Franz Neuhausen on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Franz Neuhausen (13 December 1887 – 14 April 1966) was a wealthy industrialist who became the special
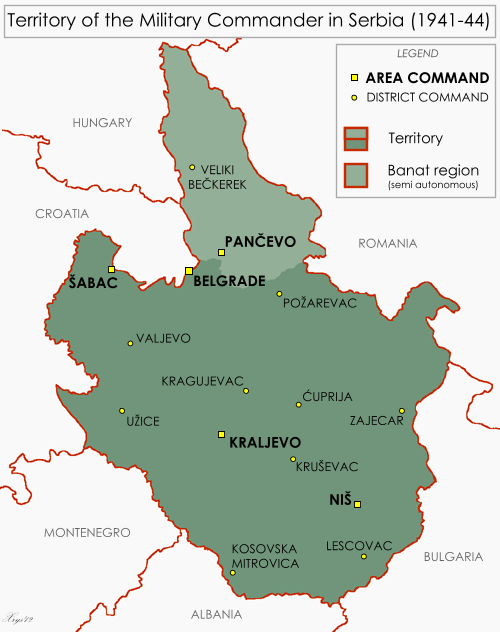 Promoted to '' NSFK-Obergruppenführer'', Neuhausen was initially appointed by Göring as
Promoted to '' NSFK-Obergruppenführer'', Neuhausen was initially appointed by Göring as
plenipotentiary
A ''plenipotentiary'' (from the Latin ''plenus'' "full" and ''potens'' "powerful") is a diplomat who has full powers—authorization to sign a treaty or convention on behalf of his or her sovereign. When used as a noun more generally, the wor ...
for economic affairs in the Territory of the Military Commander in Serbia during most of the German
German(s) may refer to:
* Germany (of or related to)
**Germania (historical use)
* Germans, citizens of Germany, people of German ancestry, or native speakers of the German language
** For citizens of Germany, see also German nationality law
**Ge ...
military occupation
Military occupation, also known as belligerent occupation or simply occupation, is the effective military control by a ruling power over a territory that is outside of that power's sovereign territory.Eyāl Benveniśtî. The international law ...
of that region of the partitioned Kingdom of Yugoslavia
The Kingdom of Yugoslavia ( sh-Latn-Cyrl, separator=" / ", Kraljevina Jugoslavija, Краљевина Југославија; sl, Kraljevina Jugoslavija) was a state in Southeast and Central Europe that existed from 1918 until 1941. From 191 ...
during World War II
World War II or the Second World War, often abbreviated as WWII or WW2, was a world war that lasted from 1939 to 1945. It involved the World War II by country, vast majority of the world's countries—including all of the great power ...
. He worked as a representative of Germany and the Nazi Party
The Nazi Party, officially the National Socialist German Workers' Party (german: Nationalsozialistische Deutsche Arbeiterpartei or NSDAP), was a far-right political party in Germany active between 1920 and 1945 that created and supported t ...
in Belgrade
Belgrade ( , ;, ; names in other languages) is the capital and largest city in Serbia. It is located at the confluence of the Sava and Danube rivers and the crossroads of the Pannonian Plain and the Balkan Peninsula. Nearly 1,166,763 mi ...
throughout the 1930s, during which he amassed a huge fortune. As a close friend and personal favourite of '' Reichsmarshall'' Hermann Göring
Hermann Wilhelm Göring (or Goering; ; 12 January 1893 – 15 October 1946) was a German politician, military leader and convicted war criminal. He was one of the most powerful figures in the Nazi Party, which ruled Germany from 1933 to 1 ...
, he became Göring's direct representative for the Four Year Plan
The Four Year Plan was a series of economic measures initiated by Adolf Hitler in Nazi Germany in 1936. Hitler placed Hermann Göring in charge of these measures, making him a Reich Plenipotentiary (Reichsbevollmächtigter) whose jurisdiction cut a ...
in the occupied territory, and was its virtual economic dictator from April 1941 until August 1944. On 18 October 1943 he succeeded Harald Turner as the Chief of the Military Administration in Serbia, and he continued to fulfill both roles until late August 1944.
Neuhausen was considered "sleazy and unscrupulous" and "notoriously corrupt". After complaints by senior Nazi officials in south-east Europe he was arrested and sent to a concentration camp, but survived to be captured by United States authorities. He was handed over by the US to the Yugoslav authorities after the war, and was sentenced to 20 years imprisonment. He was released in 1953 and died in Munich
Munich ( ; german: München ; bar, Minga ) is the capital and most populous city of the German state of Bavaria. With a population of 1,558,395 inhabitants as of 31 July 2020, it is the third-largest city in Germany, after Berlin and ...
