Flystrike on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Myiasis is the
File:UOTW 22 - Ultrasound of the Week 1.webm, Ultrasound showing maggot infestation
File:UOTW 22 - Ultrasound of the Week 2.webm, Ultrasound showing maggot infestation
File:UOTW 22 - Ultrasound of the Week 3.jpg, Ultrasound showing maggot infestation

Myiasis
reviewed and published by
Exotic Myiasis
Identification key to species of myiasis-causing fly larvae
Parasitic Insects, Mites and Ticks: Genera of Medical and Veterinary Importance: Botflies
{{Pediculosis, acariasis and other infestations Tropical diseases Sheep and goat diseases Arthropod infestations Veterinary entomology Parasitic infestations, stings, and bites of the skin
parasitic
Parasitism is a close relationship between species, where one organism, the parasite, lives on or inside another organism, the host, causing it some harm, and is adapted structurally to this way of life. The entomologist E. O. Wilson ha ...
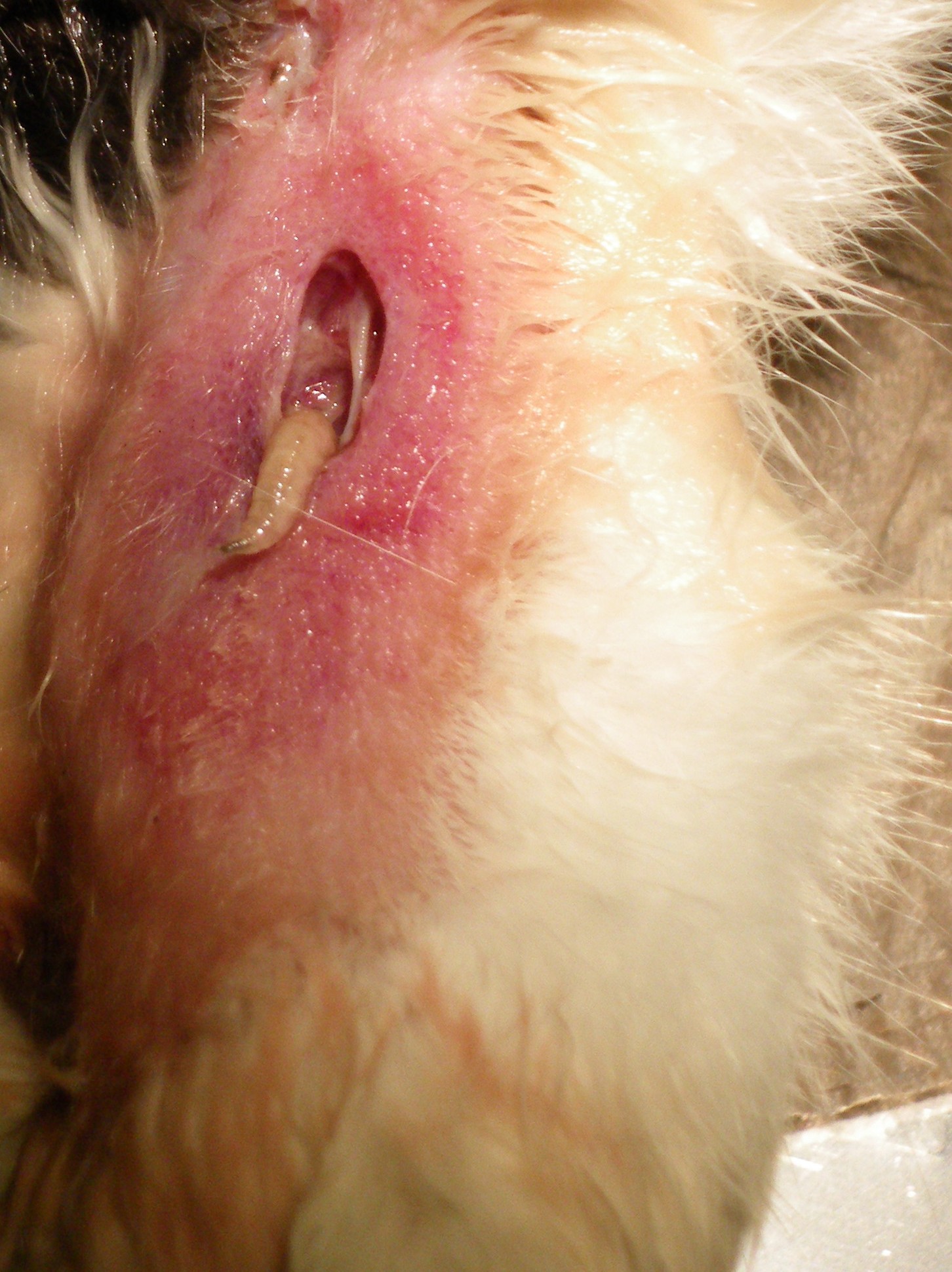
infestation of the body of a live animal by fly larva
A larva (; plural larvae ) is a distinct juvenile form many animals undergo before metamorphosis into adults. Animals with indirect development such as insects, amphibians, or cnidarians typically have a larval phase of their life cycle.
