 1968 in Georgia (U.S. state) 1968 in Tennessee April 1968 events in the United States Assassination of Martin Luther King Jr. King, Martin Luther King, Martin Luther 1960s in Atlanta History of Memphis, Tennessee