Flanders (county) on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
The County of Flanders was a historic territory in the
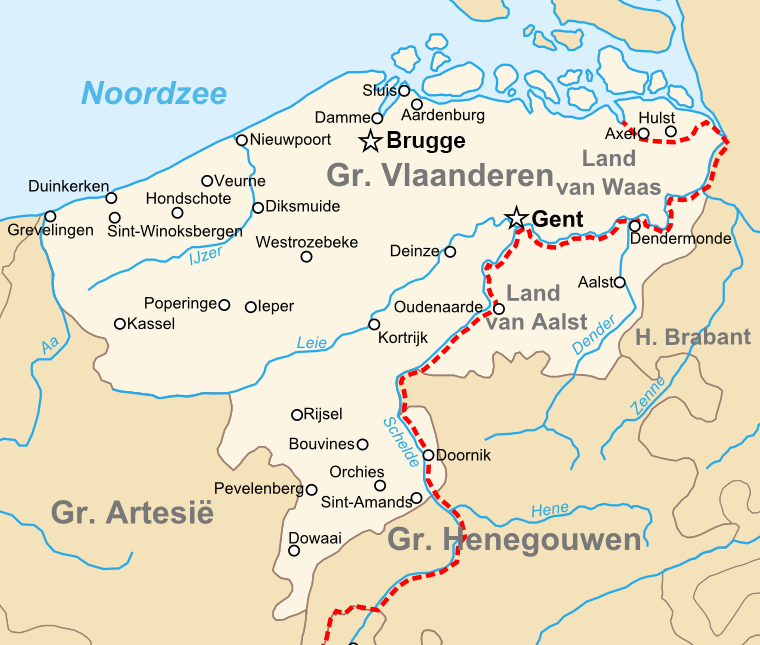 The geography of the historic County of Flanders only partially overlaps with present-day region of
The geography of the historic County of Flanders only partially overlaps with present-day region of
 The arms of the County of Flanders were allegedly created by Philip of Alsace, count of Flanders from 1168 to 1191; a climbing or rampant black lion on a gold field. In the story about the
The arms of the County of Flanders were allegedly created by Philip of Alsace, count of Flanders from 1168 to 1191; a climbing or rampant black lion on a gold field. In the story about the
 At the end of the 6th and the 7th century a new inflow emerged from the western
At the end of the 6th and the 7th century a new inflow emerged from the western
 In 751 the
In 751 the

 Militarily, economically and politically, Europe went through a deep crisis. The
Militarily, economically and politically, Europe went through a deep crisis. The
 The
The  Trade partners included England, the
Trade partners included England, the
 Flemish prosperity waned in the following century, however, owing to widespread European population decline following the
Flemish prosperity waned in the following century, however, owing to widespread European population decline following the
 Through his marriage with Margaret of Dampierre in 1369,
Through his marriage with Margaret of Dampierre in 1369,
 Under
Under
 After the extinction of the Spanish branch of the Habsburgs, the Austrian branch of the Habsburgs became counts of Flanders. Under
After the extinction of the Spanish branch of the Habsburgs, the Austrian branch of the Habsburgs became counts of Flanders. Under
Maps (900–1350)
{{coord, 51.06, 3.72, display=title 1380s in the Burgundian Netherlands Flanders Former provinces of France History of Flanders Flanders, County of 862 establishments
Low Countries
The term Low Countries, also known as the Low Lands ( nl, de Lage Landen, french: les Pays-Bas, lb, déi Niddereg Lännereien) and historically called the Netherlands ( nl, de Nederlanden), Flanders, or Belgica, is a coastal lowland region in N ...
.
From 862 onwards, the counts of Flanders
The count of Flanders was the ruler or sub-ruler of the county of Flanders, beginning in the 9th century. Later, the title would be held for a time, by the rulers of the Holy Roman Empire and Spain. During the French Revolution, in 1790, the co ...
were among the original twelve peers of the Kingdom of France
The Kingdom of France ( fro, Reaume de France; frm, Royaulme de France; french: link=yes, Royaume de France) is the historiographical name or umbrella term given to various political entities of France in the medieval and early modern period. ...
. For centuries, their estates around the cities of Ghent
Ghent ( nl, Gent ; french: Gand ; traditional English: Gaunt) is a city and a municipality in the Flemish Region of Belgium. It is the capital and largest city of the East Flanders province, and the third largest in the country, exceeded i ...
, Bruges
Bruges ( , nl, Brugge ) is the capital and largest City status in Belgium, city of the Provinces of Belgium, province of West Flanders in the Flemish Region of Belgium, in the northwest of the country, and the sixth-largest city of the countr ...
and Ypres
Ypres ( , ; nl, Ieper ; vls, Yper; german: Ypern ) is a Belgian city and municipality in the province of West Flanders. Though
the Dutch name is the official one, the city's French name is most commonly used in English. The municipality ...
formed one of the most affluent regions in Europe
Europe is a large peninsula conventionally considered a continent in its own right because of its great physical size and the weight of its history and traditions. Europe is also considered a Continent#Subcontinents, subcontinent of Eurasia ...
.
Up to 1477, the area under French
French (french: français(e), link=no) may refer to:
* Something of, from, or related to France
** French language, which originated in France, and its various dialects and accents
** French people, a nation and ethnic group identified with Franc ...
suzerainty was west of the Scheldt
The Scheldt (french: Escaut ; nl, Schelde ) is a river that flows through northern France, western Belgium, and the southwestern part of the Netherlands, with its mouth at the North Sea. Its name is derived from an adjective corresponding to ...
and was called "Royal Flanders" (Dutch: ''Kroon-Vlaanderen'', French: ''Flandre royale''). Aside from this, the counts, from the 11th century onward, held land east of the river as a fief of the Holy Roman Empire
The Holy Roman Empire was a political entity in Western, Central, and Southern Europe that developed during the Early Middle Ages and continued until its dissolution in 1806 during the Napoleonic Wars.
From the accession of Otto I in 962 unt ...
: "Imperial Flanders" (''Rijks-Vlaanderen'' or ''Flandre impériale''). Part of the Burgundian Netherlands
In the history of the Low Countries, the Burgundian Netherlands (french: Pays-Bas bourguignons, nl, Bourgondische Nederlanden, lb, Burgundeschen Nidderlanden, wa, Bas Payis borguignons) or the Burgundian Age is the period between 1384 and ...
from 1384, which had a complex relation with France, the whole county fell to the Empire after the Peace of Madrid in 1526 and the Peace of the Ladies in 1529.
Having already regained much, by 1795, the rest – within the Austrian Netherlands
The Austrian Netherlands nl, Oostenrijkse Nederlanden; french: Pays-Bas Autrichiens; german: Österreichische Niederlande; la, Belgium Austriacum. was the territory of the Burgundian Circle of the Holy Roman Empire between 1714 and 1797. The pe ...
– was acquired likewise by France under the French First Republic
In the history of France, the First Republic (french: Première République), sometimes referred to in historiography as Revolutionary France, and officially the French Republic (french: République française), was founded on 21 September 1792 ...
, recognized by treaty in 1797. Resulting from the Battle of Waterloo
The Battle of Waterloo was fought on Sunday 18 June 1815, near Waterloo (at that time in the United Kingdom of the Netherlands, now in Belgium). A French army under the command of Napoleon was defeated by two of the armies of the Sevent ...
of the same year, it passed to the newly established United Kingdom of the Netherlands
The United Kingdom of the Netherlands ( nl, Verenigd Koninkrijk der Nederlanden; french: Royaume uni des Pays-Bas) is the unofficial name given to the Kingdom of the Netherlands as it existed between 1815 and 1839. The United Netherlands was cr ...
in 1815. The former County of Flanders, except for French Flanders
French Flanders (french: La Flandre française) is a part of the historical County of Flanders in present-day France where a dialect of Dutch was or still is traditionally spoken. The region lies in the modern-day region of Hauts-de-France an ...
, is the only part of the late medieval French kingdom outside of modern-day France (Catalonia having been renounced in 1258).
Etymology
Flanders and Flemish (Dutch: ''Vlaanderen'', ''Vlaams'') are likely derived from the Frisian *''flāndra'' and *''flāmisk'' (inOld Frisian
Old Frisian was a West Germanic language spoken between the 8th and 16th centuries along the North Sea coast, roughly between the mouths of the Rhine and Weser rivers. The Frisian settlers on the coast of South Jutland (today's Northern Fries ...
''flamsk''), the roots of which are Germanic *''flaumaz'' meaning "overflow, flooding". The coastal area of Flanders was flooded twice per day from the 3rd century to the 8th century by the North Sea
The North Sea lies between Great Britain, Norway, Denmark, Germany, the Netherlands and Belgium. An epeiric sea on the European continental shelf, it connects to the Atlantic Ocean through the English Channel in the south and the Norwegian ...
at the time when the coast was frequently visited by Frisian (cattle) traders and probably largely inhabited by Frisians.
The Flemish people are first mentioned in the biography of Saint Eligius
Saint Eligius (also Eloy, Eloi or Loye; french: Éloi; 11 June 588 – 1 December 660 AD) is the patron saint of goldsmiths, other metalworkers, and coin collectors. He is also the patron saint of veterinarians, the Royal Electrical and Mech ...
(ca. 590–660), the ''Vita sancti Eligii''. This work was written before 684, but only known since 725. This work mentions the "Flanderenses", who lived in "Flandris."