, West Germany
West Germany is the colloquial term used to indicate the Federal Republic of Germany (FRG; german: Bundesrepublik Deutschland , BRD) between its formation on 23 May 1949 and the German reunification through the accession of East Germany on 3 ...
in 1966.
Early life and inter-war years
Neuhausen was born on 13 December 1887 in the town ofMerzig
Merzig (, french: Mercy, ''Moselle Franconian:'' ''Meerzisch''/''Miërzësch'') is a town in Saarland, Germany. It is the capital of the district Merzig-Wadern, with about 30,000 inhabitants in 17 municipalities on 108 km². It is situated ...
in the Rhine Province
The Rhine Province (german: Rheinprovinz), also known as Rhenish Prussia () or synonymous with the Rhineland (), was the westernmost province of the Kingdom of Prussia and the Free State of Prussia, within the German Reich, from 1822 to 1946. ...
of the German Empire
The German Empire (),Herbert Tuttle wrote in September 1881 that the term "Reich" does not literally connote an empire as has been commonly assumed by English-speaking people. The term literally denotes an empire – particularly a hereditary ...
. Nothing is known of his family or life before World War I
World War I (28 July 1914 11 November 1918), often abbreviated as WWI, was List of wars and anthropogenic disasters by death toll, one of the deadliest global conflicts in history. Belligerents included much of Europe, the Russian Empire, ...
, and he was a pilot in the German Air Force
The German Air Force (german: Luftwaffe, lit=air weapon or air arm, ) is the aerial warfare branch of the , the armed forces of Germany. The German Air Force (as part of the ''Bundeswehr'') was founded in 1956 during the era of the Cold War as ...
during that war. In the inter-war period
In the history of the 20th century, the interwar period lasted from 11 November 1918 to 1 September 1939 (20 years, 9 months, 21 days), the end of the First World War to the beginning of the Second World War. The interwar period was relative ...
he reached the rank of ''Gruppenführer
__NOTOC__
''Gruppenführer'' (, ) was an early paramilitary rank of the Nazi Party (NSDAP), first created in 1925 as a senior rank of the SA. Since then, the term ''Gruppenführer'' is also used for leaders of groups/teams of the police, fire d ...
'' (major general) in the National Socialist Flyers Corps
The National Socialist Flyers Corps (german: Nationalsozialistisches Fliegerkorps; NSFK) was a paramilitary aviation organization of the Nazi Party.
History
NSFK was founded 15 April 1937 as a successor to the German Air Sports Association; the ...
(german: Nationalsozialistisches Fliegerkorps, NSFK) which was a paramilitary Nazi Party
The Nazi Party, officially the National Socialist German Workers' Party (german: Nationalsozialistische Deutsche Arbeiterpartei or NSDAP), was a far-right political party in Germany active between 1920 and 1945 that created and supported t ...
organisation similar to the ''Sturmabteilung
The (; SA; literally "Storm Detachment") was the original paramilitary wing of the Nazi Party. It played a significant role in Adolf Hitler's rise to power in the 1920s and 1930s. Its primary purposes were providing protection for Nazi ralli ...
'' or SA. He was stationed in Belgrade
Belgrade ( , ;, ; names in other languages) is the capital and largest city in Serbia. It is located at the confluence of the Sava and Danube rivers and the crossroads of the Pannonian Plain and the Balkan Peninsula. Nearly 1,166,763 mi ...
from 1931 onwards, first as the manager of the German Transportation Office, then as the official representative or party attache (''Landesgruppenleiter'') of the Nazi Party in the Kingdom of Yugoslavia
The Kingdom of Yugoslavia ( sh-Latn-Cyrl, separator=" / ", Kraljevina Jugoslavija, Краљевина Југославија; sl, Kraljevina Jugoslavija) was a state in Southeast and Central Europe that existed from 1918 until 1941. From 191 ...
, and finally as the German consul-general
A consul is an official representative of the government of one state in the territory of another, normally acting to assist and protect the citizens of the consul's own country, as well as to facilitate trade and friendship between the people ...
, with the rank of Consul-General Major of the Luftwaffe
The ''Luftwaffe'' () was the aerial-warfare branch of the German '' Wehrmacht'' before and during World War II. Germany's military air arms during World War I, the '' Luftstreitkräfte'' of the Imperial Army and the '' Marine-Fliegerabt ...
