Four-horned antelope on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
The four-horned antelope (''Tetracerus quadricornis''), or ''chousingha'', is a small
 Though Boselaphini has no African representation today,
Though Boselaphini has no African representation today,
 The four-horned antelope feeds on grasses, herbs, shrubs, foliage, flowers and fruits. A study in Mudumalai National Park (
The four-horned antelope feeds on grasses, herbs, shrubs, foliage, flowers and fruits. A study in Mudumalai National Park (
 Breeding behaviour of the four-horned antelope has not been well studied. The age at which
Breeding behaviour of the four-horned antelope has not been well studied. The age at which
 The four-horned antelope is confined to the
The four-horned antelope is confined to the
antelope
The term antelope is used to refer to many species of even-toed ruminant that are indigenous to various regions in Africa and Eurasia.
Antelope comprise a wastebasket taxon defined as any of numerous Old World grazing and browsing hoofed mamm ...
found in India
India, officially the Republic of India (Hindi: ), is a country in South Asia. It is the List of countries and dependencies by area, seventh-largest country by area, the List of countries and dependencies by population, second-most populous ...
and Nepal
Nepal (; ne, नेपाल ), formerly the Federal Democratic Republic of Nepal ( ne,
सङ्घीय लोकतान्त्रिक गणतन्त्र नेपाल ), is a landlocked country in South Asia. It is ma ...
. Its four horns distinguish it from most other bovid
The Bovidae comprise the biological family of cloven-hoofed, ruminant mammals that includes cattle, bison, buffalo, antelopes, and caprines. A member of this family is called a bovid. With 143 extant species and 300 known extinct species, t ...
s, which have two horns (with a few exceptions, such as the Jacob sheep
The Jacob is a British breed of domestic sheep. It combines two characteristics unusual in sheep: it is piebald—dark-coloured with areas of white wool—and it is often polycerate or multi-horned. It most commonly has four horns. The ori ...
). The sole member of the genus
Genus ( plural genera ) is a taxonomic rank used in the biological classification of living and fossil organisms as well as viruses. In the hierarchy of biological classification, genus comes above species and below family. In binomial nom ...
''Tetracerus'', the species was first described by French zoologist Henri Marie Ducrotay de Blainville in 1816. Three subspecies
In biological classification, subspecies is a rank below species, used for populations that live in different areas and vary in size, shape, or other physical characteristics ( morphology), but that can successfully interbreed. Not all specie ...
are recognised. The four-horned antelope stands nearly at the shoulder and weighs nearly . Slender with thin legs and a short tail, the four-horned antelope has a yellowish brown to reddish coat. One pair of horns is located between the ears, and the other on the forehead. The posterior horns are always longer than the anterior
Standard anatomical terms of location are used to unambiguously describe the anatomy of animals, including humans. The terms, typically derived from Latin or Greek language, Greek roots, describe something in its standard anatomical position. Th ...
horns, which might be mere fur-covered studs. While the posterior horns measure , the anterior ones are long.
The four-horned antelope is diurnal (active mainly during the day). Though solitary by nature, four-horned antelopes may form loose groups of three to five –with one or more adults, sometimes accompanied by juveniles. This elusive antelope feeds on grasses, herbs, shrubs, foliage, flowers and fruits. It needs to drink water frequently; as such it stays in places near water sources. The breeding behaviour of the four-horned antelope has not been well studied. The age at which they reach sexual maturity
Sexual maturity is the capability of an organism to reproduce. In humans it might be considered synonymous with adulthood, but here puberty is the name for the process of biological sexual maturation, while adulthood is based on cultural definit ...
and the season when mating occurs have not been understood well. Gestation
Gestation is the period of development during the carrying of an embryo, and later fetus, inside viviparous animals (the embryo develops within the parent). It is typical for mammals, but also occurs for some non-mammals. Mammals during pr ...
lasts about eight months, following which one or two calves are born. They are kept concealed for the first few weeks of their birth. The young remain with the mother for about a year.