Geography
 The geography of the historic County of Flanders only partially overlaps with present-day region of
The geography of the historic County of Flanders only partially overlaps with present-day region of Flanders
Flanders (, ; Dutch: ''Vlaanderen'' ) is the Flemish-speaking northern portion of Belgium and one of the communities, regions and language areas of Belgium. However, there are several overlapping definitions, including ones related to cultu ...
in Belgium, though even there it extends beyond the present provinces of West Flanders and East Flanders. Some of the historic county is now part of France and the Netherlands. The land covered by the county is spread out over:
* Belgium
Belgium, ; french: Belgique ; german: Belgien officially the Kingdom of Belgium, is a country in Northwestern Europe. The country is bordered by the Netherlands to the north, Germany to the east, Luxembourg to the southeast, France to ...
:
** two of the five Flemish provinces: West Flanders
West Flanders ( nl, West-Vlaanderen ; vls, West Vloandern; french: (Province de) Flandre-Occidentale ; german: Westflandern ) is the westernmost province of the Flemish Region, in Belgium. It is the only coastal Belgian province, facing the No ...
and East Flanders
, native_name_lang =
, settlement_type = Province of Belgium
, image_flag = Flag of Oost-Vlaanderen.svg
, flag_size =
, image_shield = Wapen van O ...
** part of the Flemish province of Antwerp
Antwerp (; nl, Antwerpen ; french: Anvers ; es, Amberes) is the largest city in Belgium by area at and the capital of Antwerp Province in the Flemish Region. With a population of 520,504,
: the land of Bornem
Bornem (, old spelling: ''Bornhem'') is a municipality located in the Belgian province of Antwerp. The municipality comprises the village of Bornem proper, Hingene, and Weert, and . There are also the hamlets of Branst, Buitenland, Eikevlie ...
** part of the Walloon province of Hainaut: Tournaisis
The Tournaisis, or Tournai (Flemish: ''Doornik''), a territory in the Low Countries in present-day Belgium, is one of Europe's oldest town centres. Located in the Wallonia region of Belgium on the Scheldt River (French: ''L'Escaut''), northwes ...
and the region around Moeskroen (that belonged to West Flanders until 1962)
* France
France (), officially the French Republic ( ), is a country primarily located in Western Europe. It also comprises of Overseas France, overseas regions and territories in the Americas and the Atlantic Ocean, Atlantic, Pacific Ocean, Pac ...
:
** French Flanders
French Flanders (french: La Flandre française) is a part of the historical County of Flanders in present-day France where a dialect of Dutch was or still is traditionally spoken. The region lies in the modern-day region of Hauts-de-France an ...
(in the Nord departement)
*** the French westcorner: the region around Dunkirk
Dunkirk (french: Dunkerque ; vls, label=French Flemish, Duunkerke; nl, Duinkerke(n) ; , ;) is a commune in the department of Nord in northern France.
, Bergues
Bergues (; nl, Sint-Winoksbergen; vls, Bergn) is a commune in the Nord department in northern France.
It is situated to the south of Dunkirk and from the Belgian border. Locally it is referred to as "the other Bruges in Flanders". Bergues ...
and Bailleul, an area where Flemish
Flemish (''Vlaams'') is a Low Franconian dialect cluster of the Dutch language. It is sometimes referred to as Flemish Dutch (), Belgian Dutch ( ), or Southern Dutch (). Flemish is native to Flanders, a historical region in northern Belgium; ...
used to be the main language
*** Walloon Flanders, where the Picard language
Picard (, also , ) is a '' langue d'oïl'' of the Romance language family spoken in the northernmost part of France and Hainaut province in Belgium. Administratively, this area is divided between the French Hauts-de-France region and the Belgi ...
, closely related to French, was spoken.
** Artois
Artois ( ; ; nl, Artesië; English adjective: ''Artesian'') is a region of northern France. Its territory covers an area of about 4,000 km2 and it has a population of about one million. Its principal cities are Arras (Dutch: ''Atrecht'') ...
(in the Pas-de-Calais
Pas-de-Calais (, "strait of Calais"; pcd, Pas-Calés; also nl, Nauw van Kales) is a department in northern France named after the French designation of the Strait of Dover, which it borders. It has the most communes of all the departments of ...
department): removed from Flanders in 1191 and created as independent county in 1237
* Netherlands
)
, anthem = ( en, "William of Nassau")
, image_map =
, map_caption =
, subdivision_type = Sovereign state
, subdivision_name = Kingdom of the Netherlands
, established_title = Before independence
, established_date = Spanish Netherl ...
:
** Zeelandic Flanders
Zeelandic Flanders ( ; zea, Zeêuws-Vlaonderen; vls, Zêeuws-Vloandern)''Vlaanderen'' in isolation: . is the southernmost region of the province of Zeeland in the south-western Netherlands. It lies south of the Western Scheldt that separates ...
, a region between Belgium and the Western Scheldt
The Western Scheldt ( nl, Westerschelde) in the province of Zeeland in the southwestern Netherlands, is the estuary of the Scheldt river. This river once had several estuaries, but the others are now disconnected from the Scheldt, leaving th ...
in the southern part of the modern province of Zeeland
, nl, Ik worstel en kom boven("I struggle and emerge")
, anthem = "Zeeuws volkslied"("Zeelandic Anthem")
, image_map = Zeeland in the Netherlands.svg
, map_alt =
, m ...
, which from 1581 formed part of the Generality Lands
The Generality Lands, Lands of the Generality or Common Lands ( nl, Generaliteitslanden) were about one fifth of the territories of the United Provinces of the Netherlands, that were directly governed by the States-General. Unlike the seven pr ...
under control of the Dutch Republic
The United Provinces of the Netherlands, also known as the (Seven) United Provinces, officially as the Republic of the Seven United Netherlands ( Dutch: ''Republiek der Zeven Verenigde Nederlanden''), and commonly referred to in historiograph ...
.
Flag and arms
 The arms of the County of Flanders were allegedly created by Philip of Alsace, count of Flanders from 1168 to 1191; a climbing or rampant black lion on a gold field. In the story about the
The arms of the County of Flanders were allegedly created by Philip of Alsace, count of Flanders from 1168 to 1191; a climbing or rampant black lion on a gold field. In the story about the Battle of the Golden Spurs
The Battle of the Golden Spurs ( nl, Guldensporenslag; french: Bataille des éperons d'or) was a military confrontation between the royal army of France and rebellious forces of the County of Flanders on 11 July 1302 during the Franco-Flemis ...
, the arms and its corresponding battlecry ''Vlaendr'n den leeuw'' ("Flanders, the Lion!") plays a crucial role in the forming of a Flemish consciousness, which was popularised in recent times by the book ''De Leeuw van Vlaanderen'' by Hendrik Conscience. As a result, the arms of the county live on as arms of the Flemish Community
The Flemish Community ( nl, Vlaamse Gemeenschap ; french: Communauté flamande ; german: Flämische Gemeinschaft ) is one of the three institutional communities of Belgium, established by the Belgian constitution and having legal responsibilitie ...
.
It is said that Philip of Alsace brought the lion flag with him from the Holy Land
The Holy Land; Arabic: or is an area roughly located between the Mediterranean Sea and the Eastern Bank of the Jordan River, traditionally synonymous both with the biblical Land of Israel and with the region of Palestine. The term "Holy ...
, where in 1177 he supposedly conquered it from a Saracen knight, but this is a myth. The simple fact that the lion appeared on his personal seal since 1163, when he had not yet taken one step in the Levant
The Levant () is an approximate historical geographical term referring to a large area in the Eastern Mediterranean region of Western Asia. In its narrowest sense, which is in use today in archaeology and other cultural contexts, it is ...
, disproves it. In reality Philip was following a West-European trend. In the same period lions also appeared in the arms of Brabant Brabant is a traditional geographical region (or regions) in the Low Countries of Europe. It may refer to:
Place names in Europe
* London-Brabant Massif, a geological structure stretching from England to northern Germany
Belgium
* Province of Bra ...
, Luxembourg
Luxembourg ( ; lb, Lëtzebuerg ; french: link=no, Luxembourg; german: link=no, Luxemburg), officially the Grand Duchy of Luxembourg, ; french: link=no, Grand-Duché de Luxembourg ; german: link=no, Großherzogtum Luxemburg is a small lan ...
, Holland
Holland is a geographical regionG. Geerts & H. Heestermans, 1981, ''Groot Woordenboek der Nederlandse Taal. Deel I'', Van Dale Lexicografie, Utrecht, p 1105 and former Provinces of the Netherlands, province on the western coast of the Netherland ...
, Limburg and other territories. It is curious that the lion as a heraldic symbol was mostly used in border territories and neighbouring countries of the Holy Roman Empire
The Holy Roman Empire was a political entity in Western, Central, and Southern Europe that developed during the Early Middle Ages and continued until its dissolution in 1806 during the Napoleonic Wars.
From the accession of Otto I in 962 unt ...
. It was in all likelihood a way of showing independence from the emperor, who used an eagle
Eagle is the common name for many large birds of prey of the family Accipitridae. Eagles belong to several groups of genera, some of which are closely related. Most of the 68 species of eagle are from Eurasia and Africa. Outside this area, j ...
in his personal arms. In Europe the lion had been a well-known figure since Roman times, through works such as the fables of Aesop
Aesop ( or ; , ; c. 620–564 BCE) was a Greek fabulist and storyteller credited with a number of fables now collectively known as ''Aesop's Fables''. Although his existence remains unclear and no writings by him survive, numerous tales c ...
.
History
Prehistory and antiquity
The future county of Flanders had been inhabited since prehistory. During the Iron Age theKemmelberg
Kemmelberg (, ) is a hill formation in Flanders, Belgium. It is located less than a kilometer from the village of Kemmel, part of the municipality of Heuvelland in West Flanders.