...
e (maggot
A maggot is the larva of a fly (order Diptera); it is applied in particular to the larvae of Brachycera flies, such as houseflies, cheese flies, and blowflies, rather than larvae of the Nematocera, such as mosquitoes and crane flies.
...
s) which grow inside the host while feeding on its tissue. Although flies are most commonly attracted to open wound
A wound is a rapid onset of injury that involves lacerated or punctured skin (an ''open'' wound), or a contusion (a ''closed'' wound) from blunt force trauma or compression. In pathology, a ''wound'' is an acute injury that damages the epide ...
s and urine
Urine is a liquid by-product of metabolism in humans and in many other animals. Urine flows from the kidneys through the ureters to the urinary bladder. Urination results in urine being excreted from the body through the urethra.
Cellular ...
- or feces-soaked fur, some species (including the most common myiatic flies—the botfly
Botflies, also known as warble flies, heel flies, and gadflies, are a family of flies known as the Oestridae. Their larvae are internal parasites of mammals, some species growing in the host's flesh and others within the gut. '' Dermatobia hom ...
, blowfly, and screwfly) can create an infestation even on unbroken skin and have been known to use moist soil and non-myiatic flies (such as the common housefly) as vector agents for their parasitic larvae.
Because some animals (particularly non-native domestic animals) cannot react as effectively as humans to the causes and effects of myiasis, such infestations present a severe and continuing problem for livestock
Livestock are the domesticated animals raised in an agricultural setting to provide labor and produce diversified products for consumption such as meat, eggs, milk, fur, leather, and wool. The term is sometimes used to refer solely to animal ...
industries worldwide, causing severe economic losses where they are not mitigated by human action. Although typically a far greater issue for animals, myiasis is also a relatively frequent disease for humans in rural tropical regions where myiatic flies thrive, and often may require medical attention to surgically remove the parasites.
Myiasis varies widely in the forms it takes and its effects on those affected. Such variations depend largely on the fly species and where the larvae are located. Some flies lay eggs in open wounds, other larvae may invade unbroken skin or enter the body through the nose or ears, and still others may be swallowed if the eggs are deposited on the lips or on food. There can also be accidental myiasis which '' E. tenax'' can cause in humans via water containing the larvae or in contaminated uncooked food. The name of the condition derives from ancient Greek
Ancient Greek includes the forms of the Greek language used in ancient Greece and the ancient world from around 1500 BC to 300 BC. It is often roughly divided into the following periods: Mycenaean Greek (), Dark Ages (), the Archaic p ...
μυῖα (''myia''), meaning "fly".
Signs and symptoms
How myiasis affects the human body depends on where the larvae are located. Larvae may infect dead,necrotic
Necrosis () is a form of cell injury which results in the premature death of cells in living tissue by autolysis. Necrosis is caused by factors external to the cell or tissue, such as infection, or trauma which result in the unregulated dige ...
(prematurely dying) or living tissue in various sites: the skin, eyes, ears, stomach and intestinal tract, or in genitourinary sites. They may invade open wounds and lesions or unbroken skin. Some enter the body through the nose or ears. Larvae or eggs can reach the stomach or intestines if they are swallowed with food and cause gastric or intestinal myiasis.
Several different presentations of myiasis and their symptoms:
Wound
Wound myiasis occurs when fly larvae infest open wounds. It has been a serious complication of war wounds in tropical areas, and is sometimes seen in neglected wounds in most parts of the world. Predisposing factors include poor socioeconomic conditions, extremes of age, neglect, mental disability, psychiatric illness, alcoholism, diabetes, and vascular occlusive disease.Eye
Myiasis of the human eye or ophthalmomyiasis can be caused by ''Hypoderma tarandi
''Hypoderma tarandi'', also known as the reindeer warble fly and reindeer botfly, is a species of warble fly that is parasitic on reindeer.
The larvae of this fly are a skin-penetrating ectoparasite that usually infest populations of reindeer an ...
'', a parasitic botfly
Botflies, also known as warble flies, heel flies, and gadflies, are a family of flies known as the Oestridae. Their larvae are internal parasites of mammals, some species growing in the host's flesh and others within the gut. '' Dermatobia hom ...
of caribou. It is known to lead to uveitis
Uveitis () is inflammation of the uvea, the pigmented layer of the eye between the inner retina and the outer fibrous layer composed of the sclera and cornea. The uvea consists of the middle layer of pigmented vascular structures of the eye and in ...