Four-horned antelopes tend to inhabit areas with significant grass cover or heavy undergrowth, and avoid human settlements. Earlier common throughout deciduous forest
In the fields of horticulture and Botany, the term ''deciduous'' () means "falling off at maturity" and "tending to fall off", in reference to trees and shrubs that seasonally shed leaves, usually in the autumn; to the shedding of petals ...
s in India, the antelope now occurs in widely disjunct, small populations. Most of the populations are in India, and lower numbers can be found in adjoining Nepal
Nepal (; ne, नेपाल ), formerly the Federal Democratic Republic of Nepal ( ne,
सङ्घीय लोकतान्त्रिक गणतन्त्र नेपाल ), is a landlocked country in South Asia. It is ma ...
. The four-horned antelope is threatened by the loss of its natural habitat due to agricultural expansion. Moreover, the unusual four-horned skull and the horns have been a popular target for trophy hunters. The four-horned antelope is classified as Vulnerable by the International Union for the Conservation of Nature and Natural Resources (IUCN
The International Union for Conservation of Nature (IUCN; officially International Union for Conservation of Nature and Natural Resources) is an international organization working in the field of nature conservation and sustainable use of natu ...
).
Etymology
Thescientific name
In taxonomy, binomial nomenclature ("two-term naming system"), also called nomenclature ("two-name naming system") or binary nomenclature, is a formal system of naming species of living things by giving each a name composed of two parts, bo ...
of the four-horned antelope is ''Tetracerus quadricornis''. The generic name ''Tetracerus'' is the combination of two Greek words: ''tetra'' meaning "four" and ''keras'' meaning "horn". The specific name ''quadricornis'' is derived from two Latin
Latin (, or , ) is a classical language belonging to the Italic languages, Italic branch of the Indo-European languages. Latin was originally a dialect spoken in the lower Tiber area (then known as Latium) around present-day Rome, but through ...
words: ''quattuor'' meaning "four" and ''cornu'' "horn". The four-horned antelope is known by several vernacular names: ''chausingha'', ''chowsingha'', ''chousingha'' (Hindi
Hindi (Devanāgarī: or , ), or more precisely Modern Standard Hindi (Devanagari: ), is an Indo-Aryan language spoken chiefly in the Hindi Belt region encompassing parts of northern, central, eastern, and western India. Hindi has been ...
for "four horns"), ''doda'', ''ghutri'' (mainly in central India) (Hindi); ''kondu kuri'' (Kannada
Kannada (; ಕನ್ನಡ, ), originally romanised Canarese, is a Dravidian language spoken predominantly by the people of Karnataka in southwestern India, with minorities in all neighbouring states. It has around 47 million native s ...
); ''chauka'' ( Nepalese); ''nari komboo marn'' (Tamil
Tamil may refer to:
* Tamils, an ethnic group native to India and some other parts of Asia
** Sri Lankan Tamils, Tamil people native to Sri Lanka also called ilankai tamils
**Tamil Malaysians, Tamil people native to Malaysia
* Tamil language, na ...
).
Taxonomy and phylogeny
The four-horned antelope is the sole member of thegenus
Genus ( plural genera ) is a taxonomic rank used in the biological classification of living and fossil organisms as well as viruses. In the hierarchy of biological classification, genus comes above species and below family. In binomial nom ...
''Tetracerus'', and is placed under the family
Family (from la, familia) is a group of people related either by consanguinity (by recognized birth) or affinity (by marriage or other relationship). The purpose of the family is to maintain the well-being of its members and of society. Idea ...
Bovidae
The Bovidae comprise the biological family of cloven-hoofed, ruminant mammals that includes cattle, bison, buffalo, antelopes, and caprines. A member of this family is called a bovid. With 143 extant species and 300 known extinct species, t ...
. The species was first described by French zoologist Henri Marie Ducrotay de Blainville in 1816. The four-horned antelope has only one other relative in the tribe Boselaphini, the nilgai
The nilgai (''Boselaphus tragocamelus'') (, literally meaning "blue cow") is the largest Asian antelope and is ubiquitous across the northern Indian subcontinent. It is the sole member of the genus ''Boselaphus'' and was described by Peter Si ...
(''Boselaphus tragocamelus''). The Boselaphini have horns with a keel on the front and lack rings as found in other antelope groups.