History
The earliest settlements on the Kemmelberg date back 2.500 y ...
formed an important Celtic settlement. During the times of Julius Caesar, the inhabitants were part of the Belgae
The Belgae () were a large confederation of tribes living in northern Gaul, between the English Channel, the west bank of the Rhine, and the northern bank of the river Seine, from at least the third century BC. They were discussed in depth by Ju ...
, a collective name for all Celtic and Germanic tribes in the north of Gallia. For Flanders in specific these were the Menapii
The Menapii were a Belgic tribe dwelling near the North Sea, around present-day Cassel, during the Iron Age and the Roman period.
Name Attestations
They are mentioned as ''Menapii'' by Caesar (mid-1st c. BC) and Orosius (early 5th c. AD ...
, the Morini, the Nervii and the Atrebates
The Atrebates (Gaulish: *''Atrebatis'', 'dwellers, land-owners, possessors of the soil') were a Belgic tribe of the Iron Age and the Roman period, originally dwelling in the Artois region.
After the tribes of Gallia Belgica were defeated by ...
.
Julius Caesar
Gaius Julius Caesar (; ; 12 July 100 BC – 15 March 44 BC), was a Roman general and statesman. A member of the First Triumvirate, Caesar led the Roman armies in the Gallic Wars before defeating his political rival Pompey in a civil war, an ...
conquered the area around 54 BC and the population was partially romanised from the 1st to the 3rd century. The Roman road
Roman roads ( la, viae Romanae ; singular: ; meaning "Roman way") were physical infrastructure vital to the maintenance and development of the Roman state, and were built from about 300 BC through the expansion and consolidation of the Roman Re ...
that connected Cologne
Cologne ( ; german: Köln ; ksh, Kölle ) is the largest city of the German western state of North Rhine-Westphalia (NRW) and the fourth-most populous city of Germany with 1.1 million inhabitants in the city proper and 3.6 millio ...
with Boulogne-sur-Mer
Boulogne-sur-Mer (; pcd, Boulonne-su-Mér; nl, Bonen; la, Gesoriacum or ''Bononia''), often called just Boulogne (, ), is a coastal city in Hauts-de-France, Northern France. It is a Subprefectures in France, sub-prefecture of the Department ...
was used as a defense perimeter. In the south the Gallo-Romanic population was able to maintain itself, while the north became a no-mans land that also suffered from regular floods from the North Sea
The North Sea lies between Great Britain, Norway, Denmark, Germany, the Netherlands and Belgium. An epeiric sea on the European continental shelf, it connects to the Atlantic Ocean through the English Channel in the south and the Norwegian ...
.
In the coastal and Scheldt
The Scheldt (french: Escaut ; nl, Schelde ) is a river that flows through northern France, western Belgium, and the southwestern part of the Netherlands, with its mouth at the North Sea. Its name is derived from an adjective corresponding to ...
areas Saxon tribes gradually appeared. For the Romans, ''Saxon'' was a general term, and included Angles
The Angles ( ang, Ængle, ; la, Angli) were one of the main Germanic peoples who settled in Great Britain in the post-Roman period. They founded several kingdoms of the Heptarchy in Anglo-Saxon England. Their name is the root of the name ...
, Saxons
The Saxons ( la, Saxones, german: Sachsen, ang, Seaxan, osx, Sahson, nds, Sassen, nl, Saksen) were a group of Germanic
*
*
*
*
peoples whose name was given in the early Middle Ages to a large country (Old Saxony, la, Saxonia) near the Nor ...
, Jutes
The Jutes (), Iuti, or Iutæ ( da, Jyder, non, Jótar, ang, Ēotas) were one of the Germanic tribes who settled in Great Britain after the departure of the Romans. According to Bede, they were one of the three most powerful Germanic nation ...
and Erules. The coastal defense around Boulogne and Oudenburg
Oudenburg (; french: Audembourg ; vls, Oednburg; la, Aldenburgensis) is a city and municipality located in the Belgian province of West Flanders. The municipality comprises the city of Oudenburg itself and the towns of Ettelgem, Roksem and ...
, the '' Litus Saxonicum'', remained functional until about 420. These forts were manned by Saxon soldiers.
From their base land Toxandria
Texandria (also Toxiandria; later Toxandria, Taxandria), is a region mentioned in the 4th century AD and during the Middle Ages. It was situated in the southern part of the modern Netherlands and in the northern part of present-day Belgium, curren ...
the Salian Franks further expanded into the Roman empire. The first incursion into the lands of the Atrebates was turned away in 448 at Vicus Helena. But after the murder of the Roman general Flavius Aëtius
Aetius (also spelled Aëtius; ; 390 – 454) was a Roman general and statesman of the closing period of the Western Roman Empire. He was a military commander and the most influential man in the Empire for two decades (433454). He managed pol ...
in 454 and Roman emperor Valentinianus III in 455, the Salic Franks encountered hardly any resistance. From Duisburg
Duisburg () is a city in the Ruhr metropolitan area of the western German state of North Rhine-Westphalia. Lying on the confluence of the Rhine and the Ruhr rivers in the center of the Rhine-Ruhr Region, Duisburg is the 5th largest city in ...
, king Chlodio
Chlodio (probably died after 450), also Clodio, Clodius, Clodion, Cloio or Chlogio, was a Frankish king who attacked and then apparently ruled Roman-inhabited lands around Cambrai and Tournai, near the modern border of Belgium and France. He is ...
conquered Cambrai
Cambrai (, ; pcd, Kimbré; nl, Kamerijk), formerly Cambray and historically in English Camerick or Camericke, is a city in the Nord department and in the Hauts-de-France region of France on the Scheldt river, which is known locally as the ...
and Tournai
Tournai or Tournay ( ; ; nl, Doornik ; pcd, Tornai; wa, Tornè ; la, Tornacum) is a city and municipality of Wallonia located in the province of Hainaut, Belgium. It lies southwest of Brussels on the river Scheldt. Tournai is part of Eurome ...
, and he reached the Somme __NOTOC__
Somme or The Somme may refer to: Places
*Somme (department), a department of France
*Somme, Queensland, Australia
*Canal de la Somme, a canal in France
*Somme (river), a river in France
Arts, entertainment, and media
* ''Somme'' (book), a ...
. After his death two Salic kingdoms emerged. Childeric is recorded in 463 as king of Tournay and ally of the Romans against the Visigoths
The Visigoths (; la, Visigothi, Wisigothi, Vesi, Visi, Wesi, Wisi) were an early Germanic people who, along with the Ostrogoths, constituted the two major political entities of the Goths within the Roman Empire in late antiquity, or what is k ...
. He was also administrator of the province of Belgica Secunda
Gallia Belgica ("Belgic Gaul") was a province of the Roman Empire located in the north-eastern part of Roman Gaul, in what is today primarily northern France, Belgium, and Luxembourg, along with parts of the Netherlands and Germany.
In 50 BC, ...
. His son Clovis I
Clovis ( la, Chlodovechus; reconstructed Frankish: ; – 27 November 511) was the first king of the Franks to unite all of the Frankish tribes under one ruler, changing the form of leadership from a group of petty kings to rule by a single ki ...
conquered from 486 on all of Northern France.
Early Middle Ages
The abandoned coast and Scheldt region had been partially repopulated since the 4th century by Saxons and Franks from the east of theRhine
), Surselva, Graubünden, Switzerland
, source1_coordinates=
, source1_elevation =
, source2 = Rein Posteriur/Hinterrhein
, source2_location = Paradies Glacier, Graubünden, Switzerland
, source2_coordinates=
, source ...
that retained their Germanic culture and language. In the 5th century Salic Franks settled in present-day Northern-France and Wallonia
Wallonia (; french: Wallonie ), or ; nl, Wallonië ; wa, Waloneye or officially the Walloon Region (french: link=no, Région wallonne),; nl, link=no, Waals gewest; wa, link=no, Redjon walone is one of the three regions of Belgium—al ...
, primarily around the cities of Courtrai
Kortrijk ( , ; vls, Kortryk or ''Kortrik''; french: Courtrai ; la, Cortoriacum), sometimes known in English as Courtrai or Courtray ( ), is a Belgian city and municipality in the Flemish province of West Flanders.
It is the capital and large ...
, Tournai
Tournai or Tournay ( ; ; nl, Doornik ; pcd, Tornai; wa, Tornè ; la, Tornacum) is a city and municipality of Wallonia located in the province of Hainaut, Belgium. It lies southwest of Brussels on the river Scheldt. Tournai is part of Eurome ...
and Bavay. They adapted to the local Gallo-Romanic population. From the 6th century on the no-mans-land farther north was filled by Franks
The Franks ( la, Franci or ) were a group of Germanic peoples whose name was first mentioned in 3rd-century Roman sources, and associated with tribes between the Lower Rhine and the Ems River, on the edge of the Roman Empire.H. Schutz: Tools ...
from the Rhinelands and other Germanic groups from the Netherlands and Germany.
The first wave of immigration in the present day Flemish territory was accompanied by limited Christianisation. In the wake of the immigrants, missionaries tried to convert the heathen population, but had little success. The bishoprics were reinstated, usually with the same natural borders of the Late-Roman era; the Silva Carbonaria
Silva Carbonaria, the "charcoal forest", was the dense old-growth forest of beech and oak that formed a natural boundary during the Late Iron Age through Roman times into the Early Middle Ages across what is now western Wallonia. The Silva Carb ...
separated the Bishopric of Cambrai from the Bishopric of Tongeren
In church governance, a diocese or bishopric is the ecclesiastical district under the jurisdiction of a bishop.
History
In the later organization of the Roman Empire, the increasingly subdivided provinces were administratively associat ...