, glaucoma
Glaucoma is a group of eye diseases that result in damage to the optic nerve (or retina) and cause vision loss. The most common type is open-angle (wide angle, chronic simple) glaucoma, in which the drainage angle for fluid within the eye rem ...
, and retinal detachment. Human ophthalmomyiasis, both external and internal, has been caused by the larvae of the botfly.
Cause
Life cycle
The life cycle in sheep is typical of the disease. The femaleflies
Flies are insects of the order Diptera, the name being derived from the Greek δι- ''di-'' "two", and πτερόν ''pteron'' "wing". Insects of this order use only a single pair of wings to fly, the hindwings having evolved into advanced m ...
lay their eggs on the sheep in damp, protected areas of the body that are soaked with urine and feces, mainly the sheep's breech (buttocks
The buttocks (singular: buttock) are two rounded portions of the exterior anatomy of most mammals, located on the posterior of the pelvic region. In humans, the buttocks are located between the lower back and the perineum. They are composed ...
). It takes approximately eight hours to a day for the eggs to hatch, depending on the conditions. Once hatched, the larvae then lacerate the skin with their mouthparts, causing open sores. Once the skin has been breached, the larvae then tunnel through the sores into the host's subcutaneous tissue, causing deep and irritating lesion
A lesion is any damage or abnormal change in the tissue of an organism, usually caused by disease or trauma. ''Lesion'' is derived from the Latin "injury". Lesions may occur in plants as well as animals.
Types
There is no designated classif ...
s highly subject to infection. After about the second day, bacteria
Bacteria (; singular: bacterium) are ubiquitous, mostly free-living organisms often consisting of one Cell (biology), biological cell. They constitute a large domain (biology), domain of prokaryotic microorganisms. Typically a few micrometr ...
l infection
An infection is the invasion of tissues by pathogens, their multiplication, and the reaction of host tissues to the infectious agent and the toxins they produce. An infectious disease, also known as a transmissible disease or communicable dis ...
is likely and, if left untreated, causes bacterial bloodstream infections or sepsis
Sepsis, formerly known as septicemia (septicaemia in British English) or blood poisoning, is a life-threatening condition that arises when the body's response to infection causes injury to its own tissues and organs. This initial stage is follo ...
. This leads to anorexia
Anorexia nervosa, often referred to simply as anorexia, is an eating disorder characterized by low weight, food restriction, body image disturbance, fear of gaining weight, and an overpowering desire to be thin. ''Anorexia'' is a term of Gre ...
and weakness and is generally fatal if untreated.
Human vectors
There are three main fly families causing economically important myiasis in livestock and also, occasionally, in humans: *Calliphoridae
The Calliphoridae (commonly known as blow flies, blow-flies, carrion flies, bluebottles, greenbottles, or cluster flies) are a family of insects in the order Diptera, with almost 1,900 known species. The maggot larvae, often used as fishing ba ...
(blowflies)
** Some examples include '' Calliphora vomitoria'' and ''Calliphora vicina''
* Oestridae ( botflies)
* Cordylobia
''Cordylobia'' is a genus of flies from the family Calliphoridae. The larvae of ''Cordylobia'' are parasitic on mammals, especially rodents. Two species, '' C. anthropophaga'' (the tumbu fly) and '' C. rodhaini'' (Lund's fly), also are known as p ...
* Sarcophagidae
Sarcophagidae () are a family of flies commonly known as flesh flies. They differ from most flies in that they are ovoviviparous, opportunistically depositing hatched or hatching maggots instead of eggs on carrion, dung, decaying material, or o ...
(fleshflies) '' Sarcophaga barbata'' are usually found in dead and rotting meat and animal excrement, which are prime environments for them. This is because their larvae are facultative parasites
Parasitism is a close relationship between species, where one organism, the parasite, lives on or inside another organism, the host, causing it some harm, and is adapted structurally to this way of life. The entomologist E. O. Wilson ha ...
, as they feed on organic tissue and use the hosts' oxygen reserve.
Other families occasionally involved are:
* Anisopodidae
The Anisopodidae are a small cosmopolitan family of gnat-like flies known as wood gnats or window-gnats, with 154 described extant species in 15 genera, and several described fossil taxa. Some species are saprophagous or fungivorous. They are m ...
* Piophilidae
The Piophilidae are a family of "true flies", in the order Diptera. The so-called cheese flies are the best-known members, but most species of the Piophilidae are scavengers in animal products, carrion, and fungi. They may accordingly be impo ...
* Stratiomyidae
* Syrphidae
Specific myiasis
Caused by flies that need a host for larval development * ''Dermatobia hominis
The human botfly, ''Dermatobia hominis'' (Greek δέρμα, skin + βίος, life, and Latin '' hominis'', of a human), is a species of botfly whose larvae parasitise humans (in addition to a wide range of other animals, including other primates ...