The authority
In the fields of sociology and political science, authority is the legitimate power of a person or group over other people. In a civil state, ''authority'' is practiced in ways such a judicial branch or an executive branch of government.''T ...
for ''Tetracerus'' is variously indicated according to interpretations of the International Code of Zoological Nomenclature
The International Code of Zoological Nomenclature (ICZN) is a widely accepted convention in zoology that rules the formal scientific naming of organisms treated as animals. It is also informally known as the ICZN Code, for its publisher, the I ...
. The name was first published in an 1825 publication by English naturalist Thomas Hardwicke but cited the English zoologist William Elford Leach
William Elford Leach FRS (2 February 1791 – 25 August 1836) was an English zoologist and marine biologist.
Life and work
Elford Leach was born at Hoe Gate, Plymouth, the son of an attorney. At the age of twelve he began a medical appre ...
– probably by an editor – as the authority in a footnote at the end of the publication. Philip Sclater
Philip Lutley Sclater (4 November 1829 – 27 June 1913) was an England, English lawyer and zoologist. In zoology, he was an expert ornithologist, and identified the main zoogeographic regions of the world. He was Secretary of the Zoological ...
and Oldfield Thomas
Michael Rogers Oldfield Thomas (21 February 1858 – 16 June 1929) was a British zoologist.
Career
Thomas worked at the Natural History Museum on mammals, describing about 2,000 new species and subspecies for the first time. He was appo ...
listed Hardwicke as the genus authority by virtue of his being the author of the publication. However, Leach is now identified as the appropriate authority based on Article 50.1.1 of the Zoological Code.
A 1992 phylogenetic
In biology, phylogenetics (; from Greek φυλή/ φῦλον [] "tribe, clan, race", and wikt:γενετικός, γενετικός [] "origin, source, birth") is the study of the evolutionary history and relationships among or within groups ...
study showed a strong possibility of a clade
A clade (), also known as a monophyletic group or natural group, is a group of organisms that are monophyletic – that is, composed of a common ancestor and all its lineal descendants – on a phylogenetic tree. Rather than the English ter ...
consisting of Boselaphini, Bovini and Tragelaphini. Bovini consists of the genera ''Bubalus
''Bubalus'' is a genus of Asiatic bovines that was proposed by Charles Hamilton Smith in 1827. ''Bubalus'' and ''Syncerus'' form the subtribe Bubalina, the true buffaloes.
The International Code of Zoological Nomenclature and classification of ...
'', '' Bos'', ''Pseudoryx'' (saola
The saola (''Pseudoryx nghetinhensis''), also called spindlehorn, Asian unicorn, or infrequently, Vu Quang bovid, is one of the world's rarest large mammals, a forest-dwelling bovine native to the Annamite Range in Vietnam and Laos. It was descr ...
), ''Syncerus'' ( African buffalo), ''Bison
Bison are large bovines in the genus ''Bison'' (Greek: "wild ox" (bison)) within the tribe Bovini. Two extant and numerous extinct species are recognised.
Of the two surviving species, the American bison, ''B. bison'', found only in North A ...
'' and the extinct
Extinction is the termination of a kind of organism or of a group of kinds (taxon), usually a species. The moment of extinction is generally considered to be the death of the last individual of the species, although the capacity to breed and ...
''Pelorovis
''Pelorovis'' ("prodigious/monstrous sheep") is an extinct genus of African wild cattle which existed during the Pleistocene epoch.Alan Turner & Mauricio Anton: ''Evolving Eden, An Illustrated Guide to the Evolution of the African Large-Mammal ...
''. Tragelaphini consists of two genera: '' Taurotragus'' (eland) and '' Tragelaphus''. Boselaphini and Tragelaphini were predicted to be close; this was seconded by a similar study in 1999. The following cladogram is based on the 1992 study:
Colin Groves
Colin Peter Groves (24 June 1942 – 30 November 2017) was a British-Australian biologist and anthropologist. Groves was Professor of Biological Anthropology at the Australian National University in Canberra, Australia.
Education
Born in Englan ...