, while the Scheldt again became the border between the bishoprics of Cambrai and Tournai
Tournai or Tournay ( ; ; nl, Doornik ; pcd, Tornai; wa, Tornè ; la, Tornacum) is a city and municipality of Wallonia located in the province of Hainaut, Belgium. It lies southwest of Brussels on the river Scheldt. Tournai is part of Eurome ...
. Vedast and Eleutherius of Tournai
Saint Eleutherius of Tournai (french: Eleuthère) (died c. 532) is venerated as a saint and considered the first bishop of Tournai.
were assigned to reinstate the bishoprics of Arras
Arras ( , ; pcd, Aro; historical nl, Atrecht ) is the prefecture of the Pas-de-Calais department, which forms part of the region of Hauts-de-France; before the reorganization of 2014 it was in Nord-Pas-de-Calais. The historic centre of ...
and Tournai. However, these bishoprics failed to survive independently. In the late 6th century the bishopric of Arras was connected to that of Cambrai, and at the start of the 7th century the same was done to the bishoprics of Tournai and Noyon.
At the end of the 6th century the duchy of Dentelinus was created in the north of what would later constitute Neustria
Neustria was the western part of the Kingdom of the Franks.
Neustria included the land between the Loire and the Silva Carbonaria, approximately the north of present-day France, with Paris, Orléans, Tours, Soissons as its main cities. It late ...
. This duchy presumably included the bishoprics Boulogne, Thérouanne, Arras, Tournai, Cambrai and Noyon, thus the northwestern region between the North Sea and the Silva Carbonaria, an area whose outlines were very similar to the later Flanders. The duchy of Dentelinus was primarily meant as a military and strategical deterrent against Frisian and Saxon invasions. It was a cornerstone in the military defense of the Merovingian Empire. In 600 Chlothar II
Chlothar II, sometime called "the Young" (French: le Jeune), (May/June 584 – 18 October 629), was king of Neustria and king of the Franks, and the son of Chilperic I and his third wife, Fredegund. He started his reign as an infant under the ...
(584–628) was forced to temporarily cede the duchy of Dentelinus to Austrasia
Austrasia was a territory which formed the north-eastern section of the Merovingian Kingdom of the Franks during the 6th to 8th centuries. It was centred on the Meuse, Middle Rhine and the Moselle rivers, and was the original territory of the ...
, but after restoration of Austrasian dual-monarchy in 622/623 the duchy was returned.
7th century
 At the end of the 6th and the 7th century a new inflow emerged from the western
At the end of the 6th and the 7th century a new inflow emerged from the western Pas-de-Calais
Pas-de-Calais (, "strait of Calais"; pcd, Pas-Calés; also nl, Nauw van Kales) is a department in northern France named after the French designation of the Strait of Dover, which it borders. It has the most communes of all the departments of ...
. This area had been germanised in the 5th century and descendants of the Saxons
The Saxons ( la, Saxones, german: Sachsen, ang, Seaxan, osx, Sahson, nds, Sassen, nl, Saksen) were a group of Germanic
*
*
*
*
peoples whose name was given in the early Middle Ages to a large country (Old Saxony, la, Saxonia) near the Nor ...
and Franks
The Franks ( la, Franci or ) were a group of Germanic peoples whose name was first mentioned in 3rd-century Roman sources, and associated with tribes between the Lower Rhine and the Ems River, on the edge of the Roman Empire.H. Schutz: Tools ...
had settled in future Flanders and the Duchy of Brabant
The Duchy of Brabant was a State of the Holy Roman Empire established in 1183. It developed from the Landgraviate of Brabant and formed the heart of the historic Low Countries, part of the Burgundian Netherlands from 1430 and of the Habsburg ...
. New groups of germanic settlers also came in from the Netherlands and Germany. Their new settlements often received the name of their germanic leader, with '-inga haim' added. -Inga haim meant 'the settlement of the tribe of X'. For example: Petegem comes from Petta-inga-haim, which meant 'the settlement of the tribe of Petta'.
The colonisation and germanisation of Flanders took place primarily in the 6th and 7th centuries. In the 7th century the population-level had risen sufficiently to start rebuilding the religious, military and administrative infrastructure. In the area of linguistics, the situation stabilised so that a large, bilingual
Multilingualism is the use of more than one language, either by an individual speaker or by a group of speakers. It is believed that multilingual speakers outnumber monolingual speakers in the world's population. More than half of all ...
region with a linear language border
A language border or language boundary is the line separating two language areas. The term is generally meant to imply a lack of mutual intelligibility between the two languages. If two adjacent languages or dialects are mutually intelligible, no ...
could emerge in the 8th century. In Pas-de-Calais
Pas-de-Calais (, "strait of Calais"; pcd, Pas-Calés; also nl, Nauw van Kales) is a department in northern France named after the French designation of the Strait of Dover, which it borders. It has the most communes of all the departments of ...
, which had been densely populated a long time, a language barrier had emerged in the 6th–7th century, but in the 9th century a romanisation-movement started that has continued until the present day.
The Christianisation attempts in the 6th century by bishops like Eleutherius and Vedast had largely failed. Thus, in the 8th century a different strategy was chosen. A new Christianisation attempt was made under influence from king Dagobert I. He appointed several devoted missionaries from the southern parts of his kingdom to his royal domains in the northern parts of his kingdom. The missionaries were tasked with founding monasteries and abbeys there, that were to serve as centers of Christianity in a pagan region. From these centers, the conversion of the local populace could be started.
In 649 Audomar
Saint Audomar (died 670), better known as Saint Omer, was a bishop of Thérouanne, after whom nearby Saint-Omer in northern France was named.
Biography
He was born of a distinguished family of Coutances, then under the Frankish realm of Neus ...
founded an abbey at Sithiu
Saint-Omer (; vls, Sint-Omaars) is a commune and sub-prefecture of the Pas-de-Calais department in France.
It is west-northwest of Lille on the railway to Calais, and is located in the Artois province. The town is named after Saint Audomar, ...
(the Abbey of Saint Bertin
The Abbey of St. Bertin was a Benedictine monastic abbey in Saint-Omer, France. The buildings are now in ruins, which are open to the public. It was initially dedicated to but was rededicated to its second abbot, . The abbey is known for its L ...
) and in 680 Aubertus founded the Abbey of St. Vaast
The Abbey of St Vaast (french: Abbaye de Saint-Vaast) was a Benedictine monastery situated in Arras, ''département'' of Pas-de-Calais, France.
History
The abbey was founded in 667. Saint Vedast, or Vaast (c. 453–540) was the first Bisho ...
near Arras
Arras ( , ; pcd, Aro; historical nl, Atrecht ) is the prefecture of the Pas-de-Calais department, which forms part of the region of Hauts-de-France; before the reorganization of 2014 it was in Nord-Pas-de-Calais. The historic centre of ...
. The Christianisation of the population was mainly the work of missionaries like Amandus ( St. Bavo's Abbey and St. Peter's Abbey in Ghent) and Eligius (coastal region and Antwerp
Antwerp (; nl, Antwerpen ; french: Anvers ; es, Amberes) is the largest city in Belgium by area at and the capital of Antwerp Province in the Flemish Region. With a population of 520,504,
). In his 'vita', Eligius makes the first mention of the word 'Flanders', when he toured the area around 650.
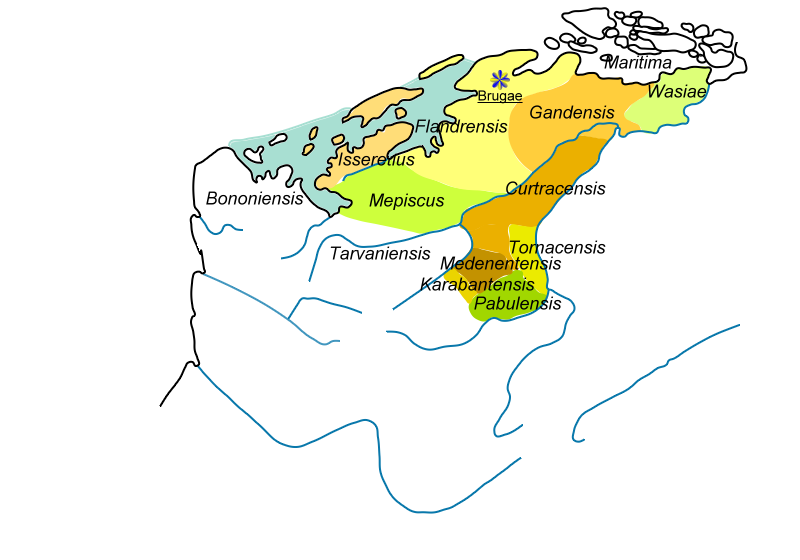
During the 7th century the first '' Gaue'' or ''pagi'' were created in the Flemish territories. Gaue were administrative subdivisions of the civitates. The Gaue from the 7th and 8th century would form the basis of the county of Flanders. The pagus Tornacensis dates from ca. 580, and from the 7th century we know of the 'pagus Cambracinsis' in 663, the pagus Taroanensis from 649 and the pagus Bracbatensis at the end of the century. From the 8th century we know of the pagus Rodaninsis from 707, the pagus Gandao from the first quarter of the 8th century, the pagus Mempiscus from 723 and the pagus Flandrensis from around 745. Lastly, the pagus Austrebatensis and the pagus Curtracensis are also counted as Merovingian gaue.
Carolingians
Carolingian
The Carolingian dynasty (; known variously as the Carlovingians, Carolingus, Carolings, Karolinger or Karlings) was a Frankish noble family named after Charlemagne, grandson of mayor Charles Martel and a descendant of the Arnulfing and Pippi ...