. It is likely that he fulfilled both political and economic intelligence work in Yugoslavia throughout the 1930s. He had effective networks in both government and political circles and kept himself well informed about political and economic conditions, becoming a wealthy industrialist in the process. With the assistance of his close friend '' Reichsmarshall'' Hermann Göring
Hermann Wilhelm Göring (or Goering; ; 12 January 1893 – 15 October 1946) was a German politician, military leader and convicted war criminal. He was one of the most powerful figures in the Nazi Party, which ruled Germany from 1933 to 1 ...
he obtained shares
In financial markets, a share is a unit of equity ownership in the capital stock of a corporation, and can refer to units of mutual funds, limited partnerships, and real estate investment trusts. Share capital refers to all of the shares of ...
in a range of mining and metal industries through dubious transactions. As a result of such deals, Neuhausen was arrested by the Gestapo
The (), abbreviated Gestapo (; ), was the official secret police of Nazi Germany and in German-occupied Europe.
The force was created by Hermann Göring in 1933 by combining the various political police agencies of Prussia into one orga ...
several times but Göring interceded on his behalf on each occasion to ensure that the serious charges were downgraded. In return, Neuhausen provided Göring with foreign currency, and when he attended the ''Reichsmarshalls birthday party each year he gave Göring a bar of gold or silver. Göring used this money to amass a huge collection of artworks and jewelry at his country estate, Carinhall
Carinhall was the country residence of Hermann Göring, built in the 1930s on a large hunting estate north-east of Berlin in the Schorfheide Forest, in the north of Brandenburg, between the lakes of Großdöllner See and Wuckersee.
History
Named ...
. As consul-general, Neuhausen negotiated the purchase of the huge Bor copper mines from the defeated French
French (french: français(e), link=no) may refer to:
* Something of, from, or related to France
** French language, which originated in France, and its various dialects and accents
** French people, a nation and ethnic group identified with Franc ...
in 1940, and subsequently became chairman of the board of the new German company that operated the mines, ''Bor Kupferbergwerke und Hütten A.G.'' in Belgrade.
Role in the occupied territory
 Promoted to '' NSFK-Obergruppenführer'', Neuhausen was initially appointed by Göring as
Promoted to '' NSFK-Obergruppenführer'', Neuhausen was initially appointed by Göring as plenipotentiary
A ''plenipotentiary'' (from the Latin ''plenus'' "full" and ''potens'' "powerful") is a diplomat who has full powers—authorization to sign a treaty or convention on behalf of his or her sovereign. When used as a noun more generally, the wor ...
general for economic affairs (''Generalbevollmächtigte für die Wirtschaft'') in the Territory of the Military Commander in Serbia, but his role soon expanded to encompass plenipotentiary responsibility for the Four Year Plan
The Four Year Plan was a series of economic measures initiated by Adolf Hitler in Nazi Germany in 1936. Hitler placed Hermann Göring in charge of these measures, making him a Reich Plenipotentiary (Reichsbevollmächtigter) whose jurisdiction cut a ...
in the occupied territory. On 9 December 1942, Neuhausen was also appointed to the important role of plenipotentiary for metal ore production in south-east Europe, which was initially limited to the occupied territory and the areas of Yugoslavia annexed by Bulgaria, and he was also empowered as plenipotentiary for labour in the occupied territory. Soon after the military administration began, Neuhausen appointed commissioners through whom he controlled the Serbian National Bank and other key economic and financial enterprises. In March 1943 Neuhausen's responsibilities for metals ore production were extended to German-occupied Greece, and after the Italian
Italian(s) may refer to:
* Anything of, from, or related to the people of Italy over the centuries
** Italians, an ethnic group or simply a citizen of the Italian Republic or Italian Kingdom
** Italian language, a Romance language
*** Regional Ita ...
surrender that September, to the previously Italian-occupied parts of Greece and Albania
Albania ( ; sq, Shqipëri or ), or , also or . officially the Republic of Albania ( sq, Republika e Shqipërisë), is a country in Southeastern Europe. It is located on the Adriatic and Ionian Seas within the Mediterranean Sea and share ...
