Firedamp on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Firedamp is any

 Firedamp is explosive at concentrations between 4% and 16%, with most explosions occurring at around 10%. It caused many deaths in coal mines before the invention of the
Firedamp is explosive at concentrations between 4% and 16%, with most explosions occurring at around 10%. It caused many deaths in coal mines before the invention of the
flammable
A combustible material is something that can burn (i.e., ''combust'') in air. A combustible material is flammable if it ignites easily at ambient temperatures. In other words, a combustible material ignites with some effort and a flammable mat ...
gas found in coal mines
Coal mining is the process of extracting coal from the ground. Coal is valued for its energy content and since the 1880s has been widely used to generate electricity. Steel and cement industries use coal as a fuel for extraction of iron fro ...
, typically coalbed methane
Coalbed methane (CBM or coal-bed methane), coalbed gas, coal seam gas (CSG), or coal-mine methane (CMM) is a form of natural gas extracted from coal beds. In recent decades it has become an important source of energy in United States, Canada, Au ...
. It is particularly found in areas where the coal is bituminous
Asphalt, also known as bitumen (, ), is a sticky, black, highly viscous liquid or semi-solid form of petroleum. It may be found in natural deposits or may be a refined product, and is classed as a pitch. Before the 20th century, the term ...
. The gas accumulates in pockets in the coal and adjacent strata and when they are penetrated the release can trigger explosions. Historically, if such a pocket was highly pressurized, it was termed a "bag of foulness".
Name
Damp is the collective name given to all gases (other than air) found in coal mines in Great Britain and North America. As well as firedamp, other damps include ''blackdamp
Blackdamp (also known as stythe or choke damp) is an asphyxiant, reducing the available oxygen content of air to a level incapable of sustaining human or animal life. It is not a single gas but a mixture of unbreathable gases left after oxygen is ...
'' (nonbreathable mixture of carbon dioxide
Carbon dioxide ( chemical formula ) is a chemical compound made up of molecules that each have one carbon atom covalently double bonded to two oxygen atoms. It is found in the gas state at room temperature. In the air, carbon dioxide is t ...
, water vapour and other gases); whitedamp (carbon monoxide and other gases produced by combustion); poisonous, explosive '' stinkdamp'' (hydrogen sulfide
Hydrogen sulfide is a chemical compound with the formula . It is a colorless chalcogen-hydride gas, and is poisonous, corrosive, and flammable, with trace amounts in ambient atmosphere having a characteristic foul odor of rotten eggs. The under ...
), with its characteristic rotten-egg odour; and the insidiously lethal '' afterdamp'' (carbon monoxide
Carbon monoxide ( chemical formula CO) is a colorless, poisonous, odorless, tasteless, flammable gas that is slightly less dense than air. Carbon monoxide consists of one carbon atom and one oxygen atom connected by a triple bond. It is the simpl ...
and other gases) which are produced following explosions of firedamp or coal dust.
Etymology
Often hyphenated as fire-damp, this term for a flammable type of underground mine gas in first part derives via the Old English ''fyr'', and from the proto-Germanic ''fūr'' for "fire" (the origin of the same word in Dutch and German, with similar original spellings in Old Saxon, Frisian, and Norse, as well as Middle Dutch and Old High German). In the second part, the meaning of "damp" (most commonly understood to imply humidity) presents evidence of having been separated from that newer, irrelevant meaning at least by the first decade of the 18th century, where the original relevant meaning of "vapor" also derives from a Proto-Germanic origin, ''dampaz'', which gave rise to its immediate English predecessor, the Middle Low German ''damp'' (with no record of an Old English intermediary). As with the derivation of the first, the proto-Germanic ''dampaz'' gave rise to many other cognates, including the Old High German ''damph'', the Old Norse ''dampi'', and the modern German ''Dampf'', the last of which still translates as "vapor".Contribution to mine deaths

 Firedamp is explosive at concentrations between 4% and 16%, with most explosions occurring at around 10%. It caused many deaths in coal mines before the invention of the
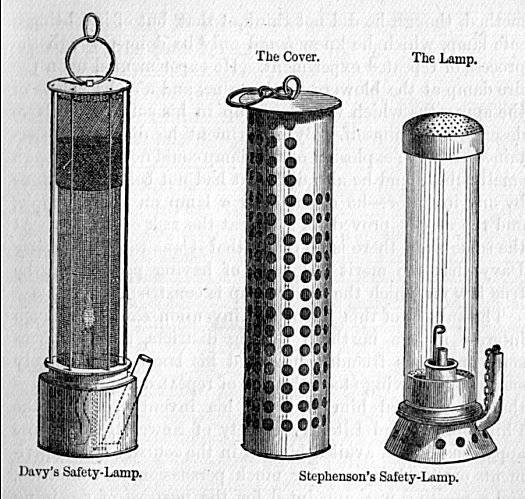
Firedamp is explosive at concentrations between 4% and 16%, with most explosions occurring at around 10%. It caused many deaths in coal mines before the invention of the Geordie lamp
The Geordie lamp was a safety lamp for use in flammable atmospheres, invented by George Stephenson in 1815 as a miner's lamp to prevent explosions due to firedamp in coal mines.