Mayors of the Palace succeeded in removing the Merovingians from power and obtaining the throne for themselves. The last Merovingian king, Childeric III, was placed in captivity at the later Abbey of Saint Bertinus in St. Omer, and his long hair, a symbol of royal power, was cut off.
Charlemagne
Charlemagne ( , ) or Charles the Great ( la, Carolus Magnus; german: Karl der Große; 2 April 747 – 28 January 814), a member of the Carolingian dynasty, was King of the Franks from 768, King of the Lombards from 774, and the first E ...
succeeded his father Pepin the Short
the Short (french: Pépin le Bref; – 24 September 768), also called the Younger (german: Pippin der Jüngere), was King of the Franks from 751 until his death in 768. He was the first Carolingian to become king.
The younger was the son of ...
in Neustria and Austrasia, and after the death of his brother Karloman he was able to reunite the entire Frankish Empire. Though he resided in Aachen
Aachen ( ; ; Aachen dialect: ''Oche'' ; French and traditional English: Aix-la-Chapelle; or ''Aquisgranum''; nl, Aken ; Polish: Akwizgran) is, with around 249,000 inhabitants, the 13th-largest city in North Rhine-Westphalia, and the 28th ...
, he spent much time travelling through his territories. In 811 he inspected the fleet that he had ordered built in Boulogne and Ghent, to protect against Viking
Vikings ; non, víkingr is the modern name given to seafaring people originally from Scandinavia (present-day Denmark, Norway and Sweden),
who from the late 8th to the late 11th centuries raided, pirated, traded and se ...
invasions.
The region comprising future Flanders was, from an economic point of view, a flourishing region, with a series of ports along the Scheldt
The Scheldt (french: Escaut ; nl, Schelde ) is a river that flows through northern France, western Belgium, and the southwestern part of the Netherlands, with its mouth at the North Sea. Its name is derived from an adjective corresponding to ...
river: Ghent
Ghent ( nl, Gent ; french: Gand ; traditional English: Gaunt) is a city and a municipality in the Flemish Region of Belgium. It is the capital and largest city of the East Flanders province, and the third largest in the country, exceeded i ...
, Tournai
Tournai or Tournay ( ; ; nl, Doornik ; pcd, Tornai; wa, Tornè ; la, Tornacum) is a city and municipality of Wallonia located in the province of Hainaut, Belgium. It lies southwest of Brussels on the river Scheldt. Tournai is part of Eurome ...
, Valenciennes
Valenciennes (, also , , ; nl, label=also Dutch, Valencijn; pcd, Valincyinnes or ; la, Valentianae) is a commune in the Nord department, Hauts-de-France, France.
It lies on the Scheldt () river. Although the city and region experienced a ...
, Cambrai
Cambrai (, ; pcd, Kimbré; nl, Kamerijk), formerly Cambray and historically in English Camerick or Camericke, is a city in the Nord department and in the Hauts-de-France region of France on the Scheldt river, which is known locally as the ...
and Lambres
Lambres (; pcd, Lambes) is a commune in the Pas-de-Calais department in the Hauts-de-France region of France.
Geography
A farming village, situated some northwest of Béthune and west of Lille at the junction of the D90 and the N43.
Populati ...
at Douai
Douai (, , ,; pcd, Doï; nl, Dowaai; formerly spelled Douay or Doway in English) is a city in the Nord département in northern France. It is a sub-prefecture of the department. Located on the river Scarpe some from Lille and from Arras, Dou ...
on the Scarpe and a number of seaports: Quentovic, Boulogne
Boulogne-sur-Mer (; pcd, Boulonne-su-Mér; nl, Bonen; la, Gesoriacum or ''Bononia''), often called just Boulogne (, ), is a coastal city in Northern France. It is a sub-prefecture of the department of Pas-de-Calais. Boulogne lies on the C ...
and Isère portus, a port at the mouth of the Yser
The Yser ( , ; nl, IJzer ) is a river that rises in French Flanders (the north of France), enters the Belgian province of West Flanders and flows through the '' Ganzepoot'' and into the North Sea at the town of Nieuwpoort.
The source of the ...
. Moreover, the region included a number of rich abbeys, such as Abbey of Saint Bertin
The Abbey of St. Bertin was a Benedictine monastic abbey in Saint-Omer, France. The buildings are now in ruins, which are open to the public. It was initially dedicated to but was rededicated to its second abbot, . The abbey is known for its L ...
, Saint Bavo's Abbey
Saint Bavo's Abbey ( nl, Sint-Baafsabdij) is a former abbey in the currently Belgian city of Ghent. It was founded in the 7th century by Saint Amand, who also founded Saint Peter's Abbey, Ghent, near the confluence of the Leie and Scheldt rive ...
, Saint-Amand Abbey and the Abbey of St. Vaast
The Abbey of St Vaast (french: Abbaye de Saint-Vaast) was a Benedictine monastery situated in Arras, ''département'' of Pas-de-Calais, France.
History
The abbey was founded in 667. Saint Vedast, or Vaast (c. 453–540) was the first Bisho ...
.
Charlemagne was succeeded by his son Louis the Pious
Louis the Pious (german: Ludwig der Fromme; french: Louis le Pieux; 16 April 778 – 20 June 840), also called the Fair, and the Debonaire, was King of the Franks and co-emperor with his father, Charlemagne, from 813. He was also King of Aqu ...
. Even during Louis' life his three sons started fighting over his heritage. They eventually concluded multiple treaties, of which the Treaty of Verdun
The Treaty of Verdun (), agreed in , divided the Frankish Empire into three kingdoms among the surviving sons of the emperor Louis I, the son and successor of Charlemagne. The treaty was concluded following almost three years of civil war and ...
, signed in 843, would be the definitive treaty. These treaties created East Francia
East Francia (Medieval Latin: ) or the Kingdom of the East Franks () was a successor state of Charlemagne's empire ruled by the Carolingian dynasty until 911. It was created through the Treaty of Verdun (843) which divided the former empire int ...
, Middle Francia and West Francia
In medieval history, West Francia (Medieval Latin: ) or the Kingdom of the West Franks () refers to the western part of the Frankish Empire established by Charlemagne. It represents the earliest stage of the Kingdom of France, lasting from ab ...
. West Francia, inherited by Charles the Bald
Charles the Bald (french: Charles le Chauve; 13 June 823 – 6 October 877), also known as Charles II, was a 9th-century king of West Francia (843–877), king of Italy (875–877) and emperor of the Carolingian Empire (875–877). After a se ...
, included the original county of Flanders, that spanned roughly between Oudenburg
Oudenburg (; french: Audembourg ; vls, Oednburg; la, Aldenburgensis) is a city and municipality located in the Belgian province of West Flanders. The municipality comprises the city of Oudenburg itself and the towns of Ettelgem, Roksem and ...
, Aardenburg and Torhout
Torhout (; french: Thourout; vls, Toeroet) is a city and municipality located in the Belgian province of West Flanders. The municipality comprises the city of Torhout proper, the villages of Wijnendale and Sint-Henricus, and the hamlet of De Dr ...
.
After the Middle-Frankish kings died out, the rulers of the West and East-Frankish Kingdoms divided the Middle-Frankish kingdom amongst themselves in the treaty of Meerssen
The Treaty of Mersen or Meerssen, concluded on 8 August 870, was a treaty to partition the realm of Lothair II, known as Lotharingia, by his uncles Louis the German of East Francia and Charles the Bald of West Francia, the two surviving sons of ...
in 870. Now Western Europe had been divided into two sides: the solid West Francia
In medieval history, West Francia (Medieval Latin: ) or the Kingdom of the West Franks () refers to the western part of the Frankish Empire established by Charlemagne. It represents the earliest stage of the Kingdom of France, lasting from ab ...
(the later France) and the loose confederation of principalities of East Francia
East Francia (Medieval Latin: ) or the Kingdom of the East Franks () was a successor state of Charlemagne's empire ruled by the Carolingian dynasty until 911. It was created through the Treaty of Verdun (843) which divided the former empire int ...
, that would become the Holy Roman Empire
The Holy Roman Empire was a political entity in Western, Central, and Southern Europe that developed during the Early Middle Ages and continued until its dissolution in 1806 during the Napoleonic Wars.
From the accession of Otto I in 962 unt ...
.
In the north these two powers were separated by the Scheldt river, which had previously separated West Francia from Middle Francia. This separation remained unchanged until the times of Charles V, Holy Roman Emperor
Charles V, french: Charles Quint, it, Carlo V, nl, Karel V, ca, Carles V, la, Carolus V (24 February 1500 – 21 September 1558) was Holy Roman Emperor and Archduke of Austria from 1519 to 1556, King of Spain ( Castile and Aragon) fr ...
.
Growth in the 9th, 10th and 11th centuries (864–1071)

Vikings
Vikings ; non, víkingr is the modern name given to seafaring people originally from Scandinavia (present-day Denmark, Norway and Sweden),
who from the late 8th to the late 11th centuries raided, pirated, traded and se ...
invaded from the north, the Magyar from the east and the Saracen
upright 1.5, Late 15th-century German woodcut depicting Saracens
Saracen ( ) was a term used in the early centuries, both in Greek and Latin writings, to refer to the people who lived in and near what was designated by the Romans as Arabia ...
s from the south. All left trails of destruction. The central authorities of the two Frankish kingdoms were unable to organise an effective defensive, causing the population to lose faith and trust in their far-removed rulers. In the wake of this power vacuum, local powerful individuals saw their chance. Often these individuals were the descendants of people associated with Charlemagne
Charlemagne ( , ) or Charles the Great ( la, Carolus Magnus; german: Karl der Große; 2 April 747 – 28 January 814), a member of the Carolingian dynasty, was King of the Franks from 768, King of the Lombards from 774, and the first E ...