(2003) recognizes three subspecies
In biological classification, subspecies is a rank below species, used for populations that live in different areas and vary in size, shape, or other physical characteristics ( morphology), but that can successfully interbreed. Not all specie ...
of the four-horned antelope on the basis of distribution and physical characteristics such as coat
A coat typically is an outer garment for the upper body as worn by either gender for warmth or fashion. Coats typically have long sleeves and are open down the front and closing by means of buttons, zippers, hook-and-loop fasteners, toggles, ...
colour, body size and the number of horns:
* ''T. q. iodes'' ( Hodgson, 1847): distributed north of the Ganges in Nepal
* ''T. q. quadricornis'' (de Blainville, 1816): distributed in peninsular India
* ''T. q. subquadricornutus'' ( Elliot, 1839) distributed in the Western Ghats and southern India
Evolution
 Though Boselaphini has no African representation today,
Though Boselaphini has no African representation today, fossil
A fossil (from Classical Latin , ) is any preserved remains, impression, or trace of any once-living thing from a past geological age. Examples include bones, shells, exoskeletons, stone imprints of animals or microbes, objects preserved ...
evidence supports its presence in the continent during as early as the late Miocene
The Miocene ( ) is the first geological epoch of the Neogene Period and extends from about (Ma). The Miocene was named by Scottish geologist Charles Lyell; the name comes from the Greek words (', "less") and (', "new") and means "less recen ...
– the two living antelopes of this tribe, in fact, have been found to have a closer relationship with the earliest bovids (like '' Eotragus'' species) than do the other bovids. This tribe originated at least 8.9 Mya, in much the same area where the four-horned antelope occurs today, and may represent the most "primitive" of all living bovids, having changed the least since the origins of the family. The extant and extinct boselaphine forms show similar development of the horn cores (the central bony part of the horn). It is thought that ancestral bovids had a diploid
Ploidy () is the number of complete sets of chromosomes in a cell, and hence the number of possible alleles for autosomal and pseudoautosomal genes. Sets of chromosomes refer to the number of maternal and paternal chromosome copies, respectiv ...
chromosome
A chromosome is a long DNA molecule with part or all of the genetic material of an organism. In most chromosomes the very long thin DNA fibers are coated with packaging proteins; in eukaryotic cells the most important of these proteins ar ...
number of 58 which has reduced in ''Tetracerus'' to 38 through a process of concatenation of some chromosomes.
Fossils of '' Protragocerus labidotus'' and '' Sivoreas eremita'' dating back to the late Miocene have been discovered in the Ngorora formation (Kenya
)
, national_anthem = " Ee Mungu Nguvu Yetu"()
, image_map =
, map_caption =
, image_map2 =
, capital = Nairobi
, coordinates =
, largest_city = Nairobi
, ...
). fossils from the same period have also been excavated in the eastern Mediterranean region. Other Miocene fossils of boselaphines discovered are of '' Miotragocerus'', '' Tragocerus'' and '' Tragoportax''. Fossils of ''Miotragoceros'' are not apparent in Africa (only ''M. cyrenaicus'' has been reported from the continent), but have significant presence in the Shiwalik Hills
The Sivalik Hills, also known as the Shivalik Hills and Churia Hills, are a mountain range of the outer Himalayas that stretches over about from the Indus River eastwards close to the Brahmaputra River, spanning the northern parts of the Indian ...
in India
India, officially the Republic of India (Hindi: ), is a country in South Asia. It is the List of countries and dependencies by area, seventh-largest country by area, the List of countries and dependencies by population, second-most populous ...
and Pakistan
Pakistan ( ur, ), officially the Islamic Republic of Pakistan ( ur, , label=none), is a country in South Asia. It is the world's List of countries and dependencies by population, fifth-most populous country, with a population of almost 24 ...
, as do several ''Tragoportax'' species. A 2005 study suggested the migration of ''Miotragoceros'' to eastern Asia around 8 Mya. Alan W. Gentry of the Natural History Museum
A natural history museum or museum of natural history is a scientific institution with natural history collections that include current and historical records of animals, plants, fungi, ecosystems, geology, paleontology, climatology, and more. ...
reported the presence of another boselaphine, '' Mesembriportax'', from Langebaanweg (South Africa
South Africa, officially the Republic of South Africa (RSA), is the southernmost country in Africa. It is bounded to the south by of coastline that stretch along the South Atlantic and Indian Oceans; to the north by the neighbouring coun ...