Origin
In 1815, Stephenson was the engine-wright at the Killing ...
and Davy lamp
The Davy lamp is a safety lamp for use in flammable atmospheres, invented in 1815 by Sir Humphry Davy.pyrite
The mineral pyrite (), or iron pyrite, also known as fool's gold, is an iron sulfide with the chemical formula Iron, FeSulfur, S2 (iron (II) disulfide). Pyrite is the most abundant sulfide mineral.
Pyrite's metallic Luster (mineralogy), lust ...
s was struck with metal tools. The presence of coal dust Coal dust is a fine powdered form of which is created by the crushing, grinding, or pulverizing of coal. Because of the brittle nature of coal, coal dust can be created during mining, transportation, or by mechanically handling coal. It is a form ...
in the air increased the risk of explosion with firedamp and could cause explosions even in the absence of firedamp. The Tyneside
Tyneside is a built-up area across the banks of the River Tyne in northern England. Residents of the area are commonly referred to as Geordies. The whole area is surrounded by the North East Green Belt.
The population of Tyneside as publishe ...
coal mines in England had the deadly combination of bituminous coal contaminated with pyrites and there was a great number of deaths in accidents caused by firedamp explosions, including 102 dead at Wallsend
Wallsend is a town in North Tyneside, England, at the eastern end of Hadrian's Wall. It has a population of 43,842 and lies east of Newcastle upon Tyne.
History Roman Wallsend
In Roman times, this was the site of the fort of Segedunum. This ...
in 1835.
The problem of firedamp in mines had been brought to the attention of the Royal Society
The Royal Society, formally The Royal Society of London for Improving Natural Knowledge, is a learned society and the United Kingdom's national academy of sciences. The society fulfils a number of roles: promoting science and its benefits, re ...
by 1677 and in 1733 James Lowther reported that as a shaft was being sunk for a new pit at Saltom near Whitehaven
Whitehaven is a town and port on the English north west coast and near to the Lake District National Park in Cumbria, England. Historically in Cumberland, it lies by road south-west of Carlisle and to the north of Barrow-in-Furness. It i ...
there had been a major release when a layer of black stone had been broken through into a coal seam. Ignited with a candle, it had given a steady flame "about half a Yard in Diameter, and near two Yards high". The flame being extinguished and a wider penetration through the black stone made, reigniting of the gas gave a bigger flame, a yard in diameter and about three yards high, which was extinguished only with difficulty. The blower was panelled off from the shaft and piped to the surface, where more than two and a half years later it continued as fast as ever, filling a large bladder in a few seconds. The society members elected Sir James Fellow but were unable to come up with any solution nor improve on the assertion (eventually found to be incorrect) of Carlisle Spedding, the author of the paper, that "this sort of Vapour, or damp Air, will not take Fire except by Flame; Sparks do not affect it, and for that Reason it is frequent to use Flint and Steel in Places affected with this sort of Damp, which will give a glimmering Light, that is a great Help to the Workmen in difficult Cases."