. In October 1943, the Germans simplified their military administration, and on 18 October 1943 his existing roles were combined with the key role of Chief of the Military Administration (''Militärverwaltungschef''). He remained the chairman of the Bor mining company, which in July 1943 brought in 6,200 Jewish
Jews ( he, יְהוּדִים, , ) or Jewish people are an ethnoreligious group and nation originating from the Israelites Israelite origins and kingdom: "The first act in the long drama of Jewish history is the age of the Israelites""The ...
forced labourers from Hungary
Hungary ( hu, Magyarország ) is a landlocked country in Central Europe. Spanning of the Carpathian Basin, it is bordered by Slovakia to the north, Ukraine to the northeast, Romania to the east and southeast, Serbia to the south, Cr ...
and territories it had occupied to alleviate the shortage of manpower to work the mine. At the mines the labourers were under the supervision of the SS and worked in knee-deep water for 12-hour shifts. Neuhausen was also chair of the German banking corporation ''Bankverein für Serbien'' in the occupied territory, as well as several other important companies. Economically, the occupied territory was very important to the Germans as a source of metals, minerals, coal and food. Neuhausen was a powerful figure who had complete control of the economy and state finances of the occupied territory, and successfully exploited them to make a significant contribution to the German war effort.
Rivalry and arrest
The presence in Belgrade of direct representatives of senior Nazi officials such as Himmler and Göring meant there were often competing interests at work. As plenipotentiary for economic affairs and a "favourite" of Göring, Neuhausen acted as a virtual economic dictator on the ''Reichsmarshall's'' behalf in the occupied territory, squeezing the maximum amount of resources out of the local economy to feed the German war machine. Neuhausen was described as being "notoriously corrupt" and "sleazy and unscrupulous", and had numerous disagreements with other senior officials of the occupation regime regarding the extent of his jurisdiction. In particular, he strenuously opposed attempts by Foreign Affairs Envoy Hermann Neubacher to give more power to the Belgrade puppet government ofMilan Nedić
Milan Nedić ( sr-Cyrl, Милан Недић; 2 September 1878 – 4 February 1946) was a Yugoslav and Serbian army general and politician who served as the chief of the General Staff of the Royal Yugoslav Army and minister of war in the R ...
. Neubacher believed that Neuhausen was corrupt and that he had amassed a huge fortune while serving in Belgrade. After a series of complaints against him by the commander-in-chief southeast Europe ''Generalfeldmarschall
''Generalfeldmarschall'' (from Old High German ''marahscalc'', "marshal, stable master, groom"; en, general field marshal, field marshal general, or field marshal; ; often abbreviated to ''Feldmarschall'') was a rank in the armies of several ...
'' (Field Marshal) Maximilian von Weichs
Maximilian Maria Joseph Karl Gabriel Lamoral Reichsfreiherr von und zu Weichs an der Glon (12 November 1881 – 27 September 1954) was a field marshal in the Wehrmacht of Nazi Germany during World War II.
Born into an aristocratic family, Weichs ...
and Neubacher himself, an agreement was reached with the Nazi Foreign Minister Joachim von Ribbentrop
Ulrich Friedrich Wilhelm Joachim von Ribbentrop (; 30 April 1893 – 16 October 1946) was a German politician and diplomat who served as Minister of Foreign Affairs of Nazi Germany from 1938 to 1945.
Ribbentrop first came to Adolf Hitler's not ...
and Himmler, and Neuhausen was subsequently arrested for corruption in August 1944. He was replaced as plenipotentiary for economic affairs by his mining chief Theo Keyser, and as Chief of the Military Administration in Serbia by Dr. Justus Danckwerts. Neuhausen spent five months in a concentration camp and, although Göring arranged his release, and the award of the Knight's Cross of the War Merit Cross
The War Merit Cross (german: Kriegsverdienstkreuz) was a state decoration of Nazi Germany during World War II. By the end of the conflict it was issued in four degrees and had an equivalent civil award. A " de-Nazified" version of the War Meri ...
to him, he still spent the remainder of the war in detention.
After the war
After being captured by US forces he was handed over to the Yugoslav authorities at the end of the war, and although sentenced to 20 years imprisonment following a trial in October 1947, he was soon paroled, then released in March 1953. Neuhausen died on 14 April 1966 inMunich
Munich ( ; german: München ; bar, Minga ) is the capital and most populous city of the German state of Bavaria. With a population of 1,558,395 inhabitants as of 31 July 2020, it is the third-largest city in Germany, after Berlin and ...
, West Germany
West Germany is the colloquial term used to indicate the Federal Republic of Germany (FRG; german: Bundesrepublik Deutschland , BRD) between its formation on 23 May 1949 and the German reunification through the accession of East Germany on 3 ...
.
Footnotes
References
Books
* * * * * * * * * * * * *Journals
*Magazines
* {{DEFAULTSORT:Neuhausen, Franz 1887 births 1966 deaths People from Merzig-Wadern People from the Rhine Province Officials of Nazi Germany Recipients of the Knights Cross of the War Merit Cross German World War I pilots National Socialist Flyers Corps members