).
Evidence of early humans" \n\n\n\n\nThe robots exclusion standard, also known as the robots exclusion protocol or simply robots.txt, is a standard used by websites to indicate to visiting web crawlers and other web robots which portions of the site they are allowed to visi ...
hunting four-horned antelope during the Mesolithic
The Mesolithic ( Greek: μέσος, ''mesos'' 'middle' + λίθος, ''lithos'' 'stone') or Middle Stone Age is the Old World archaeological period between the Upper Paleolithic and the Neolithic. The term Epipaleolithic is often used synonymo ...
period (5,000 to 8,000 years ago) have been found in the Kurnool caves of southern India and similar evidence has been found from the Chalcolithic
The Copper Age, also called the Chalcolithic (; from grc-gre, χαλκός ''khalkós'', "copper" and ''líthos'', "Rock (geology), stone") or (A)eneolithic (from Latin ''wikt:aeneus, aeneus'' "of copper"), is an list of archaeologi ...
period (3,000 years ago) in Orissa, eastern India.
Description
The four-horned antelope is one of the smallest Asian bovids. The number of its horns distinguishes it from most of the other bovids, that have two horns The four-horned antelope stands at the shoulder and weighs ; the head-and-body length is typically between .Sexual dimorphism
Sexual dimorphism is the condition where the sexes of the same animal and/or plant species exhibit different morphological characteristics, particularly characteristics not directly involved in reproduction. The condition occurs in most an ...
is not very notable, though only males possess horns.
Slender with thin legs and a short tail, the four-horned antelope has a yellowish brown to reddish coat. The underparts and the insides of the legs are white. Facial features include black markings on the muzzle and behind the ears. A black stripe marks the outer surface of each leg. Females have four teats far back on the abdomen. The hair feels coarse, more like that of a deer
Deer or true deer are hoofed ruminant mammals forming the family Cervidae. The two main groups of deer are the Cervinae, including the muntjac, the elk (wapiti), the red deer, and the fallow deer; and the Capreolinae, including the re ...
than the glossy hair typical of antelope
The term antelope is used to refer to many species of even-toed ruminant that are indigenous to various regions in Africa and Eurasia.
Antelope comprise a wastebasket taxon defined as any of numerous Old World grazing and browsing hoofed mamm ...
s. The fetlocks are marked with white patches.
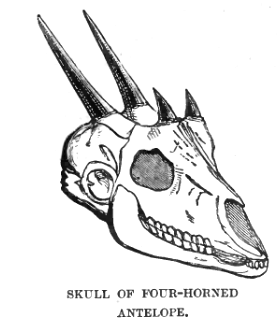
One pair of horns is located between the ears, and the other on the forehead. The posterior horns are always longer than the anterior
Standard anatomical terms of location are used to unambiguously describe the anatomy of animals, including humans. The terms, typically derived from Latin or Greek language, Greek roots, describe something in its standard anatomical position. Th ...
horns, which might be mere fur-covered studs. While the posterior horns each measures , the anterior ones measure . Horns emerge at 10 to 14 months. According to Groves, anterior horns show the poorest development in the subspecies ''T. q. subquadricornutus''. These horns measure nearly in ''T. q. quadricornis'', and nearly in ''T. q. iodes''. The posterior horn lengths for the subspecies recorded by him were: for ''T. q. quadricornis'', in ''T. q. iodes'' and in ''T. q. subquadricornutus''.
The four-horned antelope differs greatly from the nilgai in colour, is much smaller and has an extra pair of horns. The nilgai is nearly nine times heavier and two times taller than the four-horned antelope. Two deer species, the Indian muntjac and the Indian hog deer, can be confused with this antelope. The four-horned antelope, however, lacks their antler
Antlers are extensions of an animal's skull found in members of the Cervidae (deer) family. Antlers are a single structure composed of bone, cartilage, fibrous tissue, skin, nerves, and blood vessels. They are generally found only on ...
s. The chinkara
The chinkara (''Gazella bennettii''), also known as the Indian gazelle, is a gazelle species native to Iran, Afghanistan, Pakistan and India.
