Franco–Italian Agreement on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 The Franco-Italian Agreements (often called ''Mussolini-Laval Accord'') were signed in
The Franco-Italian Agreements (often called ''Mussolini-Laval Accord'') were signed in

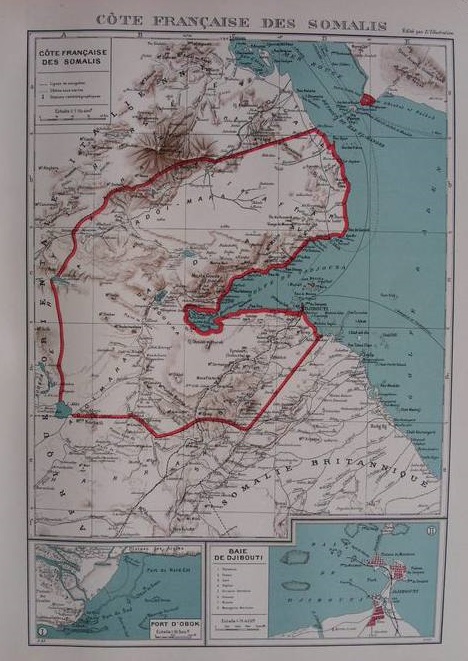 The British ceded Oltregiuba (today Jubaland) from
The British ceded Oltregiuba (today Jubaland) from 1994 ICJ Case Concerning The Territorial Dispute (Libyan Arab Jamahiriya/Chad)
Page: Top:19; Bottom:17 The agreement had the following main terms: * A small territory in French Somaliland south of Eritrean Rahayta was to be given to Italian Eritrea. * The village of Aozou and the surrounding
 The Franco-Italian Agreements (often called ''Mussolini-Laval Accord'') were signed in
The Franco-Italian Agreements (often called ''Mussolini-Laval Accord'') were signed in Rome
, established_title = Founded
, established_date = 753 BC
, founder = King Romulus (legendary)
, image_map = Map of comune of Rome (metropolitan city of Capital Rome, region Lazio, Italy).svg
, map_caption ...
by both French Foreign Minister Pierre Laval
Pierre Jean Marie Laval (; 28 June 1883 – 15 October 1945) was a French politician. During the Third Republic, he served as Prime Minister of France from 27 January 1931 to 20 February 1932 and 7 June 1935 to 24 January 1936. He again occ ...
and Italian
Italian(s) may refer to:
* Anything of, from, or related to the people of Italy over the centuries
** Italians, an ethnic group or simply a citizen of the Italian Republic or Italian Kingdom
** Italian language, a Romance language
*** Regional Ita ...
Prime Minister
A prime minister, premier or chief of cabinet is the head of the cabinet and the leader of the ministers in the executive branch of government, often in a parliamentary or semi-presidential system. Under those systems, a prime minister i ...
Benito Mussolini on 7 January 1935.
History
After its victory inWorld War I
World War I (28 July 1914 11 November 1918), often abbreviated as WWI, was one of the deadliest global conflicts in history. Belligerents included much of Europe, the Russian Empire, the United States, and the Ottoman Empire, with fightin ...
, it was agreed that Italy would not receive territories from the defeated German colonial empire. It was divided between France
France (), officially the French Republic ( ), is a country primarily located in Western Europe. It also comprises of overseas regions and territories in the Americas and the Atlantic, Pacific and Indian Oceans. Its metropolitan area ...
, Japan and the British Empire
The British Empire was composed of the dominions, colonies, protectorates, mandates, and other territories ruled or administered by the United Kingdom and its predecessor states. It began with the overseas possessions and trading posts e ...
, but Italy would be rewarded some bordering areas from the British and French colonial possessions. That was considered by Italians to be very little compensation for their sacrifices in the bloody war, which was one of the reasons of the rise to power in Italy of Mussolini's fascism
Fascism is a far-right, authoritarian, ultra-nationalist political ideology and movement,: "extreme militaristic nationalism, contempt for electoral democracy and political and cultural liberalism, a belief in natural social hierarchy an ...
.

 The British ceded Oltregiuba (today Jubaland) from
The British ceded Oltregiuba (today Jubaland) from Kenya
)
, national_anthem = " Ee Mungu Nguvu Yetu"()
, image_map =
, map_caption =
, image_map2 =
, capital = Nairobi
, coordinates =
, largest_city = Nairobi
...
to Italian Somalia
Italian Somalia ( it, Somalia Italiana; ar, الصومال الإيطالي, Al-Sumal Al-Italiy; so, Dhulka Talyaaniga ee Soomaalida), was a protectorate and later colony of the Kingdom of Italy in present-day Somalia. Ruled in the 19th centur ...
in 1924, but the French delayed some years until 1935, under Laval's leadership, and gave only a small amount of territory in eastern Africa
East Africa, Eastern Africa, or East of Africa, is the eastern subregion of the African continent. In the United Nations Statistics Division scheme of geographic regions, 10-11-(16*) territories make up Eastern Africa:
Due to the historica ...
and a desert area in the French Sahara.
Laval had succeeded Louis Barthou
Jean Louis Barthou (; 25 August 1862 – 9 October 1934) was a French politician of the Third Republic who served as Prime Minister of France for eight months in 1913. In social policy, his time as prime minister saw the introduction (in Jul ...
as Foreign Minister after the latter's assassination in Marseilles on 9 October 1934, along with King Alexander I of Yugoslavia
Alexander I ( sr-Cyrl, Александар I Карађорђевић, Aleksandar I Karađorđević, ) ( – 9 October 1934), also known as Alexander the Unifier, was the prince regent of the Kingdom of Serbia from 1914 and later the King of Yu ...