'' (human botfly)
* ''Cordylobia anthropophaga
''Cordylobia anthropophaga'', the mango fly, tumbu fly, tumba fly, putzi fly, or skin maggot fly, is a species of blow-fly common in East and Central Africa. It is a parasite of large mammals (including humans) during its larval stage. ''C. anth ...
'' (tumbu fly)
* ''Cordylobia rodhaini
''Cordylobia rodhaini'', also known as the Lund's fly, derived its common name from captain Lund, who was the first European to show symptoms of the disease caused by the larvae of the same fly. Lund’s fly belongs to the genus ''Cordylobia'', f ...
'' (Lund's fly)
* ''Oestrus ovis
''Oestrus ovis'', the sheep bot fly, is a widespread species of fly of the genus ''Oestrus''. It is known for its parasitic predation and damage to sheep, deer, goats and sometimes cattle. There have also been many records of horse, dog and huma ...
'' (sheep botfly)
* '' Hypoderma'' spp. (cattle botflies or ox warbles)
* '' Gasterophilus'' spp. (horse botfly)
* ''Cochliomyia hominivorax
''Cochliomyia hominivorax'', the New World screw-worm fly, or screw-worm for short, is a species of parasitic fly that is well known for the way in which its larvae (maggots) eat the living tissue of warm-blooded animals. It is present in the ...
'' (new world screwworm fly)
* '' Chrysomya bezziana'' (old world screwworm fly)
* '' Auchmeromyia senegalensis'' (Congo floor maggot)
* ''Cuterebra
''Cuterebra'', or rodent bots, is a genus of bot flies that attack rodents and similar animals.
Etymology
The genus name ''Cuterebra'' is a blend of the Latin words ''cutis'' : skin and ''terebra'' : borer with apparent shortening of expected ' ...
'' spp. (rodent and rabbit botfly)
Semispecific myiasis
Caused by flies that usually lay their eggs in decaying animal or vegetable matter, but that can develop in a host if open wounds or sores are present * '' Lucilia'' spp. (green-bottle fly) * ''Cochliomyia
''Cochliomyia'' is a genus in the family Calliphoridae, known as blowflies, in the order Diptera. ''Cochliomyia'' is commonly referred to as the New World screwworm flies, as distinct from Old World screwworm flies. Four species are in this genu ...
'' spp. (screw-worm fly)
* ''Phormia
''Phormia regina'', the black blow fly, belongs to the blow fly family Calliphoridae and was first described by Johann Wilhelm Meigen.
The black blow fly's wings are specialized with a sharp bend. These flies are also have well-developed calypt ...
'' spp. (black-bottle fly)
* ''Calliphora
''Calliphora'' is a genus of blow flies, also known as bottle flies, found in most parts of the world, with the highest diversity in Australia. The most widespread species in North America area ''Calliphora livida'', '' C. vicina'', and '' C. vo ...
'' spp. (blue-bottle fly)
* ''Sarcophaga
''Sarcophaga'' is a genus of true flies and the type genus of the flesh-fly family (Sarcophagidae). The members of this cosmopolitan genus are frequently known as common flesh flies.
This genus occurs essentially worldwide. These flies are gene ...
'' spp. (flesh fly or sarcophagids)
Flesh flies, or ''sarcophagids'', members of the family ''Sarcophagidae'', can cause intestinal
The gastrointestinal tract (GI tract, digestive tract, alimentary canal) is the tract or passageway of the digestive system that leads from the mouth to the anus. The GI tract contains all the major organs of the digestive system, in humans and ...
myiasis in humans if the females lay their eggs on meat or fruit.
Accidental myiasis
Also called pseudomyiasis. Caused by flies that have no preference or need to develop in a host but that will do so on rare occasions. Transmission occurs through accidental deposit of eggs on oral or genitourinary openings, or by swallowing eggs or larvae that are on food. Thecheese fly
The cheese fly (''Piophila casei'') is a species of fly whose larvae are known for infesting human foodstuffs including cured meats, smoked or salted fish, cheeses and also carrion. The larvae of this fly are known as cheese skippers, bacon sk ...
(''Piophila casei'') sometimes causes myiasis through intentional consumption of its maggots (which are contained in the traditional Sardinian delicacy casu marzu). Other flies that can accidentally cause myiasis are:
* ''Musca domestica
The housefly (''Musca domestica'') is a fly of the suborder Cyclorrhapha. It is believed to have evolved in the Cenozoic Era, possibly in the Middle East, and has spread all over the world as a commensal of humans. It is the most common f ...
'' (housefly)
* ''Fannia
Fannia (fl. around 100 AD) was a woman of ancient Rome, notable as the granddaughter of Arria Major.