A great step forward in countering the problem of firedamp came when safety lamp
A safety lamp is any of several types of lamp that provides illumination in coal mines and is designed to operate in air that may contain coal dust or gases, both of which are potentially flammable or explosive. Until the development of effectiv ...
s, intended to provide illumination whilst being incapable of igniting firedamp, were proposed by both George Stephenson
George Stephenson (9 June 1781 – 12 August 1848) was a British civil engineer and mechanical engineer. Renowned as the "Father of Railways", Stephenson was considered by the Victorians
In the history of the United Kingdom and the ...
and Humphry Davy
Sir Humphry Davy, 1st Baronet, (17 December 177829 May 1829) was a British chemist and inventor who invented the Davy lamp and a very early form of arc lamp. He is also remembered for isolating, by using electricity, several elements for ...
in response to accidents such as the Felling mine disaster
The Felling Colliery (also known as Brandling Main) in Britain, suffered four disasters in the 19th century, in 1812, 1813, 1821 and 1847. By far the worst of the four was the 1812 disaster which claimed 91 lives on 25 May 1812. The loss of life ...
near Newcastle upon Tyne
Newcastle upon Tyne ( RP: , ), or simply Newcastle, is a city and metropolitan borough in Tyne and Wear, England. The city is located on the River Tyne's northern bank and forms the largest part of the Tyneside built-up area. Newcastle is ...
, which killed 92 people on 25 May 1812. Davy experimented with brass gauze
Gauze is a thin, translucent fabric with a loose open weave. In technical terms "gauze" is a weave structure in which the weft yarns are arranged in pairs and are crossed before and after each warp yarn keeping the weft firmly in place. ...
, determining the maximum size of the gaps and the optimum wire thickness to prevent a flame passing through the gauze. If a naked flame was thus enclosed totally by such a gauze, then methane could pass into the lamp and burn safely above the flame. Stephenson's lamp (the "Geordie lamp") worked on a different principle: the flame was enclosed by glass; air access to the flame was through tubes sufficiently narrow that the flame could not burn-back in incoming firedamp and the exiting gases were too low in oxygen to allow the enclosed flame to reach the surrounding atmosphere. Both principles were combined in later versions of safety lamps.
Even after the widespread introduction of the safety lamp, explosions continued because the early lamps were fragile and easily damaged. For example the iron gauze on a Davy lamp needed to lose only one wire to become unsafe. The light was also very poor (compared with a naked flame) and there were continuous attempts to improve the basic design. The height of the cone of burning methane in a flame safety lamp can be used to estimate the concentration of the gas in the local atmosphere. It was not until the 1890s that safe and reliable electric lamps became available in collieries.
See also
*Abercarn colliery disaster
The Abercarn colliery disaster was a catastrophic explosion within the Prince of Wales Colliery in the Welsh village of Abercarn (then in the county of Monmouthshire), on 11 September 1878, killing 268 men and boys (though an exact number of cas ...
* Coalbed methane
Coalbed methane (CBM or coal-bed methane), coalbed gas, coal seam gas (CSG), or coal-mine methane (CMM) is a form of natural gas extracted from coal beds. In recent decades it has become an important source of energy in United States, Canada, Au ...
* Darr Mine Disaster
The Darr Mine disaster at Van Meter, Rostraver Township, Westmoreland County, Pennsylvania, near Smithton, killed 239 men and boys on December 19, 1907.
It ranks as the worst coal mining disaster in Pennsylvanian history. Many victims were ...
* Gresford Disaster
The Gresford disaster occurred on 22 September 1934 at Gresford Colliery, near Wrexham, Denbighshire, when an explosion and underground fire killed 266 men. Gresford is one of Britain's worst coal mining disasters: a controversial inquiry into ...
* Maypole Colliery disaster
The Maypole Colliery disaster was a mining accident on 18 August 1908, when an underground explosion occurred at the Maypole Colliery, in Abram, near Wigan, then in the historic county of Lancashire, in North West England. The final death toll ...
* Mining accident
A mining accident is an accident that occurs during the process of mining minerals or metals. Thousands of miners die from mining accidents each year, especially from underground coal mining, although accidents also occur in hard rock mining. ...
* Udston mining disaster
The Udston mining disaster occurred in Hamilton, Scotland on Saturday, 28 May 1887 when 73 miners died in a firedamp explosion at Udston Colliery. Caused, it is thought, by unauthorised shot firing the explosion is said to be Scotland's second ...
References
* "Experiments Show How Gas Explodes in a Mine", ''Popular Science
''Popular Science'' (also known as ''PopSci'') is an American digital magazine carrying popular science content, which refers to articles for the general reader on science and technology subjects. ''Popular Science'' has won over 58 awards, incl ...
'' monthly, February 1919, Unnumbered page, Scanned by Google Books: https://books.google.com/books?id=7igDAAAAMBAJ&pg=PT21
{{Authority control
Coal mining
Fuel gas
Mine safety
Natural gas safety