Taxonomy
The following six subspecies are considered valid:
* Deccan chinkara (''G. b. bennettii ...
, a gazelle, can be told apart by its light brown coat and larger, ringed horns.
Ecology and behaviour
The four-horned antelope is diurnal (active mainly during the day), though it mainly rests or ruminates in dense undergrowth at noon. Though solitary by nature, the four-horned antelope may form loose groups of three to five. Groups consist of one or more adults, sometimes accompanied by juveniles. Males and females hardly interact, except in the mating season. The antelope is shy and elusive. When alarmed, it stands motionless and may nervously leap away from the danger or even sprint. It often conceals itself in tall grasses to escape predators. The use of alarm calls to alert others is not common because the antelope tries to avoid the attention of predators. However, in extreme cases, these calls may be used to warn predators that they have been identified. Adultsmark
Mark may refer to:
Currency
* Bosnia and Herzegovina convertible mark, the currency of Bosnia and Herzegovina
* East German mark, the currency of the German Democratic Republic
* Estonian mark, the currency of Estonia between 1918 and 1927
* Finn ...
vegetation in their territories
A territory is an area of land, sea, or space, particularly belonging or connected to a country, person, or animal.
In international politics, a territory is usually either the total area from which a state may extract power resources or a ...
with a colourless secretion of preorbital gland
The preorbital gland is a paired exocrine gland found in many species of hoofed animals, which is homologous to the lacrimal gland found in humans. These glands are trenchlike slits of dark blue to black, nearly bare skin extending from the me ...
s, that soon condenses to form a white film. They maintain multiple latrine sites where piles of their pellet droppings are formed by regular use. Latrine sites can be confused with those of the barking deer but the pellets are longer and larger in four-horned antelopes. Submissive display consists of shrinking the body, lowering the head and pulling the ears back. Predators of four-horned antelopes include tiger
The tiger (''Panthera tigris'') is the largest living Felidae, cat species and a member of the genus ''Panthera''. It is most recognisable for its dark vertical stripes on orange fur with a white underside. An apex predator, it primarily pr ...
s, leopard
The leopard (''Panthera pardus'') is one of the five extant species in the genus '' Panthera'', a member of the cat family, Felidae. It occurs in a wide range in sub-Saharan Africa, in some parts of Western and Central Asia, Southern Russia, ...
s, and dholes.
Diet
 The four-horned antelope feeds on grasses, herbs, shrubs, foliage, flowers and fruits. A study in Mudumalai National Park (
The four-horned antelope feeds on grasses, herbs, shrubs, foliage, flowers and fruits. A study in Mudumalai National Park (Tamil Nadu
Tamil Nadu (; , TN) is a state in southern India. It is the tenth largest Indian state by area and the sixth largest by population. Its capital and largest city is Chennai. Tamil Nadu is the home of the Tamil people, whose Tamil language ...
, India) showed that the antelope prefers grass species of the family Cyperaceae
The Cyperaceae are a family of graminoid (grass-like), monocotyledonous flowering plants known as sedges. The family is large, with some 5,500 known species described in about 90 genera, the largest being the "true sedges" genus '' Carex'' ...
; genera ''Axonopus
''Axonopus'' is a genus of plants in the Poaceae, grass family, known generally as carpet grass. They are native primarily to the tropical and subtropical regions of the Americas with one species in tropical Africa and another on Easter Island. ...
'', '' Cynodon'', '' Digitaria'', '' Echinochloa'', '' Panicum'', '' Sehima'' and '' Sporobolus''; and the species ''Imperata cylindrica
''Imperata cylindrica'' (commonly known as cogongrass or kunai grass ) is a species of perennial rhizomatous grass native to tropical and subtropical Asia, Micronesia, Melanesia, Australia, Africa, and southern Europe. It has also been intro ...
'', '' Ottochloa nodosa'', '' Pseudanthistria umbellata'' and '' Themeda cymbaria''. The shrub '' Grewia hirsuta'' is frequently eaten. Preferred herbs include '' Helichrysum'', '' Indigofera'' and ''Tinospora
''Tinospora'' is a genus of succulent woody climbing shrubs. Thirty-four species are currently recognized. Species generally send down long aerial roots from host trees. They have corky or papery bark. They are found in tropical and sub-tropical ...