Life
Fannia is recorded in the writings of Pliny the Younger as a woman of fortitude and respectability. As with her grandmother, Fannia is des ...
'' spp. (latrine flies)
* ''Eristalis tenax
''Eristalis tenax'', the common drone fly, is a common, migratory, cosmopolitan species of hover fly. It is the most widely distributed syrphid species in the world, and is known from all regions except the Antarctic. It has been introduced int ...
'' (rat-tailed maggots)
* ''Muscina
''Muscina'' is a genus of flies that belongs to the family Muscidae, currently consisting of 27 species."ITIS Standard Report Page: Muscina." Integrated Taxonomic Information System. 20 Mar. 2009 They are worldwide in distribution and are freque ...
spp.
The adult flies are not parasitic, but when they lay their eggs in open wounds and these hatch into their larva
A larva (; plural larvae ) is a distinct juvenile form many animals undergo before metamorphosis into adults. Animals with indirect development such as insects, amphibians, or cnidarians typically have a larval phase of their life cycle.
...
l stage (also known as maggot
A maggot is the larva of a fly (order Diptera); it is applied in particular to the larvae of Brachycera flies, such as houseflies, cheese flies, and blowflies, rather than larvae of the Nematocera, such as mosquitoes and crane flies.
...
s or grub
Grub can refer to Grub (larva), of the beetle superfamily Scarabaeoidea, or as a slang term for food. It can also refer to:
Places
* Grub, Appenzell Ausserrhoden, Switzerland
* Grub, St. Gallen, Switzerland
* Grub (Amerang), a hamlet in Bavar ...
s), the larvae feed on live or necrotic tissue, causing myiasis to develop. They may also be ingested or enter through other body apertures.
Diagnosis
Myiasis is often misdiagnosed in the United States because it is rare and its symptoms are not specific. Intestinal myiasis and urinary myiasis are especially difficult to diagnose. Clues that myiasis may be present include recent travel to an endemic area, one or more non-healing lesions on the skin, itchiness, movement under the skin or pain, discharge from a central punctum (tiny hole), or a small, white structure protruding from the lesion. Serologic testing has also been used to diagnose the presence of botfly larvae in human ophthalmomyiasis.Classifications
German
German(s) may refer to:
* Germany (of or related to)
** Germania (historical use)
* Germans, citizens of Germany, people of German ancestry, or native speakers of the German language
** For citizens of Germany, see also German nationality law
**Ge ...
entomologist Fritz Zumpt describes myiasis as "the infestation of live human and vertebrate animals with dipterous larvae, which at least for a period, feed on the host's dead or living tissue, liquid body substances, or ingested food". For modern purposes however, this is too vague. For example, feeding on dead or necrotic tissue is not generally a problem except when larvae such as those of flies in the family Piophilidae attack stored food such as cheese or preserved meats; such activity suggests saprophagy rather than parasitism; it even may be medically beneficial in maggot debridement therapy (MDT).
Currently myiasis commonly is classified according to aspects relevant to the case in question:
* The classical description of myiasis is according to the part of the host that is infected. This is the classification used by ICD-10. For example:
** dermal
The dermis or corium is a layer of skin between the epidermis (with which it makes up the cutis) and subcutaneous tissues, that primarily consists of dense irregular connective tissue and cushions the body from stress and strain. It is divided ...
** sub-dermal
** cutaneous
Skin is the layer of usually soft, flexible outer tissue covering the body of a vertebrate animal, with three main functions: protection, regulation, and sensation.
Other animal coverings, such as the arthropod exoskeleton, have different d ...
(B87.0)
*** creeping, where larvae burrow through or under the skin
*** furuncular, where a larva remains in one spot, causing a boil-like lesion
** nasopharyngeal
The pharynx (plural: pharynges) is the part of the throat behind the mouth and nasal cavity, and above the oesophagus and trachea (the tubes going down to the stomach and the lungs). It is found in vertebrates and invertebrates, though its struct ...
, in the nose, sinuses or pharynx (B87.3)
** ophthalmic or ocular
Eyes are organs of the visual system. They provide living organisms with vision, the ability to receive and process visual detail, as well as enabling several photo response functions that are independent of vision. Eyes detect light and con ...
, in or about the eye (B87.2)
** auricular, in or about the ear
** gastric
The stomach is a muscular, hollow organ in the gastrointestinal tract of humans and many other animals, including several invertebrates. The stomach has a dilated structure and functions as a vital organ in the digestive system. The stomach i ...
, rectal
The rectum is the final straight portion of the large intestine in humans and some other mammals, and the gut in others. The adult human rectum is about long, and begins at the rectosigmoid junction (the end of the sigmoid colon) at the le ...