.
The county of Flanders originated from the Gau of Pagus Flandrensis, led by the Forestiers dynasty, who had been appointed by Charlemagne, who had made a small contribution by uniting small feudal territories in the higher parts of the Flemish Valley. The forestiers dynasty also strengthened the hold of the church on the relatively desolate area.
The first Margrave
Margrave was originally the medieval title for the military commander assigned to maintain the defence of one of the border provinces of the Holy Roman Empire or of a kingdom. That position became hereditary in certain feudal families in the ...
(Count) of Flanders was Baldwin I, who became count in 862, and a romantic anecdote is connected to this: Baldwin eloped with the daughter of the Frankish king Charles the Bald
Charles the Bald (french: Charles le Chauve; 13 June 823 – 6 October 877), also known as Charles II, was a 9th-century king of West Francia (843–877), king of Italy (875–877) and emperor of the Carolingian Empire (875–877). After a se ...
, Judith of West Francia. Judith, who had previously been married to two English kings, refused her father's command to return to him. After mediation by the pope, the Frankish king reconciled with his son-in-law, and gave him the title of margrave, and the corresponding feudal territories as dowry. Margrave was primarily a military appointment and some versions of the story theorize that King Charles made Baldwin Margrave in the hope that he would be killed by the Vikings.
Initially the French kings meant to secure the safety of the northern French border from Viking invasions with this act. The counts, however, made good use of the crisis situation by incorporating the surrounding plundered territories into the county. The counts expanded the influence of the original Flemish ''pagus'' over the years over all territories south and west of the Scheldt river
The Scheldt (french: Escaut ; nl, Schelde ) is a river that flows through northern France, western Belgium, and the southwestern part of the Netherlands, with its mouth at the North Sea. Its name is derived from an adjective corresponding ...
, including presentday the lordship of the Four Amts, Zeelandic Flanders
Zeelandic Flanders ( ; zea, Zeêuws-Vlaonderen; vls, Zêeuws-Vloandern)''Vlaanderen'' in isolation: . is the southernmost region of the province of Zeeland in the south-western Netherlands. It lies south of the Western Scheldt that separates ...
, the burgraviate of Aalst to the east and the County of Artois to the south, which remained part of Flanders until it became a separate county in 1237. After that date, the county of Artois at various times still came under the dominion of the count of Flanders as a separate title, until it was absorbed by the French crown.
Prosperity in the 12th and 13th century (1071–1278)
 The
The House of Flanders
The House of Flanders—also called the Baldwins ( la, Balduini, french: Baudouinides)—was a medieval ruling family that was founded by Baldwin Iron Arm, son-in-law of Charles the Bald.
From 1051, the House of Flanders also reigned ove ...
remained in power until 1119, when Baldwin VII of Flanders
Baldwin VII of Flanders (1093 – 17 July 1119) was Count of Flanders from 1111 to 1119.
Baldwin was the son of Count Robert II of Flanders and Clementia of Burgundy. He succeeded his father as count when he died on 5 October 1111.
Reign
Bald ...
died heirless, and the county was inherited by Charles the Good
Charles the Good (10842 March 1127) was Count of Flanders from 1119 to 1127. His murder and its aftermath were chronicled by Galbert of Bruges. He was beatified by Pope Leo XIII in 1882 through ''cultus'' ''confirmation''.
Early life
Charles w ...
, of the House of Denmark. He abandoned the title "Marquis of Flanders", which had been used alongside the comital style since the 10th century. The counts of Flanders were the last French lords using the title marquis, which would not be used again in France until 1504. After a short interlude under William Clito of Normandy (1127–1128), the county went to Thierry of Alsace of the House of Alsace. Under Thierry (1128–1168) and his successor Philip of Alsace, Flanders' importance and power increased.
In the second half of the 12th century, the county went through a period of great prosperity when Philip of Alsace managed to incorporate the County of Vermandois into Flanders through the inheritance of his wife. The territories he controlled now came to within 25 kilometers of Paris, and were larger than the territories his feudal lord, the French king, directly controlled.
During the rule of the House of Alsace, cities developed and new institutions were formed. The ports of Gravelines, Nieuwpoort, Damme
Damme () is a city and municipality located in the Belgian province of West Flanders, six kilometres northeast of Brugge (Bruges). The municipality comprises the city of Damme proper and the villages of Hoeke, Lapscheure, Moerkerke, Oostkerk ...
, Biervliet, Dunkirk
Dunkirk (french: Dunkerque ; vls, label=French Flemish, Duunkerke; nl, Duinkerke(n) ; , ;) is a commune in the department of Nord in northern France.
, and Mardijk were founded, as well as Calais
Calais ( , , traditionally , ) is a port city in the Pas-de-Calais department, of which it is a subprefecture. Although Calais is by far the largest city in Pas-de-Calais, the department's prefecture is its third-largest city of Arras. Th ...
by Philip's brother Matthew of Alsace
Matthew, Count of Boulogne, also known as ''Matthew of Alsace'' (–1173) was the second son of Thierry, Count of Flanders and Sibylla of Anjou. Matthew forcibly abducted the nun Marie de Boulogne, daughter of Stephen, King of England, and cons ...
. Aside from colonisation, the ports also functioned to reduce the silting of the rivers Aa, Yser
The Yser ( , ; nl, IJzer ) is a river that rises in French Flanders (the north of France), enters the Belgian province of West Flanders and flows through the '' Ganzepoot'' and into the North Sea at the town of Nieuwpoort.
The source of the ...
and Zwin, which were endangering the accessibility of Saint-Omer
Saint-Omer (; vls, Sint-Omaars) is a commune and sub-prefecture of the Pas-de-Calais department in France.
It is west-northwest of Lille on the railway to Calais, and is located in the Artois province. The town is named after Saint Audoma ...
, Ypres
Ypres ( , ; nl, Ieper ; vls, Yper; german: Ypern ) is a Belgian city and municipality in the province of West Flanders. Though
the Dutch name is the official one, the city's French name is most commonly used in English. The municipality ...
and Bruges
Bruges ( , nl, Brugge ) is the capital and largest City status in Belgium, city of the Provinces of Belgium, province of West Flanders in the Flemish Region of Belgium, in the northwest of the country, and the sixth-largest city of the countr ...
. Biervliet also served as a counter to Hollandic influence.
 Trade partners included England, the
Trade partners included England, the Baltic countries
The Baltic states, et, Balti riigid or the Baltic countries is a geopolitical term, which currently is used to group three countries: Estonia, Latvia, and Lithuania. All three countries are members of NATO, the European Union, the Euro ...
and France over sea, and the Rhineland
The Rhineland (german: Rheinland; french: Rhénanie; nl, Rijnland; ksh, Rhingland; Latinised name: ''Rhenania'') is a loosely defined area of Western Germany along the Rhine, chiefly its middle section.
Term
Historically, the Rhinelands ...
and Italy over land. The wool trade with England was of special importance to the rising cloth industry in Flanders. The wealth of many Flemish cities (as their Belltower
A bell tower is a tower that contains one or more bells, or that is designed to hold bells even if it has none. Such a tower commonly serves as part of a Christian church, and will contain church bells, but there are also many secular bell tower ...
s and cloth halls testify) came from the drapery industry. Aside from this, the grain trade
The grain trade refers to the local and international trade in cereals and other food grains such as wheat, barley, maize, and rice. Grain is an important trade item because it is easily stored and transported with limited spoilage, unlike other ...
with England and through Holland with Hamburg were also important. Saint-Omer
Saint-Omer (; vls, Sint-Omaars) is a commune and sub-prefecture of the Pas-de-Calais department in France.
It is west-northwest of Lille on the railway to Calais, and is located in the Artois province. The town is named after Saint Audoma ...
became the most important transit-port for French wine in the 12th century. These were the centuries of the breakthrough of the Flemish merchants, with their trade with England, the Baltic area and South-West France, as well as the landroutes to the Rhineland
The Rhineland (german: Rheinland; french: Rhénanie; nl, Rijnland; ksh, Rhingland; Latinised name: ''Rhenania'') is a loosely defined area of Western Germany along the Rhine, chiefly its middle section.
Term
Historically, the Rhinelands ...
and Italy, though later only the yearly fairs of Champagne. Flanders' flourishing trading towns made it one of the most urbanised parts of Europe.
In 1194, Baldwin I of Constantinople of the House of Hainaut, succeeded the House of Alsace.
The crisis of the 14th century (1278–1384)
In 1278 Guy of Dampierre, of theHouse of Dampierre
The House of Dampierre played an important role during the Middle Ages. Named after Dampierre, in the Champagne region, where members first became prominent, members of the family were later Count of Flanders, Count of Nevers, Counts and Dukes o ...
, became count of Flanders. The king of France wanted to definitively conquer Flanders, and started the Franco-Flemish War (1297–1305). Increasingly powerful in the 12th century, the territory's autonomous urban centres were instrumental in defeating the French invasion attempt, defeating the French at the Battle of the Golden Spurs
The Battle of the Golden Spurs ( nl, Guldensporenslag; french: Bataille des éperons d'or) was a military confrontation between the royal army of France and rebellious forces of the County of Flanders on 11 July 1302 during the Franco-Flemis ...
in 1302. But finally the French prevailed at the battle of Mons-en-Pévèle
The Battle of Mons-en-Pévèle (or Pevelenberg) was fought on 18 August 1304 between the French and the Flemish. The French were led by their king, Philip IV.