'' species and ''Leucas aspera
''Leucas aspera'' is a plant species within the genus ''Leucas'' and the family Lamiaceae
The Lamiaceae ( )
or Labiatae are a family of flowering plants commonly known as the mint, deadnettle or sage family. Many of the plants are aromatic ...
''. The four-horned antelope feeds on the leaves of trees such as '' Cordia wallichii'', '' Emblica officinalis'', ''Randia dumetorum
''Catunaregam spinosa'', the mountain pomegranate, is a flowering plant in the family Rubiaceae, found in South Asia and other Asian countries. Almost all parts of the plant are used as a traditional medicine in Ayurveda and fruits have been
repo ...
'' and '' Zizyphus xylopyrus''. Grasses comprise nearly 29 percent of the diet, followed by foliage from trees (nearly nine percent). Grass and browse
Browsing is a kind of orienting strategy. It is supposed to identify something of relevance for the browsing organism. When used about human beings it is a metaphor taken from the animal kingdom. It is used, for example, about people browsing o ...
were consumed in nearly equal proportions. A study in the Panna National Park (Madhya Pradesh
Madhya Pradesh (, ; meaning 'central province') is a state in central India. Its capital is Bhopal, and the largest city is Indore, with Jabalpur, Ujjain, Gwalior, Sagar, and Rewa being the other major cities. Madhya Pradesh is the second ...
, India) showed preference for ''Zizyphus mauritiana
''Ziziphus mauritiana'', also known as Indian jujube, Indian plum, Chinese date, Chinese apple, ber, and dunks is a tropical fruit tree species belonging to the family Rhamnaceae. It is often confused with the closely related Chinese jujube (' ...
'', '' Acacia nilotica'', '' A. leucophloea'' and '' A. catechu''. Babool flowers were frequently eaten. The antelope often associates with langurs under fruiting trees, just as chital frequently do. Interaction with chital, a sympatric
In biology, two related species or populations are considered sympatric when they exist in the same geographic area and thus frequently encounter one another. An initially interbreeding population that splits into two or more distinct species s ...
species, was infrequent. The antelope is wary when feeding, often raising its head and looking about its vicinity. The four-horned antelope needs to drink water frequently; as such it stays in places near water sources.
Reproduction
 Breeding behaviour of the four-horned antelope has not been well studied. The age at which
Breeding behaviour of the four-horned antelope has not been well studied. The age at which sexual maturity
Sexual maturity is the capability of an organism to reproduce. In humans it might be considered synonymous with adulthood, but here puberty is the name for the process of biological sexual maturation, while adulthood is based on cultural definit ...
is gained is doubted; two captive females had their first parturition at less than two years. The breeding season in Panna National Park probably lasts from May to July, and from June to August in Mudumalai National Park. The male approaches the female in a relaxed gait, giving out low coughs. The two may kneel and push against each other with the necks intertwined. The male makes a few short mounting attempts; the female may be foraging all the while without any reaction. Gestation
Gestation is the period of development during the carrying of an embryo, and later fetus, inside viviparous animals (the embryo develops within the parent). It is typical for mammals, but also occurs for some non-mammals. Mammals during pr ...
lasts about eight months, followed by the birth of one or two calves. The newborn has a head-and-body length of , and weighs . Juveniles are kept concealed for the first few weeks of birth. Births in Mudumalai National Park peak from February to April. Juveniles remain with their mothers for about a year.
Distribution and habitat
 The four-horned antelope is confined to the
The four-horned antelope is confined to the Indian subcontinent
The Indian subcontinent is a physiographical region in Southern Asia. It is situated on the Indian Plate, projecting southwards into the Indian Ocean from the Himalayas. Geopolitically, it includes the countries of Bangladesh, Bhutan, In ...