, or intestinal
The gastrointestinal tract (GI tract, digestive tract, alimentary canal) is the tract or passageway of the digestive system that leads from the mouth to the anus. The GI tract contains all the major organs of the digestive system, in humans and ...
/enteric for the appropriate part of the digestive system (B87.8)
** urogenital
The genitourinary system, or urogenital system, are the organs of the reproductive system and the urinary system. These are grouped together because of their proximity to each other, their common embryological origin and the use of common pathwa ...
(B87.8)
* Another aspect is the relationship between the host and the parasite and provides insight into the biology of the fly species causing the myiasis and its likely effect. Thus the myiasis is described as either:
** obligatory
An obligation is a course of action that someone is required to take, whether legal or moral. Obligations are constraints; they limit freedom. People who are under obligations may choose to freely act under obligations. Obligation exists when ther ...
, where the parasite cannot complete its life cycle without its parasitic phase, which may be specific, semispecific, or opportunistic
** facultative, incidental, or accidental, where it is not essential to the life cycle of the parasite; perhaps a normally free-living larva accidentally gained entrance to the host
Accidental myiasis commonly is enteric, resulting from swallowing eggs or larvae with one's food. The effect is called ''pseudomyiasis''. One traditional cause of pseudomyiasis was the eating of maggots of cheese flies in cheeses such as Stilton
Stilton is a village and civil parish in Cambridgeshire, England, about north of Huntingdon in Huntingdonshire, which is a non-metropolitan district of Cambridgeshire as well as a historic county of England.
History
There is evidence of Neo ...
. Depending on the species present in the gut, pseudomyiasis may cause significant medical symptoms, but it is likely that most cases pass unnoticed.
Prevention
The first control method is preventive and aims to eradicate the adult flies before they can cause any damage and is calledvector control
Vector control is any method to limit or eradicate the mammals, birds, insects or other arthropods (here collectively called " vectors") which transmit disease pathogens. The most frequent type of vector control is mosquito control using a varie ...
. The second control method is the treatment once the infestation is present, and concerns the infected animals (including humans).
The principal control method of adult populations of myiasis inducing flies involves insecticide applications in the environment where the target livestock is kept. Organophosphorus
Organophosphorus compounds are organic compounds containing phosphorus. They are used primarily in pest control as an alternative to chlorinated hydrocarbons that persist in the environment. Some organophosphorus compounds are highly effective in ...
or organochlorine
An organochloride, organochlorine compound, chlorocarbon, or chlorinated hydrocarbon is an organic compound containing at least one covalently bonded atom of chlorine. The chloroalkane class (alkanes with one or more hydrogens substituted by chlo ...
compounds may be used, usually in a spraying formulation. One alternative prevention method is the sterile insect technique
The sterile insect technique (SIT) is a method of biological insect control, whereby overwhelming numbers of sterile insects are released into the wild. The released insects are preferably male, as this is more cost-effective and the females ma ...
(SIT) where a significant number of artificially reared sterilized (usually through irradiation) male flies are introduced. The male flies compete with wild breed males for females in order to copulate and thus cause females to lay batches of unfertilized eggs which cannot develop into the larval stage.
One prevention method involves removing the environment most favourable to the flies, such as by removal of the tail. Another example is the crutching
Crutching refers to the removal of wool from around the tail and between the rear legs of a sheep for hygiene purposes. It can also refer to removing wool from the heads of sheep (''wigging'' or ''eye-wooling''). It does not refer to the proces ...
of sheep, which involves the removal of wool from around the tail and between the rear legs, which is a favourable environment for the larvae. Another, more permanent, practice which is used in some countries is mulesing
Mulesing is the removal of strips of wool-bearing skin from around the breech (buttocks) of a sheep to prevent the parasitic infection flystrike (myiasis).
The wool around the buttocks can retain feces and urine, which attracts flies. The scar t ...
, where skin is removed from young animals to tighten remaining skin – leaving it less prone to fly attack.
To prevent myiasis in humans, there is a need for general improvement of sanitation, personal hygiene, and extermination of the flies by insecticides. Clothes should be washed thoroughly, preferably in hot water, dried away from flies, and ironed thoroughly. The heat of the iron kills the eggs of myiasis-causing flies.
Treatment
This applies once an infestation is established. In many circles the first response to cutaneous myiasis once the breathing hole has formed, is to cover the air hole thickly with petroleum jelly. Lack of oxygen then forces the larva to the surface, where it can more easily be dealt with. In a clinical or veterinary setting there may not be time for such tentative approaches, and the treatment of choice might be more direct, with or without an incision. First the larva must be eliminated through pressure around the lesion and the use offorceps
Forceps (plural forceps or considered a plural noun without a singular, often a pair of forceps; the Latin plural ''forcipes'' is no longer recorded in most dictionaries) are a handheld, hinged instrument used for grasping and holding objects. Fo ...