. Laval borrowed the idea of his predecessor of a system of collective security to contain the threat of Hitler
Adolf Hitler (; 20 April 188930 April 1945) was an Austrian-born German politician who was dictator of Nazi Germany, Germany from 1933 until Death of Adolf Hitler, his death in 1945. Adolf Hitler's rise to power, He rose to power as the le ...
in Europe. On 4 January 1935 Laval went to Rome
, established_title = Founded
, established_date = 753 BC
, founder = King Romulus (legendary)
, image_map = Map of comune of Rome (metropolitan city of Capital Rome, region Lazio, Italy).svg
, map_caption ...
, the capital of Italy
Italy ( it, Italia ), officially the Italian Republic, ) or the Republic of Italy, is a country in Southern Europe. It is located in the middle of the Mediterranean Sea, and its territory largely coincides with the homonymous geographical ...
, to meet Mussolini. It was the beginning of a diplomatic offensive intended to contain Nazi Germany
Nazi Germany (lit. "National Socialist State"), ' (lit. "Nazi State") for short; also ' (lit. "National Socialist Germany") (officially known as the German Reich from 1933 until 1943, and the Greater German Reich from 1943 to 1945) was ...
by a network of alliances.
He proposed a treaty to Mussolini to define disputed parts of French Somaliland (now Djibouti
Djibouti, ar, جيبوتي ', french: link=no, Djibouti, so, Jabuuti officially the Republic of Djibouti, is a country in the Horn of Africa, bordered by Somalia to the south, Ethiopia to the southwest, Eritrea in the north, and the Red ...
) as part of Eritrea, redefine the official status of Italians in French Tunisia
)
, image_map = Tunisia location (orthographic projection).svg
, map_caption = Location of Tunisia in northern Africa
, image_map2 =
, capital = Tunis
, largest_city = capital
, ...
and give Italy a mainly-free hand to occupy Ethiopia
Ethiopia, , om, Itiyoophiyaa, so, Itoobiya, ti, ኢትዮጵያ, Ítiyop'iya, aa, Itiyoppiya officially the Federal Democratic Republic of Ethiopia, is a landlocked country in the Horn of Africa. It shares borders with Eritrea to the ...
during the Abyssinia Crisis
The Abyssinia Crisis (; ) was an international crisis in 1935 that originated in what was called the Walwal incident during the ongoing conflict between the Kingdom of Italy and the Empire of Ethiopia (then commonly known as "Abyssinia"). The Le ...
.
Italy was also to receive the Aouzou Strip, which was to be moved from French-ruled Chad to Italian-ruled Libya
Libya (; ar, ليبيا, Lībiyā), officially the State of Libya ( ar, دولة ليبيا, Dawlat Lībiyā), is a country in the Maghreb region in North Africa. It is bordered by the Mediterranean Sea to the north, Egypt to the east, Suda ...
(that issue would have some implications in World War II
World War II or the Second World War, often abbreviated as WWII or WW2, was a world war that lasted from 1939 to 1945. It involved the vast majority of the world's countries—including all of the great powers—forming two opposing ...
and in the later Toyota War
The Toyota War (, ) or Great Toyota War was the last phase of the Chadian–Libyan conflict, which took place in 1987 in Northern Chad and on the Libyan–Chadian border. It takes its name from the Toyota pickup trucks used, primarily the Toyota ...
between Libya and Chad).
In exchange for those concessions, France hoped for Italian support against German aggression, which did not occur.
The agreements were confirmed by a law of the French Parliament on 26 March 1935. The French and the Italian Parliaments ratified the 1935 agreement. Since the instruments of ratification were not exchanged, ICJ named the agreement as "Non-ratified".Page: Top:19; Bottom:17 The agreement had the following main terms: * A small territory in French Somaliland south of Eritrean Rahayta was to be given to Italian Eritrea. * The village of Aozou and the surrounding
Aozou strip
The Aouzou Strip (; ar, قطاع أوزو, Qiṭāʿ Awzū, french: Bande d'Aozou) is a strip of land in northern Chad that lies along the border with Libya, extending south to a depth of about 100 kilometers into Chad's Borkou, Ennedi Ouest ...
in French Africa Chad was to be given to Italian Libya
Libya ( it, Libia; ar, ليبيا, Lībyā al-Īṭālīya) was a colony of the Fascist Italy located in North Africa, in what is now modern Libya, between 1934 and 1943. It was formed from the unification of the colonies of Italian Cyrenaica ...
.
* Italy was given a free hand by the French government to occupy Ethiopia
Ethiopia, , om, Itiyoophiyaa, so, Itoobiya, ti, ኢትዮጵያ, Ítiyop'iya, aa, Itiyoppiya officially the Federal Democratic Republic of Ethiopia, is a landlocked country in the Horn of Africa. It shares borders with Eritrea to the ...
.
References
Sources
* G. Bruce Strang: ''Imperial Dreams: The Mussolini-Laval Accords of January 1935''. In: ''The Historical Journal'' 44, September 2001, 3, , pp. 799–809. *R. Festorazzi ''Laval Mussolini. L'impossibile Asse'', Milano: Mursia, *Langer, William L. ed., ''An Encyclopaedia of World History'', (1948), Houghton Mifflin Company, Boston. Pg. 990.See also
* Stresa Front {{Authority control Modern history of Italy 1935 in Italy 1935 in France Interwar-period treaties Treaties concluded in 1935 Treaties of the French Third Republic Treaties of the Kingdom of Italy (1861–1946) France–Italy relations Treaties involving territorial changes Pierre Laval Benito Mussolini