Prelude
The French king wanted revenge for the defeat in Battle of the Golden Sp ...
and with the subsequent treaty of Athis-sur-Orge
The Treaty of Athis-sur-Orge was a peace treaty signed on 23 June 1305 between King Philip IV of France and Robert III of Flanders. The treaty was signed at Athis-sur-Orge after the Battle of Mons-en-Pévèle and concluded the Franco-Flemish W ...
(1305) Flanders lost Lille, Douai, and Orchies to France and had to pay exorbitant fines but retained their independence as a fief of the French kingdom. During this period, Flanders experienced a period of relative prosperity with its strong cloth industry and diverse artwork. Trade in Flanders was so extensive that statues of the Madonna and Child were made in Flanders with ivory, which was only accessible on the Indian Ocean trade networks.
 Flemish prosperity waned in the following century, however, owing to widespread European population decline following the
Flemish prosperity waned in the following century, however, owing to widespread European population decline following the Black Death
The Black Death (also known as the Pestilence, the Great Mortality or the Plague) was a bubonic plague pandemic occurring in Western Eurasia and North Africa from 1346 to 1353. It is the most fatal pandemic recorded in human history, causi ...
of 1348, the disruption of trade during the Anglo-French Hundred Years' War
The Hundred Years' War (; 1337–1453) was a series of armed conflicts between the kingdoms of England and France during the Late Middle Ages. It originated from disputed claims to the French throne between the English House of Plantagen ...
(1338–1453), and increased English cloth production. Flemish weavers had gone over to Worstead and North Walsham in Norfolk
Norfolk () is a ceremonial and non-metropolitan county in East Anglia in England. It borders Lincolnshire to the north-west, Cambridgeshire to the west and south-west, and Suffolk to the south. Its northern and eastern boundaries are the Nor ...
in the 12th century and established the wool industry.
The Burgundian 15th century (1384–1506)
 Through his marriage with Margaret of Dampierre in 1369,
Through his marriage with Margaret of Dampierre in 1369, Philip the Bold
Philip II the Bold (; ; 17 January 1342 – 27 April 1404) was Duke of Burgundy and ''jure uxoris'' Count of Flanders, Artois and Burgundy. He was the fourth and youngest son of King John II of France and Bonne of Luxembourg.
Philip II w ...
, duke of Burgundy
Burgundy (; french: link=no, Bourgogne ) is a historical territory and former administrative region and province of east-central France. The province was once home to the Dukes of Burgundy from the early 11th until the late 15th century. The ...
, made an end to the independence of Flanders. Flanders became the possession of the House of Valois-Burgundy, that ruled over the Burgundian State
The Burgundian StateB. Schnerb, ''L'État bourguignon'', 1999 (french: État bourguignon; nl, Bourgondische Rijk) is a concept coined by historians to describe the vast complex of territories that is also referred to as Valois Burgundy.
It de ...
. In 1449 the city of Ghent
Ghent ( nl, Gent ; french: Gand ; traditional English: Gaunt) is a city and a municipality in the Flemish Region of Belgium. It is the capital and largest city of the East Flanders province, and the third largest in the country, exceeded i ...
revolted
In political science, a revolution ( Latin: ''revolutio'', "a turn around") is a fundamental and relatively sudden change in political power and political organization which occurs when the population revolts against the government, typically d ...
against duke Philip the Good
Philip III (french: Philippe le Bon; nl, Filips de Goede; 31 July 1396 – 15 June 1467) was Duke of Burgundy from 1419 until his death. He was a member of a cadet line of the Valois dynasty, to which all 15th-century kings of France belonge ...
. In 1453 Philip crushed the rebels at the battle of Gavere
The Battle of Gavere was fought at Semmerzake, near Gavere, in the County of Flanders (modern-day Belgium) on 23 July 1453, between the army of Philip the Good of Burgundy and the rebelling city of Ghent. The battle ended the Revolt of Ghent wit ...
, ending the revolt.
The cities of Ghent and Bruges had previously operated virtually as city-states,
and upon the death of duke Charles the Bold
Charles I (Charles Martin; german: Karl Martin; nl, Karel Maarten; 10 November 1433 – 5 January 1477), nicknamed the Bold (German: ''der Kühne''; Dutch: ''de Stoute''; french: le Téméraire), was Duke of Burgundy from 1467 to 1477. ...
attempted to re-assert this position by means of the Great Privilege that they wrested from Mary of Burgundy
Mary (french: Marie; nl, Maria; 13 February 1457 – 27 March 1482), nicknamed the Rich, was a member of the House of Valois-Burgundy who ruled a collection of states that included the duchies of Limburg, Brabant, Luxembourg, the counties of ...
, Charles' daughter and successor. In 1482 this last Burgundian ruler died, making her young son Philip I of Castile
Philip the Handsome, es, Felipe, french: Philippe, nl, Filips (22 July 1478 – 25 September 1506), also called the Fair, was ruler of the Burgundian Netherlands and titular Duke of Burgundy from 1482 to 1506, as well as the first Habsburg K ...
of the House of Habsburg
The House of Habsburg (), alternatively spelled Hapsburg in Englishgerman: Haus Habsburg, ; es, Casa de Habsburgo; hu, Habsburg család, it, Casa di Asburgo, nl, Huis van Habsburg, pl, dom Habsburgów, pt, Casa de Habsburgo, la, Domus Hab ...
the new count, and her husband Maximilian I of Austria the regent. The Flemish cities staged two more revolts, but these were ultimately subdued by the armies of the Holy Roman Empire
The Holy Roman Empire was a political entity in Western, Central, and Southern Europe that developed during the Early Middle Ages and continued until its dissolution in 1806 during the Napoleonic Wars.
From the accession of Otto I in 962 unt ...
.
The 1493 Treaty of Senlis established peace between France and the Habsburgs; per the terms of the treaty, Flanders would henceforth be a territory of the Holy Roman Empire.
The seventeen provinces in the 16th century (1506–98)
 Under
Under Charles V, Holy Roman Emperor
Charles V, french: Charles Quint, it, Carlo V, nl, Karel V, ca, Carles V, la, Carolus V (24 February 1500 – 21 September 1558) was Holy Roman Emperor and Archduke of Austria from 1519 to 1556, King of Spain ( Castile and Aragon) fr ...
(born in the Flemish city Ghent
Ghent ( nl, Gent ; french: Gand ; traditional English: Gaunt) is a city and a municipality in the Flemish Region of Belgium. It is the capital and largest city of the East Flanders province, and the third largest in the country, exceeded i ...
), Flanders became a member of the Burgundian Circle
The Burgundian Circle (german: Burgundischer Kreis, nl, Bourgondische Kreits, french: Cercle de Bourgogne) was an Imperial Circle of the Holy Roman Empire created in 1512 and significantly enlarged in 1548. In addition to the Free County of Burg ...
. The county was later involved in the Guelders Wars
The Guelders Wars (, German: ''Geldrische Erbfolgekriege'') were a series of conflicts in the Low Countries between the Duke of Burgundy, who controlled Holland, Flanders, Brabant, and Hainaut on the one side, and Charles, Duke of Guelders, ...
.
Through the Pragmatic Sanction of 1549, the County of Flanders was officially detached from France. It became an independent territory of the Holy Roman Empire
The Holy Roman Empire was a political entity in Western, Central, and Southern Europe that developed during the Early Middle Ages and continued until its dissolution in 1806 during the Napoleonic Wars.
From the accession of Otto I in 962 unt ...
. This constitutional act made Flanders part of the Seventeen Provinces
The Seventeen Provinces were the Imperial states of the Habsburg Netherlands in the 16th century. They roughly covered the Low Countries, i.e., what is now the Netherlands, Belgium, Luxembourg, and most of the French departments of Nord (F ...
, that constituted the Low Countries
The term Low Countries, also known as the Low Lands ( nl, de Lage Landen, french: les Pays-Bas, lb, déi Niddereg Lännereien) and historically called the Netherlands ( nl, de Nederlanden), Flanders, or Belgica, is a coastal lowland region in N ...
and from then on would be inherited as a whole.
The Low Countries held an important place in the Empire. For Charles personally, they were the region where he spent his childhood. Because of trade and industry and the rich cities, they were also important for the treasury. Lordship transferred to the Spanish branch of the House of Habsburg with Philip II of Spain
Philip II) in Spain, while in Portugal and his Italian kingdoms he ruled as Philip I ( pt, Filipe I). (21 May 152713 September 1598), also known as Philip the Prudent ( es, Felipe el Prudente), was King of Spain from 1556, King of Portugal from ...
, and after 1556 belonged to the Kings of Spain.
It was in Steenvoorde (In French Flanders
French Flanders (french: La Flandre française) is a part of the historical County of Flanders in present-day France where a dialect of Dutch was or still is traditionally spoken. The region lies in the modern-day region of Hauts-de-France an ...
) in 1566 that the Beeldenstorm
''Beeldenstorm'' () in Dutch and ''Bildersturm'' in German (roughly translatable from both languages as 'attack on the images or statues') are terms used for outbreaks of destruction of religious images that occurred in Europe in the 16th centu ...
broke loose. The Beeldenstorm spread through all of the Low Countries
The term Low Countries, also known as the Low Lands ( nl, de Lage Landen, french: les Pays-Bas, lb, déi Niddereg Lännereien) and historically called the Netherlands ( nl, de Nederlanden), Flanders, or Belgica, is a coastal lowland region in N ...
and eventually led to the outbreak of the Eighty Years' War
The Eighty Years' War or Dutch Revolt ( nl, Nederlandse Opstand) ( c.1566/1568–1648) was an armed conflict in the Habsburg Netherlands between disparate groups of rebels and the Spanish government. The causes of the war included the Ref ...
and the secession of the Republic of the Seven United Netherlands
The United Provinces of the Netherlands, also known as the (Seven) United Provinces, officially as the Republic of the Seven United Netherlands ( Dutch: ''Republiek der Zeven Verenigde Nederlanden''), and commonly referred to in historiograph ...