. Secondly the wound must be cleaned and disinfected. Further control is necessary to avoid further reinfestation.
Livestock may be treated prophylactically with slow-release boluses containing ivermectin
Ivermectin (, '' EYE-vər-MEK-tin'') is an antiparasitic drug. After its discovery in 1975, its first uses were in veterinary medicine to prevent and treat heartworm and acariasis. Approved for human use in 1987, today it is used to treat i ...
, which can provide long-term protection against the development of the larvae. Sheep also may be dipped, a process which involves drenching the animals in persistent insecticide to poison the larvae before they develop into a problem.
Epidemiology
The most common infected animal worldwide is the domesticsheep
Sheep or domestic sheep (''Ovis aries'') are domesticated, ruminant mammals typically kept as livestock. Although the term ''sheep'' can apply to other species in the genus '' Ovis'', in everyday usage it almost always refers to domesticated ...
, for more information see fly strike in sheep. This condition is caused by the blowfly (particularly '' Lucilia sericata'' and its sister species '' L. cuprina''), especially where the weather is often hot and wet. Blowfly strike accounts for over A$170 million a year in losses in the Australian sheep industry, the largest such losses in the world. Given the seriousness of the risk, Australian sheep farmers commonly perform preventive measures such as mulesing
Mulesing is the removal of strips of wool-bearing skin from around the breech (buttocks) of a sheep to prevent the parasitic infection flystrike (myiasis).
The wool around the buttocks can retain feces and urine, which attracts flies. The scar t ...
designed to remove the most common targets for the flies. The docking of lambs' tails (another frequently-soiled area that flies target) is also commonly practiced by sheep farmers worldwide. Maggots also occasionally infest the vulvar area, causing the condition called vulvar myiasis.
Such problems are not peculiar to Australia and New Zealand; they occur worldwide, especially in countries where livestock, particularly sheep, are kept under hot, wet, conditions, including most of Africa and the Americas, ranging from the cold temperate regions in the north, to corresponding latitudes in the south. Myiasis is also not restricted to sheep; screwworm
''Cochliomyia'' is a genus in the family Calliphoridae, known as blowflies, in the order Diptera. ''Cochliomyia'' is commonly referred to as the New World screwworm flies, as distinct from Old World screwworm flies. Four species are in this genu ...
flies (''Cochliomyia hominivorax
''Cochliomyia hominivorax'', the New World screw-worm fly, or screw-worm for short, is a species of parasitic fly that is well known for the way in which its larvae (maggots) eat the living tissue of warm-blooded animals. It is present in the ...
'' in particular) regularly cause upwards of US$100 million in annual damages to domestic cow
Cattle (''Bos taurus'') are large, domesticated, cloven-hooved, herbivores. They are a prominent modern member of the subfamily Bovinae and the most widespread species of the genus ''Bos''. Adult females are referred to as cows and adult ma ...
s and goat
The goat or domestic goat (''Capra hircus'') is a domesticated species of goat-antelope typically kept as livestock. It was domesticated from the wild goat (''C. aegagrus'') of Southwest Asia and Eastern Europe. The goat is a member of the a ...
s, though the impact has been heavily mitigated in recent years by the sterile insect technique
The sterile insect technique (SIT) is a method of biological insect control, whereby overwhelming numbers of sterile insects are released into the wild. The released insects are preferably male, as this is more cost-effective and the females ma ...
.
History


Frederick William Hope
Frederick William Hope (3 January 1797 – 15 April 1862) was an English clergyman, naturalist, collector, and entomologist, who founded a professorship at the University of Oxford to which he gave his entire collections of insects in 1849 (now ...
coined the term ''myiasis'' in 1840 to refer to diseases resulting from dipterous larvae as opposed to those caused by other insect larvae (the term for this was ''scholechiasis''). Hope described several cases of myiasis from Jamaica caused by unknown larvae, one of which resulted in death.
Even though the term ''myiasis'' was first used in 1840, such conditions have been known since ancient times. Ambroise Paré, the chief surgeon to King Charles IX and King Henry III, observed that maggots often infested open wounds.
Maggot therapy
Throughout recorded history, maggots have been used therapeutically to clean out necrotic wounds, an application known as ''maggot therapy
Maggot therapy (also known as larval therapy) is a type of biotherapy involving the introduction of live, disinfected maggots (fly larvae) into non-healing skin and soft-tissue wounds of a human or other animal for the purpose of cleaning out th ...
''.
Fly larvae that feed on dead tissue can clean wounds and may reduce bacterial activity and the chance of a secondary infection. They dissolve dead tissue by secreting digestive enzymes onto the wound as well as actively eating the dead tissue with mouth hooks, two hard, probing appendages protruding on either side of the "mouth". Maggot therapyalso known as maggot debridement therapy (MDT), larval therapy, larva therapy, or larvae therapyis the intentional introduction by a health care practitioner of live, disinfected green bottle fly maggots into the non-healing skin and soft tissue wounds of a human or other animal for the purpose of selectively cleaning out only the necrotic tissue within a wound in order to promote healing.
