Fluxgate compass on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
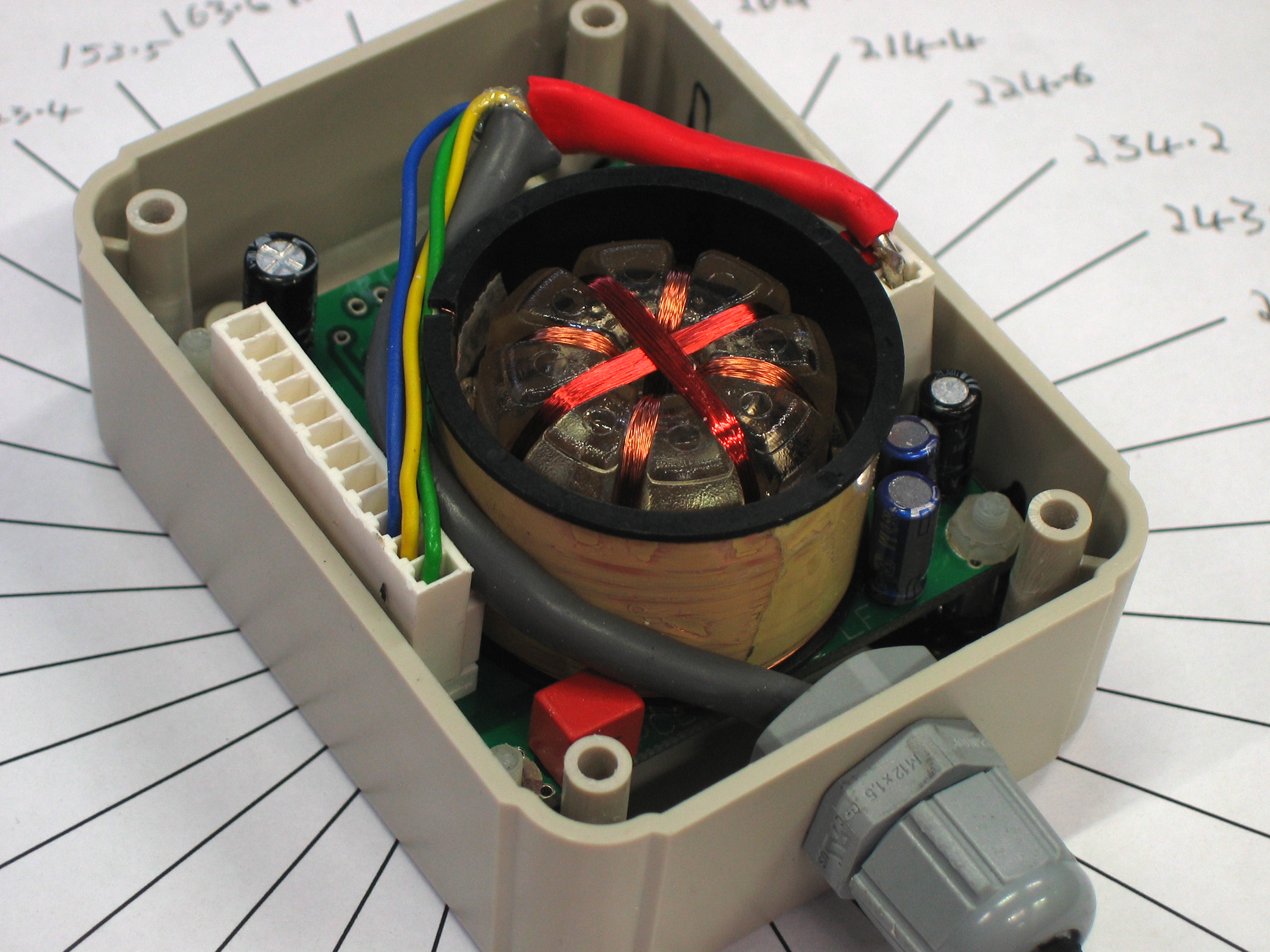 The basic fluxgate compass is a simple
The basic fluxgate compass is a simple
 The basic fluxgate compass is a simple
The basic fluxgate compass is a simple electromagnetic
In physics, electromagnetism is an interaction that occurs between particles with electric charge. It is the second-strongest of the four fundamental interactions, after the strong force, and it is the dominant force in the interactions o ...