. Originally Flanders cooperated with the northern provinces as a member of the Union of Utrecht, and also signed the Act of Abjuration in 1581, but from 1579 to 1585, in the period known as the " Calvinist Republic of Ghent", it was reconquered by the Spanish army.
The Spanish 17th century (1598–1713)
Flanders stayed under Spanish control. Through the efforts of the French kingLouis XIV
Louis XIV (Louis Dieudonné; 5 September 16381 September 1715), also known as Louis the Great () or the Sun King (), was List of French monarchs, King of France from 14 May 1643 until his death in 1715. His reign of 72 years and 110 days is the Li ...
, the entire southern part of Flanders was annexed by France, and became known as South-Flanders or French Flanders
French Flanders (french: La Flandre française) is a part of the historical County of Flanders in present-day France where a dialect of Dutch was or still is traditionally spoken. The region lies in the modern-day region of Hauts-de-France an ...
. This situation was formalised in 1678 at the Treaty of Nijmegen
The Treaties of Peace of Nijmegen ('; german: Friede von Nimwegen) were a series of treaties signed in the Dutch city of Nijmegen between August 1678 and October 1679. The treaties ended various interconnected wars among France, the Dutch Repub ...
.
The Austrian 18th century (1713–89)
 After the extinction of the Spanish branch of the Habsburgs, the Austrian branch of the Habsburgs became counts of Flanders. Under
After the extinction of the Spanish branch of the Habsburgs, the Austrian branch of the Habsburgs became counts of Flanders. Under Maria Theresa of Austria
Maria Theresa Walburga Amalia Christina (german: Maria Theresia; 13 May 1717 – 29 November 1780) was ruler of the Habsburg dominions from 1740 until her death in 1780, and the only woman to hold the position '' suo jure'' (in her own right) ...
, the Austrian Netherlands
The Austrian Netherlands nl, Oostenrijkse Nederlanden; french: Pays-Bas Autrichiens; german: Österreichische Niederlande; la, Belgium Austriacum. was the territory of the Burgundian Circle of the Holy Roman Empire between 1714 and 1797. The pe ...
flourished.
Last years (1789–97)
In 1789 a revolution broke out against emperorJoseph II
Joseph II (German: Josef Benedikt Anton Michael Adam; English: ''Joseph Benedict Anthony Michael Adam''; 13 March 1741 – 20 February 1790) was Holy Roman Emperor from August 1765 and sole ruler of the Habsburg lands from November 29, 1780 un ...
. In 1790 the county of Flanders and a separate province called West Flanders
West Flanders ( nl, West-Vlaanderen ; vls, West Vloandern; french: (Province de) Flandre-Occidentale ; german: Westflandern ) is the westernmost province of the Flemish Region, in Belgium. It is the only coastal Belgian province, facing the No ...
, which constituted the territories given back by France to the Emperor, were two of the founding members of the United States of Belgium. Just like the other parts of the Austrian Netherlands, the county of Flanders declared its independence. This took place on the Friday-market at Ghent on 4 January 1790. The "Manifest van Vlaenderen" was drawn up by Charles-Joseph de Graeve and Jean-Joseph Raepsaet.
The county of Flanders officially ceased to exist in 1795, when it was annexed by France, and divided into two departments
Department may refer to:
* Departmentalization, division of a larger organization into parts with specific responsibility
Government and military
*Department (administrative division), a geographical and administrative division within a country, ...
: Lys (present day West Flanders
West Flanders ( nl, West-Vlaanderen ; vls, West Vloandern; french: (Province de) Flandre-Occidentale ; german: Westflandern ) is the westernmost province of the Flemish Region, in Belgium. It is the only coastal Belgian province, facing the No ...
) and Escaut (present day East Flanders
, native_name_lang =
, settlement_type = Province of Belgium
, image_flag = Flag of Oost-Vlaanderen.svg
, flag_size =
, image_shield = Wapen van O ...
and Zeelandic Flanders
Zeelandic Flanders ( ; zea, Zeêuws-Vlaonderen; vls, Zêeuws-Vloandern)''Vlaanderen'' in isolation: . is the southernmost region of the province of Zeeland in the south-western Netherlands. It lies south of the Western Scheldt that separates ...
). Austria confirmed its loss in the 1797 Treaty of Campo Formio
The Treaty of Campo Formio (today Campoformido) was signed on 17 October 1797 (26 Vendémiaire VI) by Napoleon Bonaparte and Count Philipp von Cobenzl as representatives of the French Republic and the Austrian monarchy, respectively. The trea ...
.
After the French Revolution
The French Revolution ( ) was a period of radical political and societal change in France that began with the Estates General of 1789 and ended with the formation of the French Consulate in November 1799. Many of its ideas are conside ...
the county was not restored, and instead the two departments continued their existence as the provinces of East and West Flanders in the Unitarian United Kingdom of the Netherlands
The United Kingdom of the Netherlands ( nl, Verenigd Koninkrijk der Nederlanden; french: Royaume uni des Pays-Bas) is the unofficial name given to the Kingdom of the Netherlands as it existed between 1815 and 1839. The United Netherlands was cr ...
and later, after the Belgian Revolution
The Belgian Revolution (, ) was the conflict which led to the secession of the southern provinces (mainly the former Southern Netherlands) from the United Kingdom of the Netherlands and the establishment of an independent Kingdom of Belgium.
T ...
, in Belgium.
Count of Flanders title
From 1840 onwards, the title "Count of Flanders" has been appropriated by the monarchy of Belgium. As a rule it was given to the second in line of succession to the Belgian throne. The title of count of Flanders was abolished by royal decision on 16 October 2001.Important treaties and battles which involved the County of Flanders
* Battle of Cassel (1071) * Battle of Axpoele in 1128 * Peace of Peronne in 1199 *Battle of Bouvines
The Battle of Bouvines was fought on 27 July 1214 near the town of Bouvines in the County of Flanders. It was the concluding battle of the Anglo-French War of 1213–1214. Although estimates on the number of troops vary considerably among mod ...
in 1214
* Peace of Melun in 1226
* Battle of West-Kapelle in 1253
* Battle of the Golden Spurs
The Battle of the Golden Spurs ( nl, Guldensporenslag; french: Bataille des éperons d'or) was a military confrontation between the royal army of France and rebellious forces of the County of Flanders on 11 July 1302 during the Franco-Flemis ...
in 1302
* Battle of Arke in 1303
* Battle of Zierikzee
The battle of Zierikzee was a naval battle between a Flemish fleet and an allied Franco- Hollandic fleet which took place on 10 and 11 August 1304. The battle, fought near the town of Zierikzee, ended in a Franco-Dutch victory. The battle is part ...
in 1304
* Battle of Mons-en-Pevele in 1304
* Treaty of Athis-sur-Orge
The Treaty of Athis-sur-Orge was a peace treaty signed on 23 June 1305 between King Philip IV of France and Robert III of Flanders. The treaty was signed at Athis-sur-Orge after the Battle of Mons-en-Pévèle and concluded the Franco-Flemish W ...
in 1305
* Battle of Cassel (1328)
* Battle of Westrozebeke
The Battle of Roosebeke (sometimes referred by its contemporary name as Battle of Westrozebeke) took place on 27 November 1382 on the Goudberg between a Flemish army under Philip van Artevelde and a French army under Louis II of Flanders who h ...
in 1382
* Eighty Years' War
The Eighty Years' War or Dutch Revolt ( nl, Nederlandse Opstand) ( c.1566/1568–1648) was an armed conflict in the Habsburg Netherlands between disparate groups of rebels and the Spanish government. The causes of the war included the Ref ...
from 1568 to 1648
* Pacification of Ghent in 1576
* Union of Utrecht in 1579
* Act of Abjuration in 1581
See also
*History of Flanders
This article describes the history of Flanders. The definition of the territory called "Flanders" ( nl, Vlaanderen), however, has varied throughout history.
The historical county of Flanders is now split into different countries. It roughly enco ...
References
Notes
Bibliography
* (1948): "Vlaanderen, oorspronkelijke ligging en etymologie", in ''Album Prof. Dr. Frank Baur'' p. 192–220, Leuven. * (1960): ''Toponymisch woordenboek van België, Nederland, Luxemburg, Noord-Frankrijk en West-Duitsland (voor 1226)'', Tongeren. * (1977–1983): ''Algemene Geschiedenis der Nederlanden'', Fibula-Van Dishoeck, Haarlem, * (2006): ''Geschiedenis van de Nederlanden'', HBuitgevers, Baarn, * (1943): ''Korte geschiedenis van het ontstaan van het graafschap Vlaanderen van Boudewijn de IJzeren tot Robrecht den Fries'', Brussels – The Hague. * (1941–1942): "Het ontstaan van het vorstendom Vlaanderen", '' Belgisch tijdschrift voor filologie en geschiedenis'', XX, 553–572 en XXI, 53–93. * (1944): ''Vlaanderen onder de eerste graven'', Antwerp. * (1992): ''Medieval Flanders'', London, * (1949–1958): ''Algemene Geschiedenis der Nederlanden'', Haarlem – Antwerp. * (1942): "De graven van Vlaanderen en hun domein, 864–1191", ''Wetenschappelijke Tijdingen'', VII, 25–32.External links
Maps (900–1350)
{{coord, 51.06, 3.72, display=title 1380s in the Burgundian Netherlands Flanders Former provinces of France History of Flanders Flanders, County of 862 establishments