Although maggot therapy has been used in the US for the past 80 years, it was approved by the FDA as a medical device only in 2004 (along with leeches). Maggots were the first live organism to be marketed in the US according to FDA regulations, and are approved for treating neuropathic (diabetic) foot ulcers, pressure ulcers, venous stasis ulcers, and traumatic and post-surgical wounds that are unresponsive to conventional therapies. Maggots were used in medicine before this time, but were not federally regulated. In 1990, California internist Ronald Sherman began treating patients with maggots produced at his lab at the UC Irvine School of Medicine. Sherman went on to co-found Monarch Labs in 2005, which UC Irvine contracted to produce maggots for Sherman's own continuing clinical research on myiasis at the university. Monarch Labs also sells maggots to hospitals and other medical practices, the first US commercial supplier to do so since the last one closed in 1935.
In the US, demand for these fly larvae doubled after the FDA ruling. Maggot therapy is now used in more than 300 sites across the country. The American Medical Association and Centers for Medicare and Medicaid Services recently clarified the reimbursement guidelines to the wound care community for medicinal maggots, and this therapy may soon be covered by insurance. The larvae of the green bottle fly (a type of blow-fly) are now used exclusively for this purpose, since they preferentially devour only necrotic tissue, leaving healthy tissue intact. This is an important distinction, as most other major varieties of myiasitic fly larvae attack both live and dead wound tissue indiscriminately, effectively negating their benefit in non-harmful wound debridement. Medicinal maggots are placed on the wound and covered with a sterile dressing of gauze and nylon mesh. However, too many larvae placed on the wound could result in healthy tissue being eaten, efficiently creating a new wound, rendering it as a type of myiasis.
History
Maggot therapy has a long history andprehistory
Prehistory, also known as pre-literary history, is the period of human history between the use of the first stone tools by hominins 3.3 million years ago and the beginning of recorded history with the invention of writing systems. The use ...
. The indigenous people of Australia used maggot therapy, and so do the Hill Peoples of Northern Burma, and possibly the Mayans of Central America. Surgeons in Napoleon's armies recognized that wounded soldiers with myiasis were more likely to survive than those without the infestation. In the American Civil War, army surgeons treated wounds by allowing blowfly maggots to clean away the decayed tissue.
William Baer, an orthopedic surgeon at Johns Hopkins during the late 1920s, used maggot therapy to treat a series of patients with osteomyelitis, an infection of bone or bone marrow. The idea was based on an experience in World War I
World War I (28 July 1914 11 November 1918), often abbreviated as WWI, was one of the deadliest global conflicts in history. Belligerents included much of Europe, the Russian Empire, the United States, and the Ottoman Empire, with fightin ...
in which two soldiers presented to him with broken femurs after having lain on the ground for seven days without food and water. Baer could not figure out why neither man had a fever or signs of sepsis. He observed: "On removing the clothing from the wounded part, much was my surprise to see the wound filled with thousands and thousands of maggots, apparently those of the blow fly. The sight was very disgusting and measures were taken hurriedly to wash out these abominable looking creatures." However, he then saw that the wounds were filled with "beautiful pink granulation tissue" and were healing well.
Maggot therapy was common in the United States during the 1930s. However, during the second half of the twentieth century, after the introduction of antibiotics, maggot therapy was used only as a last resort for very serious wounds. Lately maggots have been making a comeback due to the increased resistance of bacteria to antibiotics.
References
External links
Myiasis
reviewed and published by
WikiVet
WikiVet is a wiki of veterinary content based on the MediaWiki platform. The website is a collaborative initiative between various veterinary schools, and its content covers the entire veterinary curriculum. WikiVet is part of the WikiVet Educatio ...
Exotic Myiasis
University of Sydney
The University of Sydney (USYD), also known as Sydney University, or informally Sydney Uni, is a public research university located in Sydney, Australia. Founded in 1850, it is the oldest university in Australia and is one of the country's ...
Department of Medical Entomology
Identification key to species of myiasis-causing fly larvae
Natural History Museum
A natural history museum or museum of natural history is a scientific institution with natural history collections that include current and historical records of animals, plants, fungi, ecosystems, geology, paleontology, climatology, and more. ...
(London)
Parasitic Insects, Mites and Ticks: Genera of Medical and Veterinary Importance: Botflies
{{Pediculosis, acariasis and other infestations Tropical diseases Sheep and goat diseases Arthropod infestations Veterinary entomology Parasitic infestations, stings, and bites of the skin