, occurring widely in disjunct and small populations. The range in India covers a vast expanse, from the foothills of the Himalayas
The Himalayas, or Himalaya (; ; ), is a mountain range in Asia, separating the plains of the Indian subcontinent from the Tibetan Plateau. The range has some of the planet's highest peaks, including the very highest, Mount Everest. Over 10 ...
in the north to the Deccan Plateau
The large Deccan Plateau in southern India is located between the Western Ghats and the Eastern Ghats, and is loosely defined as the peninsular region between these ranges that is south of the Narmada river. To the north, it is bounded by th ...
in the south. Most of the existing populations live in India, and lower numbers in adjoining Nepal
Nepal (; ne, नेपाल ), formerly the Federal Democratic Republic of Nepal ( ne,
सङ्घीय लोकतान्त्रिक गणतन्त्र नेपाल ), is a landlocked country in South Asia. It is ma ...
.
The four-horned antelope inhabits open, dry, deciduous forest
In the fields of horticulture and Botany, the term ''deciduous'' () means "falling off at maturity" and "tending to fall off", in reference to trees and shrubs that seasonally shed leaves, usually in the autumn; to the shedding of petals ...
s in hilly terrain. It prefers areas close to water bodies that are covered with grasses or heavy undergrowth. It generally keeps away from settlements.
It was earlier common throughout deciduous forests in India, but the population declined to an estimated at slightly above 10,000 mature individuals in 2001, with a decreasing trend. Numbers in Gir National Park were estimated at 256 individuals in 1974; later estimates at waterholes in the same location put them a little above 1,000. Densities of above 0.7 individuals per km2 have been considered as being healthy.
Threats and conservation
The four-horned antelope is threatened by the loss of its natural habitat due to agricultural expansion. Moreover, the unusual four-horned skull and the horns have been a popular target for trophy hunters. In India, the species is protected under Schedule I the Wildlife Protection Act of 1972 and the Nepalese population is listed in CITES Appendix III. The four-horned antelope is classified as Vulnerable on theIUCN Red List
The International Union for Conservation of Nature (IUCN) Red List of Threatened Species, also known as the IUCN Red List or Red Data Book, founded in 1964, is the world's most comprehensive inventory of the global conservation status of biolo ...
.
Major protected areas across India where four-horned antelopes occur include:
* Gir National Park in Gujarat;
* Sariska Tiger Reserve in Rajasthan;
*Bandhavgarh National Park
Bandhavgarh National Park is a national park of India, located in the Umaria district of Madhya Pradesh. Bandhavgarh, with an area of , was declared a national park in 1968 and then became Tiger Reserve in 1993. The current core area is spread ov ...
, Bori Wildlife Sanctuary
The Bori Wildlife Sanctuary is a wildlife sanctuary in Hoshangabad District of Madhya Pradesh state in central India.
The sanctuary covers an area of , located in the northern foothills of the Satpura Range. It is bounded by the Satpura Nati ...
, Kanha National Park
Kanha Tiger Reserve, also known as Kanha–Kisli National Park, is one of the tiger reserves of India and the largest national park of the state of Madhya Pradesh. The present-day Kanha area is divided into two protected areas, Hallon and Banjar ...
, Pachmarhi Biosphere Reserve, Panna Tiger Reserve, Pench Tiger Reserve, Sanjay National Park, Satpura National Park
Satpura Tiger Reserve (STR) also known as Satpura National Park is located in the Hoshangabad District (newly named Narmadapuram ) of Madhya Pradesh in India. Its name is derived from the Satpura range. It covers an area of . Satpura National Pa ...
in Madhya Pradesh;
* Tadoba Andhari Reserve in Maharashtra
Maharashtra (; , abbr. MH or Maha) is a state in the western peninsular region of India occupying a substantial portion of the Deccan Plateau. Maharashtra is the second-most populous state in India and the second-most populous country subdi ...
;
* Kumbhalgarh Wildlife Sanctuary, Ranthambore National Park, Rangayyanadurga Wildlife Sanctuary in Karnataka.
See also
* Rangayyanadurga Four–horned antelope Wildlife SanctuaryReferences
External links
* * {{Taxonbar, from1=Q273580, from2=Q10824586 Bovines Mammals of India Mammals of Nepal Fauna of Madhya Pradesh Mammals described in 1816 Taxa named by Henri Marie Ducrotay de Blainville