device that employs two or more small coils of wire around a core of highly permeable
Permeability, permeable, and semipermeable may refer to:
Chemistry
*Semipermeable membrane, a membrane which will allow certain molecules or ions to pass through it by diffusion
*Vascular permeability, the movement of fluids and molecules betwe ...
magnetic material, to directly sense the direction of the horizontal component of the Earth's magnetic field
Earth's magnetic field, also known as the geomagnetic field, is the magnetic field that extends from Earth's interior out into space, where it interacts with the solar wind, a stream of charged particles emanating from the Sun. The magnetic ...
. The advantages of this mechanism over a magnetic compass
A compass is a device that shows the cardinal directions used for navigation and geographic orientation. It commonly consists of a magnetized needle or other element, such as a compass card or compass rose, which can pivot to align itself with ...
are that the reading is in electronic form and can be digitised and transmitted easily, displayed remotely, and used by an electronic autopilot
An autopilot is a system used to control the path of an aircraft, marine craft or spacecraft without requiring constant manual control by a human operator. Autopilots do not replace human operators. Instead, the autopilot assists the operator' ...
for course correction.
To avoid inaccuracies created by the vertical component of the field, the fluxgate array must be kept as flat as possible by mounting it on gimbal
A gimbal is a pivoted support that permits rotation of an object about an axis. A set of three gimbals, one mounted on the other with orthogonal pivot axes, may be used to allow an object mounted on the innermost gimbal to remain independent of ...
s or using a fluid suspension system. All the same, inertia
Inertia is the idea that an object will continue its current motion until some force causes its speed or direction to change. The term is properly understood as shorthand for "the principle of inertia" as described by Newton in his first law ...
l errors are inevitable when the vessel is turning sharply or being tossed about by rough seas. To ensure directional readings that are adequately stable, marine fluxgate compasses always incorporate either fluid or electronic damping
Damping is an influence within or upon an oscillatory system that has the effect of reducing or preventing its oscillation. In physical systems, damping is produced by processes that dissipate the energy stored in the oscillation. Examples in ...
. An alternative is to use a 3-axis fluxgate magnetometer to provide a 3D flux vector, with the magnetic heading derived from the flux on a plane perpendicular
In elementary geometry, two geometric objects are perpendicular if they intersect at a right angle (90 degrees or π/2 radians). The condition of perpendicularity may be represented graphically using the ''perpendicular symbol'', ⟂. It ca ...
to gravity, thus providing immunity from pitching and rolling.
Fluxgate compasses and gyrocompass
A gyrocompass is a type of non-magnetic compass which is based on a fast-spinning disc and the rotation of the Earth (or another planetary body if used elsewhere in the universe) to find geographical direction automatically. The use of a gyroc ...
es complement one another nicely. The fluxgate provides a directional reference that is stable over the long term, apart from changing magnetic disturbances, and the gyrocompass is accurate over the short term, even against acceleration
In mechanics, acceleration is the rate of change of the velocity of an object with respect to time. Accelerations are vector quantities (in that they have magnitude and direction). The orientation of an object's acceleration is given by t ...
and heeling effects. At high latitude
In geography, latitude is a coordinate that specifies the north– south position of a point on the surface of the Earth or another celestial body. Latitude is given as an angle that ranges from –90° at the south pole to 90° at the north pol ...
s, where the Earth's magnetic field dips downward toward the magnetic poles, the gyro data can be used to correct for roll-induced heading errors in the fluxgate output. It can also be used to correct for the roll- and heel-induced errors that often plague fluxgate compasses installed on steel vessels.
The fluxgate compass was invented by the Eclipse-Pioneer Division of Bendix in 1943.
References
{{ReflistSee also
*Fluxgate magnetometer
A magnetometer is a device that measures magnetic field or magnetic dipole moment. Different types of magnetometers measure the direction, strength, or relative change of a magnetic field at a particular location. A compass is one such device, o ...
for more details on the measurement method.
Navigational equipment
Bendix Corporation